Central Nervous System. Chapter 11. Nervous System II. Nervous System Review. Brain and spinal cord
|
|
|
- Cassandra Higgins
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chapter 11 Nervous System II Nervous System Review Central Nervous System brain & spinal cord Peripheral Nervous System contains nerves connecting CNS to all other body parts Cranial nerves arising from the brain Spinal nerves arising from the spinal cord into somatic & autonomic nervous systems Somatic fibers connect to skin & skeletal muscles & control conscious activities; voluntary Autonomic fibers connect to viscera, glands & control subconscious activities; involuntary Central Nervous System Brain and spinal cord 1
2 Central Nervous System Brain & spinal cord connected by brainstem Brain Largest, most complex part of nervous system Consist of 2 hemispheres, diencephalon, cerebellum & brainstem Protected by cranium Spinal Cord 2 way communication between CNS & PNS Protected by vertebral column Meninges Membranes surrounding & protecting CNS 3 layers dura mater tough, outer CT attached to periosteum. Contain many blood vessels & nerves. arachnoid mater middle, web-like membrane w/out blood vessels pia mater inner, delicate membrane w/ many nerves & blood vessels to nourish cells of CNS; a band of pia mater called the denticulate ligament attaches dura mater to spinal cord subarachnoid space between arachnoid & pia contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) 2
3 Ventricles interconnected cavities within cerebral hemispheres & brain stem continuous with central canal of spinal cord filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) lateral ventricles largest; ventricles 1 & 2 third ventricle w/in midline of brain fourth ventricle w/in brainstem, in front of cerebellum cerebral aqueduct connects 3 rd & 4 th ventricles interventricular foramen connects laterals & 3 rd ventricle 3
4 Cerebrospinal Fluid secreted by choroid plexus located in pia mater circulates in ventricles, central canal of spinal cord, & subarachnoid space completely surrounds brain and spinal cord clear nutritive liquid mechanical protection (cushions) helps maintain stable ion conc. in CNS reabsorbed into blood stream by arachnoid granulations ventricles lined w/ cilia from ependymal cells; cilia aids in movement of CSF; ependymal cells regulate composition of CSF (selective) FYI Meningitis inflammation of meninges; (pia & arachnoid are most common) Subdural hematoma accumulation of blood between dura mater & arachnoid space Spinal tap measures CSF pressure Hydrocephalus - CSF pressure w/in brain; developing cranial sutures allow excess swelling. Shunt drains excess fluid away Spinal Cord Structure Continuous nerve tissue from brain thru vertebral column 31 segments starting w/ foramen magnum Cervical enlargement nerves to upper limbs Lumbar enlargement nerves to lower limbs Conus medullaris tapered area below lumbar E. Filum terminale distal portion of tail; thin cord of CT Cauda equina area below conus medullaris; consist of spinal nerves & filum terminale 4
5 Spinal Cord Structure foramen magnum to 2 nd lumbar vertebra Spinal Cord Structure Cross section resembles butterfly (gray mater) surrounded by white mater Cross section shows spinal cord by 2 grooves Anterior median fissure Posterior median sulcus Gray matter Posterior horns upper wing Anterior horns lower wing Lateral horns side protrusion Gray commissure area surrounding central canal; connects R & L wings Central canal lined w/ependymal cells; contains CSF Cross Section of Spinal Cord 5
6 Spinal Cord Structure White matter 3 areas surrounding gray matter Anterior funiculi (ventral) Posterior funiculi (dorsal) Lateral funiculi Ventral root Dorsal root Dorsal root ganglion a bundle of cell bodies outside CNS Fusion of dorsal & ventral root forms spinal nerve that passes thru intervertebral foramen Cross Section of Spinal Cord Spinal Cord Functions Center for spinal reflexes Carries nerve impulses to & from brain 6
7 Reflex Arcs Reflexes automatic, subconscious responses to stimuli. Helps maintain homeostasis Consist of receptors, sensory neurons, interneurons, motor neurons & effectors Examples sneezing, blinking, knee jerk, withdrawal Protective Withdrawal Reflex 7
8 Tracts of the Spinal Cord Ascending tracts conduct sensory impulses (afferent) to brain Descending tracts conduct motor impulses (efferent) from brain to motor neurons reaching muscles & glands Provides a 2-way communication Located in white matter Brain Functions interprets sensations determines perception stores memory reasoning makes decisions coordinates muscular movements regulates visceral activities determines personality controls emotions Major Parts cerebrum 2 hemispheres diencephalon brain stem cerebellum Cerebrum Largest part of brain Develops from forebrain Consist of 2 hemispheres 8
