Rituximab therapy in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis improves alveolar macrophage lipid homeostasis
|
|
|
- Reynard Hodges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 RESEARCH Open Access Rituximab therapy in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis improves alveolar macrophage lipid homeostasis Anagha Malur 1, Mani S Kavuru 1,3, Irene Marshall 1, Barbara P Barna 1, Isham Huizar 1, Reema Karnekar 1 and Mary Jane Thomassen 1,2* Abstract Rationale: Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP) patients exhibit an acquired deficiency of biologically active granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) attributable to GM-CSF specific autoantibodies. PAP alveolar macrophages are foamy, lipid-filled cells with impaired surfactant clearance and markedly reduced exssion of the transcription factor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) and the PPARγ-regulated ATP binding cassette (ABC) lipid transporter, ABCG1. An open label proof of concept Phase II clinical trial was conducted in PAP patients using rituximab, a chimeric murine-human monoclonal antibody directed against B lymphocyte specific antigen CD2. Rituximab treatment decreased anti-gm-csf antibody levels in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, and 7/9 patients completing the trial demonstrated clinical improvement as measured by arterial blood oxygenation. Objectives: This study sought to determine whether rituximab therapy would restore lipid metabolism in PAP alveolar macrophages. Methods: BAL samples were collected from patients - and 6-months -rituximab infusion for evaluation of mrna and lipid changes. Results: Mean PPARγ and ABCG1 mrna exssion increased 2.8 and 5.3-fold respectively (p.5) after treatment. Lysosomal phospholipase A2 (LPLA2) (a key enzyme in surfactant degradation) mrna exssion was severely deficient in PAP patients -treatment but increased 2.8-fold -treatment. In supplemental animal studies, LPLA2 deficiency was verified in GM-CSF KO mice but was not sent in macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice compared to wild-type controls. Oil Red O intensity of PAP alveolar macrophages decreased after treatment, indicating reduced intracellular lipid while extracellular free cholesterol increased in BAL fluid. Furthermore, total protein and Surfactant protein A were significantly decreased in the BAL fluid therapy. Conclusions: Reduction in GM-CSF autoantibodies by rituximab therapy improves alveolar macrophage lipid metabolism by increasing lipid transport and surfactant catabolism. Mechanisms may involve GM-CSF stimulation of alveolar macrophage ABCG1 and LPLA2 activities by distinct pathways. Keywords: PAP, Rituximab, Alveolar macrophages, Surfactant, PPARγ, ABCG1, LPLA2 * Correspondence: thomassenm@ecu.edu 1 Program in Lung Cell Biology and Translational Research, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC, USA 2 Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, East Carolina University, Brody School of Medicine, 3E-149 Brody Medical Sciences Building, Greenville, NC 27834, USA Full list of author information is available at the end of the article 212 Malur et al.; licensee BioMed Central Ltd. This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
2 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 2 of 7 Introduction Surfactant catabolism is impaired in alveolar macrophages from patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) and GM-CSF knock out (KO) mice. In the GM-CSF KO mouse, the PAP like syndrome is reversible by exogenous GM-CSF or local over-exssion of GM-CSF. Studies from GM-CSF KO mice initially suggested that PAP might be due to idiopathic defects in GM-CSF receptors or production [1]. In adults with PAP, however, no mutations in GM-CSF receptor or surfactant coding sequences have been described [2]. Moreover, studies from our lab and others reported that both monocytes and alveolar macrophages from adult PAP patients are able to produce and respond to GM- CSF [3,4]. Evidence for adult PAP as an autoimmune disease was first sented by Kitamura et al., who noted that circulating anti-gm-csf autoantibodies neutralized GM-CSF biological activity, and thus resulted in a virtual GM-CSF deficiency [5,6]. Subsequent studies in idiopathic adult PAP patients confirmed the existence of anti-gm-csf antibodies and demonstrated that autoantibody levels were clinically useful for diagnosis [7-1]. Alveolar macrophages from both PAP patients and GM-CSF KO mice display a striking deficiency in PPARγ and in the lipid transporter ABCG1 [11,12]. GM-CSF treatment increased ABCG1 exssion in macrophages in vitro and in alveolar macrophages of PAP patients in vivo. Overexssion of PPARγ by lentivirus-pparγ transduction of primary human alveolar macrophages or activation by rosiglitazone also increased ABCG1 exssion [12]. In GM-CSF KO mice, in vivo treatment with lentivirus-pparγ increased both PPARγ and ABCGI exssion while reducing lipid accumulation in the lung. More recently, we observed improved lung function and reduced lipid accumulation in GM-CSF KO mice treated in vivo with lentivirus-abcg1 [13]. Collectively, these studies suggest that surfactant accumulation in PAP alveolar macrophages stems from GM-CSF deficiency leading to PPARγ deficiency and subsequent reduction of ABCG1 exssion. Lung surfactant catabolism is also known to be dependent upon lysosomal phospholipase A2 (LPLA2) activity, an enzyme selectively exssed in alveolar macrophages but not other tissue macrophages or circulating monocytes [14]. LPLA2 activity is deficient in GM-CSF KO mice but is restored by transgenic exssion of GM-CSF [14]. Interestingly, in vitro studies provide no evidence of LPLA2 stimulation by PPARγ although induction occurs through the PPARγ heterodimer, retinoid X receptor (RXR) via stimulation by alltrans-retinoic acid [15]. Rituximab, a chimeric murine-human monoclonal antibody directed against CD2, a B lymphocyte-specific membrane antigen, has been shown to deplete human B cells in vivo [16]. Rituximab was approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 1997 for treatment of CD2 (+) B cell lymphoma and has since been in use for B cell malignancies. Subsequently, rituximab therapy was applied to treatment of autoimmune disease, and results have shown clinical benefit in systemic lupus erythematosus [17], rheumatoid arthritis [18], and Wegener s granulomatosis [19] among others. Based upon data indicating autoantibody involvement in PAP, we recently carried out the first prospective, open label, proof of concept trial of rituximab in ten patients with PAP. Results suggest that rituximab may be an effective primary therapy in this autoimmune disease [2]. The most striking clinical finding from our PAP study of rituximab was the significant improvement of oxygenation, the primary endpoint in 7/9 patients. Improvements were also noted in total lung capacity, HRCT scans and transitional dyspnea index. Importantly, neither total serum anti- GM-CSF nor serum GM-CSF neutralizing capacity were reduced following rituximab therapy. Reduction of anti-gm-csf levels in BAL fluid from the lung, however, did correlate with improvement in PaO 2 and HRCT scans. Mechanisms responsible for rituximab-mediated improvement in PAP disease activity are unclear. Our vious studies of alveolar macrophages from untreated PAP patients demonstrated dramatically reduced PPARγ and ABCG1 exssion that was reversible by either in vivo or in vitro GM-CSF treatment [11,12]. In GM-CSF KO mice, in vivo administration of lentivirus constructs containing either PPARγ or ABCG1 reduced alveolar macrophage lipid accumulation and ugulated PPARγ and ABCG1 [13,21]. Based on such observations, we hypothesized that the clinical improvement in rituximab-treated PAP patients might be due to restoration of alveolar macrophage lipid homeostasis associated with reduced GM-CSF autoantibody in the pulmonary compartment. In this paper, we investigated this hypothesis by utilizing BAL samples from the original cohort of PAP patients treated with rituximab. Methods Study design This study was a prospective, open-label, proof-ofconcept clinical trial of rituximab therapy in a group of 1 adult patients senting with moderately symptomatic, idiopathic PAP as described in detail [2]. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board at East Carolina University and informed consent was obtained from all patients. The trial was registered at clinicaltrials.gov (NCT552461).
