Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine
|
|
|
- Aubrey Townsend
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article Regulation of macrophage cholesterol efflux and liver X receptor α activation by nicotine Hongming Zhang 1, Xiaoyan Li 1, Zongjie Qian 2 1 Department of Cardiology, The General Hospital of Jinan Military Region, Jinan , P. R. China; 2 Institute of Cardiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical College, Guilin , P. R. China Received May 19, 2015; Accepted July 10, 2015; Epub September 15, 2015; Published September 30, 2015 Abstract: Objective: This study aims to investigate the characteristics of liver X receptor α (LXRα) and its target gene expression, as well as cholesterol efflux in human macrophages treated by nicotine. Methods: Human monocytederived macrophages were collected. Before apoa-i-mediated human monocyte-derived macrophage cholesterol efflux, and mrna expression of LXRα, and some of its target genes being detected, the macrophages were induced with or without nicotine. Results: Pre-incubation of Human monocyte-derived macrophages with nicotine, cholesterol efflux was suppressed to apolipoprotein AI. Nicotine also inhibited LXRαand some of its target genes mrna expression involved cholesterol metabolism, and facilitated some inflammatory genes expression. Conclusion: The changed function of cholesterol efflux and some genes expression may be the pathogenetic cause, and LXR activity of macrophage may offer potential therapeutic benefit in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Thus nicotine can regulate foam cell formation by inhibiting LXR pathway. Keywords: Nicotine, cholesterol efflux, human monocyte-derived macrophage, liver X receptor Introduction Early atherosclerotic lesion was the aggregation of macrophage rich in cholesterol under vascular endothelium. Macrophages changed into foam cells in the artery wall under various complicated mechanisms, thus started the atherosclerotic lesion. In the internal macrophage, liver X receptor (LXR) and the signal induced by LXR were important molecular basis for its lipid metabolism, and was also an important link of atherosclerosis induced by macrophages [1]. Nicotine was considered to be an important component in tobacco which causes atherosclerosis. However, the mechanism was still poorly understood. Lau et al [2] found that in LDLR -/- model, local lesions in arterial wall increased significantly after treatment by nicotine, the expression of nuclear factor κb (NFκB) upregulated, which suggested the enhanced inflammation. So nicotine induced atherosclerosis may be related with the inflammatory effect. In this study, we explored the effect of nicotine on LXR signal pathway and macrophage cholesterol efflux. Materials and methods Isolation of monocytes from peripheral blood of normal human volunteers Human monocytes were obtained from peripheral blood of normal human volunteers through Ficoll density gradient centrifugation. The monocytes were diluted in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA) and seeded in 6-well plates at a density of cells/ml. The monocytes were incubated at 37 C with 5% CO 2 for 2 hours. Adherent monocytes with the purity of more than 90% and the viability of more than 95% could then be harvested for further experimentation. Transformation of macrophages According to reference [3], the monocytes at a density of /ml were cultured in 6-well plates with RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS, 100 u/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin and mol/l phorbol 12-myri-
2 Table 1. Primers Used for RT-PCR Gene Primers (5-3 ) Product (bp) LXRα F: CTTCTGGAGACATCTCGGAGGT 410 R: CTGATAGCAATGAGCAAGGCAA ABCA1 F: ATAAGCCCTCTATACATAAATGCC 470 R: ACAGCGTAAAGTGCTTGGAATG SREBP2 F: ATAGGTGGCAGGGCAGAAAC 300 R: AATCAAGACGCTACAGCAACTCA CETP F: AAGATGCCCAAGATCTCCTG 445 R: AAGCTCTGGAGGAAATCCAC PLTP F: CTGCGAGAGGTGATTGAGAAGA 330 R: CAGGCTATGAATGTGGGAAAAG apoe F: GCGGATGGAGGAGATGGG 304 R: AGGCAGGAGGCACGGGGT MMP-9 F: CTTCCAGTACCGAGAGAAAGCC 200 R: CAAAGGTGAGAAGAGAGGGCC MIP-1α F: CGCCTGCTGCTTCAGCTACAC 200 R: TGTGGAGGTCACACGCATGTT GAPDH F: CCCATGTTCGTCATGGGTGT 140 R: TGGTCATGAGTCCTTCCACGATA ABCA1: ATP binding cassette A1; SREBP2: sterol regulatory element binding protein; PLTP: phospholipid transfer protein; CETP: cholesterol ester transfer protein. Table 2. Effect of nicotine on apoa-i mediated cholesterol efflux in macrophages (%, _ x ± s, n=20) Group 0 (ng/ml) 100 (ng/ml) Without TO ± ±1.14 With TO ± ±1.57, P<0.01, vs. groups without TO ; P<0.05, vs. groups without nicotine. state 13-acetate (PMA, Alexis Biochemicals, Lausen, Switzerland) at 37 C with 5% CO 2 for 24 hours. Determination of cholesterol efflux The cholesterol efflux was determined as previously described [4]. The cells at a density of /ml were cultured in 6-well plates with RPMI 1640 medium containing 10% FBS, 100 u/ml penicillin and 100 μg/ml streptomycin and 0.2 μci/l [3H] cholesterol (40-60 Ci/mmol; NEN, Boston, MA) for 48 h. Then they were washed with PBS and re-cultured in 6-well plates at a density of /ml. They were divided into four groups: 0 ng/ml nicotine with 2 μmol/l of TO group, 0 ng/ml nicotine without 2 μmol/l TO group, 100 ng/ml nicotine with 2 μmol/l TO group and 100 ng/ml nicotine without 2 μmol/l TO group. After culture for 24 h, the cells were washed with PBS and cultured with RPMI 1640 medium containing 10 μg/l apoa-i (Academy Bio-medical, Houston, TX) without FBS for 12 h. [3H] Cholesterol was determined in the efflux media and cells by scintillation counting. Cholesterol efflux (%) was calculated as CPM (counts/min) in the efflux media divided by total CPM (media plus cells) and multiplied by 100%. Reverse transcription polymerase chain reactions (RT-PCR) Total RNA was extracted from cells of each group by using RNAeasy kits from Qiagen (Valencia, CA). The TaqMan one-step RT-PCR Master Mix Reagent Kit was used to determine relative expression levels of mrna genes using the ABI Prism 7700 sequence detection system (Applied Biosystems) according to the manufacturer s instructions. Primer sequences used in this study were shown in Table 1. PCR reaction conditions were 94 C, 5 min; 35 cycles of 94 C, 1 min; 55 C, 1 min and 72 C, 1 min; then 72 C, 10 min. The expression levels were normalized using GAPDH as control. Data analysis SPSS 16.0 statistical software was used for statistical analysis. Measurement data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Differences between two groups were evaluated by analysis of variance (ANOVA) and t-test. P<0.05 was considered statistical significance. Results Effects of nicotine on cholesterol efflux in macrophages In this study, we found that cholesterol efflux mediated by apoa-i in macrophages obtained from human peripheral blood was decreased under 100 ng/ml nicotine. LXR activated by TO in macrophages promoted cholesterol efflux but 100 ng/ml nicotine could inhibit it (Table 2). Effects of nicotine on the expression of LXRα and its downstream genes The expression levels of LXRα, ATP binding cassette A1 (ABCA1), sterol regulatory element Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):
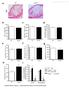
3 Figure 1. Gel electrophoresis map for PCR results of LXRα and its target genes in macrophage. M: DNA marker; 1: without TO and nicotine; 2: with TO and without nicotine; 3: nicotine 100 ng/ml without TO ; 4: nicotine 100 ng/ml with TO ; A: LXRα; B: ABCA1; C: CETP; D: SREBP2; E: apoe; F: PLTP; G: MMP-9; H: MIP-1α Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):
4 Table 3. Effect of nicotine on LXRα and its target gene expression in macrophages (%, _ x ± s, n=20) Genes 0 ng/ml nicotine without TO ng/ml nicotine with TO ng/ml nicotine without TO ng/ml nicotine with TO LXRα 29.33± ±2.58 * 18.12± ±2.74 ABCA ± ±3.34 * 17.48± ±1.78 *, SREBP ± ±2.75 * 10.73± ±1.94 *, CETP 28.09± ±2.73 * 13.75± ±2.37 *, PLTP 36.85± ±2.71 * 21.93± ±2.84 *, apoe 34.49± ±3.81 * 16.47± ±2.73 *, MMP ± ±2.19 * 41.38± ±2.23 *, MIP-1α 21.18± ±2.75 * 40.92± ±2.04 *, * P<0.01, vs. group without TO between similar saturation of nicotine; P<0.01, P<0.05 vs. group 0 ng/ml nicotine without TO ; P<0.01 vs. group 0 ng/ml nicotine without TO binding protein (SREBP2), phospholipid transfer protein (PLTP), apoe and cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) were down-regulated under nicotine; the expression levels of ABCA1, SREBP2, PLTP, apoe and CETP were up-regulated under TO Nicotine could increase the expression levels of MMP-9 and MIP-1α while TO could decrease them (Figure 1; Table 3). Discussion The characteristics of atherosclerotic lesions are the changes of lipid metabolism in arterial wall resulting in chronic inflammation of vascular wall. Circulating monocytes entered the vascular endothelial space and differentiated into macrophages. These macrophages accumulated cholesteryl ester and transformed to foam cells when oxidized low density lipoprotein (oxldl) existed which lead to the formation of atherosclerosis. LXR belongs to the nuclear receptor superfamily of ligand activated transcription factor which including LXRα (NR1H3), LXR and retinoic acid receptor (RXR) heteromers. Some metabolites of cholesterol were their endogenous activation ligand, the synthetic GW3965 and TO were their specific activators. LXR regulated the expression of target gene by directly binding the LXR response element (LXRE). It promoted or inhibited the expression of target gene through interaction with co-stimulatory factor or co-repressor. Recent studies showed that many genes involved in lipid metabolism balance, inflammatory and immune responses were regulated by LXR [1]. In macrophages, LXR regulated the balance of macrophage lipid metabolism after activating by endogenous ligand. At the same time, the activation of LXR can inhibit the expression of some proinflammatory genes [6]. In this study we found that in macrophages cultured in vitro the activated LXR could up-regulate the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism such as ABCA1, SREBP2, PLTP, apoe and CETP, it also could promote macrophage cholesterol efflux. On the contrary, the expression of genes involved in inflammatory reaction such as MMP-9 and MIP- 1α were down-regulated. When the signal regulating cholesterol balance failed in macrophages it could lead to the formation of foam cells [7]. The activation of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages was the direct cause of the formation of foam cells and artery atheromatous lesions. It is widely recognized by people that smoking is a risk factor of atherosclerosis. Nicotine is the main harmful component. In general, the physiological roles of nicotine were mediated by binding with its nicotinic acetylcholine (nach) receptor. Heeschen reported that nicotine promoted the progress of atherosclerotic plaque lesions which leading to cardiac ischemic events occurred [8]. Aicher found that nicotine activated antigen-presenting cells in lesions and mainly activated several kinases, such as ERK1/2, p38mapk and Akt. The activation of these cell kinases caused antigen presenting cells to activate innate or acquired immune function and secreted a large number of inflammatory cytokines involved in the immune and inflammatory responses, and leaded to the progression of atherosclerosis eventually [9]. Lau [2] found that nicotine leaded to the atheroscle Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):
