Skeletal System Ch. 23. Dr. Ken Thorson
|
|
|
- Josephine Harrell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Skeletal System Ch. 23 Dr. Ken Thorson
2 Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to: 1.Define and spell the terms to learn for this chapter. 2.List the various types of bones in the body. 3.Identify specific bones for each bone classification.
3 Lesson Objectives Upon completion of this lesson, students should be able to: 4.Discuss the functions of the bones of the human skeleton. 5.Explain various types of joints and body movements. 6.Describe the axial skeleton. 7.Describe the appendicular skeleton.
4 Skeletal System Makes up framework of the human body Responsible for: Providing shape and support Protecting internal organs Serving as a storage place for mineral salts, calcium, and phosphorus
5 Skeletal System Responsible for: Plays important role in formation of blood cells Providing an area for attachment of skeletal muscles
6 Skeletal System Two divisions compose skeletal system 206 bones Axial skeleton made of 80 bones Appendicular skeleton consists of remaining 126 bones
7 FIGURE 23-1 Anterior and posterior human skeleton.
8 Bones and Their Classification Bones consist of 50 percent water Remaining 50 percent is a rigid, calcified substance known as osseous tissue Pearson's Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative and Clinical Competencies, 3/e Beaman Routh Papazian-Boyce Sesser Mills Maly Copyright 2015, 2011 by Pearson Education, Inc. All Rights Reserved
9 FIGURE 23-2 Microscopic components of osseous tissue.
10 TABLE 23-1 Microscopic Components of Osseous Tissue
11 TABLE 23-1 (continued) Microscopic Components of Osseous Tissue
12 Bones and Their Classification Bones classified according to shape Six common shapes of bones are: Long Short Flat Irregular Sesamoid Sutural (wormian)
13 FIGURE 23-3 Classification of bones by shape.
14 Bones and Their Classification Six Main Functions of Bones Provide shape, support, framework of body Provide protection for body s internal organs Serve as a storage place for mineral salts, calcium, and phosphorus
15 Bones and Their Classification Six Main Functions of Bones Play important role in formation of blood cells as hemopoiesis takes place in bone marrow Provide area for attachment of skeletal muscle Help to make movement possible through articulation
16 Structure of a Long Bone Epiphysis Ends of a developing bone Diaphysis Shaft of the long bone Periosteum Membrane that forms the covering of bones, except at their articular surfaces
17 Structure of a Long Bone Compact bone Dense, hard layer of bone tissue Medullary canal Narrow space or cavity throughout the length of the diaphysis that contains yellow bone marrow, which is made of fat cells
18 Structure of a Long Bone Endosteum Tough, connective tissue membrane lining the medullary canal and containing the bone marrow Cancellous or spongy bone Reticular tissue that makes up most of the volume of bone
19 FIGURE 23-4 The features found in a long bone.
20 Bone Markings Condyle Crest Epicondyle Line Process Trochanter Tubercle Tuberosity
21 Joints and Movement A joint, called an articulation, is located at the place where two bones connect
22 Joints and Movement Joints classified according to the type of movement they provide Synarthrotic joint Produces no movement (Sutures- connect bones of the skull) Amphiarthrotic joint Permits very slight movement (intervertebral joints of spinal column) Diarthrotic joint Allows for free movement in a variety of directions (knee,elbow,shoulder)
23 FIGURE 23-5 A typical joint.
24 Joints and Movement Movements of the Body Abduction Moving a body part away from the midline Adduction Moving body part toward midline Circumduction Moving a body part in a circular motion
25 Joints and Movement Movements of the Body Dorsiflexion Bending a body part backward Eversion Turning outward Extension Straightening a flexed limb Flexion Bending (or curving) the spine
26 Joints and Movement Movements of the Body Inversion Turning inward Pronation Lying prone or face down; turning the hand so that the palm points downward Protraction Moving a body part forward
27 Joints and Movement Movements of the Body Retraction Moving a body part backward Rotation Moving body part around central axis Supination Lying supine or face upward; process of turning the palm or foot upward
