World Journal of Radiology. Imaging of the temporomandibular joint: An update
|
|
|
- Calvin Owens
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 W J R World Journl of Rdiology Submit Mnusript: Help Desk: DOI: /wjr.v6.i8.567 World J Rdiol 2014 August 28; 6(8): ISSN (online) 2014 Bishideng Publishing Group In. All rights reserved. REVIEW Imging of the temporomndibulr joint: An updte Asim K Bg, Snthosh Gddikeri, Aprn Singhl, Simms Hrdin, Benson D Trn, Josue A Medin, Joel K Curé Asim K Bg, Aprn Singhl, Simms Hrdin, Benson D Trn, Josue A Medin, Joel K Curé, Setion of Neurordiology, The Deprtment of Rdiology, Shool of Mediine, The University of Albm t Birminghm, Birminghm, AL , United Sttes Snthosh Gddikeri, Deprtment of Rdiology, University of Wshington, SS-202 Settle, WA , United Sttes Author ontributions: Bg AK ontributed to the rthritis, imges nd overll integrity, mnusript revision nd finl pprovl the mnusript; Gddikeri S ontributed to the internl derngement nd mnusript revision; Singhl A ontributed to the norml joint ntomy, ntomi vrition nd mnusript revision; Hrdin S ontributed to the ntomi vrition nd mnusript revision; Trn BD ontributed to the deposition diseses nd tumors, mnusript revision; Medin JA ontributed to the imging tehniques, mnusript revision; Curé JK ontributed to the imges, overll integrity, mnusript revision nd finl pprovl. Correspondene to: Asim K Bg, Assistnt Professor, Setion of Neurordiology, The Deprtment of Rdiology, Shool of Mediine, The University of Albm t Birminghm, JT N432, th Street South, Birminghm, AL , United Sttes. bg@ubm.edu Telephone: Fx: Reeived: Deember 28, 2013 Revised: Februry 27, 2014 Aepted: June 20, 2014 Published online: August 28, 2014 tumors re lso disussed in this rtile Bishideng Publishing Group In. All rights reserved. Key words: Temporomndibulr joint; Mgneti resonne imging; Imging; Computed tomogrphy; Antomy; Pthologies Core tip: Imging of the temporomndibulr joint: An updte is thorough review of the imging tehniques nd imging ppernes of norml ntomy, ntomi vrition nd pthologies of the temporomndibulr joint (TMJ). Numerous imges re ppropritely used for illustrtion of the key onepts of TMJ imging. Nie blend of exquisite detils nd beutiful illustrtive imges is the min feture of this rtile. The purpose of this rtile is esy understnding of mny diffiult spets of imging of the TMJ. Bg AK, Gddikeri S, Singhl A, Hrdin S, Trn BD, Medin JA, Curé JK. Imging of the temporomndibulr joint: An updte. World J Rdiol 2014; 6(8): Avilble from: URL: DOI: dx.doi.org/ /wjr.v6.i8.567 Abstrt Imging of the temporomndibulr joint (TMJ) is ontinuously evolving with dvnement of imging tehnologies. Mny different imging modlities re urrently used to evlute the TMJ. Mgneti resonne imging is ommonly used for evlution of the TMJ due to its superior ontrst resolution nd its bility to quire dynmi imging for demonstrtion of the funtionlity of the joint. Computed tomogrphy nd ultrsound imging hve speifi indition in imging of the TMJ. This rtile fouses on stte of the rt imging of the temporomndibulr joint. Relevnt norml ntomy nd biomehnis of movement of the TMJ re disussed for better understnding of mny TMJ pthologies. Imging of internl derngements is disussed in detil. Different rthropthies nd ommon INTRODUCTION Pin relted to the temporomndibulr joint (TMJ) is ommon in the generl popultion. Only bout 3%-7% of the ptients with pin relted to TMJ seek medil ttention [1,2]. Although TMJ disorders or dysfuntions re the most ommon linil onditions for imging referrls, pthologies speifi to the bone nd the joints re lso ommon. Different imging modlities re vilble to imge the TMJ, eh with inherent strengths nd weknesses. Mgneti resonne imging (MRI) is the most widely used nd is dignosti tehnique of hoie. In this rtile, we review the imging tehniques, ntomy pthology involving the TMJ with speil emphsis on MRI findings. 567 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
2 A B Anterior Figure 1 Antomy of the rnil omponent of temporomndibulr joint. A: Photogrph of skull speimen; B: 3-D volume rendered imge obtined from temporl bone Redline demonstrtes the psulr tthment. AE: Artiulr eminene; GF: Glenoid foss; LB: Lterl border; PEP: Preglenoid plne; PGP: Postglenoid plne; T: Tuberle. Embryology nd development of TMJ The TMJ is one of the lst dirthrodil joints to pper in utero nd does not emerge in the rniofil region until the 8 th week of gesttion. The mxill, mndible, musles of mstition, nd bionve dis develop embryologilly from the first brnhil rh through the 14 th week of gesttion. The TMJ is onsiderbly underdeveloped t birth in omprison to other dirthrodil joints mking it suseptible to perintl nd postntl insults. The joint ontinues developing in the erly hildhood yers s the jw is utilized for suking motions nd eventully hewing. ANATOMY OF TMJ Posterior Anterior Posterior AE PEP GF PGP AE PEP GF PGP The TMJ is ginglymorthrodil synovil joint (ltin:ginglymus = hinge joint) tht llows both bkwrd nd forwrd trnsltion s well s gliding motion [3]. Similr to the other synovil joints in the body, the TMJ hs disk, rtiulr surfes, fibrous psule, synovil fluid, synovil membrne, nd ligments. Wht mkes this joint unique is the rtiulr surfes re overed by fibrortilge insted of hyline rtilge. The rtiulr surfes of the TMJ re formed inferiorly by the mndibulr ondyle nd superiorly by the glenoid foss (lso known s mndibulr foss) nd rtiulr eminene of the temporl bone. T LB LB Artiulr surfes The mndibulr omponent onsists of the ovoid ondylr proess tht is mm wide in the trnsverse dimension nd 8-10 mm wide in the ntero-posterior dimension [3]. The pperne of the mndibulr ondyle is extremely vrible between ptients nd in different ge groups. The rnil omponent of the TMJ lies below the squmous portion of the temporl bone nterior to tympni plte. The rtiulr foss is formed entirely by the squmous portion of the temporl bone. The posterior prt of the rtiulr foss is elevted to form the posterior rtiulr ridge. In most individuls the posterior rtiulr ridge beomes thiker on the lterl spet nd forms one shped projetion known s postglenoid proess (PGP). The tympnosqumosl fissure lies t the posterior nd lterl prt of the glenoid foss, between the squmous nd tympni portion of the petrous bone nd seprtes the rtiulr surfe form the nonrtiulr surfe of the glenoid foss. Along the medil spet of the glenoid foss is the petrotympni fissure nteriorly nd the petrosqumous fissure posteriorly. The rtiulr eminene (AE) forms the nterior boundry of the glenoid foss. The AE is trnsverse bony br nterior to the glenoid foss nd medil to the posterior mrgin of the zygomti proess. The nterior slope of the AE is known s the preglenoid plne (PEP) nd rises gently from the infrtemporl surfe of the squmous bone. The mndibulr ondyle nd the rtiulr disk trvel nteriorly to the summit of the AE nd onto PEP during wide mouth opening. The gentle nterior slope filittes smooth bkwrd movement of the ondyle nd disk from the nterior position bk to neutrl position. The rtiulr tuberle is smll bony knob t the lterl spet of the AE where the lterl ollterl ligment tthes. The lterl border of glenoid foss is slightly rised from the foss joining the nterior tuberle with the PGP (Figure 1). Artiulr disk The rtiulr disk is round or ovl, bionve, vsulr fibrortilge between the ondyle nd glenoid foss. The disk is onsiderbly thinner entrlly in the intermedite zone. The tringulr nterior bnd is pproximtely 2 mm in thikness nd blends with the joint psule. The posterior bnd is pproximtely 3 mm in thikness nd ontinues s bilminr zone (lso known s retrodisl region nd posterior tthment), whih onsists of superior fibroelsti lyer (lso known s temporl lmin) tht tthes to PGP nd n inferior fibrous lyer (lso known s the inferior lmin) tht tthes to the posterior ondylr nek. The superior lyer prevents slipping of the disk during wide mouth opening nd the inferior lyer prevents exessive rottion of the disk over the ondyle. Both the lmin re seprted by loose elsti fibers with blood vessels nd nerves. These fibers tth to the posterior joint psule nd ugments disk retrtion during mouth losing. The bnds re longer in the mediolterl dimension thn in the ntero-posterior dimension [4]. The smller nterior bnd tthes nteriorly to the joint 568 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
3 A B b BZ b Jw-losing musles/ddutors The msseter is the strongest musle of mstition nd hs two prts tht blend together nteriorly. The superfiil prt origintes from the nterior two-thirds of the zygomti rh nd inserts on the lower one-third of the lterl surfe of the mndibulr rmus. The deep prt origintes from the entire zygomti rh nd inserts on the upper two-thirds of the rmus. The medil pterygoid ourses prllel to the msseter long the medil spet of the mndible. The nterior prt rises from the lterl surfe of the pltine pyrmidl proess nd the mxillry tuberosity. The posterior prt origintes from the pterygoid foss nd the medil surfe of the lterl pterygoid plte. The medil pterygoid inserts on the inferomedil surfe of the mndibulr rmus. The temporlis musle origintes from the temporlis foss nd inserts on the oronoid proess nd inner side of the mndibulr rmus. The fibers lso tth diretly to the medil side of the oronoid proess nd rmus. Figure 2 Norml ntomy. Sgittl proton density weighted losed mouth nd open mouth view of mgneti resonne imging. A: On the losed mouth view, the disk is loted posterior to the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ). It n be noted tht the bow-tie shpe of the disk: Thiker nterior bnd (red rrow) nd posterior bnd (white rrow) with thinner entrl zone (ornge rrow). Bilminr zone (BZ) is loted posterior to the posterior bnd. It n lso be noted tht the inferior joint omprtment (white rrowhed) between the disk nd the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, b) nd superior joint omprtment (red rrowhed) between the rtiulr eminene nd the disk; B: On the open mouth view (in different ptient), the thinner intermedite zone (red rrow) of the disk is interposed between the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ) nd the ondylr hed (the letter, b) in bow-tie fshion. Ornge rrowhed demonstrtes temporl lmin nd blk rrowhed indite inferior lmin. psule, ondylr hed, nd AE. Some ptients hve n dditionl ntero-medil tthment to the superior belly of the lterl pterygoid musle. Unlike its nterior nd posterior tthments, the disk is not tthed to the joint psule medilly nd lterlly. Insted, the disk is firmly tthed to the medil nd lterl poles of the mndibulr ondyle. This llows simultneous movements of the disk nd the ondyle (Figure 2). Musles The musles of mstition (medil nd lterl pterygoids, msseter, nd temporlis) in ddition to other essory musles help opening nd losing of the jw [4-6]. The lterl pterygoid in onjuntion to the stylohyoid, mylohyoid nd geniohyoid musles is used to open the jw. The temporlis, medil pterygoid, nd msseter musles lose the jw. The lterl pterygoid, prt of the msseter musle nd the medil pterygoid ssist in the nterior trnsltion of the mndible. The protrusive musles (helping forwrd movement) re used lterntely to move the jw lterlly from side to side. Individul musle origins nd tthments re listed below [4,6]. Jw-opening musles/bdutors The lterl pterygoid musle hs two bellies. The superior belly origintes from the infrtemporl surfe of the greter wing of sphenoid. The inferior belly origintes from the lterl surfe of the lterl pterygoid plte. There is wide gp between the two heds of the lterl pterygoid musle tht ome together nterior to the TMJ. The fibers from the superior hed primrily tth to the nteromedil surfe of the mndibulr nek t the pterygoid fove. Additionlly, in some ptients prt of the superior hed diretly tthes to the superomedil spet of the joint psule nd extends to the nteromedil spet of the rtiulr surfe. All of the fibers of the inferior hed tth to the pterygoid fove. Vribility in the tthment of the lterl pterygoid musle is reported with insertions of the musle desribed only to the ondyle or to the ondyle, psule, nd the disk [7-9]. The superior belly helps mintin the physiologi position of the disk in the open mouth position. This is omplished by pulling the disk forwrd with ombined trnsltion nd rottion while exerting forwrd pressure on both the ondyle nd the disk thus stbilizing their reltionship to eh other. The inferior belly pulls the ondyle forwrd out of the foss. When the inferior belly lterntely ontrts, this produes lterl movement of the jw. The digstri musle hs posterior nd n nterior belly united by n onjoined tendon. The posterior belly is tthed to the mstoid proess of the temporl bone nd extends to the hyoid bone beoming ontinuous with the intermedite tendon. A fibrous loop tthed to the hyoid holds the tendon in ple. The nterior belly extends from the tendon to the digstri foss on the lower spet of mndible ner the symphysis. Contrtion of the digstri musles pulls the symphysis menti bkwrds produing the retrusive nd opening movements of the mndible. The geniohyoid, myolohyoid, stylohyoid nd infr- 569 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