5 rosis depended on promoting the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in macrophages. The mechanism maybe nicotine directly induced the expression of inos and TNF-α in monocytes and macrophages through nach receptors. NF-κB could be activated by activated macrophages and nicotine could activate VCAM-1, COX-2 and PDGFβ after stimulating the target genes of NF-κB. These bioactive substances played important roles in the infiltration of inflammatory cells, migration and proliferation of smooth muscle cells, promoted the progress of atherosclerotic plaque lesions [5]. There were few studies on the effect of nicotine on lipid metabolism. It was reported that nicotine could inhibit the activity of CETP and PLTP [10]. In conclusion, in this study we found that nicotine could inhibit the LXR signaling pathway, affect the cholesterol efflux of macrophages and promote inflammation through LXR pathway, which may be one aspect of smoking can cause atherosclerosis. Acknowledgements This study was supported by the projects No , 2012GXNSFAA053080, s and YB Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Zongjie Qian, Department of Cardiology, the Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical College, Guilin , China. Tel: ; References [1] Levin N, Bischoff ED, Daige CL, Thomas D, Vu CT, Heyman RA, Tangirala RK and Schulman IG. Macrophage liver X receptor is required for antiatherogenic activity of LXR agonists. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2005; 25: [2] Lau PP, Li L, Merched AJ, Zhang AL, Ko KW and Chan L. Nicotine induces proinflammatory responses in macrophages and the aorta leading to acceleration of atherosclerosis in low-density lipoprotein receptor (-/-) mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2006; 26: [3] Suzuki S, Nishimaki-Mogami T, Tamehiro N, Inoue K, Arakawa R, Abe-Dohmae S, Tanaka AR, Ueda K and Yokoyama S. Verapamil increases the apolipoprotein-mediated release of cellular cholesterol by induction of ABCA1 expression via Liver X receptor-independent mechanism. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: [4] Lin GR and Bornfeldt KE. Cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors promote ABC- A1 expression and cholesterol efflux. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 290: [5] Zhang SL, Day I and Ye S. Nicotine induced changes in gene expression by human coronary artery endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 2001; 154: [6] Ricote M, Valledor AF and Glass CK. Decoding transcriptional programs regulated by PPARs and LXRs in the macrophage: effects on lipid homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: [7] Von EA, Nofer JR and Assmann G. High density lipoproteins and arteriosclerosis. Role of cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2001; 21: [8] Heeschen C, Jang JJ, Weis M, Pathak A, Kaji S, Hu RS, Tsao PS, Johnson FL and Cooke JP. Nicotine stimulates angiogenesis and promotes tumor growth and atherosclerosis. Nat Med 2001; 7: [9] Aicher A, Heeschen C, Mohaupt M, Cooke JP, Zeiher AM and Dimmeler S. Nicotine strongly activates dendritic cell-mediated adaptive immunity: potential role for progression of atherosclerotic lesions. Circulation 2003; 107: [10] Zhu PT, Bo P and Sun Y. Study on the correlation between Chinese medical syndrome types and serum levels of PLTP and CETP in coronary heart disease patients. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi 2011; 31: Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(9):
Summary and concluding remarks
 Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
Summary and concluding remarks This thesis is focused on the role and interaction of different cholesterol and phospholipid transporters. Cholesterol homeostasis is accomplished via a tightly regulated
G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille, France
 LIVER X RECEPTORS (LXRS): TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATORS OF MACROPHAGE CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille,
LIVER X RECEPTORS (LXRS): TRANSCRIPTIONAL REGULATORS OF MACROPHAGE CHOLESTEROL METABOLISM G. Chinetti-Gbaguidi and B. Staels, UR 545 INSERM, Institut Pasteur de Lille and Université de Lille 2, Lille,
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry
 Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Lipoproteins Metabolism Reference: Campbell Biochemistry and Lippincott s Biochemistry Learning Objectives 1. Define lipoproteins and explain the rationale of their formation in blood. 2. List different
Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling
 Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling Noam Zelcer and Peter Tontonoz Review series Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, UCLA,
Liver X receptors as integrators of metabolic and inflammatory signaling Noam Zelcer and Peter Tontonoz Review series Howard Hughes Medical Institute, Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine, UCLA,
Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ
 Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Research article Related Commentary, page 1538 Differential inhibition of macrophage foam-cell formation and atherosclerosis in mice by PPARα, β/δ, and γ Andrew C. Li, 1 Christoph J. Binder, 2 Alejandra
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
Leptin deficiency suppresses progression of atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice Atherosclerosis, 2007 Chiba T, Shinozaki S, Nakazawa T, et al. Present by Sudaporn Pummoung Apolipoprotein E (apoe( apoe)
 Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
Glossary For TheFatNurse s For All Ages Series Adipocytes, also known as lipocytes and fat cells, are the cells that primarily compose adipose tissue, specialized in storing energy as fat. Apolipoprotein
2.5. AMPK activity
 Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplement Fig. A 3 B phos-ampk 2.5 * Control AICAR AMPK AMPK activity (Absorbance at 45 nm) 2.5.5 Control AICAR Supplement Fig. Effects of AICAR on AMPK activation in macrophages. J774. macrophages were
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
High density lipoprotein metabolism
 High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
High density lipoprotein metabolism Lipoprotein classes and atherosclerosis Chylomicrons, VLDL, and their catabolic remnants Pro-atherogenic LDL HDL Anti-atherogenic Plasma lipid transport Liver VLDL FC
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema
 The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
The inhibition of CETP: From simply raising HDL-c to promoting cholesterol efflux and lowering of atherogenic lipoproteins Prof Dr J Wouter Jukema Dept Cardiology, Leiden University Medical Center, Leiden,
Dyslipidemia Endothelial dysfunction Free radicals Immunologic
 ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
ATHEROSCLEROSIS Hossein Mehrani Professor of Clinical Biochemistry Definition Atherosclerosis: Is a chronic inflammatory process characterized by plaque formation within the vessel wall of arteries and
By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
 Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Resveratrol could partly improve the crosstalk between canonical β-catenin/wnt and FOXO pathways in coronary artery disease patients with metabolic syndrome: A case control study By: Dr Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts
 Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
Effects of the angiotensin II type-1 receptor antagonist telmisartan on endothelial activation induced by advanced glycation endproducts Serena Del Turco, Teresa Navarra, Giuseppina Basta, Raffaele De
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng.3561
 Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
Supplementary Figure 1 Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation and APOB p.gly1829glufs8 mutation (a,b) Pedigrees of families with APOB p.gln725* mutation. (c) Pedigree of family with APOB p.gly1829glufs8
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
PPAR history of research
 PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
PPAR Rubens, 1640 PPAR history of research number of publications 3000 2000 1000 0 till now: : 16 296 publications 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 year liver, brown adipocytes, kidney, heart, skeletal muscles,
JLR Papers In Press. Published on October 16, 2003 as Manuscript D JLR200
 JLR Papers In Press. Published on October 16, 2003 as Manuscript D300024-JLR200 A method of direct measurement for the enzymatic determination of cholesterol esters Toshimi Mizoguchi 1, Toshiyuki Edano,
JLR Papers In Press. Published on October 16, 2003 as Manuscript D300024-JLR200 A method of direct measurement for the enzymatic determination of cholesterol esters Toshimi Mizoguchi 1, Toshiyuki Edano,
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview)
 Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Lipid/Lipoprotein Structure and Metabolism (Overview) Philip Barter President, International Atherosclerosis Society Centre for Vascular Research University of New South Wales Sydney, Australia Disclosures
Taylor Yohe. Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury. Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State University
 Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Atherosclerosis Development and the Inflammatory Response of Hepatocytes to Sesame Oil Supplementation Taylor Yohe Project Advisor: Dr. Martha A. Belury Department of Human Nutrition at the Ohio State
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN /07/$32.
 Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Journal of the American College of Cardiology Vol. 50, No. 24, 2007 2007 by the American College of Cardiology Foundation ISSN 0735-1097/07/$32.00 Published by Elsevier Inc. doi:10.1016/j.jacc.2007.07.081
Supporting Information Table of content
 Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Supporting Information Table of content Supporting Information Fig. S1 Supporting Information Fig. S2 Supporting Information Fig. S3 Supporting Information Fig. S4 Supporting Information Fig. S5 Supporting
Child born in year /3 will die before parents in US (diabetes)
 Child born in year 2000-1/3 will die before parents in US (diabetes) ATP III identified 6 components of the metabolic syndrome that relate to CVD 1. Abdominal obesity 2. Atherogenic dyslipidemia (elevated
Child born in year 2000-1/3 will die before parents in US (diabetes) ATP III identified 6 components of the metabolic syndrome that relate to CVD 1. Abdominal obesity 2. Atherogenic dyslipidemia (elevated
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy
 Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Oncolytic Adenovirus Complexes Coated with Lipids and Calcium Phosphate for Cancer Gene Therapy Jianhua Chen, Pei Gao, Sujing Yuan, Rongxin Li, Aimin Ni, Liang Chu, Li Ding, Ying Sun, Xin-Yuan Liu, Yourong
Nature Medicine doi: /nm.3150
 Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
Nature Medicine doi:10.1038/nm.3150 Supplementary Table 1 Primer sequences used for q-pcr analysis Gene Forward primer Reverse primer Abca1 CAGCTTCCATCCTCCTTGTC CCACATCCACAACTGTCTGG Abcg1 GTACCATGACATCGCTGGTG
 Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Acetyl CoA HMG CoA Mevalonate (C6) Dimethylallyl Pyrophosphate isopentenyl Pyrophosphate (C5) Geranyl Pyrophosphate (C10) FarnesylPyrophosphate (C15) Squalene (C30) Lanosterol (C30) 7 Dehydrocholesterol
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy. Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L.
 Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Potential Atheroprotective Effects of Ixmyelocel-T Cellular Therapy Kelly J. Ledford, Nikki Murphy, Frank Zeigler, Ronnda L. Bartel 1 Ixmyelocel-T, an expanded, autologous multicellular therapy cultured
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD
 Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Role of apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins in the development of atherosclerosis Jan Borén MD, PhD Our laboratory focuses on the role of apolipoprotein (apo) B- containing lipoproteins in normal
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL
 Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Metabolism and Atherogenic Properties of LDL Manfredi Rizzo, MD, PhD Associate Professor of Internal Medicine Faculty of Medicine, University of Palermo, Italy & Affiliate Associate Professor of Internal
Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR
 Supplement Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) Reference Human ST2 CTTGATTGATAAACAGAATG CTGATCCAGATACTGTTGAA
Supplement Supplementary Table I - Primers used for real-time quantitative PCR and RT-PCR Gene Forward Primer (5-3 ) Reverse primer (5-3 ) Reference Human ST2 CTTGATTGATAAACAGAATG CTGATCCAGATACTGTTGAA
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
DYNAMICS IN EXPRESSION OF THE IL-12 RELATED CYTOKINE TRANSCRIPTS OF IL-12A, IL-12B AND IL-23 AFTER STIMULATION OF HUMAN PBMC
 Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 7-11, 2008 Copyright 2008 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
Trakia Journal of Sciences, Vol. 6, No. 1, pp 7-11, 2008 Copyright 2008 Trakia University Available online at: http://www.uni-sz.bg ISSN 1312-1723 (print) ISSN 1313-3551 (online) Original Contribution
ESC Congress 2011 Wednesday August 31st 2011
 ESC Congress 211 Wednesday August 31st 211 stimulates endothelial CAT-1 expression and L-arginine uptake: a novel mechanism leading to endothelial-protective effects of that is profoundly impaired in patients
ESC Congress 211 Wednesday August 31st 211 stimulates endothelial CAT-1 expression and L-arginine uptake: a novel mechanism leading to endothelial-protective effects of that is profoundly impaired in patients
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui
 Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Chapter VIII: Dr. Sameh Sarray Hlaoui Lipoproteins a Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Clusters of proteins and lipids.
Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2 and 4.
 Toll Like Receptor Response and traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis: Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2
Toll Like Receptor Response and traditional risk factors for atherosclerosis: Obesity is related to a higher inflammatory responsive state of circulating cells after stimulation of toll like receptor 2
Atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory response to. Neopterin Counters Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis ORIGINAL RESEARCH
 Neopterin Counters Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Remina Shirai, MSc; Kengo Sato, PhD; Tomoyuki Yamashita, BSc; Maho Yamaguchi, BSc; Taisuke Okano, BSc; Kaho Watanabe-Kominato, MSc; Rena Watanabe,
Neopterin Counters Vascular Inflammation and Atherosclerosis Remina Shirai, MSc; Kengo Sato, PhD; Tomoyuki Yamashita, BSc; Maho Yamaguchi, BSc; Taisuke Okano, BSc; Kaho Watanabe-Kominato, MSc; Rena Watanabe,
Regulating Hepatic Cellular Cholesterol
 Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
Under circumstances of cholesterol deficiency, Sterol Regulatory Element Binding Proteins (SREBPs) via binding to DNA nuclear response elements set off genomic production of proteins and enzymes that induce
The relationship between coronary artery disease and low
 Cellular Phospholipid and Cholesterol Efflux in High-Density Lipoprotein Deficiency Michel Marcil, PhD; Rachel Bissonnette, MSc; Jérôme Vincent, DEA; Larbi Krimbou, DES; Jacques Genest, MD Background Prospective
Cellular Phospholipid and Cholesterol Efflux in High-Density Lipoprotein Deficiency Michel Marcil, PhD; Rachel Bissonnette, MSc; Jérôme Vincent, DEA; Larbi Krimbou, DES; Jacques Genest, MD Background Prospective
NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video
 NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video 혈관연구회추계학회 2007.10.13 Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon University Gil Medical Center Incheon, Korea Cytokines oxldl Ang
NAM JUNE PAIK: Rhapsody in Video 혈관연구회추계학회 2007.10.13 Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone System Kwang Kon Koh, MD, FACC, FAHA Cardiology Gachon University Gil Medical Center Incheon, Korea Cytokines oxldl Ang
Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction
 Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Andrew Zalewski, M.D. Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia Why inflammation? Population-based studies: low
Inflammation: Novel Target for Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Andrew Zalewski, M.D. Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia GlaxoSmithKline, Philadelphia Why inflammation? Population-based studies: low
Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors
 Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors Huey Jing Huang* and Ira G. Schulman { *Department of Biology, Exelixis Inc., 4757 Nexus Centre Drive, San Diego, California 92121 { Center for Molecular
Regulation of Metabolism by Nuclear Hormone Receptors Huey Jing Huang* and Ira G. Schulman { *Department of Biology, Exelixis Inc., 4757 Nexus Centre Drive, San Diego, California 92121 { Center for Molecular
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis
 Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Arteriosclerosis & Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis = hardening of arteries = arterial wall thickening + loss of elasticity 3 types: -Arteriolosclerosis -Monckeberg medial sclerosis -Atherosclerosis Arteriosclerosis,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ. Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University
 Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
