POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG.
|
|
|
- Griselda Dorsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 POLICY, PROCEDURE & GUIDELINES FOR POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS IN CUHG. Reference Number: PPG CUH CUH Revision No: 1 Review Cycle: 2 Years Author (Lead): Dr Colm Kerr, Infectious Owner: Dr A Jackson, Infectious Diseases SPR Diseases Physician Approver (Lead): Dr M O Connor Approval Date: March 2017
2 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 2 of 22 Table of Contents 1 Policy Statement Purpose Scope Legislation/Related Policies Glossary of Terms and Definitions Exposure Non occupational exposure Recipient Source Sexual exposure Mucocutaneous Percutaneous Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Post Exposure Prophylaxis Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) Roles and Responsibilities Responsibility for complying with the policy Emergency Department Infectious Disease Department Procedure Introduction Overview Initial Management of patient presenting to CUH ED for PEP or PEPSE PEP Assessment for HIV PEP Footnotes for HIV Risk Assessment Table 1: Table 2: Table 3: Guidelines for pretest counselling HIV PEP prescribing details HIV PEP follow-up PEP for Hepatitis B virus Hepatitis B Virus prescribing details PEP for Hepatitis C Virus Implementation Plan Revision and Audit References/Bibliography Appendices Appendix 1: PEP Proforma... 20
3 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 3 of Appendix 2: Patient Information Leaflet... 21
4 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 4 of 22 1 Policy Statement The Health Service Executive-South (HSE South), Cork University Hospital Group is committed to a proactive approach in minimising the risk of infection among patients who present with possible non-occupational exposure, needle stick injury (NSI) and sexual exposure to Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and the Hepatitis B virus (HBV), as well as vigilance regarding the possible acquisition of the Hepatitis C virus (HCV). 2 Purpose The purposes of this policy are to Outline the minimum management procedures for the immediate assessment, management and follow-up of exposure to blood borne viruses (BBVs) and sexually transmitted viruses such as HIV, HBV and HCV. Advise and inform patients of the steps to be taken following potential needle stick injury, non occupational and/or sexual exposure to HIV/HBV/HCV. Provide guidance on the best evidence based practice to doctors and nurses in the emergence department (ED) on the management of patients who might have exposure to HIV/HBV/HCV. 3 Scope This policy applies to all patients within the HSE-South, Cork University Hospital Group. 4 Legislation/Related Policies EMI tool kit (2012) Guidelines for the Emergency Management of Injuries (including needle-stick and sharps injuries, sexual exposure and human bites) where there is a risk of transmission of blood-borne viruses and other infectious diseases. 5 Glossary of Terms and Definitions 5.1 Exposure An exposure is taken to have occurred when blood or body fluids are inoculated into a patient, through broken skin or is in direct contact with the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose or mouth, anus or vagina. Most exposures are caused by needle stick, splash, sharp instrument, bite injuries or sexual contact. 5.2 Non occupational exposure For the purposes of this guideline, non occupational exposure is an exposure that occurs outside of the hospital workplace.
5 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 5 of Recipient The individual patient who receives the exposure. In the case of a BBV exposure incident, the recipient is exposed to blood or bodily fluids of someone else. 5.4 Source The source of the potentially infected material, e.g. the person on whom the sharp was used, the person who bites, or the source of the blood or bodily fluid. 5.5 Sexual exposure A potential bodily fluid exposure during any sex act. Whilst unprotected receptive vaginal sex is less risky than unprotected receptive anal sex, inherently it carries a risk and PEP should be considered just as seriously as a needle stick injury. There are however some differences. 5.6 Mucocutaneous Splash to the eye or mouth with source s blood or fluid. 5.7 Percutaneous An exposure through the skin (e.g. a needle stick or cut with a sharp object) or contact of non-intact skin (e.g. exposed skin that is chapped, abraded or afflicted with dermatitis) with blood, tissue or other body fluids that are potentially infectious. 5.8 Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) The administration of a drug to prevent the development of an infection after the recipient has been exposed to the infection, e.g. HIV. PEP involves administration of antiretroviral drugs to HIV-negative persons who have been exposed to HIV in an effort to prevent establishment of infection. HBV PEP involves the administration of hepatitis B vaccine and/or hepatitis B specific immunoglobulin after exposure. 5.9 Post Exposure Prophylaxis Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) PEPSE involves the administration of a drug to prevent the development of an infection after the recipient has been involved in a sexual exposure that may lead to infection such as HIV or HBV. It is similar to above Blood Borne Viruses (BBV) Blood borne viruses considered in this policy are HBV, HCV and HIV.
6 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 6 of 22 6 Roles and Responsibilities 6.1 Responsibility for complying with the policy Emergency Department Nursing and medical staff in the emergency department have a responsibility to identify and appropriately treat and refer to the Infectious Disease team patients who present to the ED with non-occupational exposure to the blood borne viruses mentioned above. Occupational exposure incidents should be reported to the department of Occupational Health Infectious Disease Department The staff of the infectious diseases department has a responsibility to discuss potential treatment and referral of patients with ED staff and to follow up referrals in the infectious disease clinic to make a decision on whether further treatment or follow up is warranted. 7 Procedure 7.1 Introduction These guidelines aim to standardise the approach, assessment and treatment of patients presenting for the first time post: Needle Stick Injury (NSI) Non Occupational Exposure Sexual Exposure To a source who may be infected with a blood borne virus such as Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV), Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) and Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). The aim is to ensure that appropriate assessment has been made and timely treatment initiated where appropriate. The patient should then be referred on for appropriate follow up. Additional consideration for e.g. Tetanus immunisation may be relevant. This is not covered in this document. Attention should also be brought to the national publication from September 2012, The Emergency Management of Injuries, which is available at This gives a very comprehensive overview of post-exposure prophylaxis. A major difference between these guidelines and the Emergency Management of Injuries Guidelines relates to the first choice of medication to be used for HIV PEP.
