Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma
|
|
|
- Coral McDonald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CSU ID: Name: Sonal Patel Differential Connexin Function Enhances Self-Renewal in Glioblastoma Cancer is one of the most common disease in the US with more than a million people affected every year. Numerous theories have been postulated to understand its cause and mechanisms, yet, with no complete cure for the disease. Several studies of the cancerous tumors have revealed that it is a chunk of heterogeneous population of cells. Previously, these cells were thought to be evolved through the clonal evolution theory where a cell undergoes series of mutation and gives rise to several of its kind and others that have similar tumorigenic potential(nowell, Peter 1976). Later in 1990s, a new theory of cancer stem cell drew large attention of many researchers(bonnet & Dick 1997; Lapidot et al. 1994). According to the Cancer Stem Cell (CSC) theory, there are a few stem cells-like cells, capable of self-renewing, that have tumorigenic capacity and are able to sustain the tumor through generation of heterogeneous population of cells. Multiple pathways could give rise to the tumor cells either from a single or multiple CSCs. Also not all types of cancers consist of CSCs as the tumor initiating cells while others such as glioblastomas (GBM) contain several self-renewing CSCs that contribute to tumor formation and propagation. Few tumors consist of biologically distinct population of CSCs such as that observed in PTEN- deficient glioblastoma(chen et al. 2010). Glioblastoma is one of the fatal and most common type of a brain tumor. Therapeutic resistance and tumor heterogeneity are the major hurdles that make the current therapies ineffective in treatment of this tumor. GBM tumor cells is known to consist of a large number of CSCs that add to the therapeutic resistance. One of the biggest barrier in understanding the biology of a tumor is the heterogeneous population of the cells with the CSCs contributing majorly. CSCs play most critical role in tumor development and are the major threat in the treatment of the disease due to its mysterious behavior. During the treatment these cells could enter the latent state with the
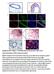
2 dangerously high risk of relapse. Also as a part of protection mechanism CSCs could revert back to non-cscs and vice versa, which could again make their detection difficult. CSCs survival largely depends on its microenvironment including growth factors, nutrients and communication with the adjacent cells(visvader & Lindeman 2012). In 1966, Loewenstein and colleagues, first implicated the role of gap junctions in tumorigenesis and since then it has been a target for many researchers(loewenstein & Kanno 1966). Gap junctions are defined as the cell to cell junctions that holds the plasma membranes in close apposition and allows for the passage of nutrients, signals and other metabolites from one cell to another. The gap is bridged by 21 connexin proteins that form channels to allow substances to pass through. These have tissue specific expression and functions in development, differentiation and metabolic homeostasis. Its dysfunction is related to connexin-type specific diseases such as cataract (Cx 46 and Cx 50)(Beyer & Berthoud 2014). Connexins were hypothesized to have a role in tumor suppression since several studies in rodent tumors and tumor cell lines have demonstrated the downregulation of connexin proteins. Also, connexin knockout mice are more prone to tumor formation when challenged with carcinogenic agents(naus & Laird 2010). In accordance with the tumor suppressive role, Cx43, one of the most widely studied connexin is known to be downregulated in GBM while its overexpression in CSCs is related to tumor latency(yu et al. 2012). However, recent data shows a more complicated role of connexins in facilitating tumor progression as opposed to suppression. Hitomi et al paper demonstrate that connexin, Cx46, is required for tumor progression in GBM. Further, it is shown that Cx46 is upregulated in CSCs and is required for the growth and maintenance of the tumor. Xenograft models T4121 and T387 which are the classical and mesenchymal subtypes have been used in this study. Figure 1 shows the presence of the gap junctions in the xenograft tumor sections and CSC spheres invitro by electron microscopy. CSCs were isolated using papain dissociation test and identified using stem cell specific markers, CD133 and α6 integrin. The functional cell-cell communication through gap junction was
3 confirmed by microinjecting the dye along with the fluorescent IgG such that the dye diffused easily through the gap junctions while the IgG being too large in size was not able to pass through, as observed by the time lapse imaging. Further the functional role of gap junctions was confirmed by similar single cell injection of the dye particles in the presence of several gap junction inhibitors such as carbenoxolone (CBX) and 1-octanol etc. As observed in figure 2, the diffusion of dye through the gap junctions is significantly reduced in CSCs isolated from both the xenograft models. Since the CSCs seem to have functional gap junctions, it would be interesting to study the effect of blocking these gap junctions on the phenotype of CSCs. To study this, growth of CSCs was checked in the presence of gap junction inhibitors. As expected, the growth of CSCs dramatically reduced upon inhibiting gap junctions (Figure 3A). Further, self-renewal ability of the CSCs was checked by sphere formation assay using range of concentrations of inhibitors. Reduction in the number of spheres formed per well as well as stem cell frequency was observed (Figure 3B and C). The reduction in the growth of CSCs was due to increased apoptosis as was observed by the increased caspase3/7 activity. Also the specificity of the inhibitor towards CSCs population was confirmed by comparing the IC50 value of CSCs vs NPCs. The effect of gap junction inhibitors on tumor growth was assayed in the presence of anti-tumor agent, temozolomide (TMZ). Inhibitor alone was able to reduce the tumor volume significantly whereas additive effect on tumor growth suppression was observed when combined with TMZ. Interestingly, the effect was also seen in orthotopic tumor model as the mice with intracranial tumors given gap junction inhibitor for 14 days demonstrated increased tumor latency as well as survival. Furthermore, gap junction inhibitors decreased the growth of the TMZ-resistant population sensitizing a large population of tumor cells to TMZ thus increasing its efficacy. After establishing the role of gap junctions in the maintenance of CSCs in GBM tumor next step was to find which connexins aid in tumor formation and maintenance. For this qpcr analysis was carried out to study the expression of different connexins in the NPCs and GBM models. Analysis
