This is a free sample of content from Mitosis. Click here for more information on how to buy the book.
|
|
|
- Isaac Rodgers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index A Actomyosin, cleavage furrow ingression, AICAR. See Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide ALIX, 157 Aminoimidazole carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR), 179 Ana2, 74 76, 89 Anaphase chromosome dynamics, sister chromatid separation and dynamics, 60 Anaphase-promoting complex (APC) activation, 18, 22 discovery, 7 8 ubiquitin ligase activity, Aneuploidy effects cell fitness, 171 genome stability, health, transcription and protein composition, molecular mechanisms cohesion defects, merotelic attachments, spindle assembly checkpoint defects, overview, 166 prospects for study, therapeutic targeting, tolerating mutations, tumorigenesis driver, inhibition, Anillin, 152 APC anaphase-promoting complex. See Anaphase-promoting complex tumor suppression, Arf6, 154 Arp2/3, 193 ASE1, metaphase spindle function, 41 Asl, 79, 89 ASPM, 90 Aurora A cilium cycle role, 84 mitosis entry role, Aurora B anaphase function, 60 cytokinesis role, 150 kinetochore regulation, B BAF, 188 Bfa1, 88 BLM, Boveri, Theodor, 4, 67 BRCA1, 90, 169 Bub1, 138, 140, , 191 Bub3, 140, 168 BUBR1, 23, , 178 C CAK. See Cdk-activating kinase CALK, 84 CAP350, 78 CBB, 89 CBF3, 131 CCDK. See Cyclin-dependent kinase CDC10, 8 Cdc14, 24, 87 CDC20, 22 23, 168 Cdc25, mitosis entry role, Cdc31, 71 cdc mutants, history of yeast cell cycle studies, 6 7 Cdk-activating kinase (CAK), mitosis entry role, 16 Cdk2, CDKRAP2, 81 Cell cycle cdc mutants, history of yeast cell cycle studies, 6 7 overview of phases, 1 2 CEN3, 8 CENP-A assembly constitutive centromere proteins in assembly, HJURP chaperone, , 133 Mis18 complex, 117 overview, centromere longevity and CENP-A maintenance during DNA replication, centromere protein recognition of CENP-A chromatin, depletion studies, 111 functional overview, 9 10, 105 histone H3 comparison, 108 nucleosome deposition at centromeres, distribution during DNA replication, 120 structure, prospects for study, 121 CENP-B box,
2 Index This is a free sample of content from Mitosis. CENP-C, , , 121, 134 CENP-E, 137, 140 CENP-H, 113, CENP-N, 108, , 119, 121 CENP-S, 109, 119, 133 CENP-T, 109, 113, 119, 121, CENP-U, 113 CENP-W, 109, 119, 133 CENP-X, 109, 119, 133 Centriole assembly cartwheel structure, elongation, Plk4 role, 73, species comparison, 74 asymmetry and cell fate decisions, duplication cycle, structure, 72 Centromere. See also CENP-A CENPs architecture, CENP-B box, 111 interactions, composition, epigenetic nature, , 131 functional overview, histone modifications, history of study, 8 9, 103 longevity and CENP-A maintenance during DNA replication, prospects for study, 121 Centrosome asymmetry and cell fate decisions, control center activity, disengagement of mother daughter linkage, disjunction at G2/M, duplication cycle, 68 history of study, 67, 69 pericentriolar material assembly, spindle pole body similarity, 69 structure, 68 Cep55, 157 CEP57, 120 CEP63, 90 Cep83, 83 Cep89, 83 Cep97, 78, 83 CEP120, 77 Cep135, 75 Cep152, 75, 79, 90 Cep164, 83 Cep192, 76, 79, 81 CEP290, 77 CFS. See Common fragile site Chk1, 86, 90 CHMP4 proteins, 157 Chromosomal instability (CIN). See also Aneuploidy cohesion defects, measurement, merotelic attachments, overview, 166 Chromosomal passenger complex (CPC), , 194 Cilia, assembly and disassembly cycle, CIN. See Chromosomal instability CIT-K. See Citron kinase Citron kinase (CIT-K), , 156 CLASP, 38, 138, 150, 169 C-Nap1, CNN, Cnp1, 9 Cohesin functional overview, 12 meiosis and stepwise removal, prophase condensation and cohesin