Muscarinic receptor signalling in Neuro-2a cells and its effects on cell survival: Elaborating pathways
|
|
|
- Douglas Cooper
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ARTICLE: ORIGINAL RESEARCH Muscarinic receptor signalling in Neuro-2a cells and its effects on cell survival: Elaborating pathways involved in neurodegenerative disorders Ricardo D Souza Third Year Medical Student School of Medicine University of Auckland Ricardo is currently a third year medical student at the University of Auckland. This research was conducted in the Molecular Neuropharmacology laboratory in the Department of Pharmacology, University of Auckland as a summer studentship over the summer of 2005/2006. ABSTRACT This study describes the effect of signalling through muscarinic acetylcholine receptors on the induction of the transcription factor EGR1, which has been implicated in long-term synaptic plasticity, memory consolidation and on a cellular level, the process of apoptosis or programmed cell death. In Neuro-2a mouse neuroblastoma cells, the cholinergic agonist carbachol led to induction of EGR1, with a mean EC50 of 2.2 μm, and this induction was completely blocked by the muscarinic antagonist atropine at 1 μm. Relative antagonist potency was found to be highest for the M3-selective antagonist 4-DAMP, as compared to the M1-selective antagonist pirenzipine and the M2-selective antagonist AFDX-116. Pertussis toxin, effectively an M2/M4-specific antagonist, completely blocked EGR1 induction. These experiments have given us evidence that a combination of M3 and M4 receptor subtypes are likely to be primarily responsible for EGR1 induction through muscarinic receptors. In experiments with rotenone, a potent mitochondrial I complex inhibitor, and serum-deprivation, where essential growth factors are not provided, we found that EGR1 induction via muscarinic stimulation did not have a protective effect on cell survival in Neuro-2a cells. EGR1 induction, by itself, is probably insufficient for preventing cell apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells. Comparing these Neuro-2a cell results with previous results from the SK-N-SH cell line indicates that the transcription factor CREB may be more influencial in the anti-apoptotic mechanism of cells than EGR1. This supports previous evidence from CREB transfection experiments in Neuro-2a cells. In summary, this research has used a cell model to complement the current understanding of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors and their involvement in survival pathways. Expanding our knowledge of these survival pathways is important in understanding the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Keywords Neuro-2a cells, Muscarinic receptors, EGR1, cell survival, apoptosis INTRODUCTION Alzheimer's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of nerve-cells that control thought, memory and language. In New Zealand, about 20,000 people over the age of 65 are affected by Alzheimer's disease. The neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) is considered to have a role in learning and memory, but levels are significantly depleted during the progression of Alzheimer's disease as a consequence of the neuronal degeneration. Research has shown that the process of apoptosis or programmed cell death plays a central role in the onset and development of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease. Cholinergic signalling through muscarinic acetylcholine receptors (machrs), previously linked to long-term changes in synaptic plasticity which underlie memory formation, 1,2 has also been shown to also protect against apoptotic cell death. 3,4 Active research over the last few years has identified some candidate 'memory molecules' which, as specific inducible transcription factors, are able to initiate programmes of gene expression relevant to both memory consolidation and anti-apoptotic signalling. EGR1 (also known as NGFI-A, krox 24, Zif268 or Tis8) is a zinc finger transcription factor whose induction does not require prior protein synthesis. 5 Evidence for its role in memory consolidation has come from a mouse EGR1 gene knockout study, with EGR1-/- mice exhibiting an impairment in long-term memory while retaining short term memory. 6 Research using cell culture models have demonstrated muscarinic-driven EGR1 activation. 7,8 Furthermore, machr antagonists which cause amnesia in humans, block neuronal EGR1 induction by cholinergic agonists in rodents. 9 Cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB) is another transcription factor which has emerged as a prime candidate memory molecule. Expressed constitutively in most cells, CREB becomes transcriptionally active following phosphorylation at Ser There is compelling evidence for the involvement of CREB in initiating transcriptional programmes relevant to neuronal survival Muscarinic cholinergic signalling in the SK-N-SH human neuroblastoma cell line has been shown to lead to CREB phosphorylation and EGR1 expression, 14 and to have enhanced cell survival during serum deprivation, an apoptosis-inducing condition. These effects were shown to be primarily driven through the M3 receptor (J.M. Greenwood, personal communication). In Neuro-2a cells, muscarinic cholinergic signalling has been found to induce EGR1 expression, but not CREB phosphorylation (J.M. Greenwood, personal communication). Our experiments aim to determine the muscarinic acetylcholine receptor (machr) subtype(s) responsible for the induction of EGR1 in mouse Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells using a range of pharmacological inhibitors.
