Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease
|
|
|
- Julian Silvester Stewart
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 312-nanometer Ultraviolet B Light (Narrow-Band UVB) Induces Apoptosis of T Cells within Psoriatic Lesions By Maki Ozawa, Katalin Ferenczi, Toyoko Kikuchi, Irma Cardinale, Lisa M. Austin, Todd R. Coven, Lauren H. Burack, and James G. Krueger From the Laboratory for Investigative Dermatology, The Rockefeller University, New York Summary Narrow-band (312 nm) ultraviolet B light (UVB) is a new form of therapy for psoriasis, but its mechanism of action is unknown. In a bilateral comparison clinical study, daily exposure of psoriatic plaques to broad-band UVB ( nm) or 312-nm UVB depleted T cells from the epidermis and dermis of psoriatic lesions. However, 312-nm UVB was significantly more depleting in both tissue compartments. To characterize the mechanism of T cell depletion, assays for T cell apoptosis were performed on T cells derived from UVB-irradiated skin in vivo and on T cells irradiated in vitro with 312-nm UVB. Apoptosis was induced in T cells exposed to mj/cm 2 of 312-nm UVB in vitro, as measured by increased binding of fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) Annexin V to CD3 cells and by characteristic cell size/granularity changes measured by cytometry. In vivo exposure of psoriatic skin lesions to 312-nm UVB for 1 2 wk also induced apoptosis in T cells as assessed by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dutp-biotin nick end labeling (TUNEL) reaction in tissue sections, by binding of FITC Annexin V to CD3 T cells contained in epidermal cell suspensions, and by detection of apoptosis-related size shifts of CD3 cells. Induction of T cell apoptosis could be the main mechanism by which 312-nm UVB resolves psoriasis skin lesions. Key words: psoriasis immunosuppression T lymphocyte apoptosis ultraviolet light Psoriasis vulgaris is a chronic inflammatory skin disease characterized by infiltration of T cells and hyperproliferation of keratinocytes in focal skin areas. In clinical studies, disease-related pathology is reversed by lymphocytetargeted drugs (1 6), whereas in xenotransplant systems, psoriasis is induced or sustained by intradermal injection of activated T cells (7, 8). Therefore, psoriasis is mediated by activated T cells. In the xenotransplant model, an epidermal hyperplasia response appears to arise from cytokines derived from T cells infiltrating into skin (7). These T cells are probably reacting to a cutaneous antigen, as clonal CD8 T cell populations have been identified (9) and as systemic administration of the costimulation blocker, CTLA4Ig, reverses clinical and pathological disease features (6). Hence, skin infiltration by activated cutaneous lymphocyte associated antigen positive T cells appears to cause a complex inflammatory tissue phenotype that includes (a) the presence of several types of activated leukocytes in skin lesions CD4 and CD8 T cells, neutrophils, and dendritic antigen presenting cells, (b) a diverse array of cytokines produced by activated leukocytes and keratinocytes, (c) proliferation of small blood vessels and epidermal keratinocytes, and (d) increased expression of leukocyte-trafficking adhesion molecules, e.g., intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1), P-selectin, E-selectin, by hyperproliferative endothelial cells or keratinocytes (10). Ultraviolet B light (UVB, nm) is used as a therapeutic modality for psoriasis and other inflammatory skin disorders. Recently, a new UVB source which emits mostly 311/312-nm light (narrow band [NB]-UVB) 1 has been introduced for treatment of psoriasis and other inflammatory dermatoses (11 14). UVB irradiation in a variety of animal and human model systems inhibits cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity responses to haptens (15, 16), and its therapeutic mechanism in psoriasis has been attributed to these immunosuppressive properties. Interestingly, irradiation of psoriatic skin lesions with standard UVB light 1 Abbreviations used in this paper: AnV, Annexin V; APC, allophycocyanin; BB, broad band; FSC, forward scatter; NB, narrow band; PerCP, peridinine chlorophyll protein; PI, propidium iodide; SSC, side scatter; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase mediated dutp-biotin nick end labeling. 711 J. Exp. Med. The Rockefeller University Press /99/02/711/08 $2.00 Volume 189, Number 4, February 15,
2 causes rapid depletion of intraepidermal T cells (17) and induction of Fas ligand on keratinocytes (18). As apoptosis is induced by in vitro UVB irradiation of T cells, or by incubation of T cells with keratinocytes expressing UVBinduced Fas ligand, it has been proposed that UVB may have immunosuppressive effects in psoriasis through induction of apoptosis in disease-mediating T cells (17, 18). Although cytotoxic effects of UVB on lymphocytes in vivo are unproven, irradiation of atopic dermatitis skin lesions with high-dose UVA (the delivered dose is 1,000-fold higher than for therapeutic UVB) has produced detectable apoptosis in dermal lymphocytes (19). We now report that 311/ 312-nm UVB is directly cytotoxic for T cells in vivo in psoriatic skin lesions. Furthermore, this new UVB source depletes T cells to a greater extent than broad-band (BB)- UVB from both epidermis and dermis of affected skin. sedimentation and then irradiated in uncovered tissue culture plates (10 6 cells/well) in PBS. After irradiation, they were suspended in RPMI 1640 with 5% heat-inactivated normal human serum (C-six Diagnostics, Inc.) with antibiotics. Flow Cytometric Detection of T Cell Apoptosis. T cell apoptosis was detected using FITC Annexin V (AnV) staining in conjunction with a membrane integrity probe (propidium iodide [PI]). In vitro irradiated PBMCs, or epidermal cell suspensions obtained from NB-UVB treated psoriatic lesions, were stained with APC anti-cd3 mab and FITC AnV (Kamiya Biomedical Co.). After washing, the cells were stained with PI, and fluorescence intensity was measured by a four-color FACSCalibur. Flow Cytometric Phenotyping of T Cells in Psoriatic Lesions. Psoriatic epidermal cell suspensions were stained with selected mabs. After washing with PBS/0.1% sodium azide/2% FBS, cells were fixed with PBS/3.75% formaldehyde and analyzed by flow cytometry within 1 wk. Flow cytometric analysis was done using CellQuest software (Becton Dickinson). Materials and Methods Reagents. The following antibodies were used by FACSCalibur analysis (Becton Dickinson): peridinine chlorophyll protein (PerCP) or allophycocyanin (APC) anti-cd3, PE anti-cd4, FITC anti-cd8 (Becton Dickinson), and isotype mouse IgG mabs. NB-UVB Treatment. 