4 hyoid musles lso hve supportive role in mndibulr movements tht re beyond the sope of this review. Biomehnis of TMJ movements Jw movement involves high level of intertion nd oordintion between bilterl mndibulr ondyles, disk, musles, nd ligments of the joints. The funtionl intertions within the TMJ re omplex nd inompletely understood [10,11]. A simplisti view of the omplex intertions in open nd losed mouth positions is desribed below. In norml joint, the thin intermedite zone of the disk is lwys interposed between the ondyle nd the temporl bone in both the losed-mouth nd open-mouth positions. This is for the prevention of rtiulr dmge. In the losed mouth position, the ondyle is entered in the glenoid foss. The disk is interposed between the ondyle inferiorly nd the glenoid foss superiorly. The rtiulr eminene is nterior to the disk (Figure 2). The norml disk is positioned suh tht the nterior bnd is in front of the ondyle nd the juntion of the posterior bnd nd bilminr zone lie immeditely bove the ondylr hed ner the 12 o lok position [1,3,4,9,12-14]. However, some ontroversy exists over the rnge of norml position of the disk [1,3,4,14-18]. Dre et l [15] suggest tht the juntion of the posterior bnd nd bilminr zone should fll within 10 degree of vertil to be within 95 perentile of norml. There is signifint vrition in reltionship of the posterior bnd nd bilminr zone in norml popultion, resulting in inpproprite lssifition of nterior disk displement [16,18]. Rmmelsberg et l [17] suggest tht disk positions of up to +30 from the vertil be onsidered norml. Mny other uthors hve proposed tht the intermedite zone be the point of referene so tht in norml joint it is interposed between the ondyle nd the temporl bone in ll joint positions [4,19,20]. Compring to the different disk positions of 12, 11 nd 10 o lok, Orsini et l [19] found the intermedite zone riterion for disk displement to be more stringent. Reently Provenzno Mde et l [20] hve suggested similr onlusions (Figure 2). IMAGING TECHNIQUES A vriety of modlities n be used to imge the TMJ. This inludes non-invsive imging modlities suh s onventionl rdiogrphs, ultrsound, Computed tomogrphy (CT) nd MRI to more invsive imging suh s rthrogrphy. Eh imging modlity hs its uses. Conventionl rdiogrphs hve limited role in evlution of the TMJ. They n be used to evlute only the bony elements of the TMJ. They do not give useful informtion when it omes to the non-bony elements suh s rtilge or djent soft tissues. They lso do not give useful informtion onerning joint effusions, whih re ommonly ssoited with pin nd dis displements. Another disdvntge onerning onventionl rdiogrphs is the problem of superimposition of djent strutures. Mny different views suh s the submentovertex, trnsmxillry, nd the trnsrnil re used to redue superimposition. Ultrsound is less expensive nd esily performed imging modlity tht n be used to evlute the TMJ. This is simple wy to look for the presene of joint effusion [21]. Ultrsound is lso used to evlute rtilge s well s disk displement with both open nd losed mouth imging [21]. It is used for imge-guided injetions for both dignosti nd therpeuti purposes [21]. Typilly, liner trnsduer of 8 MHz or higher is idel. The ptient should be lying supine with the trnsduer pled prllel to line extending from the trgus of the er to the lterl surfe of the nose over the TMJ. CT is useful to evlute the bony elements of the TMJ s well s the djent soft tissues. CT is idel for the evlution of frtures, degenertive hnges, erosions, infetion, invsion by tumor, s well s ongenitl nomlies [21]. A typil imging protool is: 120 kv, 100 ma, 1 mm ollimtion, 1 mm/rottion (pith), nd imged with losed mouth. CT lso llows 3D reonstrutions, whih n be used for evluting ongenitl nomlies nd frtures [21]. CT is predominntly done when there is suspiion of bony involvement from the MRI nd if primry bony pthologies re suspeted linilly. Reltive dvntges of CT over MRI inlude, exquisite bone detils nd 3D ssessment of ongenitl, trumti nd postsurgil onditions. Clinil evlution of the TMJ n be nonspeifi due to overlp of symptoms between internl derngement nd myofil pin dysfuntion [1]. MRI should be prt of the stndrd evlution when n internl struturl joint bnormlity is suspeted beuse MRI provides high resolution nd gret tissue ontrst. This llows for detiled evlution of the ntomy ws well s biomehnis of the joint through open nd losed mouth imging [1]. For optiml imging of the TMJ, smll bilterl surfe oils with smll field of view re used to hieve higher signl to noise rtio nd simultneous bilterl quisition. Closed mouth oronl nd xil T1 sequenes re needed to evlute the overll ntomy nd bone mrrow s well s the djent soft tissues to exlude other djent pthology. In our institution, xil T1 is obtined s lolizer [14]. Bilterl losed mouth nd open mouth T2, proton density (PD) nd dynmi sequenes re obtined in oblique sgittl plne. In our institution, dynmi imges re obtined s rpid quisition of stti imges using single shot fst spin eho (SSFSE) proton density sequene during progressive opening nd losing of the mouth. These imges re displyed sequentilly s ine loop. Mouth opening devies suh s Burnett opening devies my be used for inrementl opening of the mouth ontrolled by the ptient. It n be rgued tht pssive mouth opening with Burnet devie might not reprodue the physiologi onditions ourring during mouth opening given the possible role of the lterl pterygoid musle in dis stbiliztion during mouth opening. Oblique imging entils 30 medil 570 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
5 Tble 1 Temporomndibulr joint mgneti resonne imging protool Plne Sequene Slie thikness TR TE Mouth open/losed Axil T1 2 mm, 0 skip 500 Miniml Closed Coronl T1 3 mm, 0.5 skip 500 Miniml Closed Bilterl Sg Oblq T2 nd PD 3 mm 3500 Min nd 85 Closed nd open Bilterl Sg Oblq T2 3 mm Dynmi ine PD: Proton density; TE: Eho time; TR: Repetition time. from the true sgittl plne [1]. Plese see the tble for speifi MRI protool [1]. A totl of 8 sequenes will need to be performed (Tble 1). Arthrogrphy is n invsive imging tehnique to evlute the TMJ. This imging modlity requires injetion of rdiopque ontrst into the TMJ under fluorosopi guidne. One the ontrst is injeted, the joint n be evluted for dhesions, disk dysfuntion, s well s disk perfortion bsed on how ontrst flows in the joint. This modlity is rrely used tody beuse MRI n be used to evlute the TMJ without being invsive, exposing the ptient to possibility of llergi retion from the ontrst, possibility of infetion, or using rdition. IMAGING APPEARANCE OF NORMAL TMJ MRI On MRI, mrrow ft in the ondyle hs high T1 signl intensity. The ortil bone nd the disk hve low signl intensity on both T1 nd T2 weighted imges beuse of low proton density nd short T2 [12]. Sometimes high T2 nd PD signl intensity n be seen in the entrl portion of the disk similr to entrlly hydrted vertebrl disk [1,4]. The disk is otherwise homogeneous, hypointense nd bionve in shpe. The enter of the posterior bnd my be slightly hyperintense due to presene of loose reolr tissue (Figure 2). The disk s posterior tthment hs higher signl intensity thn musle on proton density nd T1 weighted imges seondry to ftty tissue. The bilminr zone is visible s intermedite signl intensity strutures. In losed mouth position, the juntion of the posterior bnd nd posterior tthment normlly lies bove the ondylr hed ner the 12 o lok position. The posterior bnd nd retrodiskl tissue re best depited in the open mouth position. In open mouth position, the intermedite zone lies between the ondyle nd the rtiulr eminene nd the posterior bnd is ginst the posterior surfe of the ondyle [1,9] (Figure 2). The superior belly of lterl pterygoid tthes to the nterior bnd of the disk. The inferior belly of the lterl pterygoid tthes to the nterior surfe of the ondylr nek with thin liner hypointense fibrous bnd. This bnd is seen just inferior to the position of the disk, nd n sometimes be mistken for the disk, prtiulrly when the disk is medilly or lterlly displed [22]. In the oronl plne, the disk is resent shped nd its medil nd lterl borders re tthed to the respetive spets of the ondylr hed nd joint psule. The lterl nd medil psules do not demonstrte ny outwrd bulges beyond the borders in norml ondition [1,22]. PATHOLOGIES RELATED TO ANATOMIC VARIATIONS Antomi vritions in the TMJ n be symptomti nd/or hve implitions during rthrosopy nd surgery. There n lso be severl vritions in the pperne of the mndibulr ondyles inluding intr-individul vritions between the two sides. The disese proesses n be developmentl, due to remodeling relted to mlolusion, trum or other seondry developmentl bnormlities [3]. Bifid ondyle A bi-lobed or duplited mndibulr hed is n infrequently enountered inidentl imging finding. While the etiology is unknown, theories inlude reminisene of ongenitl fibrous septum nd periprtum or erly hildhood trum. The duplited heds my lie in either n ntero-posterior or trnsverse orienttion. Dennison et l [23] hve suggested tht the term bifid ondyle should be reserved for desribing multiple ondyles in the sgittl plne only. No tretment is required for symptomti ptients. However surgery my be performed if there is displement of the dis or nkylosis of the joint spe (Figure 3). Formen of Hushke In some individuls there my be persistene of developmentl defet in the tympni plte. The tympni plte is present s n inomplete U-shped rtilginous ring t birth. Over time the ossifition proeeds lterlly nd posteriorly leving defet in the floor of the externl metus, lled the formen tympnium (formen of Hushke). With growth of the mstoid proess, this defet hnges in position from inferior to nterior nd usully loses by the 5 th yer of life. Rrely, 3-4 mm defet persists nd is found to be loted t the ntero-inferior spet of the externl uditory nl nd posteromedil to the TMJ. These ptients n present with defet or polyp on the nterior wll of the externl uditory nl (EAC) or with slivry otorrhe during mstition. TMJ tissue my lso hernite into the EAC during mstition [24,25]. During rthrosopy, there n be indvertent 571 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
6 Figure 3 Bifid ondyle. Coronl reformtted omputed tomogrphy imge through the temporomndibulr joint (TMJ) demonstrtes bifid left mndibulr ondyle. It n be noted tht one of the ondyles (rrow) is smller thn the other. Advned degenertive hnges re noted in bilterl TMJ. seondry to non-development or underdevelopment of the ondyle nd n be ongenitl or quired. Congenitl plsi or hypoplsi of the mndibulr ondyles is rre nomly nd usully ours s prt of more widespred 1 st nd 2 nd brnhil rh nomlies (e.g., Treher-Collins syndrome). Aquired ondylr hypoplsi my be seondry to lol ftors (trum, infetion, rdition) or systemi ftors (toxi gents, rheumtoid rthritis, muopolyshroidosis) [26]. Trumti vginl delivery hs been implited s use of hypoplsi [27]. Hypoplsi my involve one or both of the ondyles. Unilterl disese produes mndibulr rottion or tilt nd ssoited fil symmetry. The dignosis of bilterl ondylr hypoplsi my be delyed seondry to fil symmetry. Hypoplsti ondyles re frequently omplited with nkylosis [28]. Idiopthi ondylr resorption Idiopthi ondylr resorption (lso known s ondylysis or heerleder syndrome ) is primrily disese of TMJ ffeting teenge girls. There is rpidly progressive ondylr erosion resulting in widening of the joint spe with the hin beoming less prominent from retrognthi [29]. Mny uses hve been hypothesized inluding estrogen influene on osteogenesis, vsulr nerosis, nd TMJ internl derngement. Orthognthi surgery hs been implited s use of the disese but lso is one of the orretive pprohes for idiopthi ondylr resorption (Figure 5). Figure 4 Formen of Hushke. Sgittl reformtted omputed tomogrphy imge through the temporomndibulr joint demonstrtes fol defet (rrow) in the tympni plte. Figure 5 Idiopthi ondylr resorption. Coronl reformtted omputed tomogrphy imge through the temporomndibulr joint of young ptient demonstrtes bilterl severe ondylr resorption (rrows) without ny evidene of degenertive hnges within the joint. pssge into the EAC resulting in otologi omplitions. This formen lso n t s pth of ommunition between the EAC nd TMJ or infrtemporl foss llowing the spred of infetion, inflmmtion or tumor [24,25] (Figure 4). Condylr hypoplsi Aplsi nd hypoplsi of the mndibulr ondyle is Condylr hyperplsi Condylr hyperplsi is rre disorder hrterized by inresed volume of the mndibulr ondyle, nd is frequently ssoited with inresed volume of the rmus nd mndibulr body [30]. Condylr hyperplsi is usully unilterl proess. This disese presents in the seond nd third dedes of life during brisk periods of osteogenesis suggesting hormonl influene upon the growth disturbne. Trum hs lso been implited in symmetri ondylr hyperplsi due to hypervsulrity during heling produing induing exessive osteogenesis. The hyperplsi produes fil symmetry with the hin rotting wy from the ffeted side [30]. Resetion of the hyperplsti ondyle uses the bnorml growth to ese nd restores fil symmetry (Figure 6). Extensive pneumtiztion Extensive pneumtiztion of the mstoid bone n involve the glenoid foss nd rtiulr eminene. Knowledge of extensive pneumtiztion is neessry prior to surgery to prevent perfortions. Complitions n our during TMJ surgery due to foreful flp retrtion, dissetion or with plement of srews in ses where foss-eminene prostheses re required [31,32]. Pneumtiztion n lso provide pth of miniml resistne nd filitte the spred of pthologil tumors, inflmmtion, infetion or frture into the joint. For these resons, CT must be performed prior to TMJ surgery when ex- 572 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