Adipose Tissue as an Endocrine Organ Abdel Moniem Ibrahim, MD Professor of Physiology Cairo University Functions of Adipose Tissue Adipose tissue expresses and secretes a variety of bioactive peptides,
and Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine
 PPAR- Agonist and In-Stent Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine Peroxisome Proliferator- activated Receptors (PPAR) Lipid-activated transcription factors : => regulating
PPAR- Agonist and In-Stent Restenosis Yangsoo Jang, MD, PhD. Yonsei University College of Medicine Peroxisome Proliferator- activated Receptors (PPAR) Lipid-activated transcription factors : => regulating
Mechanisms underlying adverse effects of HDL on enos-activating pathways in patients with coronary artery disease
 Related Commentary, page 2545 Research article Mechanisms underlying adverse effects of HDL on enos-activating pathways in patients with coronary artery disease Christian Besler, 1,2,3 Kathrin Heinrich,
Related Commentary, page 2545 Research article Mechanisms underlying adverse effects of HDL on enos-activating pathways in patients with coronary artery disease Christian Besler, 1,2,3 Kathrin Heinrich,
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU. PhD THESIS Summary
 ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
ROMANIAN ACADEMY INSTITUTE OF CELLULAR BIOLOGY AND PATHOLOGY NICOLAE SIMIONESCU PhD THESIS Summary INVOLVEMENT OF ALARMIN HMGB1 IN INFLAMMATORY PROCESSES ASSOCIATED WITH VASCULAR DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERLIPIDEMIA
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins
 Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Unit IV Problem 3 Biochemistry: Cholesterol Metabolism and Lipoproteins - Cholesterol: It is a sterol which is found in all eukaryotic cells and contains an oxygen (as a hydroxyl group OH) on Carbon number
Atherosclerosis is the underlying cause of cardiovascular
 RP5-833A20.1/miR-382-5p/NFIA Dependent Signal Transduction Pathway Contributes to the Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis and Inflammatory Reaction Yan-Wei Hu, Jia-Yi Zhao, Shu-Fen Li, Jin-Lan Huang,
RP5-833A20.1/miR-382-5p/NFIA Dependent Signal Transduction Pathway Contributes to the Regulation of Cholesterol Homeostasis and Inflammatory Reaction Yan-Wei Hu, Jia-Yi Zhao, Shu-Fen Li, Jin-Lan Huang,
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
Ligand activation of LXRβ reverses atherosclerosis and cellular cholesterol overload in mice lacking LXRα and apoe
 Research article Ligand activation of LXRβ reverses atherosclerosis and cellular cholesterol overload in mice lacking LXRα and apoe Michelle N. Bradley, 1 Cynthia Hong, 1 Mingyi Chen, 1 Sean B. Joseph,
Research article Ligand activation of LXRβ reverses atherosclerosis and cellular cholesterol overload in mice lacking LXRα and apoe Michelle N. Bradley, 1 Cynthia Hong, 1 Mingyi Chen, 1 Sean B. Joseph,
Supplemental Table I.
 Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
Supplemental Table I Male / Mean ± SEM n Mean ± SEM n Body weight, g 29.2±0.4 17 29.7±0.5 17 Total cholesterol, mg/dl 534.0±30.8 17 561.6±26.1 17 HDL-cholesterol, mg/dl 9.6±0.8 17 10.1±0.7 17 Triglycerides,
INTRODUCTION. Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells
 Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
Induction of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) Expression by Angiotensin II (AngII) in the Pancreatic Islets and Beta Cells Galina Chipitsyna, Qiaoke Gong, Chance F. Gray et al. Endocrinology,
ATHEROSCLEROTIC cardiovascular complications are the leading cause of. Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease
 Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease To Decrease Plasma Adiponectin Levels Kuei-Chuan CHAN, 1 MD, Hsi-Hsien CHOU, 1 PhD, Der-Jinn WU, 1 PhD, Yi-Liang WU, 1 MD, and Chien-Ning
Diabetes Mellitus Has an Additional Effect on Coronary Artery Disease To Decrease Plasma Adiponectin Levels Kuei-Chuan CHAN, 1 MD, Hsi-Hsien CHOU, 1 PhD, Der-Jinn WU, 1 PhD, Yi-Liang WU, 1 MD, and Chien-Ning
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General
 Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Human Oxidized LDL ELISA Kit (MDA-LDL Quantitation), General For the detection and quantitation of human OxLDL in plasma, serum or other biological fluid samples Cat. No. KT-959 For Research Use Only.
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Hasoo, Manhl (2013) Regulation of liver X receptors by microrna- 155 in pulmonary fibrosis. PhD thesis.
 Hasoo, Manhl (2013) Regulation of liver X receptors by microrna- 155 in pulmonary fibrosis. PhD thesis. http://theses.gla.ac.uk/4563/ Copyright and moral rights for this thesis are retained by the author
Hasoo, Manhl (2013) Regulation of liver X receptors by microrna- 155 in pulmonary fibrosis. PhD thesis. http://theses.gla.ac.uk/4563/ Copyright and moral rights for this thesis are retained by the author
Stewart et al. CD36 ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer
 NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
NFκB (fold induction) Stewart et al. ligands promote sterile inflammation through assembly of a TLR 4 and 6 heterodimer a. mrna (fold induction) 5 4 3 2 1 LDL oxldl Gro1a MIP-2 RANTES mrna (fold induction)
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis. Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk
 The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
The New Gold Standard for Lipoprotein Analysis Advanced Testing for Cardiovascular Risk Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing The Lipid Panel Total Cholesterol = VLDL + LDL + HDL Evolution of Lipoprotein Testing
CD4-positive lymphocytes play a critical role in early
 LXR Activation Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human CD4-Positive Lymphocytes Daniel Walcher, Andreas Kümmel, Bettina Kehrle, Helga Bach, Miriam Grüb, Renate Durst, Vinzenz Hombach, Nikolaus
LXR Activation Reduces Proinflammatory Cytokine Expression in Human CD4-Positive Lymphocytes Daniel Walcher, Andreas Kümmel, Bettina Kehrle, Helga Bach, Miriam Grüb, Renate Durst, Vinzenz Hombach, Nikolaus
Original Article Adiponectin upregulates ABCA1 expression through liver X receptor alpha signaling pathway in RAW 264.
 Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(1):450-457 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0003356 Original Article Adiponectin upregulates ABCA1 expression through liver X receptor alpha signaling pathway in RAW 264.7
Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8(1):450-457 www.ijcep.com /ISSN:1936-2625/IJCEP0003356 Original Article Adiponectin upregulates ABCA1 expression through liver X receptor alpha signaling pathway in RAW 264.7
Cardiovascular Division, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School
 Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Low Endothelial Shear Stress Upregulates Atherogenic and Inflammatory Genes Extremely Early in the Natural History of Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Hyperlipidemic Juvenile Swine Michail I. Papafaklis,
Cardiology, CardioVascular Center University Hospital Zurich Zurich, Switzerland
 Modification of by the lipoxidation product malondialdehyde leads to LOX-1 dependent activation of endothelial PKCbeta-2 and adverse endothelial effects of in patients with coronary artery disease Christian
Modification of by the lipoxidation product malondialdehyde leads to LOX-1 dependent activation of endothelial PKCbeta-2 and adverse endothelial effects of in patients with coronary artery disease Christian
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Data Sheet. NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621
 Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Data Sheet NFAT Reporter (Luc) Jurkat Cell line Catalog #: 60621 Background The nuclear factor of activator T cells (NFAT) family of transcription factors plays an important role in immune response. T
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia
 Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Lipid metabolism in familial hypercholesterolemia Khalid Al-Rasadi, BSc, MD, FRCPC Head of Biochemistry Department, SQU Head of Lipid and LDL-Apheresis Unit, SQUH President of Oman society of Lipid & Atherosclerosis
Cholesterol Metabolism
 Cholesterol Metabolism Lippincott s Illustrated Review Chapter 18 Steroid Nucleus 1 2 Cholesterol was isolated from gall bladder stones in 1774 3 Sources and Elimination of Cholesterol Synthesis: 1000
Cholesterol Metabolism Lippincott s Illustrated Review Chapter 18 Steroid Nucleus 1 2 Cholesterol was isolated from gall bladder stones in 1774 3 Sources and Elimination of Cholesterol Synthesis: 1000
Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods.
 Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Supplemental Material Quantitative Real-Time PCR Quantitative Real-Time PCR was performed as same as Materials and Methods. Expression levels in the aorta were normalized to peptidylprolyl isomerase B
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona,
 Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
Marshall Tulloch-Reid, MD, MPhil, DSc, FACE Epidemiology Research Unit Tropical Medicine Research Institute The University of the West Indies, Mona, Jamaica At the end of this presentation the participant
9607 Dr. Perry Road Suite 103. Ijamsville, MD Tel: (301) Fax: (301) Ultrasensitive Samoa Human IL-33 Immunoassay
 AssayGate, Inc. 9607 Dr. Perry Road Suite 103. Ijamsville, MD 21754. Tel: (301)874-0988. Fax: (301)560-8288. Ultrasensitive Samoa Human IL-33 Immunoassay INTRODUCTION Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a cytokine
AssayGate, Inc. 9607 Dr. Perry Road Suite 103. Ijamsville, MD 21754. Tel: (301)874-0988. Fax: (301)560-8288. Ultrasensitive Samoa Human IL-33 Immunoassay INTRODUCTION Interleukin-33 (IL-33), a cytokine
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol
 Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Niacin Metabolism: Effects on Cholesterol By Julianne R. Edwards For Dr. William R. Proulx, PhD, RD Associate Professor of Nutrition and Dietetics In partial fulfillments for the requirements of NUTR342
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured
 Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
Supplemental Figure 1. Signature gene expression in in vitro differentiated Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17 and Treg cells. (A) Naïve CD4 + T cells were cultured under Th0, Th1, Th2, Th17, and Treg conditions. mrna
OxiSelect Human Oxidized HDL ELISA Kit (CML-HDL Quantitation)
 Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized HDL ELISA Kit (CML-HDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-888 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Product Manual OxiSelect Human Oxidized HDL ELISA Kit (CML-HDL Quantitation) Catalog Number STA-888 96 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Lipoproteins are submicroscopic
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate. immune responses by maintaining Btk activation
 Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Intracellular MHC class II molecules promote TLR-triggered innate immune responses by maintaining Btk activation Xingguang Liu, Zhenzhen Zhan, Dong Li, Li Xu, Feng Ma, Peng Zhang, Hangping Yao and Xuetao
Curriculum Vitae. Research Officer in Baker IDI Heart & Diabetes Institute from Aug
 Curriculum Vitae Yi Fu ( 付毅 ) (PhD, MBBS) Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute 75 Commercial Road, Prahran, Melbourne, VIC 3004 Australia Phone: +61 3 8532 1288 Email: yi.fu@bakeridi.edu.au PROFILE Research
Curriculum Vitae Yi Fu ( 付毅 ) (PhD, MBBS) Baker IDI Heart and Diabetes Institute 75 Commercial Road, Prahran, Melbourne, VIC 3004 Australia Phone: +61 3 8532 1288 Email: yi.fu@bakeridi.edu.au PROFILE Research
Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Supplemental Figure 1 ELISA scheme to measure plasma total, mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9 concentrations. 4 Plasma mature and furin-cleaved PCSK9s were measured by a sandwich
Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 deficiency leads to inhibition of macrophage proinflammatory activities and atherosclerosis in apoe-deficient mice
 RETRACTED View retraction Amendment history: Retraction (March 2012) Expression of concern (January 2012) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 deficiency leads to inhibition of macrophage proinflammatory
RETRACTED View retraction Amendment history: Retraction (March 2012) Expression of concern (January 2012) Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor-2 deficiency leads to inhibition of macrophage proinflammatory
The role of HDL-cholesterol in preventing atherosclerotic disease
 European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement F), F4 F8 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui036 The role of HDL-cholesterol in preventing atherosclerotic disease Philip Barter* The Heart Research Institute,