7 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 7 of Overview Exposure HBV, HCV, HIV Exposure possible First Aid Assessment of relative risk of exposure Assessment of risk of source Baseline blood tested for HBV, HCV, HIV Initiation of PEP if appropriate Appropriate onward referral: GP / Occupational Health / Local HIV Services 7.3 Initial Management of patient presenting to CUH ED for PEP or PEPSE If a patient presents to ED Triage for PEP Mon-Fri 9am-4.30pm, the ED NCHD could contact ID CNS ( ) or ID SpR (via CUH switchboard). This protocol should be used to assess the need for a HIV-PEP starter pack which should be dispensed and administered to patient if warranted. Follow-up with Infectious Diseases is extremely important if a starter pack is required and should be arranged as detailed below prior to the patient leaving the Department. Patients will be seen in the next ID clinic. For staff members following occupational injury, follow-up should be organised with Occupational Health.
8 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 8 of 22 To arrange follow-up with ID prior to patient s discharge from ED: Call the phone of the ID Dept ( ) and leave voic with patient s name, MRN, and brief case details, stating that patient should be booked into next clinic. Send overview referral letter to ID secretary via FAX ( ) or delivering the letter in person to the ID office (not to rely on internal post) Referral should be either a Narrative Letter or the PEP proforma in appendix 1 ONLY (NB, NOT the EMI toolkit proforma). Patients should be given the contact details of the ID CNS ( ) as a direct contact person in the ID department and should be advised to call them during working hours for counselling issues or questions due to medications/side effects. Print Patient Information Leaflet (Appendix 2) and provide to patient. Ensure that an up-to-date patient phone number is included in the referral.
9 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 9 of PEP Assessment for HIV PEP. Abbreviations BBV: Blood borne virus COHP: Country of high prevalence (of infection being discussed) CSW: Commercial sex worker GP: General practitioner/ primary care physician IVDU: Intravenous drug user OHD: Occupational Health Department
10 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 10 of 22 MSM: Man who has sex with men PEP: Post Exposure Prophylaxis UPSI: Unprotected sexual intercourse 7.5 Footnotes for HIV Risk Assessment 1) Potentially infectious material: semen or vaginal secretions, blood, CSF, synovial, pleural, peritoneal, pericardial or amniotic fluids or tissue. NOT saliva, urine or faeces, unless mixed with blood. 2) Exposure type: Percutaneous A more severe percutaneous exposure is associated with large bore, hollow needle, deep puncture, visible blood on device, or needle used in source patient s artery/vein. Less severe percutaneous exposure. E.g. solid needle or superficial scratch. Of note, outside the body HIV and Hep. C virus dry, die and become non-infectious within a few hours. Hep. B virus however can remain infectious for several days. Significant mucous membrane or non intact skin exposure Minor exposure: e.g. few drops for duration of less than 1 minute. Major exposure: more than few drops/ major splash and /or duration of several minutes or more. Cutaneous exposure: is significant only if skin is compromised i.e. chapped, abrasion, open wound or dermatitis. Assess skin integrity. Human bites The risk of HIV or HCV transmission associated with saliva is exceptionally low and HIV PEP is only extremely rarely warranted, even if the source is known to be HIV positive. If there is known or suspected to be blood in the mouth of the biter at the time of the bite, then HIV PEP may be considered, if the biter has significant risks for HIV. Sexual exposure Whilst unprotected receptive vaginal sex is less risky than unprotected receptive anal sex, inherently it carries a risk and PEP should be considered just as seriously as a needle stick injury. There are however some differences. Sexual assault PEP should be strongly considered if there has been a significant exposure (within past 72 hours) to a potentially infectious material, i.e. the source should be considered high risk for blood borne virus. Patient should be encouraged to attend the Sexual Assault Treatment Unit in SIVUH [Monday Friday, hrs. contact
11 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 11 of 22 Finola Tobin or Bleep 789. Out of hours or week-ends contact Nursing Admin ]. 3) Source unknown HIV status In exposures involving a source person with either unknown HIV status or unknown identity, it is not possible to give reassurance that the risk of HIV seroconversion is zero. However it may be possible to estimate risk e.g. is the source from high risk group e.g. IVDU, MSM, CSW, COHP of HIV? Or Is the source from a high risk environment? A needle stick injury involving a sharps bin on a geriatric ward not known to have any HIV patients is very unlikely to be a major HIV risk group, unless information to the contrary is available. Discussion of pros/ cons of PEP is important to explore. There are potentially serious life threatening drug related adverse reactions to PEP which may exceed the HIV seroconversion risk. Treatment should be tailored to patient. 4) Source is considered HIV negative If there is a HIV negative result within the past 3 months PLUS no clinical indication of a seroconversion like illness PLUS no recent high risk behaviour. 5) The exposure Should be outlined to the source (where known) and consent requested for blood to test for HIV, HBV and HCV. 6) Source is considered HIV positive If they have a positive HIV result, or a physician has diagnosed HIV or the source self reports a diagnosis of HIV. A low or undetectable HIV viral load greatly diminishes the risk of transmission, but does not completely eliminate the risk. 7) Hepatitis B and C Is much more infectious than HIV and there is a vaccine available. All attendees should be offered Hep B vaccination unless they have known immunity. Hep B IV IgG should ONLY be administered when the source is KNOWN to be Hepatitis B surface antigen positive. Administration can be delayed up to 7 days. See hepatitis B algorithm. There is no prophylaxis for Hepatitis C; follow up bloods should be performed by follow-up physician. 8) Window period: (advise patient to use condoms until outside the window period ) If NO PEP taken (e.g. arriving too late for PEP, or refusing PEP): A negative HIV result at 6 weeks is very reassuring, but a HIV test should be performed 12 weeks after the incident, the result of which can be considered conclusive. The accepted window period for Hepatitis B, syphilis and Hepatitis C is also 12 weeks. If PEP taken:
12 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 12 of 22 The window period is extended if the patient takes PEP. A HIV test should be performed 12 weeks after the end of PEP and the results of this should be considered as conclusive. In these circumstances onward referral to a specialist is expected to have occurred. 7.6 Table 1: Estimated Risk of HIV transmission per exposure (From source known to be HIV positive) From EMI guidelines Sep 2012
13 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 13 of Table 2: Estimated Risk of HIV transmission per exposure (From source of unknown HIV status) From EMI guidelines Sep 2012 There are a number of factors which may further reduce the risk of transmission e.g. HIV viral load <50, old dry blood. Other factors which increase risk of transmission e.g. high HIV viral load, intercurrent STI. In the UK, there has been no documented HIV seroconversions in health care workers following occupational exposure since 1999.