4 showed Cx46 expression to be significantly elevated in CSCs while Cx43 was high in non-csc population. It was confirmed by immunoblot analysis of Cx46 which showed enrichment in CD133+ CSC cells than in non-cscs where Cx43 levels were found to be higher. Location of Cx46 and Cx43 was evaluated by differentiating the CSCs using differentiation medium with 10% serum and removal of growth factors. Upon differentiation Cx46 levels reduced while Cx43 levels increased in agreement with the above results. Thus Cx46 is highly expressed in CSCs while Cx43 in non CSCs which increases upon differentiation of CSCs. To understand the role of Cx46 in CSCs, its self-renewal and proliferation ability was tested in the absence of Cx46. Therefore, Cx46 was knockdown (KD) in CSCs using shrna constructs. Upon Cx46 KD, growth of CSCs was stunted with induced apoptosis as assessed by caspase activity along with reduction in its self-renewal ability and stem cell frequency. If Cx46 was required for tumor formation was further assessed by injecting Cx46 KD CSCs into the brains of immunocompromised mice. Upon Cx46 KD, mice demonstrated high tumor latency and reduced tumor forming capacity compared to the controls which suggests that Cx46 is necessary for tumor formation and maintenance of CSC population in GBM tumor. Next question was, what is the physiological consequence of Cx46 high expression in CSCs? What is its effect on the resting membrane potential in CSCs? To answer these questions dye diffusion method was used to check for the relative diffusion between the CSCs upon Cx46 KD. New gap junction establishment assay showed that CSCs were quick in establishing new gap junctions compared to non CSCs as is shown in Figure 5. Also diffusion was relatively slower in Cx46 KD CSCs compared to the normal CSCs. Moreover outward current flow measured in CSCs was rather reduced than in non CSCs possibly due to inhibition of flow of potassium across the membranes which was also confirmed by the depolarized resting membrane potential in CSCs. Based on previous studies Cx43 and Cx46 expressions are known to be linked. Indeed, Cx43 KD in non CSCs leads to increased expression of Cx46 in CSCs which is in correlation with the increased resting membrane potential observed in Cx43 KD as in normal CSCs. This implicates
5 that the expression of different connexins in CSCs and non CSCs dictates differentiation that in turn affects gap junction formation and resting membrane potential. To establish the relation between Cx46 and GBM patient survival, bioinformatics analysis was carried out of data available in several datasets such as Oncomine and the National Cancer Institute (NCI) Repository for Molecular Brain Neoplasia Data (REMBRANDT). Analysis revealed poor prognosis of GBM and glioma patients upon Cx46 upregulation as is presented in Figure 6. However, no such correlation was observed between different other connexins and patient survival indicating the importance of Cx46 in CSC maintenance. Overall, although the connexins, as gap junction proteins, have been well established as exhibiting anti-tumor effect as its reduced levels correlate with the increased incidences of tumors, this paper talks about the pro tumorigenic role of one of the connexin, Cx46. Though the link between Cx43 and Cx46 has been shown in the paper it requires further detailed analysis as there could be several important proteins such as those involved in EMT, cadherins, linking these two major proteins. A study in Cx46 Knockouts and tumor development in these animals would provide further insights into the mechanism and role of Cx46 in CSCs maintenance. Another question that needs to be addressed is; what will be the effect of knockdown of both Cx46 and Cx43 in tumor formation and CSCs? Also the inhibitors used in this study target several connexins and are not specific for Cx46 thus a connexin specific inhibitor should be tested. It is also necessary to test the resistance to drugs other than TMZ since the effect of gap junctions to see if the increased efficacy is universal for GBM drugs or it is drug specific effect. However, this paper highlights an important point relating to the isotype specific role of connexins. Hence, development of therapies targeting gap junction proteins should be carefully considered, as not all proteins involved in gap junctions behave in a similar manner or have similar functions. Nevertheless, this paper adds many more questions to the GBM horizon that could contribute in unravelling the cause of this mysterious disease.
6 Beyer, E.C. & Berthoud, V.M., Connexin hemichannels in the lens. Frontiers in Physiology, 5 FEB. Bonnet, D. & Dick, J.E., Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nature Med., 3, pp Available at: Chen, R. et al., A Hierarchy of Self-Renewing Tumor-Initiating Cell Types in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell, 17(4), pp Lapidot, T. et al., A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature, 367(6464), pp Loewenstein, W.R. & Kanno, Y., Intercellular communication and the control of tissue growth: lack of communication between cancer cells. Nature, 209(5029), pp Naus, C.C. & Laird, D.W., Implications and challenges of connexin connections to cancer. Nature reviews. Cancer, 10(6), pp Nowell, Peter, C., The Clonal Evolution of Tumor Cell Populations. Science. Visvader, J.E. & Lindeman, G.J., Cancer stem cells: Current status and evolving complexities. Cell Stem Cell, 10(6), pp Yu, S.C. et al., Connexin 43 reverses malignant phenotypes of glioma stem cells by modulating E-cadherin. Stem Cells, 30(2), pp
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT
 CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
CRIPTO-1 A POSSIBLE NEW BIOMARKER IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORME PIA OLESEN, MD, PHD STUDENT Glioblastoma WHO Grade IV Glioma Heterogenic Undiffenrentiated phenotype 50% of all Gliomas Around 600 patients
Stem cells and Cancer. John Glod. December 2, 2009
 Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
Stem cells and Cancer John Glod Lehigh University Lehigh University December 2, 2009 The Tumor Microenvironment Littlepage et al Cancer Cell 2005 Cancer Stem Cells A small group of cells within the larger
TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
 Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Pr John DE VOS Département d Ingénierie Cellulaire et Tissulaire INSERM 1183 - IRMB Hôpital St Eloi - CHU de Montpellier john.devos@inserm.fr @_jdevos_ TUMOR INITIATING CELLS: THE STEM CELL THEORY OF CANCER
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells. Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles
 Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
Therapeutic implications of cancer stem cells Cédric Blanpain, MD, PhD Laboratory of stem cells and cancer WELBIO, Université Libre de Bruxelles Stem cell properties Differentiation Self-renewal Tumor
Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs)
 GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
GENReports: Market & Tech Analysis Characteristics of Cancer Stem Cells (CSCs) > Enal Razvi, Ph.D. Biotechnology Analyst, Managing Director Select Biosciences, Inc. enal@selectbio.us! Topic,IntroducEon,and,Scope!