7 dis position nd form nd 93% ury in ssessing the osseous hnges [38]. Figure 6 Condylr hyperplsi. Pnormi reformtion of the soure omputed tomogrphy dt inluding both the temporomndibulr joints of young ptient demonstrtes hyperplsi of the left ondyle (rrowhed) in omprison to the right side. Assoited hypertrophy of the rmus nd the nek (rrow) of the left hemi-mndible is lso noted. Figure 7 Extensive pneumtiztion. Coronl reformtted omputed tomogrphy imge through the right temporomndibulr joint demonstrtes lmost omplete pneumtiztion of the glenoid foss exept the entrl prt. tensive pneumtiztion is deteted in the pnormi rdiogrphs [31,32] (Figure 7). INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF TMJ Internl derngement (ID) is defined s mehnil fult of the joint tht interferes with smooth joint funtion. This is ttributed to bnorml intertion of the rtiulr dis, ondyle nd rtiulr eminene. Assoited linil fetures inlude rtiulr pin nd rtiulr noises [33]. Dis displement is the most ommon use of ID, though not ll displed diss re ssoited with derngement nd not ll derngements re used by dis displement [34]. Additionlly, it is not ler whether the displed disk is relted to onset, progression or esstion of the pin. Loose bodies nd dhesions in the joint n lso result in derngement. Up to 34% of symptomti volunteers n hve nterior dis displement nd 23% of ptients with derngement n hve norml dis position [18]. In most lrge MRI series pproximtely 80% of ptients referred for dignosti imging of the TMJ demonstrte some form of disk displement [35-37]. MRI is the imging modlity of hoie for the dignosis of internl derngement with n ury of 95% in ssessing the Dis displement The dis displement is tegorized bsed on the reltion of the displed dis with mndibulr ondyle. The displement n be nterior, nterolterl, nteromedil, lterl, medil nd posterior [39]. The most ommon pttern of dis displement re either nterior nd nterolterl ounting for more thn 80% of the uses [37]. The dis displement n be sublssified s nterior displement with redution (ADR) or nterior displement with no redution (ADNR) bsed on restortion of norml reltionship between the ondyle nd the dis on mouth opening (Figures 8 nd 9). The dis displement n be either omplete or prtil [35]. If the entire mediolterl dimension of the dis is displed, it is referred to s omplete displement. On the other hnd if only the medil or lterl portion of the dis is displed, it is referred to s prtil displement. Prtil dis displement is ommonly seen with ADR. Frequently the lterl prt of the dis is displed nteriorly while the medil prt of the dis remins in norml position (rottionl disk displement) [40]. In ADR, the nteriorly displed dis returns to the norml position on mouth opening produing reiprol lik (Figure 9). In ADNR, there is limited mouth opening nd devition of the jw to the ffeted side (losed lok). Over time, strething or perfortion of the retrodisl tissue uses deformtion of the disk leding to n improvement in jw exursion nd redued lterl devition during mouth opening (Figure 10A). The posterior bnd of the dis remins nterior to the ondyle even with mouth opening [41]. There is inresed ssoition of degenertive hnges in the TMJ with the ADNR. Although TMJ disorder with ADR nd norml ondylr ortil bone my be stble for dedes, it will eventully progress to ADNR. In study with 55 ptients, de Leeuw et l [42] hve demonstrted 75% of the ptients with long history (pproximtely 30 yers) of TMJ internl derngement hve ADNR. The ext mehnism for dis displement is unknown lthough trum with injury to the posterior dis tthment is onsidered to be the most likely use. Unenhned MRI is the imging modlity of hoie for evlution of ID. During the erly stge of ID the dis retins its norml shpe, but over time it beomes deformed by thikening of the posterior bnd nd thinning of the nterior bnd. This produes in bionvex, terdrop shped or rounded dis. The dis mintins norml bionve shpe s long s it remins on top of the ondyle during mouth opening [42]. Hene, presene of n irregulr nd rounded dis lmost lwys indites dis disese [43]. Other MRI findings tht suggest dis disese inlude dis flttening, derese in the norml intermedite to high signl intensity of the dis [44] nd presene of ter or perfortion in the hroni stge. Posterior dis displement is rre entity nd o- 573 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
8 A B Figure 8 Anterior displement with redution. A: Sgittl proton density weighted mgneti resonne imging (MRI) in the losed mouth position demonstrtes nterior displement of the disk (rrow) in front of the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ); B: Sgittl proton density weighted MRI in the open mouth position demonstrtes redution of the disk (rrow) between the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ) nd the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ). A B Figure 9 Anterior displement with no redution. A: Sgittl proton density weighted mgneti resonne imging (MRI) in the losed mouth position demonstrtes nterior displement of the disk (rrow) relted to the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ) nd nterior to the mndibulr ondyle (the letter ); B: Sgittl proton density weighted MRI in the open mouth position demonstrtes no redution of the disk (rrow) between the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ) nd the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ). A B C Figure 10 Other types of disk displement. A: Posterior disk displement. Sgittl proton density weighted mgneti resonne imging (MRI) in the losed mouth position demonstrtes posterior displement of the disk (rrow) in reltion to the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ); B: Lterl disk displement. Coronl proton density weighted demonstrtes lterl displement of the disk (rrow) in reltion to the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ); C: Pseudodisk. Sgittl proton density weighted MRI in the losed mouth position demonstrtes nterior displement of the disk (rrow) in front of the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ). The thikening of the posterior tthments (rrowheds) superior to the mndibulr ondyle is seen s pseudodisk. unts for only 0.01% to 0.001% of ll dis displements [45]. The mjor linil sign is sudden onset of loked jw in open position. MRI is helpful in the dignosis by demonstrting displement of the posterior bnd beyond 1 lok position [9] (Figure 10A). Review of ptient s linil informtion is importnt before imge interprettion s previous posterior disk plition n be mistken for n quired posterior disk displement. Anterolterl nd ntero-medil disk displements re grouped under rottionl displements while the 574 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
9 A B Figure 11 Stuk disk. A: Sgittl proton density weighted mgneti resonne imging (MRI) in the losed mouth position demonstrtes pprently norml position of the disk (rrow) in reltion to the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ). The letter demonstrtes the rtiulr eminene; B: Sgittl proton density weighted MRI in the open mouth position demonstrtes no nterior movement of the disk (rrow) with the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ), i.e., stuk to the glenoid fosss. The rtiulr eminene is denoted with letter. pure lterl nd medil displements re grouped under sidewys displement [46]. Isolted lterl displement is rre (Figure 10B). Agin these rottionl nd sidewys displements n be omplete or prtil nd with or without dis redution. Anterolterl displement is the most ommon pttern [37]. Pseudodisk A pseudo-disk is present in some ptients with n nteriorly displed disk. This hs been postulted s n dptive retion to nterior disk displement within the posterior disk tthment followed by subsequent onnetive tissue hyliniztion tht [47] ppers s bnd-like struture of low signl intensity repling the normlly bright signl of the posterior disk tthment [8,9,22] (Figure 10C). Stuk dis The stuk dis is pthologi ondition hrterized by n immobile dis in reltion to the glenoid foss nd the rtiulr eminene. This is present in both open nd losed mouth positions [9] nd is likely relted to the dhesions. It n our with or without dis displement nd n be ssoited with pin nd joint dysfuntion due to limittion of ondylr trnsltion [48,49]. This dignosis n be missed unless the TMJ is imged in both open nd losed mouth positions (Figure 11). Sgittl oblique ine imging is prtiulrly useful in evlution of stuk disk. Perforted dis Dis perfortion is reported in 5% to 15% of dernged joints dis displements [50]. It is more ommon in ptients with ADNR thn in ADR [51,52] nd is usully seen in ptients with dvned rthrosis. The prevlene of perforted dis is higher in women thn in men nd prevlent in individuls over 80 yers of ge [53]. MRI findings of dis perfortion inlude dis deformity (100%), dis displement (81%), ondylr bony hnges (68%), joint effusion (23%) nd non-visuliztion of temporl posterior tthment (TPA) of the dis (65%-68%) [54]. Conventionl nd MR rthrogrm n be helpful in the dignosis of dis perfortion by demonstrting opifition of both the joint omprtments from single lower omprtment injetion. If the disk perfortion is suspeted ft suppressed T2 weighted MRI n be obtined in sgittl nd oronl plne [55]. Absene of strething/strightening of the posterior temporl disk tthment on mouth opening lso suggests disk perfortion. Joint effusion Joint effusion represents n bnormlly lrge umultion of intr-rtiulr fluid nd is ommonly seen in symptomti ptients. A smll mount of joint fluid n be seen in symptomti ptients [56]. An effusion is more prevlent in pinful thn in non-pinful joints [16]. Although not ll ptients with joint pin hve effusion, ptients with lrge effusions ommonly experiene pin nd dis displement [57]. T2 weighted MR sequene is the best sequene for the ssessment of joint effusion. An erly joint effusion is ommonly seen surrounding the nterior bnd but lrger effusions n oupy both superior nd inferior joint spe. A lrge effusion my hve dignosti vlue s it outlines the dis nd sometimes even the dis perfortion s well s retrodisl tissue produing rthrogrphi effet [57]. Gdolinium enhned T1 weighted imging n be helpful in distinguishing plin joint effusion from synovil prolifertion. In ptients with inflmmtory rthropthies with ssoited synovil prolifertion, the proliferting synovium enhnes while the effusion does not [58]. Thikening of lterl pterygoid musle tthment (double disk sign) The ext role of lterl pterygoid musle (LPM) in the TMJ funtion is still ontroversil lthough its suggested role is in genertion of side-to-side nd protrusive jw fores [9]. There re eletromyogrphi studies showing hypertivity in the inferior tthment of the LPM in ptients with TMJ internl derngement [59]. Severl mor- 575 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
10 b ADNR of the TMJ with these morphologi hnges hving signifint ssoition with the linil symptoms of pin or restrited jw opening [60]. It is suggested tht there is signifint ssoition between the nterior dis displement nd tthment of the superior LPM to the dis lone nd not to the ondyle [61]. The interpreting rdiologist should be wre of potentil pitfll of mistking the thikened inferior LPM to n nteriorly displed dis ( double dis sign ) [9] (Figure 12). Figure 12 Double disk sign (thikening of the lterl pterygoid musle). Sgittl losed mouth proton density imge demonstrtes nterior displement of the disk (rrow hed). The thikened lterl pterygoid musle ner the mndibulr ondylr (the letter, ) tthment pper s liner hypointense struture (white rrow) inferior to the disk in the sme orienttion giving the pperne of double disk. The rtiulr eminene is denoted with letter b. Figure 13 Osteohondritis dessins. Axil omputed tomogrphy sn through the level of the temporomndibulr joint demonstrtes tiny bone frgment (rrow) t the nterior spet of the disk. It n be noted tht there re liner lueny surrounding the bone frgment. Figure 14 Loose bodies. Sgittl reformtion of the xil dtset demonstrtes multiple loose bodies in the joint vities, nteroinferior to the rtiulr eminene (blk rrow) nd immeditely posterior to the mndibulr ondyle (white rrow). phologi hnges to the superior nd inferior bellies of the LPM on MRI hve been desribed. These inlude hypertrophy, trophy nd ontrtures in ptients with Osteohondritis dissens nd vsulr nerosis Osteohondritis dissens (OCD) nd vsulr nerosis (AVN) of the mndibulr ondyle re similr pthologi entities likely represent spetrum of the sme pthophysiology [62]. Common linil fetures of OCD/AVN of the mndibulr ondyle inlude pin nd joint disbility [63]. Pin is ommonly over the joint nd long the third division of the trigeminl nerve. Other symptoms inlude ipsilterl hedhe, erhe nd spsm of mstitor musles. These n our with or without limittion of joint movements [63]. MRI is the modlity of hoie for ssessment of OCD/ AVN of the mndibulr ondyle [63]. There is deresed mrrow signl on T1 weighted sequenes in ses of AVN. T2 weighted sequenes demonstrte vrible signl hrteristis with erly AVN, heling nd OCD. Erly AVN onsistently exhibits high signl on T2WI nd ute OCD typilly demonstrted hypointense entrl frgment surrounded by zone of higher signl on both T1W nd T2W sequenes [63]. Although MRI is 78% sensitive nd 84% speifi for the dignosis of AVN, the positive preditive vlue is only 54% beuse ondylr slerosis seondry to dvned TMJ degenertive hnges hve similr MRI ppernes [64]. Rdiologi hnges of OCD nd AVN of the mndibulr ondyle re frequently ssoited with joint effusion nd internl derngement of the dis [65] (Figure 13). Loose bodies Loose bodies in synovil joint n be due to primry or seondry synovil hondromtosis. The primry type is ssoited with spontneous rtilginous metplsi in the synovium, while the seondry type is due to inorportion of osteortilginous loose bodies in the synovium in the setting of degenertive joint disese [66]. Common linil symptoms ssoited with loose bodies inlude pin, periuriulr swelling, deresed rnge of jw motion, repittion nd unilterl devition of the jw during mouth opening [67]. Pnormi rdiogrphs of the TMJ my or my not demonstrte loose bodies [68]. High resolution CT [69,70] or MRI [70] n demonstrte smll loose bodies within the TM joint spe (Figure 14). Hypermobility Ptients with hypermobile TMJ n present with n inbility to lose the jw (open lok) fter wide opening of the jw. This ours s result of trnsltion of the 576 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