23 adult patients (16 men and 7 women) received irradiation with NB-UVB (312 nm, Philips TL01) on one vertical half of the body and BB-UVB ( nm, FST72T12) on the other vertical half. Five additional patients received NB-UVB on the whole body. The minimum erythema dose for each patient was established before irradiation. On each subsequent day, NB- and BB-UVB irradiations were increased by 15% unless marked erythema developed. Treatment was terminated upon attaining clinical resolution of psoriatic lesions, typically after 4 5 wk of daily treatment (20). Histopathological Analysis. Skin punch biopsies were taken from psoriatic lesions of both NB- and BB-UVB treated sites before and after UVB treatment. Biopsies were frozen in OCT solution (Miles Diagnostic Division) for histological analysis. Unconjugated anti-cd3 mab was applied to cryosections for 60 min at room temperature. After washing with PBS, bound antibody was visualized by the avidin-biotin complex detection system (Vectastain ABC; Vector Laboratories, Inc.) with 3-amino- 9-ethylcarbazol as the chromagen. For double staining, alkaline phosphatase substrate (Vector Laboratories, Inc.) was also used. Number of CD3 cells was counted on the image analyzer using NIH image public domain software. Detection of apoptosis in tissue sections was performed by the TUNEL (TdT-mediated dutp-biotin nick end labeling) reaction as described (17). TdT (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech) and biotin-16-dutp (Boehringer Mannheim) are used for this technique. Psoriatic Epidermal Cell Suspensions. The shave biopsies were taken from eleven patients immediately before the start of treatment and after 1 and 2 wk of treatment with NB-UVB. The tissue was washed twice with sterile PBS, incubated in PBS with 1 mg/ml gentamicin (Life Technologies) for 1 h at 4 C, washed twice in PBS, and floated in 0.5% dispase (Sigma Chemical Co.) overnight at 4 C. The epidermis was removed and teased into a cell suspension after brief trypsinization. NB-UVB Irradiation In Vitro. Narrow-band fluorescent UVB lamps (TL01) were used as a light source. PBMCs were prepared from heparinized venous blood of healthy volunteers by Ficoll Results NB-UVB Depletes T Cells From Psoriatic Lesions More than BB-UVB. Psoriatic plaques in 23 patients were treated daily with NB-UVB or BB-UVB in a bilateral comparison study (20). The ability of NB-UVB or BB-UVB to deplete T cells from psoriatic lesions was studied with CD3 antibodies and quantitative image analysis using immunohistochemistry (Fig. 1 A). Both forms of UVB reduced intraepidermal T cells from lesional skin, but quantitative reductions were greater with NB-UVB (96 vs. 85% reduction, P 0.01; Fig. 1 B). Reductions in dermal CD3 cells were also greater with NB-UVB (54 vs. 29% reduction, P 0.01; Fig. 1, A and B). Flow cytometric analysis confirmed that rapid decreases in the number of CD3, CD4, and CD8 T cell subsets in psoriatic epidermis occur during the first 2 wk of treatment (Fig. 1 C). T Cell Apoptosis Is Induced by NB-UVB Irradiation. To establish the mechanism of T cell depletion from psoriatic lesions by irradiation, we examined NB-UVB treated lymphocytes for DNA fragmentation and membrane changes that typify apoptosis. TUNEL reactions showed more apoptotic cells in NB-UVB treated psoriatic lesions compared with contralateral lesions treated with BB-UVB (Fig. 2). To confirm that apoptotic cells detected in psoriatic tissue after irradiation were T cells, we performed double staining (CD3 and TUNEL). Fig. 2 (bottom) shows a psoriatic lesion taken after 2 wk of daily NB-UVB treatment. TUNEL cells stain red, and CD3 cells stain blue. Double-stained cells (indicated with arrows) were observed in the treated skin, whereas no double-positives were noted before treatment. As detection of apoptotic cells in psoriatic epidermis is problematic using the current TUNEL method (21), we used flow cytometry to examine isolated intraepidermal CD3 lymphocytes for (a) increased binding of AnV, a protein which binds to phosphatidyl serine that is expressed on T cell plasma membranes in early stages of apoptosis; and (b) forward scatter (FSC) and side scatter (SSC) alterations that typify cytoplasmic shrinkage and organelle compaction in T cells undergoing apoptosis. As a control for 712 Mechanism of Narrow-Band UVB Treatment for Psoriasis
3 Figure 1. (A) Immunohistochemical detection of T cells in psoriatic lesional skin from two patients before and after 4 wk of UVB treatment. Left, untreated psoriatic lesions; middle, 4-wk NB-UVB treated lesions; right, 4-wk BB-UVB treated lesions (original magnification: 100). (B) Quantitative analysis of T cell infiltration in psoriatic skin. Panels show mean numbers of CD3 cells in the epidermis and dermis of psoriatic lesional skin before and after treatment. n 23. SE is shown for each mean value. Cell numbers are expressed per image analysis field. (C) Phenotypic characterization of T cells infiltrating psoriatic epidermis before and after NB- UVB treatment. Flow cytometric analysis was performed on epidermal suspensions from five psoriatic patients for phenotyping of intraepidermal T cells. Panels display the number of T cells (and also CD4 or CD8 subset) in psoriatic epidermis during treatment. The numbers are normalized to per 1,000 keratinocytes. Mean percentage is shown in parentheses. Paired t test was done. P values: *P 0.05, **P 0.01, ***P Ozawa et al.
4 Figure 2. TUNEL reactions to sections of psoriatic skin during UVB treatment. Top: left, before treatment; middle, after 2 wk of NB-UVB treatment; right, after 2 wk of BB-UVB treatment (original magnification: 100). Bottom: double (CD3 and TUNEL) staining on sections of psoriatic skin from another patient after 2 wk of NB-UVB treatment. TUNEL cells stain red (left, original magnification: 100); CD3 cells stain blue (middle, original magnification: 100); double-positive cells are indicated with arrows (original magnification: 200). these experiments, PBMCs were irradiated with increasing amounts of NB-UVB (Fig. 3 A). Dual measurement of AnV binding and membrane integrity with PI makes it possible to distinguish early (AnV /PI ) and late stages of apoptosis (AnV /PI ). Hence, a flow cytometer with two lasers and four-color detection was used to simultaneously assess CD3-APC, AnV FITC, and PI staining (PE/PerCP channels) on individual cells. As shown in Fig. 3 A, doseand time-dependent increases in binding of AnV to T cells occurred after exposure of cells to NB-UVB ranging from 25 to 100 mj/cm 2. Cells progressed from an early stage of apoptosis (AnV /PI ) to a late stage of apoptosis (AnV / PI ) during 20 h after irradiation. Analysis of FSC and SSC in CD3 cells showed dose-dependent increases in a sizeshifted population (blue). Cells in this size-shifted population are displayed as blue dots in Fig. 3 A, which indicates that size-shifted cells are mostly AnV /PI, or late-stage apoptotic cells. Fig. 3 B shows analysis of T cell death in lesional epidermis from a psoriatic patient after irradiation with NB-UVB in vivo. After 2 wk of daily treatment of NB-UVB, 45% of intraepidermal T cells were AnV vs. 14% in unirradiated psoriatic epidermis (panels for patient 1). Cells in the early stage of apoptosis (AnV /PI ) were increased by fourfold in this patient. The mean value of four patients is listed in Table I. As shown in panels for patient 2, we also tracked cytotoxic effects of NB-UVB on intraepidermal T cells of 11 psoriatic patients using flow cytometry with ethidium homodimer (a vital fluorescent dye) and by examining T cells for cell shrinkage (reduced FSC signal) and increased granularity (increased SSC signal), changes that occur in apoptosis (22). Using ethidium homodimer staining, increased T cell death was detected in 10 out of 11 patients, and the mean value was % before treatment and % after treatment (listed in Table I). Using FSC and SSC analysis, the percentage of apoptotic T cells in 11 patients was % before treatment and % after treatment (paired t test; P 0.001, Table I). Hence, three independent assays (AnV binding, membrane integrity, and cell morphology assays) demonstrate cytotoxic effects of NB-UVB on a significant fraction of intraepidermal T cells. 714 Mechanism of Narrow-Band UVB Treatment for Psoriasis
