Glossary. A resource for individuals and families living with MPS. apneic episodes: Periods of time where breathing stops.
|
|
|
- Allen Joseph
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A resource for individuals and families living with MPS Glossary acetyl CoA: alpha-glucosaminide acetyltransferase (acetyl CoA: α-glucosaminide acetyltransferase): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS III-C. adenoids: The collection of lymphatic tissue at the rear of the nose. Enlargement of the adenoids may cause obstruction of breathing through the nose. adenoidectomy: A surgical procedure to remove adenoid growth. airway patency: The openness of the airways (parts of the respiratory tract through which air passes). alpha-l-iduronidase (α-l-iduronidase): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS I. alpha-n-acetylglucosaminidase (α-nacetylglucosaminidase): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS III-B. amino acid: A class of chemical compounds that can be built up to form larger polymers called proteins. In most biological systems there are 20 common amino acids that can be linked in various combinations to generate larger molecules containing ,000 amino acids. These larger molecules, or proteins, carry out most of the active functions within a cell or an organism. amniocentesis: Procedure involving withdrawal of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the growing fetus in the uterus, generally performed between the 15 th and 20 th weeks of pregnancy by inserting a needle through the abdominal wall into the uterus. Cells that are contained in the fluid can be isolated and used for prenatal diagnosis of gender and for particular genetic conditions. apneic episodes: Periods of time where breathing stops. arrhythmia: An abnormal heartbeat. arthralgia: Joint pain. arylsulfatase B (ASB): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS VI. atrophy: A wasting of tissues, organs, or the entire body, as from death and reabsorption of cells, diminished cellular proliferation, decreased cellular volume, pressure, ischemia (blockage of blood flow), malnutrition, lessened function, or hormonal changes. attenuated: Diminished, not as severe. audiometry: Hearing tests. autosomal recessive disease: A disease which follows an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance requiring the presence of two copies of a particular gene mutation in order to express clinical signs and symptoms of a condition. A pattern of inheritance seen in all MPS disorders with the exception of MPS II. autosomal recessive inheritance: A pattern of inheritance in which a non-dominant (recessive) gene on a non-sex-determining chromosome (autosome) results in a person either being a carrier of a trait or being affected. Males and females are affected with equal frequency. There is usually no family history of the trait. Instead, it is revealed when two unaffected parents who are both carriers of a particular recessive gene have a child who receives two copies of the recessive gene. A pattern of inheritance seen in all MPS disorders with the exception of MPS II. beta-galactosidase (β-galactosidase): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS IV-B. angioneurotic edema: Swelling under the skin of the face, throat, hands, or feet. anterior: Front. 1
2 Mucopolysaccharidosis beta-glucuronidase (β-glucuronidase): Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS VII. blood-brain barrier: The walls of the blood vessels of the brain (and the retina) are much more difficult for large molecules to pass through than are blood vessels elsewhere in the body. This has important implications for the ability of the body to mount an immune response and to provide protection to these tissues, although the reason for the difference is not well understood. The implications for human genetic disease are that it is far more difficult to provide therapeutic treatment to neural (brain) tissues than to other tissues in the body. Since many lysosomal storage diseases have a specific involvement in the neural tissues, it is critical to provide access to these tissues during treatment. bone marrow transplant: See stem cell transplant. bone marrow: Tissue found in the centre of most bones. It is the site in which most blood cells are made, including red blood cells, which are involved in transport of oxygen in the blood, and white blood cells, which are involved in immune response. BiPAP: Bilevel positive airway pressure, often used for people with sleep apnea to open the airway during sleep. It uses two pressure settings, one for while the person is breathing in and the other for while the person is breathing out. cardiac arrhythmia: See arrhythmia. cardiomyopathy: A general term referring to disease of, or damage to, the heart muscle. carpal tunnel: The space between the carpal bones of the wrist and the connective tissue over the flexor tendons. The carpus (wrist) consists of eight small bones known as carpals, which are joined by a band of fibrous proteins called ligaments. Nerves have to pass through the wrists in the space between the carpal bones and the ligaments. carpal tunnel syndrome: Thickening of the ligaments in the carpal tunnel causing pressure on the nerves. This can cause irreversible nerve damage if not surgically corrected. In individuals with MPS VI, carpal tunnel syndrome often occurs because of accumulation of glycosaminoglycan (GAG) deposits. carrier: An individual who has a recessive, disease-causing version of a gene at a particular site on one chromosome of a pair and a normal version of a gene at the same location on the other chromosome. By definition, carriers of a recessive condition do not have clinical signs and symptoms of the condition. cerebrospinal fluid (CSF): The fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord and that is produced in the ventricles of the brain. cervical spinal cord compression: Pressure on the neck area of the spinal cord from abnormal tissue growth nearby. chorionic villus sampling (CVS): Prenatal diagnostic procedure involving sampling the chorionic villi (part of the amniotic sac, which surrounds the growing fetus), generally performed between the 10 th and 12 th weeks of pregnancy. The test can reveal many, but not all, genetic abnormalities. The decision to have prenatal testing, and the appropriate method of prenatal diagnosis, should be discussed with your healthcare provider. Currently amniocentesis is more widely available than CVS for prenatal testing for MPS VI. chromosome: The linear, double-stranded structural unit of genetic material consisting of DNA and supporting proteins called chromatin. Human cells are expected to contain 46 chromosomes identified as 23 pairs; 22 pairs are autosomes and one pair are the sex chromosomes. cognitive function: The ability to think, reason, remember, pay attention, use judgment, and have insight (understanding one s self and situation). 2
3 A resource for individuals and families living with MPS contracture: Muscle shortening resulting in loss of motion of the joint. cord blood transplant: See stem cell transplant. cornea: The transparent circular part of the front of the eye. corneal clouding: Disruption of the clear layers of the cornea in individuals with MPS VI due to storage of glycosaminoglycans (GAG), causing a milky appearance of the eye, decreased vision, and sensitivity to light. Cloudy corneas can be replaced with a corneal transplant. corneal transplant: Surgical procedure to remove a cloudy cornea (see corneal clouding) and replace it with a healthy, donated cornea. CPAP: Continuous positive airway pressure, often used for people with sleep apnea to open the airway during sleep using a constant pressure setting. cranium: The part of the skeleton that encloses the brain. deposits: See glycosaminoglycans (GAG). DNA: The molecule that encodes the genes responsible for the structure and function of an organism and allows for transmission of genetic information to the next generation. dyspnea: Shortness of breath. dysostosis: The abnormal formation of bone caused by the lack of proper ossification (conversion of cartilage or tissues into bone). dysostosis multiplex: The abnormal formation of many bones caused by the lack of proper ossification. electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): A study of the currents in the heart that control its contraction. electromyography (EMG): Continuous recording of the electrical activity of a muscle by means of electrodes inserted into the muscle fibres. Used, although not required, to diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome (which can be diagnosed by nerve conduction studies). enamel: The hard outer covering of the crown of a tooth. enzyme: A protein that facilitates a biological reaction without itself being used up in the reaction (i.e., it acts as a catalyst). An enzyme acts by binding with the substance involved in the reaction (the substrate) and converting it into another substance (the product of the reaction). enzyme replacement therapy: A therapeutic approach for a genetic disorder whereby the missing protein is manufactured outside the body and given intravenously (injected into a vein) to the patient on a regular basis. fontanelle: A soft spot on a baby s head. galactose 6-sulfatase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS IV-A. gastrostomy (G-tube): A surgical procedure in which an opening is made into the stomach from the outside. It is usually performed to allow nutrition and/or medications to be given directly into the stomach when swallowing is difficult because of disease or obstruction of the esophagus (the tube from the mouth to the stomach). gene: Basic unit of heredity that codes for a specific protein leading to a particular characteristic or function for example, details of physical appearance or organ function. echocardiogram: Ultrasound of the heart to evaluate heart valve and heart muscle function. electroencephalogram (EEG): A record of the electric potentials in the brain recorded by attaching electrodes on the scalp. Often this procedure is used to look for seizure activity. 3
4 Mucopolysaccharidosis gene therapy: A therapeutic approach to a genetic disorder whereby a corrected copy of the gene or a new gene is inserted to replace the incorrect version. genetic code: Information carried by the DNA molecules that decides the physical traits of an offspring. The code fixes the pattern of amino acids that build body tissue proteins within a cell. genetic skeletal survey: See skeletal survey. genu valgum: Knock-knees (knees curving inward in relation to the thigh). gibbus: Abnormal angular curve of the vertebrae of the spine (synonym: kyphosis). glaucoma: A condition in which loss of vision occurs because of an abnormally high pressure in the eye. glycosaminoglycan (GAG): A long repeating chain of complex carbohydrate (sugar) molecules that is a common constituent of secretions and the connective tissue between cells. Formerly called mucopolysaccharide. heparan n-sulfatase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS III-A. hepatomegaly: Enlargement of the liver. hepatosplenomegaly: Enlargement of the liver and the spleen. (Hepatomegaly: enlargement of the liver; splenomegaly: enlargement of the spleen.) hernia: Protrusion of a part or structure (e.g., a loop of the small intestine) through the tissues normally holding it in. heterozygote: An individual possessing a variant gene and a normal gene at identical sites of homologous chromosomes (adjective: heterozygous). heterogeneity: Variations in clinical features (characteristics) within a specific disease. hip dysplasia: Abnormal hip formation. homologous chromosomes: A pair of chromosomes, one from each parent, having the same gene loci (locations) in the same order. homozygote: An