The basic mechanism of increased microvascular permeability
|
|
|
- Shannon Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Chinese Journal of Pathophysiology 2003,19 (4) : [ ] (2003) , (, ) The basic mechanism of increased microvascular permeability ZHAO Ke - sen, HUANG Qiao - bing ( Department of Pathophysiology, First Military Medical University, Guangzhou , China) A Review The increased microvascular permeability appears mainly in venule during inflammation, shock, and burns. Endothelial cells play an important role in venule permeability enhancement. There are two kinds of pathway for macromolecule extravasation. One is paracellular pathway and another is transcellular pathway, which are related to the formation of endothelial gap or transcellular openings seperately. The alter2 ation of intercellular related protein, such as occludin, claudin, zona occludens ( ZO), junctional adhesion molecule (JAM), VE - cadherin, catenin, integrin, etc, and the alteration of endothelial cytoskeleton, such as rearrangement of actin filament, formation of stress fiber and focal adhesion, etc,involve in the pathogenesis of increased microvascular permeability. [] ; ; ; ; [ KEY WORDS] Vascular permeability ;Claudin ; Occludin ; Cadherins ; Stress fiber [] R363 [] A [ ] [ ] [ ] (No ) ; ( G ) ; ( G ) Tel : ; E - mail com,,,,,,, 1,,,, 10-40m (postcapillary venule) ; m, (collecting venule ) 5 - P ( PAF) B 4 (LTB 4 ) TNF LPS -,,, 1. 1 (paracellular pathway) 1961 Majno Palade, 5 - (gap), m, (P ), McDonald, P, ( ),,,,
2 550, (vertical gap) (oblique slits), 1. 2m, (P 1 min),48 % 13,11, 112 (transcellular pathway),,feng 14 nm, nm, - VVOs,, - 3,, VVOs ( ) VVOs, (VEGF) VVOs Michel, VEGF (transcellular opening),,, (vascuolar channel),,, VVOs, (caveolae) (endocytosis) (caveolae), Fig 1 Schema of constructive protein in tight junction. 1 ( 1) (plasmalemmal vesicle), (caveolin) (LDL) Caveolae, (transcytosis) caveolae (molecular ma2 chinery function),- caveolae,src caveolin - 1, caveolin - 1 G ( Gi), caveolae Caveolae,, 2 (gap), -, (tight junc2 tion), ;, ( sealing strand), (oc2 cludin) (claudin) (zona oc2 ( VVOs, vesiculo - vascuolar organelles) cludens, ZO ) ( junction adhesion molecule, JAM) 4,N C (ZO), N C,ZO C ( 1),,, 2. 2 (adherens junction) nm,(cadherin), (tetraspanner protein) -, (VE - cadherin),n N,VE - cadherin (cluster) ; C (catenin), actin (
3 551 2), 20 (anchorage) 3,,N (Arg - Gly - Asp, RGD), RGD, ( FN VN LM ), - ( 3) ( ), Fig 2 The structure of an adherens junction. 2 ( 2) VE - cadherin,, : :,, (gap) ; : -,, ; :,,, (collagen) (laminin,lm) (fibronectin,fn) (vitronectin,vn) nm (extracellular matrix,ecm),, (ad2 hesion of endothelial to basement membrane) (integrin) () ( ), - -,10,8,,, Fig 3 The structure and function of integrins. 3 ( 2) (mechano - sensor) ECM,, G ( Rho Rac ),(),, -, :,;,,, ;,
4 552,,, (tethering property) 3, (cytoskeleton) (isometric contraction),,,,,,, (microtube) (microfilament) (thrombin), (intermediate filament),, 6-8 nm, G Rho, Ca 2 + -, C (actin),,g - actin F - acting - actin,g - actin ( F - actin),,f - actin G - actin, (assembly) (disassembly), 3. 1, Fig 4 Stress fiber. ( PAF TNF ), 4 ( 2),,, 3. 2 ( stress fiber, 4),,, -, ( myosin light (cortical zone), chain, MLC) (myosin, light chain kinase, MLCK) MLC, ATP,, (nonmuscle cell) ( F - actin),, MLCK(ML - 7), (focal MLC contact focal adhesion plaques), ;, PKC Ca PKG (hemidesmosomes) G Rho MAPK (integrin), ECM,,, MLC,,,,
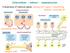
