Glial cell development in the vertebrate central nervous system
|
|
|
- Bruce McKinney
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Glial cell development in the vertebrate central nervous system Thesis by Qiao Zhou In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Biology California Institute of Technology Pasadena, CA 2003 (Submitted March 4th, 2003)
2 ii To my parents and Sally Suen
3 iii ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS First of all, I would like to thank David, for he opened my eyes to the real scientific world. I learned much from him, but especially how to be critical, rigorous, and creative. I admire his energy, his enthusiasm for science, and excellent memory. Special thanks to Vincent Dionne, Heather Eisthen, Gregory Hinkle, Rona Delay and friends at Woods Hole. Without them, I would never be here at Caltech, and because of them, three years of life at Wood Hole became more bearable. I thank Vince, who is never selfish. I thank Heather for her understanding and encouragement. Life at Woods Hole taught me that hard working and independence is simply not enough, to do good science, a rich scientific environment is absolutely necessary. For that, I am grateful to Caltech for accepting me, and I am grateful to many people at Caltech, especially past and present members of the Anderson lab for providing a superb environment. Qiu-fu Ma first taught me how to do sectioning and in situ. I respect Qiu-fu because he beat many odds and achieved much and yet remains a very decent person and true to his roots. Jae Kim is my longtime bay mate. Together, we had many stimulating discussions about science and life in large. His great sense of humor is always appreciated. Many lab members have helped me in many ways throughout the years, Hai Wang, Zhoufeng Chen, Sherry Perez, Sean Morrison, Liching Lo, Pat White, Walter Lerchner, Mark Zylka, Xinzhong Dong, Limor Gaby, Sally Lowell, and Yosuke Mukoyama. I thank my collaborators Gloria and Christian. It is a lot of fun to work with them. Gaby Mosconi will always be fondly remembered. She treats us like her own kids and makes life in the lab so much more enjoyable. I would like to thank many members of the professional staff at Caltech, especially Shelly Diamond of the FACS facility, Shirley Pease and Bruce Kennedy of the animal facility. I thank my committee members, Kai Zinn, Marianne Bronner-Fraser, and
4 iv Jose Alberola-Ila. I should have sought advice more often from them. Thanks to Kai for introducing me to rock climbing. Lastly, I thank my parents and my wife Sally, none of this would be possible without their unconditional support, love and faith in me.
5 v ABSTRACT Neurons and glial cells are the two most fundamental cell types of the vertebrate central nervous system (CNS). While neurons are directly responsible for information processing via their electrical activities, glial cells play essential supportive roles. For example, oligodendroglia insulates axons, microglia performs immune functions, and astroglia maintains homeostasis of the entire CNS. Malfunction of glial cells causes numerous debilitating diseases directly (such as glial tumors), or indirectly by disrupting the normal functions of neurons that they support (as in multiple sclerosis). Despite their functional importance, relatively little is known about the development of vertebrate CNS glial cells. Focusing on the possibility that members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bhlh) transcription factors may play important roles in the development of vertebrate glial cells, similar to their functions in neurons, I searched for novel bhlh factors expressed in glial cells. A new family of bhlh factors was found and named Olig. Intriguingly, one member of this family, Olig2, is sequentially expressed first in motoneuron progenitors and later in the oligodendroglia. The sequence and expression pattern of Olig2 is highly conserved among different vertebrate species including fish, birds and mammals. To understand the role of Olig2 in oligodendroglia development, I ectopically expressed Olig2 singly or in combination with other factors in chick embryos. My result suggests that Olig2 can promote oligodendrocyte formation in the absence of neurogenic bhlh factors, which are negative regulators of glial fate. Other groups of researchers reported that in the presence of neurogenic factors, Olig2 promotes motoneuron development instead. Olig2 gene is therefore sufficient to specify the fate of either a neuronal subtype or a glial subtype, together with neurogenic factors. To further assess whether Olig genes are required for motoneuron and oligodendroglia development, I knocked out both Olig2 and Olig1 genes in mouse. In double null mutants, spinal motoneurons and oligodendroglia precursors from the entire CNS fail to develop, demonstrating that Olig genes are absolutely necessary for the
6 vi generation of these cell types. Unexpectedly, in the absence of both Olig1 and Olig2, spinal motoneurons are transformed into V2 interneurons whereas oligodendroglial cells are respecified as astroglial cells. These results suggest that Olig genes are not involved in neuron-glia decision, but rather in specifying subtype identities of neuron and glia. Given that motoneurons and oligodendrocytes likely derive from common precursors, the expression of Olig may serve to couple the subtype identities of both neurons and glial cells sequentially generated from the same stem cells. The series of studies on Olig genes contributed on two areas of neural development. First, they shed important light on the specification of oligodendrocyte and astrocyte, the two major glial types in the vertebrate CNS. Second, they revealed that cell fate determinations of neuron and glia are not two unrelated events as often believed, on the contrary, they are deeply intertwined.