individual possessing a pair of identical genes, either both normal or both variant, at identical sites on homologous chromosomes. Hurler syndrome: Historical term for the severe end of the clinical spectrum of MPS I. Hurler-Scheie syndrome: Historical term for less-severe MPS I, the part of the clinical spectrum that is intermediate between Hurler and Scheie syndromes. Hunter syndrome: See MPS II. hyaluronidase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS IX. hydrocephalus: An abnormal increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid within the ventricles of the brain. Communicating hydrocephalus or increased pressure may be caused by obstruction to the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the ventricles or a failure to reabsorb it into the cerebral sinuses. It can be treated using a ventriculoperitoneal shunt. hypoxia: A deficiency of oxygen in the tissue or blood. inguinal hernia: Hernia occurring in the lower abdomen and groin. I-cell disease: See ML II. iduronate sulfatase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS II. individual education program (IEP): A program designed for each child within the public school system who receives special educational services. Its goals are to improve teaching, learning, and appropriate goal setting for each 4
5 A resource for individuals and families living with MPS individual. Often, a team that includes members from the school system and the family is involved in designing the IEP. intubation: The placement of a breathing tube during anesthesia. joint contracture: Fibrosis of a muscle tissue producing shrinkage and shortening of the muscle without generating any strength. It is usually a consequence of pain in or disuse of a muscle or limb. kyphosis: Abnormal angular curve of the vertebrae of the spine (synonym: gibbus). lumbar puncture: A procedure in which cerebrospinal fluid is withdrawn by means of a needle inserted into the membrane space in the region of the lower back. This procedure may be performed to measure intracranial pressure (pressure inside the head) to aid in diagnosing hydrocephalus. lysosomal enzyme: A protein found within the cytoplasm of most cells, especially leukocytes (white blood cells), kidney cells, and liver cells. It is a key component in the function of digestive processes within the cell. lysosomal storage disorder (LSD): An inborn error of metabolism resulting in a particular lysosomal enzyme deficiency. At this time there are more than 40 identifiable lysosomal storage disorders. lysosome: A specialized compartment (organelle) in the cytoplasm of cells that contains enzymes responsible for breaking down substances in the cell. melatonin: A compound involved in circadian rhythms (biological variations during a 24-hour period). It is sometimes used as a sleep aid for those with MPS disorders. atrium and the left ventricle, don t close evenly, allowing a small amount of blood to leak back into the left atrium. ML II: Also called I-cell disease. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme n-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase. An autosomal recessive disease characterized by severe psychomotor developmental delay and by many of the clinical features seen in severe MPS I. ML III: Also called pseudo-hurler polydystrophy. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme n-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase. An autosomal recessive disease with a less severe disease course than ML II, becoming apparent later in life, with survival into adulthood. Morquio syndrome: See MPS IV. MPS I: Historically called Hurler, Hurler- Scheie, and Scheie syndromes. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme alpha-l-iduronidase. An autosomal recessive, heterogeneous disease characterized by a wide range of clinical involvement, including corneal clouding, bone changes, stiff joints, large liver and spleen, and heart disease. MPS II: Also called Hunter syndrome. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme iduronate sulfatase. An X-linked recessive, heterogeneous disease characterized by a wide range of clinical involvement, including large liver and spleen, stiff joints, bone changes, and heart disease. MPS III: Also called Sanfilippo syndrome. An autosomal recessive disease classified into four types based on the enzyme deficiency. The features in each type are similar and characterized by severe central nervous system degeneration but only mild somatic (body-related) problems. Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome: See MPS VI. menarche: A woman s first menstrual period. mitral valve prolapse: A condition where flaps between two parts of the heart, the left 5
6 Mucopolysaccharidosis MPS III-A: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme heparan n-sulfatase. MPS III-B: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme alpha-n-acetylglucosaminidase. MPS III-C: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme acetyl CoA: alpha-glucosaminide acetyltransferase. MPS III-D: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme n-acetyl glucosamine 6-sulfatase. MPS IV: Also called Morquio syndrome. An autosomal recessive disease classified into two types based on the enzyme deficiency, each with a wide range of clinical manifestations. Both types are characterized by short-trunk dwarfism, fine corneal deposits, and preservation of cognitive function. MPS IV-A: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme galactose 6-sulfatase. MPS IV-B: Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme beta-galactosidase. MPS VI: Also called Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme arylsulfatase B. An autosomal recessive heterogeneous disease characterized by a wide range of clinical involvement, including corneal clouding, bone abnormalities, stiff joints, large liver, heart disease, and normal cognitive function. MPS VII: Also