A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex. Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R.
|
|
|
- Hilary Conley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A new subtype of progenitor cell in the mouse embryonic neocortex Xiaoqun Wang, Jin-Wu Tsai, Bridget LaMonica & Arnold R. Kriegstein Supplementary Figures 1-6: Supplementary Movies 1-9:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8 Supplementary Movie 1. This movie shows an example of mitotic somal translocation and org cell division. An org cell undergoes mitotic somal translocation and divides. The upper cell inherits the basal fiber whereas the lower cell rapidly extends a prominent process towards the ventricle. Images were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 2. This movie shows interkinetic nuclear migration (INM) of RG cells in mouse neocortex. An RG cell undergoes INM and divides at the VZ surface. Images were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 3. This movie shows an example of two IP cell divisions in situ. Two IP cells divide in situ without nuclear translocation. Images were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 4. This movie shows an org cell that divides and generates a daughter neuron. An org cell undergoes mitotic somal translocation and divides. The apical daughter cell acquires neuronal morphology 40h after division, and extends a leading process toward the pia. After acquiring a short trailing process, the bipolar daughter cell migrates rapidly
9 to the cortical plate. Images were acquired every 30m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 5. This movie shows an example of an asymmetric org cell division that yields a daughter org cell and a daughter neuron. Cell fate was revealed by immunostaining with anti-pax6 (progenitor marker) and anti- NeuN (neuronal marker) after 12h further culture following time-lapse imaging. Supplementary Movie 6. This movie shows an example of org cells originating from RG cells. Two days after in-utero intra-ventricular retrovirus infection at E11.5, a GFP-labelled RG cell was monitored at 15m intervals. Asymmetric division of the RG cell generates a self-renewed RG cell, which undergoes a second division. Another daughter cell undergoes mitotic somal translocation before mitosis, a defining feature of org cell behaviour. Images were acquired every 15m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 7. This movie shows centrosome behaviour in mitotic org cells. The centrosome is revealed by DsRedex-Centrin1. Frames were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second.
10 Supplementary Movie 8. This movie shows centrosome behaviour in mitotic RG cells. The centrosome is revealed by DsRedex-Centrin1. Frames were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 9. This movie shows centrosome behaviour in mitotic IP cells. The centrosome is revealed by DsRedex-Centrin1. Frames were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second.
11 Supplementary Movie 10. This movie shows interkinetic nuclear migration (INM) of group RG cells in mouse neocortex. Group of RG cell undergoes INM and divides at the VZ surface. Images were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second. Supplementary Movie 11. This movie shows no org cells mitosis after purposefully severing the apical processes of radial glial cells. We used a scalpel to remove the apical surface of the VZ in order to severe the apical processes of radial glial cells. This process disrupted INM and division of RG cells at the VZ surface and does not produce org-like cell mitosis. Images were acquired every 10m and the play rate is seven frames per second.
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
Supplementary Figure 1 Kif1a RNAi effect on basal progenitor differentiation Related to Figure 2. Representative confocal images of the VZ and SVZ of rat cortices transfected at E16 with scrambled or Kif1a
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Human cerebral cortex development from pluripotent stem cells to functional excitatory synapses Yichen Shi 1,2, Peter Kirwan 1,2, James Smith 1,2, Hugh P.C. Robinson 3 and Frederick
Distinct Behaviors of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Underlie Cortical Neurogenesis
 THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 508:28 44 (2008) Distinct Behaviors of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Underlie Cortical Neurogenesis STEPHEN C. NOCTOR, 1 * VERÓNICA MARTÍNEZ-CERDEÑO, 1 AND ARNOLD
THE JOURNAL OF COMPARATIVE NEUROLOGY 508:28 44 (2008) Distinct Behaviors of Neural Stem and Progenitor Cells Underlie Cortical Neurogenesis STEPHEN C. NOCTOR, 1 * VERÓNICA MARTÍNEZ-CERDEÑO, 1 AND ARNOLD
Development and Evolution of the Human Neocortex
 Leading Edge Review Development and Evolution of the Human Neocortex Jan H. Lui, 1,2,3 David V. Hansen, 1,2,4 and Arnold R. Kriegstein 1,2, * 1 Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and
Leading Edge Review Development and Evolution of the Human Neocortex Jan H. Lui, 1,2,3 David V. Hansen, 1,2,4 and Arnold R. Kriegstein 1,2, * 1 Eli and Edythe Broad Center of Regeneration Medicine and
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. MADM labeling of thalamic clones.
 Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
Supplementary Figure 1 MADM labeling of thalamic clones. (a) Confocal images of an E12 Nestin-CreERT2;Ai9-tdTomato brain treated with TM at E10 and stained for BLBP (green), a radial glial progenitor-specific
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and
 OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz, Iva Kelava, Johannes Vogt, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger, Denise Stenzel, Jennifer L Fish,
a 0,8 Figure S1 8 h 12 h y = 0,036x + 0,2115 y = 0,0366x + 0,206 Labeling index Labeling index ctrl shrna Time (h) Time (h) ctrl shrna S G2 M G1
 (GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
(GFP+ BrdU+)/GFP+ Labeling index Labeling index Figure S a, b, y =,x +, y =,x +,,,,,,,, Time (h) - - Time (h) c d S G M G h M G S G M G S G h Time of BrdU injection after electroporation (h) M G S G M
Supplementary figures
 Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Supplementary figures Supplementary Figure 1. B cells stimulated with pokeweed mitogen display normal mitotic figures but not cells infected with B95-8. The figures show cells stimulated with pokeweed
Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon
 REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
REVIEW ARTICLE Radial glia in the ventral telencephalon Miguel Turrero Garcıa and Corey C. Harwell Department of Neurobiology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA Correspondence C. C. Harwell, Department
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation. Reading: BCP Chapter 23
 Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Neurodevelopment II Structure Formation Reading: BCP Chapter 23 Phases of Development Ovum + Sperm = Zygote Cell division (multiplication) Neurogenesis Induction of the neural plate Neural proliferation
Cell Birth and Death. Chapter Three
 Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
Cell Birth and Death Chapter Three Neurogenesis All neurons and glial cells begin in the neural tube Differentiated into neurons rather than ectoderm based on factors we have already discussed If these
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
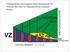 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Progenitors are Contained within Unique Domains and Tangentially Fixed. EMBRYO ADULT Migratory Behavior
Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
 9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
9996 The Journal of Neuroscience, November 5, 2003 23(31):9996 10001 Brief Communication Multipolar Migration: The Third Mode of Radial Neuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Hidenori Tabata
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Hey! The major concepts discussed relative to neural crest cell migration apply to cell migration
Mammalian Par3 Regulates Progenitor Cell Asymmetric Division via Notch Signaling in the Developing Neocortex
 Article Mammalian Par3 Regulates Progenitor Cell Asymmetric Division via Notch Signaling in the Developing Neocortex Ronald S. Bultje, 1,2,6 David R. Castaneda-Castellanos, 3,4,6 Lily Yeh Jan, 5 Yuh-Nung
Article Mammalian Par3 Regulates Progenitor Cell Asymmetric Division via Notch Signaling in the Developing Neocortex Ronald S. Bultje, 1,2,6 David R. Castaneda-Castellanos, 3,4,6 Lily Yeh Jan, 5 Yuh-Nung
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!!
 Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
THE CELL BIOLOGY OF NEUROGENESIS
 THE CELL BIOLOGY OF EUROGEESIS Magdalena Götz* and Wieland B. Huttner Abstract During the development of the mammalian central nervous system, neural stem cells and their derivative progenitor cells generate
THE CELL BIOLOGY OF EUROGEESIS Magdalena Götz* and Wieland B. Huttner Abstract During the development of the mammalian central nervous system, neural stem cells and their derivative progenitor cells generate
Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice
 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymcne Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 31 (2006) 109 122 Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice Toshiyuki Ohtsuka, a,b, * Itaru Imayoshi, b Hiromi
www.elsevier.com/locate/ymcne Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 31 (2006) 109 122 Visualization of embryonic neural stem cells using Hes promoters in transgenic mice Toshiyuki Ohtsuka, a,b, * Itaru Imayoshi, b Hiromi
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development
 Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
Ontogenesis in the CNS neurogenesis during embryonic development Formation of the neural tube neural groove neural plate neural groove neural crest notochord neural tube The developing neuroepithelium
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling
 OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz 1, Iva Kelava 1, Johannes Vogt 2, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger 1, Denise Stenzel 1, Jennifer
OSVZ progenitors of human and ferret neocortex are epithelial-like and expand by integrin signaling Simone A Fietz 1, Iva Kelava 1, Johannes Vogt 2, Michaela Wilsch-Bräuninger 1, Denise Stenzel 1, Jennifer
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus
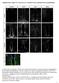 Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Supplementary Figure S1: Tanycytes are restricted to the central/posterior hypothalamus a: Expression of Vimentin, GFAP, Sox2 and Nestin in anterior, central and posterior hypothalamus. In the anterior
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration. Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota
 Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Cell Migration II: CNS Cell Migration Steven McLoon Department of Neuroscience University of Minnesota 1 Course News Coffee Hour Wednesday (Oct 18) 9:00-10:00am Surdyk s Café in Northrop Auditorium Stop
Intermediate Neuronal Progenitors (Basal Progenitors) Produce Pyramidal-- Projection Neurons for All Layers of Cerebral Cortex
 Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published January 23, 2009 Cerebral Cortex doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn260 Intermediate Neuronal Progenitors (Basal Progenitors) Produce Pyramidal-- Projection Neurons for All
Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published January 23, 2009 Cerebral Cortex doi:10.1093/cercor/bhn260 Intermediate Neuronal Progenitors (Basal Progenitors) Produce Pyramidal-- Projection Neurons for All
Neocortex Zbtb20 / NFIA / Sox9
 Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Neocortex / NFIA / Sox9 Supplementary Figure 1. Expression of, NFIA, and Sox9 in the mouse neocortex at. The lower panels are higher magnification views of the oxed area. Arrowheads indicate triple-positive
Supplementary information. The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic. Spindle Orientation
 Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
Supplementary information The Light Intermediate Chain 2 Subpopulation of Dynein Regulates Mitotic Spindle Orientation Running title: Dynein LICs distribute mitotic functions. Sagar Mahale a, d, *, Megha
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3443 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. Supplementary Figure 1 TC and SC behaviour during ISV sprouting. (a) Predicted outcome of TC division and competitive Dll4-Notch-mediated
Insulinoma-Associated 1 Has a Panneurogenic Role and Promotes the Generation and Expansion of Basal Progenitors in the Developing Mouse Neocortex
 Article Insulinoma-Associated 1 Has a Panneurogenic Role and Promotes the Generation and Expansion of Basal Progenitors in the Developing Mouse Neocortex Lilla M. Farkas, 1 Christiane Haffner, 1 Thomas
Article Insulinoma-Associated 1 Has a Panneurogenic Role and Promotes the Generation and Expansion of Basal Progenitors in the Developing Mouse Neocortex Lilla M. Farkas, 1 Christiane Haffner, 1 Thomas
Neurogenic Radial Glial Cells in Reptile, Rodent and Human: from Mitosis to Migration
 Neurogenic Radial Glial Cells in Reptile, Rodent and Human: from Mitosis to Migration Tamily Weissman 1 *, Stephen C. Noctor 2 *, Brian K. Clinton 1, Lawrence S. Honig 2,4 and Arnold R. Kriegstein 1,2,3
Neurogenic Radial Glial Cells in Reptile, Rodent and Human: from Mitosis to Migration Tamily Weissman 1 *, Stephen C. Noctor 2 *, Brian K. Clinton 1, Lawrence S. Honig 2,4 and Arnold R. Kriegstein 1,2,3
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division
 Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
Chapter 10 Cell Growth and Division 10 1 Cell Growth 2 Limits to Cell Growth The larger a cell becomes, the more demands the cell places on its DNA. In addition, the cell has more trouble moving enough
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches
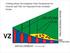 During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
During Brain Development Final Destinations for Neurons and Glia Get Separated from Germinal Niches Two mayor forms of neuronal migration: Radial and Tangential Leber & Sanes, 95 How do young neurons actually
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation
 Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
Neuroepithelial Cells and Neural Differentiation Neurulation The cells of the neural tube are NEUROEPITHELIAL CELLS Neural crest cells migrate out of neural tube Neuroepithelial cells are embryonic stem
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 12: CNS tumours 2/3 Pilocytic astrocytoma Relatively benign ( WHO grade 1) Occurs in children and young adults Mostly: in the cerebellum
Supplementary Information
 1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
1 Supplementary Information A role for primary cilia in glutamatergic synaptic integration of adult-orn neurons Natsuko Kumamoto 1,4,5, Yan Gu 1,4, Jia Wang 1,4, Stephen Janoschka 1,2, Ken-Ichi Takemaru
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza
 Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
Cytoskelet Prednáška 6 Mikrotubuly a mitóza Polarity of tubulin polymerization Nuclei Tubulin > C C Preferential addition of tubulin ar (+) ends Tubulin < C C Preferential loss of tubulin ar (+) ends Kinesin
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
DOI: 1.138/ncb222 / b. WB anti- WB anti- ulin Mitotic index (%) 14 1 6 2 T (h) 32 48-1 1 2 3 4 6-1 4 16 22 28 3 33 e. 6 4 2 Time (min) 1-6- 11-1 > 1 % cells Figure S1 depletion leads to mitotic defects
Investigating the Diversity of Radial Glia Fates in the Rat Neocortex
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-9-2010 Investigating the Diversity of Radial Glia Fates in the Rat Neocortex Abraham William Aron University
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-9-2010 Investigating the Diversity of Radial Glia Fates in the Rat Neocortex Abraham William Aron University
REVIEWS. Growth and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex: from molecules to malformations
 Growth and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex: from molecules to malformations Tao Sun 1 and Robert F. Hevner 2 Abstract The size and extent of folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex are important
Growth and folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex: from molecules to malformations Tao Sun 1 and Robert F. Hevner 2 Abstract The size and extent of folding of the mammalian cerebral cortex are important
Neural progenitor cells and their role in the development and evolutionary expansion of the neocortex
 Neural progenitor cells and their role in the development and evolutionary expansion of the neocortex Takashi Namba* and Wieland B. Huttner* The evolutionary expansion of the mammalian brain, notably the
Neural progenitor cells and their role in the development and evolutionary expansion of the neocortex Takashi Namba* and Wieland B. Huttner* The evolutionary expansion of the mammalian brain, notably the
Shaping Our Minds: Stem and Progenitor Cell Diversity in the Mammalian Neocortex
 Shaping Our Minds: Stem and Progenitor Cell Diversity in the Mammalian Neocortex Santos J. Franco 1, * and Ulrich Müller 1, * 1 Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience Department, Dorris Neuroscience Center,
Shaping Our Minds: Stem and Progenitor Cell Diversity in the Mammalian Neocortex Santos J. Franco 1, * and Ulrich Müller 1, * 1 Molecular and Cellular Neuroscience Department, Dorris Neuroscience Center,
Supplementary Figure 1. Mother centrioles can reduplicate while in the close association
 C1-GFP distance (nm) C1-GFP distance (nm) a arrested HeLa cell expressing C1-GFP and Plk1TD-RFP -3 s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 26 27 28 29 3 b 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 arrested HeLa
C1-GFP distance (nm) C1-GFP distance (nm) a arrested HeLa cell expressing C1-GFP and Plk1TD-RFP -3 s 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 11 12 13 14 16 17 18 19 2 21 22 23 24 26 27 28 29 3 b 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 arrested HeLa
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70%
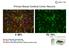 Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
Primary Mouse Cerebral Cortex Neurons V: 80% TE: 70% Pictures: 9 days after electroporation Red: MAP2 Blue: GFAP Green: GFP The cells were from Embryonic Day 14 Mouse Cerebral Cortex Primary Mouse Hippocampal
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
cell movement and neuronal migration
 cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
cell movement and neuronal migration Paul Letourneau letou001@umn.edu Chapter 16; The Cytoskeleton; Molecular Biology of the Cell, Alberts et al. 1 Cell migration Cell migration in 3 steps; protrusion,
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture
 Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
Mammalian Cerebral Cortex: Embryonic Development and Cytoarchitecture 2 The prenatal developmental of the mammalian cerebral cortex, including that of humans, is characterized by two sequential and interrelated
Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replicatio
 Cell Division Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells.
Cell Division Cell cycle The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells.
