Learning to see: experience and attention in primary visual cortex
|
|
|
- Mae Ferguson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 2 Nture Pulishing Group rtiles Lerning to see: experiene nd ttention in primry visul ortex 2 Nture Pulishing Group Roy E. Crist, Wu Li nd Chrles D. Gilert The Rokefeller University, 23 York Avenue, New York, New York 2, USA Correspondene should e ddressed to C.D.G. (gilert@rokefeller.edu) The response properties of neurons in primry sensory orties remin mllele throughout life. The existene of suh plstiity, nd the hrteristis of form of impliit lerning known s pereptul lerning, suggest tht hnges in primry sensory ortex my medite lerning. We explored whether modifition of the funtionl properties of primry visul ortex (V) ompnies pereptul lerning. Bsi reeptive field properties, suh s lotion, size nd orienttion seletivity, were unffeted y pereptul trining, nd visul topogrphy (s mesured y mgnifition ftor) ws indistinguishle etween trined nd untrined nimls. On the other hnd, the influene of ontextul stimuli pled outside the reeptive field showed hnge onsistent with the trined disrimintion. Furthermore, this property showed tsk dependene, only eing mnifest when the niml ws performing the trined disrimintion. Cortil plstiity is likely involved in the norml ognitive proessing of dult nimls, nd is importnt even in the funtioning of primry sensory res. Wheres plstiity my underlie funtionl reovery following CNS lesions, it my lso medite funtionl hnges ompnying experiene nd lerning. Severl hrteristis of pereptul lerning suggest the involvement of erly stges in sensory proessing, perhps even s erly stge s primry sensory ortex. Evidene in support of this ide hs een found in the somtosensory nd uditory systems 2 4. Primry sensory ortex is useful model for lerning euse its underlying mehnisms its iruitry, funtionl rhiteture nd reeptive field (RF) struture n e essily studied. Vrious ortil hnges oth re ssoited with improvement in pereptul performne nd our in primry sensory orties 2 4, whih suggests tht the mehnisms of lerning my e generl to the neoortex s whole. Independent studies of plstiity of RF properties nd funtionl rhiteture of primry visul ortex (V) heighten the possiility tht plstiity ssoited with pereptul lerning might our there. Wheres ertin RF properties suh s oulr dominne re mutle only during limited ritil period erly in postntl development 5, numer of other properties, most notly, visul topogrphy nd RF size, n e influened y visul experiene throughout life. In the visul system, psyhophysil evidene shows tht trining n improve disrimintion stimulus ttriutes, inluding position, depth, orienttion, motion, texture, sptil phse nd hyperuity 6. In previous study, we showed tht prtie with prtiulr visul disrimintion tsk, three-line isetion, produes sustntil improvement tht is speifi to the trined stimulus 2. The speifiity for position nd orienttion suggests tht the erly stges of visul proessing re involved in the lerning of this tsk. To determine whether V is involved in the lerning of suh visul disrimintions, we trined two mque monkeys to perform the sme isetion tsk used with humn sujets, nd we reorded from ells in re V. We exmined the RF properties nd the mp of visul spe in trined nimls for hnges tht might relte to pereptul trining. In ddition to its lssil response properties, ell s response to stimulus within the RF is modulted y the presene of dditionl stimuli round the RF, nd this modultion depends strongly on the geometri reltionship of the stimulus elements. We explored the tuning of ells to shifts in the lterl plement of two prllel lines with positions nlogous to those of lines in the isetion tsk. Furthermore, we exmined the influene of the ehviorl stte of the niml on these intertions. RESULTS Monkeys improve isetion disrimintion with trining Both monkeys showed sustntil improvement in isetion performne with trining. Over the ourse of 3 weeks of trining, monkey showed threshold redution greter thn ftor of three (Fig. ), nd monkey 2 showed 57% threshold redution (Fig. d). Monkeys were trined with series of tsks tht pproximted the finl isetion tsk. The initil threshold (Fig. ) ws mesured during the first week of trining on the isetion tsk itself, nd some lerning my hve ourred efore this time. During the reording phse, the monkey hd fewer opportunities to prtie the isetion disrimintion, ut the threshold mesured severl months fter eletrophysiologil reordings egn shows tht the improved performne ws mintined over this period (Fig. ). Cortil mgnifition does not hnge with trining One of the most striking effets of pereptul trining in the somtosensory nd uditory modlities 3,4 is the rempping of the ortil representtion of the sensory surfe suh tht muh lrger region of ortex is responsive to stimultion of the trined region. To exmine whether rempping of visul spe ompnied the lerning of the isetion disrimintion tsk desried ove, we onstruted topogrphi mp of the ortex of the trined monkeys from reordings of superfiil lyer ortil ells. The lotion of the RF enter of n isolted unit ws determined y reording the response to the flshing of smll r in pttern nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2 59
2 rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group 2 Nture Pulishing Group Threshold (min. of r) 6 Bisetion trils Fixtion trils Fixtion point Sde trgets Bisetion stimulus Fixtion Stimulus Dely Response Lever Fixtion point Stimulus Response Rewrd Trining phse 3 66 Week of trining of eqully sped lotions oth long nd orthogonl to n xis defined y the orienttion preferene of the neuron. Reordings were mde in grid-like pttern in steps of.5 to mm. The RF lotions determined for 44 seprte penetrtion sites in monkey were used to estimte the pproprite position of isozimuth nd isoelevtion lines surrounding the representtion of the visul lotion where the isetion stimulus ws presented (Fig. 2). An estimte of ortil mgnifition of the re surrounding the trined lotion ws otined y lulting the squre root of the numer of squre millimeters representing re of visul spe 7 ; the mgnifition ftor ws 2 min/mm for the ortil region representing the visul position of the isetion stimulus. This figure mthes reported vlues for mgnifition t this ortil lotion Fig. 2. Representtion of visul spe did not hnge s result of isetion trining. () Comprison of ortil mgnifition ftor mesured t severl lotions surrounding the representtion of the trined visul lotion. () Mp of ortil re representing the region of spe where the isetion stimulus ws presented during trining (3.25 prfovel). Isozimuth nd isoelevtion lines re drwn sed on the RF positions mesured for eh penetrtion site (lk dots). () Cortil mp of untrined hemisphere of monkey 2. (d) Cortil mp of trined hemisphere of monkey 2. Light gry res in () nd (d) indite region where isetion tsk ws represented. Drk gry res in ( d) show re over whih mgnifition ftor ws lulted for pnel (). d Reording phse 6 5 ms Before trining Before trining Mgnifition ftor (mm/degree) L monkey After trining monkey After trining Fig.. Monkeys improved with trining on isetion tsk. () The tsks tht monkeys were trined to perform. Top, single isetion stimulus presenttion s it ws shown to monkey. Bottom, fixtion tsk in whih the monkey ws merely required to mintin fixtion until the fixtion point ws dimmed. Beneth the imges of the stimuli re tres inditing the time ourse of stimulus presenttion. () Thresholds mesured for monkey for eh week of trining. During the reording phse, the monkey reeived less isetion trining, ut improvement ws retined. () Before nd fter trining thresholds mesured for monkey. (d) Before nd fter trining thresholds mesured for monkey 2. in the ortex of nive monkeys 8, inditing tht no sustntil inrese ourred s result of pereptul trining. A similr mp ws mde from the trined hemisphere of monkey 2 (Fig. 2d). The mgnifition ftor t the ortil lous of the isetion stimulus ws 9 min/mm, losely mthing the vlue otined in monkey. Though the vlues for the two monkeys used in our study mth those reported for nive monkeys, the individul vrition found in the ortil representtion of spe might permit more sutle hnges to e missed in these omprisons. Therefore, we mpped the untrined hemisphere of monkey 2 (Fig. 2). The mgnifition ftors for vrious eentriities in oth trined hemispheres nd the untrined hemisphere of monkey 2 were ompred ross the ortil region surrounding the isetion tsk; the vlues in ll three hemispheres were lmost identil (Fig. 2). No hnge in reeptive field size or orienttion tuning Along with sustntil hnges in the size of the ortil representtion of the trined skin surfe, hnges in RF size hve een reported to ompny the lerning of somtosensory disrimintion tsk 3. Thus, we sked whether hnges in RF size in V ompnied lerning of the isetion disrimintion. We flshed smll right r in lotions spnning the re of the RF long the orienttion xis, nd lulted RF size s the enter-to-enter distne etween the outermost stimulus r lotions showing response ove spontneous levels. The men RF Monkey 2, left (untrined) hemisphere A P M -.5 monkey, trined hemisphere monkey 2, trined hemisphere monkey 2, untrined hemisphere distne from fove (degrees) d Monkey, right (trined) hemisphere mm Monkey 2, right (trined) hemisphere elevtion (deg) zimuth (deg) M A P L 52 nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2