release from chromosome arms, sister chromatid adhesion in S phase, subunit organization, Common fragile site (CFS), 61 Condensin condensin I function, 59 60, 62 condensin II function, cytokinesis and chromosome segregation coordination, 62 prophase condensation and cohesin release from chromosome arms, subunit organization, CP110, 77 78, 83 CPAP, 75, 77 78, 90 CPC. See Chromosomal passenger complex CREST syndrome, 105 CUEDC2, 169 Cut2, 8 Cut12, Cyclin A, mitosis entry role, 18 Cyclin B. mitosis entry role, Cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) history of study, 6 7, 11 kinetochore regulation, 138 meiosis, 186 mitosis entry role, Cyclosome. See Anaphase-promoting complex Cytokinesis chromosome segregation coordination, 62 cleavage furrow ingression, defects and disease, division plane positioning, membrane formation and composition, midbody dynamics, overview, prospects for study, 158 D Dam1, 136 DSCR1, 178 Dynein, metaphase spindle function, DYRK1A,
3 Index E EB1, metaphase spindle function, Eg5, 79 ENSA, mitosis exit role, 24 ESCO1, 55 ESCO2, 55 ESCRT complexes, cytokinesis role, F Fa1, 83 Fa2, 83 FANCD2, FANCI, 62 FBF1, 83 Fbxw5, 77 Fin1, 85 FIP3, 154 FIP4, 154 Flemming, Walther, 2 4, 103 FOP, 78 G g-tubulin ring complex (g-turc), spindle pole body, g-turc. See g-tubulin ring complex GOLPH3, 154 H HDAC6, 83 HDAC8, 55 HEC1, 176 HEF1, 79, Histone H3, CENP-A comparison, 108 HJURP, 108, , 133 HP-1, 9 HRAS, 177 hsav1, 79 HSET, 179 HURP, 191 K K-RAS, 177 Kar1, 71 KIF4, 59 KIF4A, cytokinesis role, KIF14, 156 KIF20A, cytokinesis role, 149 KIF23, cytokinesis role, , 152, KIF2B, Kin4, Kinesin-4, metaphase spindle function, Kinesin-8, metaphase spindle function, 36 Kinesin-13 kinetochore regulation, 138 metaphase spindle function, Kinesin-14, metaphase spindle function, 41 Kinetochore assembly, centromere association, , components, 133 composition, DNA segregation, force generation, regulation microtubule binding, spindle assembly checkpoint signaling, spindle microtubules binding, dynamics, Klo10A, 77 KLP-19, 193 KNL, 140 KNL1, 113 KNL2, 117 L LIS1, 40 Lte1, 88 M Ma31, 140 Mad1, 140, 176 Mad2, , , Maize, history of chromosome studies, 4 5 Maturation-promoting factor (MPF), history of study, 6 7 MCAK, , 191 MCAK. See Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin MCC. See Mitotic checkpoint complex McClintock, Barbara, 4 5 MCPH1, 57 58, 90 MCRS1, 38 Meiosis acentrosomal spindle formation, asymmetric division of oocytes, cell cycle control, chromosomal segregation, cohesin stepwise removal, pairing and recombination, postrecombination events, 188 sister chromatids, monopolar attachment in meiosis I, 188, 190 spindle assembly checkpoint, 194 spindle chromosome interactions, MEN, MET, 177 Metaphase chromosome dynamics,
4 Index This is a free sample of content from Mitosis. Metaphase spindle assembly modeling in Xenopus extracts, forces and functions ASE1, 41 dynein, kinesin-4, kinesin-14, 41 9 PRC1, 41 microtubules amplification, 34 depolymerases, dynamics, 35 minus end stabilizers, nucleation, plus end dynamics, 35 tracking proteins, 37 38) severing, organizers, 32 prospects for study, 44 size control and scaling, MgcRacGAP, 118, 154 Microcephaly, defects in division symmetry, Microtubule. See Metaphase spindle Microtubule-organizing center. See Centrosome Mis12, 9, 113, 121, 134 Mis16, 118 Mis18, 117 Mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK), 35, , 191 Mitotic checkpoint complex (MCC), components and function, Mitotic spindle, eukaryote distribution, 5 6 MPF. See Maturation-promoting factor Mps1, 19 20, 138 Mps3, 71 Mst2, 79 MUS81, 82 Myosin II, 193 N Ndc80, 113, , 140 NEBD. See Nuclear envelope breakdown Nek2, 