Radial glia and neural stem cells
 Cell Tissue Res (2008) 331:165 178 DOI 10.1007/s00441-007-0481-8 REVIEW Radial glia and neural stem cells Paolo Malatesta & Irene Appolloni & Filippo Calzolari Received: 21 May 2007 /Accepted: 17 July
Cell Tissue Res (2008) 331:165 178 DOI 10.1007/s00441-007-0481-8 REVIEW Radial glia and neural stem cells Paolo Malatesta & Irene Appolloni & Filippo Calzolari Received: 21 May 2007 /Accepted: 17 July
A. Incorrect! All the cells have the same set of genes. (D)Because different types of cells have different types of transcriptional factors.
 Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Genetics - Problem Drill 21: Cytogenetics and Chromosomal Mutation No. 1 of 10 1. Why do some cells express one set of genes while other cells express a different set of genes during development? (A) Because
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Supplementary Table 3. Real-time PCR primer sequences.
 Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
Supplementary Table 2. Antibodies used for Immunofluoresence. Antibody Dilution Source Goat anti-pdx1 1:100 R&D Systems Rabbit anti-hnf6 1:100 Santa Cruz Biotechnology Mouse anti-nkx6.1 1:200 Developmental
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
doi:10.1038/nature10188 Supplementary Figure 1. Embryonic epicardial genes are down-regulated from midgestation stages and barely detectable post-natally. Real time qrt-pcr revealed a significant down-regulation
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y
 T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Dunsch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201202112/dc1 Figure S1. Characterization of HMMR and CHICA antibodies. (A) HeLa
T H E J O U R N A L O F C E L L B I O L O G Y Supplemental material Dunsch et al., http://www.jcb.org/cgi/content/full/jcb.201202112/dc1 Figure S1. Characterization of HMMR and CHICA antibodies. (A) HeLa
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell
 Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
Supplemental Materials Molecular Biology of the Cell Garcia-Alvarez et al. Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1.Expression and RNAi-mediated silencing of STIM1 in hippocampal neurons (DIV, days in vitro).
MII. Supplement Figure 1. CapZ β2. Merge. 250ng. 500ng DIC. Merge. Journal of Cell Science Supplementary Material. GFP-CapZ β2 DNA
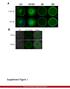 A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
A GV GVBD MI DNA CapZ β2 CapZ β2 Merge B DIC GFP-CapZ β2 Merge CapZ β2-gfp 250ng 500ng Supplement Figure 1. MII A early MI late MI Control RNAi CapZαβ DNA Actin Tubulin B Phalloidin Intensity(A.U.) n=10
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
a" b" 2N c" d" e" f" !!Aurora!A!!!CP110!
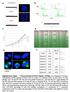 DLD1/Reference a" 2N 2N 2N/DLD1 2N/ /DLD1 c" d" e" f" TargetID 2N.AVG_Sig 2N.Det Pval.AVG_Sig.Det Pval Diff Pval DiffScore SYMBOL ILMN_26396 18.35238 0.0080058 44.81118 0.0021834 0.000323 34.90542 KRTHA4
DLD1/Reference a" 2N 2N 2N/DLD1 2N/ /DLD1 c" d" e" f" TargetID 2N.AVG_Sig 2N.Det Pval.AVG_Sig.Det Pval Diff Pval DiffScore SYMBOL ILMN_26396 18.35238 0.0080058 44.81118 0.0021834 0.000323 34.90542 KRTHA4
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts
 COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL 2009 Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts I. SHORT ANSWERS (5 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Label the three meningeal layers in the following diagram. Describe
COGNITIVE SCIENCE 107A MIDTERM EXAM 1 - FALL 2009 Name: PID: Total Pts: /100pts I. SHORT ANSWERS (5 points each for a total of 30 points) 1. Label the three meningeal layers in the following diagram. Describe
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 10
 The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
The Cell Cycle Chapter 10 Why Do Cells Divide? Unicellular 1. Reproduction Multicellular 1. Grow 2. Repair 3. Development/reproduction Types of Division Prokaryotic cells Binary fission = asexual reproduction
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013
 CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
CELL DIVISION: MITOSIS 27 FEBRUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson we: Look at related terminology Discuss the cell cycle Look at the purpose of cell division Consider what is Mitosis Look at the
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus
 Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Milestones of neuronal development in the adult hippocampus Gerd Kempermann 1,2, Sebastian Jessberger 2, Barbara Steiner 2 and Golo Kronenberg 1,3 1 Max Delbrück Center for Molecular Medicine (MDC) Berlin-Buch,
Arl13b-regulated cilia activities are essential for polarized radial glial scaffold formation
 Arl13b-regulated cilia activities are essential for polarized radial glial scaffold formation Holden Higginbotham, University of North Carolina Jiami Guo, University of North Carolina Yukako Yokota, University
Arl13b-regulated cilia activities are essential for polarized radial glial scaffold formation Holden Higginbotham, University of North Carolina Jiami Guo, University of North Carolina Yukako Yokota, University