5 553 Fig 5 The basic mechanism of increased microvascular permeability. 5 ( 13), [6 ] Kevil CG, Oshima T, Alexander B, et al. H 2 O 2 - mediated permeability: role of MAPK and occludin[j ]. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, 2000, 279 (1) : C21 - C30. [7 ] Michel CC, Neal CR. Openings through endothelial cells asso2, ciated with increased microvascular permeability[j ]. Microcir2 ( 5), culation, 1999, 6 (1) : , [8 ] Langille BL. Morphologic responses of endothelium to shear stress : reorganization of the adherens junction[j ]. Microcir2 [ ] culation, 2001, 8 (3) : [1 ] Ward PD, Tippin TK, Thakker DR. Enhancing paracellular permeability by modulating epithelial tight junctions [ J ]. Pharm Sci Technol Today, 2000, 3 (10) : [2 ] Karp G. Cell and molecular biology - concepts and experi2 ments [M]. New York : John Wiley & Sons, Inc, [3 ] McDonald D M, Thurston G, Baluk P. Endothelial gaps as sites for plasma leakage in inflammation[j ]. Microcirculation, 1999,6 (1) : [4 ] Wachtel M, Frei K, Ehler E, et al. Occludin proteolysis and increased permeability in endothelial cells through tyrosine phosphatase inhibition [ J ]. J Cell Sci, 1999, 112 ( pt23) : [5 ] Feng D, Nagy JA, Pyne K, et al. Pathways of macromolecu2 lar extravasation across microvascular endothelium in response to VPF/ VEGF and other vasoactive mediators[j ]. Microcircu2 lation, 1999, 6 (1) : [9 ] Valeski J E, Baldwin AL. Effect of early transient adherent leukocytes on venular permeability and endothelial actin cy2 toskeleton[j ]. Am J Physiol, 1999, 277 (Heart Circ. Physi2 ol 46) : H569 - H575. [10 ] Baldwin AL, Thurston G. Changes in endothelial actin cy2 toskeleton in venules with time after histamine treatment [J ]. Am J Physiol, 1995, 269 (Heart Circ Physiol 38) : H H1537. [11 ] Liu Y, Chen BP, Lu M, et al. Shear stress activation of SREBP1 in endothelial cells is mediated by integrins[j ]. Ar2 terioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2002, 22 (1) : [ 12 ] Yuan SY. Signal transduction pathway in enhanced microvas2 cular permeability[j ]. Microcirculation, 2000, 7 (6 pt 1) : [13 ]. [A]. :,. [M]. 1. :,
CELL BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH CELL JUNCTIONS AND TISSUES.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: CELL-CELL ADHESION Cells must be able to bind and interact with nearby cells in order to have functional and strong tissues Cells can in two main ways - Homophilic interactions
Intercellular indirect communication
 Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Intercellular indirect communication transmission of chemical signals: sending cell signal transmitting tissue hormone medium receiving cell hormone intercellular fluid blood neurocrine neurotransmitter
Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo
 Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
Integration of Cells into Tissues Dr Mahmood S Choudhery, PhD, Postdoc (USA) Assistant Professor Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine King Edward Medical University/Mayo Hospital Lahore 1. How
Novel roles for ICAM1 in leukocyte transendothelial migration. Michael John Allingham
 Novel roles for ICAM1 in leukocyte transendothelial migration Michael John Allingham A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of
Novel roles for ICAM1 in leukocyte transendothelial migration Michael John Allingham A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in partial fulfillment of
4. The critical role of endothelial cells in the development of inflammatory diseases
 Research Signpost Trivandrum Kerala, India Advances in the Mechanism of Cardio-Cerebral Disease, 2018: 91-121 ISBN: 978-81-308-0575-7 Editors: Ke-seng Zhao, Yong Jiang and 4. The critical role of endothelial
Research Signpost Trivandrum Kerala, India Advances in the Mechanism of Cardio-Cerebral Disease, 2018: 91-121 ISBN: 978-81-308-0575-7 Editors: Ke-seng Zhao, Yong Jiang and 4. The critical role of endothelial
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells. Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari
 Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
Animal Tissue Culture SQG 3242 Biology of Cultured Cells Dr. Siti Pauliena Mohd Bohari The Culture Environment Changes of Cell s microenvironment needed that favor the spreading, migration, and proliferation
A novel role for reactive oxygen species in the regulation of RhoA; implications for endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration.