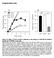
2 Figure 1. EGR1 expression in Neuro-2a cells is driven through muscarinic receptors. Immunocytochemical nuclear staining shows EGR1 expression is stimulated by cholinergic agonist carbachol (100 μm, b). EGR1 expression is similar to basal levels (H2O, a) on addition of muscarinic antagonist atropine (1 μm, c) -VE refers to absence of atropine Furthermore, we aimed to ascertain whether EGR1 induction driven through machr signalling leads to a protective response. Cell-based ELISA Quantification of immunostaining was attained using cell-based ELISA. In brief, cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Endogenous peroxidase activity was quenched using 0.6% H 2 O 2 in PBS/Triton, followed by blocking with 10% goat serum in PBS/Triton for 1h. Primary antibody incubation (EGR1 at 1/2000 dilution) was overnight at 4ºC, followed by peroxidaseconjugated secondary anti-rabbit antibody (Chemicon) at 1/200 dilution. Peroxidase conversion of the substrate o-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD) was determined by absorbance measurement at 490 nm (A490) corrected for light scatter at 650 nm. Measurements of A490-A650 were averaged for at least 3 replicate wells and were normalised to control (H 2 O) values. The data were normalised to a percentage scale and bestfit sigmoidal curves were plotted, using Graphpad Prism to calculate EC50 values and relative potencies of the antagonists. 15 METHODS These methods are based on those used by Greenwood and Dragunow (2002). Cell Culture Mouse Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells were obtained from the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, no CCL-131). They were cultured in 75 cm 2 flasks at 37ºC in a humidified atmosphere (5% CO 2 /95% air) in MEM medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum, 100 U/mL penicillin, 100 μg/ml streptomycin and 1 mm sodium pyruvate. Cells grown to confluency were harvested with 0.05% trypsin in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), washed with media and plated h prior to carbachol addition. Cells were counted using a haemocytometer, and plated at 10 4 cells/well in 96-well plates for immunocytochemistry and cell-based ELISA, and at 5 x 10 3, 10 4 and 2 x 10 4 cells/well in 96-well plates for survivalviability assays, with a constant plating volume of 0.1 ml. Where indicated, atropine sulphate, pirenzipine dihydrochloride, 4-DAMP methiodide, and AFDX-116 were added 5 min prior to addition of carbachol, while pertussis toxin was added 18 h prior to carbachol addition. Human SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells were obtained from the ATCC. Immunocytochemistry Cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde. Primary antibody incubation was overnight at 4ºC. Dilutions of rabbit polyclonal antibodies were 1/1000 for both EGR1 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology sc-189) and cleaved caspase 3 (Cell Signaling Technology 9661). This was followed by incubation with biotinylated goat anti-rabbit antibody (Sigma) and ExtrAvidin peroxidase (Sigma), each at 1/250 dilution. Antibody binding was visualised by 3,3 - diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining. Cell survival Assays For the serum starvation experiment, all wells were washed twice with serum-free medium h after plating. Water or carbachol (100 μm) diluted in serum-free medium or serum containing 10% medium (full serum medium) was added (100 μl) to respective wells. For the rotenone toxicity experiment, rotenone (1 μm) or 0.01% DMSO (vehicle) was added together with water or carbachol (100 μm), h after plating. For both experiments, plates were then incubated for 22 h. Alamar blue (10μL/well, Serotec), an indicator of cell metabolism, was added and incubation resumed for 2 h. Conversion of the alamar blue substrate was determined by excitation at 544nm and measurement of fluorescent emission at 590nm. Measurements of E590 were averaged for at least 3 replicate wells. RESULTS Muscarinic signalling leads to EGR1 induction in Neuro-2a cells, most likely driven through M3 and M4 receptors. To investigate the effects of muscarinic receptor activation on EGR1 induction, immunocytochemistry and cell-based ELISA were performed on Neuro-2a mouse neuroblastoma cells following treatment with the cholinergic agonist carbachol (100 μm). An increase in nuclear EGR1 immunostaining was observed 60 min after carbachol treatment (Figure 1). Carbachol dose-response curves for EGR1 induction in Neuro-2a cells were generated by cell-based ELISA. Cells were fixed 60 min after carbachol treatment. Induction of EGR1 had a high sensitivity to carbachol concentration with a mean EC 50 value of 2.2 μm (95% CI: μm, n = 4). The muscarinic antagonist atropine (at 1 μm) completely blocked EGR1 induction when added 5 min prior to carbachol, indicating that carbachol was driving these responses through muscarinic receptor activation (Figure 1). Pre-treatment with atropine (at 10 nm, 30 nm, 100 nm) produced right shifts in the carbachol dose-response curves, consistent with competitive inhibition of muscarinic receptors (Figure 2a). The relative antagonist potency for atropine was approximately nm. Treatment with the M1-muscarinic antagonist pirenzipine (at 1 μm, 10 μm, 100 μm) produced right shifts in the carbachol-dose response curves, but relative potency was calculated to be significantly lower than atropine at 46 nm (Figure 2b). Similar right shifts were seen for the M2-muscarinic antagonist AFDX-116 (at 1 μm, 3 μm, 10 μm), with a relative potency of 257 nm (Figure 2c). The above results suggest that neither M1 nor M2 muscarinic receptors are significantly involved in muscarinic-driven EGR1 induction. The M3-muscarinic antagonist 4-DAMP (at 10 nm, 30 nm, 100 nm), 3
3 Figure 2. Carbachol dose-response curves for EGR1 in Neuro-2a cells, in the presence of muscarinic antagonists. The M3-selective muscarinic antagonist 4-DAMP was the most potent (2.48 nm) selective antagonist. However, none of the selective antagonists had a potency comparable to that of non-selective antagonist atropine (0.098 nm). Values shown represent the mean ±SEM. Figure 4. Serum starvation induces apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells. Immunocytochemical DAB staining for cleaved caspase 3, a marker of cell apoptosis. Note the presence of apoptotic cells (dark staining) in the serum free medium (SFM, a and c), but not in the full serum medium (10% serum, FSM, b and d) condition. Figure 5. Carbachol treatment does not enhance cell survival of Neuro-2a cells cultured in stressful conditions. Wells in serum free medium conditions that were also treated with carbachol had similar fluorescence readings to wells treated with H2O (a). This means cell viability was similar in both conditions which suggests that treatment with carbachol (CCH) did not have a protective effect on cell survival. This observation was similar in the rotenone experiment (b). FS represents full serum medium (10% serum). Values shown represent the mean ± s.d.