7 vii TABLE OF CONTENTS Acknowledgements...iii Abstract...v Table of contents...vii Chapter 1 Introduction...1 References...32 Chapter 2 Identification of a Novel Family of Oligodendrocyte Lineage-Specific Basic Helix-Loop-Helix Transcription Factors...49 References...60 Chapter 3 The bhlh Transcription Factor Olig2 Promotes Oligodendrocyte Differentiation in Collaboration with Nkx References...79 Chapter 4 The bhlh Transcription Factors Olig2 and Olig1 Couple Neuronal and Glial Subtype Specification...81 References...92 Chapter 5 Summary and Future Directions...95 References Appendix I Microarray analysis of Olig mutant...106
Chapter 5. Summary and Future directions
 95 Chapter 5 Summary and Future directions 96 Much of our knowledge about glial development in the vertebrate CNS comes from studies of purified oligodendrocyte precursor cells (Raff 1989; Pfeiffer et
95 Chapter 5 Summary and Future directions 96 Much of our knowledge about glial development in the vertebrate CNS comes from studies of purified oligodendrocyte precursor cells (Raff 1989; Pfeiffer et
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011
 Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S2. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of dnscs.
 Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Supplementary Data SUPPLEMENTARY FIG. S1. Representative counting fields used in quantification of the in vitro neural differentiation of pattern of anpcs. A panel of lineage-specific markers were used
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Nerve Cells and Behavior
 Nerve Cells and Behavior 27 th September, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System and Behavior Nervous system
Nerve Cells and Behavior 27 th September, 2016 Touqeer Ahmed Ph.D. Atta-ur-Rahman School of Applied Biosciences National University of Sciences and Technology Nervous System and Behavior Nervous system
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
FLASH CARDS. Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical
 FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
FLASH CARDS www.biologicalpsych.com Kalat s Book Chapter 2 Alphabetical absolute refractory period absolute refractory period Time when neuron will not re-fire no matter how much stimulus it gets. action
The cells of the nervous system
 The cells of the nervous system LESSON N.9 - PSYCHOBIOLOGY because of the location and volume as compared to our body, the brain has always been a matter of conjecture about its fundamental role in the
The cells of the nervous system LESSON N.9 - PSYCHOBIOLOGY because of the location and volume as compared to our body, the brain has always been a matter of conjecture about its fundamental role in the
Chapter 1. Introduction
 1 Chapter 1 Introduction 2 The central nervous system (CNS) is one of the most important organs of an animal. It is also a most complicated one, comprised of hundreds of cell types and millions of cells
1 Chapter 1 Introduction 2 The central nervous system (CNS) is one of the most important organs of an animal. It is also a most complicated one, comprised of hundreds of cell types and millions of cells
Cell Type Nervous System I. Developmental Readout. Foundations. Stem cells. Organ formation. Human issues.