11 Figure 15 Ankylosis. Coronl reformtion of the xil dtset demonstrtes omplete nkylosis of the right temporomndibulr joint (TMJ) nd ner omplete nkylosis of the left TMJ with subtle residul joint spe t the enter (blk rrow). ondyle beyond the mrgins of the nterior tthment of the TMJ psule. Entrpment of the ondyle long the nterior slope of the rtiulr eminene results due to vrious biomehnil onstrints, prtiulrly mstitor musle tivity [71]. In ute ses, there is little need for imging studies s the open lok is linilly evident with relevnt linil history of wide jw opening or trum. In hroni ses MRI n give informtion bout the height nd steepness of the rtiulr eminenes s well s the shpe nd position of the dis [72]. Ankylosis Ankylosis of the TMJ n be due to fibrous dhesions or bony fusion resulting in the restrition of jw motion. It n our s sequel of previous infetion, trum surgery [73] nd in ptients with juvenile idiopthi rthritis or bifid mndibulr ondyles. MR rthrogrphy is useful for the evlution of fibrous dhesions nd three-dimensionl CT sn is neessry for surgil plnning when bony fusion is suspeted (Figure 15). TMJ ARTHRITIS Similr to other synovil joints in body, the TMJ is frequently involved in different inflmmtory rthritides. Degenertive rthritis nd rthritis seondry to rystlline deposition disese re lso ommon in TMJ. Arthritis seondry to infetion or trum n our t the TMJ. Arthritis of TMJ is disussed bsed on the pthophysiologi mehnism. Inflmmtory rthritis Juvenile idiopthi rthritis: Juvenile idiopthi rthritis (JIA) is the most ommon rheumti disese in hildhood ffeting girls more frequently thn boys. The disese predominntly ffets synovil joints. There re two peks of onset, first being between the ges of 1 nd 3 yers nd the seond pek between 8 nd 12 yers [74]. The TMJ is involved in 17% to 87% of ptients with JIA [74]. JIA n be systemi, polyrtiulr nd puirtiulr. The TMJ is more ommonly involved in ptients with polyrtiulr joint involvement [75]. The typil presenttion of TMJ involvement inludes pin, joint tenderness, repittion, stiffness nd deresed rnge of motion. Bony nkylosis n develop in some ptients s lte disese mnifesttion. Orthopntomogrm, CT, MRI nd ultrsound hve been used to evlute TMJ JIA. Orthopntomogrm nd CT predominntly identify the bony erosions seondry to TMJ involvement. Both these tehniques involve rdition exposure to young ptients. MRI nd ultrsound hve gined populrity in evlution of the TMJ in ptients with JIA beuse these tehniques hve better soft tissue resolution llowing erlier dignosis of TMJ involvement without ny ionizing rdition. Aute TMJ rthritis typilly demonstrtes joint effusion nd synovil thikening on T2 weighted imging without ny bony hnges [76]. Enhnement of the joint or perirtiulr tissue is not speifi sign of ute TMJ rthritis beuse bnorml joint enhnement n be present even in helthy ptients [76]. Condylr resorption n be better evluted on non-ft suppressed T1 weighted sequene nd suggests more hroni TMJ rthritis [76] (Figure 16). Rheumtoid rthritis: Rheumtoid rthritis (RA) is hroni inflmmtory disorder tht predominntly ffets the perirtiulr tissue suh s synovil membrne, joint psules, tendon, tendon sheths nd ligments. Internl joint omponents re seondrily involved. The prevlene of RA in the generl popultion is pproximtely 2%-2.5% with femle predominne. The pek onset of disese is yers nd pproximtely 50%-75% of ptients with RA hve TMJ involvement [77]. RA is slowly progressive disese of insidious onset with progressive destrution of the rtiulr/perirtiulr soft tissue nd the djent bones resulting in joint deformity. The TMJ is involved t lter stge of disese. TMJ involvement uses deep, dull hing pin in the preuriulr re, espeilly during hewing. Limited rnge of motion nd morning stiffness n be present [78]. The mndibulr ondyle grdully resorbs s the disese progresses. Rdiogrphi fetures of RA inlude loss of joint spe, ondylr destrution, flttening with nterior positioning of the ondyle. There my be flttening of the rtiulr eminene nd erosion of the glenoid foss. Synovil prolifertion is n erly proess in RA nd n distinguish it from other types of rthritis [79]. Synovil prolifertion is redily seen on MRI nd n be seen in ll ptients [79]. A joint effusion is lso omprtively more ommon in RA. Degenertive (osteo)rthritis Osteorthritis (OA) is hroni degenertive disese tht hrteristilly ffets the rtiulr rtilge of synovil joints nd is ssoited with simultneous remodeling of the underlying subhondrl bone with seondry involvement of the synovium. Osteorthritis is the most 577 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
12 A B s s s s Figure 16 Juvenile idiopthi rthritis. A: Sgittl proton density weighted mgneti resonne imging (MRI) in the losed mouth position demonstrtes inresed signl t the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ), extensive thikening of the synovium (the letter, s) in the retrodisl regions. It n be noted tht the thikening nd inresed signl of the synovium t other ples (rrowheds); B: Sgittl ft suppressed post ontrst T1 weighted MRI in the losed mouth position demonstrtes enhnement of signl t the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ), enhnement nd extensive thikening of the synovium (the letter, s) in the retrodisl regions. There is thikening nd enhnement of the synovium t other ples (rrowheds). still no generl onsensus s to whih imging modlity should be the gold stndrd [81] (Figure 17). Figure 17 Degenertive hnges. Sgittl reformtion of the xil dtset demonstrtes deformity of the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ), extensive slerosis of the rtiulr eminene (the letter, ) nd severe loss of joint spe. ommon joint pthology ffeting the TMJ [80]. There is ler disprity between rdiogrphi evidene of OA nd symptoms. Popultion bsed studies demonstrte tht miniml ondylr flttening is present in up to 35% of symptomti ptients while pproximtely 11% of ptients hve TMJ OA-relted symptoms [80]. The most ommon symptom of TMJ OA is pin during hewing. The pin usully strts in the perirtiulr soft tissue nd the mstitor musles tht re in protetive reflex spsm. Ftigue of mstitor musles, trismus, deresed rnge of motion, diffiulty opening the mouth nd joint repittions re other ommon symptoms. Rdiologi hllmrks of TMJ OA re rtiulr surfe ortil bone irregulrity, erosion nd osteophyte formtion [81]. Erosion is rdiologilly defined s fol re of deresed density t the ortil mrgin of the rtiulr surfe of the mndibulr ondyle nd the subhondrl region. Osteophyte formtion typilly ours t lter stge in the disese nd n stbilize nd broden the surfe re of the joint in n ttempt to better withstnd xil loding fores. Different imging modlities hve been used with vrying degree of suess. There is Metboli rthritis/rystlline rthropthies Clium pyrophosphte dehydrte deposition disese: Clium pyrophosphte dehydrte deposition disese (CPPD) is metboli rthropthy used by the deposition of lium pyrophosphte dehydrte rystls in nd round joints, espeilly within the rtiulr rtilge nd fibrortilge [82]. The spetrum of TMJ involvement rnges from symptomti disk lifition to mrked destrution of the joint with erosive hnges in the mndibulr ondyle nd the djent skull bse. Common symptoms inlude pin nd preuriulr swelling with osionl hering loss. Chewing n exerbte the pin. Other less ommon symptoms inlude TMJ liking, tinnitus, nd mlolusion. The rdiogrphi pperne of CPPD is vrible. Computed tomogrphy demonstrtes lium deposition in the disk or perirtiulr tissue. On MRI, CPP deposits typilly pper s hypointense mteril both on T1 nd T2 weighted sequenes. CT nd MRI show erosions ner both the ondyle nd foss with djent CPPD deposits [82]. The erosions my extend into the skull bse nd into the middle rnil foss. Involvement of other joints with hondrolinosis is lue to the dignosis. The differentil dignosis inludes synovil hondromtosis, synovil osteohondrom, nd osteosrom (Figure 18). Infetious rthritis TMJ infetion is usully seondry to diret extension of infetion from the djent tissue into the joint. Systemi infetions suh s tuberulosis nd syphilis n rrely involve the TMJ. TMJ infetion is more ommon in the setting of immunosuppression nd presene of other systemti diseses suh s dibetes mellitus, rheumtoid rthritis nd intrvenous drug use, et. 578 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
13 Figure 18 Clium pyrophosphte dehydrte deposition disese. Coronl reformtion of the xil dtset demonstrtes destrution of the left temporomndibulr joint with erosion nd deformity of both the mndibulr ondyle nd the glenoid foss. There is extensive extensive lium pyrophosphte dehydrte deposition disese medil to the joint spe (rrow). TUMORS AND TUMOR-LIKE CONDITIONS OF THE TMJ Figure 19 Synovil hondromtosis. Sgittl reformtion of the xil dtset demonstrtes extensive loud-like lifition (rrows) filling nd expnding the joint spe nterior to the mndibulr ondyle (the letter, ). Clifition is lso present posterior to the mndibulr ondyle. Tumors nd tumor-like onditions n ffet the TMJ. These onditions my hve similr presenttions suh s pin, swelling, nd limittion of motion. Synovil hondromtosis Synovil hondromtosis (SC) is benign ondition with hondrometplsi of the synovil membrne nd formtion of rtilginous nodules. These nodules n beome dethed nd form loose bodies whih lter lify. Synovil hondromtosis typilly involves lrge joints, suh s the knee, hip, nd elbow. It is unommon for the temporomndibulr joint to be ffeted by SC. SC typilly involves the superior omprtment of TMJ while involvement of the inferior omprtment is rre nd seondry to perfortion of the rtiulr dis. Unommon findings inlude erosion of the mndibulr ondylr hed, temporl skull bse, nd intrrnil extension. Ptients typilly present with preuriulr pin, swelling, inflmmtion, limittion of motion, nd rtiulr noises. Some ptients lso report neurologi dysfuntion, suh s hedhe nd hering loss. The dignosis of TMJ synovil hondromtosis is diffiult sine it is rre disese nd n hve similr findings to more ommon diseses, suh s hondrolinosis, osteorthritis, nd hondrosrom. The rdiologi findings of SC inlude lified loose bodies, soft tissue swelling, widening of the joint spe, irregulrities of the joint surfe, nd slerosis of the glenoid foss nd/or mndibulr ondyle. CT typilly shows lified nodules surrounding the mndibulr ondyle with degenertive hnges of the ondyle [83]. MRI typilly shows mixed solid nd fluid signl relted to the metplsi of the synovil tissue nd the fluid omponent of the umulted synovil seretions. The lified nodules re T1/T2 hypointense with surrounding T2 hyperintense effusion nd prolifertive synovium, whih enhnes fter ontrst dministrtion. MRI is preferred in evlution of SC over CT beuse of the bility to detet non-lified loose bodies, lk of rdition, nd visuliztion of the rtiulr dis [84] (Figure 19). Tretment is surgil removl of the loose bodies nd exision of the metplsti synovium. In end stge SC without synovil metplsti tivity, the tretment is often non-surgil with therpy imed towrds symptom relief. Pigmented villonodulr synovitis Pigmented villonodulr synovitis (PVNS) is benign, non-neoplsti prolifertive disorder of the synovil membrnes of joints, burse, nd tendon sheths. The disese is typilly monortiulr nd n involve ny joint but is most often seen in the knee. Primry PVNS of the TMJ is rre. There re two forms of PVNS: nodulr nd diffuse. The most ommon nodulr ptterns of PVNS inlude gint ell tumor, xnthom, xnthogrnulom, nd myeloplxom, whih ffet fol prt of the synovium [85]. Diffuse PVNS ffets nerly the entire synovium. The ext etiology of PVNS is unler. It ws originlly postulted to be n inflmmtory response to n unknown stimulus. Other theories ttribute it to repetitive intr-rtiulr hemorrhge from trum, ltered lipid metbolism, or benign neoplsti prolifertion. PVNS ommonly presents s slowly growing nd non-tender swelling of the ffeted joint. Ptients with involvement of the TMJ, n present with preuriulr mss with swelling, pin, tenderness, liking, otlgi, nd hering loss. The most sensitive method for the detetion of PV- NS is by MRI demonstrting T1/T2 hypointensity nd blooming on the GRE sequenes from prmgneti hemosiderin deposition [86]. There my be moderte to intense inhomogeneous enhnement of the synovium. CT findings re usully nonspeifi with bone erosion, subhondrl ysts, nd soft tissue mss [87]. A joint effusion my be dense from the hemosiderin. The differentil dignosis of PVNS on MRI inludes synovil hondrom- 579 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
14 tosis, rheumtoid rthritis, synovil srom, hemophili, nd synovil hemngiom. Primry nd seondry neoplsms, nd other lesions Osteohondrom is the seond most ommon neoplsti lesion ffeting the TMJ. Osteohondrom, osteom, nd ondylr hyperplsi re often diffiult to differentite both linilly nd on imging. MR nd CT my delinete the ext extent of the tumor nd its reltionship to ntomi strutures within the TMJ. Synovil ysts, gnglion ysts nd simple bone ysts my lso our. Mny benign primry bone neoplsms, suh s hondroblstom, osteom, osteoid osteom, osteoblstom, ossifying fibrom nd neurysml bone yst n lso involve the TMJ. Mlignnt primry bone neoplsms re extremely rre in TMJ but inlude hondrosrom nd osteogeni srom. There lso n be extension of tumors from djent strutures into the TMJ. Tumors from the externl er nd protid glnd n extend into the TMJ. Less thn 1% of ll tumors metstsize into the mxillofil region. Adenorinom is the most ommon metstti tumor of the jw, mking up bout 70% of ses. Reported metstsis to TMJ inludes brest, renl, lung, olon, prostte, thyroid, nd testiulr primry. CONCLUSION Imging of TMJ should be performed on se by se bsis depending upon linil signs nd symptoms. MRI is the dignosti study of hoie for evlution of disk position nd internl derngement of the joint. CT sn for evlution of TMJ is indited if bony involvement is suspeted nd should be judiiously onsidered beuse of rdition risk. Understnding of the TMJ ntomy, biomehnis, nd the imging mnifesttions of diseses is importnt to urtely reognize nd mnge these vrious pthologies. REFERENCES 1 Aiken A, Bouloux G, Hudgins P. MR imging of the temporomndibulr joint. Mgn Reson Imging Clin N Am 2012; 20: [PMID: DOI: /j.mri ] 2 Gurlnik W, Kbn LB, Merrill RG. Temporomndibulrjoint fflitions. N Engl J Med 1978; 299: [PMID: DOI: /NEJM ] 3 Alomr X, Medrno J, Cbrtos J, Clvero JA, Lorente M, Serr I, Monill JM, Slvdor A. Antomy of the temporomndibulr joint. Semin Ultrsound CT MR 2007; 28: [PMID: DOI: /j.sult ] 4 Sommer OJ, Aigner F, Rudish A, Gruber H, Fritsh H, Millesi W, Stiskl M. Cross-setionl nd funtionl imging of the temporomndibulr joint: rdiology, pthology, nd bsi biomehnis of the jw. Rdiogrphis 2003; 23: e14 [PMID: DOI: /rg.e14] 5 Sv A, Sutriu M. Funtionl ntomy of the temporomndibulr joint (II). Rev Med Chir So Med Nt Isi 2012; 116: [PMID: ] 6 Vn Eijden TM, Korfge JA, Brugmn P. Arhiteture of the humn jw-losing nd jw-opening musles. Ant Re 1997; 248: [PMID: DOI: /(SICI) ( )248:3<464::AID-AR20>3.0.CO;2-M] 7 Imnimoghddm M, Mdni AS, Hshemi EM. The evlution of lterl pterygoid musle pthologi hnges nd insertion ptterns in temporomndibulr joints with or without dis displement using mgneti resonne imging. Int J Orl Mxillof Surg 2013; 42: [PMID: DOI: /j.ijom ] 8 Toms X, Pomes J, Berenguer J, Merder JM, Pons F, Donoso L. Temporomndibulr joint soft-tissue pthology, II: Nondis bnormlities. Semin Ultrsound CT MR 2007; 28: [PMID: DOI: /j.sult ] 9 Toms X, Pomes J, Berenguer J, Quinto L, Niolu C, Merder JM, Cstro V. MR imging of temporomndibulr joint dysfuntion: pitoril review. Rdiogrphis 2006; 26: [PMID: DOI: /rg ] 10 Koolstr JH. Dynmis of the humn mstitory system. Crit Rev Orl Biol Med 2002; 13: [PMID: DOI: / ] 11 Lobbezoo F, Drngsholt M, Pek C, Sto H, Kopp S, Svensson P. Topil review: new insights into the pthology nd dignosis of disorders of the temporomndibulr joint. J Orof Pin 2004; 18: [PMID: ] 12 Hrms SE, Wilk RM. Mgneti resonne imging of the temporomndibulr joint. Rdiogrphis 1987; 7: [PMID: DOI: /rdiogrphis ] 13 Ktzberg RW. Temporomndibulr joint imging. Rdiology 1989; 170: [PMID: ] 14 Ro VM, Belr MT. MR imging of the temporomndibulr joint. Mgn Reson Imging Clin N Am 2002; 10: [PMID: DOI: /S (02) ] 15 Dre JE, Enzmnn DR. Defining the norml temporomndibulr joint: losed-, prtilly open-, nd open-mouth MR imging of symptomti subjets. Rdiology 1990; 177: [PMID: ] 16 Ktzberg RW, Westesson PL, Tllents RH, Drke CM. Antomi disorders of the temporomndibulr joint dis in symptomti subjets. J Orl Mxillof Surg 1996; 54: ; disussion [PMID: DOI: /S (96) ] 17 Rmmelsberg P, Pospieh PR, Jäger L, Pho Du JM, Böhm AO, Gernet W. Vribility of disk position in symptomti volunteers nd ptients with internl derngements of the TMJ. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol Orl Rdiol Endod 1997; 83: [PMID: DOI: / S (97) ] 18 Tllents RH, Ktzberg RW, Murphy W, Proskin H. Mgneti resonne imging findings in symptomti volunteers nd symptomti ptients with temporomndibulr disorders. J Prosthet Dent 1996; 75: [PMID: DOI: /S (96) ] 19 Orsini MG, Kuboki T, Terd S, Mtsuk Y, Ymshit A, Clrk GT. Dignosti vlue of 4 riteri to interpret temporomndibulr joint norml disk position on mgneti resonne imges. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol Orl Rdiol Endod 1998; 86: [PMID: DOI: / S (98) ] 20 Provenzno Mde M, Chilvrquer I, Fenyo-Pereir M. How should the rtiulr disk position be nlyzed? J Orl Mxillof Surg 2012; 70: [PMID: DOI: / j.joms ] 21 Vilnov JC, Breló J, Puig J, Remollo S, Niolu C, Bru C. Dignosti imging: mgneti resonne imging, omputed tomogrphy, nd ultrsound. Semin Ultrsound CT MR 2007; 28: [PMID: DOI: /j.sult ] 22 Westesson PL O-YM, Sno T, Okno T. Antomy, Pthology, nd Imging of the Temporomndibulr Joint. In: Som PM, Curtin HD, ed. Hed nd Nek Imging-2 Volume Set, 5th Edition. St. Louis: Mosby, 2011: Dennison J, Mhoney P, Herbison P, Dis G. The flse nd the true bifid ondyles. Homo 2008; 59: [PMID: 580 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
15 DOI: /j.jhb ] 24 Lout A, Mrsot-Dupuh K, Smoker WR, Lsjunis P. Formen tympnium, or formen of Hushke: pthologi ses nd ntomi CT study. AJNR Am J Neurordiol 2005; 26: [PMID: ] 25 Tozoglu U, Cglyn F, Hrorli A. Formen tympnium or formen of Hushke: ntomil one bem CT study. Dentomxillof Rdiol 2012; 41: [PMID: ] 26 Tnk W, Wright D, Iizuk T. Unilterl dysplsi of the mndibulr ondyle: report of se. J Orl Mxillof Surg 1998; 56: [PMID: ] 27 Berger SS, Stewrt RE. Mndibulr hypoplsi seondry to perintl trum: report of se. J Orl Surg 1977; 35: [PMID: ] 28 Kneym K, Segmi N, Htt T. Congenitl deformities nd developmentl bnormlities of the mndibulr ondyle in the temporomndibulr joint. Congenit Anom (Kyoto) 2008; 48: [PMID: DOI: /j x] 29 Wolford LM. Idiopthi ondylr resorption of the temporomndibulr joint in teenge girls (heerleders syndrome). Pro (Byl Univ Med Cent) 2001; 14: [PMID: ] 30 Angiero F, Frronto G, Benedienti S, Vini R, Frronto D, Mgistro S, Stefni M. Mndibulr ondylr hyperplsi: linil, histopthologil, nd tretment onsidertions. Crnio 2009; 27: [PMID: ] 31 Ldeir DB, Brbos GL, Nsimento MC, Cruz AD, Freits DQ, Almeid SM. Prevlene nd hrteristis of pneumtiztion of the temporl bone evluted by one bem omputed tomogrphy. Int J Orl Mxillof Surg 2013; 42: [PMID: ] 32 Miloglu O, Yilmz AB, Yildirim E, Akgul HM. Pneumtiztion of the rtiulr eminene on one bem omputed tomogrphy: prevlene, hrteristis nd review of the literture. Dentomxillof Rdiol 2011; 40: [PMID: ] 33 Rudish A, Innerhofer K, Bertrm S, Emshoff R. Mgneti resonne imging findings of internl derngement nd effusion in ptients with unilterl temporomndibulr joint pin. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol Orl Rdiol Endod 2001; 92: [PMID: DOI: /moe ] 34 Cholitgul W, Nishiym H, Ssi T, Uhiym Y, Fuhiht H, Rohlin M. Clinil nd mgneti resonne imging findings in temporomndibulr joint dis displement. Dentomxillof Rdiol 1997; 26: [PMID: DOI: /sj.dmfr ] 35 Lrheim TA, Westesson P, Sno T. Temporomndibulr joint disk displement: omprison in symptomti volunteers nd ptients. Rdiology 2001; 218: [PMID: DOI: /rdiology r01fe11428] 36 Ribeiro RF, Tllents RH, Ktzberg RW, Murphy WC, Moss ME, Mglhes AC, Tvno O. The prevlene of dis displement in symptomti nd symptomti volunteers ged 6 to 25 yers. J Orof Pin 1997; 11: [PMID: ] 37 Pesni D, Westesson PL, Htl M, Tllents RH, Kurit K. Prevlene of temporomndibulr joint internl derngement in ptients with rniomndibulr disorders. Am J Orthod Dentofil Orthop 1992; 101: [PMID: ] 38 Tski MM, Westesson PL, Ruberts RF. Observer vrition in interprettion of mgneti resonne imges of the temporomndibulr joint. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol 1993; 76: [PMID: ] 39 Tski MM, Westesson PL, Isberg AM, Ren YF, Tllents RH. Clssifition nd prevlene of temporomndibulr joint disk displement in ptients nd symptom-free volunteers. Am J Orthod Dentofil Orthop 1996; 109: [PMID: ] 40 Sno T, Ymmoto M, Okno T. Temporomndibulr joint: MR imging. Neuroimging Clin N Am 2003; 13: [PMID: ] 41 Som PM, Bergeron RT. Hed nd nek imging. 2nd ed. St. Louis: Mosby Yer Book, de Leeuw R, Boering G, Stegeng B, de Bont LG. TMJ rtiulr dis position nd onfigurtion 30 yers fter initil dignosis of internl derngement. J Orl Mxillof Surg 1995; 53: ; disussion [PMID: ] 43 Sueng S, Hmmoto S, Kwno K, Higshid Y, Noikur T. Dynmi MR imging of the temporomndibulr joint in ptients with rthrosis: reltionship between ontrst enhnement of the posterior disk tthment nd joint pin. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1996; 166: [PMID: DOI: /jr ] 44 Helms CA, Kbn LB, MNeill C, Dodson T. Temporomndibulr joint: morphology nd signl intensity hrteristis of the disk t MR imging. Rdiology 1989; 172: [PMID: ] 45 Chossegros C, Cheynet F, Guyot L, Bellot-Smson V, Bln JL. Posterior disk displement of the TMJ: MRI evidene in two ses. Crnio 2001; 19: [PMID: ] 46 Ktzberg RW, Westesson PL, Tllents RH, Anderson R, Kurit K, Mnzione JV, Tottermn S. Temporomndibulr joint: MR ssessment of rottionl nd sidewys disk displements. Rdiology 1988; 169: [PMID: ] 47 Konttinen YT, Ainol M, Vllel H, M J, Id H, Mndelin J, Kinne RW, Sntvirt S, Sors T, López-Otín C, Tkgi M. Anlysis of 16 different mtrix metlloproteinses (MMP-1 to MMP-20) in the synovil membrne: different profiles in trum nd rheumtoid rthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1999; 58: [PMID: ] 48 Shellhs KP, Wilkes CH. Temporomndibulr joint inflmmtion: omprison of MR fst snning with T1- nd T2- weighted imging tehniques. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1989; 153: [PMID: DOI: /jr ] 49 Roberts D, Shenk J, Joseph P, Foster T, Hrt H, Pettigrew J, Kundel HL, Edelstein W, Hber B. Temporomndibulr joint: mgneti resonne imging. Rdiology 1985; 154: [PMID: ] 50 Ktzberg RW, Westesson P-L. Dignosis of the temporomndibulr joint, 1e. Phildelphi: W. B. Sunders Co., Cholitgul W, Petersson A, Rohlin M, Akermn S. Clinil nd rdiologil findings in temporomndibulr joints with dis perfortion. Int J Orl Mxillof Surg 1990; 19: [PMID: ] 52 Kondoh T, Westesson PL, Tkhshi T, Seto K. Prevlene of morphologil hnges in the surfes of the temporomndibulr joint dis ssoited with internl derngement. J Orl Mxillof Surg 1998; 56: ; disussion [PMID: ] 53 Widmlm SE, Westesson PL, Kim IK, Pereir FJ, Lundh H, Tski MM. Temporomndibulr joint pthosis relted to sex, ge, nd dentition in utopsy mteril. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol 1994; 78: [PMID: ] 54 Kuribyshi A, Okohi K, Kobyshi K, Kurbyshi T. MRI findings of temporomndibulr joints with disk perfortion. Orl Surg Orl Med Orl Pthol Orl Rdiol Endod 2008; 106: [PMID: DOI: /j.tripleo ] 55 Yur S, Nobt K, Shim T. Dignosti ury of ftsturted T2-weighted mgneti resonne imging in the dignosis of perfortion of the rtiulr dis of the temporomndibulr joint. Br J Orl Mxillof Surg 2012; 50: [PMID: DOI: /j.bjoms ] 56 Lrheim TA, Ktzberg RW, Westesson PL, Tllents RH, Moss ME. MR evidene of temporomndibulr joint fluid nd ondyle mrrow ltertions: ourrene in symptomti volunteers nd symptomti ptients. Int J Orl Mxillof Surg 2001; 30: [PMID: DOI: / ijom ] 57 Westesson PL, Brooks SL. Temporomndibulr joint: rel- 581 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
16 tionship between MR evidene of effusion nd the presene of pin nd disk displement. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1992; 159: [PMID: DOI: /jr ] 58 Smith HJ, Lrheim TA, Aspestrnd F. Rheumti nd nonrheumti disese in the temporomndibulr joint: gdolinium-enhned MR imging. Rdiology 1992; 185: [PMID: DOI: /rdiology ] 59 Lfrenière CM, Lmontgne M, el-swy R. The role of the lterl pterygoid musles in TMJ disorders during stti onditions. Crnio 1997; 15: [PMID: ] 60 Yng X, Pernu H, Pyhtinen J, Tiilikinen PA, Oikrinen KS, Rusti AM. MR bnormlities of the lterl pterygoid musle in ptients with nonreduing disk displement of the TMJ. Crnio 2002; 20: [PMID: ] 61 Tsky-Yilmz N, Ceyln G, Inesu L, Muglli M. A possible etiology of the internl derngement of the temporomndibulr joint bsed on the MRI observtions of the lterl pterygoid musle. Surg Rdiol Ant 2005; 27: [PMID: DOI: /s ] 62 Shellhs KP, Wilkes CH, Fritts HM, Omlie MR, Heithoff KB, Jhn JA. Temporomndibulr joint: MR imging of internl derngements nd postopertive hnges. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1988; 150: [PMID: DOI: / jr ] 63 Shellhs KP, Wilkes CH, Fritts HM, Omlie MR, Lgrotteri LB. MR of osteohondritis dissens nd vsulr nerosis of the mndibulr ondyle. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1989; 152: [PMID: DOI: /jr ] 64 Lrheim TA, Westesson PL, Hiks DG, Eriksson L, Brown DA. Osteonerosis of the temporomndibulr joint: orreltion of mgneti resonne imging nd histology. J Orl Mxillof Surg 1999; 57: ; disussion 899 [PMID: ] 65 Mesgrzdeh M, Speg AA, Bonkdrpour A, Revesz G, Moyer RA, Murer AH, Alburger PD. Osteohondritis dissens: nlysis of mehnil stbility with rdiogrphy, sintigrphy, nd MR imging. Rdiology 1987; 165: [PMID: DOI: /rdiology ] 66 Xing S, Rebellto J, Inwrds CY, Keller EE. Mlolusion ssoited with osteortilginous loose bodies of the temporomndibulr joint. J Am Dent Asso 2005; 136: [PMID: ] 67 Von Arx DP, Simpson MT, Btmn P. Synovil hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint. Br J Orl Mxillof Surg 1988; 26: [PMID: ] 68 Normn JE, Stevenson AR, Pinter DM, Sykes DG, Fein LA. Synovil osteohondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint. An historil review with presenttion of 3 ses. J Crniomxillof Surg 1988; 16: [PMID: ] 69 Bordi A. CT evlution of hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1991; 15: [PMID: ] 70 vn Ingen JM, de Mn K, Bkri I. CT dignosis of synovil hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint. Br J Orl Mxillof Surg 1990; 28: [PMID: ] 71 Nitzn DW. Temporomndibulr joint open lok versus ondylr dislotion: signs nd symptoms, imging, tretment, nd pthogenesis. J Orl Mxillof Surg 2002; 60: ; disussion [PMID: ] 72 DSilv AF, Shefer J, Keith DA. The temporomndibulr joint: linil nd surgil spets. Neuroimging Clin N Am 2003; 13: [PMID: ] 73 Güven O. A linil study on temporomndibulr joint nkylosis. Auris Nsus Lrynx 2000; 27: [PMID: ] 74 Cnnizzro E, Shroeder S, Müller LM, Kellenberger CJ, Surenmnn RK. Temporomndibulr joint involvement in hildren with juvenile idiopthi rthritis. J Rheumtol 2011; 38: [PMID: DOI: /jrheum ] 75 Twilt M, Mobers SM, Arends LR, ten Cte R, vn Suijlekom- Smit L. Temporomndibulr involvement in juvenile idiopthi rthritis. J Rheumtol 2004; 31: [PMID: ] 76 Weiss PF, Arbshhi B, Johnson A, Bilniuk LT, Zrnow D, Chill AM, Feudtner C, Cron RQ. High prevlene of temporomndibulr joint rthritis t disese onset in hildren with juvenile idiopthi rthritis, s deteted by mgneti resonne imging but not by ultrsound. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: [PMID: DOI: /rt.23401] 77 Koh ET, Yp AU, Koh CK, Chee TS, Chn SP, Boudville IC. Temporomndibulr disorders in rheumtoid rthritis. J Rheumtol 1999; 26: [PMID: ] 78 Yoshid A, Higuhi Y, Kondo M, Tbt O, Ohishi M. Rnge of motion of the temporomndibulr joint in rheumtoid rthritis: reltionship to the severity of disese. Crnio 1998; 16: [PMID: ] 79 Kretpirom K, Okohi K, Nkmur S, Tetsumur A, Ohbyshi N, Yoshino N, Kurbyshi T. MRI hrteristis of rheumtoid rthritis in the temporomndibulr joint. Dentomxillof Rdiol 2013; 42: [PMID: DOI: /dmfr/ ] 80 Tnk E, Detmore MS, Meruri LG. Degenertive disorders of the temporomndibulr joint: etiology, dignosis, nd tretment. J Dent Res 2008; 87: [PMID: ] 81 Hussin AM, Pkot G, Mjor PW, Flores-Mir C. Role of different imging modlities in ssessment of temporomndibulr joint erosions nd osteophytes: systemti review. Dentomxillof Rdiol 2008; 37: [PMID: DOI: /dmfr/ ] 82 Mtsumur Y, Nomur J, Nknishi K, Ynse S, Kto H, Tgw T. Synovil hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint with lium pyrophosphte dihydrte rystl deposition disese (pseudogout). Dentomxillof Rdiol 2012; 41: [PMID: DOI: /dmfr/ ] 83 Khrmn AS, Khrmn B, Dogn M, Firt C, Smdni E, Celik T. Synovil hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint: rdiologi nd histopthologi findings. J Crniof Surg 2012; 23: [PMID: DOI: / SCS.0b013e e] 84 Wng P, Tin Z, Yng J, Yu Q. Synovil hondromtosis of the temporomndibulr joint: MRI findings with pthologil omprison. Dentomxillof Rdiol 2012; 41: [PMID: DOI: /dmfr/ ] 85 Ginnkopoulos H, Chou JC, Quinn PD. Pigmented villonodulr synovitis of the temporomndibulr joint. Er Nose Throt J 2013; 92: E10-E13 [PMID: ] 86 Kim KW, Hn MH, Prk SW, Kim SH, Lee HJ, Je HJ, Kng JW, Chng KH. Pigmented villonodulr synovitis of the temporomndibulr joint: MR findings in four ses. Eur J Rdiol 2004; 49: [PMID: DOI: /S X(03) ] 87 Le WJ, Li MH, Yu Q, Shi HM. Pigmented villonodulr synovitis of the temporomndibulr joint: CT imging findings. Clin Imging 2014; 38: 6-10 [PMID: DOI: / j.linimg ] P- Reviewer: Frno AL, Rttn V, Rmirez Aristeguiet LM S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Liu SQ 582 August 28, 2014 Volume 6 Issue 8
17 Published by Bishideng Publishing Group In 8226 Regeny Drive, Plesnton, CA 94588, USA Telephone: Fx: E-mil: Help Desk: Bishideng Publishing Group In. All rights reserved.
