EXPERIMENTAL AND THERAPEUTIC MEDICINE 16: , 2018
|
|
|
- Imogen Clark
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 1454 Effects of CoCl 2 simulated hypoxia on the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinases in renal adenocarcinoma cells and renal tubular epithelial cells XIAOYI ZHANG and LING CHEN Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, Nanjing, Jiangsu , P.R. China Received September 7, 2017; Accepted May 9, 2018 DOI: /etm Abstract. Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and chronic kidney disease (CKD) are associated with hypoxia, but the effects of hypoxia on the process of angiogenesis in the two diseases are dramatically different. Some of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP2 and MMP9, may have a role because they represent the most prominent family of proteinases associated with angiogenesis. In the present study, the differential response of human renal cell cancer cells (786 0), human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK 2) and human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC 1) to hypoxia with regards to the expression of MMP2, MMP9, MMP14, TIMP2, RECK was investigated. Cobalt chloride (CoCl 2 ) treatment was used to simulate the hypoxia environment in RCC and CKD. The expression levels of HIF 1α, RECK, MMP2, MMP9, MMP14 and TIMP2 in HK2, and HMEC 1 cells were determined by western blot analysis after incubation with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 for 24 h. It was indicated that the effects of hypoxia on the endogenous expression of RECK and MMP2 differed depending on the considered cell type. Notably, the RECK expression was significantly decreased in cells under hypoxia, whereas this expression was slightly increased in HK2 and HMEC 1 cells. Furthermore, the MMP2 expression was significantly increased in HMEC 1 cells under hypoxia, whereas the expression was slightly decreased in HK2 and cells. These results demonstrate that 786 0, HK2 and HMEC 1 cells respond differently under hypoxic conditions. Furthermore, MMP2 and RECK may serve divergent roles in HK2 and HMEC 1 cells under hypoxic conditions. Correspondence to: Dr Ling Chen, Department of Pathology, The Affiliated Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing University Medical School, 321 Zhongshan Road, Nanjing, Jiangsu , P.R. China E mail: lingpathol@126.com Key words: angiogenesis, chronic kidney disease, cobalt chloride, matrix metalloproteinases, renal cell carcinoma Introduction Renal cell carcinoma (RCC) usually has an abundant number of vessels, but they suffer from hypoxia and nutrient deprivation because abnormal vessel structure and function. The hypoxic tumour environment creates a favourable condition for tumour progression and metastasis, and it also leads to the resistance of tumour cells to radiation therapy and many chemotherapeutics (1). Hypoxia is also one of the most important mechanisms that accelerate chronic kidney disease (CKD). Compared with RCC, the angiogenic response to hypoxia in CKD is seriously inadequate, which is followed by progressive rarefaction of the peritubular capillary (PTC) network (2). Chronic tissue hypoxia can generate both an angiogenic and a fibrogenic response. However, in CKD, the balance is strongly tipped toward fibrogenesis. It has been suggested that failed angiogenesis and hypoxia may be central to progressive CKD, but the mechanisms that lead to the apparent imbalance between angiogenesis and fibrosis under hypoxia are as yet poorly understood. The angiogenic switch refers to a process during tumor progression where the balance between pro and anti angiogenic factors tilts towards a pro angiogenic outcome, resulting in normally quiescent vasculature continually sprout new vessels (3). In response to hypoxia, the expression of VEGF is increased via hypoxia inducible factor 1α (HIF 1α) that is usually considered to be a pro angiogenic factor. However, in CKD, hypoxia and HIF 1α activation are observed, but there is essentially no angiogenic response, the balance of angiogenic switch is strongly tipped towards an anti angiogenic outcome. Taken together, there may be one or more crucial molecular mediators in RCC and CKD, which control the transition from capillary vessel hyperplasia to regression. The changes of these moleculars lead to sustained vascular loss in the face of hypoxia during CKD and excessive angiogenesis during RCC. The matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) represent the most prominent family of proteinases associated with angiogenesis. In vascular tissues, MMPs can be stimulated and activated by various stimuli, including hemodynamics, oxidative stress, inflammation, hormonal factors, and hypoxia (4). Activated MMPs degrade ECM to liberate ECs from basement membrane and facilitate migration and invasion of ECs. MMPs
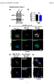
2 ZHANG and CHEN: EFFECTS OF HYPOXIA ON THE EXPRESSION LEVELS OF MMPS IN CELLS 1455 can liberate angiogenic molecules that are sequestered in the ECM. On the other hand, they may generate new fragments that inhibit angiogenesis. Moreover, vascular cell proliferation and apoptosis can also be regulated by MMPs. The vessel maturation involves recruitment of mural cells and the establishment of a basement membrane. During this process, the activities of MMPs need to be tightly regulated to avoid excessive ECM degradation and tissue damage. Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs) and RECK are endogenous protein regulators of the MMPs family. TIMPs are traditionally thought to control extracellular matrix (ECM) proteolysis through direct inhibition of MMP dependent ECM proteolysis. TIMPs also have biological activities that are independent of metalloproteinases. RECK, a membrane bound glycoprotein, is normally expressed in all cells and plays an important role in ECM remodeling and angiogenesis by negatively regulating at least three MMPs: MMP2, MMP9, and MMP14. In this study, we hypothesized that there exist some crucial molecular mediators in RCC and CKD under hypoxic condition, which controls the transition from capillary vessel hyperplasia to regression. It is also the reason why angiogenic responses to hypoxia are significantly different in renal cancer and fibrosis. Therefore, in this study, we used CoCl 2 simulated hypoxia to investigate the differential effect of hypoxia on MMPs expression between 786 0, HK2 and HMEC 1 cells. Materials and methods Cell culture and treatment. Human renal cell cancer cells (786 0), human renal tubular epithelial cells (HK 2) and human microvascular endothelial cells (HMEC 1) were obtained from the Cell Bank of Type Culture Collection of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Shanghai, China). All cells were cultured in RPMI 1640 medium (Gibco; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc., Waltham, MA, USA) containing 10% fetal calf serum at 37 C in a humidified atmosphere at 5% CO 2. The culture medium was changed every two days and cells were subcultured about once a week. For treatment with cobalt chloride (CoCl 2.6H 2 O; Sigma Aldrich; Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany), cells