 A novel role for reactive oxygen species in the regulation of RhoA; implications for endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration. Amir Aghajanian A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the
A novel role for reactive oxygen species in the regulation of RhoA; implications for endothelial permeability and leukocyte transmigration. Amir Aghajanian A dissertation submitted to the faculty of the
The recruitment of leukocytes and plasma proteins from the blood to sites of infection and tissue injury is called inflammation
 The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
The migration of a particular type of leukocyte into a restricted type of tissue, or a tissue with an ongoing infection or injury, is often called leukocyte homing, and the general process of leukocyte
REVIEWS ENDOTHELIAL CELL CELL JUNCTIONS: HAPPY TOGETHER. Elisabetta Dejana
 ENDOTHELIAL CELL CELL JUNCTIONS: HAPPY TOGETHER Elisabetta Dejana Junctional structures maintain the integrity of the endothelium. Recent studies have shown that, as well as promoting cell cell adhesion,
ENDOTHELIAL CELL CELL JUNCTIONS: HAPPY TOGETHER Elisabetta Dejana Junctional structures maintain the integrity of the endothelium. Recent studies have shown that, as well as promoting cell cell adhesion,
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center. The Golgi apparatus. Functions of the Golgi apparatus. Lysosomes: Digestive Compartments
 The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
The Golgi Apparatus: Shipping and Receiving Center The Golgi apparatus Receives (on the cis-side) many of the transport vesicles produced in the rough ER Consists of flattened membranous sacs called cisternae
Review. Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability
 Review Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability Yulia A. Komarova, Kevin Kruse, Dolly Mehta, Asrar B. Malik Abstract: The monolayer of
Review Protein Interactions at Endothelial Junctions and Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability Yulia A. Komarova, Kevin Kruse, Dolly Mehta, Asrar B. Malik Abstract: The monolayer of
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility
 Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
Molecular Cell Biology - Problem Drill 20: Cytoskeleton and Cellular Mobility Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about cytoskeletal filaments is correct? Question #1 (A) The Cytoskeleton
invited review Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability
 J Appl Physiol 91: 1487 1500, 2001. Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability invited review STEVEN M. DUDEK AND JOE G. N. GARCIA Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Johns
J Appl Physiol 91: 1487 1500, 2001. Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability invited review STEVEN M. DUDEK AND JOE G. N. GARCIA Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Johns
Microfilaments. myosin. In muscle cells. Microfilaments. Microfilaments. Video: Cytoplasmic Streaming. amoeboid movement. Pseudopodia.
 Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
Microfilaments Fig, 6-27a myosin Microfilaments protein func3ons in cellular mo3lity in addi3on to ac3n In muscle cells Thousands of ac3n filaments are arranged parallel to one another Thicker myosin filaments
The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber
 INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
INVITED BASIC SCIENCE REVIEW The dynamic regulation of blood vessel caliber Colleen M. Brophy, MD, Augusta, Ga BACKGROUND The flow of blood to organs is regulated by changes in the diameter of the blood
TNF-induced endothelial barrier disruption: beyond actin and Rho
 Review Article 1088 TNF-induced endothelial barrier disruption: beyond actin and Rho Beatriz Marcos-Ramiro * ; Diego García-Weber * ; Jaime Millán Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa, CSIC-UAM, Madrid,
Review Article 1088 TNF-induced endothelial barrier disruption: beyond actin and Rho Beatriz Marcos-Ramiro * ; Diego García-Weber * ; Jaime Millán Centro de Biología Molecular Severo Ochoa, CSIC-UAM, Madrid,
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
Peroxisomes. Endomembrane System. Vacuoles 9/25/15
 Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Contains enzymes in a membranous sac that produce H 2 O 2 Help survive environmental toxins including alcohol Help the cell use oxygen to break down fatty acids Peroxisomes Endo System Components of the
Cell Cell Communication
 IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
IBS 8102 Cell, Molecular, and Developmental Biology Cell Cell Communication January 29, 2008 Communicate What? Why do cells communicate? To govern or modify each other for the benefit of the organism differentiate
The Jobs of Cells. Food & water storage. Vacuoles & vesicles. Vacuoles in plants 10/5/2015. plant cells
 Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
Cells have 3 main jobs make energy need energy for all activities need to clean up waste produced while making energy make proteins proteins do all the work in a cell, so we need lots of them make more
Histology = the study of tissues. Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function
 { EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
{ EPITHELIAL TISSUE Histology = the study of tissues Tissue = a complex of cells that have a common function The Four Primary Tissue Types: Epithelium (epithelial tissue) covers body surfaces, lines body
Effect of early transient adherent leukocytes on venular permeability and endothelial actin cytoskeleton
 Effect of early transient adherent leukocytes on venular permeability and endothelial actin cytoskeleton J. EDWARD VALESKI AND ANN L. BALDWIN Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of
Effect of early transient adherent leukocytes on venular permeability and endothelial actin cytoskeleton J. EDWARD VALESKI AND ANN L. BALDWIN Department of Physiology, College of Medicine, University of
Reinforcing endothelial junctions prevents microvessel permeability increase and tumor cell adhesion in microvessels in vivo
 City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Publications and Research City College of New York October 2015 Reinforcing endothelial junctions prevents microvessel permeability increase and tumor
City University of New York (CUNY) CUNY Academic Works Publications and Research City College of New York October 2015 Reinforcing endothelial junctions prevents microvessel permeability increase and tumor
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) All of the following are synthesized along various sites of the endoplasmic reticulum
Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology
 Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Cell signaling Dr. Diala Abu-Hassan, DDS, PhD School of Medicine Dr.abuhassand@gmail.com Principles of Genetics and Molecular Biology www.cs.montana.edu Modes of cell signaling Direct interaction of a
Ch 2: The Cell. Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles
 Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Ch 2: The Cell Goals: Anatomy of a typical cell Cell Membrane Discussion of internal structure of a cell with emphasis on the various organelles Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Some Terminology: 1.
