Contrast-Enhanced Breast Ultrasonography
|
|
|
- Jerome Dickerson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ME rticle ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography Imaging Features With Histopathologic orrelation He Liu, MD, Yu-Xin Jiang, MD, Ji-in Liu, MD, Qing-Li Zhu, MD, Qiang Sun, MD, Xiao-Yan hang, MD Objective. The purpose of this study was to identify histopathologic correlates for the varied appearances of breast masses on contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (EUS). Methods. ontrast-enhanced ultrasonography was performed in 104 patients (age range, years) after administration of a sulfur hexafluoride microbubble contrast agent, and enhancement patterns were classified as no enhancement, peripheral enhancement, homogeneous enhancement, regional enhancement, and heterogeneous enhancement. ll patients histologic slides were reviewed and correlated with EUS findings. Results. In malignant masses, heterogeneous enhancement corresponded to tumor cell cords or clusters in a variable amount of desmoplastic stroma. Homogeneous enhancement corresponded to hypercellularity in the whole mass, or ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS) was predominant. Regional enhancement corresponded to a DIS component. Peripheral enhancement corresponded to a DIS component, hypercellularity or adenosis at the periphery, and low-degree cellularity, degeneration, fibrosis, or necrosis in the center. No enhancement was present in 1 case of low-grade DIS. In benign masses, heterogeneous enhancement corresponded to loose cell proliferation in a more sclerotic stroma. Homogeneous enhancement corresponded to diffuse hypercellularity, an inflammatory cell infiltrate, or intraductal papilloma. Regional enhancement corresponded to focal hypercellularity or intraductal papilloma within a dilated duct. No enhancement corresponded to desmoplastic stroma. Peripheral enhancement was shown in 1 case of granulomatous mastitis with an inflammatory infiltrate at the periphery and necrosis in the center. onclusions. reast mass EUS findings correlated with histologic features. Key words: breast neoplasm; contrast-enhanced ultrasonography; pathologic correlation. bbreviations EUS, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography; DIS, ductal carcinoma in situ; H&E, hematoxylin-eosin; ID, invasive ductal carcinoma Received March 5, 2009, from the Departments of Diagnostic Ultrasound (H.L., Y.-X.J., Q.-L.Z.), Surgery (Q..), and Pathology (X.-Y..), Peking Union Medical ollege Hospital, hinese cademy of Medical Sciences, eijing, hina; and Department of Radiology, Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania US (J.-.L.). Revision requested March 31, Revised manuscript accepted for publication pril 2, We thank Hanyuan Huang, MD, and Quancai ui, MD, for assistance. This research was supported by National Natural Sciences Foundation of hina grant ddress correspondence to Yu-Xin Jiang, MD, Department of Diagnostic Ultrasound, Peking Union Medical ollege Hospital, hinese cademy of Medical Sciences, 1 Shuaifuyuan, Wangfujing, eijing, hina. yuxinjiangxh@yahoo.com.cn ME rticle includes ME test New ultrasonographic techniques are being developed and studied. One such technique is contrast-enhanced ultrasonography (EUS), which has been studied to determine whether it is helpful for diagnosis. ontrast-enhanced ultrasonography has improved the ability of ultrasonography to characterize focal liver lesions. Several prospective studies have shown the comparability of this technique with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging for metastases, 1,2 and in some cases, lesions that are too small to detect with computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging are clearly shown on EUS. The literature on EUS evaluation of breast masses is relatively scant and limited to 2009 by the merican Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: /09/$3.50
2 ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography Doppler modalities, mainly studies of blood flow. 3 6 We previously published an article in which we reported on the same 104 patients as in this article. 7 In that article, breast EUS enhancement patterns were classified as no en - hancement, peripheral enhancement, homogeneous enhancement, regional enhancement, and heterogeneous enhancement. No enhancement pattern was suggestive of benignity, with sensitivity of 18.3%, specificity of 97.7%, a positive predictive value of 91.7%, a negative predictive value of 46.2%, and accuracy of 51.5%. The peripheral enhancement pattern was suggestive of malignancy, with sensitivity of 39.5%, specificity of 98.3%, a positive predictive value of 94.4%, a negative predictive value of 69.4%, and accuracy of 73.8%. Homogeneous, regional, and heterogeneous enhancement patterns did not show meaningful diagnostic information. To our knowledge, the correlation between EUS findings and pathologic features has not been well documented in large series of cases. The purpose of this study was to investigate the correlation of -mode pulse inversion harmonic EUS findings with histologic features in breast masses. Materials and Methods Patients This study design and protocol were approved by our Institutional Review oard, and all patients gave informed consent to be examined. From March 2005 to December 2005, 184 consecutive patients underwent conventional preoperative ultrasonography; 108 patients also underwent EUS. None of the masses were biopsied before the contrast studies. The inclusion criterion was the presence of masses on conventional ultrasonography. The exclusion criterion was contraindications to contrast agent administration. The contrast agent was not given if the patient had heart disease, pulmonary or respiratory disease, hypertension, or an allergy to the contrast agent or if the patient was pregnant or breastfeeding. ll patients underwent surgery (radical mastectomy with axillary dissection, n = 44; mastectomy, n = 2; or lumpectomy, n = 62) and had final pathologic diagnoses. Three of 108 cases were excluded because of poor image quality, and 1 was excluded because of missing histologic slides. s a result, 104 patients (age range, years; mean age, 44 years) were included in this study. The final pathologic diagnoses were invasive ductal carcinoma (ID; n = 35), ductal carcinoma in situ (DIS; n = 3), invasive lobular carcinoma (n = 3), mucinous carcinoma (n = 1), intraductal papillary carcinoma (n = 1), borderline phyllode tumors (n = 1), fibroadenoma (n = 30), adenosis (n = 15), intraductal papilloma (n = 9), granulomatous mastitis (n = 2), fat necrosis (n = 1), foreign body granuloma (n = 1), a cyst (n = 1), and hamartoma (n = 1). onventional and ontrast-enhanced Imaging Protocol HDI 5000 and iu22 systems (Philips Healthcare, othell, W) with a 12 5 MHz linear array transducer was used for conventional ultrasonography. n HDI 5000 system with a 7 4 MHz linear transducer and an iu22 system with an 8 4 MHz linear transducer were used for EUS. The contrast agent was SonoVue (racco Sp, Milan, Italy), which is a lyophilized powder of phospholipid-stabilized microbubbles containing sulfur hexafluoride gas with a mean diameter of 2.5 µm; the solution was reconstituted by the addition of 5 ml of sterile saline. -mode pulse inversion harmonic imaging was used for EUS, and the settings were as follows: the mechanical index was 0.06 to 0.08; the image depth was 3 or 4 cm; the single focus was at the bottom of the image; the probe was stabilized manually; and no pressure was exerted. One ultrasound physician (H.L., with 5 years of experience in breast ultrasonography) performed all conventional and EUS examinations. On conventional ultrasonography, the maximum imaging plane of the mass, which included the mass and its surrounding normal tissue if possible, was selected for EUS. fter a bolus injection of 2.4 ml of SonoVue manually via a 20-gauge cannula placed in the antecubital vein, the selected plane remained unchanged during the examination, and real-time imaging was recorded for up to 3 minutes. ll static and dynamic images were stored in the iu22 and HDI 5000 systems, and then single frames in the JPEG format and movie files in the Digital Imaging ommunications in Medicine format were exported to a personal computer. 912 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