76, NHK-1, Nuclear envelope breakdown (NEBD), 19, 59 Nucleosome. See CENP-A NudE, 40 Nuf, 154 NuMA, 191 NuSAP, 191 O Ofd1, 77 Oocyte. See Meiosis P P53, 175, 177, 180 Patronin, metaphase spindle function, 38 PCM. See Pericentriolar material PCM1, 84 Pds1, 8 Pds5, 56 Pericentriolar material (PCM), assembly, PICH, Plk1 anaphase role, 60 centrosome function, cilium cycle role, 84 cytokinesis role, 157 kinetochore regulation, 138 mitosis entry role, pericentriolar material assembly, 81 Plk4 centriole assembly role, 73, pericentriolar material assembly role, 79 PLK4, 170 Plo1, 18, POC5, 77 PP1 inhibition studies, kinetochore regulation, 139 mitosis exit role, 24 PP2A centriole assembly role, 76 inhibition studies, kinetochore regulation, 139 mitosis exit role, 24 PRC1, 41, , 152, 156 Prdm9, 186 Prometaphase, Prophase condensation and cohesin release from chromosome arms, Psh1, 118 Pyp2, 85 R Rab11, 154 Rab35, 154 Rad51, 187 Ran, 32 34, 191 Rec8, RhoA, cytokinesis role, 150 Rootlein, 78 S SA, SAC, Salamander chromosome, history of mitosis studies, 1 4 SAPK. See Stress-activated protein kinase 202
5 Index Sas-4, 79, 89 SAS-5, SAS-6, 73 76, 89 SCLT1, 83 Sea urchin embryo, history of mitosis studies, 4 5 Securin, degradation in mitosis, 7 8 Sfi1, 71 Sgo1, Shugosin, 24 Sister chromatids cohesin and adhesion in S phase, separation and dynamics in anaphase, 60 separation mechanism, Ska1, 136 SLC19A1, 178 SOC. See Spindle orientation checkpoint SPB. See Spindle pole body Spd-2, 76, SPICE1, 77 Spindle. See Metaphase spindle; Mitotic spindle Spindle assembly checkpoint, , , 194 Spindle orientation checkpoint (SOC), 87 Spindle pole body (SPB) asymmetry cellular asymmetry and spindle alignment in budding yeast, extrinsic control and end of budding yeast cell cycle, spindle pole body asymmetry and spindle alignment in budding yeast, 87 centrosome similarity, 69 control center activity, duplication cycle, mitosis entry, 18 structure, STAG2, 170 STIL, 74 75, 77, 90 Stress-activated protein kinase (SAPK), 73 SUN KASH domain, 187 Syndapin, 155 T TACC3, 81 Telomere, isolation from Tetrahymena, 9 Telophase chromosome dynamics, Topoisomerase I, 11 Topoisomerase II, 10, 60, 62 TPX2, 33, 43, 191 TTBK2, 83 U UBCH10, 169 Ubiquitinylation, sister chromatid separation role, 21 UBP6, 175 UFB. See Ultrafine DNA bridge Ultrafine DNA bridge (UFB), W Wap1, 56 Wee1, mitosis entry role, 17 X XIST, 171 XMAP215, metaphase spindle function, 37, 39 Z ZYG-1,
6
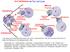
(a) Reproduction. (b) Growth and development. (c) Tissue renewal
 100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
100 µm 200 µm 20 µm (a) Reproduction (b) Growth and development (c) Tissue renewal 1 20 µm 2 0.5 µm Chromosomes DNA molecules Chromosome arm Centromere Chromosome duplication (including DNA synthesis)
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression
 Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Regulators of Cell Cycle Progression Studies of Cdk s and cyclins in genetically modified mice reveal a high level of plasticity, allowing different cyclins and Cdk s to compensate for the loss of one
Bacterial cell. Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Scaffold protein Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Origin of replication. Septum
 Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
Bacterial cell Bacterial chromosome: Double-stranded DNA Origin of replication Septum 1 2 3 Chromosome Rosettes of Chromatin Loops Chromatin Loop Solenoid Scaffold protein Scaffold protein Chromatin loop
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer. Dan Fisher. Friday 27th October Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6.