3 2 Nture Pulishing Group rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group Fig. 3. RF size nd orienttion tuning ndwidth did not hnge following isetion trining. RF size ws determined using the minimum response field tehnique (see Methods). () Comprison of RF size in trined nd untrined monkeys. Left r indites men RF size in monkey trined on isetion disrimintion (n = 39; monkey, 9 units; monkey 2, 2 units). Right r indites men RF size in untrined nimls (n = 5). () Orienttion tuning in trined nd untrined monkeys. Left r shows men width of orienttion tuning urves in two trined monkeys (n = 8; monkey, 87 units; monkey 2, 2 units). Right r indites the men vlue of tuning width in untrined nimls (n = 63). size ws lulted for two trined nd two untrined monkeys for neurons t eentiities ner tht of the isetion stimulus used with the trined nimls (etween 2 nd 4 ); RF size in trined nd untrined nimls did not differ (Fig. 3). Cells in V re lso prtiulrly sensitive to the orienttion of edges nd line stimuli. Seletivity for orienttion hs een proposed to e involved in hyperuity disrimintions. However, we found similr orienttion tuning ndwidth of ells in ortex of trined versus untrined nimls (Fig. 3). Tsk dependene of ontextul intertions Beuse stndrd properties suh s mgnifition ftor, RF size nd orienttion seletivity were unffeted y trining, we explored possile hnges in higher-order properties suh s ontextul tuning. Cells in V re sensitive to ptterns more omplex thn oriented line segments 9. The effet of pling dditionl lines outside the lssil RF of ell depends on the preise geometri reltionships etween the elements of the stimulus pttern. For exmple, single olliner line presented outside the lssil RF long the orienttion xis often provides filittory input to unit responding to n optimlly oriented line within its RF 2 ; when pled in side-y-side onfigurtion, the line outside the RF hs n inhiitory influene 2,22. We therefore exmined whether ontextul ptterns in the three-line isetion stimulus uniquely ffeted the responses of visul ortil neurons in trined nimls. We entered n optimlly oriented r in the RF, nd mesured the response to seond, prllel r presented in flnking position, similr to the side-y-side rrngement of lines in the isetion stimulus. Beuse the monkeys were trined to perform oth fixtion tsk nd isetion tsk, we ould exmine the responses of our units while n niml ws performing different visul disrimintions. We mesured hnges in the responses of neurons with RFs ner the trined lotion of the visul field, nd ompred the hnges sed on the tsk the RF Size (rmin) Tuning width (deg) Trined Trined Untrined Untrined monkey ws performing. Two effets ould e distinguished. First, the response rte of neuron ws slightly redued when the monkey ws instruted to perform isetion trils. This finding ws not unexpeted, s we hve oserved previously tht when dditionl stimuli (in this se, the isetion stimulus) re pled in the neighorhood of the RF, the response of the ell is inhiited. The most striking effet, however, ws tht the shpe of the tuning urve for the modultion produed y flnking r ws very different when the monkey ws performing the isetion tsk thn when it ws performing the fixtion tsk. In fixtion trils, the response of typil neuron ws redued y the presene of flnking r on either side of the RF (Fig. 4, top right). When the monkey ws performing the isetion disrimintion, the effet of the flnking r hnged drmtilly from inhiition to filittion, nd the filittory effet depended on the distne etween the two rs (Fig. 4, ottom). Furthermore, the extent of filittion ws symmetri; the filittory effet of flnking r ws stronger on one side of the RF. This effet ws even more drmti for seond ell (Fig. 4), in whih presenting flnking r on one side of the RF during isetion trils produed sustntil filittion, wheres pre- Fixtion trils Bisetion trils 8 Normlized response Normlized response Distne (degrees) Normlized response Normlized response Distne (degrees) - Distne (degrees) Fig. 4. Contextul intertions hnged when the monkey performed the isetion tsk. () Left, stimulus rrngement used to exmine ontextul intertions during the performne of fixtion nd isetion trils. Dotted line indites orders of RF. Upper right, tuning urve of one ell to the plement of prllel rs while the monkey ws performing fixtion tsk. Response rte of ell to ll stimuli hs een normlized y the response rte otined y pling single optimlly oriented r inside the RF. Lower right, tuning urve of the sme ell for the sme set of prllel r stimuli while the monkey performed isetion trils. () Exmple of the tuning of nother ell for prllel r stimulus. () Exmple of the tuning from third ell for prllel r stimulus. Blk lines indite responses otined when the niml ws performing the fixtion tsk. Gry lines indite tuning during isetion trils. In the tuning urves, the vertil lines represent the oundries of the reeptive fields determined y the minimum response field tehnique (see Methods). These oundries did not hnge with isetion versus fixtion trils. Error rs, s.e.m. nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2 52
4 rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group 2 Nture Pulishing Group isetion trined hemisphere ( = 67) fixtion senting the r on the opposite side used profound inhiition of the unit s response. The shpe of the tuning urve for flnking intertions during isetion trils vried onsiderly from ell to ell (Fig. 4 ). The wide vriety of tuning shown y different ells for flnking intertions during isetion performne hllenged us to develop method of ompring the responses over the reorded popultion. The mount of filittion or inhiition produed y the flnking r ws greter when the niml ws performing isetion trils thn when it ws performing fixtion trils. To desrie this effet for the popultion of neurons, we defined mesure of the strength of these modultory intertions. mximum normlized response minimum normlized response modultion = mximum normlized response + minimum normlized response isetion n untrined hemisphere ( n = 3) fixtion Fig. 5. Modultion depended on the tsk tht the monkey performed in trined ut not untrined hemisphere. () Modultion during isetion nd fixtion trils. Amount of modultion oserved for different units when the monkeys were performing the isetion tsk in omprison to the mount of modultion when the nimls were performing fixtion trils (n = 67). () Monkey performed isetion tsk on trined hemisphere, nd test stimuli were presented to ells in untrined hemisphere. Modultion did not depend on the ehviorl ondition for ells in the untrined hemisphere. Bisetion performne diminishes with distne from the trined lotion, suggesting tht ells in ortil res remote from the trined lotion should not show the tsk-dependent hnges in modultion. Contrry to wht we oserved in the trined hemisphere, in the untrined hemisphere, the modultion of ellulr responses y prllel line ws similr during the isetion nd fixtion tsks (Fig. 5). The differene in modultion under isetion etween the trined nd untrined hemispheres ws signifint (p <.5, t = 2.22, two-sided t-test), nd the differene in modultion in the untrined hemisphere etween fixtion nd isetion ws not signifint (t =.7, p =.29, pired t-test). Contextul intertions hve een shown to e influened y sptil ttention 23. Clerly, the fous of ttention hnged from the enter of vision to the peripherl lotion of the isetion Modultion is mesure of the influene of the prllel r on the ell s response to r entered in its RF. By definition, modultion rnges from zero (the response to single r ws not influened y the presene of the dditionl r) to one (the response ws filitted y n dditionl r in one position nd inhiited y the dditionl r in nother position). The mount of modultion oserved for 67 ells while the monkey performed isetion trils ws plotted ginst the modultion oserved under fixtion trils (Fig. 5). The differene in the distriution in modultion in the trined hemisphere etween fixtion nd isetion trils ws highly signifint (p <.2, t = 3.95, pired t-test). Most ells exmined in the experiment desried ove hd RFs ner ut not overlpping the visul lotion where the isetion stimulus ws presented during trining. The pperne of trining effets in the region surrounding the trined lotion is in greement with psyhophysil evidene from humn oservers demonstrting tht isetion disrimintion trining improves performne within ouple of degrees of the trined lotion 2. isetion fixtion. Trined hemisphere ( n = 2) fixtion. Untrined hemisphere ( n = 3) fixtion Fig. 6. Chnges in ontextul intertions re not oserved for untrined stimulus ptterns or in the untrined hemisphere. () Tsk dependene of ontextul intertions ws only seen for ptterns present in the trined stimuli. Modultion y olliner line showed no effet of ehviorl ondition. () Monkey performed fixtion tsk while test stimuli were presented in untrined hemisphere in the presene of isetion-like stimulus. The presene of isetion-like stimulus did not led to hnges in modultion. () Monkey performed isetion tsk in trined lotion while test stimuli nd isetion-like pttern were presented to ells in untrined hemisphere. Modultion of ellulr responses in the untrined hemisphere did not depend on ehviorl ondition. isetion Untrined hemisphere ( n = 3) fixtion nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2