4 Figure 3. Pertussis toxin (PTX) inhibits EGR1 induction by carbachol in Neuro-2a cells. EGR1 induction by carbachol is inhibited in Neuro-2a cells (a) but not in SK-N-SH cells (b). This suggests EGR1 expression in Neuro-2a cells may be driven through M2/M4 receptor subtypes. Values shown represent the mean ±SEM. produced right shifts in the dose response curves with a relatively high potency of 2.48 nm (Figure 2d), which suggests that the M3 receptor subtype is one of the receptors that can lead to EGR1 induction in Neuro- 2a cells. Overnight treatment with pertussis toxin blocks the coupling of the Gi/Go proteins with M2 and M4 muscarinic receptors, rendering them inactive. Pertussis toxin (at 100 ng/ml) inhibited EGR1 induction by carbachol (Figure 3a) suggesting that M2/M4 receptor subtypes are involved in EGR1 induction in N2a cells. A common feature of the carbachol dose-response curves is that at high concentrations of carbachol, after the peaks of the dose-response curves, there seems to be a decrease in EGR1 expression (Figure 3). This feature appears to be independent of the addition of the muscarinic antagonists. Muscarinic cholinergic signalling and EGR1 induction has no effect on cell survival in Neuro-2a cells. To investigate the effects of muscarinic cholinergic signalling on cell survival in Neuro-2a cells, we used an alamar blue fluorescence assay to measure cell metabolic activity. To induce apoptosis in these cells, we cultured them overnight in serum-free medium, thus depriving them of essential growth factors required for cell growth and survival. Levels of cleaved caspase 3 (a marker of cell apoptosis), visualised by DAB immunostaining, were higher in serum-free medium cultured cells, as compared to full-serum cultured cells (Figure 4). This indicates that serumfree medium induces apoptosis. Treatment with carbachol did not appear to have any protective effect (Figure 4). Cells (at 5,000 and 10,000 cells/well) cultured in serum-free conditions have slightly lower fluorescence readings than full-serum cultured cells (Figure 5a). This shows they have slightly lower viability. All wells were washed with serum-free medium, and this might have influenced the viability of the full-serum cultured cells (Figure 5a). In the serum-free medium wells, cells (at 5,000 and 10,000 cells/well) treated with carbachol had lower fluorescence readings than control (H 2 O-treated) cells (Figure 5a). This indicates that carbachol had a deleterious effect on cell metabolism and cell survival. This deleterious effect was not seen at 20,000 cells/well. As a further test to determine if carbachol treatment had any protective effects in Neuro-2a cells, we used a mitochondrial I complex inhibitor, rotenone to create a stressful environment for cell growth. Rotenone toxicity is most significant at 20,000 cells/well (Figure 5b). In the rotenonetreated wells, wells that were also treated with carbachol had similar fluorescence readings to wells treated with H2O (Figure 5b). This suggests that treatment with carbachol did not have a protective effect. Wells with 20,000 cells/well had relatively low fluorescence readings in both the serum starvation and the rotenone toxicity experiments (Figures 5a and 5b). DISCUSSION In this study we report the induction of EGR1 by machr activation in Neuro-2a neuroblastoma cells. The carbachol dose-response curves show that the M3-selective muscarinic antagonist 4-DAMP was the most potent (2.48 nm) selective antagonist. Pertussis toxin was shown to inhibit EGR1 expression. This suggests M2/M4 receptor involvement and taken together with the AFDX-116 data (M2-selective antagonist), implicates M4 receptors in muscarinic-driven EGR1 induction. None of the selective antagonists had a potency comparable to that of the non-selective antagonist atropine (0.098 nm). This implies that blocking cellular signalling through a single receptor subtype was unable to completely inhibit EGR1 expression. These findings collectively suggest that a combination of M3 and M4 receptor subtypes are likely to be primarily responsible for muscarinic-driven EGR1 induction. The decline in EGR1 expression, after the peaks of the dose-response curves, was apparent irrespective of the presence of selective antagonists. This may be the result of carbachol binding to a receptor to which it has lower affinity, leading to the downregulation of EGR1. It is known that EGR1 is very far downstream of the receptor, and this feature reinforces that many other factors may influence the levels of EGR1 in these cells. In the alamar blue fluorescence assays, which used serum starvation and rotenone treatment to induce apoptosis, treatment with carbachol did not appear to have any protective effect. It was noted that cells plated at a higher density (20,000 cells/well) had low viabilities under both experimental conditions. This may be an endogenously-initiated downgrading of cellular metabolism at this higher density. It is possible that this downregulation of cellular metabolism potentiates the toxic effect of rotenone, resulting in the extremely low cell viability at 20,000 cells/well (Figure 5b). This awaits further analysis. These experiments have shown that muscarinic stimulation and EGR1 induction do not have a protective effect on cell survival in Neuro-2a cells. EGR1 induction is probably, on its own, insufficient for preventing cell apoptosis in Neuro-2a cells. In Neuro-2a cells, muscarinic cholinergic signalling has been found to induce EGR1 expression, but not CREB phosphorylation (J. Greenwood, personal communication). Research using the SK-N-SH cell line has shown that treatment with carbachol induces CREB phosphorylation and EGR1 expression. 14 Carbachol treatment also has a protective effect in this cell line. The results of the Neuro-2a and SK-N-SH cell lines, if taken together, suggest that CREB phosphorylation may be more influencial in the anti-apoptotic mechanism of cholinergic signalling than EGR1 induction. This supports evidence from CREB transfection experiments in Neuro-2a and PC cells that showed CREB overexpression produced anti-apoptotic effects. 13 In the SK-N-SH cell line, the protective effects of cholinergic signalling were shown to be driven through the M3-muscarinic receptor (J. Greenwood, personal communication). In the Neuro-2a cell line, we have found that if collectively stimulated, M3 and M4 receptors do not increase cell survival. It is possible that M4-receptors drive a pro-apoptotic response 3