called Sly syndrome. Caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme betaglucuronidase. An autosomal recessive disease characterized by large liver and spleen, bone abnormalities, and a wide spectrum of severity. MPS IX: An autosomal recessive disease caused by a deficiency of the lysosomal enzyme hyaluronidase, characterized by short stature, soft-tissue masses, normal joint movement, and normal cognitive function. mucolipidosis: Term coined to denote diseases that combined clinical features common to both the mucopolysaccharidoses and the sphingolipidoses (diseases characterized by abnormal lipid or fat metabolism, affecting nerve tissue). See ML II and ML III. mucopolysaccharide: A complex carbohydrate molecule that is a common constituent of secretions and the connective tissue between cells. Although the molecules were originally called mucopolysaccharides because of their ability to form thick, mucous-like solutions, the terminology was revised to proteoglycans and subsequently to glycosaminoglycans or GAGs in recent decades. mutation: A change in the genetic material (DNA) of a cell that alters expected genetic processes. n-acetylglucosamine 6-sulfatase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in MPS III-D. n-acetylglucosaminyl-1-phosphotransferase: Lysosomal enzyme deficient in ML II/III. odontoid dysplasia: Malformation in the bones that stabilize the connection between head and neck. otitis media: Inflammation of the middle ear occurring commonly in children as a result of an infection and often causing pain and temporary hearing loss. papilledema: Swelling around the optic disc (the blind spot where the optical nerve joins the eye). Port-a-Cath: Brand name for a long-term indwelling catheter into a central vein with access through the skin. posterior: Back. precocious puberty: The early onset of sexual maturation. 6
7 A resource for individuals and families living with MPS preimplantation genetic diagnosis (PGD): Also known as preimplantation testing. A procedure used to decrease the chance of a particular genetic condition for which a fetus is specifically at risk by testing one cell from embryos from in vitro fertilization for the DNA mutation known in the family. Only embryos found not to carry the DNA mutation are transferred to the mother s uterus. pseudo-hurler polydystrophy: See ML III. psychomotor performance: The ability to coordinate mental activity with physical activity. For example, catching a ball, driving, and dancing are all examples of activities requiring good psychomotor performance. pulmonary: Of the lung, or relating to the lung. pulmonary hypertension: High blood pressure in the blood vessels supplying the lungs. recessive disease: See autosomal recessive disease and X-linked recessive disease. recombinant DNA: DNA that contains genes from different sources that have been combined by the techniques of genetic engineering. retina: A part of the eye that turns light into nerve signals for the brain, allowing your brain to process the images that you see. retinal: Of the retina, or relating to the retina. retrosternal pain: Pain behind the chest area. rhinorrhea: Thick, chronic discharge of mucus from the nose. scaphocephalic: Having a long, narrow head shape. Sanfilippo syndrome: See MPS III. scoliosis: Lateral (sideways) deviation of the spine. seizures: Disruption of electrical signals in the brain. Seizures may cause brief changes in a person s body movements, awareness, emotions, or senses such as taste, smell, vision, or hearing. sinusitis: A sinus infection. Sinus infections are common in people with MPS disorders. skeletal survey: An X-ray to examine the skeleton (the bones of the body) for problems or abnormalities. sleep apnea: A temporary cessation of breathing during sleep, generally caused by obstruction of the airway. Sly syndrome: See MPS VII. spinal fusion: Surgery to connect the spinal bones to each other to prevent slippage. spleen: A large organ situated on the left side of the body below and behind the stomach. splenomegaly: Enlargement of the spleen. stem cell: A cell whose daughter cells have the potential to develop into a variety of specialized cell types. stem cell transplant: A therapeutic treatment where stem cells from bone marrow, peripheral blood, or umbilical cord blood are infused into the bloodstream after the original bone marrow cells have been ablated (destroyed) by chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy. The cells migrate to the interior of certain bones and begin producing immature cells called committed progenitors. These committed progenitors produce colonies of cells that eventually mature into red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. The purpose is to allow the donor cells to repopulate the bone marrow and various other tissues of the recipient. Scheie syndrome: Historical term for the less severe (attenuated) end of the clinical spectrum of MPS I. 7
8 Mucopolysaccharidosis If the cells can also provide the missing gene and function to the recipient, then clinical symptoms can sometimes improve. It is important to note that the process of destroying the recipient s bone marrow cells is extremely invasive and leaves the individual with a compromised immune system and susceptible to life-threatening infections. Also, it is critical to have donor cells come from an individual with compatible tissue types in order to avoid rejection of the donor cells after the transplant. sternum: A long, flat bone, jointed with the cartilages of the first seven ribs and with the clavicle (collar bone), forming the middle part of the anterior (front) wall of the thorax (chest area). It is the vertical bone that can be felt in the middle of the chest between the ribs. swallowing study (modified barium swallow study): Videotaped X-ray of a individual s oral (mouth) and pharyngeal (throat) mechanism during eating or drinking. This procedure