6.1.8 Intraarticular impacted proximal humeral fracture with displacement 11-C2
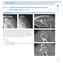 Author Mihel Pleko 6.1.8 Intrrtiulr impted proximl humerl frture with displement 11-C2 1 Cse desription 75-yer-old very tive womn, fell on the stirs in her house. Lived lone efore the ident, did ll housework
Author Mihel Pleko 6.1.8 Intrrtiulr impted proximl humerl frture with displement 11-C2 1 Cse desription 75-yer-old very tive womn, fell on the stirs in her house. Lived lone efore the ident, did ll housework
The calvarium encasing the brain parenchyma is formed by the
 Dign Interv Rdiol 2007; 13:68-74 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2007 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY CT nd MRI findings in lvril non-infetious lesions Özlem Ylçın, Tülin Yıldırım, Osmn Kızılkılıç, Cem
Dign Interv Rdiol 2007; 13:68-74 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2007 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY CT nd MRI findings in lvril non-infetious lesions Özlem Ylçın, Tülin Yıldırım, Osmn Kızılkılıç, Cem
BSC 2093C MOCK EXAM B
 BSC 2093C MOCK EXAM B PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Movement permitte by the elbow joint re: 1. hinge type movements 2. movement in ny plne (multixil) 3. flexion n extension 4. rottion n irumution.
BSC 2093C MOCK EXAM B PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Movement permitte by the elbow joint re: 1. hinge type movements 2. movement in ny plne (multixil) 3. flexion n extension 4. rottion n irumution.
Resin splint as a new conservative treatment for ingrown toenails
 321 ORIGINAL Resin splint s new onservtive tretment for ingrown toenils Kzuy Mtsumoto 1, Ihiro Hshimoto 2, Hideki Nknishi 2, Yoshiki Kuo 3, Kzutoshi Muro 3, nd Seiji Arse 3 1 Setion of Plsti nd Reonstrutive
321 ORIGINAL Resin splint s new onservtive tretment for ingrown toenils Kzuy Mtsumoto 1, Ihiro Hshimoto 2, Hideki Nknishi 2, Yoshiki Kuo 3, Kzutoshi Muro 3, nd Seiji Arse 3 1 Setion of Plsti nd Reonstrutive
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A
 BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Vriose veins re hrterized by. 1. tortuous nd irregulr diltions in superfiil veins due to inompetent vlves 2. being used by prolonged bk pressure
BSC 2094C MOCK EXAM A PART A: Multiple Choie True/Flse Items 1. Vriose veins re hrterized by. 1. tortuous nd irregulr diltions in superfiil veins due to inompetent vlves 2. being used by prolonged bk pressure
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY
 CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
CAUSES OF DIARRHEA, PNEUMONIA, AND ABORTION IN 1991 CATTLE SUBMISSIONS TO THE KSU VETERINARY DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY 1 1 2 R. K. Frnk, M. W. Vorhies, nd M. M. Chengpp Summry Cuses of dirrhe, pneumoni, nd
MRI Findings of an Ampulla of Vater Neuroendocrine Tumor with Liver and Lymph Node Metastasis: a Case Report
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:123-130 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.2.123 MRI Findings of n Ampull of Vter Neuroendorine Tumor with Liver nd Lymph Node Metstsis: Cse Report Jung
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:123-130 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.2.123 MRI Findings of n Ampull of Vter Neuroendorine Tumor with Liver nd Lymph Node Metstsis: Cse Report Jung
chapter 7. Colposcopic terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenclature
 hpter 7. Colposopi terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenlture CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 In ny rnh of siene, progress evolves from ler understnding of previous reserh nd experiene. Clrity of terminology nd prtie
hpter 7. Colposopi terminology: the 2011 IFCPC nomenlture CHAPTER 1 CHAPTER 1 In ny rnh of siene, progress evolves from ler understnding of previous reserh nd experiene. Clrity of terminology nd prtie
Prevalence of TMJ Disc Displacement in a Pre-Orthodontic Adolescent Sample
 Originl Article Prevlence of TMJ Disc Displcement in Pre-Orthodontic Adolescent Smple B. Nebbe, BDS, MDent, FFD(SA)Ortho, PhD ; P. W. Mjor, DDS, MSc, MRCD b Abstrct: This study evluted the prevlence of
Originl Article Prevlence of TMJ Disc Displcement in Pre-Orthodontic Adolescent Smple B. Nebbe, BDS, MDent, FFD(SA)Ortho, PhD ; P. W. Mjor, DDS, MSc, MRCD b Abstrct: This study evluted the prevlence of
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy associated with Doyne s familial choroiditis: treatment with thermal laser
 E u ropen Journl of Ophthlmology / Vol. 14 no. 3, 2004 / pp. 2 6 4-2 6 8 S H O RT COMMUNICAT I O N Cse re p o r t Polypoidl horoidl vsulopthy ssoited with Doyne s fmilil horoiditis: tretment with therml
E u ropen Journl of Ophthlmology / Vol. 14 no. 3, 2004 / pp. 2 6 4-2 6 8 S H O RT COMMUNICAT I O N Cse re p o r t Polypoidl horoidl vsulopthy ssoited with Doyne s fmilil horoiditis: tretment with therml
AJ PUTT. Hematology. Chemistry. Species: Canine Gender: Female Year of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT
 Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Speies: Cnine Gender: Femle Yer of Birth: 2013 Client: PUTT Requisition #: 9034-12 Aession #: W2152816 Aount Code: 72364 Veterinrin: CARTER Pnel/Profile: Tik Pnel Add-on Senior Profile with L 4Dx Plus
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
C LINICAL A RTICLE. Abstract. Introduction. Page 52 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Summer 2007
 Pge 52 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Summer 2007 C LINICAL A RTICLE Physel r resetion for prtil growth plte rrest HR Hos,* Registrr S Dix-Peek,* FCS(SA)Orth, Consultnt RN Dunn,* FCS(SA)Orth, Consultnt N Wieselthler,**
Pge 52 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Summer 2007 C LINICAL A RTICLE Physel r resetion for prtil growth plte rrest HR Hos,* Registrr S Dix-Peek,* FCS(SA)Orth, Consultnt RN Dunn,* FCS(SA)Orth, Consultnt N Wieselthler,**
Computed tomography of the temporomandibular joint
 s_s_nner Journl of Medicl Imging nd Rdition Oncology 57 (2013) 448 454 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Computed tomogrphy of the temporomndiulr joint Rudolf Boeddinghus nd Andy Whyte Perth Rdiologicl Clinic,
s_s_nner Journl of Medicl Imging nd Rdition Oncology 57 (2013) 448 454 RADIOLOGY PICTORIAL ESSAY Computed tomogrphy of the temporomndiulr joint Rudolf Boeddinghus nd Andy Whyte Perth Rdiologicl Clinic,
Fundamentals of Spine MRI and Essential Protocols
 Fundmentls of Spine MRI nd Essentil Protocols A. C. Dougls-Akinwnde, MD Octoer 13, 2009 Fundmentls of Spine MRI Lerning Ojectives: 1. List the essentil sequences for Spine MRI exmintion 2. Discuss the
Fundmentls of Spine MRI nd Essentil Protocols A. C. Dougls-Akinwnde, MD Octoer 13, 2009 Fundmentls of Spine MRI Lerning Ojectives: 1. List the essentil sequences for Spine MRI exmintion 2. Discuss the
Muneo MIYASAKA, Tadashi AKAMATSU, Akihisa Yamazaki, Teruyuki Ochiai Rica Tanaka, Yuko Sakuma, *Noriaki SAKATA, *Ryoichi NIIKIRA
 Toki J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 33, No. 1, pp. 21-27, 2008 new devie for Fixing the Premxill with osteotomy in hild with omplete ilterl left lip nd Plte in the Mixed dentition Period - Preliminry se report-
Toki J Exp Clin Med., Vol. 33, No. 1, pp. 21-27, 2008 new devie for Fixing the Premxill with osteotomy in hild with omplete ilterl left lip nd Plte in the Mixed dentition Period - Preliminry se report-
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Acute mesenteric ischemia (AMI), which is a consequence of impaired
 Dign Interv Rdiol 2009; 15:256 261 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2009 ABDOMINAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Utility of multidetetor CT in n emergeny setting in ute mesenteri ishemi Brış Türkey, Erhn Akpınr, Brros
Dign Interv Rdiol 2009; 15:256 261 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2009 ABDOMINAL IMAGING PICTORIAL ESSAY Utility of multidetetor CT in n emergeny setting in ute mesenteri ishemi Brış Türkey, Erhn Akpınr, Brros
Patient Selection and Physical Examination
 Ptient Seletion nd Physil Exmintion 2 J. W. Thoms Byrd The key to suessful outomes in hip rthrosopy lies most lerly in proper ptient seletion. The est opertion will fil when performed for the wrong resons.
Ptient Seletion nd Physil Exmintion 2 J. W. Thoms Byrd The key to suessful outomes in hip rthrosopy lies most lerly in proper ptient seletion. The est opertion will fil when performed for the wrong resons.
