Pyruvate Kinase M2 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker and Predicts Tumor Progression in Human Biliary Tract Cancer
|
|
|
- June Stone
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Pyruvate Kinase M2 Is a Novel Diagnostic Marker and Predicts Tumor Progression in Human Biliary Tract Cancer Dipok Kumar Dhar, MD 1,2 ; Steven W.M. Olde Damink, MD 2,3 ; James Hal Brindley, MD 1 ; Andrew Godfrey, MD 1 ; Michael H. Chapman, MD 1 ; Neomal S. Sandanayake, MD 1 ; Fausto Andreola, PhD 1 ; Sybille Mazurek, PhD 4 ; Tayyaba Hasan, PhD 5 ; Massimo Malago, MD 2 ; and Stephen P. Pereira, MD, PhD 1 BACKGROUND: The early diagnosis of biliary tract cancer (BTC) remains challenging, and there are few effective therapies. This study investigated whether the M2 isotype of pyruvate kinase (M2-PK), which serves as the key regulator of cellular energy metabolism in proliferating cells, could play a role in the diagnosis and therapy of BTC. METHODS: Plasma and bile M2-PK concentrations were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay in 88 patients with BTC, 79 with benign biliary diseases, and 17 healthy controls. M2-PK expression was assayed in a BTC tissue array by immunohistochemistry. The role of M2-PK in tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis was evaluated in BTC cell lines by retrovirus-mediated M2-PK transfection and short hairpin RNA silencing techniques. RESULTS: Sensitivity (90.3%) and specificity (84.3%) of bile M2-PK for malignancy were significantly higher than those for plasma M2-PK and serum carbohydrate antigen M2-PK expression was specific for cancer cells and correlated with microvessel density. M2-PK positivity was a significant independent prognostic factor by multivariable analysis. Transfection of M2-PK in a negatively expressed cell line (HuCCT-1 cells) increased cell invasion, whereas silencing in an M2-PK positive cell line (TFK cells) decreased tumor nodule formation and cellular invasion. A significant increase in endothelial tube formation was noted when supernatants from M2-PK transfected cells were added to an in vitro angiogenesis assay, whereas supernatants from silenced cells negated endothelial tube formation. CONCLUSIONS: Bile M2-PK is a novel tumor marker for BTC and correlates with tumor aggressiveness and poor outcome. Short hairpin RNA mediated inhibition of M2-PK indicates the potential of M2-PK as a therapeutic target. Cancer 2013;119: VC 2012 American Cancer Society. KEYWORDS: pyruvate kinase M2, cholangiocarcinoma, invasion, angiogenesis, diagnosis. INTRODUCTION Biliary tract cancer (BTC), comprising cholangiocarcinoma and the less common cancer of the gallbladder, is one of the deadliest malignancies after pancreatic cancer, with similar incidence and mortality rates. Surgical resection provides the best hope of survival when diagnosed at an early stage, but of the 10% to 30% of cases where surgery is feasible, only a few patients survive beyond 3 years. 1,2 In most patients, relief of biliary obstruction and palliative chemotherapy are the mainstays of therapy. In patients presenting with biliary symptoms, the diagnosis is largely based on the clinical presentation of cholestasis, abdominal pain, and weight loss, together with cross-sectional imaging studies, but it is often difficult to differentiate between BTC and benign stricturing conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). Endobiliary procedures such as forceps biopsy, or brush or aspiration cytology have high (95%-100%) specificity but are invasive and have a sensitivity of only 40% to 70%. 3 Liver biochemical abnormalities and the standard tumor markers such as carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) and carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) are of limited value. Serum levels of CA19-9 are elevated in up to 50% to 85% of patients with BTC, but CA19-9 elevation can also occur in obstructive jaundice without malignancy. Other tumor markers such as DU-PAN-2, cancer antigen 125, and RCAS1 (receptor binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells) have performed similarly or less well than CA19-9 and are not part of routine clinical practice. 4 A reliable tumor marker that could discriminate between benign biliary disease and BTC would be a useful addition to the current diagnostic work-up for BTC. One such potential biomarker is the pyruvate kinase isoenzyme type M2 (M2-PK). Pyruvate kinase plays a vital role in the final step of glycolysis, which produces pyruvate and adenosine triphosphate from glucose degradation. The M2-PK is the characteristic pyruvate kinase isoenzyme of all proliferating cells including tumor cells. A unique feature of Corresponding author: Stephen P. Pereira, MD, PhD, PhD, UCL Institute of Liver and Digestive Health, University College London Medical School, Royal Free Campus, London NW3 2PF, United Kingdom; Fax: (011) ; stephen.pereira@ucl.ac.uk We are grateful to Ms Anja Döring of ScheBo Biotech AG, Germany, for her excellent technical support for setting up the M2-PK ELISA measurement. 1 UCL Institute of Liver and Digestive Health, University College London Medical School, Royal Free Campus, London, United Kingdom; 2 Academic Department of Surgery, University College London Medical School, Royal Free Campus, London, United Kingdom; 3 Department of Surgery, Maastricht University Medical Centre, and Nutrition and Toxicology Research Institute (NUTRIM), Maastricht University, Maastricht, the Netherlands; 4 Institute for Veterinary Physiology and Biochemistry, Justus-Liebig University of Giessen, Giessen, Germany; 5 Wellman Centre for Photomedicine, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts DOI: /cncr.27611, Received: December 21, 2011; Revised: March 5, 2012; Accepted: March 15, 15, Published online August 1, 2012 in Wiley Online Library (wileyonlinelibrary.com) Cancer February 1,
2 Original Article M2-PK is that this isoenzyme may appear in different conformations: a highly active tetrameric and a nearly inactive dimeric form. The dimeric form works as a dam to build-up the intermediary macromolecules upfront in the glycolytic pathway which are subsequently used as cell building blocks such as fatty acids, amino acids and nucleic acids for cell proliferation. In tumors, M2-PK is found to be mainly in the dimeric form and has therefore been termed tumor M2-PK. 5 Currently, the dimeric form can be detected by a specific antibody raised against it which does not react with the tetrameric form. M2-PK can be detected in different body fluids, such as plasma, stool, and pleural fluid, and may have a role in the diagnosis of solid tumors including lung, ovary, cervix, breast, kidney, gastrointestinal tumors, and melanoma As yet, however, the role of M2-PK in bile as a marker for BTC has not been investigated. In this study, for the quantification of the dimeric form of M2-PK in plasma and bile samples, a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique was used, which is based on 2 monoclonal antibodies directed against the dimeric M2-PK. The antibody used for immunohistochemistry (clone DF4) was shown to discriminate between the dimeric and tetrameric forms of M2-PK and only stains the dimeric form. In western blots, the antibody stains total M2-PK protein and reflects M2-PK expression. In this study, we determined both plasma M2-PK (pm2-pk) and bile M2-PK (bm2-pk) in BTC and correlated the results with clinicopathological characteristics and patient prognosis. We also used a tissue array platform to determine the M2-PK expression pattern in BTC and correlated the results with clinicopathological parameters, including neoangiogenesis. Finally, we performed a series of in vitro studies in BTC cell lines to characterize the role of M2-PK in cell proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis, and as a potential therapeutic target. MATERIALS AND METHODS Patients A total of 167 patients were included in this study: 1) patients with histologically/cytologically proven BTC (n ¼ 88), and 2) patients with benign biliary conditions (BBC, n ¼ 79) including obstructive jaundice secondary to biliary stones or benign biliary strictures, sphincter of Oddi dysfunction, autoimmune pancreatitis, and PSC. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1. Seventeen healthy controls also donated blood samples for the study; however, data from healthy controls were not used in generating the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Informed consent was obtained from all subjects for use Table 1. Patient Characteristics Characteristic Value Tumor type Cholangiocarcinoma 82 (93%) Gallbladder cancer 6 (7%) Tumor location Intrahepatic (peripheral) 5 (6%) Perihilar (Klatskin) 62 (76%) Extrahepatic (distal) 15 (18%) Clinical T classification T1 4 (4%) T2 20 (23%) T3 34 (39%) T4 27 (31%) Unknown 3 (3%) Benign biliary conditions Choledocholithiasis 17 (22%) Primary sclerosing cholangitis 17 (22%) Benign biliary stricture 13 (16%) Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction 15 (18%) Miscellaneous a 17 (22%) a Includes hepatopancreatobiliary inflammatory conditions, including hepatitis of different causes with biliary stricture. of clinical material for research purposes, and the protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the UCL Institute of Hepatology. Measurement of M2-PK Concentrations in EDTA Plasma and Bile Samples by ELISA An ELISA kit (kindly provided as a gift from ScheBo Biotech, Giessen, Germany) was used for measuring bm2- PK and pm2-pk. In brief, diluted samples were added to 96-well plates coated with anti M2-PK antibody. After 60 minutes of incubation and several rinses, plates were incubated with a biotin-conjugated anti M2-PK monoclonal antibody for 30 minutes. Bound M2-PK molecules were detected with a streptavidin-coupled horseradish peroxidase reaction, and the plates were read at 450 nm using a spectrophotometer. All samples were assayed in duplicate. Immunohistochemistry of M2-PK and CD34 A commercially available tissue array (Stretton Scientific Ltd, UK), comprising 46 BTC samples and 2 normal biliary epithelial tissues in duplicate, was used for dual immunostaining to simultaneously localize M2-PK and microvessels. Immunostaining was done with a double staining kit according to the manufacturer s instructions (PicTrue kit, Invitrogen, UK). Sections were incubated simultaneously with anti M2-PK antibody (anti-human M2-PK antibody, ScheBo Biotech UK Ltd) and antihuman CD34 antibody overnight at 4 C. Two distinct substrate/chromogen/enzyme systems were used: 576 Cancer February 1, 2013
3 M2-PK in Biliary Tract Cancer/Dhar et al immunoglobulin G (IgG) horseradish peroxidase produced brown color (M2-PK) whereas IgG alkaline phosphatase with Fast Red produced red color (blood vessels). M2-PK staining was evaluated according to a scoring formula, and number of microvessel density (MVD) was counted as described. 11 Cell Lines Four established human BTC cell lines (HuCCT, TFK, SKCHA, and SG231) were used for this study; they were purchased from Japan Health Sciences Foundation, Japan, and DSMZ Scientifica, Germany. All cell lines were maintained in Roswell Park Memorial Institute (RPMI) medium. Transfection of M2-PK For M2-PK transfection experiments, a lentivirus vector was used for stable transfection of the full-length M2-PK gene. The M2-PK gene incorporated into the potb7 plasmid was purchased from Gene Services Ltd, Cambridge, UK. An expression vector was constructed with the psin vector (gift from Yasuhiro Ikeda, Windeyer Institute) and the M2-PK gene driven by the SFFV promoter. Coexpression of enhanced green fluorescent protein (egfp) was obtained by using an internal ribosomal entry site (IRES; gift from Chris Boshoff, University College London). HuCCT cells were infected with different clones of M2-PK recombinant virus for stable transfection and monitored by GFP expression. The clone with the highest expression of M2-PK (HuCCT-CM92) was selected for subsequent analysis. A control virus without M2-PK but with GFP insert wasusedasanegativecontrol(hucct-rig2).expression of M2-PK was checked by both western blot and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and the strongest clone was selected for further experiments. Silencing of M2-PK by Short Hairpin RNA For silencing M2-PK expression, we used a commercially available genome-wide plasmid based short hairpin RNA (SureSilencing shrna, Superarray Bioscience). According to the manufacturer, 4 distinct M2-PK specific shrna targeting sequences were designed using a proprietary algorithm and cloned into the pgeneclip hmgfp vector (Promega) to generate SureSilencing shrna plasmids. Transfection-grade SureSilencing plasmids (0.8 mg) (4 gene-specific and 1 scramble) were delivered by using the transfection reagent SureFECT to approximately 80,000 TFK cells. Silencing was confirmed by both real-time PCR and western blot. Among the 4 shrna clones (B, G, R, and Y), clone B did not inhibit M2-PK expression and was discarded. Cells transfected with the negative control plasmid were used as negative controls. Western Blot Analysis Approximately 20 lg of protein was run on precast gels and transferred onto polyvinylidene fluoride membranes (Amersham, Little Chalfont, UK). Following overnight blocking, the membrane was incubated with anti-human M2-PK antibody and then incubated with horseradish peroxidase linked secondary antibody (Dako, Glostrup, Denmark). The antigen-antibody reaction was visualized using enhanced chemiluminescence. We used anti bactin antibody (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, Mo) as protein load control. Quantitative RT-PCR Analysis Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen, Santa Clarita, Calif) and reverse transcribed with the SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System (Invitrogen Ltd, Paisley, UK). Amplification by quantitative RT-PCR (qrt-pcr) was performed using an ABI 7500 real-time PCR machine following standard procedures. M2-PK gene-specific primers (Superarray Bioscience, Frederick, Md) were used for the qrt-pcr reaction. MTS Assay Cell proliferation rate was determined by a colorimetric MTS assay (Promega, Madison, Wis). Approximately 3000 cells were added to each well in duplicate and incubated for predetermined periods before adding 20 ll of MTS Reagent to each well. Cells were incubated for another 3 hours, and the optical density was measured at 490 nm by means of spectrophotometry. Three-Dimensional Cell Culture A three-dimensional (3D) cell culture system (AlgiMatrix, Invitrogen, UK) incorporating a bioscaffold of alginate inside the 96-well plate was used. M2-PK was transfected, silenced, and the control cell lines were seeded within the scaffolds ( /well). Partial medium changes were done every 72 hours. At 3 weeks, cancer spheroids were counted from the surface and bottom of the plate in 10 randomly selected areas. Data were expressed as average number of spheroids per high-power field (400). Cell Migration Assay Tumor cell invasion was assayed in an invasion chamber (Cell Biolabs, San Diego, Calif) with 8 lm porosity polycarbonate membrane. The insert coated with Matrigel matrix was placed in each well of a 24-well plate filled with 300 ll of warm medium (RPMI without fetal bovine serum). The upper well contained suspension of tumor cells ( cells per milliliter of medium). After incubation at 37 C for 24 hours, the cells on the upper surface were gently scrubbed, and cells that had migrated through the filter were stained with AlamarBlue dye. Cancer February 1,
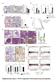
4 Original Article Figure 1. (A) Plasma and (B) bile pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK) levels of healthy controls, patients with benign biliary conditions, and biliary tract cancer are shown. (C) Pairwise comparison is shown of the pm2-pk and bm2-pk values of each individual patient with biliary tract cancer. (D) Comparison of receiver operating characteristic curves of pm2-pk, bm2-pk, and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9) is shown. Migrated cells were extracted with 200 ll of extraction solution and quantified by a spectrophotometer at 560 nm. All assays were performed in duplicate. In Vitro Angiogenesis We used 24-well plates containing early stage cocultures of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells and matrixproducing cells (TCS Angio Kit). Conditioned media from cell lines at different cultivation time points were added to the culture plate in appropriate wells and were replaced with fresh conditioned media on the fourth and seventh day of cultivation. Recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and suramin were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. Statistical Analyses Differences were compared by t test or Mann-Whitney U test as appropriate. For comparison of multiple groups, 1- way analysis of variance with Scheffe s post hoc test was used. The Spearman test was used as a measurement of correlation between continuous variables. A cutoff point for pm2-pk and bm2-pk was determined by using ROC analysis. Differences between categorical values were determined by chi-square test with Yate s correction. Survival was analyzed using the Kaplan-Meier method in combination with the log-rank test. Statistical significance was taken as P <.05 by SPSS software. RESULTS M2-PK Concentrations in Bile and Plasma Comparison of pm2-pk concentrations revealed no difference between benign biliary conditions (BBC) and healthy controls ( vs U/mL, mean standard deviation (SD), respectively, P ¼.22, analysis of variance with Scheffe s test) (Fig. 1A). However, in patients with BTC, pm2-pk level was significantly higher than in those with BBC ( vs U/ 578 Cancer February 1, 2013