9 Structure of Cerebrum corpus callosum nerve fibers connecting hemispheres convolutions or gyri ridges caused by infolding sulci -shallow grooves fissure deep grooves longitudinal fissure separates hemispheres transverse fissure separates cerebrum from cerebellum Lobes of Cerebrum Each hemisphere is into lobes named after bones covering them Frontal Parietal Temporal Occipital Insula lobe located w/in lateral sulcus; covered by frontal, parietal & temporal lobes Functions of Cerebrum interpretation initiating voluntary movements storing & retrieving memory reasoning intelligence personality 9
10 Functional Regions of Cerebral Cortex Cerebral Cortex thin layer of gray matter on surface of cerebrum; Divided into motor, sensory & association areas Motor Areas Primary Motor Areas frontal lobes;anterior to central sulcus controls voluntary muscles; skeletal Broca s Area anterior to motor area left hemisphere controls muscles needed for speech Frontal Eye Field above Broca s area controls voluntary movements of eyes & eyelids Sensory Areas Sensory fibers cross over; R hemisphere interprets info from L hemisphere Sensory Area parietal lobe; posterior to central sulcus interprets sensations on skin Visual Area occipital lobe interprets vision Auditory Area temporal lobe interprets hearing 10
11 Association Areas regions of cortex that are not primary motor or sensory areas analyze & interpret sensory experiences provide memory, reasoning, verbalization, judgment, emotions Frontal Lobe Association Areas concentrating planning problem solving consequences of behavior Parietal Lobe understanding speech word expression feelings Association Areas Temporal Lobe remember visual scenes, music & complex patterns Occipital Lobe analyze visual patterns & recognition Hemisphere Dominance both analyze impulses & send impulses to opposite side of body in over 90% of population, left hemisphere is dominant in right handed people In most Left hemisphere controls speech writing reading verbal skills computational skills Nondominant hemisphere controls nonverbal tasks motor tasks provides emotions 11
12 Memory Consequences of learning & being able to access it later Short Term working memory closed circuit circuit is stimulated over and over when impulse flow stops, memory disappears Long Term repeated stimulation changes neuron structure strengthens synaptic transmission basal ganglia masses of gray matter deep within cerebral hemispheres forms from forebrain known as caudate nucleus, putamen, & globus pallidus produce dopamine control certain motor activities Basal Nuclei Diencephalon between cerebral hemispheres & brainstem surrounds 3rd ventricle mostly gray matter contains the following thalamus hypothalamus optic tracts optic chiasm infundibulum posterior pituitary mammillary bodies pineal gland 12
13 Diencephalon Thalamus receives & directs sensory impulses to appropriate part of cerebral cortex for interpretation Hypothalamus maintains homeostasis by regulating visceral activities links nervous & endocrine systems Limbic System Located in diencephalon Functions controls emotions produces feelings recognizes life threating condition Brainstem Consist of midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata Attaches brain to spinal cord 13
14 Midbrain between diencephalon & pons contains bundles of fibers that join brainstem & spinal cord w/ higher brain contains gray matter that acts as reflex centers cerebral aqueduct connects 3 rd & 4 th ventricles cerebral peduncles bundles of nerve fibers corpora quadrigemina 4 dome protrusions that are centers for visual & auditory reflexes Brainstem Pons rounded bulge on underside of brainstem between medulla oblongata & midbrain regulate rate & depth of breathing 14
15 Medulla Oblongata enlarged continuation of spinal cord conducts ascending & descending impulses between brain and spinal cord contains cardiac, vasomotor, & respiratory control centers contains various nonvital reflex control centers (coughing, sneezing, swallowing & vomiting) Reticular Formation network of nerve fibers w/in brain stem connects to hypothalamus, basal nuclei, cerebellum, & cerebrum filters incoming sensory information arouses cerebral cortex into state of wakefulness injury causes unconsciousness Types of Sleep Slow Wave person is tired decreasing activity of reticular formation restful dreamless reduced blood pressure & respiratory rate ranges from light to heavy alternates with REM sleep between minutes Rapid Eye Movement (REM) some areas of brain active heart and respiratory rates irregular dreaming occurs 5-15 minutes 15