Getting to the root of Cancer
 Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
Cancer Stem Cells: Getting to the root of Cancer Dominique Bonnet, Ph.D Senior Group Leader, Haematopoietic Stem Cell Laboratory Cancer Research UK, London Research Institute Venice, Sept 2009 Overview
 Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery & VP Integrated Health Services University of Saskatchewan & Saskatoon Health Region
 Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
Identification and Characterization of Stem-like Cells in Human Esophageal Adenocarcinoma and Normal Epithelial Cell Lines No disclosures / conflict of interest Alan G. Casson FRCSC Professor of Surgery
High-Throughput Flow Cytometry Screening Reveals a Role for Junctional Adhesion Molecule A as a Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance Factor
 Cell Reports Article High-Throughput Flow Cytometry Screening Reveals a Role for Junctional Adhesion Molecule A as a Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance Factor Justin D. Lathia, 1,2,3,4, * Meizhang Li, 1,2,13
Cell Reports Article High-Throughput Flow Cytometry Screening Reveals a Role for Junctional Adhesion Molecule A as a Cancer Stem Cell Maintenance Factor Justin D. Lathia, 1,2,3,4, * Meizhang Li, 1,2,13
Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication and Carcinogenesis 細胞間隙交流與致癌的關係
 Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication and Carcinogenesis 細胞間隙交流與致癌的關係 Chia-Cheng Chang, Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics and Human Development Michigan State University Structures of Gap Junctions
Gap Junctional Intercellular Communication and Carcinogenesis 細胞間隙交流與致癌的關係 Chia-Cheng Chang, Ph.D. Department of Pediatrics and Human Development Michigan State University Structures of Gap Junctions
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures
 Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Type of file: PDF Size of file: 0 KB Title of file for HTML: Supplementary Information Description: Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 mir-128-3p is highly expressed in chemoresistant, metastatic
Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas
 Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Wang et al. Journal of Hematology & Oncology (2016) 9:90 DOI 10.1186/s13045-016-0323-9 RESEARCH Bmi-1 regulates stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells via modulating mirnas Open Access Xiaofeng
Cancer Stem Cells: Basic Concepts and Therapeutic Implications
 ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides Navigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev.
ANNUAL REVIEWS Further Click here to view this article's online features: Download figures as PPT slides Navigate linked references Download citations Explore related articles Search keywords Annu. Rev.
THE IMPLICATIONS OF GAP JUNCTION INHIBITION IN JURKAT CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION AND PROLIFERATION
 THE IMPLICATIONS OF GAP JUNCTION INHIBITION IN JURKAT CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION AND PROLIFERATION A thesis submitted to the Kent State University Honors College in partial fulfillment of the requirements
THE IMPLICATIONS OF GAP JUNCTION INHIBITION IN JURKAT CELL-CELL COMMUNICATION AND PROLIFERATION A thesis submitted to the Kent State University Honors College in partial fulfillment of the requirements
LETTERS. A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice
 Vol 445 4 January 27 doi:1.138/nature5372 A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice Catherine A. O Brien 1, Aaron Pollett 2, Steven Gallinger 3 & John E. Dick
Vol 445 4 January 27 doi:1.138/nature5372 A human colon cancer cell capable of initiating tumour growth in immunodeficient mice Catherine A. O Brien 1, Aaron Pollett 2, Steven Gallinger 3 & John E. Dick
EHA an overview. Christine Chomienne EHA President.