 7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
7.72 10.11.06 Cell Type Nervous System I Human issues Organ formation Stem cells Developmental Readout Axes Cell type Axon guidance 3D structure Analysis Model + + organisms Foundations Principles 1 What
Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m46057 1 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
OpenStax-CNX module: m46057 1 Nervous Tissue Mediates Perception and Response * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end
Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Identification of Positionally Distinct Astrocyte Subtypes whose Identities Are Specified by a Homeodomain Code
 Identification of Positionally Distinct Astrocyte Subtypes whose Identities Are Specified by a Homeodomain Code Christian Hochstim, 1 Benjamin Deneen, 1 Agnès Lukaszewicz, 1 Qiao Zhou, 2 and David J. Anderson
Identification of Positionally Distinct Astrocyte Subtypes whose Identities Are Specified by a Homeodomain Code Christian Hochstim, 1 Benjamin Deneen, 1 Agnès Lukaszewicz, 1 Qiao Zhou, 2 and David J. Anderson
Neurons vs. glia. Traditionally, glia have been viewed as passive cells that help to maintain the function of neurons.
 GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
GLIA Neurons vs. glia The defining characteristic of a neuron is its ability to transmit rapid electrical signals in the form of action potentials. All other neural cells that lack this property are broadly
Contact: Course outline: Contact for other times.
 Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Contact: kdelaney@uvic.ca Course outline: http://web.uvic.ca/~kdelaney/b367 Scheduled office hours: 1:00-3:00, M&Th Cunn. 259A Contact kdelaney@uvic.ca for other times. Quiz (0.5 hrs) midterm (1.4 hrs)
Man and his environment
 Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Man and his environment Dr. Elriah M. Makie 0122858517 Nervous Tissue BSc.M.Sc.MBBS Introduction The nervous system is divided into two main parts: The central nervous system (CNS) comprising the brain
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline
 Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Lecture 3 (Oct 5 th ): NEURONS AND NERVE IMPULSES Lecture Outline 1) CNS vs. PNS 2) Structure of Neurons parts of a neuron: soma, dendrites, axons 3) Glial Cells 4) Mitosis and Regeneration in Neurons
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition
 Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
Chapter 2: Cellular Mechanisms and Cognition MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. Two principles about neurons were defined by Ramón y Cajal. The principle of connectional specificity states that, whereas the principle
An Overview of Myelina0on in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System. Ian Hakkinen Neural Basis of Behavior 4/25/2013
 An Overview of Myelina0on in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System Ian Hakkinen Neural Basis of Behavior 4/25/2013 Outline Defining the Nervous System Glia - CNS and PNS - Neuron to Glia Ra0o - General
An Overview of Myelina0on in the Central and Peripheral Nervous System Ian Hakkinen Neural Basis of Behavior 4/25/2013 Outline Defining the Nervous System Glia - CNS and PNS - Neuron to Glia Ra0o - General
Chapter 7. The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
Chapter 7 The Nervous System General overview of the nervous system functions Sensory input (info travels in along afferent pathways) Integration (information is processed) Sensory neurons Spinal cord
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS
 CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
CHAPTER 48: NERVOUS SYSTEMS Name I. AN OVERVIEW OF NERVOUS SYSTEMS A. Nervous systems perform the three overlapping functions of sensory input, integration, and motor output B. Networks of neurons with
The Regulation of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms: The Role of Melatonin and Adenosine in Zebrafish
 The Regulation of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms: The Role of Melatonin and Adenosine in Zebrafish Thesis by Avni Gandhi In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy CALIFORNIA
The Regulation of Sleep and Circadian Rhythms: The Role of Melatonin and Adenosine in Zebrafish Thesis by Avni Gandhi In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy CALIFORNIA
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Tenth Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue
 Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Chapter 12: Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Overview of the NS PNS (Peripheral Nervous System) CNS (Central Nervous System) Neurons Neuroglia Synapse Some nomenclature Developed by
Sox9 is critical for suppression of neurogenesis but not initiation of gliogenesis in the cerebellum. Vong et al.
 Sox9 is critical for suppression of neurogenesis but not initiation of gliogenesis in the cerebellum Vong et al. Vong et al. Molecular Brain (2015) 8:25 DOI 10.1186/s13041-015-0115-0 Vong et al. Molecular
Sox9 is critical for suppression of neurogenesis but not initiation of gliogenesis in the cerebellum Vong et al. Vong et al. Molecular Brain (2015) 8:25 DOI 10.1186/s13041-015-0115-0 Vong et al. Molecular
Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity
 Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity Carlos M. Parras, 1,4 Carol Schuurmans, 1,3,4 Raffaella Scardigli, 1 Jaesang Kim, 2 David J.