5 M2-PK in Biliary Tract Cancer/Dhar et al ml, respectively; P <.001) (Fig. 1A). The bm2-pk concentration was U/mL in patients with BTC compared with U/mL in all noncancerous conditions (P <.001, t test; Fig. 1B), and only 4.1 U/mL (range, 1-17 U/mL) when 3 extreme values (45, 54, and 66 U/mL) in gallbladder bile samples from BBC patients collected at the time of cholecystectomy were excluded. In this cohort, the 17 patients with PSC had an average bm2-pk level of 15.2 U/mL, which was nonsignificantly higher than in the whole Benign Biliary Diseases group (12.3 U/mL). A paired analysis between pm2-pk and bm2-pk values in patients with BTC revealed that bm2- PK levels were always higher when compared with the pm2-pk level except in 1 case (Fig. 1C). ROC curves generated for bm2-pk showed 90.3% sensitivity and 84.3% specificity with a cutoff value of 24.4 U/mL, whereas the sensitivity and specificity for pm2-pk was 71.0% and 69.9%, respectively, at a cutoff value of 31.7 U/mL. The sensitivity and specificity for serum CA19-9 alone at a standard cutoff value of 37 U/mL were 69.4% and 78%, respectively (Fig. 1D). When considered as continuous variables, there was a significant positive correlation between the CA19-9 and M2-PK levels (bm2- PK and Ca19-9, P ¼.004, r 2 ¼ 39.4; pm2-pk and Ca19-9, P ¼.000, r 2 ¼ 36.4, Spearman rank correlation test). When the data were dichotomized (positive/negative) according to the set cutoff points, although bm2-pk and pm2-pk had 68.75% and 62.6% concordance with the CA19-9, respectively, they were still discordant in almost one-third of cases. When both M2-PK and CA19-9 status were taken into account, this did not improve the diagnostic sensitivity and specificity over the M2-PK alone status. Relationship Between M2-PK Status and Patient Survival Using the aforementioned cutoff values, patients were dichotomized into high (bm2-pk > 24.4 U/mL; pm2- PK > 31.7 U/mL) and low (bm2-pk 24.4 U/mL; pm2-pk 31.7 U/mL) for M2-PK. A total of 75 of 88 (85%) patients with BTC had up-to-date follow-up and outcome data. The prevalence of M2-PK positivity was significantly (P ¼.035) higher in patients aged 65 years and older, and there was a trend toward increased positivity in patients with advanced tumor T stage (P ¼.078) (Table 2). Patients with high pm2-pk levels had a shorter overall survival ( months) than patients with low M2-PK concentrations ( months) (P ¼.01, log-rank test), whereas a significant correlation could not be attained when patients were stratified by CA19-9 Table 2. Patient Characteristics Stratified by M2-PK Positivity a Parameter M2-PK Negative (n 5 21) M2-PK positive (n 5 54) Patient age, y Low ( 65) 12 (43) 16 (57).035 High (>65) 9 (19) 38 (81) Sex Male 10 (29) 25 (71).560 Female 11 (27) 29 (73) Serum bilirubin (lmol/l) Low ( 20) 7 (44) 9 (56).104 High (>20) 14 (24) 45 (76) CA19-9 level (U/mL) Low ( 37) 6 (30) 14 (70).515 High (>37) 15 (27) 40 (73) T classification T1 and T2 9 (45) 11 (55).078 T3 and T4 12 (22) 43 (78) Tumor location Intrahepatic (peripheral) 1 (20) 4 (80).896 Perihilar (Klatskin) 16 (29) 39 (71) Extrahepatic (distal) 3 (33) 6 (67) Gallbladder cancer 1 (17) 5 (83) a Numbers in parenthesis indicate percentages. positivity (P ¼.50) (Fig. 2). Multivariable analysis showed that a combination of bm2-pk and pm2-pk became an independent prognostic predictor (P ¼.04; hazard ratio ¼ 2.483) when adjusted for tumor stage, CA19-9 positivity, bilirubin level, and patient age. Besides M2-PK, patient age was the only independent predictor of survival (hazard ratio ¼ 2.038). Tissue Array: Correlation Between M2-PK and MVD M2-PK expression was not detectable in normal biliary epithelium, whereas it was detectable as cytoplasmic staining in most of the cancers (Fig. 3). Although variable amounts of infiltrating immune-competent cells were detectable in the vicinity of tumor nests, most of these cells were negative for M2-PK. Of 46 BTC cases, 17 (36%) had a score of 3 and were classified as negative for M2- PK. M2-PK positive tumors had significantly higher number of MVD when compared with M2-PK negative ones (mean SD; vs , respectively, P <.01, r 2 ¼ 71.3, P <.001, Spearman rank correlation test) (Fig. 3). Tissue M2-PK positivity was correlated with patient/tumor characteristics data provided with the tissue array slides by Stretton Scientific Ltd, UK. Lymph node metastasis was positive in 71% of patients with M2-PK positive tumors compared with P Cancer February 1,
6 Original Article Figure 2. Survival stratified by (left) pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK) and (right) carbohydrate antigen 19-9 (CA19-9). Patients with high M2-PK had significantly worse overall survival than those with low M2-PK. Figure 3. Double immunohistochemistry for pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK) (brown color) and CD34 (red color) in representative sections of biliary tract cancer shows (A) weak M2-PK expression with few blood vessels, (B, arrows) strong M2-PK expression with numerous blood vessels, and (C, arrows) negative expression in peritumoral lymphocytes ( 200). (D) Tumors with strong M2-PK expression were characterized by larger number of blood vessels, expressed as density per high-power field (HPF). 46% in those with negative tumors (P ¼.18, chi-square test). Tumors with advanced stage (T3 and T4) had significantly higher positivity for M2-PK than those with 580 lower stages (81% vs 27%, P < 0.01). The number of intratumoral infiltrating lymphocytes residing within the tumor nodules was counted in the 5 most densely Cancer February 1, 2013
7 M2-PK in Biliary Tract Cancer/Dhar et al Table 3. Correlation of Clinicopathological Parameters With M2-PK Expression in Tissue Array Parameter M2-PK P Negative Positive Sex.124 Male 8 20 Female 9 9 Age Tumor size Differentiation.256 Mild 3 4 Moderate 6 19 Poor 6 6 Unknown 2 0 Tumor location.213 Nonhilar Hilar 5 14 Unknown 0 2 Lymph node status.241 Negative 6 4 Positive 5 10 Unknown 6 15 T classification and and Microvessel density Number of intratumoral lymphocytes populated areas under a high-power objective (400) and the average used as the intratumoral lymphocyte count. There was a trend toward lower counts in M2-PK positive tumors when compared with the negative tumors ( vs , P ¼.191) (Table 3). Correlation With Cell Proliferation and Growth Strong M2-PK expression was noted in TFK, SKCHA, and SG231 cells, whereas HuCCT cells had very weak expression (Fig. 4A). For our transfection experiments, we selected TFK and HuCCT as BTC cell lines with high and low M2-PK expression, respectively. Subsequently, we transfected HuCCT cells with a full-length M2-PK gene in order to enhance M2-PK expression. For silencing of M2-PK expression in TFK cells, 4 different shrna clones (G, R, Y, and B), which are directed against 4 different locations of the PKM gene, were used. Changes in M2-PK expression both at protein (Fig. 4B,C) and messenger RNA level (data not shown) were checked in all transfected cells. All clones of shrna except clone B produced significant decrease in cell proliferation in TFK cells (Fig. 4E). M2-PK transfection of the HuCCT cell line almost doubled cell proliferation, whereas silencing of M2-PK in the TFK cell line inhibited it by up to 70% of the controls on day 5 (Fig. 4D). In M2-PK transfected HuCCT cells, there was a trend toward increased tumor nodule formation (P ¼.08; Fig. 5A,B,E), whereas silencing of M2-PK significantly inhibited tumor nodule formation when compared with the mock-treated cells (P <.01) (Fig. 5C,D,E). M2-PK and Cellular Invasion Representative photomicrographs demonstrate compact cellular growth and invasion on the under surface of the filter in transfected HuCCT cells (Fig. 6A), whereas only a few scattered cells were noted after silencing M2-PK in TFK cells (Fig. 6D). In HuCCT cells, M2-PK transfection induced a nearly 3-fold increase in the motility and invasion of the cells (P <.01; Fig. 6B). Silencing in TFK cells almost abolished the invasion through the Matrigelreconstituted basement membrane (P <.01; Fig. 6E), indicating a crucial role of M2-PK in cellular motility and invasion. M2-PK in Capillary Formation Incubation of human umbilical vascular endothelial cells with physiological concentrations of recombinant VEGF resulted in robust formation of capillary network at 7 days after initiation of the culture, whereas suramin, an angiogenesis inhibitor, almost abolished angiogenesis (Fig. 7A). A comparable angiogenic effect to that of VEGF was noted in wells supplemented with culture supernatant from M2-PK transfected HuCCT cells (Fig. 7D), which was significantly (P ¼.002) higher in comparison to wild-type HuCCT cells (Fig. 7C). Treatment with conditioned media from the M2-PK silenced cells was associated with a significant decrease in capillary formation (P ¼.019; Fig. 7F,G). DISCUSSION The results of this study provide evidence for the clinical significance and biological relevance of M2-PK in cell proliferation, growth, angiogenesis, and invasion in BTC. We demonstrated that M2-PK in bile and plasma can be used as novel diagnostic and prognostic markers for BTC, opening up the potential for earlier diagnosis of BTC and for use of M2-PK as a novel therapeutic target. pm2-pk levels were significantly higher in patients with BTC than in healthy controls (Fig. 1A), consistent with a previous report. 