Index. Index 371. Aggresome, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator,
|
|
|
- Felix Hudson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Index 371 Index Aggresome, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator, centrosome-associated inclusions, characterization of soluble and insoluble fractions, 319 formation induction, 318, 320, 321 immunocytochemistry, 319, 321 centrosome-associated proteins, immunocytochemistry, 319, 320 Western blot, 320 materials for study, overview, 305, 310 subcellular localization, 312 definition, 305 functional significance, 313, 316 protective functions, 305, 306 Alacinomycin A, proteasome inhibition, 11 α-factor, see Endoplasmic reticulumassociated degradation Amino-terminal ubiquitination, see N- terminal ubiquitination, Androgen receptor, aggresome formation, 313 Bortezomib, see VELCADE CFTR, see Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator Clasto lactacystin β-lactone, proteasome inhibition, 9, 10, 15, 16 Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), aggresomes, centrosome-associated inclusions, characterization of soluble and insoluble fractions, 319 formation induction, 318, 320, 321 immunocytochemistry, 319, 321 centrosome-associated proteins, immunocytochemistry, 319, 320 Western blot, 320 materials for study, overview, 305, 310 subcellular localization, 312 degradation in rabbit reticulocyte lysate system, 186 endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation assay, autoradiography of gels, 301, 302 HEK-293 cells, competent cell preparation, 296 harvesting of transfected cells, 297 transfection, 296, 297, 302 kinetic analysis of D508 mutant degradation, materials, , 301, 302 overview, 293, 294 solubility analysis, cell fractionation, 299, 300 solubilization of detergentinsoluble material, 300 Western blot of expression, quality control of folding, 309,
2 372 Index Defective ribosomal proteins (DRiPs), overview, 271, 272 quantitative analysis, cell fractionation, 275 denaturing gel electrophoresis, 277, 280 half-life calculation, materials, principles, 272 proteasome inhibitors, 272, 273, 279 radiolabeling of cells, 274, 275, 279 trichloroacetic acid precipitation and scintillation counting, 275, 277, 279, 280 Deubiquinating enzymes (DUBs), classes, 207 fluorescence assay, , 215 identification 209 isopeptidase T, see Isopeptidase T substrates, 207, 208 yeast enzymes, 208 DRiPs, see Defective ribosomal proteins, DUBs, see Deubiquinating enzymes, E1, adenylate assay, 30, 32 substrate preparation, 30, 31, 33 thiol ester assay, 30, 31, 33, 34 function, 23, 24, 255 purification, fast protein liquid chromatography, 29, 30 human erythrocyte fractionation, 27, 28, 32, 33 materials, 25, 26 overview, 24, 25 ubiquitin affinity column, chromatography, 28, 29, 33 preparation, 26, 27, 32 reconstitution in vitro, 24 thermosensitive E1 mutant cell line studies of ornithine decarboxylase degradation, 87, 88, 94 E2, function, 24, 224, 255 polyubiquitin chain synthesis, see Polyubiquitin, recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli, 24 E3, auto-ubiquitination assay using purified recombinant protein, 40, 41, 44 coupled immunoprecipitation and auto-ubiquitination assay, 41 materials, 39, 40 MDM2-mediated p53 ubiquitination assay, 43, 44 SCF b-trcp assay, enzyme preparation, 42 incubation conditions and immunoblotting, 42, 44 overview, 41, 42 substrate preparation, 42 function, 24, 224, 255 parkin activity, see Parkin RING domain proteins, substrate identification, 39, 256 types, 255 Edman degradation, proteasomal cleavage product analysis, 109 Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA), sumoylated transcription factors, 333, 335, 336 Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, see Mass spectrometry; Protein identification
3 Index 373 EMSA, see Electrophoretic mobility shift assay Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD), assays using reticulocyte lysate, advantages, 186, 187 affinity adsorption of protein components, affinity depletion, 197, 198, 203 histidine-tagged recombinant protein purification, 195, 197, 203 degradation quantification, calculation of percentage of protein degraded, 193, 194, 202 polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, 193 scintillation counting, 193, 202 integral membrane protein release assay, 194, 195, 202 materials, microsomes, collection and resuspension, 192, 193 preparation, 191 rabbit reticulocyte lysate preparation, 190, 191, 201 transcription/translation in vitro, 192, 201 translocation activity inactivation and