Divergent functions of the proneural genes Mash1 and Ngn2 in the specification of neuronal subtype identity Carlos M. Parras, 1,4 Carol Schuurmans, 1,3,4 Raffaella Scardigli, 1 Jaesang Kim, 2 David J.
PRONEURAL GENES AND THE SPECIFICATION OF NEURAL CELL TYPES
 PRONEURAL GENES AND THE SPECIFICATION OF NEURAL CELL TYPES Nicolas Bertrand*, Diogo S. Castro* and François Guillemot Certain morphological, physiological and molecular characteristics are shared by all
PRONEURAL GENES AND THE SPECIFICATION OF NEURAL CELL TYPES Nicolas Bertrand*, Diogo S. Castro* and François Guillemot Certain morphological, physiological and molecular characteristics are shared by all
Histology. Becoming familiar with tissues of the Human Body. structure determines function
 Histology Becoming familiar with tissues of the Human Body structure determines function Histology is the study of the microscopic structure of tissues. Familiarity with tissue structure is essential to
Histology Becoming familiar with tissues of the Human Body structure determines function Histology is the study of the microscopic structure of tissues. Familiarity with tissue structure is essential to
Meyers' A&P February 15, Unit 7. The Nervous System. I. Functions of the Nervous System. Monitors body's internal and external enviornments
 Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Unit 7 The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System Monitors body's internal and external enviornments Integrates sensory information Coordinates voluntary & involuntary responses of many other
Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous System Development
 Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, 203, 233-240 Regulation of Glial Differentiation 233 Invited Review Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous System Development YOSHIO WAKAMATSU Department of
Tohoku J. Exp. Med., 2004, 203, 233-240 Regulation of Glial Differentiation 233 Invited Review Understanding Glial Differentiation in Vertebrate Nervous System Development YOSHIO WAKAMATSU Department of
PREPARED FOR: U.S. Army Medical Research and Materiel Command Fort Detrick, Maryland
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0524 TITLE:Oligodendroglial MCT1 and Metabolic Support of Axons in Multiple Sclerosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey D. Rothstein MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0524 TITLE:Oligodendroglial MCT1 and Metabolic Support of Axons in Multiple Sclerosis PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Jeffrey D. Rothstein MD, PhD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: Johns Hopkins
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
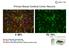 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
CHANTALE T. GUY, M5C. A Thesis. for the Degree. Doctor of Philosophy. McMaster University. (c) Copyright by Chantale T.
 ROLE AND MECHANISM OF ACTION OF TYROSINE KINASES IN MAMMARY TUMORIGENESIS By CHANTALE T. GUY, M5C. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
ROLE AND MECHANISM OF ACTION OF TYROSINE KINASES IN MAMMARY TUMORIGENESIS By CHANTALE T. GUY, M5C. A Thesis Submitted to the School of Graduate Studies in Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the
The Brain Symphony of Science
 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!! Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!!
The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!! Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 The Brain Symphony of Science https://www.youtube.com/watch?t=2&v=jb7jsfevz1u!!
