Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
|
|
|
- Easter Banks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1
2 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration in the developing CNS! also to axon growth! 2
3 Modes of Cell Migration in the Developing CNS Early postmitotic neurons migrate to the pial surface by mechanisms related to those used for cell division: - cell extends a process by adhesion to adjacent progenitor cells - nucleus translocates within the process towards the pial surface - cell retracts trailing process 3
4 Modes of Cell Migration in the Developing CNS Later, as a structure becomes thicker, progenitor cells are described as radial glia (Bergmann glia in cerebellum). Radial glia have some characteristics of astrocytes. Radial glia span the entire thickness of the tissue. 4
5 Patterns of Cell Division and Radial Migration in Cortex A small number of ventricular layer cells in developing cortex were transfected with a GFP expression vector. Cell division and migration of cells expressing GFP were followed by time lapse video recordings in living slices of cortex. 5
6 Patterns of Cell Division and Radial Migration in Cortex 6
7 Patterns of Cell Division and Radial Migration in Cortex Radial glia divide with the nucleus at the ventricular surface. Cells retain attachment to the pial surface through mitosis. A daughter cell that inherits the basal process, and will usually divide again. A cell that does not inherent the process can extend a process to the pial surface and become a radial glial cell or can migrate in association with radial glia processes. Neuron-radial glia association is mediated by CAMs, α 3 β 1 integrin & connexins. 7
8 Development of Cortex marginal zone cortical plate subplate preplate subventricular z. ventricular zone ventricular zone 8
9 Patterns of Cell Division and Radial Migration in Cortex Projection neurons for the most part migrate in this radial pattern using radial glia as their adhesive substrate. 9
10 The cortical plate is built 10
11 The cortical plate is built (mostly) from the inside out! 11
12 Spontaneous mutations in mice that resulted in motor abnormalities revealed molecules involved in cell migration. 12
13 reeler Mouse Cortical layers are inverted. Cells are generated at the correct time, and migrate in correct sequence & rate. Radial glia look normal, and in culture cells migrate on radial glia. Most CNS cell groups are affected. 13
14 reeler Mouse - Cells starting to migrate are disorganized and misdirected. - As cells reach the marginal zone, they fail to dissociate from radial glia. (Wang S et al., 2018) 14
15 Reelin - Mutation is in the reelin gene. - Reelin is a glycoprotein of the ECM secreted by Cajal-Retzius cells in the marginal layer. 15
16 Reelin VLDLr & ApoEr2: - Reelin activates the VLDL and ApoE receptors. - Both are expressed by cells migrating in the CNS. - Double kockout of these genes results in a reeler phenotype. Scrambler mutant mouse: - Brain looks similar to reeler. - Mutation is in disabled (Dab1) gene. - Dab1 is a cytoplasmic adaptor protein, which is activated by reelin through its receptors. -Dab1 has many targets. 16
17 Reelin What happens after Dab1 is activated is unclear and probably multi-faceted. 17
18 Reelin Lis1 is a target of Dab1. Lis1 mutations also result in a phenotype similar to reelin mutations. Lis1 interacts with multiple motor proteins and microtubule associated proteins. Lis1 may have a role in promoting and directing cell movement. 18
19 Reelin The final steps of neuronal migration into the cortical plate are independent of radial glia. Migrating cells must lose attachment to radial glia, use a new substrate to migrate up to the marginal zone, and ultimately stop migrating and start differentiating. Reelin has been implicated in these processes. 19
20 Reelin The reelin/dab1 pathway promotes adhesion between migrating neurons and Cajal-Retzius (CR) cells, allowing the neurons to finish migration. Reelin promotes heterphilic binding between the Ig-CAMS nectin 1 and nectin 3 and homophilic binding between N-cadherin (Cdh2). (Gil-Sanz C, et al., 2013, Neuron 79:461) 20
21 Reelin The reelin/dab1 pathway activates α5β1 integrin, which allows migrating neurons to adhere to fibronectin as they finish migration in the cortical plate. (see Sekine et al., 2012) 21
22 Reelin It has been shown that the reelin/dab1 signaling pathway activates LimK, which inactivates n-cofilin, resulting in actin stabilization. 22
23 Reelin Reelin appears to have two functions for migrating cortical neurons: As cells start migration, reelin via the Apoer2 receptor may give cells polarity and direction. As cells approach the marginal zone, reelin via the Vldlr receptor may terminate migration. Different domains of reelin activate the two receptors. (based partly on Ha et al., 2017, J Neurosci 37:960) 23
24 Hey! The reelin story is complicated. It appears that reelin may be a tropic factor at the start of migration and have a guidepost function at the end of migration (in cortex). 24