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 36
 Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 36 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University May 3, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 36 May 3, 2013 1 / 43 Outline Questions and answers Cellular communities
Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 36 Alexey Shipunov Minot State University May 3, 2013 Shipunov (MSU) Advanced Cell Biology. Lecture 36 May 3, 2013 1 / 43 Outline Questions and answers Cellular communities
(d) are made mainly of lipids and of proteins that lie like thin sheets on the membrane surface
 Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
Which of the following statements is no true? Biological membranes (a) are composed partly of amphipathic lipids (b) have hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions (c) are typically in a fluid state (d) are
The endothelium forms the inner cellular lining of blood
 Reviews Phenotypic Heterogeneity of the Endothelium I. Structure, Function, and Mechanisms William C. Aird Abstract Endothelial cells, which form the inner cellular lining of blood vessels and lymphatics,
Reviews Phenotypic Heterogeneity of the Endothelium I. Structure, Function, and Mechanisms William C. Aird Abstract Endothelial cells, which form the inner cellular lining of blood vessels and lymphatics,
I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins
 Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Lecture 6: Membranes and Cell Transport Biological Membranes I. Fluid Mosaic Model A. Biological membranes are lipid bilayers with associated proteins 1. Characteristics a. Phospholipids form bilayers
Vesiculo-Vacuolar Organelles and the Regulation of Venule Permeability to Macromolecules By Vascular Permeability Factor, Histamine, and Serotonin
 Vesiculo-Vacuolar Organelles and the Regulation of Venule Permeability to Macromolecules By Vascular Permeability Factor, Histamine, and Serotonin By Dian Feng, Janice A. Nagy, John Hipp, Harold E Dvorak,
Vesiculo-Vacuolar Organelles and the Regulation of Venule Permeability to Macromolecules By Vascular Permeability Factor, Histamine, and Serotonin By Dian Feng, Janice A. Nagy, John Hipp, Harold E Dvorak,
Shear stress induces endothelial internalization and transcytosis of insulin independently of nitric oxide potential role of the actin cytoskeleton
 Shear stress induces endothelial internalization and transcytosis of insulin independently of nitric oxide potential role of the actin cytoskeleton by Sha Guan A thesis submitted in conformity with the
Shear stress induces endothelial internalization and transcytosis of insulin independently of nitric oxide potential role of the actin cytoskeleton by Sha Guan A thesis submitted in conformity with the
Microcirculation and Edema. Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD.
 Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Microcirculation and Edema Faisal I. Mohammed MD, PhD. Objectives: Point out the structure and function of the microcirculation. Describe how solutes and fluids are exchang in capillaries. Outline what
Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 22, 2010
 Cell Biomechanics Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 22, 2010 Outline for today Tubes Vessel mechanics and disease Models Lung mechanics Technology integration Atherosclerosis is
Cell Biomechanics Linda Lowe Krentz Bioscience in the 21 st Century October 22, 2010 Outline for today Tubes Vessel mechanics and disease Models Lung mechanics Technology integration Atherosclerosis is
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments
 02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
02.12.10 Lecture 13 - Intermediate filaments Intermediate filaments Present in nearly all animals, but absent from plants and fungi Rope-like network of filaments in the cell Principle function is maintenance
Cell Membranes Valencia college
 6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
6 Cell Membranes Valencia college 6 Cell Membranes Chapter objectives: The Structure of a Biological Membrane The Plasma Membrane Involved in Cell Adhesion and Recognition Passive Processes of Membrane
A. Major parts 1. Nucleus 2. Cytoplasm a. Contain organelles (see below) 3. Plasma membrane (To be discussed in Cellular Transport Lecture)
 Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
Lecture 5: Cellular Biology I. Cell Theory Concepts: 1. Cells are the functional and structural units of living organisms 2. The activity of an organism is dependent on both the individual and collective
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions
 INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
INFLAMMATION: Cellular Functions Sequence of Vascular Events 1. Vasodilation (increased blood flow) CALOR & RUBOR 2. Increased microvascular permeability: fluids into tissues TUMOR 3. Blood flow slows
Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s
 Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
Current Topics in Membranes, Volume 43 Membrane Protein- Cytoskeleton Interaction s Edited by W. James Nelson Contributors xii i Preface xvii Previous Volumes in Series xix CHAPTER 1 Getting There Is
Lysosomes. Vacuoles. Phagocytosis. One cell engulfing another. forms a food vacuole. fuses with lysosome. Autophagy. Lysosomes use enzymes
 Lysosomes Phagocytosis One cell engulfing another forms a food vacuole fuses with lysosome Autophagy Lysosomes use enzymes to recycle the cell s own organelles and macromolecules Fig. 6-14 Nucleus 1 µm
Lysosomes Phagocytosis One cell engulfing another forms a food vacuole fuses with lysosome Autophagy Lysosomes use enzymes to recycle the cell s own organelles and macromolecules Fig. 6-14 Nucleus 1 µm
A TOUR OF THE CELL 10/1/2012
 A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
A TOUR OF THE CELL Chapter 6 KEY CONCEPTS: Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions The eukaryotic cell s genetic instructions are housed in the nucleus and carried
2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 2. Epithelial Tissues Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU HISTOLOGY: w Study of the structure and function of tissues and organs at the microscopic levels. w Tissues
Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability
 Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability Dolly Mehta and Asrar B. Malik Physiol Rev 86:279-367, 2006. doi:10.1152/physrev.00012.2005 You might find this additional information useful...