5 that negates the effects of an anti-apoptotic M3-driven response. This is relevant to Alzheimer's disease as M3 and M4 receptors are relatively well preserved in the brains of patients that had suffered from this disease. Our experiments have shown that muscarinic signalling leads to EGR1 expression in Neuro-2a cells, most likely driven through M3 and M4 receptors, but muscarinic signalling and EGR1 induction have no protective effects. It has produced evidence complementary to past research that EGR1 has a less significant role in the anti-apoptotic mechanism than CREB phosphorylation. The experiments have generated some interesting questions on the density-dependent effects of stressful conditions on cell survival, which may undergo further research. Currently, most of the drugs used in the treatment of Alzheimer's disease are modulators of acetylcholine signalling (acetylcholinesterase inhibitors). These drugs have many adverse effects because they are non-specific in their action. In our research we have successfully used a cell model to complement the current understanding of the involvement of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors in cell survival pathways. Elaborating these survival pathways is important in understanding the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, which may, in turn, result in more effective pharmacological therapies. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This research was funded by the University of Auckland. Special thanks to my supervisor Dr. Jeffrey Greenwood for his expert guidance during the project. REFERENCES 1. D. Jerusalinsky, E. Kornisiuk and I. Izquierdo Cholinergic neurotransmission and synaptic plasticity concerning memory processing Neurochem 1997;22: R. D. Blitzer, O. Gil and E. M. Landau Cholinergic stimulation enhances long-term potentiation in the CA1 region of rat hippocampus Neurosci Lett 1990;119(2): G. M. Yan, S. Z. Lin, R. P. Irwin and S. M. Paul Activation of muscarinic cholinergic receptors blocks apoptosis of cultured cerebellar granule neurons Mol Pharmacol 1995;47(2): E. H. T. Wu and Y. H. Wong Activation of muscarinic M4 receptor augments NGF-induced prosurvival Akt signalling in PC cells Cellular Signalling 2006;18: A. Gashler and V. P. Sukhatme Early growth response protein 1(EGR-1): prototype of a zinc-finger family of transcription factors Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol 1995;50: M. W. Jones, M. L. Errington, P. J. French, A. Fine, T. V. P. Bliss, S. Garel, P. Charnay, B. Bozon, S. Laroche and S. Davis A requirement for the immediate early gene Zif268 in the expression of late LTP and long-term memories Nat Neurosci 2001;4: H. von der Krammer, M. Mayhaus, C. Albrecht, J. Enderich, M. Wegner and R. M. Nitsch Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors activate expression of the EGR gene family of transcription factors J Biol Chem 1998;273: N. Katayama, E. Iwata, H. Sakurai, T. Tsuchiya and M. Tsuda Additive induction of Egr-1(zif/268) mrna expression in neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG cells via cholinergic muscarinic, a2-adrenergic, and bradykinin receptors J Neurochem 1993;60(3): P. Hughes and M. Dragunow Activation of pirenzipine-sensitive muscarinic receptors induces a specific pattern of immediate-early gene expression in rat brain neurons Mol Brain Res 1994;24: B. Mayr and M. Montminy Transcriptional regulation by the phosphorylation-dependent factor CREB Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2001;2: C. Giachino, S. De Marchis, C. Giampietro, R. Parlato, I. Perroteau, G. Schutz, A. Fasolo and P. Peretto camp response element-binding protein regulates differentiation and survival of neuborn neurons in the olfactory bulb. J Neurosci 2005;25(44): H. Bito and S. Takemoto-Kimura Ca(2+)/CREB/CBP-dependent gene regulation: a shared mechanism critical in long-term synaptic plasticity and neuronal survival Cell Calcium 2003;34(4-5): M. Walton, A. M. Woodgate, A. Muravlev, R. Xu, M. J. During and M. Dragunow CREB phosphorylation promotes nerve cell survival J. Neurochem 1999;73(5): J. M. Greenwood and M. Dragunow Muscarinic receptor-mediated phosphorylation of cyclic AMP response element binding protein in human neuroblastoma cells J. Neurochem 2002;82: M. J. Lew and J. A. Angus Analysis of competitive agonist-antagonist interactions by nonlinear regression Trends Pharmacol Sci 1995;16:
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors. Reading: BCP Chapter 6
 Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Neurotransmitter Systems II Receptors Reading: BCP Chapter 6 Neurotransmitter Systems Normal function of the human brain requires an orderly set of chemical reactions. Some of the most important chemical
Fig. S1. High K+ increases intracellular calcium level.
 Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Fig. S1. High K + increases intracellular calcium level. (A) Neuronal activation measured by calcium imaging using Fura-2. Intracellular calcium levels were continuously monitored by the fura-2 florescence
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION
 Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Supplementary Information POLO-LIKE KINASE 1 FACILITATES LOSS OF PTEN-INDUCED PROSTATE CANCER FORMATION X. Shawn Liu 1, 3, Bing Song 2, 3, Bennett D. Elzey 3, 4, Timothy L. Ratliff 3, 4, Stephen F. Konieczny
Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line
 TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
TECHNICAL DATA SHEET ValiScreen Ion Channel Cell Line Caution: For Laboratory Use. A research product for research purposes only Human TRPC6 Ion Channel Cell Line Product No.: AX-012-C Lot No.: 512-548-A
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates. Store Operated Calcium Entry
 TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
TFEB-mediated increase in peripheral lysosomes regulates Store Operated Calcium Entry Luigi Sbano, Massimo Bonora, Saverio Marchi, Federica Baldassari, Diego L. Medina, Andrea Ballabio, Carlotta Giorgi
EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes
 1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
1st Electronic Conference on Molecular Science EGF receptor transactivation is crucial for cholinergic MAP kinase signaling in human keratinocytes Wymke Ockenga, Sina Kühne, Antje Banning and Ritva Tikkanen
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Materials and Methods Human cell lines and culture conditions HCC1937 is the HCC1937-pcDNA3 cell line, which was derived from a breast cancer with a mutation in exon 20 of BRCA1
Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT
 Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
Technical Note_1 ver.1 Low Cell Binding Property of LIPIDURE -COAT 1. LIPIDURE -COAT MULTI DISH A-6MD (Cat. No. 51011617) 2. Cell; NIH 3T3 (Fibroblast, mouse) 1. 10 %CS-DMEM; DMEM (Dulbecco's Modified
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit
 AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
AMPK Phosphorylation Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3789 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
GLP-2 ELISA. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples.
 GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
GLP-2 ELISA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in human serum and plasma samples. For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2HU-E01.1 Size: 96 wells Version:
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests. Introduction
 Introduction Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests Caspase-3 is a member of caspases that plays a key role in mediating apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Upon activation, it cleaves a variety of
Introduction Caspase-3 Assay Cat. No. 8228, 100 tests Caspase-3 is a member of caspases that plays a key role in mediating apoptosis, or programmed cell death. Upon activation, it cleaves a variety of
B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small cell lung cancer
 Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Electronic Supplementary Material (ESI) for ChemComm. This journal is The Royal Society of Chemistry 2017 Experimental Methods Cell culture B16-F10 (Mus musculus skin melanoma), NCI-H460 (human non-small
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Supplementary Figure 1 AAV-GFP injection in the MEC of the mouse brain C57Bl/6 mice at 4 months of age were injected with AAV-GFP into the MEC and sacrificed at 7 days post injection (dpi). (a) Brains
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
Supplementary Figure 1 EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a-b) EGFR inhibition activates signaling pathways (a) U251EGFR cells were treated with erlotinib (1µM) for the indicated times followed
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
CONTENTS. STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1
 CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
CONTENTS STUDY DESIGN METHODS ELISA protocol for quantitation of mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Der p 1 or Der f 1 ELISA protocol for mite (Dermatophagoides spp.) Group 2 ALLERGENS RESULTS (SUMMARY) TABLE
Mouse GLP-2 EIA. Cat. No. KT-374. For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. For Research Use Only. 1 Rev.
 Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
Mouse GLP-2 EIA For the quantitative determination of GLP-2 in mouse serum or plasma. Cat. No. KT-374 For Research Use Only. 1 Rev. 11357374 PRODUCT INFORMATION Mouse GLP-2 EIA Cat. No. KT-374 INTENDED
SUPPLEMENT. Materials and methods
 SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
SUPPLEMENT Materials and methods Cell culture and reagents Cell media and reagents were from Invitrogen unless otherwise indicated. Antibiotics and Tet-certified serum were from Clontech. In experiments
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet
 colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
colorimetric sandwich ELISA kit datasheet For the quantitative detection of human TNF-alpha in serum, plasma and cell culture supernatants. general information Catalogue Number Product Name Species cross-reactivity
ab Intracellular O 2 Probe
 ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652
 Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Notch Signaling Pathway Notch CSL Reporter HEK293 Cell line Catalog #: 60652 Background The Notch signaling pathway controls cell fate decisions in vertebrate and invertebrate tissues. Notch signaling
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression. through inhibition of Hsp90
 Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Supplemental material for Hernandez et al. Dicoumarol downregulates human PTTG1/Securin mrna expression through inhibition of Hsp90 Dicoumarol-Sepharose co-precipitation. Hsp90 inhibitors can co-precipitate
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Basics of Pharmacology
 Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
Basics of Pharmacology Pekka Rauhala Transmed 2013 What is pharmacology? Pharmacology may be defined as the study of the effects of drugs on the function of living systems Pharmacodynamics The mechanism(s)
7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY. 7.1 Introduction
 268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
268 7. NOOTROPIC AND ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY 7.1 Introduction Alzheimer s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, which according to World Health Organization (WHO) affects 22 million people world wide,
Cognitive Enhancement Strategies. Florian Plattner, James A. Bibb
 Cognitive Enhancement Strategies Florian Plattner, James A. Bibb A decline in memory and cognitive function is a natural aspect of aging. In addition, cognitive deficits are comorbid with many mental disorders
Cognitive Enhancement Strategies Florian Plattner, James A. Bibb A decline in memory and cognitive function is a natural aspect of aging. In addition, cognitive deficits are comorbid with many mental disorders
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
YK142 Mouse GLP-2 EIA FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY Kasumigaseki place, 3-6-7, Kasumigaseki, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0013 Japan http://www.sceti.co.jp/english/export e-mail exp-pet@sceti.co.jp
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 2
 Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Supplementary data Supplementary Figure 1 SPHK1 sirna increases RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in RAW264.7 cell culture. (A) RAW264.7 cells were transfected with oligocassettes containing SPHK1 sirna
Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay
 The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
The Annexin V Apoptosis Assay Development of the Annexin V Apoptosis Assay: 1990 Andree at al. found that a protein, Vascular Anticoagulant α, bound to phospholipid bilayers in a calcium dependent manner.
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) Hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Figure S1 Induction of non-apoptotic death of SV40-transformed and primary DKO MEFs, and DKO thymocytes. (A-F) STS-induced non-apoptotic death of DKO MEF. (A, B) Reduced viability of DKO MEFs after exposure
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor HSE-bla HeLa Cell Line Cat. no. K Pathway Description Activation of the heat shock response/unfolded protein response (HSR/UPR) occurs in response to a
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor HSE-bla HeLa Cell Line Cat. no. K Pathway Description Activation of the heat shock response/unfolded protein response (HSR/UPR) occurs in response to a
SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72084 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect HDAC activity. Enhanced Value: It provides
SensoLyte 520 HDAC Activity Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72084 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect HDAC activity. Enhanced Value: It provides
Alpha-Tubulin Housekeeping 10,000 tests
 Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
Headquarters & Europe Office Cisbio Bioassays Phone: +33 (0)4 66 79 67 05 Fax: +33 (0)4 66 79 19 20 bioassays@cisbio.com cisbio_dd_pi_64atubpeh USA Office Cisbio US, Inc. Phone: +1 888 963 4567 Fax: +1
Pharmacologyonline 2: (2008) Newsletter Deepraj and Nandakumar
 INVESTIGATION OF ISOLATED GOAT ILEUM PREPARATION FOR THE SUITABILITY AS A TEACHING AID FOR UNDER GRADUATE AND POST GRADUATE PRACTICALS Deepraj Paul, K.Nandakumar DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY, P.E.S COLLEGE
INVESTIGATION OF ISOLATED GOAT ILEUM PREPARATION FOR THE SUITABILITY AS A TEACHING AID FOR UNDER GRADUATE AND POST GRADUATE PRACTICALS Deepraj Paul, K.Nandakumar DEPARTMENT OF PHARMACOLOGY, P.E.S COLLEGE
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA. For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma
 GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
GLP-2 (Rat) ELISA For the quantitative determination of glucagon-like peptide 2 (GLP-2) in rat serum and plasma For Research Use Only. Not For Use In Diagnostic Procedures. Catalog Number: 48-GP2RT-E01
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual)
 HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
HIV-1 p24 ELISA Pair Set Cat#: orb54951 (ELISA Manual) BACKGROUND Human Immunodeficiency Virus ( HIV ) can be divided into two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6
 BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
BIPN 140 Problem Set 6 1) The hippocampus is a cortical structure in the medial portion of the temporal lobe (medial temporal lobe in primates. a) What is the main function of the hippocampus? The hippocampus