25 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain Lineage tracing studies showed that >30% of cells in the cortex reached their final location by tangential migration mostly in the marginal and subventricular zones. 25
26 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain - Lateral and medial ganglionic eminences (LGE & MGE) of the ventral telencephalon give rise to the cells of the striatum and globus pallidus by radial migration. 26
27 Telencephalon 27
28 Striatum: caudate nucleus putamen nucleus accumbens 28
29 caudate nucleus Putamen GPe GPi 29
30 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain - MGE, caudal ganglionic eminence and preoptic area also gives rise to the GABAergic interneurons and many oligodendrocytes of cortex, which migrate tangentially. 30
31 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain origin radial destination tangential destination (cortical interneurons) pathway POA amygdala [undefined] interneurons (early) superficial migratory stream MGE globus pallidus parvalbumin & somatostatin interneurons (early) deep migratory stream LGE caudate & putamen none CGE? calretinin interneurons (late)? Calbindin expression = immature (migrating) cortical interneuron 31
32 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain - Interneurons (red) migrate from the MGE into the cortical plate in association with cortical axons (green). - Migrating cells adhere to the axons via TAG1, an Ig-like CAM. - Migrating cells are repelled [possibly] by Slit1 (blue) from the ventricular layer. 32
33 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain Thus, TAG-1 appears to be an adhesive substrate for these migrating cells. 33
34 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain The chemokine, SDF1 (Cxcl12) is expressed and secreted by the meninges and subventricular zone cells in the developing cortex. SDF1 = stromal cell-derived factor 1 Cxcl12 = C-X-C motif chemokine 12 Arno et al.,
35 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain Cells migrating from the ganglionic eminence express the chemokine receptor, CXCR4. In culture, CXCR4+ forebrain neurons migrate towards SDF1. These cells fail to migrate with a knockout of the SDF1 or CXCR4 genes. 35
36 Tangential Migration in Developing Forebrain Thus, for inhibitory neurons migrating from basal forebrain into cortex: TAG-1 appears to be a substrate for adhesion between these cells and the axons. Slit1 maybe a repulsive guidance cue. SDF1 appears to be an attractive guidance cue (i.e. tropic factor). 36
37 Interneuron Migration into Cortex in Humans Interneurons continue to migrate into medial prefrontal cortex and cingulate gyrus in humans through at least 5 months of age. Paredes MF et al. (2016) Science 354:81 37
38 Radial & Tangential Migration in the Midbrain Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra are born in the ventricular zone of the midbrain floor plate. The cells first migrate radially in association with radial glia. They express the chemokine receptor CxcR4, and are attracted to Cxcl12 (SDF1) released by the meninges. Brignani and Pasterkamp, 2017 Then they migrate tangentially. Reelin is required for this migration. Reelin is expressed by the red nucleus. 38
39 Migration in the Cerebellum 39
40 40
41 Migration in the Cerebellum 41
42 Migration in the Cerebellum 42
43 Migration in the Cerebellum 43
44 Mutations affecting molecules involved in migration result in abnormal cell distribution in the human brain. 44
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
ErbB4 migrazione II parte
 ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
ErbB4 migrazione II parte Control SVZ cells prefer to migrate on the NRG1 type III substrate the substrate preference of the neuroblasts migrating out of the SVZ explant was evaluated SVZ cells had a strong
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
Basal Ganglia. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Basal Ganglia Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Graduate School Discussion Wednesday, Nov 1, 11:00am MoosT 2-690 with Paul Mermelstein (invite your friends)
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper. Today: Wolfger von der Behrens
 Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
Systems Neuroscience Dan Kiper Today: Wolfger von der Behrens wolfger@ini.ethz.ch 18.9.2018 Neurons Pyramidal neuron by Santiago Ramón y Cajal (1852-1934, Nobel prize with Camillo Golgi in 1906) Neurons
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A
 MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
MIDTERM EXAM 1 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A FALL 2011 Name: Points: / 100 PID: I. SHORT ANSWERS (6 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Describe two contributions made by Ramon y Cajal (1852-1934) in terms
Basal Ganglia. Introduction. Basal Ganglia at a Glance. Role of the BG
 Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Basal Ganglia Shepherd (2004) Chapter 9 Charles J. Wilson Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Introduction A set of nuclei in the forebrain and midbrain area in mammals, birds, and reptiles.