Signaling Mechanisms Regulating Endothelial Permeability Dolly Mehta and Asrar B. Malik Physiol Rev 86:279-367, 2006. doi:10.1152/physrev.00012.2005 You might find this additional information useful...
Chapter 11 Intercellular Communication and Tissue Architecture
 Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
Part III Organization of Cell Populations Chapter 11 Multicellular organisms such as the human body consist of various tissues such as epithelial tissues, bones and nerves, and organs such as heart and
FTY720-Induced Human Pulmonary Endothelial Barrier Enhancement is Mediated by c-abl
 ERJ Express. Published on November 11, 2010 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00047810 FTY720-Induced Human Pulmonary Endothelial Barrier Enhancement is Mediated by c-abl Lichun Wang, Eddie T. Chiang, John T. Simmons,
ERJ Express. Published on November 11, 2010 as doi: 10.1183/09031936.00047810 FTY720-Induced Human Pulmonary Endothelial Barrier Enhancement is Mediated by c-abl Lichun Wang, Eddie T. Chiang, John T. Simmons,
Differing effects of histamine and serotonin on microvascular permeability in anaesthetized rats
 Keywords: Microcirculation, histamine, serotonin 6635 Journal of Physiology (1997), 501.3, pp. 657 662 657 Differing effects of histamine and serotonin on microvascular permeability in anaesthetized rats
Keywords: Microcirculation, histamine, serotonin 6635 Journal of Physiology (1997), 501.3, pp. 657 662 657 Differing effects of histamine and serotonin on microvascular permeability in anaesthetized rats
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw.
 Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. Early scientists who observed cells made detailed sketches of what they saw. CORK Early scientists who observed cells made detailed
Cell-cell communication and diabetes. Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln
 Cell-cell communication and diabetes Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Joseph Banks Laboratories Lincoln Connexin
Cell-cell communication and diabetes Professor Paul Squires University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Dr Claire Hills University of Lincoln Joseph Banks Laboratories Lincoln Connexin
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION
 MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
MEMBRANE STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION selective permeability permits some substances to cross it more easily than others Figure 7.1 Scientists studying the plasma Reasoned that it must be a phospholipid bilayer
Outline. Membrane Structure and Function. Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic. Chapter 5
 Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Membrane Structure and Function Chapter 5 Membrane Models Fluid-Mosaic Outline Plasma Membrane Structure and Function Protein Functions Plasma Membrane Permeability! Diffusion! Osmosis! Transport Via Carrier
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell
 Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
Lecture 5- A Tour of the Cell 1 In this lecture Prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes The organelles of the eukaryotic cell The cytoskeleton Extracellular components 2 What are cells? Cells are the fundamental unit
UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations Department: BIOLOGY. Title of Exam: Cell Biology
 Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Examination Candidate Number: Desk Number: UNIVERSITY OF YORK BSc Stage 2 Degree Examinations 2017-18 Department: BIOLOGY Title of Exam: Cell Biology Time allowed: 1 hour and 30 minutes Total marks available
Nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides
 Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Nucleic acids Nucleic acids are information-rich polymers of nucleotides DNA and RNA Serve as the blueprints for proteins and thus control the life of a cell RNA and DNA are made up of very similar nucleotides.