5 Figure 3. Flow cytometric assessment of T cell death induced by NB-UVB irradiation. All plots show only CD3 T cells as identified by FITC-CD3 or APC-CD3 staining. (A) In vitro irradiation of T cells. Peripheral blood T cells were irradiated with increasing amounts of NB-UVB, and apoptosis was assessed at either 5 or 20 h after irradiation. The top panels show simultaneous FITC AnV and PI staining on the ordinate and abscissa, respectively. The quadrants of these plots indicate live cells (AnV /PI ), early-stage apoptosis (AnV /PI ), or latestage apoptosis (AnV /PI ). Results show dose- and time-dependent increases in AnV /PI and AnV /PI cell populations. The bottom panels are plots of FSC (cell size) and SSC (granularity) for CD3 cells that are illustrated in AnV/PI plots of 20-h cells. Large CD3 cells with minimal granularity are colored red and are predominantly live cells as shown in the panel above (the same cell population is colored red in the AnV/PI plot). Smaller CD3 cells with increased granularity are colored blue. This population is apoptotic cells (Ap) as shown for blue-colored cells in the AnV/PI plots above. (B) In vivo irradiation of epidermal T cells. T cell apoptosis was assessed in epidermal cells obtained from psoriatic skin. Plots illustrate only CD3 cells in the epidermis. The panels of patient 1 quantify apoptosis in intraepidermal T cells before treatment or after 2 wk of daily irradiation with NB-UVB using the assays shown in A. The plots for patient 2 show ethidium homodimer uptake as an alternative measure of cell death (ethidium homodimer cells are apoptotic and correspond to size-shifted [Ap] cells in FSC/SSC plots for this patient). Discussion Paradoxically, the UVB spectrum ( nm) causes inflammation in irradiated skin (the sunburn reaction), whereas exposure of inflamed skin to similar amounts of UV energy resolves a number of immunologically mediated dermatoses. An action spectrum study in patients with psoriasis established that wavelengths from 290 to 300 nm produced the sunburn reaction (intense erythema and keratinocyte necrosis) but had no therapeutic benefits, whereas 313-nm UVB showed mostly therapeutic, but minimally erythemogenic potential (23). Based on this action spectrum, a fluorescent UVB source was developed for psoriasis therapy that delivers 311/312-nm ( narrow-band ) UVB (11). NB-UVB has been shown to be superior for clearing psoriasis and other inflammatory disorders compared with BB-UVB sources that emit over most of the UVB spectrum (11, 12, 24). Although BB-UVB produces a wide variety of cellular and immunosuppressive effects in skin (15, 25 29), it has been suggested that the therapeutic effectiveness in inflammatory skin disorders could be mediated by the cytotoxic effects of UVB on infiltrating lymphocytes (17). However, the only direct evidence that UV light can produce lymphocyte apoptosis in human skin comes from a 715 Ozawa et al.
6 Table I. Measurement of Intraepidermal T Cell Apoptosis in Psoriatic Skin Treated with NB-UVB by Three Different Flow Cytometry based Assays Measurement in CD3 cells* No. of patients Pretreatment Posttreatment % % Apoptotic shift (FSC/SSC) FITC AnV binding Ethidium homodimer uptake *All assays were performed with trypsinized epidermal cell suspensions. An electronic gate was set on T cells labeled with FITC-CD3 (for ethidium homodimer experiments) or APC-CD3 (for FITC AnV experiments). The apoptotic shift indicates cell shrinkage and increased cytoplasmic complexity measured by FSC/SSC as illustrated in Fig. 3. The table lists mean values for each parameter SD. P values: P 0.001, P study of high-dose UVA ( nm) used to treat patients with atopic dermatitis (19). Surprisingly, immune-modulating effects of nm UVB have not been studied previously in psoriatic skin or skin lesions of other inflammatory diseases. The results of this study show that NB-UVB causes greater depletion of T cells in psoriatic tissue than BB-UVB, and establish direct cytotoxic actions of UVB on T cells infiltrating skin lesions. The in vivo results are paralleled by in vitro experiments where exposure of T cells to moderate doses of 312-nm UVB light induced rapid apoptosis. In fact, given that 10% of UVB energy incident on skin penetrates the epidermis, there is reasonably good agreement between doses of 312-nm UVB required to kill T cells ( mj/cm 2 ) and therapeutic amounts of 312-nm UVB delivered to psoriatic lesions (300 1,200 mj/cm 2 ). The greater effectiveness of 312-nm UVB in depletion of dermal T cells is probably related to (a) somewhat deeper penetration of this wavelength in dermis compared with the composite of wavelengths present in BB-UVB sources (30, 31), and (b) the ability to deliver more Joules of UVB energy with NB- UVB sources due to a reduction in its burning potential. These investigations do not define biochemical pathways mediating the cytotoxic or immunosuppressive effects of NB-UVB. Previous studies with BB-UVB have suggested that apoptosis of epidermal T cells might be induced by interaction of Fas on T cells and upregulated Fas ligand on irradiated keratinocytes (18). Although this mechanism could also pertain to 312-nm UVB, rapid apoptosis was produced in isolated leukocytes by direct irradiation in vitro with relatively small amounts of UVB (17, 32). Potential molecular targets of UVB in T cells include p53, which is upregulated or stabilized after UVB exposure in some cells and can potentially mediate apoptosis in the setting of UVB-induced DNA damage (33, 34), or calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, which is activated after UVB exposure and leads to activation of AP24, 24-kD apoptotic protease (35, 36). In addition, low-dose UVB can inactivate signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT-1), a critical component of signal transduction, which then inhibits gene transcription (37, 38). In most cases, direct irradiation of normal skin with erythemogenic amounts of UVB prevents delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions to topical sensitizers. This altered immune reactivity has been attributed to UVB-induced depletion of Langerhans cells from epidermis (39). In a prior study, therapeutic amounts of BB-UVB did not appreciably reduce the abundance of CD1a epidermal cells in lesional psoriatic skin (17). We detected no obvious reductions in CD1a cells after irradiation of psoriatic lesions with NB-UVB (data not shown). Hence, depletion of T cells from psoriatic lesions appears to be selective for a restricted set of leukocytes. Accordingly, our studies suggest that the major therapeutic mechanism of UVB light in inflammatory dermatoses is a cytotoxic effect on skin-infiltrating T cells, where the mechanism of death is most