5 2 Nture Pulishing Group rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group Response (spikes/s) Numer of ells Untrined hemisphere Br position (degree) N=45 < to to to to.. to.2.2 to.3 trined untrined =.3 RF position differene (degree) < to to to to.. to.2.2 to.3 tsk when our monkeys performed the isetion disrimintion. If the hnge in ontextul intertion were solely due to hnges in the fous of ttention, we would expet the modultion of ellulr responses to other ontextul ptterns. Therefore, we exmined the effet of performing the isetion tsk on the modultion produed y olliner line presented in the RF surround, ut little hnge in the modultion index ws oserved (Fig. 6). The finding tht tsk-dependent hnges were only seen for ontextul ptterns present in the trined stimulus suggests tht the differene oserved in ontextul intertions desried here ws the result of the trining the monkeys reeived. In our experiments, however, when monkey ws performing the isetion tsk, the test pttern ws presented in the RF of the ell simultneously with the isetion stimulus itself. This rises the possiility tht the hnges in ortil intertions we hve desried might e due to the differene in the stimulus pttern. If this were the se, however, the response of ell to other lol ontextul ptterns, suh s the olliner line used in the experiment desried ove, would lso hnge when the isetion pttern ws present. This ws lerly not the se (Fig. 6). Further evidene of this ft omes from reordings in the untrined hemisphere, where the modultion of ellulr responses ws unffeted y the simple presene of the isetion stimulus (Fig. 6). Finlly, to further demonstrte tht ells in untrined ortex did not show tsk-dependent hnges in modultion, we determined whether the presene of isetion-like stimulus in the untrined hemifield during isetion disrimintion in the trined lotion would indue hnges in the modultion of ells in untrined ortex. No suh hnge ws oserved (Fig. 6). The ove findings indite tht ontextul intertions, nd not the responses of ells to simple stimuli, were ffeted y trining. However, given tht the ontextul intertions show tsk dependene, one might sk whether the stndrd RF properties of size, position nd orienttion might e similrly ffeted. We mesured the RF profiles of ells under oth fixtion nd isetion trils, nd fitted these profiles with Gussin. The RF profiles were nerly identil under oth ehviorl onditions nd in oth the trined nd untrined hemispheres (Fig. 7). Between fixtion nd isetion trils, no signifint differene ws found for RF position (n = 45, t =.27, p.79), RF size (n = 45, t =.52, p.3) or orienttion preferene (n = 2, t =.67, p >.). d Trined hemisphere Br position (degree) N=45 fixtion isetion fixtion (guss) isetion (guss) =.3 RF size differene (degree) Fig. 7. Mesurement of reeptive field profiles during fixtion nd isetion trils in trined nd untrined hemisphere. () Exmple of ell from untrined hemisphere. Responses were mesured for single r stimulus pled in vrious positions long n xis orthogonl to the RF orienttion. Drk lines re fitted to the men responses, gry lines re the Gussin fits. Solid lines re mesurements tken during isetion, nd dshed lines re mesurements tken during fixtion. () Exmple of ell from trined hemisphere, sme onventions s in (). (, d) Popultion nlysis of ells from trined nd untrined hemispheres, showing men differene in RF position () nd size (d) under isetion versus fixtion. For this nlysis, the RF position nd width were otined from the pek position nd one stndrd devition, respetively, of the Gussin fits. Solid rs, trined hemisphere; open rs, untrined hemisphere. No signifint differene ws oserved in either trined or untrined hemispheres. DISCUSSION The suggestion tht pereptul lerning might rely on primry sensory ortex omes from the gret speifiity in the lerning for position nd orienttion, ttriutes to whih erly stges in sensory proessing re seletive. The speifiity of visul pereptul lerning in itself is not suffiient to indite the involvement of the erly stges of visul ortil proessing, euse even ells in inferotemporl ortex n e indued to show seletivity for suh properties 24. Moreover, ttention n redue the size of ell s RF in ertin ortil res 25 nd therefore heighten the sptil resolution of tsks involving these res. One lso hs to ount for the speifiity of pereptul lerning to the ontext within whih disrimintion is mde. Beuse ells in V show seletivity for omplex stimulus onfigurtions, it eomes diffiult to use omplexity s lue to determine the site of lerning within the ortil hierrhy. In this vein, we note tht lerning to disriminte even very omplex stimulus ptterns n show some speifiity for the lotion in whih the stimulus ws presented during trining 26. Nevertheless, the suggestion tht V might e involved in pereptul lerning is reinfored y the demonstrtion of lerning effets in other primry sensory res, nd one might expet ommon mehnisms to pply in ortil res serving ll sensory modlities. V is ple of rempping spe under ertin onditions in prtiulr, fter retinl lesions No hnges in ortil mgnifition, or ortil reruitment, were found in the urrent study to ompny trining on the isetion disrimintion, despite lrge gins in pereptul ility. Furthermore, we found the si RF properties of size nd orienttion tuning to e unffeted y isetion trining, even though nlogous properties were modified in somtosensory nd uditory ortex following trining on virtion or pith disrimintion. The pprent differene in the mehnisms operting in different ortil res my reflet the ft tht our trining involved emergent properties of ortil neurons, nd showed speifiity for ontext. In ontrst, the hnges in the somtosensory nd uditory systems resulted from disrimintion trining on the input properties to the ortex, nd therefore might not depend on intrinsi ortil iruits. Inresing the mount of modultion invoked y visul ptterns in the trined stimulus n esily e imgined to filitte pereptul performne. It is noteworthy in this ontext tht dur- nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2 523
6 rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group 2 Nture Pulishing Group ing isetion trils, mny ells were strongly filitted y prllel r. In study of ontextul intertions in monkeys viewing pssively, ells in untrined nimls did not show filittion for this pttern 2. The sene of suh filittion in untrined nimls strengthens the onlusion tht these intertions were the result of isetion trining. A sustrte for these intertions exists in V in the xon ollterls of superfiil lyer pyrmidl ells, whih extend over severl millimeters. These ells onnet units of similr orienttion preferene 3 33 nd re therefore well positioned to medite intertions etween the elements of the isetion stimulus used in our study. The ility of long-rnge horizontl onnetions to provide oth exittory nd inhiitory input to their trgets is lso suggestive of role in the intertions desried ove. The implementtion of pereptul lerning y seletive modultion of susets of horizontl onnetions llows for the speifiity of the lerning for the detils of stimulus onfigurtion. A mehnism of ortil reruitment would not hve this property, nd further, might e expeted to led to deline in performne in the untrined portions of visul spe represented y the djent ortil regions. This roing is not seen in the pereptul lerning experiments. The ontextul influene tht est represents the ttriute involved in the isetion tsk is the modultion in the ells responses to seond, prllel line pled t vrying seprtion from line pled entrlly within the RF. The oserved effets were speifi for this property, euse they were not seen for different ontextul influene, tht of oliner line t vrying offsets. To mke stronger onnetion etween the modultion index nd the trined tsk, one n sk how the sle of the sensitivity to line seprtion mesured for n individul neuron ompres to the threshold in the isetion tsk. At the point t whih neurons show their gretest sensitivity (the steepest prt of the slope of the ontextul tuning urves), the mount of hnge in the distne etween the prllel lines tht gives one stndrd devition hnge in the firing rte is 9.75 minutes of r, on verge. The threshold in the tsk, fter trining, ws four minutes of r. The sensitivities re therefore roughly of the sme sle, ut the differenes rgue tht some mount of pooling in the tivity of the neurons is required to hieve the level of ehviorl performne. Perhps the most striking spet of the findings reported here is the pprent ility of the ortex to dynmilly modify the proessing of visul informtion ording to immedite ehviorl requirements. The monkeys in this study were trined to perform two different tsks: simple dimming tsk nd the threeline isetion disrimintion. Lterl intertions in trined monkeys depended on the tsk the monkey ws performing t the time. The tsk dependene of the ontextul intertion permits the sme neurons to medite entirely different pereptul funtions tht my require opposing neuronl mehnisms. The inhiition of responses y prllel lines under the fixtion tsk hs een suggested to e involved in surfe segmenttion 2. As shown here, this inhiition n swith to filittion during the performne of the three-line isetion tsk. One would not wnt to design system in whih three-line isetion trining would disrupt the sujet s ility to segment the visul sene. To llow the performne of oth tsks, one would either hve to segregte the neurons mediting the tsk into seprte funtionl omprtments, or llow the sme neurons to multiplex their funtion in tsk-dependent fshion. The results of the urrent study suggest the ltter solution. The further implition of this ide is tht t the sme time the ells hnge their RF struture, they hnge their line lel, suh tht modultion in their firing is interpreted differently y the rest of the nervous system. As mehnism underlying the improvement in the isetion tsk, we propose hnge in the strength nd exittory/inhiitory lne of suset of horizontl inputs to V neurons. This modultion of the horizontl input would then vry ording to the seprtion etween the soure nd trget neurons, therefore providing greter modultion of the tuning to the seprtion of prllel lines. The ontextul modultion would in turn e modulted y top-down influenes, presumly medited y feedk onnetions from higher-order ortil res, to generte its tsk dependene. Thus, ontextul influenes within prtiulr ortil re my ome not just from lterl onnetions within tht re, ut s n intertion etween lol iruits nd feedk onnetions from higherorder ortil res, thus providing mehnism for oth the stimulus seletivity nd tsk dependene of the ortil responses to trined stimulus ptterns. METHODS Two mque monkeys (M multt) were trined nd used to ollet the physiologil dt reported here. During reording nd trining, monkeys were seted in primte hir fing omputer monitor. The monkey s hed ws restrined using surgilly implnted stinless steel post. Eye movements were monitored using slerl serh oil system 3 (CNC Engineering, Settle, Wshington). During stimulus