16 Sleep Disorders Insomnia inability to sleep Narcolepsy extreme daytime sleepiness Sleep apnea upper airway collapses during sleep; blocks breathing; snoring Parasomnias sleep walking & sleep talking Restless leg syndrome repetitive leg jerks; leg pain at night Sleep paralysis inability to move a few minutes after waking Cerebellum 2 hemispheres inferior to occipital lobes posterior to pons & medulla oblongata vermis connects hemispheres cerebellar cortex gray matter arbor vitae white matter cerebellar peduncles allows communication between other parts of CNS coordinates skeletal muscle activity maintains posture Peripheral Nervous System Nerves that branch from CNS and connect to other body parts 16
17 Structure of Peripheral Nerve CT surrounding bundles of nerve fibers Epineurium outer most layer Perineurium surrounds each fascicle Endoneurium surrounds each axon Blood vessels located in epineurium & perineurium Nerve Fiber Classification Sensory Nerves conduct impulses to CNS Motor Nerves conduct impulses from CNS to muscles & glands Mixed Nerves contain both sensory & motor nerve fibers; most nerves Review terms Afferent towards Efferent - away Nerve Fiber Classification Nerve fibers into 4 general groups General somatic efferent fibers carry motor impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles General visceral efferent fibers carry motor impulses away from CNS to smooth muscles & glands General somatic afferent fibers carry sensory impulses to CNS from skin & skeletal muscles General visceral afferent fibers carry sensory impulses to CNS from blood vessels & internal organs 17
18 Nerve Fiber Classification Nerve fibers into 3 specialized groups Special somatic efferent fibers carry motor impulses from brain to muscles used in chewing, swallowing, speaking, & facial expressions Special visceral afferent fibers carry sensory impulses to brain from olfactory & taste receptors Special somatic afferent fibers carry sensory impulses to brain from receptors of sight, hearing, & equilibrium receptors Cranial Nerves 12 pairs 1 st & 2 nd pair originate w/in cerebrum others form from brainstem Oh Oh Oh To Touch And Feel Very Good Velvet AH Cranial Nerves Olfactory Optic Oculomotor Trochlear Trigeminal Abducens Facial Vestibulocochlear Glossopharyngeal Vagus Accessory & Hypoglossal 18
19 Cranial Nerves I and II Olfactory (I) sensory only impulses associated w/smell receptors located in upper nasal cavity Optic (II) sensory only impulses associated w/vision Cranial Nerves III and IV Oculomotor (III) motor impulses to eye muscles that raise eyelids move the eyes focus lens adjust pupil Trochlear (IV) smallest cranial nerves motor impulses to superior oblique muscles that moves the eye downward Cranial Nerve V Trigeminal (V) largest cranial nerve mixed nerves; sensory to face & motor to chewing muscles opthalmic division sensory from surface of eyes, tear glands, scalp, forehead, & upper eyelids maxillary division sensory from upper jaw, teeth, lip, palate, & skin of face mandibular division sensory from scalp, skin of jaw, lower teeth, gum, & lip motor to muscles of mastication 19
20 Cranial Nerves VI and VII Abducens (VI) motor impulses to lateral rectus muscles that move eyes to outside Facial (VII) mixed sensory from taste receptors motor to muscles of facial expression, tear glands, & salivary glands Cranial Nerves VIII and IX Vestibulocochlear (VIII) sensory forms 2 branches Vestibular - sensory from equilibrium receptors of ear Cochlear - sensory from hearing receptors of inner ear Glossopharyngeal (IX) mixed sensory from pharynx, tonsils, tongue, & carotid arteries motor to salivary glands & muscles of pharynx Vagus (X) mixed somatic motor to muscles of speech & swallowing autonomic motor to viscera sensory from pharynx, larynx, & esophagus, Cranial Nerve X 20
21 Cranial Nerves XI and XII Accessory (XI) 2 branches cranial- motor to muscles of soft palate, pharynx, larynx spinal motor to muscles in neck & back Hypoglossal (XII) motor to muscles of the tongue controls speaking, chewing, & swallowing Spinal Nerves mixed nerves provides 2-way communication between brain & limbs 31 pairs 8 cervical (C1 to C8) 12 thoracic (T1 to T12) 5 lumbar (L1 to L5) 5 sacral (S1 to S5) 1 coccygeal (Co) Adult spinal cord ends between L1-L2 vertebrae lumbar, sacral & coccygeal nerves form cauda equina & are called descending nerves each spinal nerve forms from fusion of 2 roots Dorsal root posterior branch of axons of sensory neurons Dorsal root ganglion lateral enlargement cell bodies of sensory neurons Ventral root anterior branch of axons of motor neurons;cell bodies are in spinal cord Spinal Nerves 21
22 Nerve Plexus Nerve plexus branching networks formed by spinal nerves; not in T2-T12 Cervical Plexus C1-C4 supply muscles & skin of the neck contributes to phrenic nerve associated w/diaphragm Brachial plexuses C5-T1 supply impulses to upper limbs Lumbosacral plexuses T12-S5 supply impulses from lumbar region to pelvic cavity Brachial Plexus Lumbosacral Plexus 22