14 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 14 of Table 3: PEP and PEPSE Recommendations by scenario From EMI Guidelines Sep Guidelines for pretest counselling Testing for HIV, HBV and HCV is a routine part of management following potential exposure. Baseline bloods reflect the patient s pre-existing status. This is not a test for seroconversion related to this exposure. The attached Performa s identify risk factors for blood borne virus acquisition. Follow up bloods & care will be performed either with GP, OHD or local HIV clinic.
15 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 15 of 22 Advise patients they should contact their GP/OHD/ HIV clinic if they develop any symptoms of acute viral illness. All patients should be advised to use barrier contraception (male condoms) until all follow up blood results are available HIV PEP prescribing details Only start PEP for HIV prevention if the patient presents within 72hrs of the exposure. Once prescribed the 1st dose should be taken as quickly as possible, i.e. take immediately in ED. These drugs are not available in community pharmacies and can only be dispensed by hospitals, so you must give the patient the medication (not a prescription). The treatment duration is 28 days, however a 7-day starter pack is provided until the patient is seen by Occupational Health or their local HIV clinic. GI side effects are uncommon; nausea may occur with Truvada. Severe side effects are uncommon, but include renal impairment, neutropenia and hepatotoxicity. Discuss with Emergency Medicine/Infectious Diseases Senior doctor if in doubt as to appropriate management.
16 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 16 of HIV PEP follow-up Hospital Occupational Exposure: Follow up via local Occupational Health Department. Patient should not run out of medication. Occupational Exposure but with no Occupational Health Department & PEP prescribed: Follow up via local HIV clinic. Patient should not run out of medication. Non occupational exposure & PEP prescribed: Follow up via local HIV clinic. Patient should not run out of medication. Patients with a moderate/ high risk exposure/source REGARDLESS whether PEP prescribed: Follow up in local HIV clinic. Patients who are low risk/unsuitable for PEP: Follow up GP. To arrange follow-up with ID prior to patient s discharge from ED: Call the phone of the ID Dept ( ) and leave voic with patient s name, MRN, and brief case details, stating that patient should be booked into next clinic. Send overview referral letter to ID secretary via FAX ( ) or delivering the letter in person to the ID office (not to rely on internal post) Referral should be either a Narrative Letter or the PEP proforma in appendix 1 ONLY (NB, NOT the EMI toolkit proforma). Patients should be given the contact details of the ID CNS ( ) as a direct contact person in the ID department and should be advised to call them during working hours for counselling issues or questions due to medications/side effects. Print Patient Information Leaflet (Appendix 2) and provide to patient. Ensure that an up-to-date patient phone number is included in the referral
17 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 17 of PEP for Hepatitis B virus Potential HBV exposure Immunisation Status Has the exposed patient been successfully immunised against Hep B (Hep B sab > 10 iu/ml)? YES NO No further action required regarding Hep B risk Stat dose of hepatitis B vaccine Source person known / available NO YES Complete Hepatitis B vaccination course Hepatitis B status of source known NO YES Request urgent testing of source Is source Hep B s Ag? Positive? YES NO Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin and hepatitis B vaccination Routine Hepatitis B vaccination
18 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 18 of 22 The vaccine is relatively safe, including in pregnancy it is unnecessary if the patient has been adequately vaccinated. Hepatitis B Immunoglobulin (Hepatect) is produced from blood donors, and treated to inactivate virus present. There is a risk of contamination e.g. other unknown viruses, CJD etc. Hepatitis B IgG should only be prescribed when the source is known to be HepB sag positive. The prevalence of Hepatitis B in Ireland is too low to warrant giving Hepatitis B IgG to patients where the source is unknown. The prevalence of Hepatitis B core Ab positivity in blood donors in Ireland is 0.51%, increasing to 6% in prisoner/ IVDU populations. However the prevalence of chronic active infection with Hepatitis BsAg positivity is substantially less Hepatitis B Virus prescribing details 7.14 PEP for Hepatitis C Virus PEP for hepatitis C virus is not available. Regular monitoring in follow up period could show seroconversion. In this case early referral to ID/hepatology is warranted for consideration of early treatment. The estimated risk of transmission in healthcare workers exposed to HCVinfected blood is 1-3%.
19 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 19 of 22 8 Implementation Plan Staff of the CUH group will be notified of this revision of the policy by a broadcast . It will replace the current policy and can be accessed for all healthcare workers through Q-Pulse. An abridged version can be found on the website 9 Revision and Audit Revision This policy will be reviewed at two-year intervals or earlier if indicated Audit This policy will be monitored for compliance and effectiveness by the Infectious Diseases department in order to ensure compliance with the protocol and facilitating best practice. 10 References/Bibliography 1. Sonder GJ, et al. Prophylaxis and follow-up after possible exposure to HIV, hepatitis B virus, and hepatitis C virus outside hospital: evaluation of policy BMJ 2005;330: UK Guideline for the use of post exposure prophylaxis for HIV following sexual exposure. Int J STD& AIDS : David Henderson. Managing Occupational Risks for Hepatitis C transmission in the Health Care Setting Clin Micro Rev July 2003: Guidelines for the Emergency Management of Injuries (including needlesticks and sharps injuries, sexual exposure and human bites) where there is a risk of transmission of bloodborne viruses and other infectious diseases. HPSC publication. September Available at: of the CUH group will be notified of this revision of the policy by a broadcast . It will replace the current policy and can be accessed for all healthcare workers through Q-Pulse. An abridged version can be found o
20 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 20 of Appendices 11.1 Appendix 1: PEP Proforma Affix patient addressograph here: DATE of referral: HANDWRITE patient phone number: Dear Dr Jackson / Prof Horgan, PLEASE SEE THIS PATIENT IN THE NEXT ID CLINIC. Exposure type/description: Date and time of exposure: Hours since exposure: SIGNED: Print name: Contact details: Status of HIV status: SOURCE Known or perceived risks/concerns relating to source person (if Hep B status: patient: known): PEP management: Hep C status: HIV: Hep B: Other: Checklist: Baseline tests: HIV, HepBsAg, HepBcAb, Hep C Ab FBC, U+E, LFT Pregnancy test if female Syphilis if risk involved is a sexual exposure Tetanus policy followed Hepatitis B vaccination (unless immune) Has protocol for hepatitis B and HIV PEP been followed? Advice given to use condoms for the window period Called ID CNS ( ) to leave voic Emergency contraception if indicated Patient informed regarding clinic appointment within week Patient given phone number/contact details of ID specialist nurse Check that patient s phone number is up-to-date Information leaflet given to patient Relevant medical history and/or any other comments:
21 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 21 of Appendix 2: Patient Information Leaflet Introduction This leaflet has been written to give you some basic information about Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) for HIV. What is HIV? Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system. Although it is a treatable infection, once infected you have the infection for life. It can be passed on by exposure to infected blood or other infected body fluids e.g. semen. We test for HIV by doing a blood test. If I have been exposed to HIV, what is the chance that I will become infected with HIV? This is very difficult to answer and depends on: 1) the type of exposure 2) the chance the source/person is HIV positive. Overall the risk of infection is low, but certain exposures may carry a higher risk of infection. Even if you have had definite exposure to HIV, this does NOT mean that you will definitely get infected. e.g. the risk of HIV transmission following a needle stick injury from a known HIV positive person is approximated at about 3 infections per 1000 people exposed. PEP further reduces this risk. What is Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)? PEP is the term we use for taking anti- HIV medication to reduce your chances of becoming infected with HIV. It is only useful in certain circumstances. It has been shown to prevent most (but not all) people becoming infected with HIV. The tablets work best if taken immediately after the exposure. There is no strong evidence for its use beyond 72 hours post exposure. What does PEP treatment involve? Your doctor will decide what anti HIV tablets you should take and will give you clear instructions on how to take them. You may be seen directly by a specialist who will explain this to you. Or you may be issued a 7 day starter pack from the Emergency Department containing enough PEP until you are seen by a specialist. You should NOT run out of medication. Usually PEP is taken for a 28 day course and then stopped. During this time you will be seen for regular blood tests to check for side effects. Once you have finished your PEP you will get further appointments for follow up blood tests to check for HIV and other blood borne infections. Part of the assessment and follow up care is to offer protection against Hepatitis B, and advice regarding Hepatitis C and general sexual health. What happens if I am Pregnant? You can still take PEP if you are pregnant, but you must tell the Doctor if you are pregnant or think you are pregnant. What if I am taking other medication?
22 Active Date: March 2017 Page: 22 of 22 There is a possibility that other medication may affect or be affected by PEP. It is very important to tell the Doctor if you are taking other medication (including over the counter and herbal medicines). They will check if these are ok to take with PEP. If you suffer from any of these side effects you should tell the doctor who might be able to offer treatment to help. What do I do if I miss a dose? Take the missed dose immediately, and then take the next dose at the normal time. If you don t remember until the next dose is almost due don t take extra doses, just carry on as normal. Who will look after me whilst I am taking PEP? Once you have started taking PEP you will be seen either by your Occupational Health Department or local HIV specialist. They will monitor you while you are taking PEP, arrange your blood tests, and offer support. The service, including medication, is free of charge.
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses
 Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Guidance for management of exposure events where there is a risk of transmission of blood borne viruses (HIV, Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C) in the community SUMMARY Where a child is thought to have had
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions
 Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
Contamination Incidents Frequently Asked Questions WWR- 004 Index 1. What is a contamination injury? 2. What should I do immediately if I have sustained a contamination injury? 3. What should I do immediately
To provide the guidelines for the management of healthcare workers who have had an occupational exposure to blood and/or body fluids.
 TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
TITLE/DESCRIPTION: MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO HBV, HCV, and HIV INDEX NUMBER: EFFECTIVE DATE: APPLIES TO: ISSUING AUTHORITY: 01/01/2009 01/01/2013 All GCC Countries GULF COOPERATION COUNCIL
One of your office personnel
 Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
Doug Campos-Outcalt, MD, MPA Department of Family and Community Medicine, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Phoenix HIV postexposure prophylaxis: Who should get it? CORRESPONDENCE Doug Campos-Outcalt,
MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE
 Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
Sandyford Protocols MANAGEMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSURE TO HIV: PEPSE www.hiv-druginteractions.org If you require information on occupational exposure to blood borne viruses, including HIV, please refer to the
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure. Marsh Gelbart 2010
 HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
HIV Occupational Transmission and Exposure Marsh Gelbart 2010 Rationale for Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) It was estimated that the risk for HIV transmission after percutaneous exposures involving larger
Greater Glasgow and Clyde. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts
 Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts Greater Glasgow and Clyde Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts A programme developed by Greater Glasgow and Clyde Health
Clinical Education Initiative OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS. Antonio E. Urbina, MD
 Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
Clinical Education Initiative Support@ceitraining.org OCCUPATIONAL POST- EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS Antonio E. Urbina, MD 5/22/2013 Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis [Video Transcript] 00:00:15 - [Tony]
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet. Instructions for Employees/Students:
 MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
MUSC Occupational Bloodborne Pathogen Protocol Off Campus Procedure Packet MUSC has established these protocols in accordance with the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogen Standard and Center for Disease Control recommendations
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 Clinical Practice Guidelines
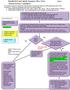 Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick and Splash Exposure Flow Chart Page 1 If ANY student experiences a needlestick or splash exposure ANY time of day/night, they need to page #11709 which will be forwarded to: (**in the event
Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis).
 LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
LTHT Infection Control Policies Needlestick Policy and Actions to be taken after Exposure to Blood and Body Fluids (including HIV Post- Exposure Prophylaxis). This policy covers the immediate actions to
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS
 NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
NEEDLESTICK INJURIES, BLOOD OR BODY FLUID EXPOSURE INFORMATION AND TEST FORMS Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV may be contracted through exposure to any body fluid, particularly blood. IMMEDIATE ACTION
INITIAL EVALUATION AND MANAGEMENT FOLLOWING EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR BODY FLUIDS
 Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Page 1 of 11 Original Date of Issue: June 1991 Reviewed 2/96 5/97 11/98 11/99 5/01 5/02 12/05 Revised 9/95 5/97 5/00 7/02 3/06 6/08 6/10 The following are the procedures to be followed when a person sustains
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens
 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens 11/22/2017 Management of Workplace Exposure to Blood-borne Pathogens BY SOLYMOLE KURUVILLA, PHD, RN, ACNP-BC DIRECTOR, OCCUPATIONAL HEALTH SERVICES
Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Option
 Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
Introduction: Transmission of bloodborne pathogens [e.g., Hepatitis B virus (HBV), Hepatitis C virus (HBC), Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)] from patients to healthcare workers (HCW) is an important
EQuIP 5 - This version June 2011 Revision Due June 2014
 Preamble Rockingham Peel Group Non-Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (NPEP) To Prevent HIV in Western Australia Protocol The purpose of this protocol is to clarify the appropriate use and methods
Preamble Rockingham Peel Group Non-Occupational Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (NPEP) To Prevent HIV in Western Australia Protocol The purpose of this protocol is to clarify the appropriate use and methods
MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES
 NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
NHS GREATER GLASGOW CONTROL OF INFECTION COMMITTEE GUIDELINE MANAGEMENT OF OCCUPATIONAL AND NON-OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOODBORNE VIRUSES INCLUDING NEEDLESTICK INJURIES & SEXUAL EXPOSURES Effective
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS
 TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
TRUST POLICY AND PROCEDURES FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION INCIDENTS Reference Number CL-RM 2014 022 Version: 2.6 Status Final Authors: Dr D.Gnanarajah, Consultant Microbiologist Dr Apoola Consultant
Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May Contains information for:
 APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
APPENDIX A Safety Regulations and Procedures Occupational Health Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan S80.10, updated, May 2018 BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE INCIDENT PACKET Contains information for:
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS
 STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
STUDENT EXPOSURE TO BLOOD OR OTHER POTENTIALLY INFECTIOUS MATERIALS (See Bloodborne Pathogen Worksheet and Post Exposure Prophylaxis consent immediately following this policy ) 1. Student must report immediately
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to,
Effective Date: 6/10/2013 Review Date: 6/10/2016
 Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
Policy Title: Sterilization and Disinfection of Patient-Care Items Policy Number: 11 6.2.2. Examples of useful items to maintain in the office sterilization log are as following: o Date and time of cycle
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury
 43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
43. Guidelines on Needle stick Injury The following information is abstracted from the South African Department of Health guidelines entitled: Management of Occupational Exposure to the Human Immunodeficiency
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids
 Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Management of Exposure to Needlestick Injuries & Body Fluids Clinical S.O.P. No.:28 Compiled by: Approved by: Review date: November 2016 DOCUMENT HISTORY Version Detail of purpose / change Author / edited
Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites
 BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
BLOOD BORNE PATHOGEN EXPOSURE CHECKLIST Exposures at Non-MUSC Clinical Sites (Students on clinical rotations at Roper Hospital, Trident Hospital, Affiliated Local Clinical Sites, Out of Town Clinical Sites,
PEDIATRIC EMERGENCY DEPARTMENT CLINICAL GUIDELINE: NON- OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURE TO BLOOD-BORNE PATHOGENS (HIV, Hepatitis B, AND Hepatitis C)
 General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
General Definition: Blood-borne pathogens are infectious agents that can be transmitted through contact with blood or certain other body fluids. The primary pathogens are HIV, Hepatitis B, and C. Before
Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP:
 Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
Clinical Sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high risk body fluids SOP: Document Control Summary Status: Replacement. Replaces: Management of clinical sharps injuries and exposure to blood and high
EXPOSURE (HIV/HEPATITIS) BLOOD & BODY FLUIDS
 Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Page(s): 1 of 11 PURPOSE To set a standardized procedure to ensure that employees are evaluated in a consistent and timely manner.. POLICY A. The treatment of Team Member exposure to bloodborne pathogens
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE)
 Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
Peninsula Dental Social Enterprise (PDSE) Inoculation Incidents and Blood Borne Viruses Version 1.0 Date approved: October 2013 Approved by: The Board Review due: March 2016 Contents Section Topic Page
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE HEPATITIS B
 DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
DEPARTMENT OF GENITO-URINARY MEDICINE MAIN TRANSMISSION ROUTES HEPATITIS B Sexual transmission Occurs in unvaccinated/non immune men who have sex with men and correlates with multiple partners, unprotected
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure
 Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Blood and Body Fluid Exposure Infection Prevention and Control Contents Policy... 1 Purpose... 1 Scope/Audience... 1 Definitions... 2 Associated documents... 2 1.1 Indications for BBFE reporting... 2 1.2
Exposure. What Healthcare Personnel Need to Know
 Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Information from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention National Center for Infectious Diseases Divison of Healthcare Quality Promotion and Division of Viral Hepatitis For additional brochures