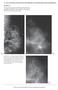
3 Liu et al Image nalysis To evaluate the enhancement pattern, microvascular imaging was created by QL software (Philips Healthcare) from a real-time contrastenhanced imaging sequence on a computer workstation. Microvascular imaging is composite imaging that is constructed through the summation of maximum-intensity pixels in consecutive imaging frames to improve visualization of tumor neovascularity. The captured imaging segment for microvascular imaging started when contrast washed in and ended when contrast began to wash out. This period lasted less than 30 seconds in all cases in our study, so motion artifacts were minimal. Two ultrasound physicians (H.L. and Q.-L.Z. by consensus) evaluated all ultrasonographic imaging without knowledge of the patients clinical data. ontrast-enhanced images were classified into 5 categories according to the distribution of enhanced areas of the mass: (1) no enhancement, with lack of enhancement after contrast agent injection (Figure 1, and ); (2) homogeneous enhancement, in which diffuse and homogeneous enhancement showed across the whole mass (Figure 2, and ); (3) peripheral enhancement, in which enhancing areas were only or more confined to the mass periphery (Figure 3, and ); (4) regional enhancement, in which part of a mass showed homogeneous enhancement (Figure 4, and ); and (5) heterogeneous enhancement, in which the mass was heterogeneously enhanced (Figure 5, and ). The difference between regional and heterogeneous enhancement was that the mass was classified as having regional enhancement if greater than 50% of the mass was enhanced homogeneously and classified as heterogeneous if less than 50% was enhanced homogeneously. Figure 1. Nonpalpable mass in the outer upper quadrant of the left breast in a 38-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed adenosis., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of mm., ontrast-enhanced sonogram showing no enhancement., Pathologic specimen showing considerable fibrosis, distortion of the glands, and a dilated duct (H&E, original magnification 60). Histologic nalysis ll of the masses were removed intact without rupture and fixed. The specimens were fixed in formaldehyde, embedded in paraffin, cut into slices of 5-mm thickness parallel to the longest axis, and stained with hematoxylin-eosin (H&E). The histologic interpretations were performed by 1 pathologist (X.-Y.., with 8 years of experience in breast disease). maximal histologic section of each mass was selected for comparison J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
4 ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography with the EUS image, which was obtained in the maximum imaging plane of the mass. For masses with no enhancement pattern or homogeneous enhancement, the pathologic features of the whole mass were noted. For masses with the peripheral enhancement pattern, the histologic findings of the tumor periphery and central area were respectively noted. For masses with the regional or heterogeneous enhancement pattern, the radiologist and pathologist compared EUS images and histologic slides in terms of masses localization and outlines, and the enhancing and nonenhancing areas were correlated with the corresponding areas in the pathologic specimens. Figure 2. Palpable mass in the upper quadrant of the right breast in a 47-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed ID., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of mm., ontrast-enhanced sonogram showing diffuse homogeneous enhancement across the whole mass., Pathologic specimen showing solid tumor nests with little intervening stroma (H&E, original magnification 60). Results ll 104 masses were solid-appearing hypoechoic masses. Forty-three were malignant; 60 were benign; and 1 was borderline. The sizes of the malignant masses were 0.5 to 7.6 cm (mean, 2.4 cm), and 21(48.8%) were smaller than 2 cm. The sizes of the benign masses were 0.5 to 7.4 cm (mean, 2.2 cm), and 34 (56.7%) were smaller than 2 cm. There was no significant difference in tumor size between the malignant and benign masses (P =.398). Histologic Findings for Malignant Masses Invasive Ductal arcinoma (n = 35) Pathologic examination showed the following characteristics. In the 15 cases with peripheral enhancement, a high-grade DIS component or a higher degree of tumor cell proliferation compared with the central part appeared at the periphery (Figure 3); low-degree cellularity, degeneration, fibrosis, and necrosis were observed in the central tumor parts. In the 10 cases with heterogeneous enhancement, tumor cell cords were present in a variable amount of desmoplastic stroma (Figure 5). In the 5 cases with homogeneous enhancement, ID was characterized by solid tumor nests with little intervening stroma (Figure 2), or it was dominated by an extensive high-grade DIS component. In the 5 cases with regional enhancement, DIS corresponded to the enhanced area. 914 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
5 Liu et al Figure 3. Palpable mass in the inner upper quadrant of the left breast in a 52-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed ID., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of mm with an irregular margin., ontrastenhanced sonogram showing enhancement mainly confined to the periphery of the mass., Pathologic specimen showing a higher degree of tumor cell proliferation at the periphery compared with the central part (H&E, original magnification 60). Figure 4. Palpable mass in the inner upper quadrant of the right breast in a 42-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed adenosis., onventional sonogram showing a hypo - echoic mass of mm with a well-defined margin., ontrast-enhanced sonogram showing regional enhancement and homogeneous enhancement in part of the mass., Pathologic specimen showing focal hypercellularity corresponding to the enhanced area (H&E, original magnification 60). J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