10 In our study, pm2-pk was higher in BBCs than in healthy controls but did not reach statistical significance (Fig. 1A). In the bile of patients with BTC, M2-PK levels were 9-fold higher in comparison to patients with BBC, including the PSC-only group (Fig. 1B), with a Cancer February 1,
8 Original Article Figure 4. (A) Strong pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK) expression was noted in all cell lines except HuCCT. (B) Gel shows M2-PK western blot of HuCCT cells following transfection with (right 3 lanes) or without (second lane from left) full-length M2-PK. (C) Gel shows M2-PK western blot of mock-treated TFK cells and TFK cells silenced with short hairpin RNAs (clones G, R, and Y). (D) Graph shows cell proliferation rates of mock-treated HuCCT, M2-PK transfected HuCCT, mock-treated TFK, and M2-PK silenced TFK cells. An MTS assay showed increased cell proliferation in M2-PK transfected HuCCT cells and significant growth inhibition in M2-PK silenced cells. (E) Antiproliferative effect of different shrna clones are shown; all clones except clone B had significant growth inhibition. sensitivity and specificity of 90.3% and 84.3%, respectively (Fig. 1D). When bm2-pk and pm2-pk values were compared, almost all patients with PSC with high plasma levels of M2-PK had low bm2-pk. Conversely, patients with BTC with low pm2-pk had high bm2-pk concentrations (Fig. 1C), pointing to a high discriminating capacity of bm2-pk for BTC and BBC. In contrast to bm2-pk, the measurement of CA19-9 and CEA in bile does not confer any additional advantage over their corresponding plasma levels. 12 M2-PK values have also been reported to be raised in inflammatory conditions such as arthritis. 13 The higher pm2-pk values in inflammatory conditions may be due to the systemic inflammatory response rather than local production of M2-PK. Indeed, in this study, M2-PK was rarely expressed by the infiltrating lymphocytes in BTC sections. Accordingly, Oehler et al 14 showed that M2-PK is expressed by neutrophils but not by lymphocytes, which may explain a higher level of circulatory M2-PK in inflammatory conditions. The treatment of BTC remains a daunting challenge for clinicians. To date, decision-making regarding the type and extent of therapy in BTC relies predominantly on cross-sectional imaging and biliary brushings. The results of this study indicate that M2-PK could be a useful prognostic marker in BTC. Indeed, M2-PK became an independent prognostic marker when analyzed with other conventional prognosticators in BTC. Similarly, in 582 Cancer February 1, 2013
9 M2-PK in Biliary Tract Cancer/Dhar et al Figure 5. Micrographs show three-dimensional spheroid formation of (A) parental HuCCT, (B) pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK)-transfected HuCCT, (C) parental TFK, and (D) M2-PK silenced TFK cells in the AlgiMatrix 3D cell culture system. (E) Graph shows mean number of spheroids per high power field. Figure 6. Micrographs show cells that migrated through the membrane, illustrating the invasive potential of (A) wild-type HuCCT, (B) pyruvate kinase M2 (M2-PK)-transfected HuCCT, (C) wild-type TFK, and (D) M2-PK silenced TFK cells. (E) Bars represent the mean standard deviation of optical density (OD) of cells measured at wavelength of 560 nm. melanoma patients, high M2-PK levels identified a group of patients with poorer survival.7 The poor outcome of tumors with high M2-PK content could be attributed to tumor progression and aggressive phenotype. In this study, M2-PK expression in tissue array was significantly raised in advanced tumor stages. Cancer February 1, 2013 M2-PK expressed by the immune-competent cells in the tumor milieu may also play a role in the aggressive phenotype of the tumor. Indeed, Zhang et al15 very recently showed that SOCS3 (suppressor of cytokine signaling 3) specifically binds to M2-PK in dendritic cells, causing dendritic cell dysfunction. Impaired antigen 583
10 Original Article Figure 7. Micrographs (magnification, 100) show capillary formation in the presence of (A) suramin, (B) recombinant vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), (C) cell culture supernatant of wild-type HuCCT, (D) supernatant of pyruvate kinase M2 (M2- PK)-transfected HuCCT cells, (E) supernatant of wild-type TFK cells, and (F) M2-PK silenced TFK cells. (G) Graph shows vascular area, and bars represent the mean standard deviation. presentation by the dysfunctional dendritic cells and a lack of production of tumor-specific lymphocytes were correlated with ineffective tumor vaccination in lung carcinoma. Whether a similar phenomenon is responsible for immune tolerance and aggressiveness of BTC warrants further investigation. In the 4 BTC cell lines studied, we found high M2- PK expression in all cell lines except in HuCCT. Similarly, in our tissue array study, high M2-PK expression (score >3) was noted in 64% of the BTC samples, whereas the normal biliary epithelial cells were all negative. These findings are in agreement with a recently published article describing M2-PK as the second highest differentially expressed gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. 16 To address the exact role of M2-PK in cellular proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis, we used TFK cells as a representative cell line with high M2-PK expression and used shrna to silence M2-PK. Silencing of M2- PK in TFK cells by shrna was accompanied by pronounced inhibition of cell proliferation (>70% on day 5 of culture). Conversely, M2-PK transfection of HuCCT cells causing high M2-PK expression increased cell proliferation by up to 50% on the third cultivation day. Silencing of M2-PK inhibited tumor growth significantly in 3D cell culture assays, with almost 80% inhibition of growth of tumor nodules, whereas transfection in HuCCT cells increased the tumor growth with enhanced sprouting of daughter nodules in the 3D cell culture assay. In keeping with these findings, we showed previously that cotransfection of oncogenic gag-a-raf fusion and wildtype M2-PK doubled colony formation in NIH 3T3 cells. 17 Very recently, Christofk et al 18,19 showed that in almost 90% of instances, tumor cells expressing the M2 isoform successfully produced tumors in mice, compared to <50% when cells expressing the M1 isoform were used. Only recently, the clinical relevance of M2-PK in tumor development has been shown in patients with Bloom syndrome, where presence of missense mutations of M2-PK results in the early development of multiple tumors. 20 In this study, transfection of M2-PK into HuCCT cells significantly increased cellular invasion, whereas silencing of M2-PK almost negated cell invasion. Similarly, a stepwise increase of pm2-pk concentrations from limited to extensive metastatic disease was noted in pancreatic carcinoma. 21 Interestingly, a differential proteome analysis on 2 hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines with high and low metastatic potentials showed that M2-PK was 1 of the 6 highly expressed proteins in the metastatic cells. 22 Angiogenesis is a hallmark of tumor aggressiveness. Thus far, the role of M2-PK in tumor angiogenesis has not been investigated. In our study, we found a significant correlation between M2-PK expression and the number of MVD. In the in vitro angiogenesis study, conditioned media from the M2-PK transfected cells significantly increased the number of nascent vessels, whereas those from the silenced cell line almost abolished angiogenesis to the same level as seen with suramin, an angiogenesis inhibitor. Although any direct correlation between M2-PK and angiogenesis is yet to be established, Duan et al 23 showed recently that M2-PK promotes angiogenesis by binding to tumor endothelial marker 8, a cell membrane protein predominantly expressed in tumor endothelium. M2-PK may also contribute to tumor angiogenesis in a 584 Cancer February 1, 2013