Anatomy of the basal ganglia. Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410
 Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Anatomy of the basal ganglia Dana Cohen Gonda Brain Research Center, room 410 danacoh@gmail.com The basal ganglia The nuclei form a small minority of the brain s neuronal population. Little is known about
Review Article Reelin in the Years: Controlling Neuronal Migration and Maturation in the Mammalian Brain
 Advances in Neuroscience, Article ID 597395, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/597395 Review Article Reelin in the Years: Controlling Neuronal Migration and Maturation in the Mammalian Brain Gabriella
Advances in Neuroscience, Article ID 597395, 19 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/597395 Review Article Reelin in the Years: Controlling Neuronal Migration and Maturation in the Mammalian Brain Gabriella
4/18/2011. Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development
 Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Physiology 67 Lecture on Neural Development 1 2 3 4 5 6 Neural cell categories After the ectodermal tissue has folded into the neural tube, another series of signaling interactions determine the type of
Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons
 Kelsom and Lu Cell & Bioscience 2013, 3:19 Cell & Bioscience REVIEW Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons Corey Kelsom and Wange Lu * Open Access Abstract GABAergic interneurons
Kelsom and Lu Cell & Bioscience 2013, 3:19 Cell & Bioscience REVIEW Development and specification of GABAergic cortical interneurons Corey Kelsom and Wange Lu * Open Access Abstract GABAergic interneurons
Synapse Formation. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Synapse Formation Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Midterm Exam Monday, Nov 13 9:30-11:30am Bring a #2 pencil!! 2 Course News Lecture schedule: Mon (Oct 31)
Cajal-Retzius Cells Instruct Neuronal Migration by Coincidence Signaling between Secreted and Contact-Dependent Guidance Cues
 Article Cajal-Retzius Cells Instruct Neuronal Migration by Coincidence Signaling between Secreted and Contact-Dependent Guidance Cues Cristina Gil-Sanz, 1 Santos J. Franco, 1 Isabel Martinez-Garay, 1,2
Article Cajal-Retzius Cells Instruct Neuronal Migration by Coincidence Signaling between Secreted and Contact-Dependent Guidance Cues Cristina Gil-Sanz, 1 Santos J. Franco, 1 Isabel Martinez-Garay, 1,2
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet?
 Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
Neuronal migration in the adult brain: are we there yet? H. Troy Ghashghaei*, Cary Lai and E. S. Anton* Abstract The generation and targeting of appropriate numbers and types of neurons to where they are
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord. Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011
 Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
Chemokine Regulation of Oligodendrocyte Development in the Spinal Cord Bob Avino Saint Louis University Senior Honors Thesis April 19, 2011 Richard J. Miller, PhD Northwestern University Feinberg School
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon
 REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
ErbB4 migrazione I parte. 3- ErbB4- NRG1
 ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
ErbB4 migrazione I parte 3- ErbB4- NRG1 1 In rodent brains postnatal neuronal migration is evident in three main areas: the cerebellum (CB), the hippocampus (Hipp) and the rostral migratory stream (RMS).