6 ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography Invasive Lobular arcinoma (n = 3) and Mucinous arcinoma (n = 1) On histopathologic review, invasive lobular carcinoma was characterized by a proliferation of tumor cells distributed in a single file ( Indian file ), with little disturbance of the background architecture. The only difference between the 1 case with peripheral enhancement and the 2 cases with heterogeneous enhancement was that adenosis rich in acinar and tubular structures was present at the periphery (Figure 6). In the 1 case of mucinous carcinoma with peripheral enhancement, the tumor cells dominated at the periphery of a mucous lake. Ductal arcinoma In Situ (n = 3) and Intraductal Papillary arcinoma (n = 1) Ductal carcinoma in situ and intraductal papillary carcinoma are solid-appearing hypoechoic masses on conventional ultrasonography, and the cystic changes in the papillary masses cannot be detected before contrast enhancement (Figure 7). One case of DIS with regional enhancement and 1 case with homogeneous enhancement were both intermediate grade, characterized by increased epithelial proliferation. The difference was that the DIS with regional enhancement was associated with sclerotic adenosis, which corresponded to the nonenhanced area. similar feature was also found in the case of intraductal papillary carcinoma with regional enhancement (Figure 7, and ). One case of DIS with no enhancement pattern was low grade and highly differentiated. In summary (Table 1), in malignant masses, heterogeneous enhancement corresponded to tumor cell cords or clusters in a variable amount of desmoplastic stroma. Homogeneous enhancement corresponded to hypercellularity in the whole mass, or DIS was predominant. Regional enhancement corresponded to a DIS component. Peripheral enhancement corresponded to a DIS component, hypercellularity or adenosis at the periphery, and low-degree cellularity, degeneration, fibrosis, or necrosis in the center. No enhancement was present in 1 case of low-grade DIS. Figure 5. Palpable mass in the outer upper quadrant of the left breast in a 56-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed ID., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of 19 8 mm with internal blood flow., ontrastenhanced sonogram showing heterogeneous enhancement (arrows)., Pathologic specimen showing tumor cell cords present in desmoplastic stroma (H&E, original magnification 150). 916 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
7 Liu et al Figure 6. Palpable mass in the inner upper quadrant of the left breast in a 51-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed invasive lobular carcinoma., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of mm with an irregular margin., ontrast-enhanced sonogram showing enhancement mainly confined to the periphery of the mass (arrows)., Pathologic specimen showing adenosis rich in acinar and tubular structures at the periphery (H&E, original magnification 60). Figure 7. Palpable mass in the upper quadrant of the right breast in 60-year-old woman. Surgical pathologic examination showed intraductal papillary carcinoma., onventional sonogram showing a hypoechoic mass of 12 9 mm., ontrast-enhanced sonogram showing regional enhancement (arrows)., Pathologic specimen showing intraductal papillary carcinoma associated with sclerotic adenosis (H&E, original magnification 60). J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
8 ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography Table 1. Histologic haracteristics of reast Lesions Enhancement Pattern Histologic haracteristics of Malignant Lesions Histologic haracteristics of enign Lesions No enhancement Low-grade DIS Desmoplastic stroma, fibrosis Homogeneous enhancement Diffuse hypercellularity or predominant DIS Diffuse hypercellularity, inflammatory cell infiltrate, or intraductal papilloma Peripheral enhancement DIS component, hypercellularity or adenosis at Inflammatory infiltrate at the periphery, necrosis the periphery, low-degree cellularity, degeneration, in the center fibrosis, or necrosis in the center Regional enhancement DIS component Focal hypercellularity or intraductal papilloma Heterogeneous enhancement Tumor cell cords in a variable amount of Loose cell proliferation in a more sclerotic stroma desmoplastic stroma Histologic Findings for enign Masses Fibroadenoma (n = 30) The 28 cases of fibroadenoma with heterogeneous enhancement showed a more sclerotic stroma characterized by low to moderate cellularity or hyalinization. The 2 cases of fibroadenoma with homogeneous enhancement revealed increased stromal cellularity and epithelial hyperplasia. denosis (n = 15) The 8 cases of adenosis with no enhancement pattern showed considerable fibrosis and distortion of the glands (Figure 1). The 6 cases of adenosis with heterogeneous enhancement were characterized by loose proliferation of acini or tubules. The 1 case of adenosis with regional enhancement showed focal hypercellularity corresponding to an enhanced area (Figure 4). Intraductal Papilloma The 3 cases of intraductal papilloma with regional enhancement and 5 cases with homogeneous enhancement revealed branching papillary fronds with fibrovascular cores; the difference was that intraductal papilloma with regional enhancement was within a cystically dilated duct, which corresponded to the nonenhanced area. The 1 case of intraductal papilloma with no enhancement pattern was probably due to its small size (3 mm) and hyalinization within the fibrovascular stalk. Granulomatous Mastitis (n = 2) One case of granulomatous mastitis with homogeneous enhancement showed a diffuse inflammatory infiltrate; the other case of granulomatous mastitis with peripheral enhancement revealed an inflammatory infiltrate at the periphery and necrosis in the center. Other One case of fat necrosis and 1 foreign body granuloma showed no enhancement pattern. One case of hamartoma showed heterogeneous enhancement. One cyst showed heterogeneous enhancement because of its thickened wall and multiple septations. One borderline phyllode tumor showed heterogeneous enhancement. In summary (Table 1), in benign masses, heterogeneous enhancement corresponded to loose cell proliferation in more sclerotic stroma. Homogeneous enhancement corresponded to diffuse hypercellularity, an inflammatory cell infiltrate, or intraductal papilloma. Regional enhancement corresponded to focal hypercellularity or intraductal papilloma within a dilated duct. No enhancement corresponded to desmoplastic stroma. Peripheral enhancement was shown in 1 case of granulomatous mastitis with an inflammatory infiltrate at the periphery and necrosis in the center. Discussion ontrast-enhanced ultrasonography was first used in breast imaging to increase the diagnostic accuracy of color or power Doppler imaging. 3 6 This was mainly due to improved visualization of the intratumoral vascular architecture after contrast agent administration. Different timeintensity curves were found for malignant and 918 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
9 Liu et al benign breast masses. 8,9 Recent research has focused on -mode pulse inversion harmonic imaging with the use of the contrast agent SonoVue, which shows neovascular morphologic features by depicting microvessel perfusion. Recent research results have revealed some new characteristics of breast masses. 10,11 However, most of them did not correlate EUS findings with histopathologic features. In this study, we classified EUS enhancement patterns as no, homogeneous, peripheral, regional, and heterogeneous enhancement and correlated them with histopathologic features. Our preliminary results show that enhanced areas correspond to intraductal carcinoma, invasive carcinoma, intraductal papilloma, fibroadenoma with increased stromal cellularity and epithelial hyperplasia, adenosis rich in acinar and tubular structures, or an inflammatory cell infiltrate; nonenhanced areas correspond to low cellularity, desmoplastic stroma, dilated ducts, degeneration, fibrosis, or necrosis. The clinical applicability of this method is now limited, but the information will be valuable in enhancing further research projects to see whether EUS is helpful for diagnosis, biopsy, and therapy in the future. onventional ultrasonography for evaluating treatment responses based on tumor size measurement has limited efficiency because a therapeutic effect may not lead to a clear reduction in size, particularly in the period immediately after therapy. review of the literature reveals that conventional ultrasonography may overestimate or underestimate residual tumors Herrada et al 14 found that final histologic results correlated with conventional ultrasonographic findings in only 66.3% of cases. Observation of changes in contrast enhancement patterns on EUS may be useful in evaluating patients responses to therapy because of their correlation with histopathologic features. Our study had the following limitations. The correlation between EUS findings and histo - pathologic features was studied in the imaging plane of the maximum tumor diameter, but it would have been better to study each tumor in its entirety. In addition, the enhancement pattern classifications were subjective, and sometimes it was difficult to differentiate between enhancement patterns. In conclusion, our study revealed that breast mass EUS findings correlated with histologic features. References 1. Dietrich F, Kratzer W, Strobe D, et al. ssessment of metastatic liver disease in patients with primary extrahepatic tumors by contrast-enhanced sonography versus T and MRI. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: lbrecht T, Hoffmann W, Schettler S, et al. -mode enhancement at phase-inversion US with air-based microbubble contrast agent: initial experience in humans. Radiology 2000; 216: Forsberg F, Goldberg, Merritt R, et al. Diagnosing breast lesions with contrast-enhanced 3-dimensional power Doppler imaging. J Ultrasound Med 2004; 23: Moon WK, Im JG, Noh DY, Han M. Nonpalpable breast lesions: evaluation with power Doppler US and a microbubble contrast agent initial experience. Radiology 2000; 217: Yang WT, Tse GM, Lam PK, Metreweli, hang J. orrelation between color power Doppler sonographic measurement of tumor vasculature and immunohistochemical analysis of microvessel density for the quantitation of angiogenesis. J Ultrasound Med 2002; 21: Yang WT, Metreweli, Lam PK, hang J. enign and malignant breast masses and axillary nodes: evaluation with echo-enhanced color power Doppler US. Radiology 2001; 220: Liu H, Jiang YX, Liu J, Zhu QL, Sun Q. Evaluation of breast lesions with contrast-enhanced ultrasound using the microvascular imaging technique: initial observations. reast 2008; 17: Huber S, Helbich T, Kettenbach J, Dock W, Zuna I, Delorme S. Effects of a microbubble contrast agent on breast tumors: computer-assisted quantitative assessment with color Doppler US early experience. Radiology 1998; 208: izzatto G, hersevani R, Ralleigh G. ontrast media in ultrasonography: basic principles and clinical applications. In: Quaia (ed). reast. erlin, Germany: Springer; 2005: Furuse F, Forsberg F, Goldberg, et al. Pulse inversion harmonic imaging for breast cancer diagnosis. Ultrasound Med iol 2003; 29(suppl):S93 S assano E, Rizzo S, ozzini, Menna S, ellomi M. ontrast enhanced ultrasound of breast cancer. ancer Imaging 2006; 6: von Minckwitz G, osta SD, Eiermann W, et al. Maximized reduction of primary breast tumor size using preoperative chemotherapy with doxorubicin and docetaxel. J lin Oncol 1999; 7: J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
10 ontrast-enhanced reast Ultrasonography 13. Fornage D, Toubas O, Morel M. linical, mammographic, and sonographic determination of preoperative breast cancer size. ancer 1987; 60: Herrada J, Iyer R, tkinson EN, Sneige N, uzdar U, Hortobabyi GN. Relative value of physical examination, mammography, and breast sonography in evaluating the size of the primary tumor and regional lymph node metastases in women receiving neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced breast carcinoma. lin ancer Res 1997; 3: J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Sub-1-cm Breast Lesions Using Contrast-Enhanced Sonography
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Sub-1-cm Breast Lesions Using Contrast-Enhanced Sonography He Liu, MD, Yuxin Jiang, MD, Qing Dai, MD, Qingli Zhu, MD, Liang Wang, MD, Jing Zhang,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Sub-1-cm Breast Lesions Using Contrast-Enhanced Sonography He Liu, MD, Yuxin Jiang, MD, Qing Dai, MD, Qingli Zhu, MD, Liang Wang, MD, Jing Zhang,
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node
 Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Lesion Imaging Characteristics Mass, Favoring Benign Circumscribed Margins Intramammary Lymph Node Oil Cyst Mass, Intermediate Concern Microlobulated Margins Obscured Margins Mass, Favoring Malignant Indistinct
Breast pathology. 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University
 Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Breast pathology 2nd Department of Pathology Semmelweis University Breast pathology - Summary - Benign lesions - Acute mastitis - Plasma cell mastitis / duct ectasia - Fat necrosis - Fibrocystic change/
Imaging in breast cancer. Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since
 Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Imaging in breast cancer Mammography and Ultrasound Donya Farrokh.MD Radiologist Mashhad University of Medical Since A mammogram report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. A mammogram
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant
 Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Radiologic and pathologic correlation of non-mass like breast lesions on US and MRI: Benign, high risk, versus malignant Poster No.: C-1161 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. Kwak,
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging?
 Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Triple-negative breast cancer: which typical features can we identify on conventional and MRI imaging? Poster No.: C-1862 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani 1, A. Gualano
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography
 Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Prediction of Postoperative Tumor Size in Breast Cancer Patients by Clinical Assessment, Mammography and Ultrasonography Eyad Fawzi AlSaeed 1 and Mutahir A. Tunio 2* 1 Consultant Radiation Oncology, Chairman
Leonard M. Glassman MD
 BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
BI-RADS The New BI-RADS Leonard M. Glassman MD FACR Former Chief of Breast Imaging American Institute for Radiologic Pathology Washington Radiology Associates, PC Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology.
 Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Armed Forces Institute of Pathology www.radpath.com Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Breast Disease www.radpath.org Armed Forces Institute of Pathology Interpretation of Breast MRI Leonard M. Glassman
Breast Pathology. Breast Development
 Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
Breast Pathology Lecturer: Hanina Hibshoosh, M.D. Reading: Kumar, Cotran, Robbins, Basic Pathology, 6th Edition, pages 623-635 Breast Development 5th week - thickening of the epidermis - milk line 5th
04/10/2018. Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast INTRADUCTAL PAPILLOMA
 Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Intraductal Papillary Neoplasms Of Breast Savitri Krishnamurthy MD Professor of Pathology Deputy Division Head The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center 25 th Annual Seminar in Pathology Pittsburgh,
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2)
 Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
Diseases of the breast (1 of 2) Introduction A histology introduction Normal ducts and lobules of the breast are lined by two layers of cells a layer of luminal cells overlying a second layer of myoepithelial
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated. FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia.
 DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
DISORDERS OF THE BREAST Dated BENIGN BREAST DISORDERS (Essential Surg 2 nd Ed, pp 540) FIBROADENOSIS Other common names: mastitis, fibrocystic disease, cystic mammary dysplasia. Fibroadenosis is the distortion
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013
 Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Ana Sofia Preto 19/06/2013 Understanding the underlying pathophysiologic processes leading to the various types of calcifications Description and illustration of the several types of calcifications, according
Case study 1. Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research
 NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
NCCN/JCCNB Seminar in Japan April 15, 2012 Case study 1 Rie Horii, M.D., Ph.D. Division of Pathology Cancer Institute Hospital, Japanese Foundation for Cancer Research Present illness: A 50y.o.premenopausal
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form
 S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
S1 ACRIN 6666 Therapeutic Surgery Form 6666 Instructions: Complete a separate S1 form for each separate area of each breast excised with the intent to treat a cancer (e.g. each lumpectomy or mastectomy).
LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR
 BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
BREAST LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE AXILLARY (MOSTLY) INTERNAL MAMMARY SUPRACLAVICULAR HISTOLOGY LOBE: (10 in whole breast) LOBULE: (many per lobe) ACINUS/I, aka ALVEOLUS/I: (many per lobule) DUCT(S): INTRA- or
Toru Nakamura 1, Takashi Fukutomi 1, Hitoshi Tsuda 2, Sadako Akashi-Tanaka 1, Kaneyuki Matsuo 1, Chikako Shimizu 1 and Kunihisa Miyakawa 3
 Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
Jpn J Clin Oncol 2000;30(10)453 457 Changes in Findings of Mammography, Ultrasonography and Contrast-enhanced Computed Tomography of Three Histological Complete Responders with Primary Breast Cancer Before
The radiologic workup of a palpable breast mass
 Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Imaging in Practice CME CREDIT EDUCTIONL OJECTIVE: The reader will consider which breast masses require further workup and which imaging study is most appropriate Lauren Stein, MD Imaging Institute, Cleveland
Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast
 Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 812129, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/812129 Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast Noriko Yoshimura, 1 Shigeru
Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 812129, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/812129 Case Report Synchronous Bilateral Solid Papillary Carcinomas of the Breast Noriko Yoshimura, 1 Shigeru
Criteria of Malignancy. Evaluation Score
 30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
30 5 Diagnostic Criteria Criteria of Malignancy Table 5.2 lists criteria in contrast-enhancing MR mammography that strongly indicate the presence of malignancy or are unspecific. Unifactorial evaluation
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI. Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD
 Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
Non-mass Enhancement on Breast MRI Aditi A. Desai, MD Margaret Ann Mays, MD Breast MRI Important screening and diagnostic tool, given its high sensitivity for breast cancer detection Breast MRI - Indications
ACRIN 6666 IM Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US
 Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Additional Evaluation: Additional Views/Targeted US For revised or corrected form check box and fax to 215-717-0936. Instructions: The form is completed based on recommendations (from ID form) for additional
Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable Breast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization
 Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable reast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization Ki Yeol Lee, MD 1 o Kyoung Seo, MD 1 nn Yi, MD 1 o-kyung Je, MD 1 Kyu Ran Cho, MD 2 Ok
Immersion Ultrasonography of Excised Nonpalpable reast Lesion Specimens after Ultrasound-Guided Needle Localization Ki Yeol Lee, MD 1 o Kyoung Seo, MD 1 nn Yi, MD 1 o-kyung Je, MD 1 Kyu Ran Cho, MD 2 Ok
MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out?
 MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out? Poster No.: C-1850 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Ben Ammar, A. Ben Miled, O. Ghdes, S. Harguem, A. Gaja, N. Mnif; Tunis/TN Keywords: Breast,
MRI BI-RADS: How to make it out? Poster No.: C-1850 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Ben Ammar, A. Ben Miled, O. Ghdes, S. Harguem, A. Gaja, N. Mnif; Tunis/TN Keywords: Breast,
The Use of Unenhanced Doppler Sonography in the Evaluation of Solid Breast Lesions
 Unenhanced Doppler Sonography of Solid Breast Lesions Jose L. del Cura 1 Elena Elizagaray Rosa Zabala Ana Legórburu Domingo Grande del Cura JL, Elizagaray E, Zabala R, Legórburu A, Grande D Received July
Unenhanced Doppler Sonography of Solid Breast Lesions Jose L. del Cura 1 Elena Elizagaray Rosa Zabala Ana Legórburu Domingo Grande del Cura JL, Elizagaray E, Zabala R, Legórburu A, Grande D Received July
Diffuse Sclerosing Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma
 PITORL ESSY iffuse Sclerosing Variant of Papillary Thyroid arcinoma Sonography and Specimen Radiography Hyun Kyung Jung, M, Soon Won Hong, M, Eun-Kyung Kim, M, Jung Hyun Yoon, M, Jin Young Kwak, M The
PITORL ESSY iffuse Sclerosing Variant of Papillary Thyroid arcinoma Sonography and Specimen Radiography Hyun Kyung Jung, M, Soon Won Hong, M, Eun-Kyung Kim, M, Jung Hyun Yoon, M, Jin Young Kwak, M The
Interpretation of Breast Pathology in the Era of Minimally Invasive Procedures
 Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Shahla Masood, M.D. Professor and Chair Department of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine University of Florida College of Medicine Jacksonville Medical Director, UF Health Breast Center Chief of Pathology
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions. Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand
 Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
Mammographic imaging of nonpalpable breast lesions Malai Muttarak, MD Department of Radiology Chiang Mai University Chiang Mai, Thailand Introduction Contents Mammographic signs of nonpalpable breast cancer
RSNA, /radiol Appendix E1. Methods
 RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
RSNA, 2016 10.1148/radiol.2016151097 Appendix E1 Methods US and Near-infrared Data Acquisition Four optical wavelengths (740 nm, 780 nm, 808 nm, and 830 nm) were used to sequentially deliver the light
Invasive Ductal Carcinoma with Fibrotic Focus: Mammographic and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