28
29 TABLE 23-3 Movements of the Body
30 TABLE 23-3 (continued) Movements of the Body
31 FIGURE 23-7 A contrasting comparison of the axial and appendicular skeleton.
32 The Axial Skeleton Central portion of the skeleton Skull Sternum Ribs Vertebrae Sacrum Coccyx Head composed of 22 bones; skull has 8 bones, and bones of the face
33
34
35 The Axial Skeleton Vertebral column, which houses the spinal cord, consists of a series of vertebrae Vertebrae divided into five regions Cervical Thoracic Lumbar Sacral Coccyx, or tailbone
36 The Axial Skeleton Ribs Form protective cage that houses heart, lungs, other vital components of body Rib cage consists of 12 pairs of ribs divided into three categories: true, false, floating ribs
37
38
39 The Appendicular Skeleton Responsible for movement Upper extremities Lower extremities Clavicles Scapula Pectoral girdle
40 The appendicular skeleton.
41 The Appendicular Skeleton Upper extremity bones Humerus Radius Ulna Carpals Metacarpals Phalanges
42
43 The Appendicular Skeleton Lower extremity bones Femur Patella Tibia Fibula Tarsals Metatarsals Phalanges
44
45 FIGURE 23-13A The male pelvis
46 FIGURE 23-13B female pelvis The
47 Critical Thinking Questions 1.How can you remember the difference between the ulna and the radius? 2.How can you remember the difference between the carpals and metacarpals?
48 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Scoliosis Abnormal lateral curvature of the spine Often diagnosed early in toddlers, children, and adolescents Appears to have an S or C shape May often appear as if either their shoulders or their legs are uneven Treatment: orthopedic braces, physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgery
49 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Lordosis Often called swayback Exaggerated curvature of lumbar spine When diagnosed in adults, may be commonly found in those who are overweight and in pregnant women When diagnosed in children, most common symptom is prominently protruding abdomen and/or buttocks
50 Common Disorders Associated Lordosis with the Skeletal System Treatment depends on patient s overall health, age, and severity of condition Overall goal of treatment is to stop the curvature and prevent spinal deformity
51 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Kyphosis Sometimes known as humpback Exaggeration of thoracic curvature
52 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Kyphosis May be result of: Congenital defect Disease process Compression fracture Faulty posture, osteoarthritis Rheumatoid arthritis, rickets, osteoporosis, or other conditions
53 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Kyphosis Rounded appearance of upper back Fatigue, mild back pain, either tender or stiff feeling within the spine In severe cases, shortness of breath
54 Common Disorders Associated Kyphosis with the Skeletal System Treatment depends on overall health and age of patient as well as cause or source of disease Physical therapy or bone-strengthening medications
55 Kyphosis.
56 Lordosis.
57 Scoliosis.
58 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Arthritis Inflammation of one or more joints Causes include: Joint injury Autoimmune disorders Normal to excessive wear and tear on joints Can occur at any age Most commonly develops in older adults
59 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Arthritis Signs and symptoms vary with every patient Joint pain and swelling Morning stiffness Warmth and redness around a joint Decreased ability to move the joint
60 Common Disorders Associated Arthritis with the Skeletal System Treatment depends on age, occupation, other activities of patient, cause and severity, joint affected Modification to daily activities and low-impact aerobic exercise
61 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Arthritis Medications to reduce joint pain and swelling Application of heat or cold Joint protection Surgery
62 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteoarthritis Most common type of arthritis resulting from years of wear and tear on joints Most frequently occurs in hips, knees, and finger joints of elderly patients Obesity, history of trauma, various genetic and metabolic diseases increase the risk of osteoarthritis Referred to as degenerative joint disease (DJD)
63 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteoarthritis Swelling and fluid accumulation around joints Aching pain associated with changes in the weather Permanent joint deformity may occur
64 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteoarthritis Treatment Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) Steroid injections to affected joint In severe cases, joint replacement
65 osteoarthritis
66 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Rheumatoid Arthritis Autoimmune disorder in which inflammation causes joints to become deformed Increased growth of both cartilage and bone Marked by inflammation, joint swelling, and joint deformity
67 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Rheumatoid Arthritis Morning joint stiffness very common Fatigue and loss of appetite Smaller joints of body are affected along with the surrounding tissue
68 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Rheumatoid Arthritis There is no cure Early detection, diagnosis, and treatment may deter pain and joint decay
69 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Rheumatoid Arthritis Medications Antirheumatic drugs Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs Corticosteroids Heat and cold treatments Low impact exercises
70 rheumatoid arthritis.