23 Autonomic Nervous System functions w/out conscious effort controls visceral activities regulates smooth & cardiac muscles, & glands efferent fibers typically lead to ganglia outside CNS 2 Divisions sympathetic prepares body for fight or flight situations; stress parasympathetic functions under normal restful conditions; maintains homeostasis Autonomic Nerve Fibers all are motor (efferent) includes 2 neurons preganglionic fibers axons of preganglionic neurons leave CNS to synapse with postganglionic fibers axons of postganglionic neurons synapse w/viscera effector Control of Autonomic Activity Controlled largely by CNS Medulla oblongata regulates cardiac, vasomotor & respiratory activities Hypothalamus regulates visceral functions; renal & digestive Limbic system & cerebral cortex control emotions 23
24 Life-Span Changes Brain cells begin to die before birth Over average lifetime, brain shrinks 10% Most cell death occurs in temporal lobes By age 90, frontal lobe has lost half its neurons Number of dendrites Decreased levels of neurotransmitters Fading memory Slowed responses and reflexes Changes increase risk of falling Sleep problems common; decrease in REM sleep Diseases or Disorders Lou Gehrig s disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) Motor neurons degenerate & replaced w/ fibrous tissue; decline of muscle function Genetic; abnormal enzyme doesn t break down O 2 free radicals Anencephaly fetus w/brainstem but lacks upper brain structures Lissencephaly smooth brain; lack of convolutions causes retardation & seizures Diseases or Disorders Cerebral palsy motor impairment caused by blocked cerebral blood vessels Parkinson disease dopamine producing neurons degenerate; leads to tremors; muscle rigidity Dementia Alzheimer 24
25 Cerebral Injuries Concussion brain jarred against cranium loss of consciousness temporary loss of memory headache recovery usually complete Cerebrovascular Accident stroke sudden interruption in blood flow brain tissues die 25
Unit Three. The brain includes: cerebrum, diencephalon, brain stem, & cerebellum. The brain lies within the cranial cavity of the skull.
 Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
Human Anatomy & Physiology 11 Divisions of the Nervous System Karen W. Smith, Instructor Unit Three BRAIN & SPINAL CORD Refer to the following URLs. Be sure to study these along with your book. http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/nervous.html
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS SYSTEM II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM. 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system.
 CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
CHAPTER 11: NERVOUS II: DIVISIONS OF THE NERVOUS OBJECTIVES: 1. Outline the major divisions of the nervous system. NERVOUS CENTRAL NERVOUS (BRAIN & SPINAL CORD) (INTERNEURONS) PERIPHERAL NERVOUS (CRANIAL
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System
 The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
The Nervous System: Central Nervous System I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS & the body by: 1. monitoring of the body 2. & information between parts of the body 3. acting as a to gather, store,
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b
 Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Unit 7b Chetek High School Mrs. Michaelsen 9.12 Meninges A. Meninges 1. The organs of the CNS are covered by membranes a. The meninges are divided into 3 layers:
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Central Nervous System
Bellringer: The central nervous system is comprised of: What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Brain. b.
 Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Bellringer: The central is comprised of: a. Brain b. Spinal cord c. Sensory receptors d. Both a and b What is the name of the outermost layer of the brain? a. Pia mater b. Dura mater c. Arachnoid d. Pons
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 14 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Introduction The purpose of the chapter is to: 1. Understand how the brain is organized, protected, and supplied
Blood supply to the brain Blood brain barrier isolates neural tissue from general circulation
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Objectives Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions. Discuss the formation, circulation, and functions of the CSF. List the main components of the medulla
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. SAEED ABUEL MAKAREM Objectives By the end of the lecture, you should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function of the nervous system.