Mammograp hy and Sonography of Invasive Ductal arcinoma reast Imaging linical Observations Shara Millman Oken 1 ecilia L. Mercado 2 Lorenzo Memeo 3 Hanina Hibshoosh 3 Oken SM, Mercado L, Memeo L, Hibshoosh
One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy
 66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
66 One or Two Clusters of Crushed Stone like Calcifications on the Mammogram Produced by Malignancy Example 2.13 A 36-year-old woman who recentlyfelt a small hard lump in the upper-outer quadrant of her
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS
 HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
HISTOMORPHOLOGICAL SPECTRUM OF BREAST LESIONS Kiran H. S, Jayaprakash Shetty, Chandrika Rao Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, Yenepoya Medical College, Mangalore. Professor, Department of Pathology,
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI. Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Pitfalls and Limitations of Breast MRI Susan Orel Roth, MD Professor of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Objectives Review the etiologies of false negative breast MRI examinations Discuss the limitations
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation
 Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Breast Pathology in Men: Radiologic-Pathologic Correlation Poster No.: C-0243 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: G. Garrido; Málaga/ES Keywords: Breast, Ultrasound, Mammography, Biopsy,
Cairo/EG, Khartoum/SD, London/UK Biological effects, Diagnostic procedure, Ultrasound, Mammography, Breast /ecr2015/C-0107
 Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Role of sono-mammography in the evaluation of clinically palapble breast masses during pregnancy & lactation with differentaition between true patholgical & false physiological lobular hyperlpasia.sudanese
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 Imaging Pathology
 Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Case Scenario 1 History and Physical 3/15/13 The patient is an 84 year old white female who presented with an abnormal mammogram. The patient has a five year history of refractory anemia with ringed sideroblasts
Benign breast lesions frequently encountered on MR
 Benign breast lesions frequently encountered on MR Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. R. Almeida 1, J. C. Marques 2 ; 1 Lisbon/PT, 2 lisbon/pt Keywords: Hemangioma,
Benign breast lesions frequently encountered on MR Poster No.: C-1385 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. R. Almeida 1, J. C. Marques 2 ; 1 Lisbon/PT, 2 lisbon/pt Keywords: Hemangioma,
CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF BENIGN EPITHELIAL CHANGES
 Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
Papillomas. Papillomas are composed of multiple branching fibrovascular cores, each having a connective tissue axis lined by luminal and myoepithelial cells ( Fig. 23-11 ). Growth occurs within a dilated
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience.
 MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
MRI features of Triple-negative breast cancer: our experience. Poster No.: C-1852 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: V. Bertani, A. Gualano, V. Londero, A. Dal Col, M. Marcon, P. 1 2
Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast:
 J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
J Korean Soc Radiol 2010;62:287-294 Cystic Hypersecretory Carcinoma of the Breast: Sonographic Features with a Histological Correlation 1 Sang Yu Nam, M.D., Boo-Kyung Han, M.D., Jung Hee Shin, M.D., Eun
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(18)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis. (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140: ; doi: /arpa.
 Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Papillary Lesions of the Breast A Practical Approach to Diagnosis (Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1052 1059; doi: 10.5858/arpa.2016-0219-RA) Papillary lesions of the breast Span the spectrum of benign,
Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided. CNB) versus mammograph-guided biopsy for suspicious microcalcifications. without definite breast mass
 Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Volume 118 No. 19 2018, 531-543 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu Diagnostic benefits of ultrasound-guided biopsy versus mammography-guided
Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings
 Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings of the Benign and Malignant Lesions 1 Chang-Seok Lee, M.D., Shin-Ho Kook, M.D., Hyun-Ja Shin, M.D. 2, Woo-Kyung Moon, M.D. 3, Eun-Joo Ko, M.D. 4, Young-Uk
Papillary Tu m o rs of the Breast: US Findings of the Benign and Malignant Lesions 1 Chang-Seok Lee, M.D., Shin-Ho Kook, M.D., Hyun-Ja Shin, M.D. 2, Woo-Kyung Moon, M.D. 3, Eun-Joo Ko, M.D. 4, Young-Uk
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions. Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea
 Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Treatment options for the precancerous Atypical Breast lesions Prof. YOUNG-JIN SUH The Catholic University of Korea Not so benign lesions? Imaging abnormalities(10% recall) lead to diagnostic evaluation,
Influence of breast cancer histology on the relationship between ultrasound and pathology tumor size measurements
 & 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Influence of breast cancer histology on the relationship between ultrasound and pathology tumor size measurements Bobbi
& 2004 USCAP, Inc All rights reserved 0893-3952/04 $30.00 www.modernpathology.org Influence of breast cancer histology on the relationship between ultrasound and pathology tumor size measurements Bobbi
Journal of Breast Cancer
 CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
CSE REPORT Journal of reast Cancer J reast Cancer 2016 December; 19(4): 459-464 Increased Malignant Microcalcifications after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in dvanced reast Cancer Gi Won Shin, Young Mi Park,
IBCM 2, April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Preoperative diagnosis and treatment planning in breast cancer The pathologist s perspective L. Mazzucchelli Istituto Cantonale di Patologia Locarno, Switzerland IBCM 2, 23-25 April 2009, Sarajevo, Bosnia
Amammography report is a key component of the breast
 Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Review Article Writing a Mammography Report Amammography report is a key component of the breast cancer diagnostic process. Although mammographic findings were not clearly differentiated between benign
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass
 Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Atypical ductal hyperplasia diagnosed at ultrasound guided biopsy of breast mass Poster No.: C-1483 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Cho, J. Chung, E. S. Cha, J. E.