71 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Gouty Arthritis Also called gout Caused by formation and accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints that result from high levels of uric acid in bloodstream Accumulation of these crystals leads to inflammation Gouty joint often very warm and very sore to the touch
72 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Gouty Arthritis After joints have been persistently affected by gout, they may become disfigured Medications available to reduce uric acid Diet rich in colorful fruits and vegetables Dietary restrictions include avoiding caffeine, alcohol, liver, and other purine-rich foods
73 Gouty arthritis of the finger joint.
74 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Bursitis Bursa is small sac of fluid that cushions and lubricates an area where joint-related tissues rub against one another Bursitis is inflammation of the bursa Joint pain Limited joint mobility Swelling Tenderness surrounding the joint
75 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Bursitis Rest Pain medication Steroid injections Aspiration of excess fluid from the bursa Antibiotics Physical therapy may be utilized to increase and promote joint movement
76 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal tunnel narrow passageway in wrist Occurs when pressure placed on median nerve Repetitive movements involving the wrist may contribute to the condition
77 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Risk factors include obesity, diabetes, and rheumatoid arthritis Pain with numbness and hand weakness Hands and fingers may feel tingly, itchy, and swollen, even if swelling is not visibly present
78 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Wrist splints at night for several weeks Hot and cold compresses Resting the hand and wrist Proper ergonomics
79 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Carpal Tunnel Syndrome NSAIDs such as ibuprofen or naproxen to relieve pain and reduce inflammation Diuretics Injections of corticosteroids Surgical procedure
80 tendons and nerves involved in carpal tunnel syndrome.
81 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Fractures Bone cracks or breaks Classified based on: Site of fracture Nature of crack or break Whether or not fracture has caused a break in skin Diagnosed based on X-ray of the broken bone
82 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Types of Fractures Closed (simple) Does not involve a break in the skin and is completely internal. Open (compound) More dangerous fractures because fracture has broken through the skin. Risk of infection or hemorrhage is greater than with a closed fracture.
83 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Types of Fractures Comminuted Part of the bone is shattered into a multitude of bony fragments. Transverse Break the shaft of bone across its longitudinal access.
84 Photo
85 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Types of Fractures Greenstick Usually occurs in young children. Only one side of shaft is broken; the other side is bent, similar to breaking a green plant stick. Spiral Spread along length of a bone and produced by twisting stresses.
86 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Types of Fractures Pott Occur in the ankle and affect both bones of the lower leg (tibia and fibula). Compression Occur in vertebrae after severe stress, such as when someone falls and lands with significant amount of force.
87 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Types of Fractures Epiphyseal Commonly seen in children in areas of bone where growth plate is undergoing calcification and the chondrocytes are dying.
88 Various types of fractures.
89 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Fractures Generally casted by a physician At times, in severe fractures, surgical intervention must be performed Common that both pins and metal plating used to stabilize joints and bones during surgery Pain and antiinflammatory medications often prescribed for patient comfort
90 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Dislocations Occurs when a bone slips out of the joint Usually follows a blow, a fall, or other trauma Usually joint capsule and ligaments tear when a dislocation occurs Often the nerves are injured
91 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Dislocations May be visibly out of place Discolored Misshapen Limited in movement Bruised or swollen Intensely painful Very difficult to move the affected joint
92 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Dislocations Patients should seek emergency treatment in hospital or urgent care setting Many physicians offices not equipped to handle this injury Procedure known as reduction used to align and reposition the joint Pain relievers and antiinflammatory medications
93 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteoporosis Characterized by progression of loss of bone density and thinning of bone tissue Affects more than 25 million Americans, mostly women ages 50 to 70 years old Subject to increased fracture potential, especially in the hips, vertebrae, wrists
94 Critical Thinking Question 1.Why might an individual be more at risk for developing osteoporosis?
95 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Higher Risk of Developing Osteoporosis Family history of osteoporosis Those who do not engage in weight-bearing exercise as part of their lifestyle Caucasian women who have never been pregnant and experience early menopause Individuals with history of frequent corticosteroid use
96 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Higher Risk of Developing Osteoporosis Individuals who excessively smoke, drink alcohol, and consume diets high in salt, fat, and caffeine Individuals who have insufficient intake of calcium or vitamin D
97 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteoporosis Decreased height and stooped posture Back pain and frequent fractures Treatment includes: Calcium and vitamin D supplementation Medications to help preserve calcium and decrease bone loss Exercise
98 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Hallux Valgus Also called a bunion Enlargement of inner portion of metatarsophalangeal joint at base of big toe Reddened skin surrounds the inflamed joint of the big toe Joint may be filled with fluid and feel tender to the touch
99 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Hallux Valgus Properly fitting shoes should be worn Proper padding and cushioning of the joint Pain medications and antiinflammatory medications
100 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Hallux Valgus Foot surgery may be required for severe cases Patient may need to be fitted with special adaptive shoes made by orthopedic shoe specialist
101 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Hammer Toe Toe bends into hammer shape or claw shape because of abnormal flexion of proximal interphalangeal joint Frequently caused by wearing shoes that are too narrow or too short or wearing extremely high heels that force the toe to bend Pain and visible joint deformation
102 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Hammer Toe Toe bends into hammer shape or claw shape because of abnormal flexion of proximal interphalangeal joint Frequently caused by wearing shoes that are too narrow or too short or wearing extremely high heels that force the toe to bend Pain and visible joint deformation
103 Common Disorders Associated Rickets with the Skeletal System Early childhood disease caused by deficiency in calcium, vitamin D, and phosphate Results in bone deformities, especially bowed legs Genetics may increase risk of developing rickets
104 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Rickets Pain and tenderness of the bones Increased likelihood of bone breakage Impaired growth and decreased height Muscle cramps Treatment: increasing vitamin and mineral intake and comfort measures, including rest and heat and ice applications
105 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteomalacia Adult onset of rickets Causes: deficiencies in calcium and vitamin D Additional causes: cancers, liver disease, kidney failure, side effects associated with antiseizure medications
106 Common Disorders Associated with the Skeletal System Osteomalacia Bone pain, bowing legs, frequent fractures Treatment similar to rickets: increasing vitamin and mineral intake and comfort measures to relieve symptoms
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ.
 General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
General osteology. General anatomy of the human skeleton. Development and classification of bones. The bone as a multifunctional organ. Composed by Natalia Leonidovna Svintsitskaya, Associate professor
The Skeletal System. Chapter 7a. Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life
 The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
The Skeletal System Skeletal System Introduction Functions of the skeleton Framework of bones The skeleton through life Chapter 7a Support Protection Movement Storage areas Minerals Lipids Hemopoiesis
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton
 Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
Chapter 6 & 7 The Skeleton Try this Make clockwise circles with your RIGHT foot, while doing this, draw the number 6 in the air with you RIGHT hand what happens to your foot???? Bony Background Adult body
The Skeletal System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
The Skeletal System Functions of Skeletal System Provides internal framework that supports the body Protects internal organs Helps fight disease by producing white blood cells 2 Functions of Skeletal System
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton:
CHAPTER 6 SKELETAL SYSTEM OBJECTIVES. On completion of this chapter, you will be able to:
 CHAPTER 6 SKELETAL SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the skeletal system. Describe various types of body movement. Describe the vertebral column. Identify abnormal
CHAPTER 6 SKELETAL SYSTEM OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter, you will be able to: Describe the skeletal system. Describe various types of body movement. Describe the vertebral column. Identify abnormal
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2. Bone Structure. Copyright 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
 Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Chapter 7 The Skeleton: Bones and Joints The Skeleton Skeletal system is made up of bones and joints and supporting connective tissue. 1. Bone Functions 1. To store calcium salts 2. To protect delicate
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move.
 Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Skeletal System The skeletal system is the framework for the muscular system to attach to so we can move. BONE: A rigid connective tissue Helps to move & support the body Protect the organs (skull, ribs)
Anatomy. Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts.
 Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Anatomy deals with the structure of the human body, and includes a precise language on body positions and relationships between body parts. Proper instruction on safe and efficient exercise technique requires
Human Skeletal System Glossary
 Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
Acromegaly Apatite Acromegaly - is a condition which involves excessive growth of the jaw, hands, and feet. It results from overproduction of somatotropin in adults (after fusion of the ossification centres
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system
 1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
1.03 Understand the functions and disorders of the skeletal system Bellringer The process of blood cell formation in the red bone marrow of bones is called: a. Erythrocytopenia b. Hemolysis c. hemopoiesis
Bones of Thorax (Rib Cage)
 Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
Musculoskeletal System (Part A-2) Module 7 -Chapter 10 Overview Muscles Attachments Bones Bone types Surface features of bones Divisions of the skeletal system Joints or Articulations Susie Turner, M.D.
NOTES SKELETAL SYSTEM
 NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
NOTES for the SKELETAL SYSTEM Anatomy & Physiology 2016 Johnson The Skeletal System I. System includes 4 basic parts: A. Bones (206 of em) B. Joints C. Cartilages D. Ligaments II. Bones have 5 basic functions:
The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action!
 Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Skeletal System The Skeletal System in Action!! The Skeletal System in Action! 5 Functions of the Skeletal System 1. Movement: Skeletal system provides points of attachment for muscles. Your legs and arms
Functions of Skeletal System
 Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Skeletal System Skeletal System Adult Human has 206 Bones This slideshow will offer fun ways to remember the names of some of the bones, and you can come up with your own tricks! Functions of Skeletal
Introduction. Physiology. Classification of Bones. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Anatomy of a Long Bone. Skeletal System and Joint Movements.
 Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Chapter 13 Skeletal System and Joint Movements Susan G. Salvo Introduction Skeletal system is composed of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and joints 206 bones in the body Bone is living tissue Skeletal system
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints
 Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
Microanatomy, Physiology of Bone & Joints The Skeleton There are 206 bones in the human body. The bones that are required in this syllabus are the cranium, mandible, clavicle, sternum, scapula, ribs, humerous,
The formation of blood cells is called. hemopoiesis. What does our bone store? Where do our bones store fat? yellow marrow.
 What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
What are the 5/6 functions of the skeletal system? support, protection, movement, blood cell formation, storage, homeostasis The formation of blood cells is called hemopoiesis What does our bone store?
Parts of the skeletal system. Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle)
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments (bone to bone)(tendon=bone to muscle) Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton Appendicular
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
CHAPTER 13 SKELETAL SYSTEM Structure and Function Functions of the skeletal system Provides shape and support Protects internal organs Stores minerals and fat Produces blood cells and platelets Assists
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System
 Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Ch. 5 - Skeletal System Bones are living, ever-changing structures. This allows them grow and adapt to new situations that the body encounters. The functions of the skeletal system: 1) support bones are
Warm-Up Activity. Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram.
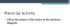 Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Warm-Up Activity Fill in the names of the bones in the skeleton diagram. Warm-Up 1. What are the 4 types of bones? Give an example of each. 2. Give 3 ways you can tell a female skeleton from a male skeleton.
Skeletal System. Chapter 7.1. Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction:
 Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7.1 Skeletal System Objective- Read 7.1 and understand that bones are alive and multifunctional. Introduction: A. Bones are very active tissues B. Each bone is made up of several types of tissues
Chapter 7 Skeletal System. Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions.
 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Chapter 7 Skeletal System Skeletal System: Bone Functions: Describe the role the skeletal system plays in each of the following functions. support protection muscle attachment - movement blood production
Skeletal System. Skeleton. Support. Function of Bones. Movement. Protection 10/15/12
 Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeleton Skeletal System 1 Axial Skeleton-Bones that form the longitudinal axis of the body (skull and spinal column). Appendicular Skeleton-Bones of the limbs and girdles. Also include joints, ligaments
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS
 Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
Skeletal System Practice Quiz and Exercises ANSWERS 1) Give the meaning of the following terms (4 marks) a) Prone b) Medial c) Posterior d) Ipsilateral a) Lying face down b) Nearer the midline c) Nearer
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
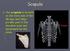 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
Exercise Science and Sports Medicine
 Unit 3 A SKELETAL SYSTEM Lecture notes I. Introduction a. The skeletal system is defined as the framework of bones, cartilage, ligaments and other connective tissues in the human body. b. Normally, the
Unit 3 A SKELETAL SYSTEM Lecture notes I. Introduction a. The skeletal system is defined as the framework of bones, cartilage, ligaments and other connective tissues in the human body. b. Normally, the
Skeletal System. By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Learning Outcomes Describe the parts of a long
Skeletal System. Supplementary Information
 Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
Skeletal System Supplementary Information COMMON ANATOMICAL TERMS Planes run through the body side to side and front to back eg. median plane Surfaces of the body are also named eg. anterior surface This
The Skeletal System ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY PART A ELAINE N. MARIEB EIGHTH EDITION
 5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
5 The Skeletal System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Skeletal System
Skeletal System Notes
 Skeletal System Notes A. Introduction 1. Skeletal system is made of organs that are called bones 2. In the adult, there are 206 bones B. Functions of bones 1. Framework: support the body s muscle fat,
Skeletal System Notes A. Introduction 1. Skeletal system is made of organs that are called bones 2. In the adult, there are 206 bones B. Functions of bones 1. Framework: support the body s muscle fat,
Skeletal System. Std. VIII
 Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Skeletal System Std. VIII The skeleton in our body serves following functions : 1. Support and shape : The skeleton provides a support or framework to all the soft parts and gives the body and its parts
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) - hemopoiesis Storage of inorganic materials (salt,
Bell Work. Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies.
 Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Bell Work Label the diagram with the layman s or everyday terms we use to talk about our bodies. (Leave space to label the appropriate medical terms as we go). The Skeletal System Standards 13) Label on
Lab-1. Miss. Lina Al-Onazy & samar Al-Wgeet =)
 Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Lab-1 Introduction The human skeleton is composed of 300 bones at birth and by the time adulthood is reached, some bones have fused together to give a total of 206 bones in the body. The human skeleton
Characteristics. Bones. Functions of the Skeleton
 Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Characteristics Bones The Introduction 206 bones hard, rigid bones cells (osteocyctes) are a mixture of a ground substance, collagen fibres, P, Ca highly resistant to compression and tension also somewhat
Chapter 7 /8 pgs SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM
 Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
Chapter 7 /8 pgs. 189-250 SKELETAL TISSUES AND THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Skeletal Tissue Introduction Bone and cartilage are a specialized types of connective tissue Individual Bones are considered separate
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy?
 CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
CHAPTER 3 What Is Anatomy? Kinesiology Books Publisher 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS The Language of Anatomy Anatomical Position Directional Terms Body Planes Movements Musculoskeletal System Human Skeleton Types
Why do we need the skeletal system?
 EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
EQ Why do we need the skeletal system? The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Divided into two divisions Axial skeleton- bones of the skull, vertebral
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary.
 Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
Bellwork: Copy the vocabulary. Arthr- joint Burs- sac Carp- wrist Chondr- cartilage Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Meta- beyond Myelo- bone marrow Osteo- bone Peri- around Pod- foot Poro- pores in the
Bone Composition. Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are:
 Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
Human Bones Bone Composition Bone is very strong for its relatively light weight The major components of bone are: Calcium carbonate Calcium phosphate Collagen Water Cortical Bone Spongy Bone Medullary
36 1 The Skeletal System Slide 1 of 40
 1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
1 of 40 The Skeleton All organisms need structural support. Unicellular organisms have a cytoskeleton. Multicellular animals have either an exoskeleton (arthropods) or an endoskeleton (vertebrates). 2
Figure ) The area that causes the lengthwise growth of a long bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 2 Page Ref:
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Short Answer Figure 5.1 Using Figure 5.1, identify the following: 1) Spongy bone is indicated by letter. Diff: 1 Page Ref:
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection: Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
SKELETAL SYSTEM. Introduction Notes (pt 1)
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
SKELETAL SYSTEM Introduction Notes (pt 1) I. INTRODUCTION 1. Bones include active, living tissues: bone tissue, cartilage, dense connective tissue, blood, and nervous tissue. 2. Bones: support and protect
PowerPoint Lecture Slides. Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College. The Skeletal System Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
PowerPoint Lecture Slides Prepared by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College CHAPTER 5 The Skeletal System 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Title Classification of Bones and Gross Anatomy
Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Bones are made of OSSEOUS TISSUE Support and Protection Body movement Blood cell formation (bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium,
Chapter 7: Skeletal System
 Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 7: Skeletal System The Skeletal System Introduction P. 182 Bone is an organ made up of tissues: It is made up of the following components. Cartilage Blood Nerves Bone Connective Bone Classification
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System. Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body
 Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Chapter 5 The Skeletal System Word skeleton comes from the Greek word meaning dried-up body The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system: Bones (Skeleton) Osseous tissue, connective type of tissue
Name Date Score. Skeletal System. Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements
 Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
Name Date Score Skeletal System True/False Indicate if the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements 1. Bones surround vital organs to protect them. 2. Bones store most of the calcium
QUICK ASSESSMENT: CONCEPT MAP
 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7th Grade THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Provides shape, strength, and support (3S s) Internal framework of the body Support and anchor for soft organs Protects soft internal organs
Classification of bones
 Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Classification of bones compact intramembranous axial histology development regional spongy Intra cartilaginous appendicular flat Irregular shape Sesamoid Long Short Wormian pneumatic Classification
Gross Anatomy. Landmarks on a typical long bone. Membranes. Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes. Periosteum Endosteum
 BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
BONE STRUCTURE Gross Anatomy Landmarks on a typical long bone Diaphysis Epiphysis Membranes Membranes Periosteum Endosteum Diaphysis Long tubular diaphysis is the shaft of the bone Collar of compact bone
5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW
 Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Unit 5 Skeletal System 5.1 BONES: AN OVERVIEW Section Objectives Identify the major structures and functions of the skeletal system. Differentiate between the two divisions (axial and appendicular) of
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 7 Skeletal System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 7 Skeletal System 1 Chapter 7 Skeletal System Bone Classification Long Bones Short Bones Flat Bones Irregular Bones Sesamoid (Round)
Skeletal system. Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Skeletal system Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Functions of Bone and The Skeletal System Support: The skeleton serves as the structural framework
Functions of the Skeletal System
 SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support: Internal framework that supports and anchors all soft organs. Protection: Bones protect soft body organs Body movement skeletal muscle attached
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE. CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement?
 PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
PRELIMINARY HSC PDHPE CQ1 How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence and respond to movement? How do the musculoskeletal and cardiorespiratory systems of the body influence
Biology v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems. Skeletomuscular system cards
 Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Biology 90166 v2 Describe the functioning of human digestive & skeletomuscular systems Skeletomuscular system cards Test yourself / test me cards Cover answer bottom 1/3; Read question / notes / diagram
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend
 Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Bellwork: Copy the prefixes. Arthr- joint Carp- wrist Costo- ribs Duc- move Flex- bend Myelo- Osteo- Pod- Tars- Meta- bone marrow bone foot ankle beyond The Skeletal System Standards 11) Outline the gross
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Skeletal Considerations for Movement. Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Skeletal Considerations for Movement Kinesiology RHS 341 Lecture 2 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa The Skeletal System Bones, cartilage, ligaments, & joints Consists of approximately 20% of total body weight Bone constitutes
Carpals Tarsals Classification of Bones Flat bones Thin, flattened, and usually curved
 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
The Skeletal System The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton Axial skeleton Appendicular skeleton Functions of Bones
The Skeletal System. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 5 The Skeletal System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Skeletal System worksheet
 Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Skeletal System worksheet Name Section A: Intro to Skeletal System The skeletal system performs vital functions that enable us to move through our daily lives. Support - The skeleton provides support and
Student Objectives. When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives:
 Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Student Objectives When you have completed the exercises in this chapter, you will have accomplished the following objectives: Classification of Joints 1. Define joint or articulation. 2. Classify joints
Chapter 5-Skeletal System
 Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
Chapter 5-Skeletal System The Skeletal System Bones Function in Support, Movement, Protection, Storage, and Blood Cell Production (p. 83) Bones Have a Hard Outer Layer Surrounding Spongy Bone (pp. 83-84)
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Skeletal Tissues. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
Skeletal Tissues Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of Bones 1. Support and protection : Bones give shape to body structure. Bones provide support to body weight. Certain bones protect vital internal organs
11/25/2012. Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! Skeletal Organization. The Skull. Skull Bones to Know Cranium
 Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
Chapter 7 Part 2: Bones! 5) Distinguish between the axial and appendicular skeletons and name the major parts of each 6) Locate and identify the bones and the major features of the bones that compose the
TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY BARBARA HERLIHY Chapter 8: Skeletal System
 Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
Link download Full : http://testbankair.com/download/test-bank-for-thehuman-body-in-health-and-illness-5th-edition-by-barbara-herlihy/ TEST BANK FOR THE HUMAN BODY IN HEALTH AND ILLNESS 5TH EDITION BY
Section 11.1 Your Skeletal System
 Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Objectives Identify the five main roles of the skeletal system. Describe the functions of bones and joints. Explain how you can keep your skeletal system healthy. Slide 1 of 24 Quick Quiz Complete each
Support and protection. Body movement. Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow)
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Functions of the Skeletal System Support and protection Body movement Blood cell formation = hemopoiesis (occurs in bone marrow) Storage of inorganic materials (salt, calcium, potassium.)
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM. Chapter 6
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM Chapter 6 Bone is made of several different tissues working together Bone or osseous tissue Cartilage Dense connective tissue epithelium Various blood forming tissues Adipose tissue
Chapter 5- The Skeletal System
 Chapter 5- The Skeletal System I. The skeletal system A. Parts of the skeletal system 1. Bones (skeleton) 2. Joints 3. Ligaments 4. Cartilage B. Two subdivisions of the skeleton 1. Axial skeleton 2. Appendicular
Chapter 5- The Skeletal System I. The skeletal system A. Parts of the skeletal system 1. Bones (skeleton) 2. Joints 3. Ligaments 4. Cartilage B. Two subdivisions of the skeleton 1. Axial skeleton 2. Appendicular
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R. Joints: Part A. Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc.