likely through apoptosis. We thank Ms. Henrietta Carbonaro for help with immunohistochemical staining, Ms. Joan Hofmann for manuscript preparation, and Dr. Ian B. Walters and Ms. Patricia Gilleaudeau for clinical assistance. This research was supported in part by a General Clinical Research Center Grant (M01-RR00102) from the National Center for Research Resources at the National Institutes of Health; by National Institutes of Health grant AI39214; and by grants or gifts from The Carl J. Herzog Foundation, the American Skin Association, The Carson Family Charitable Trust, Dr. James Murphy, and Jean Stein. L.H. Burack and T.R. Coven were supported as Rockefeller University Clinical Scholars from May 1996 through June 1997 and March 1997 through June 1998, respectively. Address correspondence to James G. Krueger, Laboratory for Investigative Dermatology, The Rockefeller University, 1230 York Ave., New York, NY Phone: ; Fax: ; kruegej@rockvax.rockefeller.edu Received for publication 15 September 1998 and in revised form 11 December Mechanism of Narrow-Band UVB Treatment for Psoriasis
7 References 1. Nicolas, J.F., N. Chamchick, J. Thivolet, J. Wijdenes, P. Morel, and J.P. Revillard CD4 antibody treatment of severe psoriasis. Lancet. 338: Weinshenker, B.G., B.H. Bass, G.C. Ebers, and G.P.A. Rice Remission of psoriatic lesions with muromonab- CD3 (Orthoclone OKT3) treatment. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 20: Cooper, K.D., O. Baadsgaard, C.N. Ellis, E. Duell, and J.J. Voorhees Mechanisms of cyclosporine A inhibition of antigen-presenting activity in uninvolved and lesional psoriatic epidermis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 94: Ellis, C.N., D.C. Gorsulowsky, T.A. Hamilton, J.K. Billings, M.D. Brown, J.T. Headington, K.D. Cooper, O. Baadsgaard, E.A. Duell, T.M. Annesley, et al Cyclosporine improves psoriasis in a double-blind study. JAMA (J. Am. Med. Assoc.). 256: Kanerva, L., J. Lauharanta, K.-M. Niemi, and A. Lassus Light and electron microscopy of psoriatic skin before and during retinoid (Ro ) and retinoid-puva treatment. J. Cutan. Pathol. 9: Krueger, J.G., E. Hayes, M. Brown, S. Kang, M.G. Lebwohl, C.A. Guzzo, B.V. Jegasothy, M.T. Goldfarb, D.J. Hecker, R.M. Mann, and J.R. Abrams Blockade of T-cell costimulation with CTLA4Ig (BMS ) reverses pathologic inflammation and keratinocyte activation in psoriatic plaques. J. Investig. Dermatol. 108:555. (Abstr.) 7. Wrone-Smith, T., and B.J. Nickoloff Dermal injection of immunocytes induces psoriasis. J. Clin. Invest. 98: Gilhar, A., M. David, R. Ullmann, T. Berkutski, and R.S. Kalish T-lymphocyte dependence of psoriatic pathology in human psoriatic skin grafted to SCID mice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 109: Chang, J.C.C., L.R. Smith, K.J. Froning, B.J. Schwabe, J.A. Laxer, L.L. Caralli, H.H. Kurland, M.A. Karasek, D.I. Wilkinson, D.J. Carlo, and S.W. Brostoff CD8 T cells in psoriatic lesions preferentially use T-cell receptor V 3 and/or V 13.1 genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 91: Nickoloff, B.J The cytokine network in psoriasis. Arch. Dermatol. 127: van Weelden, H., H. Baart de la Faille, E. Young, and J.C. van der Leun A new development in UVB phototherapy of psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 119: Green, C., J. Ferguson, T. Lakshmipathi, and B.E. Johnson nm UVB phototherapy an effective treatment for psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 119: Green, C., T. Lakshmipathi, B.E. Johnson, and J. Ferguson A comparison of the efficacy and relapse rates of narrowband UVB (TL-01) monotherapy vs. etretinate (re-tl- 01) vs. etretinate-puva (re-puva) in the treatment of psoriasis patients. Br. J. Dermatol. 127: Guckian, M., C.D. Jones, J.P. Vestey, E.J. Cooper, R. Dawe, N.K. Gibbs, and M. Norval Immunomodulation at the initiation of phototherapy and photochemotherapy. Photodermatol. Photoimmunol. Photomed. 11: Cooper, K.D Cell-mediated immunosuppressive mechanisms induced by UV radiation. Photochem. Photobiol. 63: Simon, J.C., J. Krutmann, C.A. Elmets, P.R. Bergstresser, and P.D. Cruz, Jr Ultraviolet B-irradiated antigenpresenting cells display altered accessory signaling for T-cell activation: relevance to immune responses initiated in skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 98:66S 69S. 17. Krueger, J.G., J.T. Wolfe, R.T. Nabeya, V.P. Vallat, P. Gilleaudeau, N.S. Heftler, L.M. Austin, and A.B. Gottlieb Successful ultraviolet B treatment of psoriasis is accompanied by a reversal of keratinocyte pathology and by selective depletion of intraepidermal T cells. J. Exp. Med. 182: Gutierrez-Steil, C., T. Wrone-Smith, X. Sun, J.G. Krueger, T. Coven, and B.J. Nickoloff Sunlight-induced basal cell carcinoma tumor cells and ultraviolet-b irradiated psoriatic plaques express Fas ligand (CD95L). J. Clin. Invest. 101: Morita, A., T. Werfel, H. Stege, C. Ahrens, K. Karmann, M. Grewe, S. Grether-Beck, T. Ruzicka, A. Kapp, L.-O. Klotz, et al Evidence that singlet oxygen-induced human T helper cell apoptosis is the basic mechanism of ultraviolet-a radiation phototherapy. J. Exp. Med. 186: Coven, T.R., L.H. Burack, P. Gilleaudeau, M. Keogh, M. Ozawa, and J.G. Krueger Narrowband UV-B produces superior clinical and histopathological resolution of moderate-to-severe psoriasis in patients compared with broadband UV-B. Arch. Dermatol. 133: Wrone-Smith, T., R.S. Mitra, C.B. Thompson, R. Jasty, V.P. Castle, and B.J. Nickoloff Keratinocytes derived from psoriatic plaques are resistant to apoptosis compared with normal skin. Am. J. Pathol. 151: Yoo, E.K., A.H. Rook, R. Elenitsas, F.P. Gasparro, and B.R. Vowels Apoptosis induction by ultraviolet light A and photochemotherapy in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: relevance to mechanism of therapeutic action. J. Investig. Dermatol. 107: Parrish, J.A., and K.F. Jaenicke Action spectrum for phototherapy of psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 76: El-Ghorr, A., and M. Norval Biological effects of narrow-band (311 nm TL01) UVB irradiation: a review. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. 38: Kang, K., C. Hammerberg, L. Meunier, and K.D. Cooper CD11b macrophages that infiltrate human epidermis after in vivo ultraviolet exposure potently produce IL-10 and represent the major secretory source of epidermal IL-10 protein. J. Immunol. 153: Rivas, J.M., and S.E. Ullrich Systemic suppression of delayed-type hypersensitivity by supernatants from UV-irradiated keratinocytes. An essential role for keratinocytederived IL-10. J. Immunol. 149: Ullrich, S.E Mechanism involved in the systemic suppression of antigen-presenting cell function by UV irradiation. Keratinocyte-derived IL-10 modulates antigen-presenting cell function of splenic adherent cells. J. Immunol. 152: Nishigori, C., D.B. Yarosh, S.E. Ullrich, A.A. Vink, C.D. Bucana, L. Roza, and M.L. Kripke Evidence that DNA damage triggers interleukin 10 cytokine production in UV-irradiated murine keratinocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 93: Rattis, F.-M., J. Peguet-Navarro, P. Courtellemont, G. Redziniak, and D. Schmitt In vitro effects of ultraviolet B radiation on human Langerhans cell antigen-presenting function. Cell. Immunol. 164: Ozawa et al.