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast
 Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
Intracystic papillary carcinoma of the breast Poster No.: C-1932 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: V. Dimarelos, F. TZIKOS, N. Kotziamani, G. Rodokalakis, 1 2 3 1 1 1 2 T. MALKOTSI
BI-RADS MRI: A Primer
 Erguvan- ogan et al. I- RS MRI Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING asak Erguvan-ogan 1 Gary J. Whitman 1 nne. Kushwaha 1,2 Michael J. Phelps 1,3 Peter J. empsey 1 Erguvan-ogan, Whitman GJ, Kushwaha,
Erguvan- ogan et al. I- RS MRI Women s Imaging Pictorial Essay WOMEN S IMGING asak Erguvan-ogan 1 Gary J. Whitman 1 nne. Kushwaha 1,2 Michael J. Phelps 1,3 Peter J. empsey 1 Erguvan-ogan, Whitman GJ, Kushwaha,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation
 Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
Ductal carcinoma in situ: ultrasound, mammography and MRI features with pathologic correlation Poster No.: C-2252 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Fernandes, H. A. M. R. Tinto,
BI-RADS and Breast MRI. Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018
 BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
BI-RADS and Breast MRI Kathy Borovicka, M.D. Thursday February 15, 2018 Learning Objectives Be familiar with the Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) Understand the components of a breast
Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma Coexisting with Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast: A Case Report
 31 Case Report J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 8, pp. 31 35, 2017 Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma Coexisting with Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast: A Case Report Ryoko Oi 1, 2, Ichiro Maeda 1, Yoshio Aida
31 Case Report J. St. Marianna Univ. Vol. 8, pp. 31 35, 2017 Low-grade Adenosquamous Carcinoma Coexisting with Sclerosing Adenosis of the Breast: A Case Report Ryoko Oi 1, 2, Ichiro Maeda 1, Yoshio Aida
Evolution of diagnostic ultrasound systems Current achievements in breast ultrasound
 Evolution of diagnostic ultrasound systems Current achievements in breast ultrasound Dr. Ayumi Izumori, M. D. Department of Breast Surgery, Takamatsu Heiwa Hospital Tokushima Breast Care Clinic, Japan
Evolution of diagnostic ultrasound systems Current achievements in breast ultrasound Dr. Ayumi Izumori, M. D. Department of Breast Surgery, Takamatsu Heiwa Hospital Tokushima Breast Care Clinic, Japan
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues
 A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
A712(19)- Test slide, Breast cancer tissues with corresponding normal tissues (formalin fixed) For research use only Specifications: No. of cases: 12 Tissue type: Breast cancer tissues with corresponding
ISSN X (Print) Research Article. *Corresponding author Dr. Amlendu Nagar
 Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2015; 3(3A):1069-1073 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Ultrasonography. Methods. Brief Description. Indications. Device-related Prerequisites. Technical Requirements. Evaluation Criteria
 1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
1 Ultrasonography Brief Description Imaging modality using sound waves Tissue-specific wave reflection. Indications Evaluation of palpable breast nodules Evaluation of clinically occult mammographic findings
CPC 4 Breast Cancer. Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast.
 CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
CPC 4 Breast Cancer Rochelle Harwood, a 35 year old sales assistant, presents to her GP because she has noticed a painless lump in her left breast. 1. What are the most likely diagnoses of this lump? Fibroadenoma
Effectivity of combined diffusion-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced MRI in malignant and benign breast lesions
 OI: https://doi.org/1.5114/pjr.218.74363 Received: 24.4.217 ccepted: 25.5.217 Published: 15.2.218 http://www.polradiol.com Original article Effectivity of combined diffusion-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced
OI: https://doi.org/1.5114/pjr.218.74363 Received: 24.4.217 ccepted: 25.5.217 Published: 15.2.218 http://www.polradiol.com Original article Effectivity of combined diffusion-weighted imaging and contrast-enhanced
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast:
 Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Atypical Ductal Hyperplasia of the Breast: Radiologic and Histopathologic Correlation 1 Ji Young Lee, M.D., Bo Kyoung Seo, M.D. 2, Jung Hyck Kim, M.D., Yu Whan Oh, M.D., Kyu Ran Cho, M.D., Eun Jeong Choi,
Using T2-Weighted Sequences to More Accurately Characterize Breast Masses Seen on MRI
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Westra et al. MRI of reast Masses Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.195.58 on 12/28/17 from IP address 46.3.195.58.
Here are examples of bilateral analog mammograms from the same patient including CC and MLO projections.
 Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Good afternoon. It s my pleasure to be discussing Diagnostic Breast Imaging over the next half hour. I m Wei Yang, Professor of Diagnostic Radiology and Chief, the Section of Breast Imaging as well as
Original Report. Mucocele-Like Tumors of the Breast: Mammographic and Sonographic Appearances. Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2
 Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
Katrina Glazebrook 1 Carol Reynolds 2 Received January 2, 2002; accepted after revision August 28, 2002. 1 Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St. S.W., Rochester, MN 55905. Address correspondence
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS. Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions
 SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
SIGNIFICANT OTHERS Miscellaneous Benign Breast Conditions Epworth HealthCare 1 FAT NECROSIS TRAUMATIC Cell rupture Seat-Belt injury Blunt trauma Iatrogenic injury Surgery, Flaps, Radiotherapy Pathology
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics
 Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Triple Negative Breast Cancer: Clinical Presentation and Multimodality Imaging Characteristics Poster No.: R-0141 Congress: RANZCR-AOCR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: O. H. Woo, S. Jang, K. R.
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013
 Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
Contrast-enhanced Breast MRI RSSA 2013 Prof. dr. Maurice van den Bosch University Medical Center Utrecht, the Netherlands Index 1) Breast cancer 2) Why MRI of the breast 3) Technique 4) Interpretation
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS
 BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
BREAST PATHOLOGY MCQS 1) :The most important factor in breast enlargement during pregnancy is A. stromal edema B. secretion of chorionic gonadotropin C. glandular hyperplasia D. proliferation of stroma
Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of
 Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Tiền liệt tuyến Tiền liệt tuyến Gross appearance of nodular hyperplasia in material obtained from suprapubic prostatectomy. Note the multinodular appearance and the admixture of solid and microcystic areas.
Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 3906195, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3906195 Case Report Tubular Carcinoma of the Breast: Advantages and Limitations of Breast Tomosynthesis
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS
 A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
A-005 US DIAGNOSIS OF NONPALPABLE BREAST LESIONS Hideaki Shirai M.D., M. Sakurai M.D., K. Yoshida M.D., N. Usuda M.D., H. Masuoka M.D., I. Shimokawara M.D, K. Asaishi M.D. Sapporo Kotoni Breast Clinic,
Spectrum of findings of sclerosing adenosis at breast MRI.