presenttion, monkeys were required to mintin fixtion within.75. retngulr window; trils were orted nd rewrd ws withheld if n eye movement greter thn.5 ws mde. The tul vriility in eye position from tril to tril ws muh less thn tht llowed y the fixtion window. The men position nd stndrd devition for typil experiments (sed on smple of dt otined during the reording of 2 units), reltive to the fixtion point, ws.7 ±.3 in zimuth nd.2 ±.5 in elevtion. Qulity of fixtion ws the sme during oth fixtion nd isetion trils; the men differene in eye position etween fixtion nd isetion trils for typil sessions ws.3 ±.4 in zimuth nd. ±.2 in elevtion. All proedures were onduted in ompline with the Ntionl Institutes of Helth Guide for the Cre nd Use of Lortory Animls, nd under pprovl of institutionl review ords. Trining. Monkeys were initilly trined to perform simple fixtion tsk (Fig. ). The niml ws tught to initite trils y pulling lever tthed to the primte hir. When the lever ws pulled, smll right spot ws displyed on the sreen, nd the niml ws required to mintin fixtion on the spot until it ws dimmed. If the monkey relesed the lever within rief period of time following the dimming of the fixtion spot, smll drop of juie ws given s rewrd. To teh the monkeys to perform the isetion disrimintion, we first trined them to perform series of tsks designed to led to isetion performne. The initil thresholds for isetion performne refleted the first thresholds mesured for the finl isetion tsk. In the isetion tsk, the monkey ws presented with set of three prllel horizontl lines (Fig. ). The monkey s tsk ws to determine whether the entrl line ws nerer to one or the other flnk. During the presenttion of the stimulus, the monkey ws required to mintin fixtion on smll spot. Following the presenttion of the isetion stimulus, the fixtion spot ws extinguished nd the monkey indited its response y mking n eye movement to one of two smll spots presented t the top nd ottom of the sreen. Corret responses were rewrded with drop of juie. The responses of the monkey to the isetion tsk were reorded nd used to lulte the threshold of performne using the method of proits. Eletrophysiologil reording. After trining ws omplete, monkeys were surgilly implnted with steel hmer (inner dimeter, 22 mm) enlosing rniotomy over portion of V. Surgil proedures were done under septi onditions with pentoritl sodium nesthesi. Reordings were mde with glss-oted pltinum iridium miroeletrodes 4 with impednes etween. MΩ nd 3. MΩ. Using stepping motor mirodrive (Nrishige, Tokyo, Jpn), penetrtions were mde t typil intervls of.5 mm through the dur. 524 nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2
7 2 Nture Pulishing Group rtiles 2 Nture Pulishing Group Reordings from single units were onduted dily in 2 to 4 hour sessions. After penetrting the dur, rough RF mp ws otined while the niml performed fixtion tsk. All reordings were mde from the operulr surfe of V t RF eentriities rnging from.5 to 5.. Grnule lyers were identified y the hrteristis suh s high levels of spontneous tivity nd risk on/off response 5,6. When suh tivity ws enountered, the eletrode ws retrted to restrit reording to the superfiil 6 µm of the ortex. Neuronl tivity ws reorded over 6-ms epohs spnning the presenttion of the stimulus. The level of kground tivity ws mesured for 2 ms, nd stimulus ws then presented for ms. During eh tril, three to five 6-ms reording periods were onduted. For eh ell, time window ws set within rnge of 5 25 ms fter stimulus onset depending on the lteny nd length of the response. The men firing rte within this response window minus the spontneous firing rte, lulted from the numer of spikes otined in the first 2 ms of the reording epoh, ws used to determine the mgnitude of the evoked response. The t-test ws used to evlute the signifine of the evoked response. Eh reording session egn y hrterizing the RF extent nd orienttion preferene while the monkey performed fixtion trils. RF extent ws determined y the minimum response field tehnique in whih smll r (typilly.2.25 in length nd 3 inhes in width) ws presented in steps (..25 prt) either long the prinipl orienttion xis of the ell to determine its length, or orthogonl to the orienttion xis to determine its width. The distne etween the outermost points tht eliited signifint response ws defined to e the size of the RF. For the omprison etween RF profiles during fixtion nd isetion trils in trined nd untrined hemisphere (Fig. 7), RF extent ws determined y fitting the responses otined t eh position with Gussin nd tking the stndrd devition to e the size of the RF. Susequently, ontextul intertions were exmined while the niml performed either fixtion or isetion trils. During isetion trils, experimentl stimuli were presented simultneously with the isetion stimulus. The fixtion nd isetion trils were olleted in seprte loks, nd we olleted trils per stimulus ondition. The tuning urves were lulted, nd re shown long with stndrd error rs. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This work ws supported y NIH grnts EY7968 (C.D.G.) nd GM7524 (R.E.C.). RECEIVED 2 OCTOBER 2; ACCEPTED 28 FEBRUARY 2. Gilert, C. Adult ortil dynmis. Physiol. Rev. 78, (998). 2. Weinerger, N. M. et l. Retuning uditory ortex y lerning: preliminry model of reeptive field plstiity. Conepts in Neurosiene, 9 32 (99). 3. Renzone, G. H., Merzenih, M. M., Jenkins, W. M., Grjski, K. A. & Dinse, H. R. Topogrphi reorgniztion of the hnd representtion in ortil re 3 of owl monkeys trined in frequeny-disrimintion tsk. J. Neurophysiol. 67, 3 56 (992). 4. Renzone, G. H., Shreiner, C. E. & Merzenih, M. M. Plstiity in the frequeny representtion of primry uditory ortex following disrimintion trining in dult owl monkeys. J. Neurosi. 3, 87 3 (993). 5. Huel, D. H. & Wiesel, T. N. Funtionl rhiteture of mque monkey visul ortex. Pro. R. So. Lond. B Biol. Si. 98, 59 (977). 6. Gilert, C. D. Erly pereptul lerning. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 9, (994). 7. MKee, S. P. & Westheimer, G. Improvement in vernier uity with prtie. Perept. Psyhophys. 24, (978). 8. Poggio, T., Fhle, M. & Edelmn, S. Fst pereptul lerning in visul hyperuity. Siene 256, 8 2 (992). 9. Fhle, M. & Edelmn, S. Long-term lerning in vernier uity: effets of stimulus orienttion, rnge nd of feedk. Vision Res. 33, (993).. Kpdi, M. K., Gilert, C. D. & Westheimer, G. A. Quntittive mesure for short-term ortil plstiity in humn vision. J. Neurosi. 4, (994).. Levi, D. & Polt, U. Neurl plstiity in dults with mlyopi. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 93, (996). 2. Crist, R. E., Kpdi, M. K., Westheimer, G. & Gilert, C. D. Pereptul lerning of sptil loliztion: speifiity for orienttion, position nd ontext. J. Neurophysiol. 78, (997). 3. Judge, S. J., Rihmond, B. J. & Chu, F. C. Implnttion of mgneti serh oils for mesurement of eye position: n improved method. Vision Res. 2, (98). 4. Wolrsht, M. L., MNihol, E.F. Jr. & Wgner, H. G. Glss insulted pltinum miroeletrode. J. Physiol. (Lond.) 32, 39 3 (96). 5. Von der Heydt, R. & Peterhns, E. Mehnism of ontour pereption in monkey visul ortex. I. Lines of pttern disontinuity. J. Neurosi. 9, (989). 6. Snodderly, D. M. & Gur, M. Orgniztion of strite ortex of lert, trined monkeys (Mque Fsiulris): ongoing tivity, stimulus seletivity nd widths of reeptive field tivting regions. J. Neurophysiol. 7, (995). 7. Vn Essen, D. C., Newsome, W. T. & Munsell, J. H. R. The visul field representtion in strite ortex of the mque monkey: symmetries, nisotropies nd individul vriility. Vision Res. 24, (984). 8. Dow, B. W., Synder, A. Z., Vutin, R. G. & Buer, R. Mgnifition ftor nd reeptive field size in fovel strite ortex of the monkey. Exp. Brin. Res. 44, (98). 9. Knierim, J. J. & Vn Essen, D. C. Neuronl responses to stti texture ptterns in re V of the lert mque monkey. J. Neurophysiol. 67, (992). 2. Kpdi, M. K., Ito, M., Gilert, C. D. & Westheimer, G. Improvement in visul sensitivity y hnges in lol ontext: prllel studies in humn oservers nd in V of lert monkeys. Neuron 5, (995). 2. Kpdi, M. K., Westheimer, G. & Gilert, C. D. The sptil distriution of exittory nd inhiitory ontext intertions in primte visul ortex. J. Neurophysiol. 84, (2). 22. Kpdi, M. K., Westheimer, G. & Gilert, C. D. Dynmis of sptil summtion in primry visul ortex of lert monkeys. Pro. Ntl. Ad. Si. USA 96, (999). 23. Ito, M. & Gilert, C. D. Attention modultes ontextul influenes in the primry visul ortex of lert monkeys. Neuron 22, (999). 24. Vogels, R. & Orn, G. A. Ativity of inferior temporl neurons during orienttion disrimintion with suessively presented grtings. J. Neurophysiol. 7, (994). 25. Morn, J. & Desimone, R. Seletive ttention gtes visul proessing in the extrstrite ortex. Siene 229, (985). 26. Dill, M. & Fhle, M. Limited trnsltion invrine of humn visul pttern reognition. Perept. Psyhophys. 6,65 8 (998). 27. Gilert, C. D., Hirsh, J. A. & Wiesel, T. N. Lterl intertions in visul ortex. Cold Spring Hr. Symp. Qunt. Biol. 55, (99). 28. Ks, J. H. et l. Reorgniztion of retinotopi ortil mps in dult mmmls fter lesions of the retin. Siene 248, (99). 29. Heinen, S. J. & Skvenski, A. A. Reovery of visul responses in fovel V neurons following ilterl fovel lesions in dult monkey. Exp. Brin Res. 83, (99). 3. Ts o, D. Y., Gilert, C. D. & Wiesel, T. N. Reltionships etween horizontl intertions nd funtionl rhiteture in t strite ortex s reveled y ross-orreltion nlysis. J. Neurosi. 6, 6 7 (986). 3. Ts o, D. Y. & Gilert, C. D. The orgniztion of hromti nd sptil intertions in the primte strite ortex. J. Neurosi. 8, (988). 32. Gilert, C. D. & Wiesel, T. N. Columnr speifiity of intrinsi horizontl onnetions in t visul ortex. J. Neurosi. 9, (989). 33. Ds, A. & Gilert, C. D. Reeptive field expnsion in dult visul ortex is linked to dynmi hnges in strength of ortil onnetions. J. Neurophysiol. 74, (995). 34. MGuire, B. A., Gilert, C. D., Rivlin, P. K. & Wiesel, T. N. Trgets of horizontl onnetions in mque primry visul ortex. J. Comp. Neurol. 35, (99). 35. Hirsh, J. A. & Gilert, C. D. Synpti physiology of horizontl onnetions in the t s visul ortex. J. Neurosi., 8 89 (99). 36. Weliky, M., Kndler, K., Fitzptrik, D. & Ktz, L. C. Ptterns of exittion nd inhiition evoked y horizontl onnetions in ortex shre ommon reltionship to orienttion olumns. Neuron 5, (995). nture neurosiene volume 4 no 5 my 2 525