Brain and spinal nerve. By: shirin Kashfi
 Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
Brain and spinal nerve By: shirin Kashfi Nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous system (PNS) Brain (cranial) nerves Spinal nerves Ganglions (dorsal root ganglions, sympathetic
The Nervous System PART C. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7 PART C Protection of the Central Nervous System Scalp and skin Skull and vertebral
Protection of the Brain. Overview of the Brain. Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition. Martini & Ober. Chapter 13. Lecture 20
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves Lecture 20 1 Overview of the Brain Functions Major Parts regulates visceral activities cerebrum (two hemispheres)
Chapter 9. Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Chapter 9 Nervous System Central Nervous System (CNS) vs. Peripheral Nervous System(PNS) CNS Brain Spinal cord PNS Peripheral nerves connecting CNS to the body Cranial nerves Spinal nerves Neurons transmit
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES LABORATORY OBJECTIVES: 1. Histology: Identify structures indicated on three different slides or images of nervous system tissue. These images
b. The groove between the two crests is called 2. The neural folds move toward each other & the fuse to create a
 Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Chapter 13: Brain and Cranial Nerves I. Development of the CNS A. The CNS begins as a flat plate called the B. The process proceeds as: 1. The lateral sides of the become elevated as waves called a. The
Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. 1) List the anatomical subdivisions.
 S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
S T U D Y G U I D E 8 1. Divisions of the Nervous System 1) List the anatomical subdivisions. Central N.S. Peripheral N.S. 2) List the functional subdivisions. Somatic N.S. Autonomic N.S. 2. Nerve Tissue
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System
 Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
Lecture - Chapter 13: Central Nervous System 1. Describe the following structures of the brain, what is the general function of each: a. Cerebrum b. Diencephalon c. Brain Stem d. Cerebellum 2. What structures
The Nervous System PART B
 7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
7 The Nervous System PART B PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reflex Arc Reflex
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY
 Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
Organization of The Nervous System PROF. MOUSAED ALFAYEZ & DR. SANAA ALSHAARAWY Objectives At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to: List the parts of the nervous system. List the function
C h a p t e r PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas
 C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
C h a p t e r 15 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres North Harris College Houston, Texas Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
Chapter 9 Nervous System
 Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
Chapter 9 Nervous System Introduction: A. The nervous system is composed of neurons and neuroglia. 1. Neurons transmit nerve impulses to other neurons. 2. Nerves are made up of bundles of nerve fibers
The Nervous System 7PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Nervous System 7PART B What is a reflex? What is a reflex? What is meant by the statement that
Neurology study of the nervous system. nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis
 Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Nervous System Neurology study of the nervous system nervous & endocrine systems work together to maintain homeostasis Nervous System works very fast Uses electrical signals called nerve impulses Short-lived
Cranial Nerves and Spinal Cord Flashcards
 1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
1. Name the cranial nerves and their Roman numeral. 2. What is Cranial Nerve I called, and what does it 3. Scientists who are trying to find a way to make neurons divide to heal nerve injuries often study
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Chapter 14: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Development of the Brain Three to four-week embryo: prosencephalon, mesencephalon and rhombencephalon. Five-week embryo: telencephalon (cerebrum), diencephalon
Instructor s Review for Final Exams. The Nervous System
 Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Instructor s Review for Final Exams The Nervous System Divisions of the Central Nervous System? Brain and spinal cord. Key word, central. Divisions of the nervous system Central and Peripheral Coverings
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
Chapter 10 The Nervous System: The Brain and Cranial Nerves Copyright 2015 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Overview Key Terms aphasia corpus callosum meninges basal nuclei diencephalon
meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater arachnoid mater pia mater membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system
 membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
membranes located between bone and soft tissue of the nervous system meninges Outermost layer of the meninge dura mater middle layer of the meninges, contains no blood vessels arachnoid mater Innermost
Nervous System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Nervous System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary parts of the neuron Identify the major structures of the central nervous system Identify the major structures of the peripheral nervous
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
14 - Central Nervous System. The Brain Taft College Human Physiology
 14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
14 - Central Nervous System The Brain Taft College Human Physiology Development of the Brain The brain begins as a simple tube, a neural tube. The tube or chamber (ventricle) is filled with cerebrospinal
Human Anatomy. Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
 Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
Human Anatomy Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves 1 The Spinal Cord Link between the brain and the body. Exhibits some functional independence from the brain. The spinal cord and spinal nerves serve two functions:
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Forebrain Interprets sensory
Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Bio 105
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Chapter 12b. Overview
 Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
Chapter 12b Spinal Cord Overview Spinal cord gross anatomy Spinal meninges Sectional anatomy Sensory pathways Motor pathways Spinal cord pathologies 1 The Adult Spinal Cord About 18 inches (45 cm) long
3/15/17. Outline. Nervous System - PNS and CNS. Two Parts of the Nervous System
 Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
Nervous System - PNS and CNS Bio 105 Outline I. Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System II. Peripheral Nervous System A. Autonomic Nervous Systems B. Somatic Nervous Systems III. Autonomic
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg Three Main Regions of the Brain. Forebrain
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Pg. 129 Three Main Regions of the Brain Forebrain Cerbral hemispheres Diencephalon Midbrain Brain stem Hindbrain Pons Cerebellum Medulla oblongata Interprets sensory inputs
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Peripheral Nervous System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Spinal Nerves Overview Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves are connected to the spinal cord No special names; numbered by level of vertebral column at which they
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system
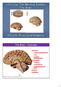
 Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Introduction and Basic structural organization of the nervous system **the slides are in bold and the book is in red Done by : razan krishan & marah marahleh INTRODUCTION The nervous system, along with
Chapter 7 Nervous System
 Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 7 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Cranial Nerves. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Cranial Nerves Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Sensory and Motor Systems Sensory Systems:
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Chapter 8 Nervous System
 Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Chapter 8 Nervous System Two message centers: Functions of these systems: 1. * 2. * Overview of the Nervous System Parts: General Functions: Functions Sensory input: Sensation via nerves Integration: interpretation
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Dispose of debris Nervous Tissue: Support Cells Ependymal cells Line cavities of the brain and spinal cord Circulate cerebrospinal fluid Nervous
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body Changes = stimuli Integration To process and interpret sensory
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day)
 Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Chapter 14: Nervous System Guided Notes (A-day) Nervous System Overview Major Function: Control the body's and. Divided into the Nervous System (CNS=Brain and Spinal Cord) and the Nervous System (PNS=Cranial
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain. MDL231 Principle of Anatomy
 Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Unit 12a: The Nervous System The Brain MDL231 Principle of Anatomy The Brain - Overview Cerebrum T PP H midbrain Cerebellum pons m.o. Brain stem medulla oblongata (M.O.) pons midbrain (mesencephalon) Diencephalon
Nervous and Endocrine System Exam Review
 Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
Directions: Read each question and complete the statement using the multiple choice responses I. Nervous System 1. The interpretation of olfactory receptor information would fall under which general function
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1
 Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Unit 7 - The Nervous System 1 I. Unit 7: The Nervous System A. Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input - gathering information a) To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body b) Changes
Anatomy & Physiology. Chapter 7 Notes Nervous System. Monitor/collecting stimuli occurring inside and outside the body
 Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 7 Notes Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1) Sensory input 2) Integration Monitor/collecting stimuli occurring inside and outside the body To process and interpret
Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 7 Notes Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1) Sensory input 2) Integration Monitor/collecting stimuli occurring inside and outside the body To process and interpret
The Brain. Brain. Spinal Cord. Cauda Equina
 The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
The Brain Brain Spinal Cord Cauda Equina The Brain Ventricles- cavities in the brain filled with cerebrospinal fluid connected to the subarachnoid space- fluid filled space surrounding the brain Brain
Laboratory Manual for Comparative Anatomy and Physiology Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
 Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Neuron Capillary Astrocyte Microglial cell Neuron Fluid-filled cavity Process of oligodendrocyte Ependymal cells Brain or spinal cord tissue Myelin sheath Nerve fibers Figure 15.1 Transparency Master 114
Nervous System. Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition)
 Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System Unit 6.6 (6 th Edition) Chapter 7.6 (7 th Edition) 1 Learning Objectives Identify the main parts (anatomy) of a neuron. Identify the 2 divisions of nervous system. Classify the major types
Nervous System: An Introduction. HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School
 Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Nervous System: An Introduction HAP Susan Chabot Lemon Bay High School Function of the Nervous System 3 overlapping functions SENSORY INPUT - Monitor changes inside and outside of the body; these changes
Unit 7: The Nervous System
 Unit 7: The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System A. Sensory input gathering information 1. To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body 2. Changes = stimuli B. Integration 1. To
Unit 7: The Nervous System I. Functions of the Nervous System A. Sensory input gathering information 1. To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body 2. Changes = stimuli B. Integration 1. To
Chapter 7 The Nervous System
