MR SIALOGRAPHY AND CONVENTIONAL SIALOGRAPHY IN SALIVARY GLAND AND DUCT PATHOLOGIES: A COMPARATIVE STUDY
|
|
|
- Della Martin
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 MR SIALOGRAPHY AND CONVENTIONAL SIALOGRAPHY IN SALIVARY GLAND AND DUCT PATHOLOGIES: A COMPARATIVE STUDY Amarnath Chellathurai 1, Sathyan Gnanasigamani 2, Shivashankar Kumaresan 3, Suhasini Balasubramaniam 4, Kanimozhi Damodarasamy 5, Komalavalli Subbiah 6, Sivakumar Kannappan 7, Balaji Selvaraj 8 1Professor and HOD, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 2Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 3Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 4Associate Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 5Junior Resident, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 6Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 7Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. 8Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis, Stanley Medical College, Chennai. ABSTRACT BACKGROUND MR Sialography has become an alternative method for imaging the salivary gland and duct. MRI is a non-invasive technique with advantages of superior tissue discrimination and multiplanar facility. MRI has no radiation hazard as compared to the conventional sialography and CT sialography; 3D CISS sequence gives details of salivary gland ducts and sialoliths. AIM To compare the accuracy of the conventional sialography and MR Sialography in the diagnosis of salivary gland and duct pathologies. MATERIALS AND METHODS A prospective study was conducted in 54 patients with clinical diagnosis of non-tumorous salivary gland pathologies; 65 salivary glands of the above patients were subjected to conventional sialography and MR Sialography. The diagnostic accuracy of conventional sialogram and MR Sialogram was studied by correlating with surgical, histopathological findings and clinical followup. Three patients were excluded from the study, as there was inability to cannulate during conventional sialography. Conventional sialogram was performed using an 800 ma fluoroscopy machine. MRI was performed using a 1.5 Tesla unit. Dedicated MRI of the salivary glands was performed comprising of T1, T2, FS, 3D CISS, DWI sequences. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The MR and conventional sialographic findings were compared with the final diagnoses. All data were calculated for the number of investigated salivary glands. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were calculated for the detection of pathologies which include acute sialadenitis (MRI during the episode and conventional sialogram after the episode), chronic sialadenitis and sialolithiasis. RESULTS AND CONCLUSION There was good correlation between MRI features and surgical, histopathological findings/clinical followup. MRI showed an overall accuracy in par with conventional sialography. Hence, MRI is extremely useful in the diagnosis of salivary gland and duct pathologies. KEYWORDS MR Sialography, Conventional Sialography, Parotitis, Sialectasis, Sialolithiasis. HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Chellathurai A, Gnanasigamani S, Kumaresan S, et al. MR sialography and conventional sialography in salivary gland and duct pathologies: a comparative study. J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci. 2016;5(37): , DOI: /jemds/2016/778 INTRODUCTION The salivary glands are tubuloacinar exocrine glands, whose ducts open into oral cavity. Financial or Other, Competing Interest: None. Submission , Peer Review , Acceptance , Published Corresponding Author: Amarnath Chellathurai, Professor and HOD, Department of Radiodiagnosis, #301, Stanley Medical College, Chennai , India. amarrd02@yahoo.co.in DOI: /jemds/2016/778 Three pairs of major salivary glands are parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. Minor salivary glands are scattered throughout oral mucosa and submucosa, palate, paranasal sinuses and trachea. The salivary glands can be imaged by X-ray, ultrasound, CT, MRI and radionuclide studies. The ductal system can be imaged by means of sialography. CT and X-ray sialography are done following injection of iodinated contrast media into the ductal system. MR Sialography is done using heavily T2 weighted acquisition techniques without administration of contrast media.(1,2) Hence, it is non-invasive and radiation free.(2) Multiplanar imaging can be done using MRI. It can also evaluate bilateral parotid and submandibular glands and their ducts. Extraluminal structures can be well J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3467
2 studied using MRI. Conventional sialography depicts the main salivary duct and intraglandular ducts up to tertiary branches. MR Sialography depicts the main duct, primary and secondary branching ducts, but could not demonstrate tertiary branches. (1,3,4) In this study, we compare the accuracy of the conventional sialography and MR Sialography in the diagnosis of salivary gland and duct pathologies. MATERIALS AND METHODS Ethical Committee clearance was obtained. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients. The patients with salivary gland symptoms were included in the study. Patients with clinical suspicion of salivary gland tumours, past salivary gland surgeries, pacemaker, claustrophobia, pregnancy were excluded from the study. It is a prospective study conducted in 54 patients who were referred with clinical diagnosis of acute sialadenitis, chronic sialadenitis and sialolithiasis; 65 salivary glands of the above patients were subjected to conventional sialography and MR Sialography. MR Sialography was done in all patients at first visit. Conventional sialography was done on the same day in all patients except cases of acute sialadenitis, for whom it was deferred and done after resolution of symptoms. The acute sialadenitis patients were followed up with their treatment. Rest of the patients were followed up with histopathological reports and surgical specimens. Three patients were excluded from the study, as there was inability to cannulate the duct in conventional sialography even after repeated attempts. Conventional Sialography Conventional sialography was performed by using Allengers 800 ma fluoroscopic equipment. Plain radiographs were obtained in standard antero-posterior and lateraloblique projections to detect radiopaque sialoliths. (1,5,6) Secretagogue-like fresh lemon was used before the commencement of the study, so that the intraoral opening of the parotid and submandibular ducts could be visualised well. After identifying the opening, lacrimal dilators are used to dilate it to facilitate cannulation. (1) Sialographic cannulas which are connected to polyethylene tube are inserted into the duct and connected to a 5-mL syringe. Non ionic iodinated contrast media iohexol is used; ml of contrast for parotid and ml for submandibular gland are injected slowly by using manual pressure. The injection is performed under fluoroscopic control to achieve optimum ductal