were seeded into 6 well plates at a density of 1x10 5 /well. After 90% confluence was reached, they were treated with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 for 24 h. Western blot analysis. Cells were lysed in lysis buffer. After centrifugation, the supernatant was collected and quantified. The same amount of total protein was separated by 12% SDS PAGE and then transferred to a PVDF membrane. The membrane was then incubated overnight at 4 C with antibodies against RECK, HIF 1α, MMP2, MMP9, MMP14, TIMP2 or β tubulin. After incubation with the secondary antibody labelled with HRP at 37 C for 1 h, protein bands were visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence (ECL). The relative protein levels were calculated by comparison to the amount of β tubulin protein. The source and dilution of unconjugated antibodies used in this study are as follows: HIF 1α (rabbit pab; NB SS, 1:1,000; Novus Biologicals, Ltd., Cambridge, UK), RECK (goat pab; AF1734, 1:1,000; R&D Systems, Inc., Minneapolis, MN, USA), MMP2 (rabbit pab; NB , 1:1,000; Novus Biologicals), MMP9 (rabbit mab; ab76003, 1:1,000; Abcam, Cambridge, UK), MMP14 (rabbit mab; ab51074, 1:1,000; Abcam), TIMP2 (rabbit pab; BS1366, 1:500; Bioworld Technology, Inc., St. Louis Park, MN, USA), VEGF A (rabbit pab; BS2431, 1:500; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), β Tubulin (Mouse pab; BS1482 M, 1:1,000; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), Fluorescein (FITC) conjugated Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (BS10950, 1:200; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugated Goat Anti Rabbit IgG (BS13278, 1:3,000; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugated Goat Anti Mouse IgG (BS12478, 1:3,000; Bioworld Technology, Inc.), Horseradish Peroxidase (HRP) conjugated Rabbit Anti Goat IgG (BS30503, 1:3,000; Bioworld Technology, Inc.). Cell proliferation assay. HK2, and HMEC 1 cells were seeded into 96 well plates at a density of 5x10 3 /well. After adherence of cells, they were treated with CoCl 2 at different concentrations for various periods of time as indicated. Six duplicate wells were set up for each sample. MTT (5 mg/ml) was added to the medium at 10 ml/well followed by incubation at 37 C for 4 h. After the medium was removed, cells were lysed with 150 µl dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO). Absorbance of each well was measured by a microplate reader at 490 nm wavelength. Immunofluorescent staining. Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 30 min at room temperature and immersed in 0.2% Triton X 100 for 10 min at 4 C. After blocking with 4% BSA for 1 h at 37 C, cells were incubated overnight at 4 C with primary antibody (1:50) in PBS. Cells were then incubated with fluorophore conjugated secondary antibody (1:200) in 4% BSA for 1 h at 37 C, and then stained DAPI (1:500) for 5 min at room temperature. For the negative control, PBS was used in place of the primary antibody. Cells were viewed under the fluorescence microscope equipped with a digital camera. Statistical analysis. Each experiment was performed at least three times. All results are presented as the mean ± standard deviation. All analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 5 software. Statistical analysis was performed using one way analysis of variance with Tukey' s post hoc test. All analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism 5 software (GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). P<0.05 was considered to indicate a statistically significant difference. Results Chemical hypoxia model. CoCl 2 is a chemical hypoxia agent which leads to the stabilization of HIF1 α and the expression of hypoxia responsive genes. Indeed, we observed the up regulation of HIF 1α in HK2 and HMEC 1 cells after incubation with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 800 µmol/l for 24 h (Fig. 1A). The protein expression level of HIF 1α was rapidly up regulated in a dose dependent manner with the increase of CoCl 2 concentration, and with a peak response occurring at 150 µmol/l CoCl 2 groups. Then the HIF 1α expression began to gradually decrease when concentration of CoCl 2 was higher than 150 µmol/l. It should be noted that, in cells, HIF 1α was continuously expressed and maintained at a relatively high level under normoxia, which was associated with the
3 1456 Figure 1. Establishment of chemical hypoxia models. (A) Expression levels of HIF 1α in HK2, and HMEC 1 cells were determined by western blot analysis after incubation with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 800 µmol/l for 24 h. (B) Representative images from immunohistochemical staining for HIF 1α in HK2 cells after treatment with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 800 µmol/l for 24 h were indicated (magnification, x200). (C) To examine the effects of varying concentrations of CoCl 2 on cells, cell morphological observation was performed under a microscope (magnification, x200). (D) Effects of CoCl 2 on cell survival rate of HMEC 1, HK2 and cells. In all cases, at least three independent experiments were performed. HIF 1α, hypoxia inducible factor 1α; HK2, human renal tubular epithelial cells; 786 0, human renal cell cancer cells; HMEC 1, human microvascular endothelial cells. loss of the von Hippel Lindau (VHL) gene product in RCC. At low CoCl 2 concentration (150 µmol/l), HIF 1α expression was slightly up regulated in cells (P=0.0086), whereas when the concentration of CoCl 2 was higher than 400 µmol/l (P=0.0415), reversely, it was significantly decreased compared with normoxic group (Fig. 1A). We also observed the distribution of HIF 1α in HK2 cells treated with CoCl 2 by using cellular immunofluorescence staining technique. The data in Fig. 1B suggested that HIF 1α molecule always distributed in the nucleus, not in the cytoplasm, at a relatively uniform density when HK2 cells were treated with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 800 µmol/l for 24 h. Exposure to CoCl 2 at 150 µmol/l for 24 h considerably enhanced the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of FITC stain in HK2 cells (P=0.0008). Chemical hypoxia affects cellular morphology and proliferation. To examine the effects of varying concentrations of CoCl 2 on cells, morphological observation was firstly performed under microscope (Fig. 1C). At low CoCl 2 concentration (150 µmol/l), there was no significant change in cell morphology except that some vacuoles was observed in the cytoplasm, whereas when concentration of CoCl 2 was higher than 500 µmol/l, cells were gradually elongated. The cells treated by high CoCl 2 concentration (500 µmol/l) for 24 h began to shrink and were easier to die. In order to further evaluate the cytotoxicity of CoCl 2 at different concentrations, MTT assay was used to observe cell proliferation and cell survival rate was calculated (Fig. 1D). The data revealed that CoCl 2 treatment caused the loss of cell viability in a dose dependent manner. Effects of chemical hypoxia on the expression of MMPs are dramatically different. In the present study, the HMEC 1, HK2 and cells treated with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 were used to further explore the responses of MMPs to hypoxia in RCC and CKD. Their endogenous MMPs protein levels under normoxia and chemical hypoxia conditions were examined by western blot. After treated with low CoCl 2 concentration (150 µmol/l) for 24 h, we found that RECK expression was down regulated in cells (P=0.0325). However, in HK2 and HMEC 1 cells, RECK expression was obviously up regulated (P= and ; Fig. 2). The MMP2 expression was increased in HMEC 1 cells in chemical hypoxia (P=0.0092). However, it was decreased in