 How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
How deregulated cell cycles (might) trigger cancer http://www.igmm.cnrs.fr Dan Fisher Friday 27th October 2017 Lucie Fisher, 3 Eddie Fisher, 6 1 transformed cells transformed cells Structure of this lecture
Mitotic spindle assembly:
 Mitotic spindle assembly: May the force be with you Roy van Heesbeen Van_Heesbeen.indd 1 9-7-2015 11:10:00 ISBN: 978-94-6233-037-5 Printed by: Gildeprint Copyright 2015 R.G.H.P. van Heesbeen Cover: Mitosis
Mitotic spindle assembly: May the force be with you Roy van Heesbeen Van_Heesbeen.indd 1 9-7-2015 11:10:00 ISBN: 978-94-6233-037-5 Printed by: Gildeprint Copyright 2015 R.G.H.P. van Heesbeen Cover: Mitosis
The Cell Cycle. Packet #9. Thursday, August 20, 2015
 1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
1 The Cell Cycle Packet #9 2 Introduction Cell Cycle An ordered sequence of events in the life of a dividing eukaryotic cell and is a cellular asexual reproduction. The contents of the parent s cell nucleus
How Cells Divide. Chapter 10
 How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
How Cells Divide Chapter 10 Bacterial Cell Division Bacteria divide by binary fission. -the single, circular bacterial chromosome is replicated -replication begins at the origin of replication and proceeds
基醫所. The Cell Cycle. Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU
 基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
基醫所 The Cell Cycle Chi-Wu Chiang, Ph.D. IMM, NCKU 1 1 Introduction to cell cycle and cell cycle checkpoints 2 2 Cell cycle A cell reproduces by performing an orderly sequence of events in which it duplicates
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.12 - CELL DIVISION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL DIVISION Cell division is the process by which one cell splits into two or more daughter cells. Cell division generally requires that cells produce enough materials,
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
BIOLOGY. The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE. In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for..
 Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
Mitosis THE CELL CYCLE In unicellular organisms, division of one cell reproduces the entire organism Multicellular organisms use cell division for.. Development from a fertilized cell Growth Repair Cell
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
2014 Pearson Education, Inc.
 2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
2 The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
BIOLOGY 4/6/2015. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Unduplicated. Chromosomes. Telophase
 10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
10-2 Cell Division The Cell Cycle Interphase Mitosis Prophase Cytokinesis G 1 S G 2 Chromatin in Parent Nucleus & Daughter Cells Chromatin Daughter Nuclei Telophase Mitotic Anaphase Metaphase Use what
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12
 The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
The Cell Cycle CHAPTER 12 The Key Roles of Cell Division cell division = reproduction of cells All cells come from pre-exisiting cells Omnis cellula e cellula Unicellular organisms division of 1 cell reproduces
Cell Division and Mitosis
 Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
Chromatin-Uncoiled DNA during interphase Cell Division and Mitosis Chromosomes-Tightly coiled DNA Chromatid-One half of a duplicated chromosome. Each is identical and called sister chromatids Centromere-The
The Cell Cycle. Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D
 The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
The Cell Cycle Dr. SARRAY Sameh, Ph.D Overview When an organism requires additional cells (either for growth or replacement of lost cells), new cells are produced by cell division (mitosis) Somatic cells
BIOLOGY. Cell Cycle - Mitosis. Outline. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. identical daughter cells. I. Overview II.