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s
 Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous Tissue Nervous tissue is the term for groups of organized cells in the nervous system, which is the organ system that controls the body s movements, sends and carries signals to and from the different
Nervous System. Master controlling and communicating system of the body. Secrete chemicals called neurotransmitters
 Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Nervous System Master controlling and communicating system of the body Interacts with the endocrine system to control and coordinate the body s responses to changes in its environment, as well as growth,
Human Histology The Nervous System. Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed
 Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Human Histology The Nervous System Dr. Rawaa Salim Hameed The organization of the nervous system Anatomically, the nervous system is divided into:- Neurohistology Structurally, nerve tissue consists of
Nervous system part 1. Danil Hammoudi.MD
 Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Nervous system part 1 Danil Hammoudi.MD The central nervous system (CNS) is formed by : the brain spinal cord. These elements are enclosed within the skull and spinal vertebral canal. They are covered
Cellular components of CNS
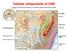 Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Cephalization. Nervous Systems Chapter 49 11/10/2013. Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells
 Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Nervous Systems Chapter 49 Cephalization Nervous systems consist of circuits of neurons and supporting cells Nervous system organization usually correlates with lifestyle Organization of the vertebrate
Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling
 Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 48 Neurons, Synapses, and Signaling PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
! BIOL 2401! Week 5. Nervous System. Nervous System
 Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Collin County Community College! BIOL 2401! Week 5 Nervous System 1 Nervous System The process of homeostasis makes sure that the activities that occur in the body are maintained within normal physiological
Master of Science In Psychology. John J. Donovan, Chair Roseanne J. Foti Neil M. Hauenstein. February 28, 2003 Blacksburg, Virginia
 The Spillover Effects of Motivational Processes in a Dual Task Setting Yvette Quintela Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
The Spillover Effects of Motivational Processes in a Dual Task Setting Yvette Quintela Thesis submitted to the Faculty of the Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State University in partial fulfillment
Functions of Nervous System Neuron Structure
 Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
Chapter 10 Nervous System I Divisions of the Nervous System Cell Types of Neural Tissue neurons neuroglial cells Central Nervous System brain spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System nerves cranial nerves
BIOL241 - Lecture 12a
 Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
Cranial Nerves, source: training.seer.cancer.gov Nervous System Overview BIOL241 - Lecture 12a 1 Topics Divisions of the NS: CNS and PNS Structure and types of neurons Synapses Structure and function of
General Functions (3) 1.Sensory gathers information 2.Integrative information is brought together 3.Motor responds to signals, homeostasis
 Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
Nervous System Responsible for being aware of the world, coordinating body functions and maintaining homeostasis Information from inside and outside the body is brought to the brain and spinal cord, stimulating
April 29, Neurophysiology. Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University,
 April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
April 29, 2016 Neurophysiology Chul-Kyu Park, Ph.D. Assistant Professor Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine, Gachon University, Cells in the brain Neurons glia 1. Astrocytes 2. Microglia
THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD
 Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Station 9 : THE SPINAL CORD The spinal cord is a long thin bundle of nerve cells that extends from the medulla of the brainstem all the way down the vertebral column. The spinal cord is made up of gray
Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells
 Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2011) 68:3995 4008 DOI 10.1007/s00018-011-0770-y Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells Huisheng
Cell. Mol. Life Sci. (2011) 68:3995 4008 DOI 10.1007/s00018-011-0770-y Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences REVIEW Specification of neuronal and glial subtypes from human pluripotent stem cells Huisheng
Inner ear development Nervous system development
 Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the
 In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
In vivo reprogramming reactive glia into ipscs to produce new neurons in the cortex following traumatic brain injury Xiang Gao 1, Xiaoting Wang 1, Wenhui Xiong 1, Jinhui Chen 1, * 1 Spinal Cord and Brain
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM
 NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
NURSE-UP INTRODUCTION TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM Body s primary communication and control system. Integrates and regulates body function Collects information specialized nervous
LESSON 2.3 WORKBOOK. How fast do our neurons signal?
 Glial cell several classes of non-neuronal cells of the nervous system. LESSON 2.3 WORKBOOK How fast do our neurons signal? Remember that winning goal you scored, that snowball you dodged or the cup of
Glial cell several classes of non-neuronal cells of the nervous system. LESSON 2.3 WORKBOOK How fast do our neurons signal? Remember that winning goal you scored, that snowball you dodged or the cup of
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Chapter 10
 PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
PowerPoint Lecture Outlines to accompany Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Shier Butler Lewis Chapter 10 Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Hemispheric interaction: when and why is yours better than mine?