reconstitution, alkylation, 198, 199 proteolysis, 198, 199, 202 SRP receptor α-subunit repopulation of inactivated membranes, 199, 201 assays with yeast membranes, cytosol, data collection and analysis, 181 materials, prepro α-factor substrate translocation into microsomes, 178, 179, 182 pro α-factor degradation cytosol assay, 179, 182, 183 purified proteasome reconstitution assay, 179, 180, 183 pro α-factor export cytosol assay, 180, 181, 183 purified proteasome reconstitution assay, 181, 183 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator as model substrate, autoradiography of gels, 301, 302 HEK-293 cells, competent cell preparation, 296 harvesting of transfected cells, 297 transfection, 296, 297, 302 kinetic analysis of Δ508 mutant degradation, materials, , 301, 302 overview, 293, 294 solubility analysis, cell fractionation, 299, 300 solubilization of detergentinsoluble material, 300 Western blot of expression, overview, 175, 176, 186 quality control of protein folding, 309, 310 substrates, 293 yeast mutant screening, cloning of functional wild-type genes, 287 colony immunoblotting for detection of mutated cell clones, cycloheximide decay experiment,
4 374 Index ethylmethane sulfonate mutagenesis, 284, 285, 287 genome-wide screen, materials, 290, 292 multitransformation of yeast, 291, 292 overview, 289, 290 materials, 284 overview, 283, 284, 287 Epoxomicin, proteasome inhibition, 9 ERAD, see Endoplasmic reticulumassociated degradation Ethylmethane sulfonate mutagenesis, see Endoplasmic reticulumassociated degradation Fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC), E1, 29, 30 human core proteasome particle, 100, 101 FPLC, see Fast protein liquid chromatography Gel filtration, isopeptidase T, proteasome assembly and maturation, 246, 247, 253 Gliotoxin, proteasome inhibition, 11 High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), see Protein identification; Reversedphase high-performance liquid chromatography HPLC, see High-performance liquid chromatography Huntingtin, aggresome formation, 313 Id2, ubiquitination, 256, 257, 259 IFN-γ, see Interferon-γ Immunoprecipitation, E3, 41 parkin, 358, 360, 368 pulse chase analysis of proteasome maturation, 252, 253 sumoylated proteins, 330, 331, 336 ubiquitination assay, 227, 228 Interferon-γ (IFN-γ), antigen presentation enhancement mechanisms, 307 Isopeptidase T (USP5), fluorescence assay, 211, 215 high-performance liquid chromatography assay, 211, 212 materials, 210 purification, affinity chromatography, 215 anion-exchange chromatography, bacteria growth and induction, 215, 217 cell pellet lysis and sonication, 215 gel filtration, 215, 216 materials, 210, 211 yeast homolog, 208 Lactacystin, proteasome inhibition, 9, 15, 16 LMP1, ubiquitination, 256, 257, 259 LMP2A, ubiquitination, 256, 257, 259 MALDI-directed nanoesi-ms/ms, protein identification, 142 Mass spectrometry (MS), proteasomal cleavage product analysis, 108, 109 protein identification, see Protein identification synthetic peptide purity analysis for digestion assay, 104 ubiquitination enrichment of tagged proteins, affinity tags, 166 elution from beads, 166
5 Index 375 on-bead digestions, 166, 168, 171, 172 solution digestions, 168, 171, 172 literature searches, 160, 162 materials, 154 matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry of proteins, 156, 171 model peptides, gluc fragmentation, 162 synthesis, 160 tryptic peptide fragmentation, 162, 166 overview, 153, 154 peptide identification, 168, 169, 171, 172 tandem mass spectrometry of peptides, 157, 160 ubiquitination site identification, 168, 169, 171, 172 Matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry, see Mass spectrometry; Protein identification MDM2, p53 ubiquitination assay, 43, 44 MG132, proteasome inhibition, 6, 7 MG262, proteasome inhibition, 8 Microsome, see Endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation MS, see Mass spectrometry Multiple myeloma, see VELCADE, MyoD, ubiquitination, 256, 257, 259 NF-κB, see Nuclear factor-κb NIP-LLL-VS, proteasome inhibition, 7 N-terminal ubiquitination, evidence, 258 overview, pathology, protein conjugation and degradation cultured cell extracts, fractionation, preparation, 262 degradation intact cell studies, 267, 268 in vitro, 266, 267 proteasome inhibitor effects, 267, 268 protein half-life determination, 267, 268 labeling of protein substrates, biosynthetic labeling, 264, 265 overview, 263 radioiodination, 264 materials, reticulocyte lysate preparation, 261, 262 ubiquitination in vitro, 265, 266 protein stability effects, 256, 257 Nuclear factor-κb (NF-κB), proteasome regulation, 308 ODC, see Ornithine decarboxylase Ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), function, 83 ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation, materials for characterization, 84 overview, 83, 84 purified reconstitution system, degradation conditions and analysis, 92, 94 expression plasmids, 88, 89, 94 proteasome purification, 92 purification of recombinant proteins, 90, 91 recombinant protein expression in Escherichia coli, 90 reticulocyte lysate system, degradation reaction, 85, 86