 2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
2 Cell Cycle - Mitosis CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Overview II. Mitotic Phase I. Prophase II. III. Telophase IV. Cytokinesis III. Binary fission
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Lectures by Erin
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!!
 Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
Why do cells divide? Cells divide in order to make more cells they multiply in order to create a larger surface to volume ratio!!! Chromosomes Are made of chromatin: a mass of genetic material composed
10-2 Cell Division. Slide 1 of 38. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
1 of 38 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called
Why do cells reproduce?
 Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
Outline Cell Reproduction 1. Overview of Cell Reproduction 2. Cell Reproduction in Prokaryotes 3. Cell Reproduction in Eukaryotes 1. Chromosomes 2. Cell Cycle 3. Mitosis and Cytokinesis Examples of Cell
-The cell s hereditary endowment of DNA -Usually packaged into chromosomes for manageability
 Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Binary Fission-Bacterial Cell Division -Asexual reproduction of prokaryotes -No mitosis -Circular DNA and organelles replicate, the copies migrate to opposite sides of the elongating cell, and the cell
Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
Cell Theory 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 1: Mitosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Cell theory: All organisms are made of cells All cells arise from preexisting cells How do new cells arise? Cell division the reproduction
10-2 Cell Division. Chromosomes
 Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
Cell Division In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis.
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp 1
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Key Concepts in Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Video: Sea Urchin Embryonic Development (time-lapse)
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Dr. Wendy era Houston Community College Biology 1406 Key Concepts in Chapter 12 1. Most cell division results in genetically identical daughter cells. 2. The mitotic phase alternates
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle. 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions
 Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Campbell Biology in Focus (Urry) Chapter 9 The Cell Cycle 9.1 Multiple-Choice Questions 1) Starting with a fertilized egg (zygote), a series of five cell divisions would produce an early embryo with how
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 22: The Mechanics of Cell Division Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about mitosis is correct? Question #1 (A) Mitosis involves the dividing
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules. LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07. Processes occurring during cell cycle
 Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Cell Cycle, Mitosis, and Microtubules LS1A Final Exam Review Friday 1/12/07 Processes occurring during cell cycle Replicate chromosomes Segregate chromosomes Cell divides Cell grows Cell Growth 1 The standard
Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division
 The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
The Cell Cycle and Cellular Reproduction Chapter 9 Outline Interphase Mitotic Stage Cell Cycle Control Apoptosis Mitosis Mitosis in Animal Cells Cytokinesis Cancer Prokaryotic Cell Division 1 2 Interphase
Cell Cycle - Introduction
 Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Cell Cycle - Introduction Key Concepts Cell division results in two identical cells During cell division the ability to organize DNA in time and space (location in the cell) is critical! The mitotic phase
Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle
 What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
What molecule stores your genetic information or determines everything about you? DNA a nucleic acid How are DNA molecules arranged in the nucleus? As you can see DNA is: Chapter 8 The Cell Cycle 1. Arranged
10-2 Cell Division mitosis. cytokinesis. Chromosomes chromosomes Slide 1 of 38
 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm, is called cytokinesis. Chromosomes
Mitosis. AND Cell DiVISION
 Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Mitosis AND Cell DiVISION Cell Division Characteristic of living things: ability to reproduce their own kind. Cell division purpose: When unicellular organisms such as amoeba divide to form offspring reproduction
Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Meiosis Lecture 10 Fall 2008
 Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
Mitosis & 1 Cellular Reproduction, Part 2: Lecture 10 Fall 2008 Mitosis Form of cell division that leads to identical daughter cells with the full complement of DNA Occurs in somatic cells Cells of body
The Cell Cycle 4/10/12. Chapter 12. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division
 LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
LECTURE PREENTATION For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, teven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Overview: The Key
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair
 Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Cell division functions in 1. reproduction, 2. growth, and 3. repair What do you think you are looking at here??? Can something like you or I do this??? Fig. 12.1 How did you start out? How did you grow?