11 M2-PK in Biliary Tract Cancer/Dhar et al paracrine fashion by mast cell degranulation and release of angiogenic factors. 24 Interestingly, Terada et al 25 showed that the density of mast cells was significantly higher in BTC than in normal liver and hepatocellular carcinoma. Results of the shrna-based treatment raise the possibility of designing a novel antitumor treatment by targeting M2-PK, either alone or in combination with chemotherapeutic agents shown to be effective in this condition. Very recently, a selective small molecule inhibitor that inhibits cell proliferation has been described. 26 Moreover, a synergistic antitumor effect by a small molecule inhibitor raised against M2-PK, along with other anticancer agents such as cisplatin or gefitinib, has also been reported. 27 As such, a strategy of M2-PK inhibition would be a potential therapeutic approach in BTC. FUNDING SOURCES This study was supported in part by US National Institutes of Health grant PO1CA84203, UK Medical Research Council grant (G ), and Charitable Research Fund East and North Herts National Health Service Trust. Dipok Kumar Dhar is a Jason Boas Research Fellow, and this work was partly funded by the Jason Boas Charitable Fund. The work was undertaken at UCL Hospital/UCL, which receives a proportion of funding from the UK Department of Health s National Institute for Health Research Biomedical Research Centres funding scheme. CONFLICT OF INTEREST DISCLOSURE Sybille Mazurak was an employee of Schebo Biotech AG until June 2012 and owns stock in the company. REFERENCES 1. West J, Wood H, Logan RF, Quinn M, Aithal GP. Trends in the incidence of primary liver and biliary tract cancers in England and Wales Br J Cancer. 2006;94: Patel T. Cholangiocarcinoma controversies and challenges. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8: Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Enders FB, Halling KC, Lindor KD. Utility of serum tumor markers, imaging, and biliary cytology for detecting cholangiocarcinoma in primary sclerosing cholangitis. Hepatology. 2008;48: Nehls O, Gregor M, Klump B. Serum and bile markers for cholangiocarcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 2004;24: Mazurek S. Pyruvate kinase type M2: a key regulator of the metabolic budget system in tumor cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2011;43: Kaura B, Bagga R, Patel FD. Evaluation of the Pyruvate Kinase isoenzyme tumor (Tu M2-PK) as a tumor marker for cervical carcinoma. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2004;30: Ugurel S, Bell N, Sucker A, Zimpfer A, Rittgen W, Schadendorf D. Tumor type M2 pyruvate kinase (TuM2-PK) as a novel plasma tumor marker in melanoma. Int J Cancer. 2005;117: Hathurusinghe HR, Goonetilleke KS, Siriwardena AK. Current status of tumor M2 pyruvate kinase (Tumour M2-PK) as a biomarker of gastrointestinal malignancy. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007;14: Elia S, Massoud R, Guggino G, et al. Tumor type M2-pyruvate-kinase levels in pleural fluid versus plasma in cancer patients: a further tool to define the need for invasive procedures. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2008;33: Li YG, Zhang N. Clinical significance of serum tumour M2-PK and CA19-9 detection in the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Liver Dis. 2009;41: Dhar DK, Wang TC, Tabara H, et al. Expression of trefoil factor family members correlates with patient prognosis and neoangiogenesis. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11: Ohshio G, Manabe T, Watanabe Y, et al. Comparative studies of DU-PAN-2, carcinoembryonic antigen, and CA19-9 in the serum and bile of patients with pancreatic and biliary tract diseases: evaluation of the influence of obstructive jaundice. Am J Gastroenterol. 1990;85: Oremek GM, Müller R, Sapoutzis N, Wigand R. Pyruvate kinase type tumor M2 plasma levels in patients afflicted with rheumatic diseases. Anticancer Res. 2003;23(2A): Oehler R, Weingartmann G, Manhart N, et al. Polytrauma induces increased expression of pyruvate kinase in neutrophils. Blood. 2000;95: Zhang Z, Liu Q, Che Y, et al. Antigen presentation by dendritic cells in tumors is disrupted by altered metabolism that involves pyruvate kinase M2 and its interaction with SOCS3. Cancer Res. 2010;70: Hass HG, Nehls O, Jobst J, Frilling A, Vogel U, Kaiser S. Identification of osteopontin as the most consistently over-expressed gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma: detection by oligonucleotide microarray and real-time PCR analysis. World J Gastroenterol. 2008;14: Le Mellay V, Houben R, Troppmair J, et al. Regulation of glycolysis by Raf protein serine/threonine kinases. Adv Enzyme Regul. 2002;42: Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH, et al. The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 2008;452: Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Wu N, Asara JM, Cantley LC. Pyruvate kinase M2 is a phosphotyrosine-binding protein. Nature. 2008;452: Akhtar K, Gupta V, Koul A, Alam N, Bhat R, Bamezai RN. Differential behavior of missense mutations in the intersubunit contact domain of the human pyruvate kinase M2 isozyme. J Biol Chem. 2009;284: Cerwenka H, Aigner R, Bacher H, et al. TUM2-PK (pyruvate kinase type tumor M2), CA19-9 and CEA in patients with benign, malignant and metastasizing pancreatic lesions. Anticancer Res. 1999;19: Ding SJ, Li Y, Shao XX, et al. Proteome analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cell strains, MHCC97-H and MHCC97-L, with different metastasis potentials. Proteomics. 2004;4: Duan HF, Hu XW, Chen JL, et al. Antitumor activities of TEM8- Fc: an engineered antibody-like molecule targeting tumor endothelial marker 8. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2007;99: Ryu H, Walker JK, Kim S, et al. Regulation of M2-type pyruvate kinase mediated by the high-affinity IgE receptors is required for mast cell degranulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2008;154: Terada T, Matsunaga Y. Increased mast cells in hepatocellular carcinoma and intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Hepatol. 2000;33: Vander Heiden MG, Christofk HR, Schuman E, et al. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of pyruvate kinase M2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79: Guo W, Zhang Y, Chen T, et al. Efficacy of RNAi targeting of pyruvate kinase M2 combined with cisplatin in a lung cancer model. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2011;137: Cancer February 1,
Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells in lung-cancer-associated pleural effusion
 Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
Received: 1 May 2016 Revised: 19 June 2016 Accepted: 10 July 2016 DOI: 10.1111/crj.12527 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Diagnostic and prognostic significance of receptor-binding cancer antigen expressed on SiSo cells
(a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel)
 Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
Supplementary Figure 1. Functional enrichment analyses of secretomic proteins. (a) Significant biological processes (upper panel) and disease biomarkers (lower panel) 2 involved by hrab37-mediated secretory
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS. showed that all three replicates had similar growth trends (Figure 4.1) (p<0.05; p=0.0000)
 CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
CHAPTER 4 RESULTS 4.1 Growth Characterization of C. vulgaris 4.1.1 Optical Density Growth study of Chlorella vulgaris based on optical density at 620 nm (OD 620 ) showed that all three replicates had similar
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer
 Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Correlation between expression and significance of δ-catenin, CD31, and VEGF of non-small cell lung cancer X.L. Liu 1, L.D. Liu 2, S.G. Zhang 1, S.D. Dai 3, W.Y. Li 1 and L. Zhang 1 1 Thoracic Surgery,
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the
 Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
Supplementary Figure 1. HOPX is hypermethylated in NPC. (a) Methylation levels of HOPX in Normal (n = 24) and NPC (n = 24) tissues from the genome-wide methylation microarray data. Mean ± s.d.; Student