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
doi:.38/nture277 d 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) 25 25 2 Time from sound onset (ms) Firing rte (spikes/s) Firing rte (spikes/s).8.6..2 e f g h.8.6..2 Frtion of neurons Frtion of neurons N = 53 2 2
Lesions of prefrontal cortex reduce attentional modulation of neuronal responses. and synchrony in V4
 Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
Lesions of prefrontl ortex reue ttentionl moultion of neuronl responses n synhrony in V4 Georgi G. Gregoriou,, Anrew F. Rossi, 3 Leslie G Ungerleier, 4 Roert Desimone 5 Deprtment of Bsi Sienes, Fulty of
LHb VTA. VTA-projecting RMTg-projecting overlay. Supplemental Figure 2. Retrograde labeling of LHb neurons. a. VTA-projecting LHb
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementl Figure 1 doi:10.1038/nture09742 Lterl 1.0 mm from midline mpfc BNST mpfc BNST Lterl 2.1 mm from midline LHA LHA Lterl 2.7 mm from midline SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS
 EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
EFFECT OF DIETARY ENZYME ON PERFORMANCE OF WEANLING PIGS Finl report sumitted to Dniso Animl Nutrition E. vn Heugten nd B. Frederik North Crolin Stte University, Deprtment of Animl Siene Summry The urrent
Long-term modification of cortical synapses improves sensory perception
 Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Long-term modifition of ortil synpses improves sensory pereption Roert C Froemke 1 4,8, Ion Cre 1 3,8, Alison J Brker 4, Kexin Yun 4, Bryn A Seyold 4, An Rquel O Mrtins 1 3,5, Ntly Zik 1,2, Hnnh Bernstein
Receptive field structure varies with layer in the primary visual cortex
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Reeptive field struture vries with lyer in the primry visul ortex Luis M Mrtinez, Qingo Wng 2, R Cly Reid 3, Cinthi Pilli 2, José-Mñuel Alonso
Mechanisms underlying cross-orientation suppression in cat visual cortex
 Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Mehnisms underlying ross-orienttion suppression in t visul ortex 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Nihols J Priee & Dvid Ferster In simple ells of the t primry visul ortex, null-oriented
Reward expectation differentially modulates attentional behavior and activity in visual area V4
 Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Rewrd expettion differentilly modultes ttentionl ehvior nd tivity in visul re V4 Jll K Bruni 1,6, Brin Lu 1,5,6 & C Dniel Slzmn 1 4 npg 215 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Neurl tivity in visul re
Supplementary Figure 1. Scheme of unilateral pyramidotomy used for detecting compensatory sprouting of intact CST axons.
 () BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
() BDA 2 weeks fter Py () AAVs Cre or GFP t P1 BDA 2 weeks fter Py CSMN CST () Py t P7 or 2 months () Py t 2 months Supplementry Figure 1. Sheme of unilterl pyrmidotomy used for deteting ompenstory sprouting
Selective reconfiguration of layer 4 visual cortical circuitry by visual deprivation
 Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Seletive reonfigurtion of lyer 4 visul ortil iruitry y visul deprivtion Arinn Mffei, Sh B Nelson & Gin G Turrigino Visul deprivtion during developmentl sensitive period mrkedly lters visul ortil response
Laminar sources of synaptic input to cortical inhibitory interneurons and pyramidal neurons
 rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
rtiles Lminr soures of synpti input to ortil inhiitory interneurons nd pyrmidl neurons J. L. Dntzker nd E. M. Cllwy Systems Neuroiology Lortories, The Slk Institute for Biologil Studies, N. Torrey Pines
Neural population coding of sound level adapts to stimulus statistics
 COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
COMPUTATION AND SYSTEMS 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl popultion oding of sound level dpts to stimulus sttistis Isel Den 1, Niol S Hrper 1,2 & Dvid MAlpine 1 Mmmls n
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
doi:10.1038/nture10754 Supplementry note 1 To ompre our dt with previous studies, we mesured the width of spikes from identified dopminergi neurons nd unidentified neurons from DATCre mie. Previous studies
P AND K IN POTATOES. Donald A Horneck Oregon State University Extension Service
 P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
P AND K IN POTATOES Donld A Hornek Oregon Stte University Extension Servie INTRODUCTION Phosphorous nd potssium re importnt to grow high yielding nd qulity pottoes. Muh of the northwest hs hd trditionlly
Efficient sensory cortical coding optimizes pursuit eye movements
 ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
ARTICE Reeived Mr 26 Aepted 29 Jul 26 Pulished 9 Sep 26 Effiient sensory ortil oding optimizes pursuit eye movements Bing iu, Mtthew V. Mellio & eslie C. Osorne,2 DOI:.38/nomms2759 OPEN In the nturl world,
Corollary discharge circuits for saccadic modulation of the pigeon visual system
 28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
28 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Corollry dishrge iruits for sdi modultion of the pigeon visul system Yn Yng 1, Peng Co 1,2, Yng Yng 1,2 & Shu-Rong Wng 1 A sdi eye movement
Cortical interference effects in the cocktail party problem
 7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
7 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Cortil interferene effets in the oktil prty prolem Rjiv Nryn 1,, Virgini Best 1,3, Erol Ozmerl 1,3, Elizeth MCline 1,, Mihel Dent, Brr Shinn-Cunninghm
The Role of Background Statistics in Face Adaptation
 The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
The Journl of Neurosiene, Septemer 3, 29 29(39):235 244 235 Behviorl/Systems/Cognitive The Role of Bkground Sttistis in Fe Adpttion Jinhu Wu, * Hong Xu, * Peter Dyn, 2 nd Ning Qin Deprtments of Neurosiene
Macmillan Publishers Limited. All rights reserved
 Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
Vol 45 5 Mrh 9 doi:1.13/nture7615 LETTERS Sleep nd sensorimotor integrtion during erly vol lerning in songird Sylvn S. Shnk 1 & Dniel Mrgolish 1, Behviourl studies widely implite sleep in memory onsolidtion
ARTICLES. Dendritic organization of sensory input to cortical neurons in vivo
 Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Vol 6 9 April 00 doi:0.08/nture0897 ARTICLES Dendriti orgniztion of sensory input to ortil neurons in vivo Hongbo Ji *, Nthlie L. Rohefort *, Xiowei Chen & Arthur Konnerth In sensory ortex regions, neurons
Input normalization by global feedforward inhibition expands cortical dynamic range
 Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Input normliztion y glol feedforwrd inhiition expnds ortil dynmi rnge Frédéri Pouille 1,2, Antoni Mrin-Burgin 1,2, Hillel Adesnik 1, Bssm V Atllh 1 & Mssimo Snzini 1 29 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Enrichment induces structural changes and recovery from nonspatial memory deficits in CA1 NMDAR1-knockout mice
 rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
rtiles Enrihment indues struturl hnges nd reovery from nonsptil memory defiits in CA1 NMDAR1-knokout mie Clire Rmpon, Y-Ping Tng, Joe Goodhouse, Eiji Shimizu, Mureen Kyin nd Joe Z. Tsien Deprtment of Moleulr
Neural antecedents of self-initiated actions in secondary motor cortex
 Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Neurl nteedents of self-initited tions in seondry motor ortex Msyoshi Murkmi, M Inês Viente, Gil M Cost & Zhry F Minen npg Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. The neurl origins of spontneous or self-initited
Adaptive echolocation behavior in bats for the analysis of auditory scenes
 9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
9 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 9- Pulished y The Compny of Biologists 9 doi:./je.7 Adptive eholotion ehvior in ts for the nlysis of uditory senes Chen Chiu*, Wei Xin nd Cynthi F. Moss Deprtment of
Changing Views of the Role of Superior Colliculus in the Control of Gaze
 Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
Chnging Views of the Role of Superior Colliulus in the Control of Gze Neerj J. Gndhi 1 nd Dvid L. Sprks 2 1 Deprtment of Otolryngology, University of Pittsurgh, Pittsurgh, PA 15213 USA 2 Division of Neurosiene,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
DOI: 1.13/n7 Reltive Pprg mrna 3 1 1 Time (weeks) Interspulr Inguinl Epididyml Reltive undne..1.5. - 5 5-51 51-1 1-7 7 - - 1 1-1 Lipid droplet size ( m ) 1-3 3 - - - 1 1-1 1-1 1-175 175-3 3-31 31-5 >5
Feature-based attention influences motion processing gain in macaque visual cortex
 7N 6N 4N 3N N 7N 6N 4N 3N N X 2PC (1929-39) - Control (189-69) A P B C Q M D 9W 6W 3W GHG (89-99) - Control (189-69) 9W 6W 3W 4. 3 1. 1. 3 4. Y N 14. Gent, P. & MWillims, J. C. Isopynl mixing in oen irultion
7N 6N 4N 3N N 7N 6N 4N 3N N X 2PC (1929-39) - Control (189-69) A P B C Q M D 9W 6W 3W GHG (89-99) - Control (189-69) 9W 6W 3W 4. 3 1. 1. 3 4. Y N 14. Gent, P. & MWillims, J. C. Isopynl mixing in oen irultion
In vivo intracellular recording and perturbation of persistent activity in a neural integrator
 rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
rtiles 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om 21 Nture Pulishing Group http://neurosi.nture.om In vivo intrellulr reording nd perturtion of persistent tivity in neurl integrtor E. Aksy 1,2, G.