is often ordered to evaluate for obstruction or aspiration (inhalation of foods). The results from this procedure may allow a therapist to better identify ways to safely feed the individual and ways to help the family make appropriate modifications. umbilical hernia: A hernia in which bowel or connecting tissue protrudes through the abdominal wall under the skin at the umbilicus (navel). urinary: Of the urine, or found in the urine. urticaria: Hives. ventriculoperitoneal shunt: A thin tube that drains fluid from the brain into the abdominal cavity. Used in the treatment and management of hydrocephalus. X-linked recessive disease: A disease that follows a pattern of inheritance in which a mutation in a gene on the X chromosome causes males to have clinical features of a particular condition, as they only have one X chromosome. A pattern of inheritance seen in MPS II. trachea: The air tube from the mouth to the lungs. Around the level of the middle of the chest, it divides into the right and left main bronchi. tracheostomy: A surgical procedure in which a hole is made into the trachea through the neck to relieve obstruction to breathing. A curved breathing tube is usually inserted through the hole. trigger finger: A condition caused by a thickening of the tendon that bends the fingers, often experienced as swelling in the palm of the hand as the finger is moved. 8
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Inheritance patterns. Lysosomal function. Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): Keys to Early Recognition and Intervention
 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): Keys to Early Recognition and Intervention Lindsay Torrice, MSN, CPNP PC Clinical Instructor
39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): Keys to Early Recognition and Intervention Lindsay Torrice, MSN, CPNP PC Clinical Instructor
A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease
 A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease Annick Raas-Rothschild, MD Pediatrician-Medical Geneticist Director of the Rare Diseases institute Institute of Genetics Sheba Tel Hashomer Medical Center Annick.rothschild@sheba.health.gov.il
A Rare disease: MPS III San Filippo disease Annick Raas-Rothschild, MD Pediatrician-Medical Geneticist Director of the Rare Diseases institute Institute of Genetics Sheba Tel Hashomer Medical Center Annick.rothschild@sheba.health.gov.il
Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (MPS VII) Sly
 Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (MPS VII) Sly 0845 389 9901 mps@mpssociety.org.uk www.mpssociety.org.uk What is Sly Disease? Sly Disease is a mucopolysaccharide storage disorder also known
Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis VII (MPS VII) Sly 0845 389 9901 mps@mpssociety.org.uk www.mpssociety.org.uk What is Sly Disease? Sly Disease is a mucopolysaccharide storage disorder also known
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Hurler Syndrome (Severe Type) -A Rare Case Report
 Annals of Dental Research (2012) Vol 2 (1): 26-30 Mind Reader Publications: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Hurler Syndrome (Severe Type) -A Rare Case Report
Annals of Dental Research (2012) Vol 2 (1): 26-30 Mind Reader Publications: All Rights Reserved Annals of Dental Research www.adres.yolasite.com Case Report Hurler Syndrome (Severe Type) -A Rare Case Report
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) II
 A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) II Table of Contents Founded in 1984, The Canadian Society for Mucopolysaccharide and Related Diseases Inc. (The Canadian MPS Society) is committed
A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) II Table of Contents Founded in 1984, The Canadian Society for Mucopolysaccharide and Related Diseases Inc. (The Canadian MPS Society) is committed
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Guide to Understanding Fucosidosis
 Guide to Understanding Fucosidosis 0845 389 9901 mps@mpssociety.org.uk www.mpssociety.org.uk Contents What is Fucosidosis? What Causes Fucosidosis? How Common is Fucosidosis? Does Fucosidosis Affect Individuals
Guide to Understanding Fucosidosis 0845 389 9901 mps@mpssociety.org.uk www.mpssociety.org.uk Contents What is Fucosidosis? What Causes Fucosidosis? How Common is Fucosidosis? Does Fucosidosis Affect Individuals
A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) VI
 A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) VI Table of Contents Founded in 1984, The Canadian Society for Mucopolysaccharide and Related Diseases Inc. (The Canadian MPS Society) is committed
A Guide to Understanding Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) VI Table of Contents Founded in 1984, The Canadian Society for Mucopolysaccharide and Related Diseases Inc. (The Canadian MPS Society) is committed
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
A Guide to Understanding MPS VII
 A Guide to Understanding MPS VII Sly Syndrome Table of Contents Introduction...2 What causes MPS VII?...3 How common is MPS VII?...4 How is MPS VII inherited?...4 How is MPS VII diagnosed?...5 Prenatal
A Guide to Understanding MPS VII Sly Syndrome Table of Contents Introduction...2 What causes MPS VII?...3 How common is MPS VII?...4 How is MPS VII inherited?...4 How is MPS VII diagnosed?...5 Prenatal
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease
 Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Understanding Late-Onset Pompe Disease What Is a Lysosome? Millions of tiny units called cells make up the human body. Each cell has its own job to keep the body running. Within each cell, there are organelles,
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is mandated and administered by the Illinois Department of
Most mammalian cells are located in tissues where they are surrounded by a complex extracellular matrix (ECM) often referred to as connective tissue.
 GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS Most mammalian cells are located in tissues where they are surrounded by a complex extracellular matrix (ECM) often referred to as connective tissue. The ECM contains three major classes
GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS Most mammalian cells are located in tissues where they are surrounded by a complex extracellular matrix (ECM) often referred to as connective tissue. The ECM contains three major classes
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II THE BODY SYSTEMS Anatomy & Physiology II The Body Systems Michelle Cochrane 2014 All rights reserved. This material is subject to copyright and may not be reprinted or reproduced
What s New in Newborn Screening?
 What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
What s New in Newborn Screening? Funded by: Illinois Department of Public Health Information on Newborn Screening Newborn screening in Illinois is administered by the Illinois Department of Public Health.
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole
 CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
CHAPTER 2 Terms Pertaining to the Body as a Whole OBJECTIVES 1. Define terms that apply to the structural organization of the body. 2. Identify the body cavities and the organs contained within the cavities.
OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION
 Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives October Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body, all the way from our head to our toes. Did you
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Definitions. You & Your New Transplant ` 38
 Definitions Acute Short, relatively severe Analgesic Pain medicine Anemia A low number of red blood cells Anesthetic Medication that dulls sensation in order to reduce pain Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
Definitions Acute Short, relatively severe Analgesic Pain medicine Anemia A low number of red blood cells Anesthetic Medication that dulls sensation in order to reduce pain Acute Tubular Necrosis (ATN)
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Mitral Regurgitation
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION Mitral Regurgitation Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment This handout describes mitral regurgitation, a disease of the mitral valve. It explains how this disease is
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III
 orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III Disease name: Mucolipidosis Type 2 and 3 ICD 10: E77.0 Synonyms: Mucolipidosis type 2 - I-cell disease N-acetyl-glucosamine
orphananesthesia Anesthesia recommendations for patients suffering from Mucolipidosis II and III Disease name: Mucolipidosis Type 2 and 3 ICD 10: E77.0 Synonyms: Mucolipidosis type 2 - I-cell disease N-acetyl-glucosamine
Growing bones. Baby s s bones are made from cartilage Babies have 300 bones Adults have 206. bones
 Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Body Systems Objectives Students should be able to list the different body systems Students should be able to give a general function of each of the body systems Students should be able to tell the differences
Introduction. Study detail of structure - - Gross Anatomy. Study all structures in one part of body Study of internal structures as relate to skin
 Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Introduction What is Anatomy and Physiology? Anatomy study of the shape and structure of body parts and their relationships to one another Physiology study of how the body functions individually and cooperatively
Inguinal Hernia. Hernia Awareness Month. What is a Hernia? Common Hernia Types
 Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
Hernia Awareness Month What is a Hernia? A hernia occurs when an organ pushes through an opening in the muscle or tissue that holds it in place. For example, the intestines may break through a weakened
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Fatty Acids Synthesis L3
 Fatty Acids Synthesis L3 The pathway for fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas, oxidation occurs in the mitochondria. The other major difference is the use of nucleotide co-factors. Oxidation
Fatty Acids Synthesis L3 The pathway for fatty acid synthesis occurs in the cytoplasm, whereas, oxidation occurs in the mitochondria. The other major difference is the use of nucleotide co-factors. Oxidation
October. Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives
 October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
October OHIO STATE UNIVERSITY EXTENSION Cloverbud Investigators: Career Detectives Background: Today we are going to learn about our bones and how they join together to hold up our body all the way from
3. There are three pairs of salivary glands that have three important functions. These are: a)
 Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Reference: 1. Use the human systems in your textbook.. 2. Pig instruction packet. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1. What is the process of digestion? 2. List three major glands involved in this process? 3. There are
Functions of the Skeletal System. Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure. Classification of Bones. Bone Shapes
 Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Chapter 6: Osseous Tissue and Bone Structure Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Support 2. Storage of minerals (calcium) 3. Storage of lipids (yellow marrow) 4. Blood cell production (red marrow) 5. Protection
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Friday, January 4. Bell Work:
 Friday, January 4 Bell Work: Red green colorblindness is an X linked trait and is recessive. A male who is normal marries a woman who is a carrier, what is the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? 1 Genetic
Friday, January 4 Bell Work: Red green colorblindness is an X linked trait and is recessive. A male who is normal marries a woman who is a carrier, what is the phenotypic ratio of their offspring? 1 Genetic
Anatomy notes-thorax.
 Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
Anatomy notes-thorax. Thorax: the part extending from the root of the neck to the abdomen. Parts of the thorax: - Thoracic cage (bones). - Thoracic wall. - Thoracic cavity. ** The thoracic cavity is covered
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body The Human Body Composed of many different organs and tissues All parts work together: To sustain life Allow activity Injury or illness impairs functions 3-3 Cranial located in
Bones are made up of bone cells and tissues Hard, dense and smooth outer materials, which are made of calcium, give bones there shape and strength.
 1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
1. 2. 3. 4. To protect your body and give it shape. To protect your internal organs. To provide a scaffolding for your muscles, allowing you to move. To store minerals and make blood cells. Bones are made
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
Skeletal System Tour Lab. Station Label the bones on your answer sheet.
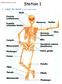 Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Station 1 1. Label the bones on your answer sheet. Station 2 2. Label the joints on your answer sheet. Fixed Pivot Hinge Hinge Gliding Ball and Socket Hinge Swivel Gliding Gliding Ball and Socket Types
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Homeostasis Practice Test
 Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
Name: ate: 1. Which statement explains the importance of maintaining a constant internal environment to ensure proper enzyme functioning? A. hanges in ph and temperature will cause the enzyme reaction
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
RADPrimer Curriculum Breast Topics Covered Basic Intermediate 225
 Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Breast Anatomy & Normal Variants 11 Breast Imaging Modalities 13 BI RADS Lexicon 3 Mammography: Masses 9 Mammography: Calcifications 17 Mammography: Additional Findings 8 Ultrasound Features 10 Ultrasound
Unusual Mucopolysaccharidoses cases. Tim Hutchin and Louise Allen Newborn Screening and Biochemical Genetics, Birmingham Children s Hospital
 Unusual Mucopolysaccharidoses cases Tim Hutchin and Louise Allen Newborn Screening and Biochemical Genetics, Birmingham Children s Hospital A Brief MPS History Lesson.. In 1917 Hunter (type II) reported
Unusual Mucopolysaccharidoses cases Tim Hutchin and Louise Allen Newborn Screening and Biochemical Genetics, Birmingham Children s Hospital A Brief MPS History Lesson.. In 1917 Hunter (type II) reported
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins
 Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
Large veins of the thorax Brachiocephalic veins Right brachiocephalic vein: formed at the root of the neck by the union of the right subclavian & the right internal jugular veins. Left brachiocephalic
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Skeletal System The Skeletal System Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support Protect internal organs Allows your body to move Stores and produced materials that your body needs You have 206 bones
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Lab Report Sheet. Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did)
 Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Appendix 107 108 Lab Report Sheet Title: Hypothesis (What I Think Will Happen) Materials (What We Used) Procedure (What We Did) Observations and Results (What I Saw and Measured) Worksheet prepared by
Epithelial Tissues. Types of Epithelial Tissues: Lining of Kidney
 Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Epithelial Tissues Covers the entire body surface and most of the body s inner cavities Outer epidermis (skin) protects from injury and drying out Inner epidermal tissue (on internal surfaces) often serves
Chapter 16. Organ Donation: Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems Tissues. Epithelial Tissue. Epithelial Tissue
 Chapter 16 Organ Donation: Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems 16.1 Tissues A is a group of similar cell types that perform a common function Four main types of tissues Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue,
Chapter 16 Organ Donation: Tissues, Organs, and Organ Systems 16.1 Tissues A is a group of similar cell types that perform a common function Four main types of tissues Epithelial Tissue Epithelial tissue,
Outline. Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory. Organization of the Human Body. Tissue - Epithelium. Tissues 3/2/ Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc
 Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Outline Bio 105: Tissues Laboratory Laboratory 5 Reading: Chapter 4 I. Cell to cell contact II. Body Cavities III. Membranes IV. Homeostasis V. Integumentary System I. Includes skin, hair and nails 1 2
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body
 Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Chapter 1- An Orientation to the Human Body Overview of Anatomy and Physiology: -Anatomy- of body parts and their relationships to one another. -Gross or Macroscopic= large and easily observable -Microscopic=
Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH)
 HLH Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) Information for families hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this leaflet This booklet has been produced jointly between PID UK, Great Ormond