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Burford et al. 1.173/pnas.1339311 SI Materials and Methods β-arrestin Recruitment Assay. PathHunter human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) expressing either μ-opioid receptors (U2OS- OPRM1)
Supporting Information Burford et al. 1.173/pnas.1339311 SI Materials and Methods β-arrestin Recruitment Assay. PathHunter human osteosarcoma cells (U2OS) expressing either μ-opioid receptors (U2OS- OPRM1)
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras
 Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Psych 181: Dr. Anagnostaras Lecture 5 Synaptic Transmission Introduction to synaptic transmission Synapses (Gk., to clasp or join) Site of action of most psychoactive drugs 6.5 1 Synapses Know basic terminology:
Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H2 CRE-bla HEK 293T Cell Line
 GeneBLAzer Validation Packet Version No.: 1Sep Page 1 of 5 Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cell Line GeneBLAzer H HEK 93T DA Cells GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cells Catalog Numbers K17
GeneBLAzer Validation Packet Version No.: 1Sep Page 1 of 5 Optimization of the GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cell Line GeneBLAzer H HEK 93T DA Cells GeneBLAzer H CRE-bla HEK 93T Cells Catalog Numbers K17
- 1 - Cell types Monocytes THP-1 cells Macrophages. LPS Treatment time (Hour) IL-6 level (pg/ml)
 Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Supplementary Table ST1: The dynamic effect of LPS on IL-6 production in monocytes and THP-1 cells after GdA treatment. Monocytes, THP-1 cells and macrophages (5x10 5 ) were incubated with 10 μg/ml of
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells
 Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Supporting Information for Development of a near-infrared fluorescent probe for monitoring hydrazine in serum and living cells Sasa Zhu, Weiying Lin,* Lin Yuan State Key Laboratory of Chemo/Biosensing
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Validation & Assay Performance Summary CellSensor DBE-bla MDA-MB-468 Cell Line Cat. no. K1814 Pathway Description The phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) signaling cascade is essential for cell growth
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA)
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for NTRK1 (TRKA) Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line
 Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Apoptosis Mediated Cytotoxicity of Curcumin Analogues PGV-0 and PGV-1 in WiDr Cell Line Endah Puji Septisetyani, Muthi Ikawati, Barinta Widaryanti and Edy Meiyanto* ) Cancer Chemoprevention Research Center,
Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as
 Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
Supplementary Figure 1. Basal level EGFR across a panel of ESCC lines. Immunoblots demonstrate the expression of phosphorylated and total EGFR as well as their downstream effectors across a panel of ESCC
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al
 Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Supplementary Material Rescue of mutant rhodopsin traffic by metformin-induced AMPK activation accelerates photoreceptor degeneration Athanasiou et al Supplementary Figure 1. AICAR improves P23H rod opsin
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics
 Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Drug Receptor Interactions and Pharmacodynamics Dr. Raz Mohammed MSc Pharmacology School of Pharmacy 22.10.2017 Lec 6 Pharmacodynamics definition Pharmacodynamics describes the actions of a drug on the
Mouse Adiponectin Immunoassay Kit
 Antibody and Immunoassay Services Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Mouse Adiponectin Immunoassay Kit Catalogue Number: 32010 For the quantitative determination of mouse adiponectin
Antibody and Immunoassay Services Li Ka Shing Faculty of Medicine, The University of Hong Kong Mouse Adiponectin Immunoassay Kit Catalogue Number: 32010 For the quantitative determination of mouse adiponectin
Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of
 SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
SUPPLEMENTAL DATA Inhibition of TGFβ enhances chemotherapy action against triple negative breast cancer by abrogation of cancer stem cells and interleukin-8 Neil E. Bhola 1, Justin M. Balko 1, Teresa C.
Functions of Lysosomes
 Functions of Lysosomes Intro - Degradation of cell components -Cell death -Autophagy 1st - Exocytosis / Secretory pathway - Calcium signalling 2nd O BayDH., (2009) Phosphatidylcholine Intro Phosphatidylcholine
Functions of Lysosomes Intro - Degradation of cell components -Cell death -Autophagy 1st - Exocytosis / Secretory pathway - Calcium signalling 2nd O BayDH., (2009) Phosphatidylcholine Intro Phosphatidylcholine
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
Assay Report. Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Assays Enzymatic Study of Compounds from Client
 Assay Report Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Assays Enzymatic Study of Compounds from Client Page 1 of 27 Client_HDAC _Year Month Day 1 Client_HDAC_Year Month Year HDAC Inhibitor Assays Study Sponsor:
Assay Report Histone Deacetylase (HDAC) Inhibitor Assays Enzymatic Study of Compounds from Client Page 1 of 27 Client_HDAC _Year Month Day 1 Client_HDAC_Year Month Year HDAC Inhibitor Assays Study Sponsor:
NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254)
 Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
Assay Biotechnology Company www.assaybiotech.com Tel: 1-877-883-7988 Fax: 1-877-610-9758 NF-κB p65 (Phospho-Thr254) Colorimetric Cell-Based ELISA Kit Catalog #: OKAG02015 Please read the provided manual
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
doi: 10.1038/nature06994 A phosphatase cascade by which rewarding stimuli control nucleosomal response A. Stipanovich*, E. Valjent*, M. Matamales*, A. Nishi, J.H. Ahn, M. Maroteaux, J. Bertran-Gonzalez,
EXOTESTTM. ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids
 DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
DATA SHEET EXOTESTTM ELISA assay for exosome capture, quantification and characterization from cell culture supernatants and biological fluids INTRODUCTION Exosomes are small endosome-derived lipid nanoparticles
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES
 8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
8. CHAPTER IV. ANTICANCER ACTIVITY OF BIOSYNTHESIZED SILVER NANOPARTICLES 8.1. Introduction Nanobiotechnology, an emerging field of nanoscience, utilizes nanobased-systems for various biomedical applications.