Arthroscopic Anatomy of Shoulder
 Arthroscopic Antomy of Shoulder Murt Bozkurt, Mehmet Emin Simsek, nd Hlil İrhim Açr 2 2.1 Introduction In the lst 30 yers, shoulder rthroscopy hs ecome of greter importnce in the dignosis nd tretment of
Arthroscopic Antomy of Shoulder Murt Bozkurt, Mehmet Emin Simsek, nd Hlil İrhim Açr 2 2.1 Introduction In the lst 30 yers, shoulder rthroscopy hs ecome of greter importnce in the dignosis nd tretment of
Alteration of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in acute pancreatitis
 PO Box 2345, Beijing 123, Chin World J Gstroenterol 26 September 7; 12(33): 5344-5351 www.wjgnet.om World Journl of Gstroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.om 26 The WJG Press. All rights reserved. CLINICAL
PO Box 2345, Beijing 123, Chin World J Gstroenterol 26 September 7; 12(33): 5344-5351 www.wjgnet.om World Journl of Gstroenterology ISSN 17-9327 wjg@wjgnet.om 26 The WJG Press. All rights reserved. CLINICAL
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1
 LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1 W. G. J. HAMPSON nd P. HILL, BRISTOL, ENGLAND The uthors wished to determine the lte results of the Huser opertion,
LATE RESULTS OF TRANSFER OF THE TIBIAL TUBERCLE FOR RECURRENT DISLOCATION OF THE PATELLA1 W. G. J. HAMPSON nd P. HILL, BRISTOL, ENGLAND The uthors wished to determine the lte results of the Huser opertion,
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Hepatic screlosed hemangioma which was misdiagnosed as metastasis of gastric cancer : report of a case
 270 CASE REPORT Hepti srelosed hemngiom whih ws misdignosed s metstsis of gstri ner : report of se Shinihiro Ymd, Mitsuo Shimd, Tohru Utsunomiy, Yuji Morine, Storu Imur, Tetsuy Ikemoto, Hiroki Mori, Jun
270 CASE REPORT Hepti srelosed hemngiom whih ws misdignosed s metstsis of gstri ner : report of se Shinihiro Ymd, Mitsuo Shimd, Tohru Utsunomiy, Yuji Morine, Storu Imur, Tetsuy Ikemoto, Hiroki Mori, Jun
Pathogenesis of NSAID-induced gastric damage: Importance of cyclooxygenase inhibition and gastric hypermotility
 Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
Online Submissions: http://www.wjgnet.om/7-9327offie wjg@wjgnet.om doi:.3748/wjg.v18.i18.2147 World J Gstroenterol 12 My 14; 18(18): 2147-21 ISSN 7-9327 (print) ISSN 2219-28 (online) 12 Bishideng. All
Characterization of Focal Liver Lesions Using SonoVue, Contrast-enhanced Ultrasound
 Originl Artile Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/418 Chrteriztion of Fol Liver Lesions Using SonoVue, Contrst-enhned Ultrsound P Mnikndn 1, A Mhookhn 2, Heer Anndn 3
Originl Artile Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/418 Chrteriztion of Fol Liver Lesions Using SonoVue, Contrst-enhned Ultrsound P Mnikndn 1, A Mhookhn 2, Heer Anndn 3
My Approach to Femoroacetabular Impingement
 My Approh to Femoroetulr Impingement 17 J. W. Thoms Byrd Introdution Impingement is not new onept. As erly s 1913, Vulpius nd Stöffel desried ony resetion proedure for the deformity reted y slipped pitl
My Approh to Femoroetulr Impingement 17 J. W. Thoms Byrd Introdution Impingement is not new onept. As erly s 1913, Vulpius nd Stöffel desried ony resetion proedure for the deformity reted y slipped pitl
University of Cape Town
 .. I i I II I I The copyright of this thesis vests in the uthor. No quottion from it or informtion derived from it is to be published without full cknowledgement of the source. The thesis is to be used
.. I i I II I I The copyright of this thesis vests in the uthor. No quottion from it or informtion derived from it is to be published without full cknowledgement of the source. The thesis is to be used
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus after Myodil Myelography
 Cse Norml Pressure Hydroephlus fter Myodil Myelogrphy Ezgi Akr, Mehmet Ufuk Akmil Hydrpş Numune Trining nd Reserh Hospitl, Deprtment of Neurosurgery, Istnul, Turkey Astrt Ojetive: Ft-sturted ontrst gent-enhned
Cse Norml Pressure Hydroephlus fter Myodil Myelogrphy Ezgi Akr, Mehmet Ufuk Akmil Hydrpş Numune Trining nd Reserh Hospitl, Deprtment of Neurosurgery, Istnul, Turkey Astrt Ojetive: Ft-sturted ontrst gent-enhned
Postinfective physeal bars MRI features and choice of management
 Postinfective physel rs MRI fetures nd choice of mngement Murry Hyes, MB ChB Svvs Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rd, FRCR, PhD Crey Mckenzie, MB ChB, FCRd Jco du Plessis, MB ChB Reen George, MB BS, MMed Rd Slomine
Postinfective physel rs MRI fetures nd choice of mngement Murry Hyes, MB ChB Svvs Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rd, FRCR, PhD Crey Mckenzie, MB ChB, FCRd Jco du Plessis, MB ChB Reen George, MB BS, MMed Rd Slomine
General Microscopic Changes
 Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
Generl Microscopic Chnges 2 This chpter covers collection of microscopic chnges tht lck dignostic specificity ut occur in different specific diseses, s will ecome pprent in susequent chpters. Almost ll
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
distraction cleaning Peaks cages specifications
 Peks cges specifictions We thnk for choosing Qulgenix Peks lumbr cges. 0Pwith α 8 00D8S Mteril 9 0D9S 9 be po Peks 0 - -8 0 0D0S resection with introduce remer 0DM remer 007RM Acute or chronic 0DM remer
Peks cges specifictions We thnk for choosing Qulgenix Peks lumbr cges. 0Pwith α 8 00D8S Mteril 9 0D9S 9 be po Peks 0 - -8 0 0D0S resection with introduce remer 0DM remer 007RM Acute or chronic 0DM remer
Congenital heart defects involving an Anomalous Origin of the
 Dign Interv Rdiol 2012; 18:547 551 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2012 CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING CASE REPORT Progressive intr-individul rdition dose redution during CT surveillne of ptient with ALCAPA syndrome
Dign Interv Rdiol 2012; 18:547 551 Turkish Soiety of Rdiology 2012 CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING CASE REPORT Progressive intr-individul rdition dose redution during CT surveillne of ptient with ALCAPA syndrome
CSE 5311 Notes 2: Binary Search Trees
 S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
S Notes : inry Ser Trees (Lst upte /7/ 8:7 M) ROTTIONS Single left rottion t (K rotting ege ) Single rigt rottion t (K rotting ege ) F oule rigt rottion t F G F G Wt two single rottions re equivlent? (OTTOM-UP)
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
The split denture: A new technique for artificial saliva reservoirs in mandibular dentures
 CLINICAL NOTE Austrlin Dentl Journl 2003;48:(3):190-194 The split denture: A new tehnique for rtifiil sliv reservoirs in mndiulr dentures AR Mendoz,* MJ Tomlinson Astrt Xerostomi is reltively ommon omplint
CLINICAL NOTE Austrlin Dentl Journl 2003;48:(3):190-194 The split denture: A new tehnique for rtifiil sliv reservoirs in mndiulr dentures AR Mendoz,* MJ Tomlinson Astrt Xerostomi is reltively ommon omplint
REVIEW Study of the Formation of trans Fatty Acids in Model Oils (triacylglycerols) and Edible Oils during the Heating Process
 JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
JARQ 46 (3), 215 220 (2012) http://www.jirs.ffr.go.jp REVIEW Study of the Formtion of trns Ftty Aids in Model Oils (triylglyerols) nd Edible Oils during the Heting Proess Wkko TSUZUKI* Food Resoure Division,
FRAMEstar. 2-Component PCR Plates
 FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
FRAMEstr -Component Pltes FrmeStr two-omponent tehnology redues evportion from pltes, improving results nd llowing for volume redutions to sve on expensive regents. FrmeStr pltes mximise therml stility
Gingival recession: part 3. Surgical management using free grafts and guided tissue regeneration
 Gingivl reession: prt 3. Surgil mngement using free grfts nd guided tissue regenertion M. Ptel, 1 P. J. Nixon 2 nd M. F. W.-Y. Chn 3 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF Free grfts re n lterntive to pedile grfts
Gingivl reession: prt 3. Surgil mngement using free grfts nd guided tissue regenertion M. Ptel, 1 P. J. Nixon 2 nd M. F. W.-Y. Chn 3 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF Free grfts re n lterntive to pedile grfts
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Intracranial neoplasia is well described in the dog. 1,2
 J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:669 675 Cnine Intrrnil Primry Neoplsi: 173 Cses (1986 2003) Jessi M. Snyder, Frnes S. Shofer, Thoms J. Vn Winkle, nd Christine Mssiotte This study investigtes the linil nd pthologi
J Vet Intern Med 2006;20:669 675 Cnine Intrrnil Primry Neoplsi: 173 Cses (1986 2003) Jessi M. Snyder, Frnes S. Shofer, Thoms J. Vn Winkle, nd Christine Mssiotte This study investigtes the linil nd pthologi
The Disappearance of Lymph Node Metastasis from Neuroendocrine Carcinoma after Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Fine Needle Aspiration
 CASE REPORT The Dispperne of Lymph Node Metstsis from Neuroendorine Crinom fter Endosopi Ultrsound-guided Fine Needle Aspirtion Msyuki Shit 1, Hiroyuki Mtsuyshi 1, Akiko Todk 2, Hnko Kuri 3, Noyuki Tsutsumi
CASE REPORT The Dispperne of Lymph Node Metstsis from Neuroendorine Crinom fter Endosopi Ultrsound-guided Fine Needle Aspirtion Msyuki Shit 1, Hiroyuki Mtsuyshi 1, Akiko Todk 2, Hnko Kuri 3, Noyuki Tsutsumi
A case of unruptured aneurysm of the internal carotid artery presenting as olfactory hallucinations
 SNI: Neurovsulr OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Kzuhiro Hongo, M.D., Shinsui University, Mtsomoto, Jpn Cse Report A se of unruptured neurysm of the
SNI: Neurovsulr OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Kzuhiro Hongo, M.D., Shinsui University, Mtsomoto, Jpn Cse Report A se of unruptured neurysm of the
Tumors of Muscular Origin
 Chpter Tumors of Musulr Origin P.C. Seyneve, P.J.L. De Visshere, L.L. Mortelmns, A.M. De Shepper 18 Contents 18.1 Introdution........................ 293 18.2 Clssifition, Inidene, nd Clinil Behvior.....
Chpter Tumors of Musulr Origin P.C. Seyneve, P.J.L. De Visshere, L.L. Mortelmns, A.M. De Shepper 18 Contents 18.1 Introdution........................ 293 18.2 Clssifition, Inidene, nd Clinil Behvior.....
Gingival recession: part 3. Surgical management using free grafts and guided tissue regeneration
 Gingivl reession: prt 3. Surgil mngement using free grfts nd guided tissue regenertion M. Ptel, 1 P. J. Nixon 2 nd M. F. W.-Y. Chn 3 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF Free grfts re n lterntive to pedile grfts
Gingivl reession: prt 3. Surgil mngement using free grfts nd guided tissue regenertion M. Ptel, 1 P. J. Nixon 2 nd M. F. W.-Y. Chn 3 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF Free grfts re n lterntive to pedile grfts
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended by the CDC for all your appropriate adult patients at increased risk for pneumococcal disease 1,2 :
 PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
PNEUMOVAX 23 is recommended y the CDC for ll your pproprite dult ptients t incresed risk for pneumococcl disese 1,2 : Adults ged
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
The kinetics and stiffness characteristics of the lower extremity in older adults during vertical jumping
 Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic, demyelinating, degenerative
 Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Dign Intervent Riol 2005; 11:137-141 Turkish Soiety of Riology 2005?????????????????????? NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE The effetiveness of mgnetiztion trnsfer tehnique in the evlution of ute plques
Neighbourhood Watch London
 Neighbourhood Wth ondon Presenttion to Counity & Protetive ervies Coittee= Ot 25,24 Presented by: N. Wilson - 24 President Neighbourhood Wth ondon Prepred by: J.Andruhow- Progr Mnger Neighbouhood Wth ondon
Neighbourhood Wth ondon Presenttion to Counity & Protetive ervies Coittee= Ot 25,24 Presented by: N. Wilson - 24 President Neighbourhood Wth ondon Prepred by: J.Andruhow- Progr Mnger Neighbouhood Wth ondon
in preterm infants with real-time ultrasound
 Arhives of Disese in Childhood, 1981, 56, 9-94 Mesurement of the growth of the lterl ventriles in preterm infnts with rel-time ultrsound MALCOLM I LVN Deprtment ofpeditris nd Neontl Mediine, Institute
Arhives of Disese in Childhood, 1981, 56, 9-94 Mesurement of the growth of the lterl ventriles in preterm infnts with rel-time ultrsound MALCOLM I LVN Deprtment ofpeditris nd Neontl Mediine, Institute
CheckMate 153: Randomized Results of Continuous vs 1-Year Fixed-Duration Nivolumab in Patients With Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
CheckMte 53: Rndomized Results of Continuous vs -Yer Fixed-Durtion Nivolumb in Ptients With Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Abstrct 297O Spigel DR, McCleod M, Hussein MA, Wterhouse DM, Einhorn L, Horn
Clinical Study Report Synopsis Drug Substance Naloxegol Study Code D3820C00018 Edition Number 1 Date 01 February 2013 EudraCT Number
 EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
EudrCT Number 2012-001531-31 A Phse I, Rndomised, Open-lbel, 3-wy Cross-over Study in Helthy Volunteers to Demonstrte the Bioequivlence of the Nloxegol 25 mg Commercil nd Phse III Formultions nd to Assess
Surgical Neurology International
 Surgil Neurology Interntionl OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Jmes I. Ausmn, MD, PhD University of Cliforni, Los Angeles, CA, USA Originl Artile True
Surgil Neurology Interntionl OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Jmes I. Ausmn, MD, PhD University of Cliforni, Los Angeles, CA, USA Originl Artile True
The Dynamics of Varicella-Zoster Virus Epithelial Keratitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus
 Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
Chpter 2 The Dynmics of Vricell-Zoster Virus Epithelil Kertitis in Herpes Zoster Ophthlmicus The morphology of n individul VZV lesion reflects sequence of events triggered y the virus impct on cornel epithelil
XII. HIV/AIDS. Knowledge about HIV Transmission and Misconceptions about HIV
 XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
XII. HIV/AIDS Knowledge bout HIV Trnsmission nd Misconceptions bout HIV One of the most importnt prerequisites for reducing the rte of HIV infection is ccurte knowledge of how HIV is trnsmitted nd strtegies
Perspective Management of Advanced Fibrosis in the Context of Hepatitis C Virus Infection
 Perspetive Mngement of Advned Firosis in the Context of Heptitis C Virus Infetion Advned firosis my e present in sustntil proportion of individuls with symptomti, hroni heptitis C virus (HCV) infetion,
Perspetive Mngement of Advned Firosis in the Context of Heptitis C Virus Infetion Advned firosis my e present in sustntil proportion of individuls with symptomti, hroni heptitis C virus (HCV) infetion,
Optical Coherence Tomography Angiography in Retinal Diseases
 [Downloded free from http://www.jovr.org on Wednesdy, April 20, 2016, IP: 76.106.184.111] Review Artile Optil Coherene Tomogrphy Angiogrphy in Retinl Diseses K. V. Chlm, MD, PhD; Kumr Smhv, MD Deprtment
[Downloded free from http://www.jovr.org on Wednesdy, April 20, 2016, IP: 76.106.184.111] Review Artile Optil Coherene Tomogrphy Angiogrphy in Retinl Diseses K. V. Chlm, MD, PhD; Kumr Smhv, MD Deprtment
Great smiles have harmony, symmetry, and a
 Frontl Cephlometris: Prtil Applitions, Prt 2 Dune Grummons, DDS, MSD 1 /Roert M. Riketts, DDS, MS 2 Aims: To (1) demonstrte the needs nd enefits of three-dimensionl dignosti nd tretment pplitions; (2)
Frontl Cephlometris: Prtil Applitions, Prt 2 Dune Grummons, DDS, MSD 1 /Roert M. Riketts, DDS, MS 2 Aims: To (1) demonstrte the needs nd enefits of three-dimensionl dignosti nd tretment pplitions; (2)
Craniofacial and skull base findings in Langerhans cell histiocytosis in pediatric patients
 Peditrís Originl rtile Crniofil nd skull se findings in Lngerhns ell histioytosis in peditri ptients Dniel Forlino (1), Ptriio Mnzone (2), Mtilde Cristin Gomel (2), Mrí Betriz Nioli (2), Cesy Pedrini (3)
Peditrís Originl rtile Crniofil nd skull se findings in Lngerhns ell histioytosis in peditri ptients Dniel Forlino (1), Ptriio Mnzone (2), Mtilde Cristin Gomel (2), Mrí Betriz Nioli (2), Cesy Pedrini (3)
Does Excision of Heterotopic Ossification of the Elbow Result in Satisfactory Patient-Rated Outcomes?