filling. Spot radiographs were obtained in anteroposterior and lateral-oblique projections to document the examination. Post evacuation radiography was obtained in all patients by repeating the administration of lemon. (1,5,4) MRI with MR Sialography MR imaging was performed on a 1.5T scanner (Siemens, Magnetom, Aera) using head coil. Prior to MR imaging, the patients were given lemon juice to stimulate salivation. Axial fast spin-echo T2 weighted fat suppressed sequence (2.0 min) and axial fast spin-echo T1 weighted sequence (2.01 min) were obtained in all patients. For MR Sialography, three-dimensional CISS sequence was performed. Contralateral glands and ducts were also evaluated and served as a control. The 3D CISS sequence with field of view 250, slice thickness 1 mm, TR 2350 ms, TE-569 ms, matrix size x 448, scan time - 4 min 20 secs was acquired in the axial plane. Total scan time was 8 min 21 secs. The acquired 3D CISS data were reformatted with a Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP) and Multiplanar Reconstruction (MPR) in order to generate axial images and oblique sagittal images parallel to the submandibular/parotid duct. Diffusion weighted imaging was done in cases suspected to have abscess. Fig. 1: 3D CISS in a Healthy Volunteer showing Normal Appearance of a. Bilateral Submandibular Gland Duct, b. Bilateral Parotid Gland Duct, c. Entire Course of the Left Submandibular Duct in Sagittal Reformation Fig 2: 3D MIP (Maximum Intensity Projection) showing Bilateral Parotid and Submandibular Ducts in a Single Image Image Interpretation The conventional and MR Sialographic images were read by two experienced investigators independently. Acute sialadenitis was diagnosed when there was altered signal intensity in the gland with local pain and swelling in the region. Chronic sialadenitis was diagnosed when there was change in the calibre of the duct, sialectasis. Sialoliths were identified when there was filling defect or void in the course of the duct. Images were interpreted as normal if there were no ductal dilatation, cystic lesions, sialoliths, cystic structures and tumour. DISCUSSION Sialolithiasis In cases of salivary obstruction, the most common complaint was local pain and swelling. Systemic symptoms were J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3468
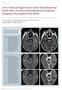
3 present in a few patients. Sialolithiasis is most commonly noted in the submandibular glands. (7,4) X-ray, USG and CT enable the identification of calculus. Ultrasound is however inferior to CT in differentiating a solitary large ductal calculus from a cluster of small calculi. The effect of the calculi and patency of the ductal system can be identified by conventional sialography, DSS or MR Sialography. MRI sialography is useful to look for strictures following passage of calculus. (8,9) Conventional sialography, DSS are invasive techniques and cannot be performed in the acute setting due to the possibility of exacerbating the symptoms associated with the existing infection. The act of instrumentation of the already inflamed gland will irritate and may cause post-traumatic oedema or stricture, which will aggravate the infection. The inflammatory products enter the periphery of the gland due to the retrograde injection of the contrast. This may also cause displacement of the calculus. (10,8) MR Sialography is a non-invasive technique. It can demonstrate ductal patency comparable to other techniques. MR Sialogram has the advantage of demonstrating the part of the duct on either side of the stricture or obstruction. MRI can identify the areas of stricture, where the stone had already resided. Fig. 3: a. MR Sialogram MIP Image, b. T2 FS Coronal Image, c. Axial CT Neck of a 29 yrs. Male Patient showing Calculus in the Right Parotid Duct causing Obstruction of the Duct cystic degeneration of neoplasms with or without superimposed infection. (6,10,8,9) Fig. 4: a. MR Sialogram MIP Image, b. Axial T2 FS Neck of a 39 yrs. Male Patient showing Calculus in the Left Submandibular Duct causing Obstruction of the Duct with Adjacent Inflammation Occasionally, an abscess in the gland that is associated with infiltration of the subcutaneous tissue might be present. In such cases, the presence of sialolith as the cause for the abscess should be excluded on a non-enhanced CT scan, US scan or conventional radiograph. Contrast-enhanced CT and MR imaging are currently the best ways to demonstrate a glandular abscess. Because of the fatty attenuation and intensity that is intrinsic to the parotid glands, particularly as one ages abscesses are particularly well seen on enhanced CT scans and postcontrast fat-saturated T1-weighted MR images. Diffusion weight imaging has been useful in detection of the abscess. The differential diagnosis for abscess include superinfected HIV related cysts, suppurative parotid lymph nodes and Fig. 5: a. Axial T2 FS b. MR Sialogram MIP Image, c. DWI d. ADC Images at the Floor of Mouth showing Calculus in the Left Submandibular Duct causing Obstruction of the Duct with Adjacent Abscess (Arrow). E. Axial CT Image of the same Patient showing Calculus Sialadenitis The most common cause of acute sialadenitis is infection. This is most commonly due to pathogens ascending from the oral cavity due to decreased salivary flow in conditions like J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3469
4 prior infections, dehydration, surgery, irradiation and obstructing lesions such as stones or tumours. Imaging is useful in detecting and defining the location of non-palpable and multiple calculi. Occasionally, a mucus plug instead of the calculus may be a cause of ductal obstruction and consequent acute sialadenitis. US shows diffusely enlarged gland with hypoechogenicity, heteroechoic pattern and increased vascularity in acute stages. Abscess formation may or may not be present. In chronic stages, the gland may be normal or small in size with decreased echogenicity and vascularity and heteroechoic pattern. (7,6) On CT and MR imaging, sialadenitis appears as moderate-to-intensely enhancing, diffusely enlarged salivary gland with or without abscess formation. Intraparenchymal and regional lymphadenopathy may be present. There is associated soft tissue stranding of adjacent fat and cervical fascia. As MRI is more sensitive to oedema, it picks up early sialadenitis and even inflammation of salivary ductal walls (Sialodochitis). (7,4,9) MRI can evaluate both glands simultaneously and MRI in coronal plane is very helpful in delineating the relationship of salivary gland lesions with other structures in the floor of mouth as in ranula (A mucous retention cyst) and in demonstrating the invasion of skull base, especially in parotid malignancy. (3,8,9) Fig. 6: a & b MR of a 47 yrs. Female- a. Axial T2FS showing Hyperintensity in the Right Parotid Gland b. MR Sialogram MIP Image Normal, c. Conventional Sialography Performed after the Treatment Fig. 7: a & b MR of a 21 yrs. Female- a. Coronal T2FS showing Hyperintensity in the Left Parotid Gland b. MR Sialogram MIP Image-Normal The causes for chronic sialadenitis include recurrent infection (Mycobacterial infections, syphilis, cat-scratch fever, toxoplasmosis, actinomycosis), prior irradiation, autoimmune disease, sarcoidosis and idiopathic. (4,10) On MR Sialography, it reveals pruning or truncation of major ducts and globular peripheral collections, as periphery of the gland is the usual site of initiation of this pathologic process. Presence of microabscesses may mimic peripheral collections of the autoimmune process. In these cases of painful salivary gland associated with chronic sialadenitis, in the absence of calculi, MR Sialogram gives a clue about the ductal system. Strictures lead to stasis of the secretions and aggravate the infection.