Supporting Information
 Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
Copyright WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, 69469 Weinheim, Germany, 212. Supporting Information for Adv. Funct. Mater., DOI:.2/adfm.2122233 MnO Nanocrystals: A Platform for Integration of MRI and Genuine
In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis aubl
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 3 Number 10 (2014) pp. 169-176 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article In-vitro assay for Cytotoxicity activity in ethonolic extract of fruit rind of Couropita Guianensis
Mouse C-peptide EIA. Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY
 Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Mouse C-peptide EIA Cat. No. YII-YK013-EX FOR LABORATORY USE ONLY TOYO 2CHOME, KOTO-KU, TOKYO, 135-0016, JAPAN http://www.cosmobio.co.jp e-mail : export@cosmobio.co.jp Phone : +81-3-5632-9617 FAX : +81-3-5632-9618
Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit
 Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
Product Manual Total Phosphatidic Acid Assay Kit Catalog Number MET- 5019 100 assays FOR RESEARCH USE ONLY Not for use in diagnostic procedures Introduction Phosphatidic Acid (PA) is a critical precursor
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol
 L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
L6 GLUT4myc Cell Growth Protocol Background: Parental L6 cells selected for high fusion (2, 3) were stably transfected with a rat GLUT4 cdna carrying a myc epitope (recognized by the commercially available
Fang et al. NMuMG. PyVmT unstained Anti-CCR2-PE MDA-MB MCF MCF10A
 A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
A NMuMG PyVmT 16.5+.5 47.+7.2 Fang et al. unstained Anti-CCR2-PE 4T1 Control 37.6+6.3 56.1+.65 MCF1A 16.1+3. MCF-7 3.1+5.4 MDA-M-231 42.1+5.5 unstained Secondary antibody only Anti-CCR2 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB
 Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Electrical Stimulation Control Nerve Regeneration via the p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase and CREB Kenji Kawamura, Yoshio Kano. Kibi International University, Takahashi-city, Japan. Disclosures: K.
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration
 Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
Programmed necrosis, not apoptosis, is a key mediator of cell loss and DAMP-mediated inflammation in dsrna-induced retinal degeneration The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please
System. From Classical to Online Monitoring of G-ProteinCoupled Receptor. Stimulation in Living Cells. Application Note No.
 System Application Note No. 6 / December 2008 From Classical to Online Monitoring of G-ProteinCoupled Receptor Stimulation in Living Cells From Classical to Online Monitoring of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
System Application Note No. 6 / December 2008 From Classical to Online Monitoring of G-ProteinCoupled Receptor Stimulation in Living Cells From Classical to Online Monitoring of G-Protein-Coupled Receptor
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update
 NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
NNZ-2566 in Rett Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders Role and Update 1 Overview The natural growth factor IGF-1 is broken down in the body to IGF-1[1-3] NNZ-2566 is an analogue of IGF-1[1-3] developed
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Improvements in Live Cell Analysis of G Protein Coupled Receptors using Second Generation BD Calcium Assay Kits
 1 Current Chemical Genomics, 8, 2, 1-15 Open Access Improvements in Live Cell Analysis of G Protein Coupled Receptors using Second Generation BD Calcium Assay Kits Xiao Li*, Isabel Llorente and Mike Brasch
1 Current Chemical Genomics, 8, 2, 1-15 Open Access Improvements in Live Cell Analysis of G Protein Coupled Receptors using Second Generation BD Calcium Assay Kits Xiao Li*, Isabel Llorente and Mike Brasch
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified
 Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Cell culture and animal model A549 and A549-fLuc cells were maintained in high glucose Dulbecco modified Eagle medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum at 37 C in humidified atmosphere containing
Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting
 The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
The schedule and the manual of basic techniques for cell culture Advanced Protocol for Gene Transfection & Western Blotting Schedule Day 1 26/07/2008 Transfection Day 3 28/07/2008 Cell lysis Immunoprecipitation
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70
 Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
Optimization of a LanthaScreen Kinase assay for ZAP70 Overview This protocol describes how to develop a LanthaScreen kinase assay designed to detect and characterize kinase inhibitors. The development
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES AND TABLES Supplementary Figure S1: CaSR expression in neuroblastoma models. A. Proteins were isolated from three neuroblastoma cell lines and from the liver metastasis of a MYCN-non
hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGEND Fig. S1. Generation and characterization of. (A) Coomassie staining of soluble hexahistidine tagged GRP78 devoid of the KDEL motif (GRP78-His) on SDS-PAGE. This protein was expressed
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells
 Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
Indonesian Journal of Cancer Chemoprevention, 2017, 8(1): 27-31 ISSN: 2088 0197 Cinnamomum Essential Oil Prevents DNA Damage- Induced by Doxorubicin on CHO-K1 Cells Layung Sekar Sih Wikanthi, Nindi Wulandari,
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology
 USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
USMLE Step 1 - Problem Drill 14: Pharmacology Question No. 1 of 10 1. shift dose response curves to the right, decrease potency and increase the EC50. Question #01 (A) Receptors (B) Non-competitive antagonists
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figures S1-S9. Supplementary Methods
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION SUMO1 modification of PTEN regulates tumorigenesis by controlling its association with the plasma membrane Jian Huang 1,2#, Jie Yan 1,2#, Jian Zhang 3#, Shiguo Zhu 1, Yanli Wang
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71127 Unit Size Kit Size 1 kit 500 assays (96-well) or 1250 assays (384-well) This kit is optimized to detect the activity of human immunodeficiency
SensoLyte 490 HIV-1 Protease Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 71127 Unit Size Kit Size 1 kit 500 assays (96-well) or 1250 assays (384-well) This kit is optimized to detect the activity of human immunodeficiency