4 ZHANG and CHEN: EFFECTS OF HYPOXIA ON THE EXPRESSION LEVELS OF MMPS IN CELLS 1457 Figure 2. (A F) Effects of chemical hypoxia on the expression levels of MMPs differed. (A, C and E) Expression levels of RECK, MMP2, MMP9 and MMP14 in HK2, and HMEC 1 cells were determined by western blot analysis after incubation with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 200 µmol/l for 24 h. (B, D and F) Normalized densitometric quantitation. * P<0.05, # P>0.05 as indicated. In all cases, at least three independent experiments were performed. MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; HK2, human renal tubular epithelial cells; 786 0, human renal cell cancer cells; HMEC 1, human microvascular endothelial cells. HK2 and cells (P= and ; Fig. 2). We also noticed that MMP9 expression was gradually decreased after up regulation of HIF 1α by CoCl 2 in HMEC 1 and HK2 cells. Compared with control group, we did not find significant change of MMP14 expression in cells in chemical hypoxia (P>0.05; Fig. 2). We also found that MMP14 expression was slightly decreased in HK2, HMEC 1 and cells (Fig. 2). TIMP2 selectively interacts with MMP14 to facilitate the cell surface activation of prommp2. At lower concentrations of TIMP 2, the activation is enhanced while at higher concentrations the activation is inhibited. The ratio between TIMP 2 and MMP 2 is critical to the activity of MMP 2. The expression levels of TIMP2 and RECK were also determined by western blot. The data in Fig. 3 suggested that the TIMP2 expression was obviously decreased in HMEC 1 cells at low concentration of CoCl 2 (150 µmol/l). However, at high concentration of CoCl 2 (>500 µmol/l) group, the expression of TIMP2 was increased significantly in HMEC 1 cells although cells began to shrink at the moment. Similar results were also found in HK2 and cells. Discussion In the present study, we investigated the differential response of 786 0, HK2 and HMEC 1 cells to hypoxia on expression of MMPs. Following exposure to low concentration of CoCl 2 (150 µmol/l), cells induce hypoxia adaptive responses via HIF 1α up regulation (Fig. 1). However, high concentration of CoCl 2 (>500 µmol/l) cause cells injury or atrophy, probably by cobalt ion (Co 2+ ), injured cells lose the ability to furthest up regulate HIF 1α expression. Fig. 2 showed that RECK expression was down regulated in cells after treated with low concentration of CoCl 2.
5 1458 Figure 3. Effects of chemical hypoxia on the expression levels of TIMP2 in 786 0, HK2 and HMEC 1 cells. (A) Expression levels of TIMP2 in HK2, and HMEC 1 cells were determined by western blot analysis after incubation with varying concentrations of CoCl 2 from 0 to 800 µmol/l for 24 h. (B) Normalized densitometric quantitation. * P<0.05. In all cases, at least three independent experiments were performed. TIMP, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase; HK2, human renal tubular epithelial cells; 786 0, human renal cell cancer cells; HMEC 1, human microvascular endothelial cells. Recent studies have provided a potential mechanism by which some tumor cells reduce RECK expression in response to hypoxia. It is that RECK is a target of at least three groups of mirnas (mir 15b/16, mir 21 and mir 372/373) and mir 372/373 are up regulated in response to hypoxia through HIF 1α and TWIST1, whereas mir 21 is up regulated by RAS signaling pathway. Hypoxia and RAS signaling pathway cooperatively down regulate this tumor suppressor and thereby promote malignant cell behavior (5). However, we also observed that, in HK2 and HMEC 1 cells, RECK expression was obviously upregulated in chemical hypoxia induced CoCl 2. This different phenomenon suggested that the mechanism of RECK modulation within and HK2 cells may be different though they receive the same hypoxic signal. We observed that endogenous MMP2 protein level was increased in HMEC 1 cells at low concentration of CoCl 2 (150 µmol/l). In recent studies, normoxic HMEC 1 cells are found to constitutively release MMP2 proteins by ELISA and gelatin zymography analyses, whereas hypoxic HMEC 1 cells enhance the secretion of latent form of MMP2, but not the activated form (6). Similar results were observed in human macrovascular ECs (EAhy 926) in ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury. Hypoxia of macrovascular ECs enhance MMP 2 production and secretion, whereas reoxygenation that take place in reperfusion further increases its level (7). In general, hypoxia results in an upward tendency of vascular MMP 2 expression and secretion in vitro However, we also observed the slightly decrease of MMP2 expression in HK2 cells in chemical hypoxia. Previous studies about ischemic kidneys have reported this different phenomenon. Ischemia and hypoxia in this organ led to a decrease in MMPs and an elevation in TIMP expression accompanied by fibrosis. In this study, however, increased TIMP2 expression did not occur in hypoxic renal epithelial cells but in atrophic ones treated with high concentration of CoCl 2 (Fig. 3). These results suggest that the decrease in MMPs and elevation in TIMP expression may do not occur simultaneously in ischemic kidney. There are four homologous members of the TIMP family from TIMP1 to TIMP4. TIMP2 is constitutively expressed in all normal tissues but demonstrates reduced expression in human cancer cells (8). In the present study, we found that endogenous TIMP2 expression in HMEC 1 cells was obviously decreased at low concentration of CoCl 2 (150 umol/l). Some studies have shown that hypoxia reduces secretion of TIMP 2 protein by HUVEC and EaHy926 cells and reduced TIMP 2 levels enhance endothelial cell migration and proliferation (9). However, others have found that normoxic HMEC 1 cells constitutively released TIMP2 proteins and the secretion of TIMP 2 is not altered in response to hypoxia. Interestingly, hypoxic HMEC 1 cells display lower abilities to migrate and organize in tube like structures compared to normoxic cells, despite increased MMP2 levels (7). A possible explanation for this different phenomenon is that ECs of different origin may respond differently to environmental stimuli. In this study, we also found that, at high concentration of CoCl 2 (500 umol/l), the expression of TIMP2 was increased significantly in HMEC 1 cells although cells began to shrink at the moment (Fig. 3). These results suggest that increased TIMP 2 levels in injured endothelial cells may play a different role in endothelial cell migration and proliferation compared with that in hypoxic HMEC 1 cells. Further study will be required to