6 376 Index lysate preparation and fractionation, 85 recombinant protein expression, 85 thermosensitive E1 mutant cell line studies, 87, 88, 94 p21, ubiquitination, PA28, functions, 307 pathology, 312, 313 subunits, 307 PA700, chaperone-like activity assay, citrate synthase thermal aggregation, 79 insulin reductive aggregation, 79 materials, 76 substrates, 78, 79 conformational remodeling of Ub 5 - dihydrofolate reductase, 77, 79 functions, ATPase activity, 74, 307 chaperone-like activity, 74, 75, 307 isopeptidase activity, 73, 74 polyubiquitin chain binding, 73 protein remodeling activity, 75 orientation within proteasome, 71, 72 proteasome core particle association assay, 76, 78, 79 purification from bovine red cells, chromatography, 78 extraction, materials, 76 structure, 306 PAGE, see Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis Parkin, antibodies for analysis, dot blot screening, 355, 356 production, 354, 355 Western blot characterization, 356, 357, 368 brain immunohistochemistry, 361, 363 immunofluorescence microscopy in neurons, 357, 358 materials for study, 353, 354 protein protein interactions, 352, 353 RING domain, 352 structure, 352 ubiquitin ligase activity, brain extracts, 363, 364, 369 neuron lysates, 360, 361, 368 parkin transfected cell activity against brain substrates, , immunoprecipitation, 358, 360, 368 substrates, overview, 353 neural parkin, 366 Parkinson disease (PD), gene mutations, 352 parkin studies, see Parkin pathophysiology, 351 ubiquitination in Lewy bodies, 352 PD, see Parkinson disease Peptide mass fingerprinting, protein identification, 120, 148 Peripheral myelin protein-22 (PMP22), aggresome formation, 313 PMP22, see Peripheral myelin protein- 22 Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), see also Electrophoretic mobility shift assay; Western blot, defective ribosomal proteins, 277, 280 endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation 181, 193 human proteasome core particle, 102
7 Index 377 proteasome assembly and maturation nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electrophoresis conditions, 250 gel preparation, 249, 250, 253 in-gel peptidase assay, 250 Western blot, 250 pulse chase analysis of maturation, protein identification techniques with mass spectrometry, see Protein identification ubiquitination assay, 154 unconjugated ubiquitin assay, 236, 237 yeast proteasomes, denaturing gel electrophoresis, 68 native gel electrophoresis, Polyubiquitin, synthesis of chains linked through K48 and K63, deblocking reactions, 51, 52, 54 K48-Ub 2 synthesis and purification, 49 51, 54 K48-Ub 4 synthesis and purification, 52, 54 K48-Ub x synthesis and purification, 52 K63-Ub 3 synthesis and purification, 53 materials, 48, 49, 54 overview, 47, 48 yield and recovery, 53, 54 PR-11, proteasome inhibition, 10, 11, 16 PR-39, proteasome inhibition, 10, 11, 16 Presenelin-1, aggresome formation, 313 Proteasome, assembly and maturation, see Proteasome assembly and maturation core particle, peptidases, 72, 73 structure, 72 functions, cell cycle regulation, 307, 308 nuclear factor-κb regulation, 308 protein degradation, human core particle, cleavage product analysis, Edman degradation, 109 examples, mass spectrometry, 108, 109 reversed-phase highperformance liquid chromatography, 107, 113 denaturing gel electrophoresis, 102 fluorogenic substrates for peptidase assay, 103, 113 proteasome inhibitor testing, 103 purification, ammonium sulfate precipitation, 100 batch adsorption, 99, 100, 112, 113 buffer exchange and concentration, 102 erythrocyte preparation and hypotonic lysis, 99, 112 fast protein liquid chromatography, 100, 101 glycerol gradient centrifugation, 101, 113 materials, 98, 99 synthetic peptide digestion, incubation conditions, 104, 106 preparative digestion, 106, 113 purity requirements and analysis, 104 rationale for assay, 103 solvation, 104, 113 Western blot, 102, 103 whole protein digestion, incubation conditions, 106, 107