Creating Identical Body Cells
 Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
Creating Identical Body Cells 5.A Students will describe the stages of the cell cycle, including DNA replication and mitosis, and the importance of the cell cycle to the growth of organisms 5.D Students
The Cell Cycle CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS SECOND EDITION URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 9 The Cell Cycle Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION Overview: The Key
The Cell Cycle. Chapter 12. Biology. Edited by Shawn Lester. Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Edited by Shawn Lester PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions
PowerPoint Image Slideshow
 COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
COLLEGE BIOLOGY PHYSICS Chapter 10 # Cell Chapter Reproduction Title PowerPoint Image Slideshow CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 12 The Cell Cycle 2014 Pearson
Prentice Hall Biology Slide 1 of 38
 Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Prentice Hall Biology 1 of 38 2 of 38 In eukaryotes, cell division occurs in two major stages. The first stage, division of the cell nucleus, is called mitosis. The second stage, division of the cell cytoplasm,
Chapter 14. Cell Division
 Chapter 14 Cell Division 14.1. The Cell Cycle A eukaryotic cell cannot divide into two, the two into four, etc. unless two processes alternate: doubling of its genome (DNA) in S phase (synthesis phase)
Chapter 14 Cell Division 14.1. The Cell Cycle A eukaryotic cell cannot divide into two, the two into four, etc. unless two processes alternate: doubling of its genome (DNA) in S phase (synthesis phase)
Cell cycle and Apoptosis. Chalermchai Mitrpant
 Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Cell cycle and Apoptosis 2556 Chalermchai Mitrpant Overview of the cell cycle Outline Regulatory mechanisms controlling cell cycle Progression of the cell cycle Checkpoint of the cell cycle Phases of the
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!!
 Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Centrosome & Centrioles,It s Structure,Function!! CENTROSOME In cell biology, the centrosome (Latin centrum center and Greek soma body ) is an organelle that serves as the main microtubule organizing center
Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle The Key Roles of Cell Division The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind is the one characteristic that best distinguishes living things from nonliving things.
Cell Division. During interphase, a cell s DNA is in a loose form called. It condenses into tightly coiled structures called chromosomes during.
 Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Cell Division The is a cell s total DNA. Prokaryotes DNA is found mostly in a single called the and also in small circles called. Eukaryotes have several DNA double helices packaged into. During interphase,
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Chromosomes Chromosomes were first observed by the German embryologist Walther Fleming in 1882. Chromosome number varies among organisms most
Lecture 10. G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints. G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint
 Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Lecture 10 G1/S Regulation and Cell Cycle Checkpoints Outline: G1/S regulation and growth control G2 repair checkpoint Spindle assembly or mitotic checkpoint Paper: The roles of Fzy/Cdc20 and Fzr/Cdh1
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction
 Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Chapter 8: Cellular Reproduction 1. The Cell Cycle 2. Mitosis 3. Meiosis 2 Types of Cell Division 2n 1n Mitosis: occurs in somatic cells (almost all cells of the body) generates cells identical to original
Name. A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
A.P. Biology Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Name Living species MUST possess the ability to r if they are to flourish. The Cell Cycle follows the life of a cell from its o until its d. The Key Roles Of Cell
Mitosis and Cytokinesis
 B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase); and plant and animal cytokinesis. The
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells. 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells
 8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
8.4 The cell cycle multiplies cells! Cell division is a highly orchestrated process! The cell cycle is an ordered sequence of events that extends from the time a cell is first formed from a dividing parent
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division. Unicellular organisms
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology Course No: BNG2003 Credits: 3.00 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell
General Biology. Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells, or cell division
 General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
General Biology Course No: BNG2003" Credits: 3.00 " " " 8. The Cell Cycle Prof. Dr. Klaus Heese Overview: The Key Roles of Cell Division The continuity of life is based upon the reproduction of cells,
BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS
 Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Biology Multiple Choice 016044 BIOLOGY LTF DIAGNOSTIC TEST CELL CYCLE & MITOSIS TEST CODE: 016044 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by five suggested answers
Genetics. Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division
 Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
Genetics Instructor: Dr. Jihad Abdallah Lecture 2 The cell cycle and Cell Division 1 The cell cycle Living cells go through a series of stages known as the cell cycle. They undergo a continuous alternation
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview. Cellular Organization of the Genetic Material. Distribution of Chromosomes During Eukaryotic Cell Division
 CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
CH 9: The Cell Cycle Overview The ability of organisms to produce more of their own kind best distinguishes living things from nonliving matter The continuity of life is based on the reproduction of cells,
Prof. R. V. Skibbens. BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century. Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer.
 Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
Prof. R. V. Skibbens August 31, 2015 BIOS 10 and BIOS 90: BioScience in the 21 st Century Cell Cycle, Cell Division and intro to Cancer Cell Cycle Why a cell cycle? What is the goal? trauma growth development
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT. Activity #3
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION/HEREDITY UNIT Unit 1 Part 3 Chapter 12 Activity #3 INTRODUCTION CELL CYCLE NAME DATE PERIOD The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes,
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category:
 Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Monday, October 6 Put these items into the appropriate category: Active Transport Facilitated Diffusion Osmosis Simple Diffusion The smell of rotten eggs spreading through the room Requires ATP expenditure
Omnis cellula e cellula
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Omnis cellula e cellula 1855- Rudolf Virchow German scientist all cells arise from a previous cell Every cell from a cell In order for this to be true, cells must have the ability
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities
 Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis/Meiosis Simulation Activities In this simulation, you will demonstrate an understanding of mitosis, meiosis, segregation, independent assortment, and crossing over, all processes involved with
Mitosis & Meiosis. Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair
 Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Mitosis & Meiosis Diploid cells- (2n)- a cell that has 2 of each chromosome - 1 from mom, 1 from dad = 1 pair The pair is called homologous chromosomes The homologous chromosomes contain the same gene
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
The Cell Cycle Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Why do cells divide? For reproduction asexual reproduction For growth one-celled organisms from fertilized
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle Objectives Describe how cell reproduction contributes to repair and growth. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell division. Compare and contrast asexual and sexual
MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes
 1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
1 Name: Date: MITOSIS AND THE CELL CYCLE PowerPoint Notes THE FUNCTIONS OF CELL DIVISION 1. Cell division is vital for all. living organisms This is the only process that can create. new cells 2. Cell
Cell cycle control (mammalian)
 Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Apr. 21, 2005 Cell cycle control (mammalian) Basic mechanisms & protein components Checkpoints Chap. 21, by Lodish et al., 5 th ed. 2004 Chap. 17, by Alberts et al., 4 th ed. 2002 鍾明怡 mychung@vghtpe.gov.tw
Genetics and Cellular Function
 Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
Genetics and Cellular Function DNA replication and the cell cycle Mitosis Mitosis Mitosis: division of cells that results in daughter cells with the same the genetic information that the original cell
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION PART I ANIMAL CELL CYCLE INTERPHASE
 CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
CELL CYCLE INTRODUCTION The nuclei in cells of eukaryotic organisms contain chromosomes with clusters of genes, discrete units of hereditary information consisting of double-stranded DNA. Structural proteins
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis
 Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
Breaking Up is Hard to Do (At Least in Eukaryotes) Mitosis Prokaryotes Have a Simpler Cell Cycle Cell division in prokaryotes takes place in two stages, which together make up a simple cell cycle 1. Copy
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide
 The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
The Cell Cycle and How Cells Divide 1 Phases of the Cell Cycle The cell cycle consists of Interphase normal cell activity The mitotic phase cell divsion INTERPHASE Growth G 1 (DNA synthesis) Growth G 2
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
 Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth & Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence Getting from there to here Cell
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all.