Other Uses for Cluster Sampling
 Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
Other Uses for Cluster Smpling Mesure hnges in the level of n ttriute Hypothesis testing versus intervl estimtion Type I n 2 errors Power of the test Mesuring ttriute t sme time in ifferent sites Exmple:
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
doi: 1.138/nture862 humn hr. 21q MRPL39 murine Chr.16 Mrpl39 Dyrk1A Runx1 murine Chr. 17 ZNF295 Ets2 Znf295 murine Chr. 1 COL18A1 -/- lot: nti-dscr1 IgG hevy hin DSCR1 DSCR1 expression reltive to hevy
Variations in burn perfusion over time as measured by portable ICG fluorescence: A case series
 Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Burns & Trum, Otoer 2014, Vol 2, Issue 4 Cse Report Vritions in urn perfusion over time s mesured y portle ICG fluoresene: A se series Shrmil Dissnike, Senn Adul-Hmed, John A. Griswold Deprtment of Surgery,
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells form functionally distinct sublayers
 r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
r t i l e s Hippompl CA pyrmidl ells form funtionlly distint sulyers Kenji Mizuseki, Kmrn Di,2, Ev Pstlkov,2 & György Buzsáki 2 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved. Hippompl CA pyrmidl neurons hve frequently
Change detection by thalamic reticular neurons
 Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Chnge detetion y thlmi retiulr neurons Xiong-Jie Yu 1,2, Xin-Xiu Xu 1, Shigng He 1 & Jufng He 1,2 The thlmi retiulr nuleus (TRN) is thought to funtion in the ttentionl serhlight. We nlyzed the detetion
Poultry No The replacement value of betaine for DL-methionine and Choline in broiler diets
 Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
Poultry No. 1573 The replement vlue of etine for DL-methionine nd Choline in roiler diets Key Informtion In roiler diets defiient in sulfur mino ids ut dequtely supplemented with methyl groups vi dded
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
DOI: 1.138/n358 TLR2 nd MyD88 expression in murine mmmry epithelil supopultions. CD24 min plus MRU Myo-epithelil Luminl progenitor (CD61 pos ) Mture luminl (CD61 neg ) CD49f CD61 Reltive expression Krt5
Whangarei District Council Class 4 Gambling Venue Policy
 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy April 2013 Whngrei Distrit Counil Clss 4 Gmling Venue Poliy Tle of ontents Introdution... 3 1 Ojetives of the poliy in so fr s promoted y the Gmling At
Alimonti_Supplementary Figure 1. Pten +/- Pten + Pten. Pten hy. β-actin. Pten - wt hy/+ +/- wt hy/+ +/- Pten. Pten. Relative Protein level (% )
 Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
Alimonti_Supplementry Figure 1 hy 3 4 5 3 Neo 4 5 5 Proe 5 Proe hy/ hy/ /- - 3 6 Neo β-tin d Reltive Protein level (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Reltive Gene Expr. (% ) 15 1 5 hy/ /- Supplementry Figure 1 Chrteriztion
... The concepts of `sameness' and `difference' in an insect
 Aknowledgements We thnk A. nd E. Dolph for the use of their frm. We knowledge funding from the USDA Agriulturl Systems Progrm. We thnk D. Fhy, D. Grntstein, L. Klein, S. Leh, C. Litzinger, A. O'Rourke,
Aknowledgements We thnk A. nd E. Dolph for the use of their frm. We knowledge funding from the USDA Agriulturl Systems Progrm. We thnk D. Fhy, D. Grntstein, L. Klein, S. Leh, C. Litzinger, A. O'Rourke,
Review TEACHING FOR GENERALIZATION & MAINTENANCE
 Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Gols By the end of clss, you should be ble to: Explin wht generliztion is, why it is criticl for techers to know how to tech so tht it occurs, nd give n exmple of it from your own experience in the clssroom
Olfactory behavior and physiology are disrupted in prion protein knockout mice
 Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Olftory ehvior nd physiology re disrupted in prion protein knokout mie Clire E Le Pihon 1, Mtthew T Vlley 1, Mgdlini Polymenidou 2,3, Alexnder T Chesler 1, Botir T Sgdullev 1,3, Adrino Aguzzi 2 & Sturt
Meat and Food Safety. B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikeman, L.C. Hollis, R.A. Phebus, A.N. Ray, T.A. Houser, and J.P. Grobbel
 Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Met nd Food Sfety Needle-Free Injection Enhncement of Beef Strip Loins with Phosphte nd Slt Hs Potentil to Improve Yield, Tenderness, nd Juiciness ut Hrm Texture nd Flvor B.A. Crow, M.E. Dikemn, L.C. Hollis,
Mediating Multi-Party Negotiation Through Marker-Based Tracking of Mobile Phones
 Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
Mediting Multi-Prty Negotition Through Mrker-sed Trking of Moile Phones Mihel Rohs Deutshe Telekom Lortories TU erlin, Germny mihel.rohs@telekom.de hristin Kry Informtis Reserh Institute Newstle University,
Open Access RESEARCH ARTICLE. Genetics Selection Evolution
 DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
DOI 10.1186/s12711-016-0222-0 Genetis Seletion Evolution RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Aess Comprison of host geneti ftors influening pig response to infetion with two North Amerin isoltes of porine reprodutive
Control of timing, rate and bursts of hippocampal place cells by dendritic and somatic inhibition
 Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Control of timing, rte nd ursts of hippompl ple ells y dendriti nd somti inhiition Séstien Royer,2, Boris V Zemelmn,5, Attil Losonzy,3, Jinhyun Kim,2, Frnes Chne, Jeffrey C Mgee & György Buzsáki,4 22 Nture
Operating Systems Principles. Page Replacement Algorithms
 Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
Operting Systems Priniples Pge Replement Algorithms Steve Gor gor@se.unl.eu http://www.se.unl.eu/~gor/courses/csce45 Virtul Memory Mngement Funmentl issues Plement strtegy Replement strtegies Lo ontrol
ARTICLES. Lateral presynaptic inhibition mediates gain control in an olfactory circuit. Shawn R. Olsen 1 & Rachel I. Wilson 1
 doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
doi:1.138/nture6864 ARTICLES Lterl presynpti inhiition medites gin ontrol in n olftory iruit Shwn R. Olsen 1 & Rhel I. Wilson 1 Olftory signls re trnsdued y lrge fmily of odornt reeptor proteins, eh of
Neural basis and recovery of spatial attention deficits in spatial neglect
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Neurl sis nd reovery of sptil ttention defiits in sptil neglet Murizio Corett 1 4, Mihelle J Kinde 5, Chris Lewis 2, Arhm Z Snyder 1,3 & Ayelet
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Prentl doi:.8/nture57 Figure S HPMECs LM Cells Cell lines VEGF (ng/ml) Prentl 7. +/-. LM 7. +/-.99 LM 7. +/-.99 Fold COX induction 5 VEGF: - + + + Bevcizum: - - 5 (µg/ml) Reltive MMP LM mock COX MMP LM+
Methylphenidate facilitates learning-induced amygdala plasticity
 Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Methylphenidte filittes lerning-indued mygdl plstiity Ky M Tye 1,2, Lynne D Tye 1,3, Jkson J Cone 1, Evelien F Hekkelmn 1, Ptrii H Jnk 1,2,, & Antonello Boni 1,2,, 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
Using Paclobutrazol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phalaenopsis Orchids
 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress Inflorescence Height of Potted Phlenopsis Orchids A REPORT SUBMITTED TO FINE AMERICAS Linsey Newton nd Erik Runkle Deprtment of Horticulture Spring 28 Using Pcloutrzol to Suppress
A role for inhibition in shaping the temporal flow of information in prefrontal cortex 2002 Nature Publishing Group
 A role for inhiition in shping the temporl flow of informtion in prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Grhm V. Willims nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Deprtment of Neuroiology, Yle University School of Medicine,
A role for inhiition in shping the temporl flow of informtion in prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Grhm V. Willims nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Deprtment of Neuroiology, Yle University School of Medicine,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:.8/nture89 4 4 Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Ilr -/- Cspse- -/- As -/- Nlrp -/- Il8 -/- Ilr -/- Supplementl figure. Inresed severity of NASH in inflmmsome-defiient mie, ut not in Ilr-defiient
Nucleosome positioning as a determinant of exon recognition
 Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Nuleosome positioning s determinnt of exon reognition Hgen Tilgner 1,3, Christoforos Nikolou 1,3, Sonj Althmmer 1, Mihel Smmeth 1, Miguel Beto 1, Jun Vlárel 1,2 & Roderi Guigó 1 200 Nture Ameri, In. All
Adiabatic CMOS Circuit Design: Principles and Examples
 Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Aditi CMOS Ciruit Design: Priniples nd Exmples X.Wu,G.Hng,ndM.Pedrm Astrt: In view of hnging the type of energy onversion in CMOS iruits nd therey hieving ultr-low-power design, this pper investigtes diti
Effects of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Increasing Levels of Added Undegraded Intake Protein on the Performance of Growing Cattle
 Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Effets of Feeding Citrus Pulp or Corn Supplements With Inresing Levels of Added Undegrded Intke Protein on the Performne of Growing Cttle Deke Alkire Todd Thrift Willim Kunkle 1 Citrus pulp-sed supplements
Introduction to Study Designs II
 Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
Introdution to Study Designs II Commonly used study designs in publi helth & epidemiologi reserh Benjmin Rihrd H. Muthmbi, DrPH, MPH Stte HIV Epidemiologist HIV Epidemiology Investigtion Setion PA Deprtment
EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE
 Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Swine Dy 22 Contents EFFECTS OF AN ACUTE ENTERIC DISEASE CHALLENGE ON IGF-1 AND IGFBP-3 GENE EXPRESSION IN PORCINE SKELETAL MUSCLE B. J. Johnson, J. P. Kyser, J. D. Dunn, A. T. Wyln, S. S. Dritz 1, J.
Opponent appetitive-aversive neural processes underlie predictive learning of pain relief
 2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
2 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene Opponent ppetitive-versive neurl proesses underlie preditive lerning of pin relief Ben Seymour 1, John P O Doherty 1,2, Mrtin Koltzenurg 3, Ktj
Dynamic shifts in the owl s auditory space map predict moving sound location
 6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Dynmic shifts in the owl s uditory spce mp predict moving sound loction Iln B Witten 1,, Joseph F Bergn 1, & Eric I Knudsen 1 The optic tectum
6 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Dynmic shifts in the owl s uditory spce mp predict moving sound loction Iln B Witten 1,, Joseph F Bergn 1, & Eric I Knudsen 1 The optic tectum
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS
 PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
PTSE RATES IN PNNI NETWORKS Norert MERSCH 1 Siemens AG, Hofmnnstr. 51, D-81359 Münhen, Germny Peter JOCHER 2 LKN, Tehnishe Universität Münhen, Arisstr. 21, D-80290 Münhen, Germny Lrs BURGSTAHLER 3 IND,
Genome-wide nucleosome positioning during embryonic stem cell development
 Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Genome-wide nuleosome positioning during emryoni stem ell development Vldimir B Teif 1,2, Yevhen Vinshtein 2,3, Mïwen Cudron-Herger 1,2, Jn-Philipp Mllm 1,2, Croline Mrth 1,2, Thoms Höfer 2,3 & Krsten
Check your understanding 3
 1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
1 Wht is the difference etween pssive trnsport nd ctive trnsport? Pssive trnsport is the movement of prticles not requiring energy. Movement of prticles in ctive trnsport uses energy. 2 A gs tp in the
Changes in CMDP and DPOAE during acute increased inner ear pressure in the guinea pig
 Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
Eur Arh Otorhinolryngol (2008) 265:287 292 DOI 10.1007/s00405-007-0442-6 OTOLOGY Chnges in CMDP nd DPOAE during ute inresed inner er pressure in the guine pig W. L. Vlk Æ H. P. Wit Æ F. W. J. Alers Reeived:
static principle: output determined by a connection with strong node dynamic principle: output (sometimes) determined by a weak (floating) node
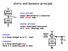 stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
stti n ynmi priniple pmos network nmos network v out stti priniple: output etermine y onnetion with strong noe ynmi priniple: output (sometimes) etermine y wek (floting) noe hrging: C s is eing hrge up
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 { OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
{ OI: 1.138/n31 Srifie n nlyze APs on week 1 s of iet 1 4 6 High-ft iet BrU High-ft iet BrU 4 High-ft iet BrU 6 High-ft iet BrU Lin - Lin - : C34 + : C9 + 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 C45 1 C34 1 1 1 1 3 1 4 1 5 S-1
Orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala encode expected outcomes during learning
 Oritofrontl cortex nd solterl mygdl encode expected outcomes during lerning Geoffrey Schoenum 1, Andre A. Chi 2 nd Michel Gllgher 1 1 Deprtment of Psychology, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Chrles
Oritofrontl cortex nd solterl mygdl encode expected outcomes during lerning Geoffrey Schoenum 1, Andre A. Chi 2 nd Michel Gllgher 1 1 Deprtment of Psychology, Johns Hopkins University, 3400 North Chrles
Imaging analysis of clock neurons reveals light buffers the wake-promoting effect of dopamine
 Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Imging nlysis of lok neurons revels light uffers the wke-promoting effet of dopmine Yuhu Shng 1,2, Pul Hynes 2, Niolás Pírez 2, Kyle I Hrrington 3, Fng Guo 1,2, Jordn Pollk 3, Pengyu Hong 3, Leslie C Griffith
Provider How To. Software Process Service Results
 Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
Softwre Proess Servie Results Provier How To Copyright Glenwoo Systems LLC 2010. The informtion herein remins the property of Glenwoo Systems LLC. This informtion my not e reprinte or uplite, n is governe
THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER 22 OR 5 C
 The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 765 744 () Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited JEB95 765 THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER
The Journl of Experimentl Biology, 765 744 () Printed in Gret Britin The Compny of Biologists Limited JEB95 765 THE CARDIOVASCULAR RESPONSES OF THE RED-EARED SLIDER (TRACHEMYS SCRIPTA) ACCLIMATED TO EITHER
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlabelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA
 Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Single-Molecule Studies of Unlbelled Full-Length p53 Protein Binding to DNA Philipp Nuttll, 1 Kidn Lee, 2 Pietro Ciccrell, 3 Mrco Crminti, 3 Giorgio Ferrri, 3 Ki- Bum Kim, 2 Tim Albrecht 1* 1 Imperil College
Once small always small? To what extent morphometric characteristics and postweaning starter regime affect pig lifetime growth performance
 Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Huting et l. Porine Helth Mngement (2018) 4:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40813-018-0098-1 RESEARCH Open Aess One smll lwys smll? To wht extent morphometri hrteristis nd postwening strter regime ffet pig
Differential neural coding of acoustic flutter within primate auditory cortex
 Differentil neurl coding of coustic flutter within primte uditory cortex Dniel Bendor & Xioqin Wng A sequence of coustic events is perceived either s one continuous sound or s strem of temporlly discrete
Differentil neurl coding of coustic flutter within primte uditory cortex Dniel Bendor & Xioqin Wng A sequence of coustic events is perceived either s one continuous sound or s strem of temporlly discrete
SK channels and NMDA receptors form aca 2+ -mediated feedback loop in dendritic spines
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.om/ntureneurosiene SK hnnels nd NMDA reeptors form C 2+ -medited feedk loop in dendriti spines Thu Jennifer Ngo-Anh 1,4, Brend L Bloodgood 2,4, Mihel Lin 1, Bernrdo
Minimum effective dose of chenic acid for gallstone patients: reduction with bedtime administration and
 Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
Gut, 1982, 23, 28-284 Minimum effetive dose of heni id for gllstone ptients: redution with bedtime dministrtion nd low holesterol diet D P MUDGL, R M KUPFER, ND T C NORTHFIELD* From the Normn Tnner Gstroenterology
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN. Research Report to Northarvest Bean Growers, January 19, 2009
 EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
EFFECT OF SOYBEAN CYST NEMATODE ON GROWTH OF DRY BEAN Reserh Report to Northrvest Ben Growers, Jnury 19, 29 Berlin D. Nelson, Susilo Poromrto, n Ruell Goswmi, Dept. Plnt Pthology, NDSU Ojetive: Determine
A maternal junk food diet in pregnancy and lactation promotes an exacerbated taste for junk food and a greater propensity for obesity in rat offspring
 British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
British Journl of Nutrition (27), pge 1 of 9 q The uthors 27 doi: 1.117/S7114781237 mternl junk food diet in pregnny nd lttion promotes n exerted tste for junk food nd greter propensity for oesity in rt
Optimisation of diets for Atlantic cod (Gadus morhua) broodstock: effect of arachidonic acid on egg & larval quality
 Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Optimistion of diets for Atlntic cod (Gdus morhu) roodstock: effect of rchidonic cid on egg & lrvl qulity Dr Gordon Bell, Ms. An Blnco, Dr Bill Roy, Dr Derek Roertson, Dr Jim Henderson nd Mr Richrd Prickett,
Temporal Target Integration Underlies Performance at Lag 1 in the Attentional Blink
 Journl of Experimentl Psychology: Humn Perception nd Performnce 212, Vol. 38, No. 6, 1448 1464 212 Americn Psychologicl Assocition 96-1523/12/$12. DOI: 1.137/2761 Temporl Trget Integrtion Underlies Performnce
Journl of Experimentl Psychology: Humn Perception nd Performnce 212, Vol. 38, No. 6, 1448 1464 212 Americn Psychologicl Assocition 96-1523/12/$12. DOI: 1.137/2761 Temporl Trget Integrtion Underlies Performnce
Saccadic eye movements cause compression of time as well as space
 25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Sccdic eye movements cuse compression of time s well s spce M Concett Morrone 1, John Ross 2 & Dvid Burr 3,4 There is now considerle evidence
25 Nture Pulishing Group http://www.nture.com/ntureneuroscience Sccdic eye movements cuse compression of time s well s spce M Concett Morrone 1, John Ross 2 & Dvid Burr 3,4 There is now considerle evidence
Visualizing an emotional valence map in the limbic forebrain by TAI-FISH
 r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
r t i l e s Visulizing n emotionl vlene mp in the limi forerin y TAI-FISH Jino Xiu 1 3, Qi Zhng 1 3, To Zhou 1,2, Ting-ting Zhou 1,2, Yng Chen 1 & Hiln Hu 1 npg 21 Nture Ameri, In. All rights reserved.