 Hemispheric interaction: when and why is yours better than mine? Nicolas Cherbuin A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of the Australian National University, Canberra, Australia September,
Hemispheric interaction: when and why is yours better than mine? Nicolas Cherbuin A thesis submitted for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy of the Australian National University, Canberra, Australia September,
DEVELOPMENT. Michiya Sugimori 1,2, Motoshi Nagao 1, Nicolas Bertrand 3, *, Carlos M. Parras 3,, François Guillemot 3 and Masato Nakafuku 1,4,5,
 AND DISEASE 1617 Development 134, 1617-1629 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.001255 Combinatorial actions of patterning and HLH transcription factors in the spatiotemporal control of neurogenesis and gliogenesis
AND DISEASE 1617 Development 134, 1617-1629 (2007) doi:10.1242/dev.001255 Combinatorial actions of patterning and HLH transcription factors in the spatiotemporal control of neurogenesis and gliogenesis
Polarity and Segmentation. Chapter Two
 Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
Polarity and Segmentation Chapter Two Polarization Entire body plan is polarized One end is different than the other Head vs. Tail Anterior vs. Posterior Front vs. Back Ventral vs. Dorsal Majority of neural
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008
 BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
BIOL2005 WORKSHEET 2008 Answer all 6 questions in the space provided using additional sheets where necessary. Hand your completed answers in to the Biology office by 3 p.m. Friday 8th February. 1. Your
48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells
 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes
48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells 48a A&P: Nervous System -! Introduction, Physiology, and Cells! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes
Stem Cells. RapidCommunication. Transient Expression of Olig1 Initiates the Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells
 Stem Cells RapidCommunication Transient Expression of Olig1 Initiates the Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells Veerakumar Balasubramaniyan, Nienke Timmer, Britta Kust,
Stem Cells RapidCommunication Transient Expression of Olig1 Initiates the Differentiation of Neural Stem Cells into Oligodendrocyte Progenitor Cells Veerakumar Balasubramaniyan, Nienke Timmer, Britta Kust,
Cells of the Nervous System
 Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
Cells of the Nervous System Layout of the Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) Brain (in the skull) Spinal Cord (in the spine) Interprets sensory input, initiates movement, and mediates complex
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli
 The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
The nervous system regulates most body systems using direct connections called nerves. It enables you to sense and respond to stimuli The basic function of nervous system are: Receive sensory input internal
BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY
 BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY Natalia Surzenko, PhD Research Assistant Professor UNC Chapel Hill Nutrition Research Institute October 13, 2015 MY JOURNEY Tallinn, Estonia Aiken,
BRAIN REJUVENATION HOW TO KEEP BRAIN STEM CELLS HAPPY Natalia Surzenko, PhD Research Assistant Professor UNC Chapel Hill Nutrition Research Institute October 13, 2015 MY JOURNEY Tallinn, Estonia Aiken,
Chapter Nervous Systems
 The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
The Nervous System Chapter Nervous Systems Which animals have nervous systems? (Which do not) What are the basic components of a NS? What kind of fish performs brain operations? What differentiates one
Cellular Neurobiology course December/January calendar and deadlines (updated )
 Cellular Neurobiology course 2016-17 December/January calendar and deadlines (updated 20-12-2016) Thu December 22 Scadenza ricerca articoli per il Topic# 3 (prorogato a 28 dicembre) Wed December 28 Scadenza
Cellular Neurobiology course 2016-17 December/January calendar and deadlines (updated 20-12-2016) Thu December 22 Scadenza ricerca articoli per il Topic# 3 (prorogato a 28 dicembre) Wed December 28 Scadenza
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS
 Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nervous Tissue and Histology of CNS Functions of Nervous System Like the CPU of a computer, the nervous system is the master controlling system of the body. It is designed to constantly and rapidly adjust
Nerve Cell Flashcards
 1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
1. What does the word innervates mean? Refers to a nerve supplying a muscle or organ. For example, The phrenic nerve innervates the diaphragm muscle. 2. 3 parts of the Nervous System 1. Central Nervous
Transduction of graded Hedgehog signaling by a combination of Gli2 and Gli3 activator functions in the developing spinal cord
 Research article 3593 Transduction of graded Hedgehog signaling by a combination of Gli2 and Gli3 activator functions in the developing spinal cord Qiubo Lei, Alice K. Zelman, Ed Kuang, Shike Li and Michael
Research article 3593 Transduction of graded Hedgehog signaling by a combination of Gli2 and Gli3 activator functions in the developing spinal cord Qiubo Lei, Alice K. Zelman, Ed Kuang, Shike Li and Michael
Outline. Animals: Nervous system. Neuron and connection of neurons. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Animals: Nervous system Neuron and connection of neurons Outline 1. Key concepts 2. An Overview and Evolution 3. Human Nervous System 4. The Neurons 5. The Electrical Signals 6. Communication between Neurons
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System
 Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Nerve tissue & the Nervous System The human nervous system, by far the most complex system in the body, is formed by a network of many billion nerve cells (neurons), all assisted by many more supporting
Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD
 FTD Minicourse April, 2009 Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD Li Gan, Ph.D Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease University of California, San Francisco Outline Why study inflammation in neurodegeneration?