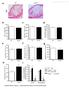
3 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 3 of 7 Cell collection Bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was carried out prior to and 6 months after therapy as described [3,2,22]. Cytospins were stained with Oil Red O to detect intracellular neutral lipids and counterstained with Gill s hematoxylin. Oil Red O intensity was quantified using a modified scoring system viously described [21,23]: +++ = strongly positive; ++ = positive; and + = weakly positive. Mice Animal studies were conducted in conformity with Public Health Service (PHS) Policy on humane care and use of laboratory animals and were approved by the institutional animal care committee. The GM-CSF KO mice were generated by Dr. Glenn Dranoff and have been viously described [24]. Macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice have been viously described [25]. Animals studied were age (8 12 week old) and gender-matched to wild type C57Bl/6 controls obtained from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME). BAL cells were obtained as described earlier [25]. For all experiments 5 7 mice per group were used. RNA purification and analysis Total cellular RNA was extracted by Lipid RNeasy protocol (Qiagen, Valencia, CA). Exssion of mrna was determined by real time RT-PCR using the ABI Prism 73 Detection System (TaqMan; Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA.) according to the manufacturer s instructions. RNA specimens were analyzed in duplicate using primer/probe sets for human PPARγ, ABCA1, ABCG1, LPLA2 and the housekeeping gene, glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) (ABI) or murine LPLA2 and GAPDH (ABI) as viously described [12]. Threshold cycle (CT) values for genes of interest were normalized to GAPDH and used to calculate the relative quantity of mrna exssion. Data were exssed as a fold change in mrna exssion relative to control values [26]. Cholesterol analysis Cholesterol was measured in BAL fluid using the Abcam (Cambridge, MA) Cholesterol Assay according to the manufacturer s instructions. Cholesterol content was exssed as μg/μl of cholesterol. Surfactant protein-a (SP-A) ELISA SP-A was measured in BAL fluid with an ELISA kit (Biovendor, Candler, NC) according to manufacturer s instructions. Total protein in BAL fluid was measured by BCA protein assay (Pierce, Rockford, MA). Statistical analysis Parametric data are sented as means (±SEM) and nonparametric data are sented as medians and ranges. A Fold change in PPAR γ mrna NV mean ± SEM C Fold change in ABCA1 mrna NV mean ± SEM B Fold change in ABCG1 mrna NV mean ± SEM D Fold change in LPLA2 mrna 2 1 NV mean ± SEM Figure 1 Gene exssion of lipid regulators is increased -rituximab therapy. Alveolar macrophage gene exssion was measured by RT-PCR in PAP patients before and 6 months rituximab therapy. Increases are shown in: (A) PPARγ; (B) ABCG1; (C) ABCA1; and (D) LPLA2 (n = 6).
4 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 4 of 7 Statistical comparisons of parametric data were made with Student s t test. Nonparametric data were compared with Wilcoxon test. P.5 was considered significant. Results PPARγ and ABC lipid transporter exssion levels are elevated in alveolar macrophages from patients with PAP Compared to -treatment levels, rituximab increased PAP alveolar macrophage PPARγ and ABCG1 mrna exssion by a mean of 2.8 and 5.3-fold respectively (p.5, n = 6) (Figures 1A and B). Although, no significant differences in mrna exssion levels of ABCA1 between healthy controls and PAP baseline alveolar macrophages were found, levels became elevated after rituximab, with a mean increase of 3.2 fold (p <.5, n = 6) compared to -treatment (Figure 1C). LPLA2 exssion is deficient -treatment and elevated by rituximab therapy Examination of LPLA2, also indicated restorative effects of rituximab. Mean LPLA2 levels were significantly reduced compared to healthy controls in PAP patients -treatment (p <.5, n = 6). Compared to treatment, however, LPLA2 mrna exssion significantly increased -rituximab by a mean of 2.8-fold (p <.5) (Figure 1D). LPLA2 exssion is not deficient in macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice Previous studies from our laboratory and others had reported reduced exssion of LPLA2 or PPARγ in GM-CSF KO mice [12,14]. Since both of these genes were deficient in -treatment PAP alveolar macrophages and ugulated by rituximab therapy, we sought A % Oil Red O Positive Cells (Intensity) B % Oil Red O Positive Cells (Intensity) Pre-treatment Post-treatment Figure 3 Intracellular lipid staining is decreased rituximab therapy in PAP alveolar macrophages. Cytospin parations of alveolar macrophages were stained with Oil Red O and intensity was quantified using a modified scoring viously described [21,23]; (++ + = strongly positive, ++ = positive; + = weakly positive. A minimum of 1 cells on cytospins from each of 5 paired and therapy samples were scored. Fold change in mouse LPLA2 mrna exssion C57Bl/6 w/t PPARγ KO GM-CSF KO p =.69 Figure 2 LPLA2 gene exssion is decreased in alveolar macrophages from GM-CSF KO mice as compared to wild type C57Bl6. LPLA2 in macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice was not different from wild type (n = 6 mice per group). cholesterol μg/μl p =.4 Figure 4 Extracellular cholesterol is increased in PAP bronchoalveolar lavage fluid rituximab therapy (n = 8).
5 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 5 of 7 to determine whether PPARγ might be involved in LPLA2 regulation. Therefore we investigated LPLA2 mrna exssion in BAL-derived cells from C57 wildtype, GM-CSF KO, and macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice (Figure 2). As anticipated, GM-CSF KO animals exhibited significant LPLA2 mrna deficiency ( 2.5-fold, p =.69) compared to wild-type mice (Figure 2). LPLA2 was not deficient, however, in macrophage-specific PPARγ KO mice which were similar to wild-type (Figure 2). These data strongly suggest that LPLA2 regulation is independent of PPARγ. Intracellular lipid is reduced in PAP alveolar macrophages Heavy (+++) intensity of Oil Red O staining characterized PAP alveolar macrophages prior to rituximab treatment (Figure 3A). Post-treatment, alveolar macrophages exhibited a shift toward less Oil Red O staining, indicating a reduction of intracellular neutral lipid (p =.5, n = 6, Figure 3B). Extracellular cholesterol is increased -rituximab Because cholesterol is a component of surfactant and ABCG1 has been shown to increase cholesterol transport [27] we measured cholesterol in the BAL fluid. Rituximab increased levels of extracellular cholesterol sent in PAP BAL fluid -treatment compared to -treatment (p =.4, n = 8, Figure 4). Surfactant protein-a (SP-A) is decreased in BAL fluid following rituximab treatment SP-A is a component is one of the four surfactant proteins and has been reported to be elevated in BAL fluid A ng/ml of SPA in BAL Fluids NV mean ± SEM B μg/ml Protein in BAL Fluids NV mean ± SEM Figure 5 Extracellular surfactant protein A (A) and total protein (B) are decreased in PAP bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (n =8, p =.4 SP-A; p =.2 protein).
6 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 6 of 7 from patients with PAP [1]. Both SP-A and total protein were measured - and -treatment and were found to be decreased (Figure 5, n =8, p =.4 SP-A; p =.2 protein) indicating reduced extracellular accumulation of surfactant protein. Discussion The findings sented here indicate that rituximab treatment can have an impact upon restoration of alveolar macrophage lipid homeostasis in PAP patients. Previous results indicated that rituximab treatment reduced anti-gm-csf autoantibody levels in the BAL fluids of PAP patients studied here even though serum levels were not significantly affected [2]. Moreover, rituximab treatment was associated with clinical pulmonary improvement in terms of gas exchange (room air PaO 2 ) and radiographic evidence of disease (by high resolution computed tomography of the chest). Data sented here confirm the positive therapeutic effects of rituximab on PAP lung with respect to enhanced alveolar macrophage functional activity and exssion of lipid regulatory genes, PPARγ, ABCG1, and LPLA2. Results confirmed our initial hypothesis regarding the importance of PPARγ and ABCG1 in maintaining alveolar macrophage lipid metabolism. Compared to baseline, both of these genes were significantly ugulated by rituximab treatment. An unexpected finding was the deficiency of LPLA2 in untreated PAP patients, a situation that was significantly reversed by rituximab therapy. Our data are the first to note deficient LPLA2 in alveolar macrophages of untreated PAP patients and the ugulation of LPLA2 after rituximab therapy. As mentioned viously in this paper, LPLA2 has also been found to be deficient in GM-CSF null mice [14]. LPLA2 activity was restored in bi-transgenic mice in vivo by exssion of GM-CSF in type II alveolar epithelial cells under control of a surfactant protein C promoter [14]. Investigation of LPLA2 in THP-1 myeloid cells also indicated no stimulation by GM-CSF or the PPARγ ligand, Troglitazone [15]. Results of our supplemental animal studies are the first to indicate that LPLA2 is not deficient in macrophagespecific PPARγ KO mice. Thus LPLA2 deficiency in PAP does not appear to involve PPARγ although RXR is part of the PPARγ heterodimer. While these findings indicate distinct regulatory pathways for ABCG1 and LPLA2, further studies are necessary to establish the mechanisms by which GM-CSF corrects LPLA2 deficiency in PAP. In summary, data indicate that clinical improvement -rituximab treatment in a viously described cohort of PAP patients is associated with improved lipid homeostasis in alveolar macrophages from the same patients. Findings also indicate that reconstruction of lipid homeostasis in PAP alveolar macrophages is an intricate process requiring ugulation of the transcription factor PPARγ, lipid transporter ABCG1, and the surfactant catabolic enzyme, LPLA2. Although PPARγ dependence of ABCG1 has been established by studies in PAP and in GM-CSF KO mice [12,13,21], mechanisms regulating LPLA2 remain to be explored. Nevertheless, restoration of biologically active GM-CSF via rituximab therapy appears to be a successful means for improving lipid homeostasis in PAP alveolar macrophages. Abbreviations PAP: Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis; GM-CSF: Granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; ABC: ATP binding cassette; ABCG1: ABCA1, Lipid transporter; LPLA2: Lysosomal phospholipase A2. Competing interests Genentech funded the clinical trial. Authors contributions AM contributed to acquisition of the data, analysis and intertation of data, drafting of the manuscript and final approval of the version to be published; MSK contributed to the conception and design, acquisition of the data, analysis and intertation of data and final approval of the version to be published, IM contributed to acquisition of the data and final approval of the version to be published; BPB contributed to the design, analysis and intertation of data, drafting of the manuscript and final approval of the version to be published; IH contributed to the acquisition and intertation of data and final approval of the version to be published; RK contributed to the acquisition of data and final approval of the version to be published; MJT contributed to the conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and intertation of data, drafting of the manuscript and final approval of the version to be published. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Funding sources Supported by Genentech and the National Institute of Health in part by grant RO1-AI Author details 1 Program in Lung Cell Biology and Translational Research, Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC, USA. 2 Division of Pulmonary, Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, East Carolina University, Brody School of Medicine, 3E-149 Brody Medical Sciences Building, Greenville, NC 27834, USA. 3 Current address: Division of Pulmonary & Critical Care Medicine, Thomas Jefferson University & Hospital, 834 Walnut St., Suite 65, Philadelphia, PA 1917, USA. Received: 1 February 212 Accepted: 16 May 212 Published: 14 June 212 References 1. Trapnell BC, Whitsett JA: GM-CSF regulates pulmonary surfactant homeostasis and alveolar macrophage-mediated innate host defense. Annu Rev Physiol 22, 64: Huizar I, Kavuru MS: Alveolar proteinosis syndrome: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. Curr Opin Pulm Med 29, 15: Thomassen MJ, Yi T, Raychaudhuri B, Malur A, Kavuru MS: Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a disease of decreased availability of GM-CSF rather than an intrinsic cellular defect. Clin Immunol 2, 95: Carraway MS, Ghio AJ, Carter JD, Piantadosi CA: Detection of granulocytemacrophage colony-stimulating factor in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2, 161: Kitamura T, Tanaka N, Watanabe J, Uchida K, Kanegasaki S, Yamada Y, Nakata K: Idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis as an autoimmune disease with neutralizing antibody against granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. J Exp Med 1999, 19:
7 Malur et al. Respiratory Research 212, 13:46 Page 7 of 7 6. Tanaka N, Watanabe J, Kitamura T, Yamada Y, Kanegasaki S, Nakata K: Lungs of patients with idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis exss a factor which neutralizes granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. FEBS Lett 1999, 442: Bonfield TL, Kavuru MS, Thomassen MJ: Anti-GM-CSF titer dicts response to GM-CSF therapy in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Clin Immunol 22, 15: Bonfield TL, Russell D, Burgess S, Malur A, Kavuru MS, Thomassen MJ: Autoantibodies against granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor are diagnostic for pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 22, 27: Seymour JF, Doyle IR, Nakata K, Presneill JJ, Schoch OD, Hamano E, Uchida K, Fisher R, Dunn AR: Relationship of anti-gm-csf antibody concentration, surfactant protein A and B levels, and serum LDH to pulmonary parameters and response to GM-CSF therapy in patients with idiopathic alveolar proteinosis. Thorax 23, 58: Kitamura T, Uchida K, Tanaka N, Tsuchiya T, Watanabe J, Yamada Y, Hanaoka K, Seymour JF, Schoch OD, Doyle I, et al: Serological diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2, 162: Bonfield TL, Farver CF, Barna BP, Malur A, Abraham S, Raychaudhuri B, Kavuru MS, Thomassen MJ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorgamma is deficient in alveolar macrophages from patients with alveolar proteinosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23, 29: Thomassen MJ, Barna BP, Malur A, Bonfield TL, Farver CF, Malur A, Dalrymple H, Kavuru MS, Febbraio M: ABCG1 is deficient in alveolar macrophages of GM-CSF knock-out mice and patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinsosis. J Lipid Res 27, 48: Malur A, Huizar I, Wells G, Barna BP, Malur AG, Thomassen MJ: Lentivirus- ABCG1 instillation reduces lipid accumulation and improves lung compliance in GM-CSF knock-out mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 211, 415: Abe A, Hiraoka M, Wild S, Wilcoxen SE, Paine R