test whether these multiple functions of TIMP2 are truly implicated in CKD in renal fibrosis and cancer. We observed that endogenous MMP9 expression was gradually decreased after up regulation of HIF 1α by CoCl 2 in HMEC 1 and HK2 cells. Previous studies have shown that the amount of secreted MMP9 proteins by normoxic HMEC 1 cells is so small that they are undetectable in cell supernatants by ELISA or gelatin zymography analyses (6). Many studies suggest that MMP 9 has a distinct role in angiogenic switch by regulating the bioavailability of VEGF A in tumors. Macrophages, neutrophils and mast cells initiate angiogenesis by MMP9 mediated activation of VEGF. MMP9 has also been reported to be a negative prognostic factor in RCC. Recent studies have shown that protein expressions of MMP9 in cells are significantly higher than that in HK 2 cells and MMP9 overexpression in RCC tissues is correlated with vasculogenic mimicry that is one of the modes of vessel formation in tumors (10). However, in other cancer models, MMP9 generates ECM fragments like tumstatin, a potent suppressor of tumor vasculature formation, resulting in increased tumor growth and pathological vascularization in MMP9 deficient mice (11). Taken together, MMPs can generate both angiogenesis inhibiting as well as promoting
6 ZHANG and CHEN: EFFECTS OF HYPOXIA ON THE EXPRESSION LEVELS OF MMPS IN CELLS 1459 signals. Depending on the time frame of MMP expression and the availability of substrates, the effects of MMPs on angiogenesis might be diverse. This illustrates that one MMP can have opposing effects in different tumor types. In addition, in MMP9 deficient mice, the PTC rarefaction is significantly attenuated following Ischemia reperfusion injury (12). MMP14 is a central regulator of cellular migration and involved in inflammation, angiogenesis, cancer cell invasion, epithelial morphogenesis and so on. We observed that MMP14 expression was slightly decreased under chemical hypoxia in HMEC 1 cells. Others have shown that hypoxia inhibits the mrna expression of MMP14 in human macrovascular ECs (EAhy 926), whereas reoxygenation that take place in reperfusion upregulates MMP14 mrna expression (7). It should be noted that ECs of different origin may respond differently to environmental stimuli. In vitro wound healing migration model, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) are stimulated to migrate by byphorbol 12 myristate 13 acetate (PMA), the expression of MMP14 is up regulated and its activity can modulate endothelial migration, invasion, and formation of capillary tubes (13). It was found that MMP14 is expressed selectively at the tip of growing vessels where ECM degradation is needed (14). Furthermore, MMP14 performs not only as a matrix degrading enzyme, but also a signaling molecule on ECs (15). We also observed that the MMP14 expression had a decreasing tendency in cells with the up regulation of HIF 1α. Actually, many studies have reported that hypoxia induce MMP14 expression in tumor cell lines such as retinal glial cells and hepatocellular carcinoma cells (16,17). Whereas some other studies showed that hypoxia does not induce MMP14 mrna and protein expression in breast cancer TICs. Instead, hypoxia results in trafficking of preexisting MMP14 from cytoplasmic storage pools to cell surface (18). MMP14 expression was also decreased in HK2 cells when treated with low concentration of CoCl 2. This result suggested that the effects of hypoxia on MMP14 in renal epithelial cells may have an important role in renal fibrosis. The mechanisms of MMPs regulation by hypoxia are not fully understood. Recent studies suggested that the expression and activity could be regulated by hypoxia via some micrornas (19). Taken together, activity and function of MMPs in RCC and CKD seem not to be uniform. It is necessary to develop valid experimental models that allow the further study of MMPs involved in RCC and CKD. In summary, in this study, we found that the effects of hypoxia on the endogenous expression of RECK and MMP2 are dramatically different depending on the considered cell type. These differences may contribute to their different angiogenesis response. It is important to note that these results are found in single cells in vitro. We need more effective experimental models for mimicking in vivo tissue environment, such as co culture systems or animal model. In fact, in our other study, co culture systems of HMEC 1 with cells or HK2 cells were established to explore the influence of different parenchymal cells on RECK expression, proliferation and angiogenesis of adjacent endothelial cell (20). These results suggest that RECK or MMP2 protein may be a key molecule involved in the regulation of angiogenesis in RCC and chronic renal disease. It may be a potential target for the clinical treatment of these two diseases. Acknowledgements The authors would like to thank Dr Shanmei Du and Dr Yiping Li of the Department of Pathology, Medical School of Southeast University (Nanjing, China) for their constructive comments and excellent technical assistance. Funding No funding was received. Availability of data and materials The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request. Authors' contributions LC and XZ conceived and designed the experiments. XZ performed the experiments. LC and XZ jointly analyzed the results, drafted the manuscript and performed critical revisions. Ethics approval and consent to participate Not applicable. Consent for publication Not applicable. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. References 1. Muz B, de la Puente P, Azab F and Azab AK: The role of hypoxia in cancer progression, angiogenesis, metastasis, and resistance to therapy. Hypoxia (Auckl) 3: 83 92, Farris AB, Adams CD, Brousaides N, Della Pelle PA, Collins AB, Moradi E, Smith RN, Grimm PC and Colvin RB: Morphometric and visual evaluation of fibrosis in renal biopsies. J Am Soc Nephrol 22: , Baeriswyl V and Christofori G: The angiogenic switch in carcinogenesis. Semin Cancer Biol 19: , Chen Q, Jin M, Yang F, Zhu J, Xiao Q and Zhang L: Matrix metalloproteinases: Inflammatory regulators of cell behaviors in vascular formation and remodeling. Mediators Inflamm 2013: , Loayza Puch F, Yoshida Y, Matsuzaki T, Takahashi C, Kitayama H and Noda M: Hypoxia and RAS signaling pathways converge on, and cooperatively downregulate, the RECK tumor suppressor protein through micrornas. Oncogene 29: , Basilico N, Magnetto C, D'Alessandro S, Panariti A, Rivolta I, Genova T, Khadjavi A, Gulino GR, Argenziano M, Soster M, et al: Dextran shelled oxygen loaded nanodroplets reestablish a normoxia like pro angiogenic phenotype and behavior in hypoxic human dermal microvascular endothelium. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 288: , Ben Yosef Y, Lahat N, Shapiro S, Bitterman H and Miller A: Regulation of endothelial matrix metalloproteinase 2 by hypoxia/reoxygenation. Circ Res 90: , Galm O, Suzuki H, Akiyama Y, Esteller M, Brock MV, Osieka R, Baylin SB and Herman JG: Inactivation of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 gene by promoter hypermethylation in lymphoid malignancies. Oncogene 24: , 2005.