FTD Minicourse April, 2009 Microglia, Inflammation, and FTD Li Gan, Ph.D Gladstone Institute of Neurological Disease University of California, San Francisco Outline Why study inflammation in neurodegeneration?
Function of the Nervous System
 Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Nervous System Function of the Nervous System Receive sensory information, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands to form a response Composed of neurons (functional unit of the nervous system)
Blood & Nervous Tissue. Blood. Nervous Tissue 10/13/2008. BY: Jeremiah Peters, Brett Maggard, Miranda Asher, and Benjamin Oakes
 Blood & Nervous Tissue BY: Jeremiah Peters, Brett Maggard, Miranda Asher, and Benjamin Oakes Blood Fluid within blood vessels Doesn t connect or give mechanical support Transports Nutrients, wastes, respiratory
Blood & Nervous Tissue BY: Jeremiah Peters, Brett Maggard, Miranda Asher, and Benjamin Oakes Blood Fluid within blood vessels Doesn t connect or give mechanical support Transports Nutrients, wastes, respiratory
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Decrease in glial-glial cell interactions after exposure to mercury
 Decrease in glial-glial cell interactions after exposure to mercury Introduction Cailin McCloskey Neurobiology Short Report Bio 324 / Neurobiology Wheaton College, Norton, Massachusetts, USA April 24,
Decrease in glial-glial cell interactions after exposure to mercury Introduction Cailin McCloskey Neurobiology Short Report Bio 324 / Neurobiology Wheaton College, Norton, Massachusetts, USA April 24,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Histology of Nervous Tissue and The Spinal Cord This lab involves two laboratory exercises: 1) Histology of Nervous Tissue, and 2) Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves,
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS. a. afferent division CHAPTER 12 ORGANIZATION OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS T he nervous system organizes and coordinates the millions of impulses received each day to make communication with and enjoyment of our environment possible.
Student Name CHAPTER 12 NERVOUS SYSTEM CELLS T he nervous system organizes and coordinates the millions of impulses received each day to make communication with and enjoyment of our environment possible.
To see the world in a grain of sand And heaven in a wild flower, Hold infinity in the palm of your hand, And eternity in an hour.
 To see the world in a grain of sand And heaven in a wild flower, Hold infinity in the palm of your hand, And eternity in an hour. -William Blake This thesis is dedicated to my family for always believing
To see the world in a grain of sand And heaven in a wild flower, Hold infinity in the palm of your hand, And eternity in an hour. -William Blake This thesis is dedicated to my family for always believing
Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue. Nervous System. Basic Divisions of the Nervous System C H A P T E R 12.
 C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
C H A P T E R 12 Fundamentals of the Nervous System and Nervous Tissue Nervous System Sensory input Integration Motor output Figure 12.1 Basic Divisions of the Nervous System Brain CNS Spinal cord Nerves
Neurogenin3 Participates in Gliogenesis in the Developing Vertebrate Spinal Cord
 Developmental Biology 253, 84 98 (2003) doi:10.1006/dbio.2002.0868 Neurogenin3 Participates in Gliogenesis in the Developing Vertebrate Spinal Cord Jeffrey Lee,*, Yuanyuan Wu,* Yingchuan Qi, Haipeng Xue,
Developmental Biology 253, 84 98 (2003) doi:10.1006/dbio.2002.0868 Neurogenin3 Participates in Gliogenesis in the Developing Vertebrate Spinal Cord Jeffrey Lee,*, Yuanyuan Wu,* Yingchuan Qi, Haipeng Xue,
regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries
 regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries primary and secondary events during SCI traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) main goal is to
regenerative medicine in the brain and the spinal cord spinal cord injuries primary and secondary events during SCI traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) traumatic spinal cord injury (SCI) main goal is to
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord
 What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
What Cell Make Up the Brain and Spinal Cord Jennifer LaVail, Ph.D. (http://anatomy.ucsf.edu/pages/lavaillab/index.html) What kinds of cells are these?" Neuron?" Epithelial cell?" Glial cell?" What makes
Regionalization of the nervous system. Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004
 Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Regionalization of the nervous system Paul Garrity 7.68J/9.013J February 25, 2004 Patterning along: Rostral/Caudal (AP) axis Dorsal/Ventral (DV) axis Start with DV axial patterning in Spinal Cord Dorsal/Ventral
Developmental Biology
 Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
Developmental Biology 362 (2012) 141 153 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Developmental Biology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/developmentalbiology Dual function of suppressor of
Overview. Unit 2: What are the building blocks of our brains?