8 378 Index preparative digestion, 107 immunoproteasome subunits, 72 ornithine decarboxylase degradation, see Ornithine decarboxylase protein identification in complexes, see Protein identification regulatory particles, see PA28; PA700 structural overview, 4, 97, 98, 243, 244, 306 yeast proteasome, denaturing gel electrophoresis, 68 native gel electrophoresis, peptidase activity assay, 67, 69 purification, affinity purification, conventional purification, 61 64, 68, 69 core particle, 63, 64 66, 69 holoenzyme, 62, 63, 65, 68, 69 lid and base, 66, 67, 69 materials, 60, 61 overview, 59, 60 regulatory particle, 64 66, 69 structure, subunits, 58, 59 Proteasome assembly and maturation, gel filtration, 246, 247, 253 materials, nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, electrophoresis conditions, 250 gel preparation, 249, 250, 253 in-gel peptidase assay, 250 Western blot, 250 peptidase assay, 247 pulse chase analysis of maturation, gel electrophoresis and autoradiography, immunoprecipitation, 252, 253 in vivo pulse chase, 251, 253 overview, 251 protein extraction and trichloroacetic acidprecipitable counts, 252, 253 Western blot, 247, 249, 250, 253 yeast culture and protein extraction, 246, 253 model, 243, 244 Proteasome inhibitors, characterization, IC50 determination, 11, 12, 17 kinetic parameters and type of inhibition, 13, 14 proteasome preparation, 11, 16 reversibility assay, 12, 13, 17, 18 clinical applications, 3, 4 defective ribosomal protein quantification, 272, 273, 279 pure proteasome testing, 103 small molecule inhibitors, lactone derivatives, clasto lactacystin β-lactone, 9, 10, 15, 16 lactacystin, 9, 15, 16 overview, 9, 15 noncompetitive inhibitors, alacinomycin A, 11 gliotoxin, 11 PR-11, 10, 11, 16 PR-39, 10, 11, 16 nonspecific inhibitors, 6 peptide aldehydes, MG132, 6, 7 overview, 6, 15 PSI, 7 peptide boronic acids, MG262, 8 overview, 8, 15 PS-341, 8, Z-LLL-boronate, 8 peptide epoxyketones, epoxomicin, 9
9 Index 379 overview, 8, 15 YU101, 9 YU102, 9 peptide vinyl sulfones, aminohexanoic acid derivatives of trileucine vinyl sulfone, 7, 8 NIP-LLL-VS, 7 overview, 7, 15 Z-LLL-VS, 7 research applications, 5, 14 ritonavir, 10 stock solution preparation, 5, 6, 14, 15 VELCADE treatment of multiple myeloma, see VELCADE Protein identification, mass spectrometry, database searching, 144, 145, 149 liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, in-gel digested samples, 139, 140 in-solution digested samples, 140, 149 on-bead digestion, 142, 149 principles, 127 lyophilization and reconstitution of samples, 137 MALDI-directed nanoesi-ms/ MS, 142 materials, peptide mass fingerprinting, 120, 148 sample introduction, nano-electrospray ionization, 137, 139 spotting techniques for matrixassisted laser desorption, 137, 149 tandem mass spectrometry, 137 sample preparation with gels, automated in-gel digestion, band excision, 132 Coomassie staining of gels, extraction from unstained gels, 142, 144 manual in-gel digestion, 132, 134 polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, 127, 129, 148 silver staining of gels, 131, 132, 149 Spyro Ruby staining of gels, 131, 148 sequence-tag approach, 121, 124, 127, 148 success rates, 142 top-down protein identification, 144 validation of search results, 148 overview of techniques, 117, 148 PS-341, see VELCADE PSI, proteasome inhibition, 7 Pulse chase analysis, see Defective ribosomal proteins; Proteasome assembly and maturation Reticulocyte lysate, see also Endoplasmic reticulumassociated degradation, cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator degradation, 186 N-terminal ubiquitination see N-terminal ubiquitination ornithine decarboxylase and ubiquitin-independent proteasomal degradation, degradation reaction, 85, 86 lysate preparation and fractionation, 85 recombinant protein expression, 85 sumoylated protein analysis, 333
10 380 Index Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography, proteasomal cleavage product analysis, 107, 113 synthetic peptide purity analysis for digestion assay, 104 Rhodopsin, aggresome formation, 313 RING domain proteins, see E3; Parkin Ritonavir, proteasome inhibition, 10 SCF b-trcp, see E3 Sequence-tag approach, protein identification, 121, 124, 127, 148 Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO), sumoylated protein analysis, gel mobility shift assay of transcription factors, 333, 335, 336 immunoprecipitation, 330, 331, 336 in vitro HeLa cytosolic extract preparation, 332, 333 rabbit reticulocyte lysate translated proteins, 333 recombinant SUMO-1 and Ubc-9 expression, 332 materials, 330 overview, 329 sumoylating enzymes, 