7 Lahat N, Bitterman H, Engelmayer Goren M, Rosenzweig D, Weiss Cerem L and Rahat MA: Reduced TIMP 2 in hypoxia enhances angiogenesis. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 300: C557 C566, Lin H, Pan JC, Zhang FM, Huang B, Chen X, Zhuang JT, Wang H, Mo CQ, Wang DH and Qiu SP: Matrix metalloproteinase 9 is required for vasculogenic mimicry by clear cell renal carcinoma cells. Urol Oncol 33: 168.e9 e16, Hamano Y, Zeisberg M, Sugimoto H, Lively JC, Maeshima Y, Yang C, Hynes RO, Werb Z, Sudhakar A and Kalluri R: Physiological levels of tumstatin, a fragment of collagen IV alpha3 chain, are generated by MMP 9 proteolysis and suppress angiogenesis via alphav beta3 integrin. Cancer Cell 3: , Lee SY, Hörbelt M, Mang HE, Knipe NL, Bacallao RL, Sado Y and Sutton TA: MMP 9 gene deletion mitigates microvascular loss in a model of ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 301: F101 F109, Galvez BG, Matías Román S, Albar JP, Sánchez Madrid F and Arroyo AG: Membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase is activated during migration of human endothelial cells and modulates endothelial motility and matrix remodeling. J Biol Chem 276: , Kachgal S, Carrion B, Janson IA and Putnam AJ: Bone marrow stromal cells stimulate an angiogenic program that requires endothelial MT1 MMP. J Cell Physiol 227: , Ando K, Ishibashi T, Ohkawara H, Inoue N, Sugimoto K, Uekita H, Hu C, Okamoto Y, Takuwa Y and Takeishi Y: Crucial role of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1 MMP) in RhoA/Rac1 dependent signaling pathways in thrombin stimulated endothelial cells. J Atheroscler Thromb 18: , Noda K, Ishida S, Shinoda H, Koto T, Aoki T, Tsubota K, Oguchi Y, Okada Y and Ikeda E: Hypoxia induces the expression of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in retinal glial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46: , Miyoshi A, Kitajima Y, Ide T, Ohtaka K, Nagasawa H, Uto Y, Hori H and Miyazaki K: Hypoxia accelerates cancer invasion of hepatoma cells by upregulating MMP expression in an HIF 1alpha independent manner. Int J Oncol 29: , Li J, Zucker S, Pulkoski Gross A, Kuscu C, Karaayvaz M, Ju J, Yao H, Song E and Cao J: Conversion of stationary to invasive tumor initiating cells (TICs): Role of hypoxia in membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1 MMP) trafficking. PLoS One 7: e38403, Hu J, Ni S, Cao Y, Zhang T, Wu T, Yin X, Lang Y and Lu H: The Angiogenic Effect of microrna 21 Targeting TIMP3 through the Regulation of MMP2 and MMP9. PLoS One 11: e , Zhang X, Liu L, Liu J, Cheng Z, Wang Z, Shi C, Ding F, Chen S and Chen P: Endothelial cells co cultured with renal carcinoma cells significantly reduce RECK expression under chemical hypoxia. Cell Biol Int 41: , 2017.
Influence of c-src on Hypoxic Resistance to Paclitaxel in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells and Reversal of FV-429
 Influence of c-src on Hypoxic Resistance to Paclitaxel in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells and Reversal of FV-429 Qinglong Guo 1a, Lu Lu 1a, Yan Liao a, Xiaoping Wang a, Yi Zhang a, Yicheng Liu a, Shaoliang
Influence of c-src on Hypoxic Resistance to Paclitaxel in Human Ovarian Cancer Cells and Reversal of FV-429 Qinglong Guo 1a, Lu Lu 1a, Yan Liao a, Xiaoping Wang a, Yi Zhang a, Yicheng Liu a, Shaoliang
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting. protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in. acute kidney injury
 Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
Sestrin2 and BNIP3 (Bcl-2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa-interacting protein3) regulate autophagy and mitophagy in renal tubular cells in acute kidney injury by Masayuki Ishihara 1, Madoka Urushido 2, Kazu Hamada
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia!
 Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Mechanisms of Gene Regulation and Signal! Transduction in Hypoxia! Lorenz Poellinger! Dept. of Cell and Molecular Biology! Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden! Normoxia - O 2 availability is in balance
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8. Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath
 Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Neoplasia 18 lecture 8 Dr Heyam Awad MD, FRCPath ILOS 1. understand the angiogenic switch in tumors and factors that stimulate and inhibit angiogenesis. 2. list the steps important for tumor metastasis
Product Datasheet. CD133 Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg
 Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIAL Supplementary Methods Culture of cardiomyocytes, fibroblasts and cardiac microvascular endothelial cells The isolation and culturing of neonatal rat ventricular cardiomyocytes was
Tissue repair. (3&4 of 4)
 Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Tissue repair (3&4 of 4) What will we discuss today: Regeneration in tissue repair Scar formation Cutaneous wound healing Pathologic aspects of repair Regeneration in tissue repair Labile tissues rapid
Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies. Traditional Hypothesis Stress
 3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
3/1/212 Role of Inflammatory and Progenitor Cells in Pulmonary Vascular Remodeling: Potential Role for Targeted Therapies K.R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, CO 845 Prominent Fibroproliferative
Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis)
 Product Manual Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis) Catalog Number CBA-200 50 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Angiogenesis, or neovascularization,
Product Manual Endothelial Tube Formation Assay (In Vitro Angiogenesis) Catalog Number CBA-200 50 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Angiogenesis, or neovascularization,
Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry
 Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Original Paper 2015 The Author(s). 2015 Published The Author(s) by S. Karger AG, Basel Published online: November 27, 2015 www.karger.com/cpb Published by S. Karger AG, Basel 2194 1421-9778/15/0376-2194$39.50/0
Endothelial PGC 1 - α 1 mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes
 Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Endothelial PGC-1α mediates vascular dysfunction in diabetes Reporter: Yaqi Zhou Date: 04/14/2014 Outline I. Introduction II. Research route & Results III. Summary Diabetes the Epidemic of the 21st Century
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium. fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production
 Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Supplementary Information Reduction of metastatic and angiogenic potency of malignant cancer by Eupatorium fortunei via suppression of MMP-9 activity and VEGF production Aeyung Kim, Minju Im, Nam-Hui Yim
Introduction: 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis. PI3K/Akt
 Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Fas-ligand (CD95-L; Fas-L) Fas (CD95) Fas (apoptosis) 年 了 不 度 Fas Fas-L 力 不 Fas/Fas-L T IL-10Fas/Fas-L 不 年 Fas signal-mediated apoptosis 度降 不 不 力 U-118, HeLa, A549, Huh-7 MCF-7, HepG2. PI3K/Akt FasPI3K/Akt
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects.
 Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
Supplementary Table 1. Characteristics of Subjects. a includes one patient who had an aqueous sample taken from the same eye twice b includes one patients who had an aqueous sample taken from the same
Correspondence to: Jun-nian Zheng, * These authors contributed equally to this paper.
 Decreased expression of CHIP leads to increased angiogenesis via VEGF-VEGFR2 pathway and poor prognosis in human renal cell carcinoma Chao Sun 1, 2, 4, *, Hai-long Li 1, 2, *, Hai-rong Chen 6, *, Mei-lin
Decreased expression of CHIP leads to increased angiogenesis via VEGF-VEGFR2 pathway and poor prognosis in human renal cell carcinoma Chao Sun 1, 2, 4, *, Hai-long Li 1, 2, *, Hai-rong Chen 6, *, Mei-lin
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness. Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D.
 Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Tumor microenvironment Interactions and Lung Cancer Invasiveness Pulmonary Grand Rounds Philippe Montgrain, M.D. February 26, 2009 Objectives Review epithelial mesenchymal transition (EMT), and its implications
Product Datasheet. DARC Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5
 Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis
 Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Heterotypy and Angiogenesis Tumors are perpetual wounds 1. Normally stroma and epithelia converse at a distance. 2. Juxtaposition of stroma and epithelia is indicative of tissue damage. 4. Activate strategies
Journal Club Semmler Lorenz
 Beer et al. 2015 - Analysis of the Secretome of Apoptotic Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Impact of Released Proteins and Exosomes for Tissue Regeneration Journal Club 13.11.2017 1 Introduction to
Beer et al. 2015 - Analysis of the Secretome of Apoptotic Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells: Impact of Released Proteins and Exosomes for Tissue Regeneration Journal Club 13.11.2017 1 Introduction to
Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Supplementary Materials and Methods Immunoblotting Immunoblot analysis was performed as described previously (1). Due to high-molecular weight of MUC4 (~ 950 kda) and MUC1 (~ 250 kda) proteins, electrophoresis
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis
 Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inflammatory Cells and Metastasis Experimentelle Krebsforschung SS 07 Gerhard Christofori Institute of Biochemistry and Genetics Department of Clinical-Biological Sciences Center of Biomedicine University
Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment
 Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment 1, Ph.D. Henna Bazai 1, Anita Sekula 1, William Fogler 2, Ted Smith 2, John Magnani 2 and Abdel Kareem
Inhibition of E-Selectin or E-selectin together with CXCR4 Re-sensitizes Multiple Myeloma to Treatment 1, Ph.D. Henna Bazai 1, Anita Sekula 1, William Fogler 2, Ted Smith 2, John Magnani 2 and Abdel Kareem
Supplementary Figure (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were
 Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
Supplementary Figure 1. Gd@C 82 (OH) 22 nanoparticles did not affect cell viability and apoposis. MDA-MB-231, MCF-7, MCF-10A and BT549 cells were treated with PBS, Gd@C 82 (OH) 22, C 60 (OH) 22 or GdCl
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells
 The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
The effect of insulin on chemotherapeutic drug sensitivity in human esophageal and lung cancer cells Published in: Natl Med J China, February 10, 2003; Vol 83, No 3, Page 195-197. Authors: JIAO Shun-Chang,
Berberine Sensitizes Human Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin Through mir-93/ PTEN/Akt Signaling Pathway
 Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
Chen Accepted: et al.: February Berberine 24, Sensitizes 2015 Ovarian Cancer Cells to Cisplatin www.karger.com/cpb 956 1421-9778/15/0363-0956$39.50/0 Original Paper This is an Open Access article licensed
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells
 PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
PUMA gene transfection can enhance the sensitivity of epirubicin-induced apoptosis of MCF-7 breast cancer cells C.-G. Sun 1 *, J. Zhuang 1 *, W.-J. Teng 1, Z. Wang 2 and S.-S. Du 3 1 Department of Oncology,
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA
 PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
PATHOBIOLOGY OF NEOPLASIA Department of Pathology Gadjah Mada University School of Medicine dr. Harijadi Blok Biomedis, 6 Maret 2009 [12] 3/17/2009 1 The pathobiology of neoplasia Normal cells Malignant
Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
 Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3215463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3215463 Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Oncology Volume 2016, Article ID 3215463, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3215463 Research Article Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Expression in Indonesian Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension
 Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Role of Inflammation in Pulmonary Hypertension K. R. Stenmark University of Colorado Denver, USA Prominent Fibroproliferative Changes are Observed in the Lung Vasculature of Infants With Pulmonary Arterial
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal. regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation
 Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Amniotic fluid stem cells provide considerable advantages in epidermal regeneration: B7H4 creates a moderate inflammation microenvironment to promote wound repair Qing Sun 1, +, Fang Li 1, +, Hong Li 2,
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This is a well written and well executed study describing a novel mechanism of pro-angiogenic signalling which may, potentially, help to explain
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): This is a well written and well executed study describing a novel mechanism of pro-angiogenic signalling which may, potentially, help to explain
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis
 The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
The Process of Angiogenesis & Inhibition of Angiogenesis and/or Lymphangiogenesis Nam Deuk Kim, Ph.D. Pusan National University Contents Part 1. The process of angiogenesis Part 2. The role of angiopoietins
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION Collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen types
I TESSUTI: Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli Studi di Genova
 I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
I TESSUTI: 1. Repair, Radiosensitivity, Recruitment, Repopulation, Reoxygenation 2. Acute and chronic hypoxia 3. Tissue microenvironment and tissue organization Dott.ssa Liliana Belgioia Università degli
Essential Medium, containing 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/ml penicillin and 100 µg/ml streptomycin. Huvec were cultured in
 Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Supplemental data Methods Cell culture media formulations A-431 and U-87 MG cells were maintained in Dulbecco s Modified Eagle s Medium. FaDu cells were cultured in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium, containing
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016)
 International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
International Conference on Biomedical and Biological Engineering (BBE 2016) Injury Mechanism of Sub-Micron Calcium Oxalate Monohydrate and Dihydrate Crystals on Renal Epithelial Cells Poonam BHADJA, Kai
The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer
 Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
Ang2 Ang1 The Angiopoietin Axis in Cancer Tie2 An Overview: The Angiopoietin Axis Plays an Essential Role in the Regulation of Tumor Angiogenesis Growth of a tumor beyond a limiting size is dependent upon
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176
 human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
human Total Cathepsin B Catalog Number: DY2176 This DuoSet ELISA Development kit contains the basic components required for the development of sandwich ELISAs to measure natural and recombinant human Total
Safranal inhibits the migration and invasion of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by overcoming epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (2): 817-821 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Safranal inhibits the migration and invasion of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by overcoming epithelial-mesenchymal
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (2): 817-821 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info Safranal inhibits the migration and invasion of human oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by overcoming epithelial-mesenchymal
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION. Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent
 CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
CHAPTER VII CONCLUDING REMARKS AND FUTURE DIRECTION Stathmin in Prostate Cancer Development and Progression Androgen deprivation therapy is the most used treatment of de novo or recurrent metastatic PCa.