 The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
The questions below refer to the following terms. Each term may be used once, more than once, or not at all. a) telophase b) anaphase c) prometaphase d) metaphase e) prophase 1) DNA begins to coil and
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8
 Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8 1. Importance of Cell Division 2. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle 3. Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Mitosis 5. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells 6. Sexual Iife cycle 7. Meiosis 8.
Cellular Reproduction Chapter 8 1. Importance of Cell Division 2. Eukaryotic Cell Cycle 3. Eukaryotic Chromosomes 4. Mitosis 5. Cytokinesis in animal and plant cells 6. Sexual Iife cycle 7. Meiosis 8.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 2007-2008 Getting from there to here Going from egg to baby. the original
The Process of Cell Division
 Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
Lesson Overview 10.2 The Process of Cell Division THINK ABOUT IT What role does cell division play in your life? Does cell division stop when you are finished growing? Chromosomes What is the role of chromosomes
KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular
 Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
Chapter 10 Chapter 10 KEY CONCEPT Cells have distinct phases of growth, reproduction, and normal functions. The cell cycle has 4 main stages. The cell cycle is a regular pattern of growth, DNA replication,
U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151).
 Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Cell Division Study Guide U3.2.3: Eukaryotic chromosomes are linear DNA molecules associated with histone proteins. (Oxford Biology Course Companion page 151). 1. Describe the structure of eukaryotic DNA
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division
 Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
Chapter 12 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at the end of a sentence And now look at you How did you get from there to
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
APGRU4L1 Chap 12 Extra Reading Cell Cycle and Mitosis Dr. Ramesh Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2)
 Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Montana Comprehensive Assessment System (MontCAS, Phase 2) Criterion-Referenced Test (CRT) Common Constructed-Response Item Release Science, Grade 10 2008 OFFICE OF PUBLIC INSTRUCTION 2008 Measured Progress.
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division 2007-2008 The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division 2007-2008 Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a
Mitosis Notes AP Biology Mrs. Laux
 I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
I. Cell Cycle-includes interphase and mitosis (IPPMAT) A. Interphase 1. accounts for 90% of the cycle 2. cell grows and copies its chromosomes in preparation for cell division 3. produces proteins and
Cell Division. The Process of Cell Division Section Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division 12/8/2010
 The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
The Process of Cell Division Section 10.2 Biology B Section 10.2: The Process of Cell Division The student will investigate and understand common mechanisms of inheritance and protein synthesis. Key concepts
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis
 Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 2. Mitosis and Meiosis Chromosome Theory of Heredity What structures within cells correspond to genes? The development of genetics took a major step forward by accepting the notion that the genes
Chapter 12. living /non-living? growth repair renew. Reproduction. Reproduction. living /non-living. fertilized egg (zygote) next chapter
 Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Chapter 12 How cells divide Reproduction living /non-living? growth repair renew based on cell division first mitosis - distributes identical sets of chromosomes cell cycle (life) Cell Division in Bacteria
Mitosis. An Introduction to Genetics. An Introduction to Cell Division
 Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
Mitosis An Introduction to Genetics An Introduction to Cell Division DNA is Packaged in Chromosomes Cell Cycle Mitosis and Cytokinesis Variations in Cell Division Cell Division and Cancer An Introduction
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Biology Mo Test: Q3 Mr. Rellinger Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which event occurs during interphase? The cell carries
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET
 Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Unit 6: CELL DIVISION PACKET This packet is designed to help you understand several concepts about Cell Division. As you practice the exercises on each handout, you will be able to: Use a model to illustrate
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division. AP Biology
 Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Biology is the only subject in which multiplication is the same thing as division Chapter 12. The Cell Cycle: Cell Growth, Cell Division Where it all began You started as a cell smaller than a period at
Cell Cycle and Mitosis
 Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Name Period A# THE CELL CYCLE The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that take place in a eukaryotic cell between its formation and the moment it replicates