(7,4) Fig. 8: a, b: Conventional Sialography, c. 3D CISS MIP Image in a 22 Years Female Patient showing Multiple Tiny Globular Collections (Of Contrast Material in Conventional Sialography) in the Bilateral Parotid Gland. Patient was Diagnosed to have Sjogren s Syndrome J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3470
5 Fig. 9: a & b- MR of a 16 yrs. Female - a. Coronal b. Axial T2FS showing Sialectasis of the Right Submandibular Gland STATISTICAL ANALYSIS The MR and conventional sialographic findings were compared with the final diagnoses. All data were calculated for the number of investigated salivary glands. Sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative predictive values were calculated for the detection of the acute sialadenitis (MRI during the episode and conventional sialogram after the episode), chronic sialadenitis and sialolithiasis. Chronic sialadenitis was the most frequent diagnosis, found in twenty six salivary glands (Sixteen parotid glands and ten submandibular glands). Patients referred with clinical diagnosis of acute sialadenitis, underwent MRI with MR Sialography during the acute phase, which showed altered signals in gland with normal ductal system. Conventional sialography was done after a course of antibiotic in nineteen glands (Twelve parotid glands and seven submandibular glands), which also showed normal ductal system. Sialolithiasis was diagnosed in fifteen glands (Six parotid and nine submandibular). MRI was false negative in two patients. MRI has an additional advantage of demonstrating adjacent soft tissue pathology. Five of patients with sialolithiasis showed abscess formation (With help of diffusion weighted imaging) due to obstruction. In two other investigated glands, parenchymal cystic lesion (n=1) (Fig. 10) and intraparotid lymphadenitis (n=1) were the diagnosis (Table 1). Fig. 10: 64 yr. Male Patient with Right Parotid Swelling and Pain, had Cystic Lesion in the Superficial Lobe of the Parotid with Normal Ductal Structures. Diagnosis of Cystic Warthin s Tumour was made on HPE Diagnosis No. of Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Gland Chronic sialadenitis Acute sialadenitis Sialolithiasis Others Table 1: Final Diagnosis of the Cases included in the Study Acute sialadenitis, chronic sialadenitis and sialolithiasis were the three frequent diagnoses sensitivity, specificity and positive and negative predictive values for MR Sialography and conventional sialography were tabulated in Table 2. Acute Sialadenitis Chronic Sialadenitis Sialolithiasis Performance MR Conventional MR Conventional MR Conventional Measure Sialogram Sialogram Sialogram Sialogram Sialogram Sialogram Sensitivity (%) Specificity (%) PPV (%) NPV (%) Table 2: Statistical Analysis Sensitivity of MR Sialography and conventional sialography for diagnosing chronic sialadenitis was 78% and 94%, specificity being 96% and 100% respectively. False negatives in MRI were due to lower spatial resolution of the MRI. The changes in the secondary and tertiary branches were depicted in the Conventional sialography, which were not seen on MR Sialography. Positive and negative predictive values for Conventional sialography were 98% and 92% respectively, and 91% and 95% for MR Sialography. The patients with acute sialadenitis underwent MRI with MR Sialography during the acute phase and Conventional sialography was done after a course of antibiotics. MR and Conventional sialography showed normal ductal system in all examined. The sensitivity and specificity for both modalities were 100%. However, MRI was superior to conventional sialography, as it could be done in acute phase. Imaging in the acute phase identified a case of intraparotid lymphadenitis, and hence Conventional sialography was deferred for that patient. Sensitivity of MR Sialography and conventional sialography for diagnosing sialolithiasis was 73% and 92%, specificity being 96% and 95% respectively. Positive and J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3471
6 negative predictive values for Conventional sialography were 94% and 97% respectively, and 91% and 90% for MR Sialography. MR Sialography showed false-negative results in two glands, which were due to small non-obstructing sialoliths. Sialectasis was identified in two patients due to chronic sialadenitis due to obstructing calculus. CONCLUSION From our study, we conclude that MR Sialography is a promising non-invasive technique for diagnosing the ductal abnormalities in major salivary glands. The advantages of MR Sialogram include no radiation hazard and non-invasive nature. Both the salivary glands can be easily imaged without change of the patient position. Images can be obtained with use of standard protocols and do not require special procedures (Cannulation). MRI can be done in acute sialadenitis, where conventional sialography is contraindicated. This adds to an additional benefit of differentiating the pathologies with similar presentation as in intraparotid lymphadenitis. Ductal structures can also be visualized on either side of the obstruction, and even in cases of complete obstruction of the ductal system. MR Sialography has an excellent sensitivity for visualization of oedema in the salivary parenchyma, which is more difficult to diagnose with CT. MR Sialography has the following limitations. The first being, low spatial resolution because of which secondary and tertiary branches could not be clearly visualised, and difficult to distinguish between complete and partial obstructions of the ductal system. In conclusion, our results show that MR Sialography with a heavily T2-weighted sequence is a promising diagnostic tool and carries the potential to replace invasive imaging methods like X-ray sialography in patients suspected of having sialadenitis and/or sialolithiasis. However, conventional and digital subtraction sialography continue to be the standard technique for imaging the duct system. REFERENCES 1. Kalinowski M, Heverhagen JT, Rehberg E, et al. Comparative study of MR sialography and digital subtraction sialography for benign salivary gland disorders. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23(9): Koontz NA, Kralik SF, Fritsch MH, et al. MR sialography: a pictorial review. Neurographics 2014;4(3): Uddin SM. Does MR sialography have a greater diagnostic accuracy than conventional x-ray and digital subtraction sialography in detecting salivary glands disease? A literature review. NJR 2011;1(1): Yousem DM, Kraut MA, Chalian AA. Major salivary gland imaging. Radiology 2000;216(1): Gadodia A, Seith A, Sharma R, et al. Magnetic resonance sialography using CISS and HASTE sequences in inflammatory salivary gland diseases: comparison with digital sialography. ACTA radiologica 2010;51(2): Rastogi R, Bhargava S, Mallarajapatna GJ, et al. Pictorial essay: salivary gland imaging. Indian Journal of Radiology and Imaging 2012;22(4): Bialek EJ, Jakubowski W, Zajkowski P, et al. US of the major salivary glands: anatomy and spatial relationships, pathologic conditions, and pitfalls. Radio Graphics 2006;26(3): Becker M, Marchal F, Becker CD, et al. Sialolithiasis and salivary ductal stenosis: diagnostic accuracy of mr sialography with a three-dimensional extended-phase conjugate-symmetry rapid spin-echo sequence. Radiology 2000;217(2): Jager L, Menauer F, Holzknecht N, et al. Sialolithiasis: MR sialography of the submandibular duct-an alternative to conventional sialography and US. Radiology 2000;216(3): Reddy SS, Rakesh N, Namita Raghav, et al. Sialography: report of 3 cases. Indian J Dent Res 2009;20(4): J. Evolution Med. Dent. Sci./eISSN , pissn / Vol. 05/ Issue 00/ June 00, 2016 Page 3472
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Diagnostic accuracy of MR sialography in sialolithiasis and salivary ductal stenosis
 The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 45 50 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine (2013) 44, 45 50 Egyptian Society of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine The Egyptian Journal of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrnm
Role of convencional sialography in the diagnosis of benign salivary diseases
 Role of convencional sialography in the diagnosis of benign salivary diseases Poster No.: C-1379 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Magalhães, I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, M. Gomes,
Role of convencional sialography in the diagnosis of benign salivary diseases Poster No.: C-1379 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Magalhães, I. Ferreira, A. B. Ramos, M. Gomes,
Comparative Study of MR Sialography and Digital Subtraction Sialography for Benign Salivary Gland Disorders
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1485 1492, October 2002 Comparative Study of MR Sialography and Digital Subtraction Sialography for Benign Salivary Gland Disorders Marc Kalinowski, Johannes T. Heverhagen, Elisabeth
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1485 1492, October 2002 Comparative Study of MR Sialography and Digital Subtraction Sialography for Benign Salivary Gland Disorders Marc Kalinowski, Johannes T. Heverhagen, Elisabeth
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES. Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS
 SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
SALIVARY GLAND DISEASES Omar alnoubani MD,MRCS Salivary Glands Overview Parotid gland Sublingual gland Submandibular gland Salivary glands - Types 3 Major Salivary Glands Parotid Submandibular Sublingual
INFECTION. HIV Infection DWI
 HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
HIV Infection INFECTION DWI Fig Axial CT and MRI images show multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the neck as well as in the parotid gland bilaterally. These nodes were suppurative with positive diffusion.
Review of Literature NJR 2011;1(1):70 77;Available online at
 Page70 Review of Literature NJR 2011;1(1):70 77;Available online at www.nranepal.org Does MR Sialography Have A Greater Diagnostic Accuracy Than Conventional X-Ray And Digital Subtraction Sialography In
Page70 Review of Literature NJR 2011;1(1):70 77;Available online at www.nranepal.org Does MR Sialography Have A Greater Diagnostic Accuracy Than Conventional X-Ray And Digital Subtraction Sialography In
Salivary Glands. The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major
 Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Salivary Glands Where Are Your Salivary Glands? The glands are found in and around your mouth and throat. We call the major salivary glands the parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands. They all secrete
Benign pathology of the salivary glands.
 Benign pathology of the salivary glands. Poster No.: C-2047 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Price, S. R. Rice, S. Patel, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords: Ear / Nose / Throat,
Benign pathology of the salivary glands. Poster No.: C-2047 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Price, S. R. Rice, S. Patel, S. Morley, T. Beale; London/UK Keywords: Ear / Nose / Throat,
Modern Sialography for Screening of Salivary Gland Obstruction
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:276-280, 2010 Modern Sialography for Screening of Salivary Gland Obstruction Oscar Hasson, DDS* Purpose: To revisit and reintroduce sialography as an important tool for the assessment
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 68:276-280, 2010 Modern Sialography for Screening of Salivary Gland Obstruction Oscar Hasson, DDS* Purpose: To revisit and reintroduce sialography as an important tool for the assessment
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas
 Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
Anatomical and Functional MRI of the Pancreas MA Bali, MD, T Metens, PhD Erasme Hospital Free University of Brussels Belgium mbali@ulb.ac.be Introduction The use of MRI to investigate the pancreas has
A CASE OF A Huge Submandibular Pleomorphic Adenoma
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery Volume 4 Number 2 S VERMA Citation S VERMA.. The Internet Journal of Head and Neck Surgery. 2009 Volume 4 Number 2. Abstract Pleomorphic adenoma
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 39/ May 14, 2015 Page 6787
 ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
ROLE OF HIGH RESOLUTION SONOGRAPHY IN CHARACTERIZATION OF SOLID SALIVARY GLAND TUMORS Sheetal Singh 1, Amlendu Nagar 2, Pramod Sakhi 3, Sachin Kataria 4, Kumud Julka 5, Anup Gupta 6 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast
 MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
MRI Abdomen Protocol Pancreas/MRCP with Contrast Reviewed By: Brett Mollard, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: July 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 Standard uses: 1. Characterization of cystic and solid
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders. Raymond P. Wood. History
 Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
Chapter 10: Salivary Gland Disorders Raymond P. Wood Dysfunction of the salivary glands is usually manifested in one of two ways: swelling of the gland, either diffuse or discrete, or by dry mouth (xerostomia).