 EHA an overview Christine Chomienne EHA President www.ehaweb.org EHA activities Career development Calls are open now EHA Learning Center Annual congress EHA promotes excellence in research, education
EHA an overview Christine Chomienne EHA President www.ehaweb.org EHA activities Career development Calls are open now EHA Learning Center Annual congress EHA promotes excellence in research, education
Evidence for a Hierarchy within Breast Cancer Stem Cells: Relevance to Metastasis and Therapy
 University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2012-07-30 Evidence for a Hierarchy within Breast Cancer Stem Cells: Relevance to Metastasis and Therapy
University of Miami Scholarly Repository Open Access Dissertations Electronic Theses and Dissertations 2012-07-30 Evidence for a Hierarchy within Breast Cancer Stem Cells: Relevance to Metastasis and Therapy
Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness
 Manuscript EMBO-2012-83706 Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness Gaëlle Lapouge, Benjamin Beck, Dany Nassar, Christine Dubois, Sophie Dekoninck
Manuscript EMBO-2012-83706 Skin squamous cell carcinoma propagating cells increase with tumour progression and invasiveness Gaëlle Lapouge, Benjamin Beck, Dany Nassar, Christine Dubois, Sophie Dekoninck
Predictive Biomarkers in GBM
 Predictive Biomarkers in GBM C. David James, Ph.D. Professor & Associate Director, Brain Tumor Research Center Dept. Neurological Surgery and Helen Diller Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California
Predictive Biomarkers in GBM C. David James, Ph.D. Professor & Associate Director, Brain Tumor Research Center Dept. Neurological Surgery and Helen Diller Comprehensive Cancer Center, University of California
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0644 TITLE: Targeting Cell Polarity Machinery to Exhaust Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Chun-Ju Chang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Purdue University West Lafayette,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0644 TITLE: Targeting Cell Polarity Machinery to Exhaust Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Chun-Ju Chang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Purdue University West Lafayette,
TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TMA-BERN COHORT-2
 Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1 TMA-VARESE COHORT-1 TOTAL SAMPLES #5 GLEASON SCORE Number Percentage 6 16 32% = 7 17 34% >7 17 34% TUMOR STAGE T2C 28 56% T3A- 21 42% T3C-T4 1 2% NODE STATUS N 42 84% N1 8 16% PSA
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of tumorous sphere-forming CSCs and CAF feeder cells. The LEAP (Laser-Enabled Analysis and Processing) platform with laser manipulation to efficiently purify lung
Hypothesis of Cancer Stem Cells and Stem Cells of Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers for their Identification
 C CRIMSON PUBLISHERS Wings to the Research Modern Research in Dentistry ISSN 2637-7764 Review Article Hypothesis of Cancer Stem Cells and Stem Cells of Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers for their Identification
C CRIMSON PUBLISHERS Wings to the Research Modern Research in Dentistry ISSN 2637-7764 Review Article Hypothesis of Cancer Stem Cells and Stem Cells of Head and Neck Cancer Biomarkers for their Identification
Hematopoiesis. - Process of generation of mature blood cells. - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human)
 Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
Hematopoiesis - Process of generation of mature blood cells - Daily turnover of blood cells (70 kg human) 1,000,000,000,000 total cells 200,000,000,000 red blood cells 70,000,000,000 neutrophils Hematopoiesis
LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT by activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and predicts poor survival of glioma patients
 Zhang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:225 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6 RESEARCH Open Access LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT
Zhang et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:225 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0864-6 RESEARCH Open Access LGR5, a novel functional glioma stem cell marker, promotes EMT
Glioma-initiating cells support glioblastoma heterogeneity at the level of integrin α5β1
 Glioma-initiating cells support glioblastoma heterogeneity at the level of integrin α5β1 MERCIER Marie-Cécile, 2th year PhD student Laboratoire de Biophotonique et Pharmacologie, UMR7213 CNRS Faculty of
Glioma-initiating cells support glioblastoma heterogeneity at the level of integrin α5β1 MERCIER Marie-Cécile, 2th year PhD student Laboratoire de Biophotonique et Pharmacologie, UMR7213 CNRS Faculty of
Phenotypic Heterogeneity among Tumorigenic Melanoma Cells from Patients that Is Reversible and Not Hierarchically Organized
 Article Phenotypic Heterogeneity among Tumorigenic Melanoma Cells from Patients that Is Reversible and Not Hierarchically Organized Elsa Quintana, 1,2,3,4,8 Mark Shackleton, 1,2,3,4,8,9 Hannah R. Foster,
Article Phenotypic Heterogeneity among Tumorigenic Melanoma Cells from Patients that Is Reversible and Not Hierarchically Organized Elsa Quintana, 1,2,3,4,8 Mark Shackleton, 1,2,3,4,8,9 Hannah R. Foster,
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Diseases of the skeleton
 Diseases of the skeleton Flexibility Protection of vital organs Strength Skeletal defects impact human health Developmental diseases Degenerative diseases Fins regenerate and grow rapidly following amputation
Diseases of the skeleton Flexibility Protection of vital organs Strength Skeletal defects impact human health Developmental diseases Degenerative diseases Fins regenerate and grow rapidly following amputation
Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note
 Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26
Tumorsphere Culture of Cancer Stem Cells (CSC) with the Cancer Stem Cell Medium, Application Note Interest in any of the products, request or order them at Bio-Connect. Bio-Connect B.V. T NL +31 (0)26
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER. Andrew Leask.
 CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0479 TITLE: Roles of microrna-mediated Drug Resistance in Tumor Stem Cells of Small Cell Lung Carcinoma PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Award Number: W81XWH TITLE: Synthetic Lethal Gene for PTEN as a Therapeutic Target. PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D.
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0151 TITLE: Synthetic Lethal Gene for PTEN as a Therapeutic Target PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical
AD Award Number: W81XWH-12-1-0151 TITLE: Synthetic Lethal Gene for PTEN as a Therapeutic Target PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Kounosuke Watabe, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Mississippi Medical
TITLE: Targeting Cell Polarity Machinery to Exhaust Breast Cancer Stem Cells
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0644 TITLE: Targeting Cell Polarity Machinery to Exhaust Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Chun-Ju Chang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Purdue University West Lafayette,
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-15-1-0644 TITLE: Targeting Cell Polarity Machinery to Exhaust Breast Cancer Stem Cells PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Chun-Ju Chang CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Purdue University West Lafayette,
Anti-tumor Effects of Activated Human Natural Killer Cells in Orthotopic Human Brain Tumor Models
 Anti-tumor Effects of Activated Human Natural Killer Cells in Orthotopic Human Brain Tumor Models William Murphy, PhD Depts. of Dermatology and Internal Medicine Neal Goodwin, PhD Jackson Laboratories
Anti-tumor Effects of Activated Human Natural Killer Cells in Orthotopic Human Brain Tumor Models William Murphy, PhD Depts. of Dermatology and Internal Medicine Neal Goodwin, PhD Jackson Laboratories
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of mir mimics and anti-mirs on DTPs a, Representative fluorescence microscopy images of GFP vector control or mir mimicexpressing parental and DTP
Quantification of early stage lesions for loss of p53 should be shown in the main figures.
 Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): Expert in prostate cancer The manuscript "Clonal dynamics following p53 loss of heterozygosity in Kras-driven cancers" uses a number of novel genetically engineered
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression
 Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Hematopathology. Analysis of SHIP1 as a potential biomarker of Disease Progression Carlos E. Bueso-Ramos, M.D., Ph.D Department of Hematopathology The University of Texas M.
Opposing effects of low versus high concentrations of vitamins/dietary ingredients Vitamin C and niacin on colon cancer stem cells (CSCs)
 Opposing effects of low versus high concentrations of vitamins/dietary ingredients Vitamin C and niacin on colon cancer stem cells (CSCs) Colorectal cancer is one of the global causes of cancer deaths.
Opposing effects of low versus high concentrations of vitamins/dietary ingredients Vitamin C and niacin on colon cancer stem cells (CSCs) Colorectal cancer is one of the global causes of cancer deaths.
PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype to promote glioblastoma migration and invasion
 Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Xu et al. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2018) 37:158 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0841-0 RESEARCH PBX3/MEK/ERK1/2/LIN28/let-7b positive feedback loop enhances mesenchymal phenotype
Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells
 Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF has been designed to meet your requirements for
Extended Mammosphere Culture of Human Breast Cancer Cells Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF has been designed to meet your requirements for
Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer?
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
AD Award Number: W81XWH-10-1-0592 TITLE: Does EMT Contribute to Radiation Resistance in Human Breast Cancer? PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Anupama Munshi, Ph.D CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Oklahoma
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL. PhD THESIS
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL PhD THESIS THE IMPORTANCE OF TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS IN CEREBRAL TUMOR DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY ABSTRACT PhD COORDINATOR: Prof. univ. dr. DRICU Anica PhD
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICINE AND PHARMACY CRAIOVA PhD SCHOOL PhD THESIS THE IMPORTANCE OF TUMOR ANGIOGENESIS IN CEREBRAL TUMOR DIAGNOSIS AND THERAPY ABSTRACT PhD COORDINATOR: Prof. univ. dr. DRICU Anica PhD
Supplementary Figures
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1 DOT1L regulates the expression of epithelial and mesenchymal markers. (a) The expression levels and cellular localizations of EMT markers were confirmed by
Glioblastoma Multiforme
 Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
Glioblastoma Multiforme Highly malignant, invasive, difficult-to-treat primary brain tumor" " Frequency: 9,000 cases/year (peak age, 55 65 years)" " Recurrence: rapid growth; size may double every 10 days"
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
Supplementary Figure 1 MSI2 interactors are associated with the riboproteome and are functionally relevant. (a) Coomassie blue staining of FLAG-MSI2 immunoprecipitated complexes. (b) GO analysis of MSI2-interacting
September 20, Submitted electronically to: Cc: To Whom It May Concern:
 History Study (NOT-HL-12-147), p. 1 September 20, 2012 Re: Request for Information (RFI): Building a National Resource to Study Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) The MDS Cohort Natural History Study (NOT-HL-12-147).
History Study (NOT-HL-12-147), p. 1 September 20, 2012 Re: Request for Information (RFI): Building a National Resource to Study Myelodysplastic Syndromes (MDS) The MDS Cohort Natural History Study (NOT-HL-12-147).
The crossroads between cancer stem cells and aging
 REVIEW Open Access The crossroads between cancer stem cells and aging Sara Santos Franco 1,2, Hadas Raveh-Amit 2, Julianna Kobolák 2, Mohammed H. Alqahtani 3, Ali Mobasheri 3,4, András Dinnyes 1,2,5* From
REVIEW Open Access The crossroads between cancer stem cells and aging Sara Santos Franco 1,2, Hadas Raveh-Amit 2, Julianna Kobolák 2, Mohammed H. Alqahtani 3, Ali Mobasheri 3,4, András Dinnyes 1,2,5* From
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
doi:10.1038/nature12215 Supplementary Figure 1. The effects of full and dissociated GR agonists in supporting BFU-E self-renewal divisions. BFU-Es were cultured in self-renewal medium with indicated GR
EFFICACY OF GAP JUNCTION ENHANCERS AND ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS IN MAMMARY CARCINOMA MODELS STEPHANIE NICOLE SHISHIDO
 EFFICACY OF GAP JUNCTION ENHANCERS AND ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS IN MAMMARY CARCINOMA MODELS by STEPHANIE NICOLE SHISHIDO B.S., Pennsylvania State University, 2008 M.S., California State University, 2010 AN
EFFICACY OF GAP JUNCTION ENHANCERS AND ANTINEOPLASTIC DRUGS IN MAMMARY CARCINOMA MODELS by STEPHANIE NICOLE SHISHIDO B.S., Pennsylvania State University, 2008 M.S., California State University, 2010 AN
Extended Neurosphere Culture of Brain Tumor Stem Cells with the PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF
 Extended Neurosphere Culture of Brain Tumor Stem Cells with the PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF While adherent cultures of brain tumor cells in
Extended Neurosphere Culture of Brain Tumor Stem Cells with the PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF Application Note The PromoCell 3D Tumorsphere Medium XF While adherent cultures of brain tumor cells in
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI. The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement.
 Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Beverly A. Teicher, PhD DCTD/NCI The content reflects my professional opinions, not an NCI policy statement. Outline 1. Transplantable Syngeneic Tumors 2. Human Tumor Xenografts 3. Disseminated Disease
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer. MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola
 Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
Profiles of gene expression & diagnosis/prognosis of cancer MCs in Advanced Genetics Ainoa Planas Riverola Gene expression profiles Gene expression profiling Used in molecular biology, it measures the
CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow
 White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
White Paper September 2016 CD34+ Cells: A Comparison of Stem and Progenitor Cells in Cord Blood, Peripheral Blood, and the Bone Marrow Lily C. Trajman, PhD Introduction: Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
Cancer stem cells old concepts, new insights
 Review (2008) 15, 947 958 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1350-9047/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/cdd Cancer stem cells old concepts, new insights L Vermeulen 1, MR Sprick 1, K Kemper 1,
Review (2008) 15, 947 958 & 2008 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 1350-9047/08 $30.00 www.nature.com/cdd Cancer stem cells old concepts, new insights L Vermeulen 1, MR Sprick 1, K Kemper 1,
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bredel M, Scholtens DM, Yadav AK, et al. NFKBIA deletion in
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Bredel M, Scholtens DM, Yadav AK, et al. NFKBIA deletion in
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Current and Future Treatment Options for Glioblastoma
 Current and Future Treatment Options for Glioblastoma Santosh Kesari, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN Chair, Department of Translational Neurosciences and Neurotherapeutics John Wayne Cancer Institute & Pacific Neuroscience
Current and Future Treatment Options for Glioblastoma Santosh Kesari, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN Chair, Department of Translational Neurosciences and Neurotherapeutics John Wayne Cancer Institute & Pacific Neuroscience
TGF-b Receptor Inhibitors Target the CD44 high /Id1 high Glioma-Initiating Cell Population in Human Glioblastoma
 rticle TGF-b Receptor Inhibitors Target the CD44 high /Id1 high Glioma-Initiating Cell Population in Human Glioblastoma Judit nido, 1 ndrea Sáez-orderías, 1 lba Gonzàlez-Juncà, 1 Laura Rodón, 1 Gerard
rticle TGF-b Receptor Inhibitors Target the CD44 high /Id1 high Glioma-Initiating Cell Population in Human Glioblastoma Judit nido, 1 ndrea Sáez-orderías, 1 lba Gonzàlez-Juncà, 1 Laura Rodón, 1 Gerard
Stem Cells. Induced Stem Cells
 Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Induced Stem Cells Stem Cells Mouse and human somatic cells can either be reprogrammed to a pluripotent state or converted to another lineage with a combination of transcription factors suggesting that
Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases
 Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases Dusten Unruh, PhD 8 th Annual Brain Metastases Research and Emerging Therapy Conference Tissue
Tissue Factor/PAR2 signaling enhances the malignancy and radiation resistance of lung cancer brain metastases Dusten Unruh, PhD 8 th Annual Brain Metastases Research and Emerging Therapy Conference Tissue
IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS
 IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS An Internship Report Presented to the Faculty of the Biology Program California State University Channel Islands
IN VITRO AND IN VIVO CHARACTERIZATION OF CANCER STEM CELLS IN PRIMARY COLORECTAL CANCER MODELS An Internship Report Presented to the Faculty of the Biology Program California State University Channel Islands
Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells or Tumor-Initiating Cells
 Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6624-6648; doi:10.3390/ijms14046624 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem
Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6624-6648; doi:10.3390/ijms14046624 Review OPEN ACCESS International Journal of Molecular Sciences ISSN 1422-0067 www.mdpi.com/journal/ijms Regulation of Ovarian Cancer Stem
Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under normal and pathologic conditions Interleukins,
 Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
Cytokines http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072507470/student_view0/chapter22/animation the_immune_response.html Cytokines modulate the functional activities of individual cells and tissues both under
GLIOMA STEM CELLS ADAPT TO RESTRICTED NUTRITION THROUGH PREFERENTIAL GLUCOSE UPTAKE. by WILLIAM ALEXANDER FLAVAHAN
 GLIOMA STEM CELLS ADAPT TO RESTRICTED NUTRITION THROUGH PREFERENTIAL GLUCOSE UPTAKE by WILLIAM ALEXANDER FLAVAHAN Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
GLIOMA STEM CELLS ADAPT TO RESTRICTED NUTRITION THROUGH PREFERENTIAL GLUCOSE UPTAKE by WILLIAM ALEXANDER FLAVAHAN Submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements For the degree of Doctor of Philosophy
Cell-cell communication and diabetes. Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln
 Cell-cell communication and diabetes Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Joseph Banks Laboratories Lincoln Connexin
Cell-cell communication and diabetes Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Joseph Banks Laboratories Lincoln Connexin
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis
 Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Radiation-induced induced Genomic Instability and Bystander Effects: implications for radiation leukaemogenesis University of Dundee Medical School Eric G Wright Professor of Experimental Haematology The
Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma
 Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma JP Hugnot «Brain plasticity, Neural stem cells and Glial tumors» INSERM U1051-UM2 Institut des Neurosciences de Montpellier Montpellier 1-Stem cells and Brain Stem Cells
Cancer Stem Cells & Glioblastoma JP Hugnot «Brain plasticity, Neural stem cells and Glial tumors» INSERM U1051-UM2 Institut des Neurosciences de Montpellier Montpellier 1-Stem cells and Brain Stem Cells
Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
 Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Anna Vidal Department of Hemato Oncology IDIBAPS, Barcelona, Spain B cell lymphoid malignancies seen
Daratumumab, a novel human CD38 monoclonal antibody for the treatment of B cell Non Hodgkin Lymphoma Anna Vidal Department of Hemato Oncology IDIBAPS, Barcelona, Spain B cell lymphoid malignancies seen
Mathematical Modeling of PDGF-Driven Glioblastoma Reveals Optimized Radiation Dosing Schedules
 Mathematical Modeling of PDGF-Driven Glioblastoma Reveals Optimized Radiation Dosing Schedules Kevin Leder, Ken Pittner, Quincey LaPlant, Dolores Hambardzumyan, Brian D. Ross, Timothy A. Chan, Eric C.