 Unit 2: What are the building blocks of our brains? Overview In the last unit we discovered that complex brain functions occur as individual structures in the brain work together like an orchestra. We
Unit 2: What are the building blocks of our brains? Overview In the last unit we discovered that complex brain functions occur as individual structures in the brain work together like an orchestra. We
ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT
 ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT THESIS SUBMITTED TO BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE, INDIA FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
ROLE OF BDNF IN ENRICHED ENVIRONMENT MEDIATED AMELIORATION OF HYPOBARIC HYPOXIA INDUCED MEMORY IMPAIRMENT THESIS SUBMITTED TO BHARATHIAR UNIVERSITY, COIMBATORE, INDIA FOR THE DEGREE OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY
Communicated by Dominick P. Purpura, Albert Einstein College of Medicine, Bronx, NY, September 30, 2002 (received for review July 8, 2002)
 Differential modulation of BMP signaling promotes the elaboration of cerebral cortical GABAergic neurons or oligodendrocytes from a common sonic hedgehog-responsive ventral forebrain progenitor species
Differential modulation of BMP signaling promotes the elaboration of cerebral cortical GABAergic neurons or oligodendrocytes from a common sonic hedgehog-responsive ventral forebrain progenitor species
NG2-Glia (Polydendrocytes)
 NG2-Glia (Polydendrocytes) ii One liner Colloquium Chapter Title Digital Library of Life Sciences The Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences is an innovative information resource for researchers,
NG2-Glia (Polydendrocytes) ii One liner Colloquium Chapter Title Digital Library of Life Sciences The Colloquium Digital Library of Life Sciences is an innovative information resource for researchers,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue. Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells. The Nervous System. The Nervous System 21/12/2010
 Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Nervous tissue, charachteristics, neurons, glial cells Functional Organization of Nervous Tissue The Nervous System Components Brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors Responsible for Sensory perceptions,
Short Communication. In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the. mouse
 1 Short Communication In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the mouse Payam Dibaj 1, Eike D. Schomburg 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Experimental Medicine, Göttingen,
1 Short Communication In vivo recording of nerve conduction velocity of spinal CNS fibers in the mouse Payam Dibaj 1, Eike D. Schomburg 1,2 1 Max-Planck-Institute for Experimental Medicine, Göttingen,
Nervous System. Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI
 Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
Nervous System Overview.I Histology.II Electrical Signals.III Signal Transmission at Synapses Neurotransmitters.V Neural Circuits.VI Repairs.VII Pathology.VIII.IV 1 Controls and integrates all body activities
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology
 BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
BI 232: Human Anatomy & Physiology Roster Business Course Introduction and Syllabus Notecard Name E-mail Why you are taking the course Something interesting you did over break Lecture Tips Use the Study
B108 BC Neurons and Glial Cells *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m62431 1 B108 BC Neurons and Glial Cells * Melodye Gold Based on Human Biology Chapter 17.2: Neurons and Glial Cells by OpenStax Willy Cushwa This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
OpenStax-CNX module: m62431 1 B108 BC Neurons and Glial Cells * Melodye Gold Based on Human Biology Chapter 17.2: Neurons and Glial Cells by OpenStax Willy Cushwa This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX