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
Salivary Gland Imaging. Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016
 Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Salivary Gland Imaging Mary Scanlon MD FACR October 2016 Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal anatomy Discuss work up, management and differential diagnosis of commonly referred clinical scenarios
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology
 Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Ultrasound Interpretation of Non-Thyroid Neck Pathology Kevin T. Brumund, M.D., F.A.C.S. Associate Professor of Surgery Head and Neck Surgery University of California, San Diego Health Sciences VA Medical
Childhood Illnesses of the Salivary Gland
 Childhood Illnesses of the Salivary Gland Otávio Piltcher Clinical Case Natália is 3 years old and has received all the routine vaccines. She presents periodic swelling on the left side of the parotid
Childhood Illnesses of the Salivary Gland Otávio Piltcher Clinical Case Natália is 3 years old and has received all the routine vaccines. She presents periodic swelling on the left side of the parotid
3D high-resolution MR imaging can provide reliable information
 Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
Published April 11, 2013 as 10.3174/ajnr.A3472 ORIGINAL RESEARCH HEAD & NECK High-Resolution MRI of the Intraparotid Facial Nerve Based on a Microsurface Coil and a 3D Reversed Fast Imaging with Steady-State
 INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD INTRAUTERINE DEVICE = IUD CONGENITAL DISORDERS Pyometra = pyometrea is a uterine infection, it is accumulation of purulent material in the uterine cavity. Ultrasound is usually
1. Resident Doctor, 2. Professor, Geetanjali Medical College & Hospital, Udaipur, Rajasthan.
 International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) www.ijmse.com Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
International Journal of Medical Science and Education An official Publication of Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) www.ijmse.com Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
Disclosure. Acknowledgement. What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Rectal cancer imaging. None
 What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
What is the Best Workup for Rectal Cancer Staging: US/MRI/PET? Zhen Jane Wang, MD Assistant Professor in Residence UC SF Department of Radiology Disclosure None Acknowledgement Hueylan Chern, MD, Department
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging. technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts,
 SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
SECRETIN AUGMENTED MRCP Riccardo MANFREDI, MD, MBA, FESGAR Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) is an imaging technique that is able to non-invasively assess bile and pancreatic ducts, in
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Major Salivary Glands: Sonographic Anatomy and Pathologic Conditions
 Major Salivary Glands: Sonographic Anatomy and Pathologic Conditions Poster No.: C-0452 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, I. Tritou, E. Sfakianaki ; Rethymno, CR/GR, 1
Major Salivary Glands: Sonographic Anatomy and Pathologic Conditions Poster No.: C-0452 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, I. Tritou, E. Sfakianaki ; Rethymno, CR/GR, 1
Original Article Diagnostic value of high-frequency ultrasound for submandibular gland sialolithiasis
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3076-3082 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016258 Original Article Diagnostic value of high-frequency ultrasound for submandibular gland sialolithiasis Hong-Yan Chen 1*,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(2):3076-3082 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0016258 Original Article Diagnostic value of high-frequency ultrasound for submandibular gland sialolithiasis Hong-Yan Chen 1*,
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor
 MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
MR Tumor Staging for Treatment Decision in Case of Wilms Tumor G. Schneider, M.D., Ph.D.; P. Fries, M.D. Dept. of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, Saarland University Hospital, Homburg/Saar, Germany
Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis
 Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
Original article: Study of validity of ultrasonographic diagnosis in relation to Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC) diagnosis *Dr Rajvi Matalia, ** Dr Y.P.Sachdev, ***Dr D.S.Kulkarni *Junior Resident,
Acute Sialadenitis in Childhood: CT Findings and Clinical Manifestation according to the Gland Involvements
 Acute Sialadenitis in Childhood: CT Findings and Clinical Manifestation according to the Gland Involvements Poster No.: C-0669 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Lee; Bucheon/KR Keywords:
Acute Sialadenitis in Childhood: CT Findings and Clinical Manifestation according to the Gland Involvements Poster No.: C-0669 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Lee; Bucheon/KR Keywords:
Neuroradiology MR Protocols
 Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Neuroradiology MR Protocols Brain protocols N 1: Brain MRI without contrast N 2: Pre- and post-contrast brain MRI N 3 is deleted N 4: Brain MRI without or pre-/post-contrast (seizure protocol) N 5: Pre-
Imaging Technique. Ultrasound Imaging of the Salivary Glands. Parotid Gland. The Major Salivary Glands. Parotid Gland: Stenson s Duct.
 Ultrasound Imaging of the Salivary Glands Edward G. Grant MD Professor & Chairman, Dept of Radiology USC Keck School of Medicine edgrant@usc.edu edgrant@usc.edu Imaging Technique Linear array transducer
Ultrasound Imaging of the Salivary Glands Edward G. Grant MD Professor & Chairman, Dept of Radiology USC Keck School of Medicine edgrant@usc.edu edgrant@usc.edu Imaging Technique Linear array transducer
Evaluation of Neck Mass. Disclosure. Learning Objectives 3/24/2014. Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ. Nothing to disclose
 Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Evaluation of Neck Mass Karen T. Pitman MD, FACS Banner MDACC, Gilbert AZ Nothing to disclose Disclosure Learning Objectives 1. Describe a systematic method to evaluate a patient with a neck mass 2. Select
Submandibular sialolithiasis with CT and scintigraphy: CT values and salivary gland excretion in the submandibular glands
 Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 227-31 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.227 Submandibular sialolithiasis with CT and scintigraphy: CT values and salivary gland excretion in the submandibular
Imaging Science in Dentistry 2017; 47: 227-31 https://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2017.47.4.227 Submandibular sialolithiasis with CT and scintigraphy: CT values and salivary gland excretion in the submandibular
Chapter 7 General conclusions and suggestions for future work
 Chapter 7 General conclusions and suggestions for future work Radiation therapy (RT) is one of the principle treatment modalities for the management of cancer. In recent decades, advances in the radiation