III, Shayman JA: Lysosomal phospholipase A2 is selectively exssed in alveolar macrophages. J Biol Chem 24, 279: Abe A, Poucher HK, Hiraoka M, Shayman JA: Induction of lysosomal phospholipase A2 through the retinoid X receptor in THP-1 cells. J Lipid Res 24, 45: Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, Varns C, Shen D, Wei A, McClure A, Dallaire BK: Overview of the clinical development of rituximab: first monoclonal antibody approved for the treatment of lymphoma. Semin Oncol 1999, 26: Anolik J, Sanz I, Looney RJ: B cell depletion therapy in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Rheumatol Rep 23, 5: Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, Stevens RM, Shaw T: Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 24, 35: Stone JH, Merkel PA, Spiera R, Seo P, Langford CA, Hoffman GS, Kallenberg CGM, St Clair EW, Turkiewicz A, Tchao NK, et al: Rituximab versus Cyclophosphamide for ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N Engl J Med 21, 363: Kavuru MS, Malur A, Marshall I, Barna BP, Meziane M, Huizar I, Dalrymple H, Karnekar R, Thomassen MJ: An Open-Label Trial of Rituximab Therapy in Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis. Eur Respir J 211, 38: Malur A, Baker AD, McCoy AJ, Wells G, Barna BP, Kavuru MS, Malur AG, Thomassen MJ: Restoration of PPARgamma reverses lipid accumulation in alveolar macrophages of GM-CSF knockout mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 211, 3:L73 L Thomassen MJ, Buhrow LT, Connors MJ, Kaneko FT, Erzurum SC, Kavuru MS: Nitric oxide inhibits inflammatory cytokine production by human alveolar macrophages. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 1997, 17: Iyonaga K, Suga M, Yamamoto T, Ichiyasu H, Miyakawa M, Ando M: Elevated bronchoalveolar concentrations of MCP-1 in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis. Eur Respir J 1999, 14: Dranoff G, Crawford AD, Sadelain M, Ream B, Rashid A, Bronson RT, Dickersin GR, Bachurski CJ, Mark EL, Whitsett JA, et al: Involvement of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in pulmonary homeostasis. Science 1994, 264: Malur A, Mccoy AJ, Arce S, Barna BP, Kavuru MS, Malur AG, Thomassen MJ: Deletion of PPARγ in alveolar macrophages is associated with a Th-1 pulmonary inflammatory response. J Immunol 29, 182: Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD: Analysis of relative gene exssion data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2( Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 21, 25: Kennedy MA, Barrera GC, Nakamura K, Baldan A, Tarr P, Fishbein MC, Frank J, Francone OL, Edwards PA: ABCG1 has a critical role in mediating cholesterol efflux to HDL and venting cellular lipid accumulation. Cell Metab 25, 1: doi:1.1186/ Cite this article as: Malur et al.: Rituximab therapy in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis improves alveolar macrophage lipid homeostasis. Respiratory Research :46. Submit your next manuscript to BioMed Central and take full advantage of: Convenient online submission Thorough peer review No space constraints or color figure charges Immediate publication on acceptance Inclusion in PubMed, CAS, Scopus and Google Scholar Research which is freely available for redistribution Submit your manuscript at
PU.1 regulation of human alveolar macrophage differentiation requires granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
 Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L1132 L1136, 2003. First published August 1, 2003; 10.1152/ajplung.00216.2003. PU.1 regulation of human alveolar macrophage differentiation requires granulocyte-macrophage
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 285: L1132 L1136, 2003. First published August 1, 2003; 10.1152/ajplung.00216.2003. PU.1 regulation of human alveolar macrophage differentiation requires granulocyte-macrophage
ERJ Express. Published on April 8, 2011 as doi: /
 ERJ Express. Published on April 8, 2011 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00197710 TITLE: An Open-Label Trial of Rituximab Therapy in Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis AUTHORS: Mani S. Kavuru 1, Anagha Malur 1, Irene
ERJ Express. Published on April 8, 2011 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00197710 TITLE: An Open-Label Trial of Rituximab Therapy in Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis AUTHORS: Mani S. Kavuru 1, Anagha Malur 1, Irene
Hong yan Yu, Xue feng Sun, Yan xun Wang, Zuo jun Xu and Hui Huang *
 Yu et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:87 CASE REPORT Open Access Whole lung lavage combined with Granulocytemacrophage colony stimulating factor inhalation for an adult case of refractory pulmonary
Yu et al. BMC Pulmonary Medicine 2014, 14:87 CASE REPORT Open Access Whole lung lavage combined with Granulocytemacrophage colony stimulating factor inhalation for an adult case of refractory pulmonary
P ulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare disease
 528 MISCELLANEOUS Clinical significance of anti-gm-csf antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis F-C Lin, G-D Chang, M-S Chern, Y-C Chen, S-C Chang... See end of article for authors affiliations...
528 MISCELLANEOUS Clinical significance of anti-gm-csf antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis F-C Lin, G-D Chang, M-S Chern, Y-C Chen, S-C Chang... See end of article for authors affiliations...
Targeted PPAR deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism
 Targeted PPAR deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism Anna D. Baker, * Anagha Malur, * Barbara P. Barna, * Shobha Ghosh, Mani S. Kavuru, * Achut G. Malur, and Mary Jane Thomassen
Targeted PPAR deficiency in alveolar macrophages disrupts surfactant catabolism Anna D. Baker, * Anagha Malur, * Barbara P. Barna, * Shobha Ghosh, Mani S. Kavuru, * Achut G. Malur, and Mary Jane Thomassen
Clinical significance of anti-gm-csf antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
 Thorax Online First, published on March 3, 2006 as 10.1136/thx.2005.054171 Clinical significance of anti-gm-csf antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis Fang-Chi Lin, MD; Geen-Dong Chang,
Thorax Online First, published on March 3, 2006 as 10.1136/thx.2005.054171 Clinical significance of anti-gm-csf antibodies in idiopathic pulmonary alveolar proteinosis Fang-Chi Lin, MD; Geen-Dong Chang,
Long term follow up of whole lung lavage in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
 EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 763-768, 2014 Long term follow up of whole lung lavage in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis XIAOYAN ZHOU, GUOCHU LU, ZHEN YU, FEI GAO and TAO BIAN Department
EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 8: 763-768, 2014 Long term follow up of whole lung lavage in patients with pulmonary alveolar proteinosis XIAOYAN ZHOU, GUOCHU LU, ZHEN YU, FEI GAO and TAO BIAN Department
Serum Antibody Against Granulocyte/Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and KL-6 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 349-354 Distinct Markers for I-PAP 349 Serum Antibody Against Granulocyte/Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and KL-6 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Case
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2006, 208, 349-354 Distinct Markers for I-PAP 349 Serum Antibody Against Granulocyte/Macrophage Colony-Stimulating Factor and KL-6 in Idiopathic Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Case
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
 Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Sara R. Greenhill and Darrell N. Kotton Chest 2009;136;571-577 DOI 10.1378/chest.08-2943 The online version of this article, along with updated information and services can
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Sara R. Greenhill and Darrell N. Kotton Chest 2009;136;571-577 DOI 10.1378/chest.08-2943 The online version of this article, along with updated information and services can
2011 HESI Emerging Issues. Alveolar macrophage changes in response to inhaled drugs: Factors distinguishing adaptive from adverse effects.
 2011 HESI Emerging Issues Alveolar macrophage changes in response to inhaled drugs: Factors distinguishing adaptive from adverse effects. HESI Annual Meeting, June 2011 Jan Klapwijk Head of Pathology GSK
2011 HESI Emerging Issues Alveolar macrophage changes in response to inhaled drugs: Factors distinguishing adaptive from adverse effects. HESI Annual Meeting, June 2011 Jan Klapwijk Head of Pathology GSK
Prevalence and healthcare burden of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis
 McCarthy et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:129 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0846-y LETTER TO THE EDITOR Prevalence and healthcare burden of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis Cormac
McCarthy et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases (2018) 13:129 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-018-0846-y LETTER TO THE EDITOR Prevalence and healthcare burden of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis Cormac
Pulmonary Macrophage Transplantation Therapy
 Pulmonary Macrophage Transplantation Therapy Rare Pediatric Respiratory Disease: Science Shapes Precision Care Conference Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine La Jolla, CA July 6, 2017 Bruce Trapnell,
Pulmonary Macrophage Transplantation Therapy Rare Pediatric Respiratory Disease: Science Shapes Precision Care Conference Sanford Consortium for Regenerative Medicine La Jolla, CA July 6, 2017 Bruce Trapnell,
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
Exogenous Granulocyte Macrophage Colony- Stimulating Factor Administration for Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
 Exogenous Granulocyte Macrophage Colony- Stimulating Factor Administration for Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis MANI S. KAVURU, EUGENE J. SULLIVAN, RITA PICCIN, MARY JANE THOMASSEN, and JAMES K. STOLLER
Exogenous Granulocyte Macrophage Colony- Stimulating Factor Administration for Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis MANI S. KAVURU, EUGENE J. SULLIVAN, RITA PICCIN, MARY JANE THOMASSEN, and JAMES K. STOLLER
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Aldridge et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900655106 Fig. S1. Flow diagram of sublethal (a) and lethal (b) influenza virus infections. (a) Infection of lung epithelial cells by influenza virus
Supporting Information Aldridge et al. 10.1073/pnas.0900655106 Fig. S1. Flow diagram of sublethal (a) and lethal (b) influenza virus infections. (a) Infection of lung epithelial cells by influenza virus
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
P ulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP) is a rare respiratory
 39 PAEDIATRIC LUNG DISEASE Anti-GM-CSF antibodies in paediatric pulmonary alveolar proteinosis P Latzin, M Tredano, Y Wüst, J de Blic, T Nicolai, B Bewig, F Stanzel, D Köhler, M Bahuau, M Griese... See
39 PAEDIATRIC LUNG DISEASE Anti-GM-CSF antibodies in paediatric pulmonary alveolar proteinosis P Latzin, M Tredano, Y Wüst, J de Blic, T Nicolai, B Bewig, F Stanzel, D Köhler, M Bahuau, M Griese... See
Rare cause of dyspnoea: protein accumulation in the lungs
 Rare cause of dyspnoea: protein accumulation in the lungs Interstitial or diffuse lung disorders are disorders affecting the spaces between the alveoli and blood vessels (the so-called interstitium) in
Rare cause of dyspnoea: protein accumulation in the lungs Interstitial or diffuse lung disorders are disorders affecting the spaces between the alveoli and blood vessels (the so-called interstitium) in
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Spontaneous arthritis and ankylosis in male DBA/ 1 mice: further evidence for a role of behavioral factors in stress-induced arthritis
 Braem et al. Biological Procedures Online 2012, 14:10 Biological Procedures Online SHORT REPORT Open Access Spontaneous arthritis and ankylosis in male DBA/ 1 mice: further evidence for a role of behavioral
Braem et al. Biological Procedures Online 2012, 14:10 Biological Procedures Online SHORT REPORT Open Access Spontaneous arthritis and ankylosis in male DBA/ 1 mice: further evidence for a role of behavioral
The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database
 Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
Nielen et al. BMC Family Practice 2013, 14:79 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access The validity of the diagnosis of inflammatory arthritis in a large population-based primary care database Markus MJ Nielen 1*,
SIGNIFICANT REDUCTION OF GRANULOMAS IN Nrf2-DEFICIENT MICE INFECTED WITH MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS
 Short Communication SIGNIFICANT REDUCTION OF GRANULOMAS IN Nrf2-DEFICIENT MICE INFECTED WITH MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS S. Mizuno 1, M. Yamamoto 2 and I. Sugawara 1* (Received on 17.7.2009; Accepted after
Short Communication SIGNIFICANT REDUCTION OF GRANULOMAS IN Nrf2-DEFICIENT MICE INFECTED WITH MYCOBACTERIUM TUBERCULOSIS S. Mizuno 1, M. Yamamoto 2 and I. Sugawara 1* (Received on 17.7.2009; Accepted after
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases
 Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Immunological Aspect of Ozone in Rheumatic Diseases Prof. Dr. med. Z. Fahmy Chief Consulting Rheumatologist Augusta Clinic for Rheumatic Diseases And Rehabilitation Bad Kreuznach Germany Rheumatoid arthritis
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Case report. Key words: chronic interstitial pneumonitis, intravenous immunoglobulin, pulmonary alveolar proteinosis, pulse methylprednisolone
 Case report A combination of intravenous immunoglobulin and pulse methylprednisolone extended survival in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis with chronic interstitial pneumonitis: a case report Nongnapa Jirarattanasopa
Case report A combination of intravenous immunoglobulin and pulse methylprednisolone extended survival in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis with chronic interstitial pneumonitis: a case report Nongnapa Jirarattanasopa
A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma
 Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
Douglas et al. BMC Cancer 2012, 12:425 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access A new score predicting the survival of patients with spinal cord compression from myeloma Sarah Douglas 1, Steven E Schild 2 and Dirk
Successful treatment of pneumomediastinum in a patient with interstitial lung disease due to anti-synthetase syndrome: A case report
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Successful treatment of pneumomediastinum in a patient with interstitial lung disease due to anti-synthetase syndrome: A case report Roy
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGE PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Successful treatment of pneumomediastinum in a patient with interstitial lung disease due to anti-synthetase syndrome: A case report Roy
A lveolar proteinosis (AP) is an uncommon lung disorder
 252 MISCELLANEOUS Relationship of anti-gm-csf antibody concentration, surfactant protein A and B levels, and serum LDH to pulmonary parameters and response to GM-CSF therapy in patients with idiopathic
252 MISCELLANEOUS Relationship of anti-gm-csf antibody concentration, surfactant protein A and B levels, and serum LDH to pulmonary parameters and response to GM-CSF therapy in patients with idiopathic
Supplemental Data. Epithelial-Macrophage Interactions Determine Pulmonary Fibrosis Susceptibility in. Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome
 Page 1 Supplemental Data Epithelial-Macrophage Interactions Determine Pulmonary Fibrosis Susceptibility in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome Lisa R. Young, Peter M. Gulleman, Chelsi W. Short, Harikrishna Tanjore,
Page 1 Supplemental Data Epithelial-Macrophage Interactions Determine Pulmonary Fibrosis Susceptibility in Hermansky-Pudlak Syndrome Lisa R. Young, Peter M. Gulleman, Chelsi W. Short, Harikrishna Tanjore,
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity
 Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Role of BAFF in B cell Biology and Autoimmunity B cell development in health and disease: B-lymphocytes or B cells, and the antibodies they produce, are crucial mediators of humoral immunity, providing
Sample size calculation for multicentre efficacy trials of blood-stage malaria antigens
 Bosomprah Malaria Journal 2013, 12:253 METHODOLOGY Open Access Sample size calculation for multicentre efficacy trials of blood-stage malaria antigens Samuel Bosomprah Abstract Background: Sample size
Bosomprah Malaria Journal 2013, 12:253 METHODOLOGY Open Access Sample size calculation for multicentre efficacy trials of blood-stage malaria antigens Samuel Bosomprah Abstract Background: Sample size
Update on ChILD. R. Paul Guillerman, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatric Radiology
 Update on ChILD R. Paul Guillerman, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatric Radiology Objectives Review recent advances in the imaging of childhood interstitial lung disease (ChILD) Diseases under-recognized,
Update on ChILD R. Paul Guillerman, MD Associate Professor Department of Pediatric Radiology Objectives Review recent advances in the imaging of childhood interstitial lung disease (ChILD) Diseases under-recognized,
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 : Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI) Type of Article: Clinical Images Title: Successful
: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: International Journal of Case Reports and Images (IJCRI) Type of Article: Clinical Images Title: Successful
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by
 Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
Supplementary table I. Real-time primers used in the study. The fold change was obtained by normalizing the gene expression number to those of HPRT, then comparing the samples to untreated or naive mice.
GPR120 *** * * Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon. UCP1 mrna ***
 a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
a GPR120 GPR120 mrna/ppia mrna Arbitrary Units 150 100 50 Liver BAT iwat ewat mwat Ileum Colon b UCP1 mrna Fold induction 20 15 10 5 - camp camp SB202190 - - - H89 - - - - - GW7647 Supplementary Figure
APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme
 276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
276 Eur. Cytokine Netw., Vol. 17 n 4, December 06, 276-80 APRIL is increased in serum of patients with brain glioblastoma multiforme Joanna Iłżecka 1, Marek Iłżecki 2 1 Department of Neurology, Medical
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP), first. Wash-out kinetics and efficacy of a modified lavage technique for alveolar proteinosis
 Eur Respir J ; 4: 48 474 DOI:.83/9393.7 CopyrightßERS Wash-out kinetics and efficacy of a modified lavage technique for alveolar proteinosis Francesco Bonella*, Peter C. Bauer*, Matthias Griese #, Thomas
Eur Respir J ; 4: 48 474 DOI:.83/9393.7 CopyrightßERS Wash-out kinetics and efficacy of a modified lavage technique for alveolar proteinosis Francesco Bonella*, Peter C. Bauer*, Matthias Griese #, Thomas
New Insights on Mechanisms of Foamy Macrophage (FM) Induction and Persistence
 New Insights on Mechanisms of Foamy Macrophage (FM) Induction and Persistence Marian Laderoute, Ph.D. Medical Sciences -Immunology Lab Director Immune System Management Clinic & Lab 80 Aberdeen Street,
New Insights on Mechanisms of Foamy Macrophage (FM) Induction and Persistence Marian Laderoute, Ph.D. Medical Sciences -Immunology Lab Director Immune System Management Clinic & Lab 80 Aberdeen Street,
Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F10 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model.
 A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
A B16F1 s.c. Lung LN Distant lymph nodes Colon B B16F1 s.c. Supplementary Figure 1. Deletion of Smad3 prevents B16F1 melanoma invasion and metastasis in a mouse s.c. tumor model. Highly invasive growth
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE WIPAWEE WONGCHANA
 IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
IMMUNOTOOLS: EFFECT OF NOTCH-DEFICIENT MACROPHAGES TO AUTOIMMUNE DISEASE 22-02-2017 WIPAWEE WONGCHANA WHAT DO YOU SEE? Allergy Ref: http://carrington.edu/blog/medical/vaccines/smallpox-andsmallpox-vaccine/
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Vasculitis
 New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2011 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Vasculitis Report on EULAR 2011 presentations Anti-TNF failure and response to rituximab
New Evidence reports on presentations given at EULAR 2011 Rituximab for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Vasculitis Report on EULAR 2011 presentations Anti-TNF failure and response to rituximab
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
Supporting Information Franco et al. 10.1073/pnas.1015557108 SI Materials and Methods Drug Administration. PD352901 was dissolved in 0.5% (wt/vol) hydroxyl-propyl-methylcellulose, 0.2% (vol/vol) Tween
The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis
 Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
Kajbaf and Lalau BMC Pharmacology and Toxicology 2013, 14:22 RESEARCH ARTICLE The prognostic value of blood ph and lactate and metformin concentrations in severe metformin-associated lactic acidosis Farshad
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity. Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China
 Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
Regulatory B cells in autoimmunity Liwei Lu University of Hong Kong, China Multiple functions of B cells in immunity LeBien and Tedder, Blood (2008) B cell functions in autoimmune pathogenesis The Immunopathogensis
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Gaohong Sheng 1, Peng Chen 2,3, Yanqiu Wei 1, Jiaojiao Chu 1, Xiaolei Cao 4 and Hui-Lan Zhang 1*
 Sheng et al. Respiratory Research (2018)19:163 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0862-4 RESEARCH Open Access Better approach for autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis treatment: inhaled or subcutaneous
Sheng et al. Respiratory Research (2018)19:163 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0862-4 RESEARCH Open Access Better approach for autoimmune pulmonary alveolar proteinosis treatment: inhaled or subcutaneous
The Dilemmas of Treating Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications: A Case Report
 report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com The Dilemmas of Treating Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications: A Report Abstract Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP) is
report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com The Dilemmas of Treating Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Implications: A Report Abstract Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP) is
Rituximab treatment for ANCA-associated vasculitis in childhood
 Rituximab treatment for ANCA-associated vasculitis in childhood DISCLOSURE I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose Katharine Moore MD Nov 14, 2012 University of Colorado School of Medicine
Rituximab treatment for ANCA-associated vasculitis in childhood DISCLOSURE I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose Katharine Moore MD Nov 14, 2012 University of Colorado School of Medicine
Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer
 He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
He et al. BMC Gastroenterology 2013, 13:87 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Combined use of AFP, CEA, CA125 and CAl9-9 improves the sensitivity for the diagnosis of gastric cancer Chao-Zhu He 1,2, Kun-He Zhang
Supplement Material. Spleen weight (mg) LN cells (X106) Acat1-/- Acat1-/- Mouse weight (g)
 Supplement Material A Spleen weight (mg) C Mouse weight (g) 1 5 1 2 9 6 3 2 5 2 1 5 Male LN cells (X16) 4 ** ** Female B 3 2 1 Supplemental Figure I. Spleen weight (A), Inguinal lymph node (LN) cell number
Supplement Material A Spleen weight (mg) C Mouse weight (g) 1 5 1 2 9 6 3 2 5 2 1 5 Male LN cells (X16) 4 ** ** Female B 3 2 1 Supplemental Figure I. Spleen weight (A), Inguinal lymph node (LN) cell number
Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 )
 770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
770 771 Supplementary Table 1. The primers used for quantitative RT-PCR. Gene name Forward (5 > 3 ) Reverse (5 > 3 ) Human CXCL1 GCGCCCAAACCGAAGTCATA ATGGGGGATGCAGGATTGAG PF4 CCCCACTGCCCAACTGATAG TTCTTGTACAGCGGGGCTTG
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated
 Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Supplementary fig. 1. Crystals induce necroptosis does not involve caspases, TNF receptor or NLRP3. A. Mouse tubular epithelial cells were pretreated with zvad-fmk (10µM) and exposed to calcium oxalate
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays
 Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Examination of Mechanisms of Hepatotoxicity of Anti-diabetic PPARγ Agonists Using Applied Biosystems Rat Whole Genome Microarrays Lu Zhang b, Lei Guo a, Leming Shi a, Weida Tong a, Yongming Sun b, Gary
Rituximab for auto-immune alveolar proteinosis, a real life cohort study
 Soyez et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:74 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0780-5 RESEARCH Open Access Rituximab for auto-immune alveolar proteinosis, a real life cohort study Berenice Soyez 1,2,3,
Soyez et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:74 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0780-5 RESEARCH Open Access Rituximab for auto-immune alveolar proteinosis, a real life cohort study Berenice Soyez 1,2,3,
SAVARA CORPORATE PRESENTATION (NASDAQ: SVRA) NOVEMBER 2018
 SAVARA CORPORATE PRESENTATION (NASDAQ: SVRA) NOVEMBER 2018 SAFE HARBOR STATEMENT Savara Inc. ( Savara or the Company ) cautions you that statements in this presentation that are not a description of historical
SAVARA CORPORATE PRESENTATION (NASDAQ: SVRA) NOVEMBER 2018 SAFE HARBOR STATEMENT Savara Inc. ( Savara or the Company ) cautions you that statements in this presentation that are not a description of historical
Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that MIF was detected in the fractions of
 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1. Western blot analysis indicated that was detected in the fractions of plasma membrane and cytosol but not in nuclear fraction isolated from Pkd1 null
BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented
 Supplemental Materials Figure S1. Cultured BMDCs express CD11c BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented with 15 ng/ml GM-CSF. Media was changed and fresh
Supplemental Materials Figure S1. Cultured BMDCs express CD11c BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented with 15 ng/ml GM-CSF. Media was changed and fresh
Investigation of novel autoantibodies in Sjogren s syndrome utilizing Sera from the Sjogren s international collaborative clinical alliance cohort
 Suresh et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:38 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0023-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Investigation of novel autoantibodies in Sjogren s syndrome utilizing Sera from the Sjogren s international
Suresh et al. BMC Ophthalmology (2015) 15:38 DOI 10.1186/s12886-015-0023-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Investigation of novel autoantibodies in Sjogren s syndrome utilizing Sera from the Sjogren s international
Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):16374-16378 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010359 Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang
Review B cell targeted therapies Edward Keystone
 Available online http://arthritis-research.com/contents/7/s3/s13 Review B cell targeted therapies Edward Keystone Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada Corresponding author: Edward
Available online http://arthritis-research.com/contents/7/s3/s13 Review B cell targeted therapies Edward Keystone Department of Medicine, University of Toronto, Ontario, Canada Corresponding author: Edward
DNA vaccine, peripheral T-cell tolerance modulation 185
 Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Subject Index Airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR) animal models 41 43 asthma inhibition 45 overview 41 mast cell modulation of T-cells 62 64 respiratory tolerance 40, 41 Tregs inhibition role 44 respiratory
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
Supplementary Figure 1 CD4 + T cells from PKC-θ null mice are defective in NF-κB activation during T cell receptor signaling. CD4 + T cells were isolated from wild type (PKC-θ- WT) or PKC-θ null (PKC-θ-KO)
GM-CSF Autoantibody-positive Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis with Simultaneous Myeloproliferative Neoplasm
 CASE REPORT GM-CSF Autoantibody-positive Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis with Simultaneous Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Naoto Imoto 1, Nakashima Harunori 2, Katsuya Furukawa 1, Naoyuki Tange 1,3, Atsushi
CASE REPORT GM-CSF Autoantibody-positive Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis with Simultaneous Myeloproliferative Neoplasm Naoto Imoto 1, Nakashima Harunori 2, Katsuya Furukawa 1, Naoyuki Tange 1,3, Atsushi
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT) and NQO1-null (NQO1-/-) mice.
 competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
competes with 20S proteasome for binding with C/EBP leading to its stabilization and Relative mrna levels Supplement Figure S1. Real Time PCR analysis of mrna levels of C/EBPα and PU.1 in wild type (WT)
Assessment and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a reference center
 Campo et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2013, 8:40 RESEARCH Assessment and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a reference center Open Access Ilaria Campo 1, Francesca Mariani 1, Giuseppe
Campo et al. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases 2013, 8:40 RESEARCH Assessment and management of pulmonary alveolar proteinosis in a reference center Open Access Ilaria Campo 1, Francesca Mariani 1, Giuseppe
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Supplemental Material. Results
 Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
Supplemental Material Results Fractionation of mouse plasma by high-resolution SEC. APOA1 eluted as a single major peak in fractions 16 of plasma (the apparent size of mature, lipidated HDL) when it was
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland Approved for public release; distribution unlimited
 AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
AD (Leave blank) Award Number: W81XWH-07-1-0345 TITLE: Second-Generation Therapeutic DNA Lymphoma Vaccines PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Larry W. Kwak, M.D., Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Texas
Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy: a case report
 Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Bisicchia and Tudisco BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2013, 14:285 CASE REPORT Open Access Re-growth of an incomplete discoid lateral meniscus after arthroscopic partial resection in an 11 year-old boy:
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults
 Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
Clinical Commissioning Policy: Rituximab for the treatment of idiopathic membranous nephropathy in adults Reference: NHS England: 16047/P NHS England INFORMATION READER BOX Directorate Medical Operations
% of live splenocytes. STAT5 deletion. (open shapes) % ROSA + % floxed
 Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Supp. Figure 1. a 14 1 1 8 6 spleen cells (x1 6 ) 16 % of live splenocytes 5 4 3 1 % of live splenocytes 8 6 4 b 1 1 c % of CD11c + splenocytes (closed shapes) 8 6 4 8 6 4 % ROSA + (open shapes) % floxed
Rapid and Robust B Cell Depletion in Preliminary Results of a Phase 2 Study of Ublituximab, Novel Glycoengineered Anti-CD20 Mab, RMS Patients
 Rapid and Robust B Cell Depletion in Preliminary Results of a Phase 2 Study of Ublituximab, Novel Glycoengineered Anti-CD20 Mab, RMS Patients Amy Lovett-Racke, PhD May 26, 2017 2 Slide 1 2 Go to slide
Rapid and Robust B Cell Depletion in Preliminary Results of a Phase 2 Study of Ublituximab, Novel Glycoengineered Anti-CD20 Mab, RMS Patients Amy Lovett-Racke, PhD May 26, 2017 2 Slide 1 2 Go to slide
Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ
 Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
ANCA associated vasculitis in China
 ANCA associated vasculitis in China Min Chen Renal Division, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, P. R. China 1 General introduction of AAV in China Disease spectrum and ANCA type Clinical
ANCA associated vasculitis in China Min Chen Renal Division, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing 100034, P. R. China 1 General introduction of AAV in China Disease spectrum and ANCA type Clinical
Goals. Goals. From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice
 From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice Zachary T Freeman Goals Understand relevant immunology related to humanized mice Understand three main components that contribute to formation of humanized
From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice Zachary T Freeman Goals Understand relevant immunology related to humanized mice Understand three main components that contribute to formation of humanized
From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice. Zachary T Freeman
 From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice Zachary T Freeman Goals Understand relevant immunology related to humanized mice Understand three main components that contribute to formation of humanized
From Bench to Cageside: Immunology of Humanizing Mice Zachary T Freeman Goals Understand relevant immunology related to humanized mice Understand three main components that contribute to formation of humanized
Lysosomal Phospholipase A2 is Selectively Expressed in Alveolar Macrophages*
 JBC Papers in Press. Published on August 4, 2004 as Manuscript M407834200 Lysosomal phospholipase A2 Lysosomal Phospholipase A2 is Selectively Expressed in Alveolar Macrophages* Akira Abe, * Miki Hiraoka,
JBC Papers in Press. Published on August 4, 2004 as Manuscript M407834200 Lysosomal phospholipase A2 Lysosomal Phospholipase A2 is Selectively Expressed in Alveolar Macrophages* Akira Abe, * Miki Hiraoka,
Hereditary Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Pathogenesis, Presentation, Diagnosis, and Therapy
 Hereditary Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Pathogenesis, Presentation, Diagnosis, and Therapy Takuji Suzuki 1, Takuro Sakagami 1, Lisa R. Young 2,3, Brenna C. Carey 1, Robert E. Wood 2, Maurizio Luisetti
Hereditary Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Pathogenesis, Presentation, Diagnosis, and Therapy Takuji Suzuki 1, Takuro Sakagami 1, Lisa R. Young 2,3, Brenna C. Carey 1, Robert E. Wood 2, Maurizio Luisetti
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Serum KL-6 in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: China compared historically with Germany and Japan
 Original Article Serum KL-6 in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: China compared historically with Germany and Japan Wen-Liang Guo*, Zi-Qing Zhou*, Lu Chen, Zhu-Quan Su, Chang-Hao Zhong, Yu Chen, Shi-Yue
Original Article Serum KL-6 in pulmonary alveolar proteinosis: China compared historically with Germany and Japan Wen-Liang Guo*, Zi-Qing Zhou*, Lu Chen, Zhu-Quan Su, Chang-Hao Zhong, Yu Chen, Shi-Yue
Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker
 A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
A Study of the Origin of Pulmonary Macrophages Using the Ch6diak-Higashi Marker Kent J. Johnson, MD, Peter A. Ward, MD, Gary Striker, MD, and Robin Kunkel, MS Using bone marrow reconstitution techniques
4. Th1-related gene expression in infected versus mock-infected controls from Fig. 2 with gene annotation.
 List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
List of supplemental information 1. Graph of mouse weight loss during course of infection- Line graphs showing mouse weight data during course of infection days 1 to 10 post-infections (p.i.). 2. Graph
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies. Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018
 Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
Targeting tumour associated macrophages in anti-cancer therapies Annamaria Gal Seminar Series on Drug Discovery Budapest 5 January 2018 Macrophages: Professional phagocytes of the myeloid lineage APC,
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A
 Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A case report with a review of literature. Abstract Background Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a rare lung disorder,
Alveolar proteinosis in a patient recovering from Pneumocystis carinii infection: A case report with a review of literature. Abstract Background Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis is a rare lung disorder,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
Supporting Information Desnues et al. 10.1073/pnas.1314121111 SI Materials and Methods Mice. Toll-like receptor (TLR)8 / and TLR9 / mice were generated as described previously (1, 2). TLR9 / mice were
IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia
 Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Supplementary Figures IL-34 is a tissue-restricted ligand of CSF1R required for the development of Langerhans cells and microglia Yaming Wang, Kristy J. Szretter, William Vermi, Susan Gilfillan, Cristina
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy. Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L.
 Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
METHODS. participated in the study. Each subject had a normal physical examination, chest
 METHODS Subjects Thirty-four subjects (20 men and 14 women, mean age 28.5 ± 1.2 yr) participated in the study. Each subject had a normal physical examination, chest radiograph, electrocardiogram, and laboratory
METHODS Subjects Thirty-four subjects (20 men and 14 women, mean age 28.5 ± 1.2 yr) participated in the study. Each subject had a normal physical examination, chest radiograph, electrocardiogram, and laboratory
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population
 Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Lack of association of IL-2RA and IL-2RB polymorphisms with rheumatoid arthritis in a Han Chinese population J. Zhu 1 *, F. He 2 *, D.D. Zhang 2 *, J.Y. Yang 2, J. Cheng 1, R. Wu 1, B. Gong 2, X.Q. Liu
Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
 Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
Case Report Accumulation of periostin in acute exacerbation of familial idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis Keisuke Murata 1, Yasuhiko Koga 1, Norimitsu Kasahara 1, Yoshimasa Hachisu 1, Satoshi Nunomura 2, Nozomi
MATERIALS AND METHODS. Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
MATERIALS AND METHODS Antibodies (Abs), flow cytometry analysis and cell lines Neutralizing antibodies specific to mouse Dll1, Dll4, J1 and J2 were prepared as described. 1,2 All other antibodies used
Pair-fed % inkt cells 0.5. EtOH 0.0
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
MATERIALS AND METHODS Histopathological analysis Liver tissue was collected 9 h post-gavage, and the tissue samples were fixed in 1% formalin and paraffin-embedded following a standard procedure. The embedded
Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3
 Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
Supplemental Figure Legends. Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in Luminal A breast cancers harboring ERBB3 ErbB3 gene copy number gain. Supplemental Figure S1. ERBB3 mrna levels are elevated in
JOMA REVIEW ARTICLE ABSTRACT. Epidemiology. Classification INTRODUCTION
 REVIEW ARTICLE Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Where 10.5005/jp-journals-10070-0010 Do We Stand? 1 Mandeep K Sodhi, 2 S Narayanan ABSTRACT Aim: This review intends to recapitulate the knowledge about pulmonary
REVIEW ARTICLE Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis Where 10.5005/jp-journals-10070-0010 Do We Stand? 1 Mandeep K Sodhi, 2 S Narayanan ABSTRACT Aim: This review intends to recapitulate the knowledge about pulmonary
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis
 Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
Mechanisms of Cell Injury: Loss of Calcium Homeostasis SCPA610: Cellular Pathology Amornrat N. Jensen, Ph.D. amornrat.nar@mahidol.ac.th Leading questions Why is intracellular calcium important for the