Human height. Length of some nerve and muscle cells. Chicken egg. Frog egg. Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
 10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
10 m 1 m 0.1 m 1 cm Human height Length of some nerve and muscle cells Chicken egg Unaided eye 1 mm Frog egg 100 µm 10 µm 1 µm 100 nm 10 nm Most plant and animal cells Nucleus Most bacteria Mitochondrion
Role of Endothelial Cell Cytoskeleton in Control of Endothelial Permeability
 657 Role of Endothelial Cell Cytoskeleton in Control of Endothelial Permeability D. Michael Shasby, Sandra S. Shasby, James M. Sullivan, and Michael J. Peach From the Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology,
657 Role of Endothelial Cell Cytoskeleton in Control of Endothelial Permeability D. Michael Shasby, Sandra S. Shasby, James M. Sullivan, and Michael J. Peach From the Departments of Medicine and Pharmacology,
Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01
 Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. For multiple choice questions,
Cell Biology (BIOL 4374 and BCHS 4313) Third Exam 4/24/01 Name SS# This exam is worth a total of 100 points. The number of points each question is worth is shown in parentheses. For multiple choice questions,
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade)
 HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
HOMEWORK RUBRICS MECHANOTRANSDUCTION UNIT: HOMEWORK #1 (20 pts towards your grade) 1. Mesenchymal stem cells (MSC) cultured on extracellular matrices with different stiffness exhibit diverse lineage commitment
Structure of Plasma membrane
 Structure of Plasma membrane Lipids in Plasma membrane Lipid Functions in Plasma membrane Movements of lipid molecules Movements of lipid molecules Cholesterol in plasma membranes Cholesterol in plasma
Structure of Plasma membrane Lipids in Plasma membrane Lipid Functions in Plasma membrane Movements of lipid molecules Movements of lipid molecules Cholesterol in plasma membranes Cholesterol in plasma
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells
 Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
Plasma Membrane & Movement of Materials in Cells Why do cells need to control what enters and exits? Plasma membrane boundary between the cell and its environment Homeostasis maintaining the cells environment
1 General introduction
 General introduction 1 Chapter 1 Index 1. Multiple sclerosis 1.1 Clinical features and diagnosis 1.2 Etiology 1.3 Pathology 1.4 Treatment 1.5 Animal model: experimental allergic encephalomyelitis 2. Cellular
General introduction 1 Chapter 1 Index 1. Multiple sclerosis 1.1 Clinical features and diagnosis 1.2 Etiology 1.3 Pathology 1.4 Treatment 1.5 Animal model: experimental allergic encephalomyelitis 2. Cellular
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 7
 A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
A Tour of the Cell Chapter 7 Cytology: Study of Cells Light Microscopes uses light & a set of lenses Magnification ratio of object s image size to its real size Resolution measures the clarity of the image
Role of the Endothelial Surface Coat
 S7 Role of the Endothelial Surface Coat in Microvascular Permeability Christopher Charles Michel Division of Biomedical Sciences, Imperial College School of Medicine, London, UK The luminal glycocalyx
S7 Role of the Endothelial Surface Coat in Microvascular Permeability Christopher Charles Michel Division of Biomedical Sciences, Imperial College School of Medicine, London, UK The luminal glycocalyx
Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit. Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power?
 AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
AP Biology Reading Packet 2- Cells Unit Name Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell 1. What is resolving power? 2. How is an electron microscope different from a light microscope and what is the difference between
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR
 INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
INFLAMMATION & REPAIR Lecture 7 Chemical Mediators of Inflammation Winter 2013 Chelsea Martin Special thanks to Drs. Hanna and Forzan Course Outline i. Inflammation: Introduction and generalities (lecture
HYPOTHESIS IN PANCREATOLOGY
 HYPOTHESIS IN PANCREATOLOGY Tensegrity Model Hypothesis: May This Paradigm Be Useful to Explain Hepatic and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis in Patients with Persistent Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus Infection?
HYPOTHESIS IN PANCREATOLOGY Tensegrity Model Hypothesis: May This Paradigm Be Useful to Explain Hepatic and Pancreatic Carcinogenesis in Patients with Persistent Hepatitis B or Hepatitis C Virus Infection?
Femke Hillen, Veerle Melotte, Judy R. van Beijnum and Arjan W. Griffioen
 1 Endothelial cell biology Femke Hillen, Veerle Melotte, Judy R. van Beijnum and Arjan W. Griffioen Abstract Vascular endothelial cells are organized as a thin layer on the interior surface of all vessels
1 Endothelial cell biology Femke Hillen, Veerle Melotte, Judy R. van Beijnum and Arjan W. Griffioen Abstract Vascular endothelial cells are organized as a thin layer on the interior surface of all vessels
INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION
 INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION Wenjun Guo and Filippo G. Giancotti Abstract During progression from tumour growth to metastasis, specific integrin signals enable cancer cells to detach from
INTEGRIN SIGNALLING DURING TUMOUR PROGRESSION Wenjun Guo and Filippo G. Giancotti Abstract During progression from tumour growth to metastasis, specific integrin signals enable cancer cells to detach from
In the lung, endothelial cells (EC) serve as a. FTY720-induced human pulmonary endothelial barrier enhancement is mediated by c-abl
 Eur Respir J 211; 38: 78 88 DOI: 1.1183/931936.4781 CopyrightßERS 211 -induced human pulmonary endothelial barrier enhancement is mediated by c-abl L. Wang, E.T. Chiang, J.T. Simmons, J.G.N. Garcia and
Eur Respir J 211; 38: 78 88 DOI: 1.1183/931936.4781 CopyrightßERS 211 -induced human pulmonary endothelial barrier enhancement is mediated by c-abl L. Wang, E.T. Chiang, J.T. Simmons, J.G.N. Garcia and
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease
 Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Roles of Flow Mechanics in Vascular Cell Biology in Health and Disease Shu Chien Dept. of Bioengineering & Medicine UC, San Diego Presented by Ming-Shaung Ju Dept. of Mech. Eng., NCKU, Tainan Background
Chapter 5 - Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 5 - Membrane Structure and Function The Plasma Membrane --the fluid mosaic model (S.J Singer) -- semi-permeable --fluid portion is a double layer of phospholipids, called the phospholipid bilayer
Chapter 5 - Membrane Structure and Function The Plasma Membrane --the fluid mosaic model (S.J Singer) -- semi-permeable --fluid portion is a double layer of phospholipids, called the phospholipid bilayer
BL 424 Test pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points.
 BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
BL 424 Test 3 2010 150 pts name Multiple choice have one choice each and are worth 3 points. 1. The plasma membrane functions as a a. selective barrier to the passage of molecules. b. sensor through which
Breaking the VE-cadherin bonds.
 Breaking the VE-cadherin bonds. Julie Gavard To cite this version: Julie Gavard. Breaking the VE-cadherin bonds.. FEBS Letters, Wiley, 2008, epub ahead of print. .
Breaking the VE-cadherin bonds. Julie Gavard To cite this version: Julie Gavard. Breaking the VE-cadherin bonds.. FEBS Letters, Wiley, 2008, epub ahead of print. .
The Regulation and Perturbation of Vascular Endothelial Permeability
 The Regulation and Perturbation of Vascular Endothelial Permeability Susan M. Armstrong A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Institute of Medical
The Regulation and Perturbation of Vascular Endothelial Permeability Susan M. Armstrong A thesis submitted in conformity with the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy Institute of Medical
What Are Cell Membranes?
 What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
What Are Cell Membranes? Chapter 5, Lesson 1 24 Directions Match each term in Column A with its meaning in Column B. Write the letter on the line. Column A 1. cytoplasm 2. cytosol 3. extracellular matrix
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents:
 Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
Cellular Physiology (PHSI3009) Contents: Cell membranes and communication 2 nd messenger systems G-coupled protein signalling Calcium signalling Small G-protein signalling o RAS o MAPK o PI3K RHO GTPases
The contractile apparatus and mechanical properties of airway smooth muscle
 Eur Respir J 2; 15: 6±616 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 SERIES "THE AIRWAY SMOOTH MUSCLE CELL" Edited by F. Chung and P. Sterk
Eur Respir J 2; 15: 6±616 Printed in UK ± all rights reserved Copyright #ERS Journals Ltd 2 European Respiratory Journal ISSN 93-1936 SERIES "THE AIRWAY SMOOTH MUSCLE CELL" Edited by F. Chung and P. Sterk
MCB Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier
 MCB 252 -Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier MCB 252 Spring 2017 MCB 252 Cell Biology Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly Reading: Lodish 17.2-17.3, 17.7 MCB 252 Actin Cytoskeleton
MCB 252 -Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly- Prof. David Rivier MCB 252 Spring 2017 MCB 252 Cell Biology Topic 19 Regulation of Actin Assembly Reading: Lodish 17.2-17.3, 17.7 MCB 252 Actin Cytoskeleton
Ultrastructural observations on the microvasculature in advanced gastric carcinomas
 Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 785-792 001: 10.14670/HH-16.785 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Ultrastructural observations on the microvasculature in advanced
Histol Histopathol (2001) 16: 785-792 001: 10.14670/HH-16.785 http://www.hh.um.es Histology and Histopathology Cellular and Molecular Biology Ultrastructural observations on the microvasculature in advanced
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function
 Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes.
Chapter 7: Membrane Structure and Function Name Period Concept 7.1 Cellular membranes are fluid mosaics of lipids and proteins 1. The large molecules of all living things fall into just four main classes.
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG)
 In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
In vitro scratch assay: method for analysis of cell migration in vitro labeled fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) 1 Dr Saeb Aliwaini 13/11/2015 Migration in vivo Primary tumors are responsible for only about 10%
Copyright 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Blood Vessel Structure
 Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
Blood Vessel Structure Structure of Blood Vessel Walls Arteries and veins Tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica externa Lumen Central blood-containing space Capillaries Endothelium with sparse basal
A Tour of the Cell. Chapter 6. Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Overview: The Fundamental Units of Life
 Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Slide 1 Chapter 6 A Tour of the Cell PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan
Probiotics the Good Neighbor: Guarding the Gut Mucosal Barrier
 American Journal of Infectious Diseases 5 (3): 188-192, 2009 ISSN 1553-6203 2009 Science Publications Probiotics the Good Neighbor: Guarding the Gut Mucosal Barrier R.K. Rao, D.B. Polk, A. Seth and F.
American Journal of Infectious Diseases 5 (3): 188-192, 2009 ISSN 1553-6203 2009 Science Publications Probiotics the Good Neighbor: Guarding the Gut Mucosal Barrier R.K. Rao, D.B. Polk, A. Seth and F.