Chapter 7 General conclusions and suggestions for future work Radiation therapy (RT) is one of the principle treatment modalities for the management of cancer. In recent decades, advances in the radiation
Contents. Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology. Ultrasound Nodule Characteristics
 Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Contents Basic Ultrasound Principles and Terminology Basic Ultrasound Principles... 1 Ultrasound System... 2 Linear Transducer for Superficial Images and Ultrasound-Guided FNA... 3 Scanning Planes... 4
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis. Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně
 Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
Role of Imaging Methods in Diagnosis of Acute Pancreatitis Válek V. Radiologická klinika, FN Brno a LF MU v Brně New Classification: Acute Pancreatitis 2007 revision of Atlanta classification and definitions
Sialadenitis without Stones. Case. University of California, San Francisco 11/6/2014
 Andrew H. Murr, MD Professor and Chairman Roger Boles, MD Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education Department of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery Sialadenitis without Stones: RAI, Autoimmune, and
Andrew H. Murr, MD Professor and Chairman Roger Boles, MD Endowed Chair in Otolaryngology Education Department of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery Sialadenitis without Stones: RAI, Autoimmune, and
Sialoendoscopy-Assisted Sialolithectomy for Submandibular Hilar Calculi
 J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71:295-301, 2013 Sialoendoscopy-Assisted Sialolithectomy for Submandibular Hilar Calculi Deng-Gao Liu, SMD,* Lan Jiang, SMD, Xiao-Yan Xie, SMD, Zu-Yan Zhang, DDS, PhD, Lei Zhang,
J Oral Maxillofac Surg 71:295-301, 2013 Sialoendoscopy-Assisted Sialolithectomy for Submandibular Hilar Calculi Deng-Gao Liu, SMD,* Lan Jiang, SMD, Xiao-Yan Xie, SMD, Zu-Yan Zhang, DDS, PhD, Lei Zhang,
FISH BONE : THE REASON BEHIND SUBMANDIBULAR SIALADENTITS - A UNIQUE CASE REPORT
 Oral Surgery Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 3, May-June 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. FISH BONE : THE REASON BEHIND SUBMANDIBULAR
Oral Surgery Case Report International Journal of Clinical And Diagnostic Research ISSN 2395-3403 Volume 5, Issue 3, May-June 2017 Glorigin Lifesciences Private Limited. FISH BONE : THE REASON BEHIND SUBMANDIBULAR
1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? 2. What is the embryologic origin of minor salivary glands?
 Salivary Gland Chapters 37, 38, 39, 40 Shapiro 1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? Outpouchings of oral ectoderm in the 6th 8 th week 2. What is the
Salivary Gland Chapters 37, 38, 39, 40 Shapiro 1. What is the embryologic origin of the major salivary glands, and when do they develop? Outpouchings of oral ectoderm in the 6th 8 th week 2. What is the
Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group. Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer. Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i & 11-1C-106i
 Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Greater Manchester, Lancashire & South Cumbria Strategic Clinical Network & Senate Head & Neck Clinical Sub Group Network Agreed Imaging Guidelines for UAT and Thyroid Cancer Measure Nos: 11-1C-105i &
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Imaging of liver and pancreas
 Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Imaging of liver and pancreas.. Disease of the liver Focal liver disease Diffusion liver disease Focal liver disease Benign Cyst Abscess Hemangioma FNH Hepatic adenoma HCC Malignant Fibrolamellar carcinoma
Sialendoscopy for Obstructive Salivary Gland Disorders
 Disclosures Sialendoscopy for Obstructive Salivary Gland Disorders None Otolaryngology Head Jolie Chang, MD Assistant Professor Otolaryngology, Head University of California, San Francisco November 8,
Disclosures Sialendoscopy for Obstructive Salivary Gland Disorders None Otolaryngology Head Jolie Chang, MD Assistant Professor Otolaryngology, Head University of California, San Francisco November 8,
High Resolution Ultrasound of the Submandibular Gland
 DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26094:2276 Radiology Section Review Article High Resolution Ultrasound of the Submandibular Gland Prashant Madhukarrao Onkar, Chetana Ramesh Ratnparkhi, Kajal Mitra ABSTRACT Submandibular
DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2017/26094:2276 Radiology Section Review Article High Resolution Ultrasound of the Submandibular Gland Prashant Madhukarrao Onkar, Chetana Ramesh Ratnparkhi, Kajal Mitra ABSTRACT Submandibular
Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal Glands in Indian Population
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. V January. (2018), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 17, Issue 01 Ver. V January. (2018), PP 26-30 www.iosrjournals.org Computed Tomography of Normal Adrenal
Methods. Yahya Paksoy, Bülent Oğuz Genç, and Emine Genç. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24: , August 2003
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1364 1368, August 2003 Retrograde Flow in the Left Inferior Petrosal Sinus and Blood Steal of the Cavernous Sinus Associated with Central Vein Stenosis: MR Angiographic Findings
Radiologic Imaging Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
 Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Radiologic Imaging X-ray has always been the golden rule in diagnosing and treating podiatric patients. Unfortunately, for some patients the diagnosis is not as evident. That is when we need to utilize
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University
 Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Alice Fung, MD Oregon Health and Science University Disclosure Comments The speaker Alice Fung, MD Has relevant financial relationships to disclose. Received honorarium from (Guerbet). This individual
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
TABLES. Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging. Conclusions. Author (Year) Classification Process/Evid ence Class
 TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
TABLES Imaging Modalities Evidence Tables Table 1 Computed Tomography (CT) Imaging Author Clark (1986) 9 Reformatted sagittal images in the differential diagnosis meningiomas and adenomas with suprasellar
NEURO PROTOCOLS MRI NEURO PROTOCOLS (SIEMENS SCANNERS)
 Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Page 1 NEURO PROTOCOLS Brain Stroke Brain Brain with contrast Brain for seizures Brain for MS Brain for Pineal gland Sella FAST Scan for hydrocephalus MRA/MRV Brain MRA carotids 8 th nerve Cranial nerves
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline
 Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
Abdomen Sonography Examination Content Outline (Outline Summary) # Domain Subdomain Percentage 1 2 3 Anatomy, Perfusion, and Function Pathology, Vascular Abnormalities, Trauma, and Postoperative Anatomy
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity.