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Overview of the Nervous System (some basic concepts) Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Coffee Hour Tuesday (Sept 11) 10:00-11:00am Friday (Sept 14) 8:30-9:30am Surdyk s
Brain Development III
 Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Brain Development III Neural Development In the developing nervous system there must be: 1. The formation of different regions of the brain. 2. The ability of a neuron to differentiate. 3. The ability
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia
 Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
Teach-SHEET Basal Ganglia Purves D, et al. Neuroscience, 5 th Ed., Sinauer Associates, 2012 Common organizational principles Basic Circuits or Loops: Motor loop concerned with learned movements (scaling
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Development of the Nervous System. Leah Militello, class of 2018
 Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Development of the Nervous System Leah Militello, class of 2018 Learning Objectives 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest including timing and germ layer involved. 2. Describe
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence. L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia
 Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
Brain anatomy and artificial intelligence L. Andrew Coward Australian National University, Canberra, ACT 0200, Australia The Fourth Conference on Artificial General Intelligence August 2011 Architectures
GBME graduate course. Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia
 GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
GBME graduate course Chapter 43. The Basal Ganglia Basal ganglia in history Parkinson s disease Huntington s disease Parkinson s disease 1817 Parkinson's disease (PD) is a degenerative disorder of the
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible:
 NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
NERVOUS SYSTEM The neurvous system senses, interprets, and responds to changes in the environment. Two types of cells makes this possible: the neuron and the supporting cells ("glial cells"). Neuron Neurons
Huntington s Disease & MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE
 Huntington s Disease & Early Nervous System Development MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD The cups fell to the floor with a crash. Was this the alarm signal? Or was it forgetting
Huntington s Disease & Early Nervous System Development MARY ET BOYLE, PH.D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD The cups fell to the floor with a crash. Was this the alarm signal? Or was it forgetting
Embryology of the Nervous System. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Embryology of the Nervous System Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota In the blastula stage embryo, the embryonic disk has two layers. During gastrulation, epiblast cells migrate
Announcement. Danny to schedule a time if you are interested.
 Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Announcement If you need more experiments to participate in, contact Danny Sanchez (dsanchez@ucsd.edu) make sure to tell him that you are from LIGN171, so he will let me know about your credit (1 point).
Biological Bases of Behavior. 3: Structure of the Nervous System
 Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Biological Bases of Behavior 3: Structure of the Nervous System Neuroanatomy Terms The neuraxis is an imaginary line drawn through the spinal cord up to the front of the brain Anatomical directions are
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month
 Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Development of the Nervous System 1 st month day 1 - fertilization of egg day 6 - uterine implantation day 18 - trilaminar (3-layered) disc (blastoderm, embryo) ectoderm (dorsal) - nervous system and skin
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching. Intention and Executive Control
 Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
Prospective Memory as a Specific Form of Task Switching Intention and Executive Control Yehene E, Meiran N, Soroker N Taskalternationcostwithoutask alternation:measuringintentionality. A behavioral dissociation
A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex. Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R.
 A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R. Kriegstein Supplementary Figures 1-6: Supplementary Movies 1-9: Supplementary
A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R. Kriegstein Supplementary Figures 1-6: Supplementary Movies 1-9: Supplementary
Inner ear development Nervous system development
 Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Upcoming Sessions April 22: Nervous System Development Lecture April 24: Reviews of Axonal Pathfinding in Sensory Systems April 29: Inner Ear Development Lecture May 1: May 6: May 8: Auditory System Pathfinding
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003
 Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Study Guide Unit 2 Psych 2022, Fall 2003 Subcortical Anatomy 1. Be able to locate the following structures and be able to indicate whether they are located in the forebrain, diencephalon, midbrain, pons,
Neocortex. Cortical Structures in the Brain. Neocortex Facts. Laminar Organization. Bark-like (cortical) structures: Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12
 Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Neocortex Shepherd (2004) Chapter 12 Rodney Douglas, Henry Markram, and Kevan Martin Instructor: Yoonsuck Choe; CPSC 644 Cortical Networks Cortical Structures in the Brain Bark-like (cortical) structures:
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders
 Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Making Things Happen 2: Motor Disorders How Your Brain Works Prof. Jan Schnupp wschnupp@cityu.edu.hk HowYourBrainWorks.net On the Menu in This Lecture In the previous lecture we saw how motor cortex and
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Brainstem. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Brainstem Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Change in Lab Sequence Week of Oct 2 Lab 5 Week of Oct 9 Lab 4 2 Goal Today Know the regions of the brainstem. Know
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D.
 Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
Basal Ganglia George R. Leichnetz, Ph.D. OBJECTIVES 1. To understand the brain structures which constitute the basal ganglia, and their interconnections 2. To understand the consequences (clinical manifestations)
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. March 1, 2012 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the main
Course Booklet. We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you.
 Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
Exams Stressing You Out? Take Action! Course Booklet NEUR 1202 Carleton University* *TranscendFinals is not affiliated with the university We have felt the pain that Neuroscience is giving you. Our mission
4. The notion that all living things are related was put forward by: A) Charles Darwin. B) Alfred Russel Wallace. C) Gregor Mendel. D) both a and b.
 *see the end of the exam for multiple choice correct answers and all matching answers* 1. Phineas Gage's animal behavior was a result of damage to: A) the frontal lobes. B) the temporal lobes. C) the parietal
*see the end of the exam for multiple choice correct answers and all matching answers* 1. Phineas Gage's animal behavior was a result of damage to: A) the frontal lobes. B) the temporal lobes. C) the parietal
A. General features of the basal ganglia, one of our 3 major motor control centers:
 Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Reading: Waxman pp. 141-146 are not very helpful! Computer Resources: HyperBrain, Chapter 12 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, Ph.D. April 22, 2010 THE BASAL GANGLIA Objectives: 1. What are the
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
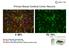 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Chapter 11 Development and Diseases
 Chapter 11 Development and Diseases Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Axon Growth/Target innervation
Chapter 11 Development and Diseases Fertilization Development of the Nervous System Cleavage (Blastula, Gastrula) Neuronal Induction- Neuroblast Formation Cell Migration Axon Growth/Target innervation
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, Jeremy Miller Scientist I
 Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Gene co-expression networks in the mouse, monkey, and human brain July 16, 2013 Jeremy Miller Scientist I jeremym@alleninstitute.org Outline 1. Brief introduction to previous WGCNA studies in brain 2.
Basal Ganglia General Info
 Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Basal Ganglia General Info Neural clusters in peripheral nervous system are ganglia. In the central nervous system, they are called nuclei. Should be called Basal Nuclei but usually called Basal Ganglia.
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012
 Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Embryonic MGE Cells as a Treatment for Epilepsy December 1, 2012 Scott C. Baraban, PhD University of California, San Francisco American Epilepsy Society Annual Meeting Disclosure Name of Commercial Interest
Chapter 8. Control of movement
 Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Chapter 8 Control of movement 1st Type: Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle: Ones that moves us Muscles contract, limb flex Flexion: a movement of a limb that tends to bend its joints, contraction of a flexor
Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments
 02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development
 Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture
 Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2002, 22(10):4002 4014 Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex Christopher B. Reid 1,2 and Christopher A. Walsh
The Journal of Neuroscience, May 15, 2002, 22(10):4002 4014 Evidence of Common Progenitors and Patterns of Dispersion in Rat Striatum and Cerebral Cortex Christopher B. Reid 1,2 and Christopher A. Walsh
Exam 2 PSYC Fall (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
 Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Exam 2 PSYC 2022 Fall 1998 (2 points) What 2 nuclei are collectively called the striatum? (2 points) Match a brain structure that is located closest to the following portions of the ventricular system
Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3
 Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Name KEY Lab Section Nsci 2100: Human Neuroanatomy 2017 Examination 3 On this page, write your name and lab section. On your bubble answer sheet, enter your name (last name, space, first name), internet
Nervous System. Lecture 4
 Nervous System Lecture 4 Neurons Functional unit of the nervous system Also called the nerve cell Soma or body Axon Dendrites Neuroglial cells support cells Schwann cells produce myelin in PNS Oligodendrocytes