Mathematical Modeling of PDGF-Driven Glioblastoma Reveals Optimized Radiation Dosing Schedules Kevin Leder, Ken Pittner, Quincey LaPlant, Dolores Hambardzumyan, Brian D. Ross, Timothy A. Chan, Eric C.
Tumors of the Nervous System
 Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Tumors of the Nervous System Peter Canoll MD. PhD. What I want to cover What are the most common types of brain tumors? Who gets them? How do they present? What do they look like? How do they behave? 1
Blood 101 Introduction Blood and Marrow & Overview of Bone Marrow Failure Diseases. Dr. M. Sabloff October 16 th 2010
 Blood 101 Introduction Blood and Marrow & Overview of Bone Marrow Failure Diseases Dr. M. Sabloff October 16 th 2010 Normal Marrow knee joint white is articular cartilage Adjacent to this is the red marrow
Blood 101 Introduction Blood and Marrow & Overview of Bone Marrow Failure Diseases Dr. M. Sabloff October 16 th 2010 Normal Marrow knee joint white is articular cartilage Adjacent to this is the red marrow
A CD123-targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC), IMGN632, designed to eradicate Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) cells while sparing normal bone marrow
 A CD123-targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC), IMGN632, designed to eradicate Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) cells while sparing normal bone marrow Yelena Kovtun, Gregory Jones, Charlene Audette, Lauren
A CD123-targeting Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC), IMGN632, designed to eradicate Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) cells while sparing normal bone marrow Yelena Kovtun, Gregory Jones, Charlene Audette, Lauren
Reference: NHS England 1602
 Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Clofarabine for refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) as a bridge to stem cell transplantation Reference: NHS England 1602 First published: TBC
Clinical Commissioning Policy Proposition: Clofarabine for refractory or relapsed acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) as a bridge to stem cell transplantation Reference: NHS England 1602 First published: TBC
The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance
 The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance Florian A. Siebzehnrubl, Daniel J. Silver, Bugra Tugertimur, Loic P. Deleyrolle, Dorit Siebzehnrubl, Matthew R. Sarkisian, Kelly
The ZEB1 pathway links glioblastoma initiation, invasion and chemoresistance Florian A. Siebzehnrubl, Daniel J. Silver, Bugra Tugertimur, Loic P. Deleyrolle, Dorit Siebzehnrubl, Matthew R. Sarkisian, Kelly
RINDOPEPIMUT (CDX-110) IN GLIOBLASTOMA
 RINDOPEPIMUT (CDX-110) IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORM GEINO 2014 Dra Estela Pineda Madrid Hospital Clínic Barcelona EGFRvIII in glioblastoma multiform The most common mutation of EGFR in GBM Expressed in 30%
RINDOPEPIMUT (CDX-110) IN GLIOBLASTOMA MULTIFORM GEINO 2014 Dra Estela Pineda Madrid Hospital Clínic Barcelona EGFRvIII in glioblastoma multiform The most common mutation of EGFR in GBM Expressed in 30%
Animals in cancer research
 Animals in cancer research Journal Impact Factor: 3.96 A. All five male BALB/c nu/nu mice in the XXXX group showed transplanted tumors after 28 days. B. Three mice of five in XXXX group showed small tumor
Animals in cancer research Journal Impact Factor: 3.96 A. All five male BALB/c nu/nu mice in the XXXX group showed transplanted tumors after 28 days. B. Three mice of five in XXXX group showed small tumor
Meeting Report. From December 8 to 11, 2012 at Atlanta, GA, U.S.A
 Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
Meeting Report Affiliation Department of Transfusion Medicine and Cell Therapy Name Hisayuki Yao Name of the meeting Period and venue Type of your presentation Title of your presentation The 54 th Annual
The Hierarchical Organization of Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis
 The Hierarchical Organization of Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis NORMAL Hematopoie2c Stem Cell (HSC) Leukemia Stem Cells (LSC) MPP MLP CMP Leukemic Progenitors MEP GMP B/NK ETP Leukemic Blasts Erythrocytes
The Hierarchical Organization of Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis NORMAL Hematopoie2c Stem Cell (HSC) Leukemia Stem Cells (LSC) MPP MLP CMP Leukemic Progenitors MEP GMP B/NK ETP Leukemic Blasts Erythrocytes
Programmed Cell Death (apoptosis)
 Programmed Cell Death (apoptosis) Stereotypic death process includes: membrane blebbing nuclear fragmentation chromatin condensation and DNA framentation loss of mitochondrial integrity and release of
Programmed Cell Death (apoptosis) Stereotypic death process includes: membrane blebbing nuclear fragmentation chromatin condensation and DNA framentation loss of mitochondrial integrity and release of
Glioma cancer stem cells mediate immune suppression that can be reversed with STAT3 blockade
 Glioma cancer stem cells mediate immune suppression that can be reversed with STAT3 blockade Jun Wei Department of Neurosurgery October 23, 2009 Immune suppression in Malignant Glioma Patients Mechanisms
Glioma cancer stem cells mediate immune suppression that can be reversed with STAT3 blockade Jun Wei Department of Neurosurgery October 23, 2009 Immune suppression in Malignant Glioma Patients Mechanisms
Supplemental Table S1
 Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
Supplemental Table S. Tumorigenicity and metastatic potential of 44SQ cell subpopulations a Tumorigenicity b Average tumor volume (mm ) c Lung metastasis d CD high /4 8. 8/ CD low /4 6./ a Mice were injected
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells
 let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