High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7779-7783 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info High expression of fibroblast activation protein is an adverse prognosticator in gastric cancer. Hu Song 1, Qi-yu Liu 2, Zhi-wei
Layered-IHC (L-IHC): A novel and robust approach to multiplexed immunohistochemistry So many markers and so little tissue
 Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Page 1 The need for multiplex detection of tissue biomarkers. There is a constant and growing demand for increased biomarker analysis in human tissue specimens. Analysis of tissue biomarkers is key to
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay RT-PCR and Western Blot
 Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Islet viability assay and Glucose Stimulated Insulin Secretion assay Islet cell viability was determined by colorimetric (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5- diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay using CellTiter
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction
 Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Navigating the Biliary Tract with CT & MR: An Imaging Approach to Bile Duct Obstruction Ann S. Fulcher, MD Medical College of Virginia Virginia Commonwealth University Richmond, Virginia Objectives To
Evaluation of tumor M2-pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK) as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer
 Bandara et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1360-3 RESEARCH Evaluation of tumor M2-pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK) as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer
Bandara et al. World Journal of Surgical Oncology (2018) 16:56 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-018-1360-3 RESEARCH Evaluation of tumor M2-pyruvate kinase (Tumor M2-PK) as a biomarker for pancreatic cancer
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
DOI: 10.1038/ncb2607 Figure S1 Elf5 loss promotes EMT in mammary epithelium while Elf5 overexpression inhibits TGFβ induced EMT. (a, c) Different confocal slices through the Z stack image. (b, d) 3D rendering
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
DOI: 1.138/ncb3355 a S1A8 + cells/ total.1.8.6.4.2 b S1A8/?-Actin c % T-cell proliferation 3 25 2 15 1 5 T cells Supplementary Figure 1 Inter-tumoral heterogeneity of MDSC accumulation in mammary tumor
CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 3713-3718 CircHIPK3 is upregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in epithelial ovarian cancer N. LIU 1, J. ZHANG 1, L.-Y. ZHANG 1, L.
Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases
 Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
Brief Communication Downregulation of serum mir-17 and mir-106b levels in gastric cancer and benign gastric diseases Qinghai Zeng 1 *, Cuihong Jin 2 *, Wenhang Chen 2, Fang Xia 3, Qi Wang 3, Fan Fan 4,
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and
 Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
Supplementary Information Luciferase reporter assay HEK293FT cells were transiently transfected with reporters, N3-ICD construct and increased amounts of wild type or kinase inactive EGFR. Transfections
CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay
 Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
Product Manual CytoSelect Tumor- Endothelium Adhesion Assay Catalog Number CBA- 215 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Cancer metastasis comprises several
RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using
 Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Supplementary Information Materials and Methods RNA extraction, RT-PCR and real-time PCR. Total RNA were extracted using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen,Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of. granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon. cancer
 An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
An epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-inducing potential of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in colon cancer Yaqiong Chen, Zhi Zhao, Yu Chen, Zhonglin Lv, Xin Ding, Renxi Wang, He Xiao,
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this. study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319,
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319, NCI-H1373, PC-3, PC-9,
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell lines and tissue samples. The 18 human NSCLC cell lines used in this study included eight adenocarcinoma cell lines (ADCs; A427, A549, LC319, NCI-H1373, PC-3, PC-9,
Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis
 Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Original papers Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF)-C, VEGF-D, VEGFR-3 and D2-40 expressions in primary breast cancer: Association with lymph node metastasis Aydan Eroğlu 1, A F, Cevriye Ersöz 2,
Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v)
 SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIAL AND METHODS Soft Agar Assay. For each cell pool, 100,000 cells were resuspended in 0.35% (w/v) top agar (LONZA, SeaKem LE Agarose cat.5004) and plated onto 0.5% (w/v) basal agar.
Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2018; 22: 5525-5530 Expression of mir-1294 is downregulated and predicts a poor prognosis in gastric cancer Y.-X. SHI, B.-L. YE, B.-R. HU, X.-J.
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2
 Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Supplementary Fig. 1: ATM is phosphorylated in HER2 breast cancer cell lines. (A) ATM is phosphorylated in SKBR3 cells depending on ATM and HER2 activity. Upper panel: Representative histograms for FACS
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells
 Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Effects of metallothionein-3 and metallothionein-1e gene transfection on proliferation, cell cycle, and apoptosis of esophageal cancer cells Z.Q. Tian 1, Y.Z. Xu 1, Y.F. Zhang 1, G.F. Ma 1, M. He 1 and
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis
 Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
Supplementary Figure 1: STAT3 suppresses Kras-induced lung tumorigenesis (a) Immunohistochemical (IHC) analysis of tyrosine 705 phosphorylation status of STAT3 (P- STAT3) in tumors and stroma (all-time
BIT 120. Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture
 BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
BIT 120 Copy of Cancer/HIV Lecture Cancer DEFINITION Any abnormal growth of cells that has malignant potential i.e.. Leukemia Uncontrolled mitosis in WBC Genetic disease caused by an accumulation of mutations
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES, LEGENDS AND METHODS
 A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
A Hepatocyte Growth Factor Receptor (Met) Insulin Receptor hybrid governs hepatic glucose metabolism Arlee Fafalios, Jihong Ma, Xinping Tan, John Stoops, Jianhua Luo, Marie C. DeFrances and Reza Zarnegar
CytoSelect 24- Well Cell Invasion Assay (Basement Membrane, Fluorometric Format)
 Product Manual CytoSelect 24- Well Cell Invasion Assay (Basement Membrane, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA- 111 12 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
Product Manual CytoSelect 24- Well Cell Invasion Assay (Basement Membrane, Fluorometric Format) Catalog Number CBA- 111 12 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction
The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells
 1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
1 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION The toll-like receptor 4 ligands Mrp8 and Mrp14 play a critical role in the development of autoreactive CD8 + T cells Karin Loser 1,2,6, Thomas Vogl 2,3, Maik Voskort 1, Aloys
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test
 FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
FGL2 A new biomarker for cancer in a simple blood test WHO IS FGL2 Human gene (chromosome 7) is 7 kb long, 2 exons, monomer protein 70 KD, tetramer in solution. Fibrinogen-like protein 2 (Fgl2), a member
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR
 Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Gastric Carcinoma with Lymphoid Stroma: Association with Epstein Virus Genome demonstrated by PCR Pages with reference to book, From 305 To 307 Irshad N. Soomro,Samina Noorali,Syed Abdul Aziz,Suhail Muzaffar,Shahid
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico
 Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Colangitis Esclerosante Primaria: Manejo Clínico y Endoscópico Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques Associate Professor
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth.