Tissue renewal and Repair. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science
 Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
Tissue renewal and Repair Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD Email: nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Faculty of Science Topic Objectives 1. Describe processes of tissue repair, regeneration
IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING
 IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING Nancy J. Poindexter, Ryan Williams, Garth Powis, Sunil Chada, and Elizabeth A. Grimm & Introgen Therapeutics, Inc., Houston, TX IL-24/MDA 24/MDA-77 is a Tumor Suppressor
IL-24 AND ITS ROLE IN WOUND HEALING Nancy J. Poindexter, Ryan Williams, Garth Powis, Sunil Chada, and Elizabeth A. Grimm & Introgen Therapeutics, Inc., Houston, TX IL-24/MDA 24/MDA-77 is a Tumor Suppressor
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
Supporting Information Pang et al. 10.1073/pnas.1322009111 SI Materials and Methods ELISAs. These assays were performed as previously described (1). ELISA plates (MaxiSorp Nunc; Thermo Fisher Scientific)
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST. No conflicts of interest
 DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
DECLARATION OF CONFLICT OF INTEREST No conflicts of interest University Heart Centre Tübingen Angiogenic actions of platelets Meinrad Gawaz, MD, FESC Tübingen, Germany ESC 2011 Paris GPIb GPIb GPVI TxA2
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl
 mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
mirna Dr. S Hosseini-Asl 1 2 MicroRNAs (mirnas) are small noncoding RNAs which enhance the cleavage or translational repression of specific mrna with recognition site(s) in the 3 - untranslated region
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation
 Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Reduction of angiocidin contributes to decreased HepG2 cell proliferation Guan XG 1, Guan XQ 2, Feng K 3, Jian R 3, Tian D 1, Tian D 1, Tong HB 1, *Sun X 1 1. Life Science Research Center, Beihua University,
Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN
 Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN Liexiang Zhang 1,3,*, Wei Jin 2, Jing Zheng 3, Yuxiang Dai 2,Yue Song 1, Hongbin Ni 2, 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum
Inhibiting mirna-30a-3p has anti-tumor effects in glioma cancer via PTEN Liexiang Zhang 1,3,*, Wei Jin 2, Jing Zheng 3, Yuxiang Dai 2,Yue Song 1, Hongbin Ni 2, 1. Department of Neurosurgery, Nanjing Drum
B-cell. Astrocyte SCI SCI. T-cell
 RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
RF #2015 P-01 PI: Azizul Haque, PhD Grant Title: Targeting Enolase in Spinal Cord Injury 12-month Technical Progress Report Progress Report (First Six Months): Enolase is one of the most abundantly expressed
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice
 Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Effect of a nutrient mixture on the localization of extracellular matrix proteins in HeLa human cervical cancer xenografts in female nude mice Publication from the Dr. Rath Research Institute Experimental
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance
 Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
Signaling Vascular Morphogenesis and Maintenance Douglas Hanahan Science 277: 48-50, in Perspectives (1997) Blood vessels are constructed by two processes: vasculogenesis, whereby a primitive vascular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
DOI:.38/ncb3399 a b c d FSP DAPI 5mm mm 5mm 5mm e Correspond to melanoma in-situ Figure a DCT FSP- f MITF mm mm MlanaA melanoma in-situ DCT 5mm FSP- mm mm mm mm mm g melanoma in-situ MITF MlanaA mm mm
Boucher et al NCOMMS B
 1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
1 Supplementary Figure 1 (linked to Figure 1). mvegfr1 constitutively internalizes in endothelial cells. (a) Immunoblot of mflt1 from undifferentiated mouse embryonic stem (ES) cells with indicated genotypes;
Healing & Repair. Tissue Regeneration
 Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
Healing & Repair Dr. Srikumar Chakravarthi Repair & Healing: Are they same? Repair :Regeneration of injured cells by cells of same type, as with regeneration of skin/oral mucosa (requires basement membrane)
p = formed with HCI-001 p = Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-002 Control Bevacizumab + 17AAG Bevacizumab 17AAG
 A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
A.. Relative # of ECs associated with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 ol b p < 0.001 Relative # of blood vessels that formed with HCI-001 1.4 1.2 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 l b p = 0.002 Control IHC:
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture:
 Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
Transformation of Normal HMECs (Human Mammary Epithelial Cells) into Metastatic Breast Cancer Cells: Introduction - The Broad Picture: Spandana Baruah December, 2016 Cancer is defined as: «A disease caused
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER. Andrew Leask.
 CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
CCN1: A NOVEL TARGET FOR PANCREATIC CANCER Andrew Leask CIHR Group in Skeletal Development and Remodeling, Division of Oral Biology and Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, Schulich School of Medicine
CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells
 Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
Effect of ST2825 on the proliferation and apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells Y. Deng, J. Sun and L.D. Zhang Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery Institute, Southwest Hospital, Third Military
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells
 CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
CD34 + VEGFR-3 + progenitor cells have a potential to differentiate towards lymphatic endothelial cells Tan YZ et al. J Cell Mol Med. (2014 Mar;18(3):422-33) Denise Traxler-Weidenauer April 2014 Introduction
IMMP8-1. Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells
 IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
IMMP8-1 Different Mechanisms of Androg and IPAD on Apoptosis Induction in Cervical Cancer Cells Assanan Dokmaikaew* Tipaya Ekalaksananan** Dr.Chamsai Pientong** ABSTRACT Androg and IPAD are recently known
Sequence Coverage (%) Profilin-1 P UD 2
 Protein Name Accession Number (Swissprot) Sequence Coverage (%) No. of MS/MS Queries Mascot Score 1 Reference Cytoskeletal proteins Beta-actin P60709 37 14 298 Alpha-actin P68032 33 10 141 20 Beta-actin-like
Protein Name Accession Number (Swissprot) Sequence Coverage (%) No. of MS/MS Queries Mascot Score 1 Reference Cytoskeletal proteins Beta-actin P60709 37 14 298 Alpha-actin P68032 33 10 141 20 Beta-actin-like
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
DOI: 10.1038/ncb3021 Supplementary figure 1 Characterisation of TIMPless fibroblasts. a) Relative gene expression of TIMPs1-4 by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) in WT or ΔTimp fibroblasts (mean ±
Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for evaluating cell proliferation and invasion using multicellular tumor spheroids.
 The Next Step in the Evolution of 3D Culture: Utilizing Extracellular Matrix to Enhance Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models for Proliferation and Invasion Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for
The Next Step in the Evolution of 3D Culture: Utilizing Extracellular Matrix to Enhance Multicellular Tumor Spheroid Models for Proliferation and Invasion Overview of methodology, tools and reagents for
TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0560 TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrew S. Kraft, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-12-1-0560 TITLE: Overcoming Resistance to Inhibitors of the Akt Protein Kinase by Modulation of the Pim Kinase Pathway PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Andrew S. Kraft, MD CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION:
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A)
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats
 Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
Pharmaceutical The effect of ulinastatin combined with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on directional repairing of liver ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats Objective: To investigate repairing effect
Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells
 [Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
[Chinese Journal of Cancer 27:8, 102-108; August 2008]; 2008 Sun Yat-Sen University Cancer Center Basic Research Paper Effect of starvation-induced autophagy on cell cycle of tumor cells Jun-Na Ge, 1 Dan
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons
 SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
SIBLINGs, cancer's multifunctional weapons 6/18/08 Akeila Bellahcène and Vincent Castronovo of the Metastasis Research laboratory of the University of Liège are among the first researchers to have discovered
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1
 Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
Integrin v 3 targeted therapy for Kaposi s sarcoma with an in vitro evolved antibody 1 CHRISTOPH RADER, 2 MIKHAIL POPKOV, JOHN A. NEVES, AND CARLOS F. BARBAS III 2 Department of Molecular Biology and The
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION. Tang Feng 1, Hongchi Yu 1, Qing Xia 1, Yunlong Ma 1, Hongmei Yin 2, Yang Shen 1 and Xiaoheng Liu 1.
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 41), pp: 69577-69593 Cross-talk mechanism between endothelial cells and hepatocellular carcinoma cells via growth factors and integrin pathway promotes tumor angiogenesis and cell
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No. 41), pp: 69577-69593 Cross-talk mechanism between endothelial cells and hepatocellular carcinoma cells via growth factors and integrin pathway promotes tumor angiogenesis and cell
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
The Hallmarks of Cancer
 The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
The Hallmarks of Cancer Theresa L. Hodin, Ph.D. Clinical Research Services Theresa.Hodin@RoswellPark.org Hippocrates Cancer surgery, circa 1689 Cancer Surgery Today 1971: Nixon declares War on Cancer
Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells
 Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 14 (2006) 3218 3222 Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells Chuandong Fan, a,c Weiwei Wang, a,c Baoxiang Zhao, b, Shangli Zhang
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 14 (2006) 3218 3222 Chloroquine inhibits cell growth and induces cell death in A549 lung cancer cells Chuandong Fan, a,c Weiwei Wang, a,c Baoxiang Zhao, b, Shangli Zhang
Collagenase Assay Kit
 Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Collagenase Assay Kit Catalog # 31 and 32 For Research Use Only - Not Human or Therapeutic Use INTRODUCTION The collagenases are members of the matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) family and degrade collagen
Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2
 ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 785-798, 2017 Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2 Hai-li Lang 1*, Guo-wen
ONCOLOGY REPORTS 38: 785-798, 2017 Glioma cells enhance angiogenesis and inhibit endothelial cell apoptosis through the release of exosomes that contain long non-coding RNA CCAT2 Hai-li Lang 1*, Guo-wen
Organic Semiconducting Photoacoustic. Nanodroplets for Laser-Activatable Ultrasound. Imaging and Combinational Cancer Therapy
 Organic Semiconducting Photoacoustic Nanodroplets for Laser-Activatable Ultrasound Imaging and Combinational Cancer Therapy Wei Tang, Zhen Yang *, Sheng Wang, Zhantong Wang, Jibin Song, Guocan Yu, Wenpei
Organic Semiconducting Photoacoustic Nanodroplets for Laser-Activatable Ultrasound Imaging and Combinational Cancer Therapy Wei Tang, Zhen Yang *, Sheng Wang, Zhantong Wang, Jibin Song, Guocan Yu, Wenpei
Product Datasheet. IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB Unit Size: 0.1 ml
 Product Datasheet IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB110-87052 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 2 Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications,
Product Datasheet IGF-I R Antibody (3G5C1) NB110-87052 Unit Size: 0.1 ml Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Reviews: 2 Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ONCOLOGY 54: , 2019
 326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
326 Paclitaxel resistant gastric cancer MGC 803 cells promote epithelial to mesenchymal transition and chemoresistance in paclitaxel sensitive cells via exosomal delivery of mir 155 5p MEI WANG 1,2, RONG
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer
 Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
Low levels of serum mir-99a is a predictor of poor prognosis in breast cancer J. Li 1, Z.J. Song 2, Y.Y. Wang 1, Y. Yin 1, Y. Liu 1 and X. Nan 1 1 Tumor Research Department, Shaanxi Provincial Tumor Hospital,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via
 Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Materials microrna-200b and microrna-200c promote colorectal cancer cell proliferation via targeting the reversion-inducing cysteine-rich protein with Kazal motifs Supplementary Table 1.
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red)
 Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