Nervous System Lecture 4 Neurons Functional unit of the nervous system Also called the nerve cell Soma or body Axon Dendrites Neuroglial cells support cells Schwann cells produce myelin in PNS Oligodendrocytes
Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons
 Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons Guillermina López-Bendito 1, Katherine Sturgess 1, Ferenc Erdélyi 2, Gábor Szabó 2, Zoltán Molnár 1 and Ole Paulsen 3 1 Department
Preferential Origin and Layer Destination of GAD65-GFP Cortical Interneurons Guillermina López-Bendito 1, Katherine Sturgess 1, Ferenc Erdélyi 2, Gábor Szabó 2, Zoltán Molnár 1 and Ole Paulsen 3 1 Department
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes
 Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Notes Blood Supply to the Brain MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. LEARNING OBJECTIVES After study of the assigned learning
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Development of the Central Nervous System
 Development of the Central Nervous System an ongoing process, through adolescence and maybe even adult hood? the nervous system is plastic Experience plays a key role Dire consequences when something goes
Development of the Central Nervous System an ongoing process, through adolescence and maybe even adult hood? the nervous system is plastic Experience plays a key role Dire consequences when something goes
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy
 NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
NS219: Basal Ganglia Anatomy Human basal ganglia anatomy Analagous rodent basal ganglia nuclei Basal ganglia circuits: the classical model of direct and indirect pathways + Glutamate + - GABA - Gross anatomy
MOVEMENT OUTLINE. The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement
 MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
MOVEMENT 2 Dr. Steinmetz 3 OUTLINE The Control of Movement: Muscles! Motor Reflexes Brain Mechanisms of Movement Mirror Neurons Disorders of Movement Parkinson s Disease Huntington s Disease 1 4 TYPES
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Peter Hitchcock, PH.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-commercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Biological Bases of Behavior. 8: Control of Movement
 Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
Biological Bases of Behavior 8: Control of Movement m d Skeletal Muscle Movements of our body are accomplished by contraction of the skeletal muscles Flexion: contraction of a flexor muscle draws in a
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review
 The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
The Neuroscience of Addiction: A mini-review Jim Morrill, MD, PhD MGH Charlestown HealthCare Center Massachusetts General Hospital Disclosures Neither I nor my spouse/partner has a relevant financial relationship
Expression of liver X receptor is essential for formation of superficial cortical layers and migration of later-born neurons
 Expression of liver X receptor is essential for formation of superficial cortical layers and migration of later-born neurons Xiaotang Fan*, yun-jin Kim*, Didier outon*, Margaret Warner*, and Jan-Åke ustafsson*
Expression of liver X receptor is essential for formation of superficial cortical layers and migration of later-born neurons Xiaotang Fan*, yun-jin Kim*, Didier outon*, Margaret Warner*, and Jan-Åke ustafsson*
VL VA BASAL GANGLIA. FUNCTIONAl COMPONENTS. Function Component Deficits Start/initiation Basal Ganglia Spontan movements
 BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
BASAL GANGLIA Chris Cohan, Ph.D. Dept. of Pathology/Anat Sci University at Buffalo I) Overview How do Basal Ganglia affect movement Basal ganglia enhance cortical motor activity and facilitate movement.
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL 2009 Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts I. SHORT ANSWERS (5 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Label the three meningeal layers in the following diagram. Describe
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL 2009 Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts I. SHORT ANSWERS (5 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Label the three meningeal layers in the following diagram. Describe
Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo
 Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心.
 神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
神經解剖學 NEUROANATOMY BASAL NUCLEI 盧家鋒助理教授臺北醫學大學醫學系解剖學暨細胞生物學科臺北醫學大學醫學院轉譯影像研究中心 http://www.ym.edu.tw/~cflu OUTLINE Components and Pathways of the Basal Nuclei Functions and Related Disorders of the Basal Nuclei
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1.
 Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Genesis of cerebellar interneurons and the prevention of neural DNA damage require XRCC1. Youngsoo Lee, Sachin Katyal, Yang Li, Sherif F. El-Khamisy, Helen R. Russell, Keith W. Caldecott and Peter J. McKinnon.
Medical Neuroscience Tutorial
 Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Pain Pathways Medical Neuroscience Tutorial Pain Pathways MAP TO NEUROSCIENCE CORE CONCEPTS 1 NCC1. The brain is the body's most complex organ. NCC3. Genetically determined circuits are the foundation
Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
 9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
Development of the Nervous System
 Development of the Nervous System OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest. 2. Name and describe the formation of the primary and secondary embryological compartments
Development of the Nervous System OBJECTIVES 1. Describe the formation and fate of the neural tube and neural crest. 2. Name and describe the formation of the primary and secondary embryological compartments
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
9.14 Class 32 Review. Limbic system
 9.14 Class 32 Review Limbic system 1 Lateral view Medial view Brainstem, sagittal section Sensory- Perceptual Motor Behavior Major functional modules of the CNS Motivation Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with
9.14 Class 32 Review Limbic system 1 Lateral view Medial view Brainstem, sagittal section Sensory- Perceptual Motor Behavior Major functional modules of the CNS Motivation Courtesy of MIT Press. Used with
The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents
 HIPPOCAMPUS 16:1032 1060 (2006) COMMENTARY The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents Lydia Danglot,* Antoine Triller, and Serge Marty ABSTRACT: Interneurons are GABAergic neurons responsible
HIPPOCAMPUS 16:1032 1060 (2006) COMMENTARY The Development of Hippocampal Interneurons in Rodents Lydia Danglot,* Antoine Triller, and Serge Marty ABSTRACT: Interneurons are GABAergic neurons responsible
Cellular components of CNS
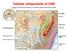 Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
Cellular components of CNS Cellular components of CNS Neurons Glial cells: Astrocytes (including radial glia), oligodendrocytes, microglia, ependymal cells Epithelial cells of choroid plexus Endothelial
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord
 SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
SOME BASIC TERMINOLOGY CNS: Central Nervous System: Brain + Spinal Cord CEREBROSPINAL FLUID (CSF): The fluid filling the ventricles, cerebral aqueduct, central canal, and subarachnoid space. It is a filtrate
CNS Developmental. Anke van Eekelen, PhD. Telethon Institute for Child Health Research
 CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
CNS Developmental Anke van Eekelen, PhD Telethon Institute for Child Health Research (Some slides are modified versions of Prof. Alan Harvey s Neuroscience lecture at ANHB and Dr. Joanne Britto s Dev Neuroscience
The human brain. of cognition need to make sense gives the structure of the brain (duh). ! What is the basic physiology of this organ?
 The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The human brain The human brain! What is the basic physiology of this organ?! Understanding the parts of this organ provides a hypothesis space for its function perhaps different parts perform different
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29:
 The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
The basal forebrain: Questions, chapter 29: 7) What is the "basal forebrain", and what is its involvement in Alzheimer' s Disease? The acetylcholine-containing neurons of the nucleus basalis of Meynart
Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome. 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders
 Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders Genetics is Complicated! Deletion 22q13: Therapies Under Investigation Intranasal insulin
Potential Treatment and Current Research in Phelan-McDermid Syndrome 11/16/2016 Frambu Center for Rare Disorders Genetics is Complicated! Deletion 22q13: Therapies Under Investigation Intranasal insulin
Connections of basal ganglia
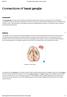 Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Connections of basal ganglia Introduction The basal ganglia, or basal nuclei, are areas of subcortical grey matter that play a prominent role in modulating movement, as well as cognitive and emotional
Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Resource https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-017-0056-2 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Conserved properties of dentate gyrus neurogenesis across postnatal development
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009
 Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
Basal ganglia Sujata Sofat, class of 2009 Basal ganglia Objectives Describe the function of the Basal Ganglia in movement Define the BG components and their locations Describe the motor loop of the BG