8 30. Everett, M.A., E. Yeargers, R.M. Sayre, and R.L. Olson Penetration of epidermis by ultraviolet rays. Photochem. Photobiol. 5: Bruls, W.A.G., H. Slaper, J.C. van der Leun, and L. Berrens Transmission of human epidermis and stratum corneum as a function of thickness in the ultraviolet and visible wavelengths. Photochem. Photobiol. 40: Yaron, I., R. Yaron, S.F. Oluwole, and M.A. Hardy UVB irradiation of human-derived peripheral blood lymphocytes induces apoptosis but not T-cell anergy: additive effects with various immunosuppressive agents. Cell. Immunol. 168: Schwartz, S.M., and M.R. Bennett Death by any other name. Am. J. Pathol. 147: Cotton, J., and D.F. Spandau Ultraviolet B-radiation dose influences the induction of apoptosis and p53 in human keratinocytes. Radiat. Res. 147: Wright, S.C., Q.S. Wei, D.H. Kinder, and J.W. Larrick Biochemical pathways of apoptosis: nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide deficient cells are resistant to tumor necrosis factor or ultraviolet light activation of the 24-kD apoptotic protease and DNA fragmentation. J. Exp. Med. 183: Wright, S.C., U. Schellenberger, L. Ji, H. Wang, and J.W. Larrick Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II mediates signal transduction in apoptosis. FASEB J. 11: Aragane, Y., D. Kulms, T.A. Luger, and T. Schwarz Down-regulation of interferon -activated STAT1 by UV light. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 94: Aragane, Y., A. Schwarz, T.A. Luger, K. Ariizumi, A. Takashima, and T. Schwarz Ultraviolet light suppresses IFN- -induced IL-7 gene expression in murine keratinocytes by interfering with IFN regulatory factors. J. Immunol. 158: Murphy, G.M., P.G. Norris, A.R. Young, M.F. Corbett, and J.L.M. Hawk Low-dose ultraviolet-b irradiation depletes human epidermal Langerhans cells. Br. J. Dermatol. 129: Mechanism of Narrow-Band UVB Treatment for Psoriasis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Involvement of IL-21 in the epidermal hyperplasia of psoriasis Roberta Caruso 1, Elisabetta Botti 2, Massimiliano Sarra 1, Maria Esposito 2, Carmine Stolfi 1, Laura Diluvio 2,
Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and PUVA therapy in the treatment of early-stage mycosis fungoides: a right left comparative study
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2005; 21: 281 286 Blackwell Munksgaard Copyright r Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 Narrow band UVB (311 nm), psoralen UVB (311 nm) and therapy in the treatment of early-stage
Pravit Asawanonda, MD, DSc, and Yaowalak Nateetongrungsak, MD Bangkok, Thailand
 Methotrexate plus narrowband UVB phototherapy versus narrowband UVB phototherapy alone in the treatment of plaque-type psoriasis: A randomized, placebo-controlled study Pravit Asawanonda, MD, DSc, and
Methotrexate plus narrowband UVB phototherapy versus narrowband UVB phototherapy alone in the treatment of plaque-type psoriasis: A randomized, placebo-controlled study Pravit Asawanonda, MD, DSc, and
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases
 Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
Narrow-band UVB PHOTOTHERAPY for Skin Diseases By Dr. Manal Bosseila Cairo University, Egypt HISTORICAL ASPECT In 1978: Irradiation cabin with broad band UVB tubes was introduced for psoriasis & uremic
EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF NARROW BAND ULTRAVIOLET B THERAPY IN CHRONIC PLAQUE PSORIASIS
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF NARROW BAND ULTRAVIOLET B THERAPY IN CHRONIC PLAQUE PSORIASIS 1 4 Mohammad Majid Paracha, Irfanullah, Zafar Ali, Said Amin ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EFFECTIVENESS AND SAFETY OF NARROW BAND ULTRAVIOLET B THERAPY IN CHRONIC PLAQUE PSORIASIS 1 4 Mohammad Majid Paracha, Irfanullah, Zafar Ali, Said Amin ABSTRACT Objectives: To determine
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY
 THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
THE EFFECTS OF REPEATED SUB-ERYTHEMAL EXPOSURES OF UVR ON HUMAN IMMUNITY Joanna Narbutt Department of Dermatology Medical University of Lodz, Lodz, Poland Photoimmunosuppression ULTRAVIOLET RADIATION DNA
Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder I Nakaya, Kousik
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES 1-19 T H 2 response to cysteine-proteases requires dendritic cell-basophil cooperation via ROS mediated signaling Hua Tang, Weiping Cao, Sudhir Pai Kasturi, Rajesh Ravindran, Helder
OBSERVATION. Trimethylpsoralen Bath PUVA Is a Remittive Treatment for Psoriasis Vulgaris
 OBSERVATION Trimethylpsoralen Bath PUVA Is a Remittive Treatment for Psoriasis Vulgaris Evidence That Epidermal Immunocytes Are Direct Therapeutic Targets Todd R. Coven, MD; Frank P. Murphy, MD; Patricia
OBSERVATION Trimethylpsoralen Bath PUVA Is a Remittive Treatment for Psoriasis Vulgaris Evidence That Epidermal Immunocytes Are Direct Therapeutic Targets Todd R. Coven, MD; Frank P. Murphy, MD; Patricia
Vitiligo is an acquired cutaneous disorder of
 Narrow-band ultraviolet B is a useful and well-tolerated treatment for vitiligo Lubomira Scherschun, MD, Jane J. Kim, MD, and Henry W. Lim, MD Detroit, Michigan Background: The treatment of vitiligo remains
Narrow-band ultraviolet B is a useful and well-tolerated treatment for vitiligo Lubomira Scherschun, MD, Jane J. Kim, MD, and Henry W. Lim, MD Detroit, Michigan Background: The treatment of vitiligo remains
The Role of Epidermal Langerhans Cells in NB-UVB-Induced Immunosuppression
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. E1-E9, 2013 The Role of Epidermal Langerhans Cells in NB-UVB-Induced Immunosuppression KUMIKO TAGUCHI 1, ATSUSHI FUKUNAGA 1,, KANAKO OGURA 1, and CHIKAKO NISHIGORI
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 59, No. 1, pp. E1-E9, 2013 The Role of Epidermal Langerhans Cells in NB-UVB-Induced Immunosuppression KUMIKO TAGUCHI 1, ATSUSHI FUKUNAGA 1,, KANAKO OGURA 1, and CHIKAKO NISHIGORI
Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12
 1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
1 Supplementary Data Figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. IL-12 serum levels and frequency of subsets in FL patients. (A) IL-12 serum levels measured by multiplex ELISA (Luminex) in FL patients before
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of ultraviolet radiation on cutaneous T cells di Nuzzo, S. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of ultraviolet radiation on cutaneous T cells di Nuzzo, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): di Nuzzo, S. (2000). Effects of ultraviolet
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of ultraviolet radiation on cutaneous T cells di Nuzzo, S. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): di Nuzzo, S. (2000). Effects of ultraviolet
Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris
 IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
IJMAMR 5 (2017) 1-6 ISSN 2053-1834 Comparison of the efficacy of PUVA versus BBUVB in the treatment of psoriasis vulgaris Tran Hau Khang* and Le Huu Doanh National Hospital of Dermatology and Venereology,
Effective Narrow-Band UVB Radiation Therapy Suppresses the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Normalized Psoriasis Plaques
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effective Narrow-Band UVB Radiation Therapy Suppresses the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Psoriasis Plaques Leanne M. Johnson-Huang 1, Mayte Suárez-Fariñas 1,2, Mary Sullivan-Whalen 1, Patricia Gilleaudeau
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effective Narrow-Band UVB Radiation Therapy Suppresses the IL-23/IL-17 Axis in Psoriasis Plaques Leanne M. Johnson-Huang 1, Mayte Suárez-Fariñas 1,2, Mary Sullivan-Whalen 1, Patricia Gilleaudeau
Fluorochrome Panel 1 Panel 2 Panel 3 Panel 4 Panel 5 CTLA-4 CTLA-4 CD15 CD3 FITC. Bio) PD-1 (MIH4, BD) ICOS (C398.4A, Biolegend) PD-L1 (MIH1, BD)
 Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
Additional file : Table S. Antibodies used for panel stain to identify peripheral immune cell subsets. Panel : PD- signaling; Panel : CD + T cells, CD + T cells, B cells; Panel : Tregs; Panel :, -T, cdc,
SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES
 SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES CORRELATION BETWEEN VITAMIN D, UVB, AND MS Researchers are finding a strong association between vitamin D levels, UVB exposure and multiple sclerosis (MS). According to the Mayo
SUN HEALTH TECHNOLOGIES CORRELATION BETWEEN VITAMIN D, UVB, AND MS Researchers are finding a strong association between vitamin D levels, UVB exposure and multiple sclerosis (MS). According to the Mayo
Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y.