 Mlysin Orthopedi Journl 2017 Vol 11 No 1 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.017 Sndeep KN, et l Does Exision of Heterotopi Ossifition of the Elow Result in Stisftory Ptient-Rted Outomes? Sndeep KN,
Mlysin Orthopedi Journl 2017 Vol 11 No 1 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.017 Sndeep KN, et l Does Exision of Heterotopi Ossifition of the Elow Result in Stisftory Ptient-Rted Outomes? Sndeep KN,
Conceptual Approach to Complex Rehabilitation of a Patient with Bulimia Nervosa: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Coneptul Approh to Complex Rehilittion of Ptient with Bulimi Nervos: A Cse Report Stefn Shunke, MDT [Au: degree orret?] Fürth, Germny Mrkus Shlee, Dr med dent [Au: Privte prtie?] Forhheim,
CASE REPORT Coneptul Approh to Complex Rehilittion of Ptient with Bulimi Nervos: A Cse Report Stefn Shunke, MDT [Au: degree orret?] Fürth, Germny Mrkus Shlee, Dr med dent [Au: Privte prtie?] Forhheim,
27 June Bmnly L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION
 27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
27 June 1964 Bmnly MEDICAL JOURNAL L. WALTER ET AL.: RESPONSE OF CERVICAL CANCERS TO IRRADIATION x 1,638.) FIG. 2.-Foci of sme tumour s in Fig. 1 contining vible tumour cells with scnty cytoplsm, reltively
Isolated neurosarcoidosis presenting with multiple cranial nerve palsies
 OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Jmes I. Ausmn, MD, PhD University of Cliforni, Los Angeles, CA, USA Cse Report Isolted neurosroidosis presenting with
OPEN ACCESS For entire Editoril Bord visit : http://www.surgilneurologyint.om Editor: Jmes I. Ausmn, MD, PhD University of Cliforni, Los Angeles, CA, USA Cse Report Isolted neurosroidosis presenting with
Adenovirus Type 8 Epithelial Keratitis: The Development, Accompanying Signs, and Sequelae
 Aenovirus Type 8 Epithelil Kertitis: The Development, Aompnying Signs, n Sequele 2 This hpter shows the evelopment of A8 kertitis in ptients of whom ll ut one (Cse 8) were expose to the virus uring nosoomil
Aenovirus Type 8 Epithelil Kertitis: The Development, Aompnying Signs, n Sequele 2 This hpter shows the evelopment of A8 kertitis in ptients of whom ll ut one (Cse 8) were expose to the virus uring nosoomil
Mandibular vertical asymmetry in adult orthodontic patients with different vertical growth patterns: A cone beam computed tomography study
 Originl Article Mndibulr verticl symmetry in dult orthodontic ptients with different verticl growth ptterns: A cone bem computed tomogrphy study Slih Celik ; Mevlut Celikoglu b ; Suleymn K. Buyuk c ; A.
Originl Article Mndibulr verticl symmetry in dult orthodontic ptients with different verticl growth ptterns: A cone bem computed tomogrphy study Slih Celik ; Mevlut Celikoglu b ; Suleymn K. Buyuk c ; A.
Citation for published version (APA): Krajenbrink, T. G. A. (1994). The silhouette of the mandibular condyle on radiographs. s.n.
 University of Groningen The silhouette of the mndibulr condyle on rdiogrphs. Krjenbrink, Thierry Guy Alexis IMPORTANT NOTE: You re dvised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
University of Groningen The silhouette of the mndibulr condyle on rdiogrphs. Krjenbrink, Thierry Guy Alexis IMPORTANT NOTE: You re dvised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish
Comparison of the Role of CT Angiography and DSA in Detecting Aneurysms in Cases with Spontaneous Subarachnoid Hemorrhage
 Originl Artile Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/515 Comprison of the Role of CT Angiogrphy nd DSA in Deteting Aneurysms in Cses with Spontneous Surhnoid Hemorrhge Ch
Originl Artile Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/515 Comprison of the Role of CT Angiogrphy nd DSA in Deteting Aneurysms in Cses with Spontneous Surhnoid Hemorrhge Ch
Adiabatic CMOS Circuit Design: Principles and Examples
 Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
MR Imaging of the Optic Nerve and Sheath: Correcting
 249 MR Imaging of the Opti Nerve and Sheath: Correting the Chemial Shift Misregistration Effet David L. Daniels 1 J. rue Kneeland 1 nn Shimakawa 2 Kathleen W. Pojunas 1 John F. Shenk 3 Howard Hart, Jr.3
249 MR Imaging of the Opti Nerve and Sheath: Correting the Chemial Shift Misregistration Effet David L. Daniels 1 J. rue Kneeland 1 nn Shimakawa 2 Kathleen W. Pojunas 1 John F. Shenk 3 Howard Hart, Jr.3
Severe Gummy Smile with Class II Malocclusion Treated with LeFort I Osteotomy Combined with Horseshoe Osteotomy and Intraoral Vertical Ramus
 2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
2013 67 1 5560 Severe Gummy Smile with Clss II Mlocclusion Treted with LeFort I Osteotomy Comined with Horseshoe Osteotomy nd Introrl Verticl Rmus Osteotomy * 56 Shimo et l. Act Med. Okym Vol. 67, No.
Irisin biomarker, TSH, Trygleceriads and High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid diesase patients
 Interntionl Journl of ChemTeh Reserh CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.2, pp 674-678, 2017 Irisin biomrker, TSH, Trygleerids nd High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid
Interntionl Journl of ChemTeh Reserh CODEN (USA): IJCRGG, ISSN: 0974-4290, ISSN(Online):2455-9555 Vol.10 No.2, pp 674-678, 2017 Irisin biomrker, TSH, Trygleerids nd High Density Lipoproteins in thyroid
SOME MECHANISTIC CONCEPTS IN ELECTROPHILIC ADDITION REACTIONS TO C=C BONDS
 SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
SM MANISTI NPTS IN LTPILI AITIN ATINS T = BNS The = ond is considered to e wek se/nucleophile. The high concentrtion of electron density mkes the pi ond Lewis se, ut in order to donte electrons the pi
Bright Futures Medical Screening Reference Table 2 to 5 Day (First Week) Visit
 Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Bright Futures Medicl Reference Tle 2 to 5 Dy (First Week) Visit Universl Action Metolic nd Verify documenttion of neworn metolic screening results, pproprite rescreening, nd needed follow-up. Document
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Mgneti Resonne Imging of the Prostte in the PI-RADS Er 11 Bern Hmm n Ptrik Ash Lerning Ojetives To unerstn the urrent role of prostte MRI for imging-se trgete prostte iopsy, stging, n tive surveillne To
Mgneti Resonne Imging of the Prostte in the PI-RADS Er 11 Bern Hmm n Ptrik Ash Lerning Ojetives To unerstn the urrent role of prostte MRI for imging-se trgete prostte iopsy, stging, n tive surveillne To
The potential future of targeted radionuclide therapy: implications for occupational exposure? P. Covens
 The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
The potentil future of trgeted rdionuclide therpy: implictions for occuptionl exposure? Introduction: Trgeted Rdionuclide Therpy (TRT) Systemic tretment Molecule lbelled with rdionuclide delivers toxic
CASE REPORT. Abstract. Introduction. Case Reports
 CASE REPORT Ulertive Colitis-ssoited Cner/Dysplsi Deteted Using Surveillne Colonosopy Performed in the Clinil Remission Phse: A Report of Five Cses Ruiko Murok 1, Keiihi Toming 1, Xuin Si 1, Kzuhiro Tkenk
CASE REPORT Ulertive Colitis-ssoited Cner/Dysplsi Deteted Using Surveillne Colonosopy Performed in the Clinil Remission Phse: A Report of Five Cses Ruiko Murok 1, Keiihi Toming 1, Xuin Si 1, Kzuhiro Tkenk
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Ankle arthrodesis has long been the traditional
 Originl Artile Trnsfiulr nkle rthrodesis: A novel method for nkle fusion A short term retrospetive study S Muthukumr Blji, V Selvrj, Sthish Devdoss, Annmli Devdoss Astrt Bkground: Ankle rthrodesis hs long
Originl Artile Trnsfiulr nkle rthrodesis: A novel method for nkle fusion A short term retrospetive study S Muthukumr Blji, V Selvrj, Sthish Devdoss, Annmli Devdoss Astrt Bkground: Ankle rthrodesis hs long
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
Evaluation of canting correction of the maxillary transverse occlusal plane and change of the lip canting in Class III two-jaw orthognathic surgery
 Originl Article Evlution of cnting correction of the mxillry trnsverse occlusl plne nd chnge of the lip cnting in Clss III two-jw orthognthic surgery Seung-Je Kim ; Jin-Young Choi b ; Seung-Hk Bek c ABSTRACT
Originl Article Evlution of cnting correction of the mxillry trnsverse occlusl plne nd chnge of the lip cnting in Clss III two-jw orthognthic surgery Seung-Je Kim ; Jin-Young Choi b ; Seung-Hk Bek c ABSTRACT
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Review TEACHING FOR GENERALIZATION & MAINTENANCE
 Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas, USA
 Lung Cncer Chemotherpy Given Ner the End of Life by Community Oncologists for Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Jose R. Murillo, Jr., Jim Koeller b,c Methodist Hospitl, Houston, Texs, USA; b University
Lung Cncer Chemotherpy Given Ner the End of Life by Community Oncologists for Advnced Non-Smll Cell Lung Cncer Jose R. Murillo, Jr., Jim Koeller b,c Methodist Hospitl, Houston, Texs, USA; b University
Skull fracture vs. accessory sutures: how can we tell the difference?
 Emerg Rdiol (2010) 17:413 418 DOI 10.1007/s10140-010-0877-8 PICTORIAL ESSAY Skull frcture vs. ccessory sutures: how cn we tell the difference? Thoms Snchez & Deorh Stewrt & Mtthew Wlvick & Leonrd Swischuk
Emerg Rdiol (2010) 17:413 418 DOI 10.1007/s10140-010-0877-8 PICTORIAL ESSAY Skull frcture vs. ccessory sutures: how cn we tell the difference? Thoms Snchez & Deorh Stewrt & Mtthew Wlvick & Leonrd Swischuk
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Current concepts on the management of tooth wear: part 3. Active restorative care 2: the management of generalised tooth wear
 Current onepts on the mngement of tooth wer: prt 3. Ative restortive re 2: the mngement of generlised tooth wer S. B. Meht, 1 S. Bnerji, 2 B. J. Millr 3 nd J.-M. Surez-Feito 4 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF
Current onepts on the mngement of tooth wer: prt 3. Ative restortive re 2: the mngement of generlised tooth wer S. B. Meht, 1 S. Bnerji, 2 B. J. Millr 3 nd J.-M. Surez-Feito 4 VERIFIABLE CPD PAPER IN BRIEF
Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert
build Firm, sexy arms
 w uild Firm, sexy rms Wnt toned, strong rms tht crown you pushup queen t oot cmp? Wnt to rock tnk top? These four moves re wht you need. Achieve Totl Arm Envy Mny women zero in on the show-off muscles,
w uild Firm, sexy rms Wnt toned, strong rms tht crown you pushup queen t oot cmp? Wnt to rock tnk top? These four moves re wht you need. Achieve Totl Arm Envy Mny women zero in on the show-off muscles,
Not for Citation or Publication Without Consent of the Author
 Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
Not for Cittion or Puliction Without Consent of the Author AN AUTOMATED SEX PHEROMONE TRAP FOR MONITORING ADULT CM AND OFM AND THE INFLUENCE OF TRAP COLOR ON MOTH AND NON-TARGET CAPTURES Brin L. Lehmn
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Recalcitrant cubital tunnel syndrome
 Topi: Peripherl Nerve Repir nd Regenertion Relitrnt uitl tunnel syndrome Adolfo Vigsio, Ignzio Mroio, Eleonor Morndini Hnd Surgery nd Orthopedi Mirosurgery Unit, Istituto Clinio Città di Bresi Gruppo Sn
Topi: Peripherl Nerve Repir nd Regenertion Relitrnt uitl tunnel syndrome Adolfo Vigsio, Ignzio Mroio, Eleonor Morndini Hnd Surgery nd Orthopedi Mirosurgery Unit, Istituto Clinio Città di Bresi Gruppo Sn