let-7 Regulates Self Renewal and Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Fengyan Yu, 1,2 Herui Yao, 1 Pengcheng Zhu, 2 Xiaoqin Zhang, 1 Qiuhui Pan, 1 Chang Gong, 1 Yijun Huang, 3 Xiaoqu Hu, 1 Fengxi Su,
TEB. Id4 p63 DAPI Merge. Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge
 a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
a Duct TEB b Id4 p63 DAPI Merge Id4 CK8 DAPI Merge c d e Supplementary Figure 1. Identification of Id4-positive MECs and characterization of the Comma-D model. (a) IHC analysis of ID4 expression in the
Emerging Role of MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer
 Emerging Role of MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
Emerging Role of MicroRNA in Pancreatic Cancer The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Accessed Citable Link
GENERAL SUMMARY Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro
 Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
Corpus luteum is a transient endocrine structure formed from the ruptured ovarian follicle. Its main function is to secrete P 4, a pro-gestational hormone, essential for establishment and maintenance of
Discussing the Evolving Role of Cancer Stem Cells
 EXPERT PANEL LOCAL INSIGHTS Discussing the Evolving Role of Cancer Stem Cells Lee M. Ellis, MD Professor of Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology William C. Liedtke Jr. Chair in Cancer Research The
EXPERT PANEL LOCAL INSIGHTS Discussing the Evolving Role of Cancer Stem Cells Lee M. Ellis, MD Professor of Surgery, Department of Surgical Oncology William C. Liedtke Jr. Chair in Cancer Research The
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Supplementary Information Temozolomide suppresses MYC via activation of TAp63 to inhibit progression of human glioblastoma Tomohiro Yamaki, Yusuke Suenaga, Toshihiko Iuchi, Jennifer Alagu, Atsushi Takatori,
Fetal Arsenic Exposure and Adult Cancer
 Fetal Arsenic Exposure and Adult Cancer Michael P. Waalkes Inorganic Toxicology Group National Toxicology Program Arsenic Exposure Millions of people worldwide Are exposed to elevated levels of arsenic
Fetal Arsenic Exposure and Adult Cancer Michael P. Waalkes Inorganic Toxicology Group National Toxicology Program Arsenic Exposure Millions of people worldwide Are exposed to elevated levels of arsenic
The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic. Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer
 Nutrition & Metabolism (in press) The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer Joshua J. Meidenbauer, Purna Mukherjee and
Nutrition & Metabolism (in press) The Glucose Ketone Index Calculator: A Simple Tool to Monitor Therapeutic Efficacy for Metabolic Management of Brain Cancer Joshua J. Meidenbauer, Purna Mukherjee and
Nicholas Szerlip, MD Department of Neurosurgery Wayne State University Karmanos Cancer Institute
 Nicholas Szerlip, MD Department of Neurosurgery Wayne State University Karmanos Cancer Institute Many different names (Heregulin, Aria) Found when investigating ligands that activated HER2 (it actually
Nicholas Szerlip, MD Department of Neurosurgery Wayne State University Karmanos Cancer Institute Many different names (Heregulin, Aria) Found when investigating ligands that activated HER2 (it actually
A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM. Collaborative Opportunity
 A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM Collaborative Opportunity March 2014 PURPOSE Cancer Research UK funded Investigators have established in vitro and in vivo models of CSCs for use
A NOVEL CANCER STEM CELL (CSC) DRUG DISCOVERY PLATFORM Collaborative Opportunity March 2014 PURPOSE Cancer Research UK funded Investigators have established in vitro and in vivo models of CSCs for use
Founded in 2016 to develop life-changing therapies against debilitating aggressive cancers that have limited treatment options
 Founded in 2016 to develop life-changing therapies against debilitating aggressive cancers that have limited treatment options Integrated platform technology for discovery of novel molecular targets and
Founded in 2016 to develop life-changing therapies against debilitating aggressive cancers that have limited treatment options Integrated platform technology for discovery of novel molecular targets and
Cancer Stem Cells, Therapeutic Implications
 June 2015 KUWAIT MEDICAL JOURNAL 97 Review Article Ali Ahmad, Zahraa Habeeb, Mohammed Al-Mousa, Ghyath Al-Shawaf, Mariam Al-Awadi, Ardeshir Algooneh Department of Internal Medicine, Al-Amiri Hospital,
June 2015 KUWAIT MEDICAL JOURNAL 97 Review Article Ali Ahmad, Zahraa Habeeb, Mohammed Al-Mousa, Ghyath Al-Shawaf, Mariam Al-Awadi, Ardeshir Algooneh Department of Internal Medicine, Al-Amiri Hospital,
Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis
 Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
Research article Hunk is required for HER2/neu-induced mammary tumorigenesis Elizabeth S. Yeh, 1 Thomas W. Yang, 1 Jason J. Jung, 1 Heather P. Gardner, 1 Robert D. Cardiff, 2 and Lewis A. Chodosh 1 1 Department
UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and HDAC1
 EMBO reports - Peer Review Process File - EMBOR-2015-40244 Manuscript EMBOR-2015-40244 UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and
EMBO reports - Peer Review Process File - EMBOR-2015-40244 Manuscript EMBOR-2015-40244 UTX inhibits EMT-induced breast CSC properties by epigenetic repression of EMT genes in cooperation with LSD1 and
International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science
 1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
1 International Graduate Research Programme in Cardiovascular Science This work has been supported by the European Community s Sixth Framework Programme under grant agreement n LSHM-CT-2005-01883 EUGeneHeart.