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College C H A P T E R 8 Joints: Part A Warm Up 11/28/16 Happy Thanksgiving welcome back! J (be ready to share something fun you did over
Articulations Chapter 9
 Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
Articulations Chapter 9 Biology 210 Instructor: John McGill Original PowerPoint: Jack Bagwell Supplemental Notes: Beth Wyatt Last updated: October 2, 2007 INTRODUCTION TO ARTICULATIONS DEFINITION Articulations
The Skeletal System. Functions of the Skeletal System
 11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
11/15/17 The Skeletal System The Skeletal System 1 Functions of the Skeletal System Provide support and structure Protects vital internal organs Storage site for minerals Site for blood formation Bones
The Skeletal System. Support Systems Unit 2
 The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 Vocabulary- combining forms Arthr/o joint Sacr/o Sacrum Cervic/o neck Spondyl/o vertebrae Chondr/o cartilage Stern/o Sternum Cost/o rib Ten/o, Tend/o, Tendon
The Skeletal System Support Systems Unit 2 Vocabulary- combining forms Arthr/o joint Sacr/o Sacrum Cervic/o neck Spondyl/o vertebrae Chondr/o cartilage Stern/o Sternum Cost/o rib Ten/o, Tend/o, Tendon
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES
 UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
UNIT 4 - SKELETAL SYSTEM LECTURE NOTES 4.01 FUNCTIONS OF THE SKELETAL SYSTEM A. Support 1. Provides a framework for the body 2. Supports soft tissue 3. Serves as a point of attachment for ligaments, tendons,
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) Answers to Activity Questions
 Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Answers to Pre-Lab Quiz (p. 171) 1. Holds bones together; allows the rigid skeleton some flexibility so that gross body movements can occur 2. c, amount of movement allowed by the joint 3. synovial 4.
Chapter 09 Articulations Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Chapter 09 Articulations An Introduction to Articulations Articulations Body movement occurs at joints (articulations) where two bones connect Joint Structure Determines direction and distance of movement
Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System
 I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
I. Functions of the Skeletal System A. the body Anatomy & Physiology Skeletal System B. of vital organs C. Provide for movement D. storage (calcium & phosphate) E. cell formation II. Bone Structure A.
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 7 TH GRADE SCIENCE INTRODUCTION Skeletal system is made up of your bones, ligaments, and tendons. It determines : the shape and symmetry of the body acts as protection for your organs
Chapters 6 & 7. The Skeletal System. Our bones
 Chapters 6 & 7 The Skeletal System Our bones The human skeleton has 206 bones, which are divided into 4 types: 1. Long 2. Short 3. Flat 4. irregular 1 Long bones In the arms and legs Femur Ulna Tibia Humerus
Chapters 6 & 7 The Skeletal System Our bones The human skeleton has 206 bones, which are divided into 4 types: 1. Long 2. Short 3. Flat 4. irregular 1 Long bones In the arms and legs Femur Ulna Tibia Humerus
The Skeletal System. Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
 5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
5 The Skeletal System Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints Cartilages Ligaments Two subdivisions of the skeleton
Due in Lab. Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary
 Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Due in Lab 1. Skeletal System 33-34 2. Skeletal System 26 3. PreLab 6 Due next week in lab - Scientific America Article Select one article to read and complete article summary Cell Defenses and the Sunshine
Skeletal System. Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
Skeletal System Chapter 6.1 Human Anatomy & Physiology Overview of Skeletal System Bones Joints Skeletal System Cartilage Tendons (bone to muscle) Ligaments (bone to bone) Function of the Skeletal System
I. Introduction. Unit Two. of the Skeletal System. II. Classification of Joints. URLs for this chapter:
 8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
8 URLs for this chapter: http://www.vh.org/adult/provider/radiology/joint Fluoro/JointFluoroHP.html of the Skeletal System Karen Webb Smith Unit Two http://www.science.ubc.ca/~biomania/tutorial/bonejt/
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL
 LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
LEVEL 3 DIPLOMA IN AROMATHERAPY MODULE 10 KNOWLEDGE OF ANATOMY, PHYSIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY FOR COMPLEMENTARY THERAPIES THE ARTICULAR SYSTEM COURSE MANUAL CHRISTINA LYNE christina@aromalyne.com 1 THE ARTICULAR
10/4/18. Skeletal System. 1 Copyright 2016 by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Introduction. Physiology. Anatomy. Bone Cells.
 Introduction Skeletal System Chapter 19 206 bones in the body Bones are living tissue Mammals have remarkably similar bone structure - Humans, elephants, giraffes, bats, and whales all have 7 cervical
Introduction Skeletal System Chapter 19 206 bones in the body Bones are living tissue Mammals have remarkably similar bone structure - Humans, elephants, giraffes, bats, and whales all have 7 cervical
Types of Body Movements
 Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
Types of Body Movements Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Synovial joints allow the body a tremendous range of movements. Each movement at a synovial joint results from the contraction or relaxation of the muscles
The Skeletal System PART A. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Skeletal System 5 PART A The Skeletal System Parts of the skeletal system Bones (skeleton) Joints
Understand the skeletal system:
 Understand the skeletal system: Including axial and appendicular skeleton All joints in the body All major bones Development of bones & bone growth Training effects on the skeletal system All movements
Understand the skeletal system: Including axial and appendicular skeleton All joints in the body All major bones Development of bones & bone growth Training effects on the skeletal system All movements