Review Article Endogenous Proliferation after Spinal Cord Injury in Animal Models
 Stem Cells International Volume 2012, Article ID 387513, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/387513 Review Article Endogenous Proliferation after Spinal Cord Injury in Animal Models Ashley McDonough 1, 2, 3 and
Stem Cells International Volume 2012, Article ID 387513, 16 pages doi:10.1155/2012/387513 Review Article Endogenous Proliferation after Spinal Cord Injury in Animal Models Ashley McDonough 1, 2, 3 and
Part I: The Cell Cycle
 Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Cellular Differentiation Part I: The Cell Cycle During your lifetime, trillions of your cells will undergo the cell cycle. This process allows you to grow, heal, and maintain your vital tissues and organs.
Early events of neural development
 Early events of neural development Goals: 1) to discuss the origins of cells in the nervous system 2) to discuss how neural stem cells generate diverse cell types in the nervous system The next four lectures
Early events of neural development Goals: 1) to discuss the origins of cells in the nervous system 2) to discuss how neural stem cells generate diverse cell types in the nervous system The next four lectures
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex
 Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Yukako Yokota 1, H. T. Ghashghaei 1, Christine Han 1, Hannah Watson 1, Kenneth J. Campbell 2,
Radial Glial Dependent and Independent Dynamics of Interneuronal Migration in the Developing Cerebral Cortex Yukako Yokota 1, H. T. Ghashghaei 1, Christine Han 1, Hannah Watson 1, Kenneth J. Campbell 2,
Cells of the nervous system
 Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
Neurobiology Cells of the nervous system Anthony Heape 2011 1 Cells of the nervous system Neuroglia : part 2 The non excitable cells of the nervous system that provide support to neuronal survival and
The neuron. Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex
 The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
The neuron Biocytin labeled pyramidal neuron recorded in piriform cortex Discovery of the neuron (A) Reticularist Doctrine (B) Neuron Doctrine Exception.GAP JUNCTIONS between neurons Neuronal shape Dendrites
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Ch 12 BIOL 221 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Ch 12 BIOL 221 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Supplemental Information. Induction of Expansion and Folding. in Human Cerebral Organoids
 Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
Cell Stem Cell, Volume 20 Supplemental Information Induction of Expansion and Folding in Human Cerebral Organoids Yun Li, Julien Muffat, Attya Omer, Irene Bosch, Madeline A. Lancaster, Mriganka Sur, Lee
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance
 Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Chapter 8 The Cellular Basis of Reproduction and Inheritance PowerPoint Lectures for! Biology: Concepts and Connections, Fifth Edition! Campbell, Reece, Taylor, and Simon Lectures by Chris Romero Objective:
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2)
 Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain. - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function
 Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
Prss56, a novel marker of adult neurogenesis in the mouse brain - Supplemental Figures 1 to 5- Brain Structure and Function Alexandre Jourdon 1,2, Aurélie Gresset 1, Nathalie Spassky 1, Patrick Charnay
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
LIS-less neurons don t even make it to the starting gate
 Published Online: 12 September, 2005 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200506140 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 2, 2019 JCB: COMMENT LIS-less neurons don t even make it to the starting
Published Online: 12 September, 2005 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200506140 Downloaded from jcb.rupress.org on January 2, 2019 JCB: COMMENT LIS-less neurons don t even make it to the starting
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Chapter 10. Cell Cycle - Mitosis
 Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Chapter 10 Cell Cycle - Mitosis WHAT CELL REPRODUCTION ACCOMPLISHES Cell division plays important roles in the lives of organisms. Cell division replaces damaged or lost cells permits growth allows for
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic
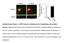 Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supplementary Figure 1. mir124 does not change neuron morphology and synaptic density. Hippocampal neurons were transfected with mir124 (containing DsRed) or DsRed as a control. 2 d after transfection,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
Supporting Information Plikus et al. 10.1073/pnas.1215935110 SI Text Movies S1, S2, S3, and S4 are time-lapse recordings from individually cultured Period2 Luc vibrissa follicles show that circadian cycles
Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex?