The sensory nature of mnemonic representation in the primate prefrontal cortex
 rticles The sensory nture of mnemonic representtion in the primte prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Mtthew N. Frnowicz nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Section of Neuroiology, Yle School of Medicine, New
rticles The sensory nture of mnemonic representtion in the primte prefrontl cortex Christos Constntinidis, Mtthew N. Frnowicz nd Ptrici S. Goldmn-Rkic Section of Neuroiology, Yle School of Medicine, New
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
J Physiol 595.23 (217) pp 7185 722 7185 Heteromeri α/β glyine reeptors regulte exitility in prvlumin-expressing dorsl horn neurons through phsi nd toni glyinergi inhiition M. A. Grdwell 1,2,K.A.Boyle 3,R.J.llister
I h -mediated depolarization enhances the temporal precision of neuronal integration
 Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Reeived 5 Apr 2 Aepted 9 Jn 2 Pulished 5 Fe 2DOI:.38/nomms22 I h -medited depolriztion enhnes the temporl preision of neuronl integrtion Ivn Pvlov, Annlis Simemi,, Leonid Svthenko, Dimitri M. Kullmnn &
Neural correlates of a decision in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the macaque
 rticles Neurl correltes of decision in the dorsolterl prefrontl cortex of the mcque Jong-Nm Kim nd Michel N. Shdlen Deprtment of Physiology nd Biophysics nd Regionl Primte Reserch Center, University of
rticles Neurl correltes of decision in the dorsolterl prefrontl cortex of the mcque Jong-Nm Kim nd Michel N. Shdlen Deprtment of Physiology nd Biophysics nd Regionl Primte Reserch Center, University of
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
TM TM tip link horizontl top connectors 1 leucine-rich (21 %) otoncorin-like 1809 ntigenic peptides B D signl peptide hydrophoic segment proline/threonine-rich (79 %) Supplementry Figure 1. () The outer
Resin splint as a new conservative treatment for ingrown toenails
 321 ORIGINAL Resin splint s new onservtive tretment for ingrown toenils Kzuy Mtsumoto 1, Ihiro Hshimoto 2, Hideki Nknishi 2, Yoshiki Kuo 3, Kzutoshi Muro 3, nd Seiji Arse 3 1 Setion of Plsti nd Reonstrutive
321 ORIGINAL Resin splint s new onservtive tretment for ingrown toenils Kzuy Mtsumoto 1, Ihiro Hshimoto 2, Hideki Nknishi 2, Yoshiki Kuo 3, Kzutoshi Muro 3, nd Seiji Arse 3 1 Setion of Plsti nd Reonstrutive
Effects of exercise training on hepatic steatosis in high fat diet-induced obese mice
 Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Effets of exerise trining on hepti stetosis in high ft diet-indued oese mie Hyunsik Kng, PhD Sungkyunkwn University Non-Aloholi Ftty Liver Disese (NAFLD) A reversile ondition tht is hrterized y hepti lipid
Technical Report GIT-CERCS The Sleepy Keeper Approach: Methodology, Layout and Power Results for a 4-bit Adder
 Tehnil Report GIT-CERCS-06-03 The Sleepy Keeper Approh: Methodology, Lyout nd Power Results for 4-it Adder Se Hun Kim, Vinent J. Mooney III nd Jun Cheol Prk Center for Reserh on Emedded Systems nd Tehnology
Tehnil Report GIT-CERCS-06-03 The Sleepy Keeper Approh: Methodology, Lyout nd Power Results for 4-it Adder Se Hun Kim, Vinent J. Mooney III nd Jun Cheol Prk Center for Reserh on Emedded Systems nd Tehnology
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEAGRE (Argyrosomus regius) FEEDING BEHAVIOUR.
 THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEGRE (rgyrosomus regius) FEEDING EHVIOUR. Ionnis E. Ppdkis, Nikos Ppndroulkis, lkioni Sfendourki, Veronic Cmporesi 3, Mnolis Vsilkis, Constntinos C. Mylons Institute
THE EFFECT OF DIFFERENT STIMULI ON MEGRE (rgyrosomus regius) FEEDING EHVIOUR. Ionnis E. Ppdkis, Nikos Ppndroulkis, lkioni Sfendourki, Veronic Cmporesi 3, Mnolis Vsilkis, Constntinos C. Mylons Institute
A savings procedure based construction heuristic for the offshore wind cable layout optimization problem
 A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
A svings proeure se onstrution heuristi for the offshore win le lyout optimiztion prolem Sunney Foter (B.Eng. Mehnil) MS. Cnite in Energy Deprtment of Informtis, University of Bergen, Norwy sunney.foter@stuent.ui.no
Kiwanis Dawn Busters of Metairie of the Louisiana Mississippi West Tennessee District of Kiwanis International
 Clu of Dwn Busters Kiwnis Dwn Busters of Metirie of the Louisin Mississippi West Tennessee Distrit of Kiwnis Interntionl KIWANIS MOTTO: Serving the Children of the World DEFINING STATEMENT OF KIWANIS:
Clu of Dwn Busters Kiwnis Dwn Busters of Metirie of the Louisin Mississippi West Tennessee Distrit of Kiwnis Interntionl KIWANIS MOTTO: Serving the Children of the World DEFINING STATEMENT OF KIWANIS:
Early depolarizing GABA controls critical-period plasticity in the rat visual cortex
 Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Erly depolrizing GABA ontrols ritil-period plstiity in the rt visul ortex Gbriele Deidd,5, Mnuel Allegr,,5, Chir Cerri, Shovn Nskr, Guillume Bony, Giuli Zunino 4, Yuri Bozzi,4, Mtteo Cleo,6 & Lur Cnedd,6
Two different lateral amygdala cell populations contribute to the initiation and storage of memory
 rticles Two different lterl mygdl cell popultions contriute to the initition nd storge of memory J. Christopher Rep, Jeff Muller, John Apergis, Theres M. Desrochers, Yu Zhou nd Joseph E. LeDoux W.M. Keck
rticles Two different lterl mygdl cell popultions contriute to the initition nd storge of memory J. Christopher Rep, Jeff Muller, John Apergis, Theres M. Desrochers, Yu Zhou nd Joseph E. LeDoux W.M. Keck
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CD169 + MACROPHAGES PRESENT LIPID ANTIGENS TO MEDIATE EARLY ACTIVATION OF INVARIANT NKT CELLS IN LYMPH NODES Ptrii Brrl, Polo Polzell, Andres Brukuer, Nio vn Rooijen, Gurdyl S.
NeuroGrid: recording action potentials from the surface of the brain
 t e h n i l r e p o r t s NeuroGrid: reording tion potentils from the surfe of the rin Dion Khodgholy, Jennifer N Gelins, Thoms Thesen 2, Werner Doyle 2, Orrin Devinsky 2, George G Mllirs 3 & György Buzsáki
t e h n i l r e p o r t s NeuroGrid: reording tion potentils from the surfe of the rin Dion Khodgholy, Jennifer N Gelins, Thoms Thesen 2, Werner Doyle 2, Orrin Devinsky 2, George G Mllirs 3 & György Buzsáki
The effects of color on brightness
 rticles The effects of color on rightness R. Beu Lotto nd Dle Purves Deprtment of Neuroiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medicl Center, Durhm, North Crolin 27710, USA Correspondence should e ddressed to
rticles The effects of color on rightness R. Beu Lotto nd Dle Purves Deprtment of Neuroiology, Box 3209, Duke University Medicl Center, Durhm, North Crolin 27710, USA Correspondence should e ddressed to
TNF-a Downregulates Filaggrin and Loricrin through c-jun N-terminal Kinase: Role for TNF-a Antagonists to Improve Skin Barrier
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
ORIGINAL ARTICLE TNF- Downregultes Filggrin nd Loririn through -Jun N-terminl Kinse: Role for TNF- Antgonists to Improve Skin Brrier Byung Eui Kim, Mihel D. Howell,, Emm Guttmn,, Ptrii M. Gilleudeu, Irm
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 % ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
% ells with ili (mrke y A-Tu) Reltive Luiferse % ells with ili (mrke y Arl13) % ells with ili DOI: 1.138/n2259 A-Tuulin Hoehst % Cilite Non-ilite -Serum 9% 8% 7% 1 6% % 4% +Serum 1 3% 2% 1% % Serum: -
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
Supplementry Figure S1 - UTR m - 3HA - 2-1 hgh - 1 Uiquitin *! *! lk distl promoter m K3R/ K121R-3HA UTR hgh founder lines - HA - - founder lines TG- E1 L A2 B1 F9 G6 H4 H6 B C D2 G1 H3 J2 L - 7 IP: lk
The kinetics and stiffness characteristics of the lower extremity in older adults during vertical jumping
 Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
Journl of Sports Siene nd Mediine (2008) 7, 379-386 http://www.jssm.org Reserh rtile The kinetis nd stiffness hrteristis of the lower extremity in older dults during vertil jumping Li-I Wng Deprtment of