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Supplementary Information Supplementary Fig. 1. Elevated Usp9x in melanoma and NRAS mutant melanoma cells are dependent on NRAS for 3D growth. a. Immunoblot for Usp9x protein in NRAS mutant melanoma cells
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation
 Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Construction of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line that stably expresses stathmin with a Ser25 phosphorylation site mutation J. Du 1, Z.H. Tao 2, J. Li 2, Y.K. Liu 3 and L. Gan 2 1 Department of Chemistry,
Cancer cells in vitro
 Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Supplementary Figure S1 Cancer cells in vitro Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Pretreatment with anti-u-par (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with Control IgG (18h) Acid Wash/Pretreatment with anti-u-par
Liver Cancer. Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine
 Liver Cancer Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine Primary Liver Cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) : > 80% Derived
Liver Cancer Su Jong Yu, M.D. Department of Internal Medicine, Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine Primary Liver Cancer Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) : > 80% Derived
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers
 Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Biochemistry of Cancer and Tumor Markers The term cancer applies to a group of diseases in which cells grow abnormally and form a malignant tumor. It is a long term multistage genetic process. The first
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set
 Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Human Urokinase / PLAU / UPA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10815 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma
 Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Characterization and significance of MUC1 and c-myc expression in elderly patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma Y.-J. Hu 1, X.-Y. Luo 2, Y. Yang 3, C.-Y. Chen 1, Z.-Y. Zhang 4 and X. Guo 1 1 Department
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
TECHNICAL BULLETIN. Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20 C
 Phospho-Stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20
Phospho-Stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 ELISA Kit for detection of human, mouse, or rat phospho-stat3 (ptyr 705 ) and pan-stat3 in cell and tissue lysates Catalog Number RAB0447 Storage Temperature 20
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM. Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator
 Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell
 Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell migration in gastric cancer cell lines Yan-Shen Shan 1, Hui-Ping Hsu 1, Ming-Derg Lai 2,3, Meng-Chi Yen 2,4, Wei-Ching Chen
Argininosuccinate synthetase 1 suppression and arginine restriction inhibit cell migration in gastric cancer cell lines Yan-Shen Shan 1, Hui-Ping Hsu 1, Ming-Derg Lai 2,3, Meng-Chi Yen 2,4, Wei-Ching Chen
RNA preparation from extracted paraffin cores:
 Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Supplementary methods, Nielsen et al., A comparison of PAM50 intrinsic subtyping with immunohistochemistry and clinical prognostic factors in tamoxifen-treated estrogen receptor positive breast cancer.
Advances in Computer Science Research, volume 59 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016)
 7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
7th International Conference on Education, Management, Computer and Medicine (EMCM 2016) Expression of Beta-Adrenergic Receptor in Glioma LN229 Cells and Its Effect on Cell Proliferation Ping Wang1, Qingluan
Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer
 Original Article DOI: 10.21276/awch.1782 Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Mohd Rafey 1, Kafil Akhtar 1 *, Atia Z Rab 2 and Shahid A Siddiqui
Original Article DOI: 10.21276/awch.1782 Serum Ca 15-3: A Useful Tumor Marker in the Prognostication of Locally Advanced Breast Cancer Mohd Rafey 1, Kafil Akhtar 1 *, Atia Z Rab 2 and Shahid A Siddiqui
MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands)
 Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Supplemental data Materials and Methods Cell culture MTC-TT and TPC-1 cell lines were cultured in RPMI medium (Gibco, Breda, The Netherlands) supplemented with 15% or 10% (for TPC-1) fetal bovine serum
Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers
 日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
日大医誌 75 (1): 10 15 (2016) 10 Original Article Implications of Progesterone Receptor Status for the Biology and Prognosis of Breast Cancers Naotaka Uchida 1), Yasuki Matsui 1), Takeshi Notsu 1) and Manabu
Product Datasheet. DARC Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg. Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5
 Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
Product Datasheet DARC Antibody NB100-2421 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at -20C. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 5 Protocols, Publications, Related Products, Reviews, Research Tools and Images at: www.novusbio.com/nb100-2421
(a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable
 Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
Supplementary Figure 1. Frameshift (FS) mutation in UVRAG. (a) Schematic diagram of the FS mutation of UVRAG in exon 8 containing the highly instable A 10 DNA repeat, generating a premature stop codon
April 5, :45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5*
 April 5, 2016 11:45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR CHAIR: DANNY A. MILNER, JR., BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL, BOSTON, MA VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5* *VIGNETTES
April 5, 2016 11:45 AM 1:45 PM MARRIOTT MARQUIS HOTEL & MARINA, MIRAMAR CHAIR: DANNY A. MILNER, JR., BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL, BOSTON, MA VIGNETTE 1 VIGNETTE 2 VIGNETTE 3* VIGNETTE 4* VIGNETTE 5* *VIGNETTES
Product Datasheet. CD133 Antibody NB Unit Size: 0.1 mg
 Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Product Datasheet CD133 Antibody NB120-16518 Unit Size: 0.1 mg Store at 4C short term. Aliquot and store at -20C long term. Avoid freeze-thaw cycles. Publications: 8 Protocols, Publications, Related Products,
Tumor Immunology. Tumor (latin) = swelling
 Tumor Immunology Tumor (latin) = swelling benign tumor malignant tumor Tumor immunology : the study of the types of antigens that are expressed by tumors how the immune system recognizes and responds to
Tumor Immunology Tumor (latin) = swelling benign tumor malignant tumor Tumor immunology : the study of the types of antigens that are expressed by tumors how the immune system recognizes and responds to
CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Southern California Los Angeles, CA 90033
 AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-01-0264 TITLE: Function of Klotho and is MicroRNA in Prostate Cancer and Aging PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Shao-Yao Ying, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Southern California
AD Award Number: W81XWH-07-01-0264 TITLE: Function of Klotho and is MicroRNA in Prostate Cancer and Aging PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Shao-Yao Ying, Ph.D. CONTRACTING ORGANIZATION: University of Southern California
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression
 Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
Cytokine Arrays Reveal Black Ops Tactics of Tumor-induced Immunosuppression Jarad J Wilson, Ph.D. Technical Support & Marketing Specialist Ruo-Pan Huang, MD, Ph.D. Founder and CEO What are Antibody Arrays?
PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human
 Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Anti-CD19-CAR transduced T-cell preparation PBMC from each patient were suspended in AIM V medium (Invitrogen) with 5% human AB serum (Gemini) and 300 international units/ml IL-2 (Novartis). T cell proliferation
Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2017; 21: 3397-3401 Expression of long non-coding RNA linc-itgb1 in breast cancer and its influence on prognosis and survival W.-X. LI 1, R.-L.
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535
 Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Data Sheet PD-1 / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #: 60535 Product Description Recombinant Jurkat T cell expressing firefly luciferase gene under the control of NFAT response elements with constitutive
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/55957 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Dekker T.J.A. Title: Optimizing breast cancer survival models based on conventional
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting
 mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
mir-509-5p and mir-1243 increase the sensitivity to gemcitabine by inhibiting epithelial-mesenchymal transition in pancreatic cancer Hidekazu Hiramoto, M.D. 1,3, Tomoki Muramatsu, Ph.D. 1, Daisuke Ichikawa,
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r
 Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
Real-time imaging reveals the single steps of brain metastasis fo mation r Yvonne Kienast, Louisa von Baumgarten, Martin Fuhrmann, Wolfgang E.F. Klinkert, Roland Goldbrunner, Jochen Herms and Frank Winkler
MSc CANCER CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (2008/9)
 Faculty of Medicine and Biological Sciences Department of Biochemistry MSc CANCER CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (2008/9) COURSE AIMS AND STRUCTURE Background The MSc in Cancer Cell and Molecular Biology is
Faculty of Medicine and Biological Sciences Department of Biochemistry MSc CANCER CELL AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY (2008/9) COURSE AIMS AND STRUCTURE Background The MSc in Cancer Cell and Molecular Biology is
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value
 Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
Study on the expression of MMP-9 and NF-κB proteins in epithelial ovarian cancer tissue and their clinical value Shen Wei 1,a, Chen Juan 2, Li Xiurong 1 and Yin Jie 1 1 Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology,
WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER?
 CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
CANCER STAGING TNM and prognosis in CRC WHAT SHOULD WE DO WITH TUMOUR BUDDING IN EARLY COLORECTAL CANCER? Alessandro Lugli, MD Institute of Pathology University of Bern Switzerland Maastricht, June 19
m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation and tumorigenicity of endometrial cancer
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Articles https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0174-4 In the format provided by the authors and unedited. m 6 A mrna methylation regulates AKT activity to promote the proliferation
Serum IL-8 and IL-12 Levels in Breast Cancer
 Medical Oncology, vol. 24, no. 2, 163 168, 2007 Copyright 2007 by Humana Press Inc. All rights of any nature whatsoever reserved. 1357-0560/(Online)1559-131X/07/24:163 168/$30.00 Original Article Serum
Medical Oncology, vol. 24, no. 2, 163 168, 2007 Copyright 2007 by Humana Press Inc. All rights of any nature whatsoever reserved. 1357-0560/(Online)1559-131X/07/24:163 168/$30.00 Original Article Serum
(A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish wild type (P1+P2), targeted (P1+P2) and excised (P1+P3)14-
 1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
1 Supplemental Figure Legends Figure S1. Mammary tumors of ErbB2 KI mice with 14-3-3σ ablation have elevated ErbB2 transcript levels and cell proliferation (A) PCR primers (arrows) designed to distinguish
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data
 Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Statistical Analysis of Biomarker Data Gary M. Clark, Ph.D. Vice President Biostatistics & Data Management Array BioPharma Inc. Boulder, CO NCIC Clinical Trials Group New Investigator Clinical Trials Course
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs
 Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Supplementary Fig. 1 p38 MAPK negatively regulates DC differentiation. (a) Western blot analysis of p38 isoform expression in BM cells, immature DCs (idcs) and mature DCs (mdcs). A myeloma cell line expressing
Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Decreased expression of mir-490-3p in osteosarcoma and its clinical significance B. TANG, C. LIU, Q.-M. ZHANG, M. NI Department of Orthopedics,
York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
 MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
MATERIALS AND METHODS Study population Blood samples were obtained from 15 patients with AS fulfilling the modified New York criteria, 6 RA patients and 10 age- and gender-matched healthy controls (HCs).
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay
 Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
Hepatitis B Antiviral Drug Development Multi-Marker Screening Assay Background ImQuest BioSciences has developed and qualified a single-plate method to expedite the screening of antiviral agents against
P atients with primary breast cancer have an increased risk of developing contralateral breast cancer1. When
 OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: BONE METASTASES BREAST CANCER Received 23 July 2013 Accepted 19 August 2013 Published 5 September 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to C.W.D. (ducaiwen@
OPEN SUBJECT AREAS: BONE METASTASES BREAST CANCER Received 23 July 2013 Accepted 19 August 2013 Published 5 September 2013 Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to C.W.D. (ducaiwen@
Impact of hyper-o-glcnacylation on apoptosis and NF-κB activity SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS 3D culture and cell proliferation- MiaPaCa-2 cell culture in 3D was performed as described previously (1). Briefly, 8-well glass chamber slides were evenly coated with 50 µl/well
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology
 Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Bihong Zhao, M.D, Ph.D Department of Pathology 04-28-2009 Is tumor self or non-self? How are tumor antigens generated? What are they? How does immune system respond? Introduction Tumor Antigens/Categories
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set
 Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
Human LDL Receptor / LDLR ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK10231 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized in
MELANOMA CANCER TEST
 MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
MELANOMA CANCER TEST Efficacy Evaluation of Antitumor Activity of Alka Vita - Alkahydroxy in the LOX-GFP Human Melanoma Model Final Report by: Anti-Cancer Lab San Diego California March 4, 2005 Efficacy
Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor
 Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
Figures Part of introduction Figure 1. Possible role of oncogene activation, receptor, G-protein mutation, or tumor supressor gene deletion in the induction of thyroid carcinoma. ( by James A Fagin, M.D.)
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer
 Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Molecular Testing in Lung Cancer Pimpin Incharoen, M.D. Assistant Professor, Thoracic Pathology Department of Pathology, Ramathibodi Hospital Genetic alterations in lung cancer Source: Khono et al, Trans
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer)
 Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) The Bile Duct System (Biliary Tract) A network of bile ducts (tubes) connects the liver and the gallbladder to the small intestine. This network begins in the liver
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando?
 Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
Tratamiento endoscópico de la CEP. En quien como y cuando? Andrés Cárdenas, MD, MMSc, PhD, AGAF, FAASLD GI / Liver Unit, Hospital Clinic Institut de Malalties Digestives i Metaboliques University of Barcelona
L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells are more responsive to IFN-γ. (A) Flow
 A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
A MHCI B PD-L1 Fold expression 8 6 4 2 Fold expression 3 2 1 No tx 1Gy 2Gy IFN Py117 Py117 Supplementary Figure 1. Radiation and IFN-γ enhance MHCI expression and PD- L1 on PyMT tumor cells but Py117 cells
Human TSH ELISA Kit. User Manual
 Human TSH ELISA Kit User Manual Catalog number: GTX15585 GeneTex Table of Contents A. Product Description... 2 B. Kit Components... 3 C. Additional Required Materials (not included)... 3 D. Reagent Preparation...
Human TSH ELISA Kit User Manual Catalog number: GTX15585 GeneTex Table of Contents A. Product Description... 2 B. Kit Components... 3 C. Additional Required Materials (not included)... 3 D. Reagent Preparation...
Index. Index 439. Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305
 Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
Index 439 Index A Aequorin, 84, 94 Affinity precipitation, 372, 376 381 AP-1, 100 Asthma, 170, 305 B Bioassay, 185, comparison with ELISA, 318 GM-CSF bioassay, 351 IL-2 bioassay, 185 192, 300 IL-3 IL-6
EDUCATION PRACTICE. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Patients With a Rising Alkaline Phosphatase at Annual Follow-up.
 CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:32 36 EDUCATION PRACTICE Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Patients With a Rising Alkaline Phosphatase at Annual Follow-up PHUNCHAI CHARATCHAROENWITTHAYA and
CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY 2007;5:32 36 EDUCATION PRACTICE Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Patients With a Rising Alkaline Phosphatase at Annual Follow-up PHUNCHAI CHARATCHAROENWITTHAYA and
Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A)
 Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Supplemental Figures Figure S1: Effects on haptotaxis are independent of effects on cell velocity A) Velocity of MV D7 fibroblasts expressing different GFP-tagged Ena/VASP family proteins in the haptotaxis
Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(4):1175-1179 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000102 Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
Int J Clin Exp Med 2014;7(4):1175-1179 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0000102 Letter to Editor Tissue micro arrays for immunohistochemical detection of inflammatory infiltrates in renal cell carcinoma
Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer
 Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
Young Investigator Award, Global Breast Cancer Conference 2018 Only Estrogen receptor positive is not enough to predict the prognosis of breast cancer ㅑ Running head: Revisiting estrogen positive tumors
RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit
 RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit Catalog #: ELH-GZMB User Manual Last revised April 15, 2016 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
RayBio Human Granzyme B ELISA Kit Catalog #: ELH-GZMB User Manual Last revised April 15, 2016 Caution: Extraordinarily useful information enclosed ISO 13485 Certified 3607 Parkway Lane, Suite 100 Norcross,
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supporting Information Fujishita et al. 10.1073/pnas.0800041105 SI Text Polyp Scoring. Intestinal polyps were counted as described (1). Briefly, the small and large intestines were excised, washed with
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