 A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
A pictorial review of the Benign and Malignant Conditions involving the Salivary Glands and Oral Cavity. Poster No.: C-2266 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Lavelle, J. F. Gerstenmaier,
Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE:
 Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE: This lecture describes the most common indications for referred
Practical CT and MRI Anthony J. Fischetti, DVM, MS, DACVR Department Head of Diagnostic Imaging The Animal Medical Center, New York OBJECTIVE: This lecture describes the most common indications for referred
Cystic Head and Neck Lesions
 Cystic Head and Neck Lesions Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 19 March 2018 Key points Huge variety of cystic lesions in H&N May be cystic, necrotic, or solid but cystic-appearing Patient age, clinical
Cystic Head and Neck Lesions Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 19 March 2018 Key points Huge variety of cystic lesions in H&N May be cystic, necrotic, or solid but cystic-appearing Patient age, clinical
Pleomorphic adenoma head and neck
 Pleomorphic adenoma head and neck Poster No.: C-1042 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. E. Pérez Montilla, I. Bravo Rey, E. Roldán Romero, F. BravoRodríguez; Cordoba/ES Keywords:
Pleomorphic adenoma head and neck Poster No.: C-1042 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. E. Pérez Montilla, I. Bravo Rey, E. Roldán Romero, F. BravoRodríguez; Cordoba/ES Keywords:
Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Dilatation of Stensen s Duct
 The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. TRIOLOGICAL SOCIETY CANDIDATE THESIS Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Dilatation of Stensen s Duct Yang
The Laryngoscope VC 2011 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. TRIOLOGICAL SOCIETY CANDIDATE THESIS Diagnosis and Treatment of Congenital Dilatation of Stensen s Duct Yang
Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XVIII, nº 70, pág. 61-70, Abr.-Jun., 2006 Pediatric Retroperitoneal Masses Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Marilyn J. Siegel Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE
 RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
RADIOLOGY TEACHING CONFERENCE John Athas, MD Monica Tadros, MD Columbia University, College of Physicians & Surgeons Department of Otolaryngology- Head & Neck Surgery September 27, 2007 CT SCAN IMAGING
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
The following images were all acquired using a CTI Biograph
 Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Positron Emission Tomography/ Computed Tomography Imaging of Head and Neck Tumors: An Atlas Michael M. Graham, MD, PhD, and Yusuf Menda, MD Department of Radiology, University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA. Address
Imaging Work-Up of a Neck Mass - Adults & Children
 Disclosures Imaging Work-Up of a Neck Mass - Adults & Children I have nothing to disclose Christine M Glastonbury MBBS Professor of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery and
Disclosures Imaging Work-Up of a Neck Mass - Adults & Children I have nothing to disclose Christine M Glastonbury MBBS Professor of Radiology & Biomedical Imaging Otolaryngology-Head & Neck Surgery and
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI
 Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Emerging Techniques in Breast Imaging: Contrast-Enhanced Mammography and Fast MRI Lilian Wang, M.D. Breast Imaging Section Department of Radiology Northwestern Medicine Overview Rationale for new imaging
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis
 73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
73. Urinary Bladder and Male Pelvis Urinary bladder carcinoma is best locally staged with MRI. It is important however to note that a thickened wall (> 5 mm) is a non-specific finding seen in an underfilled
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines SINUS MRI Original Date: November 2007 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 70540, 70542, 70543 Last Review Date: July 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July
CASE REPORT CECT EVALUATION OF AN ISOLATED LONG SEGMENT IVC THROMBUS IN A PATIENT WITH ACUTE ON CHRONIC PANCREATITIS: A CASE REPORT
 CECT EVALUATION OF AN ISOLATED LONG SEGMENT IVC THROMBUS IN A PATIENT WITH ACUTE ON CHRONIC PANCREATITIS: A Pronami Borah 1, Biswajit Borah 2, Kangkana Mahanta 3, Rudra K. Gogoi 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
CECT EVALUATION OF AN ISOLATED LONG SEGMENT IVC THROMBUS IN A PATIENT WITH ACUTE ON CHRONIC PANCREATITIS: A Pronami Borah 1, Biswajit Borah 2, Kangkana Mahanta 3, Rudra K. Gogoi 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012
 Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
Soft Tissue Tumour & Sarcoma Imaging Guidelines 2012 Version Control This is a controlled document please destroy all previous versions on receipt of a new version. Date Approved: March 2011 reissued April
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies
 Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Original article: Comparative study of high resolusion ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosing traumatic knee injuries & pathologies Dr. Rakesh Gujjar*, Dr. R. P. Bansal, Dr. Sandeep
Introduction to Sialendoscopy and Salivary Duct Surgery
 Disclosures Introduction to Sialendoscopy and Salivary Duct Surgery None Otolaryngology Head Jolie Chang, MD Assistant Professor Otolaryngology, Head University of California, San Francisco November 6,
Disclosures Introduction to Sialendoscopy and Salivary Duct Surgery None Otolaryngology Head Jolie Chang, MD Assistant Professor Otolaryngology, Head University of California, San Francisco November 6,
Original Research Article
 ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
ROLE OF IN INTERNAL DERANGEMENT OF KNEE JOINT IN CORRELATION WITH ARTHROSCOPY Onteddu Joji Reddy 1, Jamkhana Abdul Gafoor 2, Balla Suresh 3, Polysetty Obuleswar Prasad 4 1Professor and HOD, Department
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases
 GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
GI cycle - Lecture 14 436 Teams Radiology of hepatobiliary diseases Objectives 1. To Interpret plan x-ray radiograph of abdomen with common pathologies. 2. To know the common pathologies presentation.
First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body
 Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Clinical Oncological Imaging First Clinical Experiences with Simultaneous Multi-Slice Accelerated Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Throughout the Body Valentin Tissot, M.D. 1 ; Olivier Legeas, M.D. 1 ; Isabelle
Diagnostic Imaging
 www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Diagnostic Imaging Diagnostic Imaging is no longer limited to radiography. Major technological advancements have lead to the use of new and improved imaging technologies. The
11/10/2015. Prostate cancer in the U.S. Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning. NIH estimates for 2015.
 Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
Multi-parametric MRI of Prostate Diagnosis and Treatment Planning Temel Tirkes, M.D. Associate Professor of Radiology Director, Genitourinary Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS. Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3
 PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
PAPILLARY THYROID CARCINOMA PRESENTING AS A LATERAL NECK MASS MASS Dr. Pamela Hanson DO PGY3 MK CASE PRESENTATION 28 yo Female presented to the ENT Clinic in October 2016, with the complaint of chronic
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Normal Tongue: Qualitative Evaluation of Fat-suppressed Contrast Enhanced Images
 Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 49 1, 2 21-28, 2003 21 Original Article Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Normal Tongue: Qualitative Evaluation of Fat-suppressed Contrast Enhanced Images Yasunori
Bulletin of the Osaka Medical College 49 1, 2 21-28, 2003 21 Original Article Magnetic Resonance Imaging of the Normal Tongue: Qualitative Evaluation of Fat-suppressed Contrast Enhanced Images Yasunori
Recurrent Parotid Enlargement - A study of clinical, sialographic. and treatment aspects of 68 cases
 Ceylon J. mei. Sci. 29 (No. 2 December) 1986. pp. 53 59. Recurrent Parotid Enlargement - A study of clinical, sialographic. and treatment aspects of 68 cases N. A. de S. A M A R A T U N G A Division of
Ceylon J. mei. Sci. 29 (No. 2 December) 1986. pp. 53 59. Recurrent Parotid Enlargement - A study of clinical, sialographic. and treatment aspects of 68 cases N. A. de S. A M A R A T U N G A Division of
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]
![General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ] General Imaging. Imaging modalities. Incremental CT. Multislice CT Multislice CT [ MDCT ]](/thumbs/76/74079340.jpg) General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
General Imaging Imaging modalities Conventional X-rays Ultrasonography [ US ] Computed tomography [ CT ] Radionuclide imaging Magnetic resonance imaging [ MRI ] Angiography conventional, CT,MRI Interventional
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Clinical Applications
 C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
C H A P T E R 16 Clinical Applications In selecting pulse sequences and measurement parameters for a specific application, MRI allows the user tremendous flexibility to produce variations in contrast between
DIAGNOSIS OF SALIVARY GLAND DISORDERS
 DIAGNOSIS OF SALIVARY GLAND DISORDERS Diagnosis of salivary gland disorders edited by K. GRAAMANS Department of oj Otorhinolaryngology, Vniversity University Hospital Vtrecht, Ulrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
DIAGNOSIS OF SALIVARY GLAND DISORDERS Diagnosis of salivary gland disorders edited by K. GRAAMANS Department of oj Otorhinolaryngology, Vniversity University Hospital Vtrecht, Ulrecht, Utrecht, The Netherlands
3D MR SIALOGRAPHY AS A TOOL TO INVESTIGATE RADIATION-INDUCED XEROSTOMIA: FEASIBILITY STUDY
 doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.062 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 5, pp. 1310 1319, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
doi:10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.01.062 Int. J. Radiation Oncology Biol. Phys., Vol. 68, No. 5, pp. 1310 1319, 2007 Copyright 2007 Elsevier Inc. Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0360-3016/07/$ see front
Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II ( )
 King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
King Saud University College of Dentistry Dept. of Oral Medicine & Diagnostic Sciences Division of Oral & Maxillofacial Radiology Course Description 343 DDS- Clinical Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology II
Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT?
 Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT? Alina Uzelac, D.O. Assistant Clinical Professor Neuroradiology UCSF Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging San Francisco General Hospital Overview CT MRI
Imaging: When to get MRI, CT or PET-CT? Alina Uzelac, D.O. Assistant Clinical Professor Neuroradiology UCSF Department of Radiology and Biomedical Imaging San Francisco General Hospital Overview CT MRI
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 01 Page January
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i1.28 Diagnostic Accuracy of Magnetic Resonance
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم. Prof soha Talaat
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Ovarian tumors The leading indication for gynecologic surgery. Preoperative characterization of complex solid and cystic adnexal masses is crucial for informing patients about possible
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 09/Jan 29, 2015 Page 1533
 EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
EVALUATION OF CERVICAL LYMPHNODES BY ULTRASONOGRAPHY IN CORRELATION WITH FNAC Aaditya Kumar Singh 1, Purnima Hegde 2, Anil Kumar Sakalecha 3, T. N. Suresh 4, P. N. Sreeramulu 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis
 Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
Intraluminal gas in non-perforated acute appendicitis: a CT sign of gangrenous appendicitis Poster No.: C-978 Congress: ECR 202 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: D. Plata Ariza, E. MARTINEZ CHAMORRO, J.
MR Microscopy of the Parotid Glands in Patients with Sjögren s Syndrome: Quantitative MR Diagnostic Criteria
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1207 1214, May 2005 MR Microscopy of the Parotid Glands in Patients with Sjögren s Syndrome: Quantitative MR Diagnostic Criteria Yukinori Takagi, Misa Sumi, Tadateru Sumi, Yoko
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1207 1214, May 2005 MR Microscopy of the Parotid Glands in Patients with Sjögren s Syndrome: Quantitative MR Diagnostic Criteria Yukinori Takagi, Misa Sumi, Tadateru Sumi, Yoko
A GIANT SIALOLITH WITH PERFORATION OF THE FLOOR OF MOUTH.
 ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 A GIANT SIALOLITH WITH PERFORATION OF THE FLOOR OF MOUTH. *Sanjana V. Nemade *Vidya V. Rokade. *Dr. Netra A. Pathak *Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical college and General
ISSN: 2250-0359 Volume 3 Issue 4 2013 A GIANT SIALOLITH WITH PERFORATION OF THE FLOOR OF MOUTH. *Sanjana V. Nemade *Vidya V. Rokade. *Dr. Netra A. Pathak *Smt. Kashibai Navale Medical college and General
Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu
 2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
2009 Radiological anatomy of frontal sinus By drtbalu Anatomy of frontal sinus is highly variable. Precise understanding of these variables will help a surgeon to avoid unnecessary complications during
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
RADIOLOGY (MEDICAL IMAGING)
 RADIOLOGY (MEDICAL IMAGING) Radiology is the study of the diagnosis of disease by the use of radiant energy (radiation). In the past this meant the use of X-rays to make an image. Today many other forms
RADIOLOGY (MEDICAL IMAGING) Radiology is the study of the diagnosis of disease by the use of radiant energy (radiation). In the past this meant the use of X-rays to make an image. Today many other forms