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 107 (2006) No. 1, p. 71 80 71) Are Both Embryonic Migratory Pathways Preserved in the Adult Brain Cerebral Cortex? Šimonová Z., Dutt J. Department of Neuroscience of the Institute
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth.4257
 Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
Supplementary Figure 1 Screen for polypeptides that affect cellular actin filaments. (a) Table summarizing results from all polypeptides tested. Source shows organism, gene, and amino acid numbers used.
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published December 22, Cerebral Cortex, 2014, 1 10
 Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published December 22, 2014 Cerebral Cortex, 2014, 1 10 doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu291 Original Article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prenatal Exposure to Autism-Specific Maternal Autoantibodies
Cerebral Cortex Advance Access published December 22, 2014 Cerebral Cortex, 2014, 1 10 doi: 10.1093/cercor/bhu291 Original Article ORIGINAL ARTICLE Prenatal Exposure to Autism-Specific Maternal Autoantibodies
Neurogenesis during development of the vertebrate central nervous system
 Review Neurogenesis during development of the vertebrate central nervous system Judith TML Paridaen * & Wieland B Huttner ** Abstract During vertebrate development, a wide variety of cell types and tissues
Review Neurogenesis during development of the vertebrate central nervous system Judith TML Paridaen * & Wieland B Huttner ** Abstract During vertebrate development, a wide variety of cell types and tissues
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
DOI: 0.038/ncb33 a b c 0 min 6 min 7 min (fixed) DIC -GFP, CenpF 3 µm Nocodazole Single optical plane -GFP, CenpF Max. intensity projection d µm -GFP, CenpF, -GFP CenpF 3-D rendering e f 0 min 4 min 0
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Ch 4 BIOL 100 Cell Cycle and Mitosis The Key Roles of Cell Division Cell division Cellular reproduc2on An ability of organisms that best dis2nguishes living things from nonliving ma:er Cell Division Unicellular
Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 Are Expressed Sequentially by Radial Glia, Intermediate Progenitor Cells, and Postmitotic Neurons in Developing Neocortex
 The Journal of Neuroscience, January 5, 2005 25(1):247 251 247 Brief Communication Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 Are Expressed Sequentially by Radial Glia, Intermediate Progenitor Cells, and Postmitotic Neurons
The Journal of Neuroscience, January 5, 2005 25(1):247 251 247 Brief Communication Pax6, Tbr2, and Tbr1 Are Expressed Sequentially by Radial Glia, Intermediate Progenitor Cells, and Postmitotic Neurons
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods
 Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Current Literature In Basic Science Recipes for Making Human Interneurons from Stem Cells Require Multiple Factors, Careful Timing, and Long Maturation Periods Directed Differentiation and Functional Maturation
Asymmetric Inheritance of Centrosome- Associated Primary Cilium Membrane Directs Ciliogenesis after Cell Division
 Asymmetric Inheritance of Centrosome Associated Primary Cilium Membrane Directs Ciliogenesis after Cell Division Judith T.M.L. Paridaen, Michaela WilschBräuninger, and Wieland B. Huttner, Max Planck Institute
Asymmetric Inheritance of Centrosome Associated Primary Cilium Membrane Directs Ciliogenesis after Cell Division Judith T.M.L. Paridaen, Michaela WilschBräuninger, and Wieland B. Huttner, Max Planck Institute
Supplementary Figure S1
 Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
Supplementary Figure S1 Supplementary Figure S1. PARP localization patterns using GFP-PARP and PARP-specific antibody libraries GFP-PARP localization in non-fixed (A) and formaldehyde fixed (B) GFP-PARPx
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:10.1038/nature11306 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Basic characterization of GFP+ RGLs in the dentate gyrus of adult nestin-gfp mice. a, Sample confocal images