 Chapter 7 The Nervous System Fxns of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor Δs occurring inside and outside the body (Δs = stimuli) 2. Integration to process and interpret
Chapter 7 The Nervous System Fxns of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor Δs occurring inside and outside the body (Δs = stimuli) 2. Integration to process and interpret
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES
 NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
NOTES CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System LECTURE NOTES I. Divisions of the Nervous System two major divisions A. Central Nervous System (CNS) 1. brain 2. spinal cord B. Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES
 BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
BRAIN PART I (A & B): VENTRICLES & MENINGES Cranial Meninges Cranial meninges are continuous with spinal meninges Dura mater: inner layer (meningeal layer) outer layer (endosteal layer) fused to periosteum
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord. Major Divisions of the nervous system:
 Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Central Nervous System (CNS) -> brain and spinal cord Major Divisions of the nervous system: Afferent (sensory input) -> cell bodies outside of the central nervous system (CNS), carry info into the CNS
Nervous System. Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson
 Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
Nervous System Human Anatomy & Physiology P. Wilson 1 2 Types of cells in the nervous system: Neurons & Neuroglial cells Neuroglial (aka glial) cells perform functions that are vital to neurons by filling
7.2.notebook January 15, 2016
 7.2 Central Nervous System 1 I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS controls & coordinates the body by: 1. monitoring activities of the body 2. communicating & exchanging information between parts
7.2 Central Nervous System 1 I. Anatomy of the nervous system A. The CNS controls & coordinates the body by: 1. monitoring activities of the body 2. communicating & exchanging information between parts
4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum
 4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum White Matter = myelinated tracts or nerves Gray Matter = unmyelinated tracts or nerves Brain: gray matter on outside, white matter inside
4 main parts 1) Cerebrum 2) Diencephalon 3) Brain stem 4) Cerebellum White Matter = myelinated tracts or nerves Gray Matter = unmyelinated tracts or nerves Brain: gray matter on outside, white matter inside
Chapter 13. The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves. Spinal Cord. Spinal Cord Protection. Meninges. Together with brain forms the CNS Functions
 Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
Spinal Cord Chapter 13 The Spinal Cord & Spinal Nerves Together with brain forms the CNS Functions spinal cord reflexes integration (summation of inhibitory and excitatory) nerve impulses highway for upward
By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr.
 The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
The Nervous System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences College of Agriculture & Veterinary Medicine RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Highly complex system of two
Synapse Homework. Back page last question not counted. 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts. 26/34 students answered correctly!
 Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Synapse Homework Back page last question not counted 26/34 students answered correctly! 4 pts total, each question worth 0.18pts Business TASS hours extended! MWF 1-2pm, Willamette 204 T and Th 9:30-10:30am,
Unit 3 : Nervous System
 Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
Unit 3 : Nervous System Mind Map Structural Classification The nervous Tissue Disorders of The nervous system Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System The brain Spinal Cord Sensory
The Nervous System. Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes =
 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System input gathering To monitor occurring inside and outside the body Changes = To process and sensory input and decide if is needed output A response to integrated
Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for
 Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
Chapter 13 Outline Note: Please refer to handout Spinal Plexuses and Representative Spinal Nerves for what you need to know from Exhibits 13.1 13.4 I. INTRODUCTION A. The spinal cord and spinal nerves
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Student Name CHAPTER 13 CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM Approximately one hundred billion neurons make up the brain. Everything we are and everything we hope to become are centered in this structure, which is about
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374
 Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Ch 13: Central Nervous System Part 1: The Brain p 374 Discuss the organization of the brain, including the major structures and how they relate to one another! Review the meninges of the spinal cord and
Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet
 1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
1. What are the two parts of the CNS? 2. What are the four functions of the CNS Anatomy & Physiology Central Nervous System Worksheet 3. What are the four functions of the meninges? (p430) 4. Starting
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels
 M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
M555 Medical Neuroscience Lab 1: Gross Anatomy of Brain, Crainal Nerves and Cerebral Blood Vessels Anatomical Directions Terms like dorsal, ventral, and posterior provide a means of locating structures
Human Nervous System:
 OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
OLLI Brain: Making Sense of Our World: Lecture 3 Human Nervous System: The Motor & Sensory Divisions Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings Organization of the Nervous
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves. Origin of the Brain
 Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Chapter 18: The Brain & Cranial Nerves BIO 218 Fall 2015 Origin of the Brain The brain originates from a structure called the neural tube, which arises during a developmental stage called neurulation.
Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer.
 Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord membrane covering the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three membrane Meninges
Ms. K. GOWRI. M.Pharm., Lecturer. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM (CNS) central nervous system consists of brain and spinal cord membrane covering the brain and spinal cord are surrounded by three membrane Meninges
Dura mater is the outermost layer next to the inside of the cranial cavity and forms the internal periosteum. In some regions, it extends inward
 11.1: Introduction The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. Communication to the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is by
11.1: Introduction The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord. The brainstem connects the brain to the spinal cord. Communication to the peripheral nervous system (PNS) is by
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II
 Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Biology 3201 Unit 1: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium II Ch. 12 The Nervous System (Introduction and Anatomy) The Nervous System - Introduction Cells, tissues, organs and organ systems must maintain a biological
Model 3-50B or 3-88 III VIII. Olfactory Nerve. Optic Nerve. Oculomotor Nerve. Trochlear Nerve. Trigeminal Nerve. Abducens Nerve.
 Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Model 3-50B or 3-88 I Olfactory Nerve II Optic Nerve Oculomotor Nerve III IV Trochlear Nerve Trigeminal Nerve V VI Abducens Nerve Glossopharyngeal Nerve IX VII Facial Nerve VIII Vestibocochlear Nerve or
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System
 Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Functional Organization of the Central Nervous System Hierarchical orgnization CNS consists of the brain and the spinal cord The brain analyzes and interprets the information Response messages are
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
Good Morning! Take out your notes and vocab 1-10! Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring inside and outside the body (changes = stimuli) 2.
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives
 The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
The Brain and Cranial Nerves Student Objectives Chapter 14 Textbook and Laboratory Manual Name the major regions of the brain and describe their functions Name the ventricles of the brain and describe
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System. Anatomy of the CNS
 CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
CHAPTER 13&14: The Central Nervous System Anatomy of the CNS in human consists of brain and spinal cord as stated earlier neurons have little support from their extracellular matrix and depend on glial
Somatic Nervous Systems. III. Autonomic Nervous System. Parasympathetic Nervous System. Sympathetic Nervous Systems
 7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
7/21/2014 Outline Nervous System - PNS and CNS I. II. Two Parts of the Nervous System Central Nervous System vs Peripheral Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System A. B. Brain and Spinal Cord III. Autonomic
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD. Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of
 ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
ANATOMY OF SPINAL CORD Khaleel Alyahya, PhD, MEd King Saud University School of Medicine @khaleelya OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, students should be able to: Describe the external anatomy of the
Sheep Brain Dissection
 Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
Sheep Brain Dissection Mammalian brains have many features in common. Human brains may not be available, so sheep brains often are dissected as an aid to understanding the mammalian brain since he general
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES NERVOUS SYSTEM TISSUES: HISTOLOGY SLIDES
 ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
ACTIVITY 7: NERVOUS SYSTEM HISTOLOGY, BRAIN, CRANIAL NERVES OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 14 & 15 McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal
 I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
I. Anatomy of the Brain A. Cranial Meninges and Ventricles of the Brain 1. Meninges a. Dura mater 1) Endosteal/Periosteal Layer - Outer 2) Meningeal Layer - Inner 3) Falx cerebri a) Superior sagittal sinus
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System. 1. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? 3. What kind of neuroglia myelinates axons in the PNS?
 . What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
. What N.S. division controls skeletal muscles? Nervous System SRS Review %. Central nervous system %. Peripheral nervous system %. Afferent division %. Somatic division %. Autonomic division %. Sympathetic
Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) 2. Diencephalon -interbrain ( ) -diencephalons, thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus -hollow space =
 Week 2 -neural plate Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) Week 3 -neural groove Week 4 -neural tube (ice cream cone view) 1. Prosencephalon - 2. Mesencephalon - 3. Rhombencephalon - Week 5 -brain
Week 2 -neural plate Development of the Central Nervous System (CNS) Week 3 -neural groove Week 4 -neural tube (ice cream cone view) 1. Prosencephalon - 2. Mesencephalon - 3. Rhombencephalon - Week 5 -brain
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves
 Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
Chapter 13 Brain and Cranial Nerves 13-1 Brain and Cranial Nerves Brain Part of CNS contained in cranial cavity Control center for many of body s functions Much like a complex computer but more Parts of
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Nervous System. Chapter 7. Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. Elaine N. Marieb. Seventh Edition
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 7 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 7 The Nervous System Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input gathering information To monitor changes occurring
Chapter 13! Chapter 13 Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves!
 Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
Chapter 13! The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves! SECTION 13-1! The brain and spinal cord make up the central nervous system, and the cranial nerves and spinal nerves constitute the peripheral nervous system!
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th
 3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
3 rd week ectoderm thickens to form neural plate, which is later flanked by neural folds This neural groove deepens, forming a neural tube by 4 th week differentiates into the CNS = brain development begins