European Heart Journal Supplements (2005) 7 (Supplement F), F4 F8 doi:10.1093/eurheartj/sui036 The role of HDL-cholesterol in preventing atherosclerotic disease Philip Barter* The Heart Research Institute,
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA)
 HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
HRB IMDA Oct HRB 2010 IMDA Seminar 28 th Oct 2010 Potential mechanisms for the resolution of atherosclerosis by conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) Dr. Orina Belton, School of Biomolecular and Biomedical Science,
Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium. fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production
 Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005
 Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
Annals of Oncology Advance Access published January 10, 2005 Original article Annals of Oncology doi:10.1093/annonc/mdi077 Expression of survivin and bax/bcl-2 in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-g
PPARg phosphorylation mediated by JNK MAPK: a potential role in macrophage-derived
 Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2006 Sep; 27 (9): 1146 1152 Full-length article PPARg phosphorylation mediated by JNK MAPK: a potential role in macrophage-derived foam cell formation 1 Ran YIN 2, Yu-gang DONG
Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 2006 Sep; 27 (9): 1146 1152 Full-length article PPARg phosphorylation mediated by JNK MAPK: a potential role in macrophage-derived foam cell formation 1 Ran YIN 2, Yu-gang DONG
Patrick Linsel-Nitschke and Alan R. Tall
 HDL AS A TARGET IN THE TREATMENT F ATHERSCLERTIC CARDIVASCULAR DISEASE Patrick Linsel-Nitschke and Alan R. Tall Abstract Lipid abnormalities are among the key risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Indeed,
HDL AS A TARGET IN THE TREATMENT F ATHERSCLERTIC CARDIVASCULAR DISEASE Patrick Linsel-Nitschke and Alan R. Tall Abstract Lipid abnormalities are among the key risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Indeed,
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11):
 902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
902 Biomed Environ Sci, 2014; 27(11): 902-906 Letter to the Editor Curcuminoids Target Decreasing Serum Adipocyte-fatty Acid Binding Protein Levels in Their Glucose-lowering Effect in Patients with Type
Supplemental Information. T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism
 Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Immunity, Volume 33 Supplemental Information T Cells Enhance Autoimmunity by Restraining Regulatory T Cell Responses via an Interleukin-23-Dependent Mechanism Franziska Petermann, Veit Rothhammer, Malte
Is it really that simple? Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics
 Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Alyssa Hasty, PhD Associate Professor Molecular Physiology and Biophysics Why we care about hepatic lipogenesis Control of lipid synthesis What can go wrong in humans Animal models dlto study lipoprotein
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis. Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University
 Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Novel function of NADPH oxidase in atherosclerosis Yun Soo Bae Department of Life Science Ewha Womans University Recent understanding of ROS: act as second messengers e e Catalase/peroxidase O 2 H 2 O
Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice
 Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Supplementary Methods: Cell isolation. Spleen and lymph nodes (axillary, inguinal) were removed from mice and gently meshed in DMEM containing 10% FBS to prepare for single cell suspensions. CD4 + CD25
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers
 Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
Table S1. Quantitative RT-PCR primers Gene Forward Primer Reverse Primer Human ApoB gcaagcagaagccagaagta ccatttggagaagcagtttgg Human ApoA1 gaaagctgcggtgctgac agtggccaggtccttcact Human MTP acggccattcccattgtg
MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway.
 MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway. *Randon T. Hall I, Joseph L. Witztum2, Yury I. Miller2 From the IMSTP-SURF Program and 2Division of Endocrinology and
MinimallyModifiedLDLInducesActinPolymerization Macrophages viacd14signalingpathway. *Randon T. Hall I, Joseph L. Witztum2, Yury I. Miller2 From the IMSTP-SURF Program and 2Division of Endocrinology and
Invited Review. Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases
 Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Histol Histopathol (2000) 15: 557-571 Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Invited Review Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in the pathogenesis of atherosclerotic cardiovascular
Paraoxonase Responses to Exercise and Niacin Therapy in Men with Metabolic Syndrome. James Kyle Taylor
 Paraoxonase Responses to Exercise and Niacin Therapy in Men with Metabolic Syndrome by James Kyle Taylor A dissertation submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of
Paraoxonase Responses to Exercise and Niacin Therapy in Men with Metabolic Syndrome by James Kyle Taylor A dissertation submitted to the Graduate Faculty of Auburn University in partial fulfillment of
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms
 TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
TD-BF01: Innate immunity to microorganisms I. Toll receptors (adapted from Takeuchi, O. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:443; Kawai, T. et al. (1999) Immunity 11:115; Hemmi, H. et al. (2000) Nature 408:740; Muzio,
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by. Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam
 Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Biochemistry Department Plasma lipoproteins & atherosclerosis by Prof.Dr. Maha M. Sallam 1 1. Recognize structures,types and role of lipoproteins in blood (Chylomicrons, VLDL, LDL and HDL). 2. Explain
Integrative Physiology
 Integrative Physiology Acute Psychological Stress Accelerates Reverse Cholesterol Transport via Corticosterone-Dependent Inhibition of Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption Reija Silvennoinen, Joan Carles
Integrative Physiology Acute Psychological Stress Accelerates Reverse Cholesterol Transport via Corticosterone-Dependent Inhibition of Intestinal Cholesterol Absorption Reija Silvennoinen, Joan Carles
Liver X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target
 Review Article www.ijpsonline.com Liver X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target M. B. PATEL*, N. A. OZA, I. S. ANAND, S. S. DESHPANDE AND C. N. PATEL Department of Pharmacology, Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy
Review Article www.ijpsonline.com Liver X Receptor: A Novel Therapeutic Target M. B. PATEL*, N. A. OZA, I. S. ANAND, S. S. DESHPANDE AND C. N. PATEL Department of Pharmacology, Shri Sarvajanik Pharmacy