Stepwise Recruitment of Transcellular and Paracellular Pathways Underlies Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Stroke
 Article Stepwise Recruitment of Transcellular and Paracellular Pathways Underlies Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Stroke Daniel Knowland, 1,8 Ahmet Arac, 2,3,8 Kohei J. Sekiguchi, 4,5 Martin Hsu, 1 Sarah
Article Stepwise Recruitment of Transcellular and Paracellular Pathways Underlies Blood-Brain Barrier Breakdown in Stroke Daniel Knowland, 1,8 Ahmet Arac, 2,3,8 Kohei J. Sekiguchi, 4,5 Martin Hsu, 1 Sarah
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s
 Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s The basic facts about proteinuria and FSGS A primer on proteinuria Endothelium and glycocalyx Podocytes Pathology
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis and the Nephro6c Syndrome Dr. A. Gangji Dr. P. Marge>s The basic facts about proteinuria and FSGS A primer on proteinuria Endothelium and glycocalyx Podocytes Pathology
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes
 Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure B. Animal Cell Adhesion C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport D. Active Transport E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis
A. Membrane Composition and Structure. B. Animal Cell Adhesion. C. Passive Processes of Membrane Transport. D. Active Transport
 Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cellular Membranes A. Membrane Composition and Structure Lecture Series 5 Cellular Membranes B. Animal Cell Adhesion E. Endocytosis and Exocytosis A. Membrane Composition and Structure The Fluid Mosaic
Cytology. Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges
 Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Chapter 7: A Tour of the Cell Cytology Light microscopy resolving power Electron microscopy TEM SEM Cell fractionation Ultracentrifuges Prokaryotic cells Nucleoid No organelles with membranes Ribosomes
Cells. Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function. Cells. Plasma Membrane
 Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Unit 3 Cell Structure and Function Cells Cell theory The cell is the basic unit of life The cells of all living things exhibit the seven characteristics of life All living things are made of cells Cells
Chapter 2: The Cell. Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College
 Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Chapter 2: The Cell Ryan R. Williams, M.D., Ph.D. August 29 th, 2018 West Los Angeles College Introduction There are two types of cells in the body: Sex cells Sperm in males and oocytes in females Somatic
Plasma (cell) membrane
 Plasma Membrane 1. Chemical composition of the plasmalemma 2. Models of cell membrane structure 3. Structure and functions of membrane proteins carriers (transporters) channels receptors 4. Cell coat (glycocalyx)
Plasma Membrane 1. Chemical composition of the plasmalemma 2. Models of cell membrane structure 3. Structure and functions of membrane proteins carriers (transporters) channels receptors 4. Cell coat (glycocalyx)
Critical Review Nitric Oxide, S-Nitrosation, and Endothelial Permeability
 Critical Review Nitric Oxide, S-Nitrosation, and Endothelial Permeability Walter N. Duran 1 * Annie V. Beuve 1 Fabiola A. Sanchez 2 1 Department of Pharmacology and Physiology; New Jersey Medical School;
Critical Review Nitric Oxide, S-Nitrosation, and Endothelial Permeability Walter N. Duran 1 * Annie V. Beuve 1 Fabiola A. Sanchez 2 1 Department of Pharmacology and Physiology; New Jersey Medical School;
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues. Short Answer. Figure 3.1
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 3 Cells and Tissues Short Answer Figure 3.1 Using Figure 3.1, match the following: 1) The illustration of simple cuboidal epithelium is. Answer:
Cell Motility. Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD
 Cell Motility Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Laboratory of Somatic Reprogramming and Stem Cell Aging Center for Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cnedu
Cell Motility Junfeng Ji ( 纪俊峰 ), PhD Professor Laboratory of Somatic Reprogramming and Stem Cell Aging Center for Stem Cell and Tissue Engineering School of Medicine Zhejiang University Email: jijunfeng@zju.edu.cnedu
Cells. Variation and Function of Cells
 Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
Cells Variation and Function of Cells Plasma Membrane= the skin of a cell, it protects and nourishes the cell while communicating with other cells at the same time. Lipid means fat and they are hydrophobic
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5
 AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
AP Biology Cells: Chapters 4 & 5 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The was the first unifying principle of biology. a. spontaneous generation
Endothelial cell junctions and the regulation of vascular permeability and leukocyte transmigration
 Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6: 1453 1460 DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03087.x REVIEW ARTICLE Endothelial cell junctions and the regulation of vascular permeability and leukocyte transmigration
Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6: 1453 1460 DOI: 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2008.03087.x REVIEW ARTICLE Endothelial cell junctions and the regulation of vascular permeability and leukocyte transmigration
1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma membrane?
 Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
Chapter 3 Reading Guide The Cellular Level of Organization Name 1. or is the study of cellular structure and function. Section 3.1 Parts of a Cell 2. What is the purpose and characteristics of the plasma