HLH Haemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis (HLH) Information for families hello@piduk.org 0800 987 8986 www.piduk.org About this leaflet This booklet has been produced jointly between PID UK, Great Ormond
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
CHAPTER 3. The Human Body National Safety Council
 CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
CHAPTER 3 The Human Body Lesson Objectives 1. Describe the primary areas of the body. 2. List the 10 body systems and explain a key function of each. 3. For each body system, describe at least 1 injury
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
2
 1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1 2 Although the term "cardiomyopathy" could theoretically apply to almost any disease affecting the heart, it is usually reserved for "severe myocardial disease leading to heart failure".cardiomyopathy
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation
 1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
1.45_Internet Assignment #1: The Human Body: An Orientation Go to the following website to complete the following Activities, Quizzes, and Reading: http://wps.aw.com/bc_marieb_hap_9_oa/218/55856/14299219.cw/index.html
Early Diagnosis of the Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): An Orthopedic Perspective. Disclosures
 Early Diagnosis of the Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): An Orthopedic Perspective Director, Skeletal Health and Dysplasia Program Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington Disclosures 1. I am an
Early Diagnosis of the Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS): An Orthopedic Perspective Director, Skeletal Health and Dysplasia Program Seattle Children s Hospital University of Washington Disclosures 1. I am an
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation Procedure (TAVI)
 Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
Page 1 of 5 Procedure (TAVI) Introduction Aortic stenosis (AS) is a common heart valve problem associated with heart failure and death. Surgical valve repair or replacement is recommended if AS patients
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS
 GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
GLOSSARY OF COMMON MEDICAL TERMS PROCEDURES craniotomy: making a surgical incision through the cranium (the part of the skull that encloses the brain); usually done to relieve pressure around the brain.
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
UMC HEALTH SYSTEM Lubbock, Texas :
 Consent for Commonly Performed Procedures in the Adult Critical Care Units I, the undersigned, understand that the adult intensive and intermediate care units ( critical care units ) are places where seriously
Consent for Commonly Performed Procedures in the Adult Critical Care Units I, the undersigned, understand that the adult intensive and intermediate care units ( critical care units ) are places where seriously
Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology for Exercise. Unit Reference Number H/600/9013
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION PAPER Paper number MPAPEH2.01 Please insert this reference number in the appropriate boxes on your candidate answer sheet Title Time allocation 60 minutes Mock Paper Level 2 Anatomy
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin
 Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
Name Class Date Station # Laboratory Investigation 24A Chapter 24A: Human Skin Human Anatomy & Physiology: Integumentary System You may refer to pages 415-421 in your textbook for a general discussion
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 22. Body Organization & Structure
 Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
Chapter 22 Body Organization & Structure Start-Up Activity Too Cold for Comfort Hold a few pieces of ice in one hand. Hold the ice until the cold is uncomfortable. Then release the ice into the dish. Compare
February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701
![February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 February [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701](/thumbs/74/69742203.jpg) February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
February 2009 [KU 1010] Sub. Code: 4701 B.Sc (Nursing ) DEGREE EXAMINATION Maximum : 75 marks SECTION A (ANATOMY) 1. Describe the uterus under the following heads: a) Situation b) Normal position c) Parts
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Frog Dissection. Name: Block:
 Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
International Journal of Current Research in Sciences
 Review Article International Journal of Current Research in Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 www.ijcrims.com Coden: IJCRPP(USA) http://s-o-i.org/1.15/ijcrms-2016-2-1-9 MEDICAL ASPECTS OF CARBOHYDRATES: HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDES
Review Article International Journal of Current Research in Sciences ISSN: 2454-5716 www.ijcrims.com Coden: IJCRPP(USA) http://s-o-i.org/1.15/ijcrms-2016-2-1-9 MEDICAL ASPECTS OF CARBOHYDRATES: HETEROPOLYSACCHARIDES
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal
 What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
What are the main functions of the male reproductive system? 1. Produce sperm 2. Deposit sperm into the female 3. Provide a pathway for the removal of urine Where is sperm produced? -In the 2 testes What