 Spectrum of findings of sclerosing adenosis at breast MRI. Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: F. Vasselli 1, F. Pediconi 2, M. Telesca 2, M. Luciani 2, V. Casali 2,
Spectrum of findings of sclerosing adenosis at breast MRI. Poster No.: C-0738 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: F. Vasselli 1, F. Pediconi 2, M. Telesca 2, M. Luciani 2, V. Casali 2,
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING
 OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
OPTO-ACOUSTIC BREAST IMAGING A Novel Fusion of Functional and Morphologic Imaging Reni S. Butler, MD A. Thomas Stavros, MD F. Lee Tucker, MD Michael J. Ulissey, MD PURPOSE 1. Explain opto-acoustic (OA)
Complex cystic breast lesions, which are defined as lesions
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Value of Ultrasonographic Features for Assessing Malignant Potential of Complex Cystic Breast Lesions Jin-Peng Yao, MD, Yu-Zhi Hao, MD, Qing Chang, MD, Cheng-Yun Geng, MD, Yu Chen, MD,
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Value of Ultrasonographic Features for Assessing Malignant Potential of Complex Cystic Breast Lesions Jin-Peng Yao, MD, Yu-Zhi Hao, MD, Qing Chang, MD, Cheng-Yun Geng, MD, Yu Chen, MD,
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast
 Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
Benign, Reactive and Inflammatory Lesions of the Breast Marilin Rosa, MD Associate Member Section Head of Breast Pathology Department of Anatomic Pathology Program Director, Breast Pathology Fellowship
BREAST PATHOLOGY. Fibrocystic Changes
 BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
BREAST PATHOLOGY Lesions of the breast are very common, and they present as palpable, sometimes painful, nodules or masses. Most of these lesions are benign. Breast cancer is the 2 nd most common cause
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 SAM - Breast MRI 1
 National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
National Diagnostic Imaging Symposium 2013 December 8-12, 2013 Disney s Yacht Club Resort Lake Buena Vista, Florida Self Assessment Module Questions, Answers and References Day SAM Title - Each SAM title
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? IBDC
 Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Does elastography change the indication to biopsy? A LEXANDRA A THANASIOU, M D DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY CURIE INSTITUTE PARIS, FRANCE IBDC Ultrasound Detected Cancers Physician-performed ultrasound increases
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas
 Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Malignant transformation of fibroadenomas Poster No.: C-2503 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. N. Elias, M. A. Rudner, L. M. Yano, P. C. Moraes, Y. 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 2 Chang, M. B.
Histopathological Spectrum of Neoplastic and Non-neoplastic Breast Lesions: A Two Years Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/69 Histopathological Spectrum of Neoplastic and Non-neoplastic Breast Lesions: A Two Years Study Moolamalla Manasa
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2017/69 Histopathological Spectrum of Neoplastic and Non-neoplastic Breast Lesions: A Two Years Study Moolamalla Manasa
THE MALE BREAST CARCINOMA: EARLY DETECTION HOPE. Author (s) Supreethi Kohli a, Pragya Garg b
 Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
Case Report ABSTRACT - Male breast cancer is exceptionally rare and accounts for less than 0.25% of male malignancies and approximately 0.5-1% of all breast cancer (both genders). Mammography of the male
ORIGINAL ARTICLE EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS USING X-RAY MAMMOGRAM WITH HISTOPATHOLOGICAL CORRELATION
 Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Available online at www.journalijmrr.com INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF MODERN RESEARCH AND REVIEWS IJMRR ISSN: 2347-8314 Int. J. Modn. Res. Revs. Volume 3, Issue 10, pp 807-814, October, 2015 ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Interpretation of Positron Emission Mammography: Feature Analysis and Rates of Malignancy
 Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research Deepa Narayanan 1,2 Kathleen S. Madsen 3 Judith E. Kalinyak 1 Wendie. erg 4,5 Narayanan D, Madsen KS, Kalinyak JE, erg W 1 Naviscan,
Women s Imaging Original Research Women s Imaging Original Research Deepa Narayanan 1,2 Kathleen S. Madsen 3 Judith E. Kalinyak 1 Wendie. erg 4,5 Narayanan D, Madsen KS, Kalinyak JE, erg W 1 Naviscan,
BREAST MRI. VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece
 BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
BREAST MRI VASILIKI FILIPPI RADIOLOGIST CT MRI & PET/CT Departments Hygeia Hospital, Athens, Greece Breast ΜR Imaging (MRM) Breast MR imaging is an extremely powerful diagnostic tool, that when used in
Papillary Lesions of the breast
 Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Papillary Lesions of the breast Emad Rakha Professor of Breast Pathology The University of Nottingham Papillary lesions of the breast are a heterogeneous group of disease, which are characterised by neoplastic
Architectural Distortion of
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Gaur et al. rchitectural Distortion of the reast Residents Section Pattern of the Month Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.203.116 on 01/05/18 from IP address
Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(3) : 132 Imaging of giant breast masses with pathological correlation M Muttarak, B Chaiwun ABSTRACT Ultrasonography (US) and mammography are the
Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ).
 SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
SOLID TUMORS WORKSHOP Cases for review Prostate Cancer Case #1: 75 y/o Male (treated and followed by prostate cancer oncology specialist ). January 2009 PSA 4.4, 20% free; August 2009 PSA 5.2; Sept 2009
PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1
 5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
5/19/2014 PAAF vs Core Biopsy en Lesiones Mamarias Case #1 Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology of Breast: Correlation with Needle Core Biopsy 64-year-old woman Mass in breast Syed Hoda, MD CD31 Post-Radiation
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM am am : Clinician s requirements from breast imaging
 Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Detailed Program of the second BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 Day one, 2 nd November BREAST IMAGING AND INTERVENTIONS PROGRAM 2012 9.00 AM 9.10 am Introduction 9.10 am - 9.30 am : Clinician
Index. C Calcifications fat necrosis 1, 61 fat necrosis 4, 69 nipple/peri-areolar involvement 1, 165
 A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
A ADH. See Atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH) American College of Radiology (ACR), BI-RADS background parenchymal enhancement, 8, 9, 81, 82 fibroglandular tissue guidelines, 6 American Joint Committee on
Segmental Breast Calcifications
 Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Residents Section Pattern of the Month Chen et al. Segmental reast Calcifications Residents Section Pattern of the Month Residents inradiology Po-Hao Chen 1 Erica T. Ghosh 1,2 Priscilla J. Slanetz 1,2
Original Report. Metaplastic Carcinoma of the Breast: Clinical, Mammographic, and Sonographic Findings with Histopathologic Correlation
 Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
Isil Günhan-ilgen 1 ysenur Memis 1 Esin Emin Üstün 1 Osman Zekioglu 2 Necmettin Özdemir 2 Received July 30, 2001; accepted after revision December 6, 2001. 1 Department of Radiology, Ege Üniversity Hospital,
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019. AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division
 BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
BARC/2013/E/019 BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF MAMMOGRAPHY PERFORMED IN OUR HOSPITAL by Surita Kantharia Medical Division BARC/2013/E/019 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY COMMISSION BARC/2013/E/019 AUDIT OF
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN
 Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
Ultrasound of the Breast BASICS FOR THE ORDERING CLINICIAN Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Skin Breast Parenchyma Pectoralis Fascia Pectoralis Breast Ultrasound Anatomy Indications for Breast Ultrasound Palpable