Revised April WGH ER #5 Hospital Rd. Whitehorse Phone: (867) Outside of Whitehorse: Local Community Health Centre/Clinic/ER
 Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Where to access care Who to consult and when Please consult whenever questions arise on how to proceed with postexposure management and when exposure is beyond the scope of guidelines. Blood and Body Fluid
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis
 Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Blood-Borne Pathogens and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Christopher Behrens MD Northwest Association of Occupational and Environmental Medicine October 2017 with thanks to Shireesha Dhanireddy MD Disclosures
Infection Control Standard Precautions. CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients
 Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
Infection Control Standard Precautions Standard Precautions Hand Hygiene CDC Recommendations: Application of Standard Precautions for All Patients Component Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) Gloves Mask,
HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS. All clinical areas of the Trust. Prevent spread of Hepatitis B virus
 Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Trust Policy and Procedure PP(15)027 Document Ref No: HEPATITIS B GUIDANCE FOR THE PROTECTION OF HEALTH CARE WORKERS AND PATIENTS For use in: For use by: For use for: Document owner: Status: All clinical
Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep
 Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep Peter Meacher MD (Chief Medical Officer) Anthony Vavasis MD (Director of Medicine) Callen-Lorde Community Health Center Objectives - at the end of the
Non-Occupational Post-Exposure HIV Prophylaxis npep Peter Meacher MD (Chief Medical Officer) Anthony Vavasis MD (Director of Medicine) Callen-Lorde Community Health Center Objectives - at the end of the
Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis. Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018
 Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018 Indications for Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis: occupational and non-occupational
Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis Laila AL Dabal MD FRCP MSc Infectious Diseases Unit Dubai Health Authority 15 March 2018 Indications for Pre and Post Exposure Prophylaxis: occupational and non-occupational
Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting
 Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
Link to this article online for CPD/CME credits Management of sharps injuries in the healthcare setting Anna Riddell, 1 Ioana Kennedy, 2 C Y William Tong 1 3 1 Department of Infection, Barts Health NHS
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B
 PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL
PROTOCOL FOR THE MANAGAMENT OF SEXUAL EXPOSUE TO HIV, HBV AND HCV: POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS FOR HIV (PEPSE) AND HEPATITIS B Printed copies must not be considered the definitive version DOCUMENT CONTROL
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK)
 POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
POLICY ON BLOOD AND BODY FLUID EXPOSURE (NEEDLE STICK) Dated: January 1, 2018 Supersedes: Blood and Body Fluid Exposure (Needle stick) dated July 1, 2015 I. POLICY It is the policy of New York Medical
SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison
 SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
SIV/SHIV SIV/SHIV Exposure Medical Response Guidance for the University of Wisconsin-Madison 1.0 Instructions: Information in this guidance is meant to inform both laboratory staff and health professionals
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY
 CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
CONTINUING CARE ADMINISTRATIVE MANUAL POLICY NUMBER III-10 DATE Draft June 8, 2010 PAGE 1 OF 3 APPROVED BY: SITE: CATEGORY TITLE: Vice President & Senior Operating Officer, Rehab & Continuing Care Edmonton
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses
 Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] 2014 Aim To raise awareness of the key information and procedures in NHS Lanarkshire's Control of Infection
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy. Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011
 HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
HEPATITIS B INFECTION and Pregnancy Caesar Mensah Communicable Diseases & Infection Control Specialist, UK June 2011 HEPATITIS B 26/07/2011 What is Hepatitis B? It is inflammation (infection) of the liver
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]
![The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV]](/thumbs/93/112976583.jpg) The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
The Prevention of Infection with Blood Borne Viruses [BBV] Control of Infection Manual Section G Study Morning 25 th November 2014 Marissa Herron Occupational Health Support Nurse [BBV] Aim To raise awareness
TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING
 POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
POST ASSAULT MEDICATIONS Terri Stewart RN Naomi Sugar MD TO DECREASE THE CHANCE OF GETTING Pregnant STDs Chlamydia Gonorrhea Trichomonas Hep B HIV EMERGENCY CONTRACEPTION Plan B Levonorgestrel PLAN B Plan
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Management
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Policy Definitions Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials.
Sharps Injuries Management
 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents This procedural document supersedes: PAT/IC 14 v.5 Sharps Injuries Management and other blood or body fluid exposure incidents
Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions
 Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
Infection Prevention and Control Assurance - Standard Operating Procedure 8 (IPC SOP 8) Sharps and Blood/Body Fluid Contamination Injury Immediate Actions Why we have a procedure? The Health and Social
HIV PrEP in Ireland. Information booklet for people who are accessing PrEP themselves or are considering accessing PrEP
 HIV PrEP in Ireland Information booklet for people who are accessing PrEP themselves or are considering accessing PrEP The HSE Sexual Health and Crisis Pregnancy Programme (SHCPP) and the HIV PrEP working
HIV PrEP in Ireland Information booklet for people who are accessing PrEP themselves or are considering accessing PrEP The HSE Sexual Health and Crisis Pregnancy Programme (SHCPP) and the HIV PrEP working
Definitions. Appendix A
 Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
Definitions Appendix A 1. Blood means human blood, human blood components, and products made from human blood. 2. Bloodborne Pathogens means pathogenic microorganisms that are present in human blood and
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS.
 SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
SHARPS PROCEDURE PROCEDURE FOR THE SAFE USE & DISPOSAL OF SHARPS AND THE MANAGEMENT OF SHARPS INJURIES AND BLOOD EXPOSURE INCIDENTS February 2012 Version 1.0 1 CONTENTS Section Page 1.0 Introduction 3
Blood Borne Pathogens
 Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
Bloomer School District Blood Borne Pathogens Developed by: Tammy Kornesczuk, RN Act Rather Than Re-act School Staff tend to be nurturing and care-taking people Don t rush to help without putting on gloves
El Paso - Ambulatory Clinic Policy and Procedure
 Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Regulation Reference: Title: NEEDLESTICK INJURIES/EXPOSURES TO BODY FLUIDS, CARE & FOLLOW UP Policy Number: EP 7.3 Effective Date: 6/2010 Policy Statement: A system is established and maintained to assure
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines
 Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
Sunny Smiles Clinical Guidelines Accidental Inoculation Injury - Guidance for healthcare professionals on dealing with needle-stick injuries to members Date Written: April 2010 Contents 1 Local Contacts...3
INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES
 Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
Reference Number: UHB 019 Version Number: 2 Date of Next Review: October 2018 Previous Trust/LHB Reference Number: UHB075 INFECTION CONTROL PROCEDURE FOR NEEDLESTICK AND SIMILAR SHARPS INJURIES INTRODUCTION
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: F:
 University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
University of Louisville Campus Health Services 401 East Chestnut Street Suite110 P: 502-852-2708 F: 502-852-0660 hlthoff@louisville.edu Training Objectives Understand the OSHA Bloodborne Pathogens Regulation
Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION
 Addressograph or Name D.O.B Address Clinic no DOB Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION The use of PEP following
Addressograph or Name D.O.B Address Clinic no DOB Post Exposure Prophylaxis for HIV following Sexual Exposure (PEPSE) Assessment Proforma PART A: FOR COMPLETION AT INITIAL PRESENTATION The use of PEP following
For. Correctional. Officers. Your. Health Risks. in Correctional Settings. Facts. About HIV
 For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
For Correctional Officers Your Health Risks in Correctional Settings Facts About HIV Working in close quarters with inmates in a correctional facility puts correctional officers (COs) at increased risk
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post-Exposure Chemophrophylaxis
 Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
Bloodbourne Pathogens (BBP) Audience: All personnel in the. Purpose: The purpose of this document is to establish UTMB policy for the initiation of prophylaxis after occupational exposure to the human
BAY-ARENAC BEHAVIORAL HEALTH AUTHORITY POLICIES AND PROCEDURES MANUAL
 Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Page: 1 of 8 Policy Bay-Arenac Behavioral Health Authority (BABHA) is committed to high standards of employee and consumer safety practices. This standard will include the prevention, surveillance, identification
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions
 Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
Emergency Department Blood/Body Fluid Exposure Instructions For employees sent to the Emergency Department after hours to be evaluated for needle stick / body fluid exposure 1. Floor or unit Charge RN
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy
 Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Prevention and Management of Occupational Exposure to Blood Borne Viruses, Post Exposure Prophylaxis and Prevention of Sharps Injuries Policy Author(s) & Designation Lead Clinician if appropriate In consultation
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Sue Sebazco, Arlington, Texas A Webber Training Teleclass
 Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
Bloodborne Pathogens Across the Continuum of Care Objectives Sue Sebazco, RN, BS, CIC Infection Control/Employee Health Director Arlington, TX Pittsburg Mercy Health System skrystofiak@mercy.pmhs.org Define
determine need but regimen does not change based on risk factor ED medicine attending meets
 HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
HIV PEP Guidelines after Sexual Assault Harborview Medical Center January 2015 Initial risk assessment and discussion with patient about risk and PEP is by clinician who does exam (SANE, Ob-Gyn resident,
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES. Prevention of Transmission for School Staff
 CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
CMC Annual Review of BLOODBORNE DISEASES Prevention of Transmission for School Staff Standard on Bloodborne Pathogens OSHA sets the standard of care We must have standards to follow in schools for everyone
Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
 Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Occupational exposure Occupational exposure refers to exposure to potential blood-borne infections (HIV, HBV and HCV) that may occur in healthcare settings during performance
Post Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP) Occupational exposure Occupational exposure refers to exposure to potential blood-borne infections (HIV, HBV and HCV) that may occur in healthcare settings during performance
Testing for HIV in Practice - Seminar. Case History. 19 year old black African patient registered with the practice 5 years (since age 14).
 Joint RCGP / BHIVA Multidisciplinary Conference HIV in Primary Care: All you need to know Friday 25 January 2013 Friday 25 January 2013, Royal College of General Practitioners, London HIV in Primary Care
Joint RCGP / BHIVA Multidisciplinary Conference HIV in Primary Care: All you need to know Friday 25 January 2013 Friday 25 January 2013, Royal College of General Practitioners, London HIV in Primary Care
Question 1. Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6. What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus. B. Blood Borne Viruses
 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus B. Blood Borne Viruses C. Basic Blood Viruses Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based
Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based Virus B. Blood Borne Viruses C. Basic Blood Viruses Blood Borne Viruses: Some important basic facts 6 Question 1 What does BBV stand for? A. Blood Based
A. Background for Trainer: B. What OSHA Requires: Bloodborne Pathogens. Lesson Plan 6080a
 Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Lesson Plan 6080a This training session outline is designed to follow the accompanying booklet, OSHA s Bloodborne Pathogens Standard. The booklet reviews what employees who are potentially exposed to the
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Universal Precautions Parkway School District 2012-2013 Revised 9/19/2012 What Are Bloodborne Pathogens(BBPs) Bloodborne pathogens (BBPs) are disease causing microorganisms carried
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control
 Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
Bloodborne Pathogens and Exposure Control 2016 Information in the Exposure Control Plan The Bloodborne Pathogen Exposure Control Plan was developed to communicate information to you about: - Your risk
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard. An Overview
 The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
The Bloodborne Pathogen Standard An Overview The Standard l In 1990, OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration), developed the Bloodborne Pathogen Standard to protect workers by limiting occupational
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP)
 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Healthcare facilities are high-risk areas for exposure to bloodborne pathogens, so protect yourself and remind others to do the same. There are three bloodborne pathogens of
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft:
 Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
Guidelines for Implementing Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis For The Prevention of HIV in Youth Peter Havens, MD MS Draft: 10-2-2015 Clinical studies demonstrate that when a person without HIV infection takes
Blood borne Pathogen
 Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
Blood borne Pathogen Training For Certified Nursing Assistants Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection Control Update (Formerly HIV/AIDS) 1 0 In-service Hour Meets the Blood borne Pathogens & Infection
NEOMED ACADEMIC POLICY
 (A) PURPOSE The purpose of this Policy is to delineate the management of incidents of exposure to blood-borne pathogens that occur to students while they are in the educational setting. (B) SCOPE This
(A) PURPOSE The purpose of this Policy is to delineate the management of incidents of exposure to blood-borne pathogens that occur to students while they are in the educational setting. (B) SCOPE This
3/23/2016. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures. Managing Bloodborne Pathogen Exposures
 This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
This webinar begins at 11 a.m., Eastern. You will not hear anything over your telephone line until the program starts. If the system did not prompt you to enter your phone number and receive a call back,
EU Directive for Safer Sharps. Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant
 EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
EU Directive for Safer Sharps Anna Pronyszyn Infection Prevention Nurse Conusultant Regulation and Legislation Health and Social Care Act 2008 Occupier s Liability Act 1957 Health and Safety at Work Act
Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse. Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse. Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse
 Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse Agenda Pre-evaluation Minimizing Your Risk Emergency Service Worker Exposures Scenarios Questions
Diane Lockman, Public Health Nurse Marilyn Mitchell, Registered Nurse Sue Mulhall, Public Health Nurse Agenda Pre-evaluation Minimizing Your Risk Emergency Service Worker Exposures Scenarios Questions
FAMILY HIV CENTER NJ CARES SANE
 HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
HIV, Hepatitis B & C Postexposure Prophylaxis for Sexual Assault Victims Update for Case Managers Susan Burrows-Clark, RN, MSN, CNS, C. 10/17/11 Antiretroviral Postexposure Prophylaxis After Sexual, Injection-Drug
What does the HIV Pharmacy Team need to know about PEP
 What does the HIV Pharmacy Team need to know about PEP Rosy Weston Senior Lead Pharmacist Sexual Health and HIV St. Mary s Hospital Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust London November 2008 Objectives
What does the HIV Pharmacy Team need to know about PEP Rosy Weston Senior Lead Pharmacist Sexual Health and HIV St. Mary s Hospital Imperial College Healthcare NHS Trust London November 2008 Objectives
National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV
 National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV These guidelines outline the management of individuals who have been exposed (or suspect they have been exposed)
National guidelines for post-exposure prophylaxis after non-occupational exposure to HIV These guidelines outline the management of individuals who have been exposed (or suspect they have been exposed)
I M ENDING HIV PATIENT INFORMATION. endinghiv.org.au/prep
 I M ENDING HIV PrEP PATIENT INFORMATION endinghiv.org.au/prep THIS BOOKLET PROVIDES YOU WITH INFORMATION ABOUT Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV. CONTENTS 06 Who will benefit from PrEP? 04 What is
I M ENDING HIV PrEP PATIENT INFORMATION endinghiv.org.au/prep THIS BOOKLET PROVIDES YOU WITH INFORMATION ABOUT Pre-Exposure Prophylaxis (PrEP) for HIV. CONTENTS 06 Who will benefit from PrEP? 04 What is
Bloodborne Pathogens. Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN
 Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Bloodborne Pathogens Kathleen Stefek, RN, MSN What are Bloodborne Pathogens? Infectious agents carried in the blood and other body fluids that are capable of infecting a host (people like you and me) with
Hepatitis B Control. Table of Contents
 Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
Control Table of Contents 1.0 INTRODUCTION... 1 2.0 GOALS... 1 3.0 DEFINITIONS... 1 4.0 CASE MANAGEMENT... 3 5.0 HEPATITIS B POST- EXPOSURE MANAGEMENT... 4 TABLE 1: HEPATITIS B POST EXPOSURE PROPHYLAXIS...
Bloodborne Pathogens. Exposure Control Plan
 Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan Maryland Institute College of Art Revision Date(s): January 2007/January 2008 Maryland Institute College of Art (MICA) Subject: Occupational/Non-occupational
Colgate University. Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan
 Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Colgate University Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Control Plan COLGATE UNIVERSITY BLOODBORNE PATHOGENS EXPOSURE CONTROL PLAN I. STATEMENT OF POLICY It is the policy of Colgate University (CU) to limit or
Answering basic questions about HIV
 Answering basic questions about HIV Sixth Edition This booklet is for you if you have basic questions about HIV such as what it is, how it is transmitted and how it affects the body. If you have HIV and
Answering basic questions about HIV Sixth Edition This booklet is for you if you have basic questions about HIV such as what it is, how it is transmitted and how it affects the body. If you have HIV and
Blood Borne Pathogens. Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N.
 Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
Blood Borne Pathogens Becky Walch, R.N. Micheel Valdez, L.V.N. Examples of Blood Borne Pathogens Hepatitis B Hepatitis C Other Hepatitis HIV Hepatitis Hepatitis means inflammation of the liver. Hepatitis
patients with blood borne viruses Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled Document Lead:
 CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
CONTROLLED DOCUMENT Procedure for the management of patients with blood borne viruses CATEGORY: CLASSIFICATION: PURPOSE Controlled Document Number: Version Number: 4 Controlled Document Sponsor: Controlled
Exposure. Blood. Department of Health & Human Services
 Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
Exposure to Blood What Health-Care Workers Need to Know Department of Health & Human Services OCCUPATIONAL EXPOSURES TO BLOOD Introduction Health-care workers are at risk for occupational exposure to bloodborne
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING PREVENTION AND MANAGEMENT OF INOCULATION OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts)
 SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
SHARPS SAFETY POLICY INCLUDING OR CONTAMINATION INCIDENTS (e.g. sharps, bites, scratches or cuts) Solent NHS Trust policies can only be considered to be valid and up-to-date if viewed on the intranet.
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors
 Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
Post-Exposure Prophylaxis Review for International Visitors Case Presentation 27 yo nurse presents to Urgent Care for a needlestick 2 days ago from a diabetic lancet. Source patient (SP): 35 yo male known
Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care
 Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care Author: Josie Smith, Marion Lyons Page 1 of 13 October 2006 Status : Final Contents: Page: Executive Summary 3 Introduction
Primary Care Services for blood borne viral hepatitis prevention, treatment and care Author: Josie Smith, Marion Lyons Page 1 of 13 October 2006 Status : Final Contents: Page: Executive Summary 3 Introduction
HIV and PEP. LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED
 HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
HIV and PEP LTC Rose Ressner WRNMMC ID staff Oct 2014 UNCLASSIFIED Disclaimer The views expressed in this presentation are those of the speaker and do not reflect the official policy of the Department
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Prophylaxis
 01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
01.02 Blood Borne Pathogens (BBP) Occupational Post Exposure Purpose Audience Establish protocol for management of occupational exposures to blood or potentially infectious materials. All employees of
Management of Needlestick and Mucous Membrane Exposures To Blood/Body Fluids
 Management of Needlestick and Mucous Membrane Exposures To Blood/Body Fluids August 2004 Table Of Contents Protocol - Management of Needlestick and Mucous Membrane Exposures to Blood/Body Fluids Assessment
Management of Needlestick and Mucous Membrane Exposures To Blood/Body Fluids August 2004 Table Of Contents Protocol - Management of Needlestick and Mucous Membrane Exposures to Blood/Body Fluids Assessment