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Effects of biological response modifiers in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis Goedkoop, A.Y. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Goedkoop, A.
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial
 Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
Received: 10.7.2011 Accepted: 5.12.2011 Original Article Comparison of the narrow band UVB versus systemic corticosteroids in the treatment of lichen planus: A randomized clinical trial Fariba Iraji, 1
Soe Janssens, Stan Pavel, Coby Out-Luiting, Rein Willemze and Frank de Gruijl. British Journal of Dermatology 2005; 152:
 4 Normalized UV induction of Langerhans cell depletion and neutrophil infiltrates after artificial UVB hardening of patients with polymorphic light eruption Soe Janssens, Stan Pavel, Coby Out-Luiting,
4 Normalized UV induction of Langerhans cell depletion and neutrophil infiltrates after artificial UVB hardening of patients with polymorphic light eruption Soe Janssens, Stan Pavel, Coby Out-Luiting,
Relationship between UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th2 imbalance
 Relationship between UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th2 imbalance H.Y. Li 1,2, F.R. Zhang 1,3 and D.Q. Deng 4 1 Shandong Provincial Hospital for Skin Diseases, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong,
Relationship between UV-irradiated HaCaT cell cytokines and Th1/Th2 imbalance H.Y. Li 1,2, F.R. Zhang 1,3 and D.Q. Deng 4 1 Shandong Provincial Hospital for Skin Diseases, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong,
T Cell Activation. Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009
 T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
T Cell Activation Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly March 18, 2009 Phases of Adaptive Immune Responses Phases of T cell responses IL-2 acts as an autocrine growth factor Fig. 11-11 Clonal Expansion of T cells
Original Article. A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B
 Original Article A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B Amoolya Bhat 1 *, Subramanya H 2, PS Murthy 3 and Santosh
Original Article A Study of Histopathological Changes Seen in Chronic Plaque Psoriasis, Before and After Treatment with Narrow Band Ultraviolet B Amoolya Bhat 1 *, Subramanya H 2, PS Murthy 3 and Santosh
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Review Article. Narrow band UVB phototherapy in dermatology
 Review Article Narrow band UVB phototherapy in dermatology Sunil Dogra, Amrinder Jit Kanwar Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research,
Review Article Narrow band UVB phototherapy in dermatology Sunil Dogra, Amrinder Jit Kanwar Department of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education & Research,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 February 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2014 August ; 134(8): 2071 2074. doi:10.1038/jid.2014.141. A possible role for IL-17A in establishing Th2 inflammation
Project manager. Dr. Nicola Zerbinati. Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ
 Project manager Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ INTRODUCTION Artificial ultraviolet rays (UV) such as sunbeds, lamps, solar panels, are used both in the beauty and medical field,
Project manager Therapeutic protocols of monochromatic source 355 nm λ INTRODUCTION Artificial ultraviolet rays (UV) such as sunbeds, lamps, solar panels, are used both in the beauty and medical field,
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels
 Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
Post Kala-azar Dermal Leishmaniasis (PKDL) from the field to the cellular and the subcellular levels A M EL Hassan Institute of Endemic Diseases University of Khartoum Introduction PKDL is a VL related
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features
 Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
Effective activity of cytokine-induced killer cells against autologous metastatic melanoma including cells with stemness features Loretta Gammaitoni, Lidia Giraudo, Valeria Leuci, et al. Clin Cancer Res
A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients
 Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Volume 1, Issue 3 Research Article A Retrospective Study on the Risk of Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer in PUVA and Narrowband UVB Treated Patients Darukarnphut P, Rattanakaemakorn P *, Rajatanavin N Division
Predictive role of cutaneous lymphocyteassociated antigen (CLA) in TNF-α inhibitor treatment of psoriasis
 Predictive role of cutaneous lymphocyteassociated antigen (CLA) in TNF-α inhibitor treatment of psoriasis Thesis of doctoral (PhD) dissertation Dr. Jókai Hajnalka, MD Semmelweis University School of Doctoral
Predictive role of cutaneous lymphocyteassociated antigen (CLA) in TNF-α inhibitor treatment of psoriasis Thesis of doctoral (PhD) dissertation Dr. Jókai Hajnalka, MD Semmelweis University School of Doctoral
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS. Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT
 ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
ACTIVATION AND EFFECTOR FUNCTIONS OF CELL-MEDIATED IMMUNITY AND NK CELLS Choompone Sakonwasun, MD (Hons), FRCPT Types of Adaptive Immunity Types of T Cell-mediated Immune Reactions CTLs = cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Supplementary Table 1
 Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Supplementary Table 1 Flow Cytometry Antibodies Antibody Fluorochrome Clone Vendor CD45 PE-cyanine 7 30-F11 D ioscience CD3 Pacific lue 17A2 iolegend (San Diego, CA) CD11b APC M1/70 iolegend (San Diego,
Photochemotherapy MM /09/2004. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service: Home; Office
 Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 08/25/2017 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Technical Resources. BD Immunocytometry Systems. FastImmune Intracellular Cytokine Staining Procedures
 FastImmune Intracellular Cytokine Staining Procedures BD has developed protocols for the detection of intracellular cytokines in activated lymphocytes and in activated monocytes. The procedures have been
FastImmune Intracellular Cytokine Staining Procedures BD has developed protocols for the detection of intracellular cytokines in activated lymphocytes and in activated monocytes. The procedures have been
Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory, T-cell mediated
 Narrowband UVB Treatment Increases Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Patients With Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Seyamak Saleky, MD; Işıl Bulur, MD; Zeynep Nurhan Saraçoğlu, MD PRACTICE POINTS The 25-hydroxyvitamin
Narrowband UVB Treatment Increases Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels in Patients With Chronic Plaque Psoriasis Seyamak Saleky, MD; Işıl Bulur, MD; Zeynep Nurhan Saraçoğlu, MD PRACTICE POINTS The 25-hydroxyvitamin
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
BD Flow Cytometry Reagents Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-20 Cell Analyzer
 Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-2 Cell Analyzer Proper multicolor panel design takes into account fluorochrome brightness, antigen density, co-expression, and
Multicolor Panels Designed for Optimal Resolution with the BD LSRFortessa X-2 Cell Analyzer Proper multicolor panel design takes into account fluorochrome brightness, antigen density, co-expression, and
Photochemotherapy MM /09/2004. HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service: Home; Office
 Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Photochemotherapy Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.015 11/09/2004 Line(s) of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration June 1, 2016 Section: Medicine Place(s) of Service:
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: van Seters M, van Beurden M, ten Kate FJW, et al. Treatment
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2014 April 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Invest Dermatol. 2013 October ; 133(10): 2311 2314. doi:10.1038/jid.2013.239. Mechanisms of contact sensitization offer insights
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Original Policy Date
 MP 2.01.58 Light Therapy for Vitiligo Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy
MP 2.01.58 Light Therapy for Vitiligo Medical Policy Section Medicine Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Created with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical Policy
Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood
 Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood Christopher A Fraker, Ph.D., University of Miami - Miami, Florida
Application Information Bulletin: Human NK Cells Phenotypic characterizing of human Natural Killer (NK) cell populations in peripheral blood Christopher A Fraker, Ph.D., University of Miami - Miami, Florida
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was
 Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplementary Figure 1 IMQ-Induced Mouse Model of Psoriasis. IMQ cream was painted on the shaved back skin of CBL/J and BALB/c mice for consecutive days. (a, b) Phenotypic presentation of mouse back skin
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis
 Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Supplemental Table 1. Primer sequences for transcript analysis Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Primer Sequence (5 3 ) Mmp2 Forward CCCGTGTGGCCCTC Mmp15 Forward CGGGGCTGGCT Reverse GCTCTCCCGGTTTC Reverse CCTGGTGTGCCTGCTC
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY
 ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
ACTIVATION OF T LYMPHOCYTES AND CELL MEDIATED IMMUNITY The recognition of specific antigen by naïve T cell induces its own activation and effector phases. T helper cells recognize peptide antigens through
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry:
 Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Optimizing Intracellular Flow Cytometry: Simultaneous Detection of Cytokines and Transcription Factors An encore presentation by Jurg Rohrer, PhD, BD Biosciences 10.26.10 Outline Introduction Cytokines
Cellular Immune response. Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU
 Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cellular Immune response Jianzhong Chen, Ph.D Institute of immunology, ZJU Concept of adaptive immune response T cell-mediated adaptive immune response I. Concept of immune response A collective and coordinated
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/23854 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Marel, Sander van der Title: Gene and cell therapy based treatment strategies
HHS Public Access Author manuscript J Invest Dermatol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 January 01.
 RNA-seq Permits a Closer Look at Normal Skin and Psoriasis Gene Networks David Quigley 1,2,3 1 Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco,
RNA-seq Permits a Closer Look at Normal Skin and Psoriasis Gene Networks David Quigley 1,2,3 1 Helen Diller Family Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California at San Francisco, San Francisco,
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
SCIENTIFIC PAPER ABSTRACT Vitiligo Treatment with Monochromatic Excimer Light and Tacrolimus: Results of an Open Randomized Controlled Study Nistico` S., Chiricozzi A., M.D., Rosita Saraceno R., Schipani
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a. Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease
 Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
Interferon γ regulates idiopathic pneumonia syndrome, a Th17 + CD4 + T-cell-mediated GvH disease Nora Mauermann, Julia Burian, Christophe von Garnier, Stefan Dirnhofer, Davide Germano, Christine Schuett,
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation
 Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
Supplementary material; Title; Extracellular vesicles are transferred from melanocytes to keratinocytes after UVA irradiation Authors; Petra Wäster 1, Ida Eriksson 1, Linda Vainikka 1, Inger Rosdahl 2,
X P. Supplementary Figure 1. Nature Medicine: doi: /nm Nilotinib LSK LT-HSC. Cytoplasm. Cytoplasm. Nucleus. Nucleus
 a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
a b c Supplementary Figure 1 c-kit-apc-eflu780 Lin-FITC Flt3-Linc-Kit-APC-eflu780 LSK Sca-1-PE-Cy7 d e f CD48-APC LT-HSC CD150-PerCP-cy5.5 g h i j Cytoplasm RCC1 X Exp 5 mir 126 SPRED1 SPRED1 RAN P SPRED1
Keywords: Psoriasis vulgaris Zinc pyrithione Betamethasone dipropionate
 CLINICAL EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF A COMBINED FORMULATION OF ZINC PYRITHIONE 0.25% AND BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE MICRONIZED 0.05% IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE PLAQUE PSORIASIS. Abstract Background
CLINICAL EFFICACY AND SAFETY OF A COMBINED FORMULATION OF ZINC PYRITHIONE 0.25% AND BETAMETHASONE DIPROPIONATE MICRONIZED 0.05% IN THE TREATMENT OF MILD TO MODERATE PLAQUE PSORIASIS. Abstract Background
ab Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit
 ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel
 Analyze A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Alexa Fluor is a registered trademark of Life Technologies
Analyze A step-by-step approach to build and analyze a multicolor panel For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Alexa Fluor is a registered trademark of Life Technologies
Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell?
 Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Abbas Chapter 2: Sarah Spriet February 8, 2015 Question 1. Kupffer cells, microglial cells and osteoclasts are all examples of what type of immune system cell? a. Dendritic cells b. Macrophages c. Monocytes
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Light Therapy for Psoriasis Protocol Medical Benefit Effective Date Next Review Date Preauthorization Review Dates Preauthorization is required.
 Protocol Light Therapy for Psoriasis (20147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/16 Next Review Date: 03/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/16, 03/17 Preauthorization is required. The following
Protocol Light Therapy for Psoriasis (20147) Medical Benefit Effective Date: 07/01/16 Next Review Date: 03/18 Preauthorization Yes Review Dates: 03/16, 03/17 Preauthorization is required. The following
Successful treatment of lichen planus with sulfasalazine in 20 patients
 Successful treatment of lichen planus with sulfasalazine in 20 patients A. Bauzá, MD, A. España, MD, P. Gil, MD, P. Lloret, MD, and F. J. Vázquez Doval, MD From the Department of Dermatology, University
Successful treatment of lichen planus with sulfasalazine in 20 patients A. Bauzá, MD, A. España, MD, P. Gil, MD, P. Lloret, MD, and F. J. Vázquez Doval, MD From the Department of Dermatology, University
STUDY. A Randomized Comparison of Methods of Selecting Narrowband UV-B Starting Dose to Treat Chronic Psoriasis
 ONLINE FIRST STUDY A Randomized Comparison of Methods of Selecting Narrowband UV-B Starting Dose to Treat Chronic Psoriasis Robert S. Dawe, MBChB, MD, FRCP; Heather M. Cameron, MBChB, MRCGP; Susan Yule,
ONLINE FIRST STUDY A Randomized Comparison of Methods of Selecting Narrowband UV-B Starting Dose to Treat Chronic Psoriasis Robert S. Dawe, MBChB, MD, FRCP; Heather M. Cameron, MBChB, MRCGP; Susan Yule,
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Effector Responses: Cell- and Antibody-Mediated Immunity Copyright 2013 by W. H.
Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD-
 Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Supplementary Methods Blocking antibodies and peptides. Rat anti-mouse PD-1 (29F.1A12, rat IgG2a, k), PD- L1 (10F.9G2, rat IgG2b, k), and PD-L2 (3.2, mouse IgG1) have been described (24). Anti-CTLA-4 (clone
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis
 Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
Naive, memory and regulatory T lymphocytes populations analysis Jaen Olivier, PhD ojaen@beckmancoulter.com Cellular Analysis application specialist Beckman Coulter France Introduction Flow cytometric analysis
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
doi:1.138/nature1554 a TNF-α + in CD4 + cells [%] 1 GF SPF 6 b IL-1 + in CD4 + cells [%] 5 4 3 2 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of microbiota on cytokine profiles of T cells in GALT. Frequencies of TNF-α
Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis
 Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis Vincent Laufer Rheumatology JC October 17 Disclosures NIH 2
Manuscript: OX40 signaling is involved in the autoactivation of CD4 + CD28 - T cells and contributes to pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis Vincent Laufer Rheumatology JC October 17 Disclosures NIH 2
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information CD200 Expressing Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Cells Initiate Tumor Growth Chantal S Colmont 1, Antisar BenKetah 1, Simon H Reed 2, Nga Voong 3, William Telford 3, Manabu Ohyama 4,
Supporting Information CD200 Expressing Human Basal Cell Carcinoma Cells Initiate Tumor Growth Chantal S Colmont 1, Antisar BenKetah 1, Simon H Reed 2, Nga Voong 3, William Telford 3, Manabu Ohyama 4,
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1
 Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
Immunology - Lecture 2 Adaptive Immune System 1 Book chapters: Molecules of the Adaptive Immunity 6 Adaptive Cells and Organs 7 Generation of Immune Diversity Lymphocyte Antigen Receptors - 8 CD markers
In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay
 Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN. (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
 Supplementary methods Flow cytometric analysis of DCs. DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
Supplementary methods Flow cytometric analysis of DCs. DC were seeded into tissue culture dishes in IMDM 2% FCS, and added with PMN (1:1; PMN: DC) for 16h also in the presence of DNAse (100 U/ml); DC were
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy
 Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Supplementary Figure 1. Example of gating strategy Legend Supplementary Figure 1: First, gating is performed to include only single cells (singlets) (A) and CD3+ cells (B). After gating on the lymphocyte
Monocyte subsets in health and disease. Marion Frankenberger
 Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Monocyte subsets in health and disease Marion Frankenberger main cellular components: Leukocytes Erythrocytes Composition of whole blood Monocytes belong to the cellular components of peripheral blood
Summary. DOI /j x
 PHOTOBIOLOGY DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06533.x Comparison of the 308-nm excimer laser and a 308-nm excimer lamp with 311-nm narrowband ultraviolet B in the treatment of psoriasis K. Köllner, M.B. Wimmershoff,
PHOTOBIOLOGY DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06533.x Comparison of the 308-nm excimer laser and a 308-nm excimer lamp with 311-nm narrowband ultraviolet B in the treatment of psoriasis K. Köllner, M.B. Wimmershoff,
Immune Checkpoints. PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich
 Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
Immune Checkpoints PD Dr med. Alessandra Curioni-Fontecedro Department of Hematology and Oncology Cancer Center Zurich University Hospital Zurich Activation of T cells requires co-stimulation Science 3
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencemag.org/content/348/6241/aaa825/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A mucosal vaccine against Chlamydia trachomatis generates two waves of protective memory T cells Georg Stary,* Andrew Olive,
www.sciencemag.org/content/348/6241/aaa825/suppl/dc1 Supplementary Materials for A mucosal vaccine against Chlamydia trachomatis generates two waves of protective memory T cells Georg Stary,* Andrew Olive,
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast
 Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Supplementary Figure 1. Double-staining immunofluorescence analysis of invasive colon and breast cancers. Specimens from invasive ductal breast carcinoma (a) and colon adenocarcinoma (b) were staining
Atopic dermatitis (AD) is a common chronic skin. Phototherapy in the management of atopic dermatitis: a systematic review.
 Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2007; 23: 106 112 Blackwell Munksgaard r 2007 The Authors Journal compilation r 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard Review article Phototherapy in the management of atopic dermatitis:
Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed 2007; 23: 106 112 Blackwell Munksgaard r 2007 The Authors Journal compilation r 2007 Blackwell Munksgaard Review article Phototherapy in the management of atopic dermatitis:
Adaptive Immunity. Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214,
 Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Adaptive Immunity Jeffrey K. Actor, Ph.D. MSB 2.214, 500-5344 Lecture Objectives: Understand role of various molecules including cytokines, chemokines, costimulatory and adhesion molecules in the development
Evaluation of Apoptotic Cells Induced by Ultraviolet Light B Radiation in Epidermal Sheets Stained by the TUNEL Technique
 Evaluation of Apoptotic Cells Induced by Ultraviolet Light B Radiation in Epidermal Sheets Stained by the TUNEL Technique Hiroyuki Okamoto, Kana Mizuno, Taketo Itoh, Kiyoji Tanaka,* and Takeshi Horio Department
Evaluation of Apoptotic Cells Induced by Ultraviolet Light B Radiation in Epidermal Sheets Stained by the TUNEL Technique Hiroyuki Okamoto, Kana Mizuno, Taketo Itoh, Kiyoji Tanaka,* and Takeshi Horio Department
Follicular Lymphoma. ced3 APOPTOSIS. *In the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans 131 of the organism's 1031 cells die during development.
 Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Harvard-MIT Division of Health Sciences and Technology HST.176: Cellular and Molecular Immunology Course Director: Dr. Shiv Pillai Follicular Lymphoma 1. Characterized by t(14:18) translocation 2. Ig heavy
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Flow Cytometry. What is flow cytometry?
 Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
Flow Cytometry Flow Cytometry What is flow cytometry? Flow cytometry is a popular laser-based technology to analyze the characteristics of cells or particles. It is predominantly used to measure fluorescence
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice
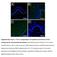 Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Supplementary Figure 1: Fn14 is upregulated in the epidermis and dermis of mice undergoing AD- and psoriasis-like disease. Immunofluorescence staining for Fn14 (green) and DAPI (blue) in skin of naïve
Efficacy of blue light vs. red light in the treatment of psoriasis: a double-blind, randomized comparative study
 DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04039.x JEADV ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of blue light vs. red light in the treatment of psoriasis: a double-blind, randomized comparative study M.M. Kleinpenning,* M.E. Otero,
DOI: 10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04039.x JEADV ORIGINAL ARTICLE Efficacy of blue light vs. red light in the treatment of psoriasis: a double-blind, randomized comparative study M.M. Kleinpenning,* M.E. Otero,
C. Incorrect! MHC class I molecules are not involved in the process of bridging in ADCC.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation. Abul K. Abbas UCSF. FOCiS
 1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
1 Antigen Presentation and T Lymphocyte Activation Abul K. Abbas UCSF FOCiS 2 Lecture outline Dendritic cells and antigen presentation The role of the MHC T cell activation Costimulation, the B7:CD28 family
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION
 Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
Scott Abrams, Ph.D. Professor of Oncology, x4375 scott.abrams@roswellpark.org Kuby Immunology SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 11 T-Cell Activation, Differentiation, and Memory Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and