329 SOD-1, see Superoxide dismutase-1 SUMO, see Small ubiquitin-related modifier Sumoylation, see Small ubiquitinrelated modifier Superoxide dismutase-1 (SOD-1), aggresome formation, 313 Tandem mass spectrometry, see Mass spectrometry; Protein identification Ubiquitin, amino-terminal ubiquitination, see N-terminal ubiquitination chain synthesis see E2; Polyubiquitin functions, 223, 237, 306 mass spectrometry see Mass spectrometry, pathology, 224, 231, 232 site identification on proteins, 168, 169, 171, 172 Western blot see Western blot, Ubiquitin-activating enzyme, see E1 Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme, see E2 Ubiquitin ligase, see E3 USP5, see Isopeptidase T VELCADE, antitumor activity, 340 multiple myeloma management, dosage and administration, 343, 344 drug storage and preparation, 343, 348, 349 Food and Drug Administration approval, 340 infusion-related event management, 344, 345 materials, 340 monitoring, 348 patient selection, 340, 343 toxicity management, asthenia, 345 cytopenias, 346 gastrointestinal, 345, 346 neuropathies, proteasome inhibition, 8, 339, 340 structure, 341 Western blot, centrosome-associated proteins, 320 cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator expression,
11 Index 381 human proteasome core particle, 102, 103 parkin antibody characterization, 356, 357, 368 ubiquitination assay, blocking and probing of blots, 230, 231 gel electrophoresis, 228, 229 heat activation of proteins on blots, 230 immunoprecipitation, 227, 228 materials, , 231 membrane transfer, 229, 230 overview, 154, 224, 226, 227 sample preparation, 227, 231 verification of ubiquitination YU101, proteasome inhibition, 9 YU102, proteasome inhibition, 9 Z-LLL-boronate, proteasome inhibition, 8 Z-LLL-VS, proteasome inhibition, 7
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004
 The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004 Ubiquitous Quality Control of Life C S Karigar and K R Siddalinga Murthy The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2004 is shared by Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin
The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2004 Ubiquitous Quality Control of Life C S Karigar and K R Siddalinga Murthy The Nobel Prize in Chemistry for 2004 is shared by Aaron Ciechanover, Avram Hershko and Irwin
Proteasomes. When Death Comes a Knock n. Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001
 Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
Proteasomes When Death Comes a Knock n Warren Gallagher Chem412, Spring 2001 I. Introduction Introduction The central dogma Genetic information is used to make proteins. DNA RNA Proteins Proteins are the
Proteins. Amino acids, structure and function. The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka
 Proteins Amino acids, structure and function The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka O O HO N N HN OH Ser65-Tyr66-Gly67 The Nobel prize in chemistry 2008 Osamu Shimomura,
Proteins Amino acids, structure and function The Nobel Prize in Chemistry 2012 Robert J. Lefkowitz Brian K. Kobilka O O HO N N HN OH Ser65-Tyr66-Gly67 The Nobel prize in chemistry 2008 Osamu Shimomura,
MCB130 Midterm. GSI s Name:
 1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
1. Peroxisomes are small, membrane-enclosed organelles that function in the degradation of fatty acids and in the degradation of H 2 O 2. Peroxisomes are not part of the secretory pathway and peroxisomal
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk
 Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Supplementary Figure 1. Normal T lymphocyte populations in Dapk -/- mice. (a) Normal thymic development in Dapk -/- mice. Thymocytes from WT and Dapk -/- mice were stained for expression of CD4 and CD8.
Study of different types of ubiquitination
 Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Study of different types of ubiquitination Rudi Beyaert (rudi.beyaert@irc.vib-ugent.be) VIB UGent Center for Inflammation Research Ghent, Belgium VIB Training Novel Proteomics Tools: Identifying PTMs October
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
 Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
Why would you want to study proteins associated with viruses or virus infection? Receptors Mechanism of uncoating How is gene expression carried out, exclusively by viral enzymes? Gene expression phases?
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
Supplementary Table 1. Cell sphingolipids and S1P bound to endogenous TRAF2. Sphingolipid Cell pmol/mg TRAF2 immunoprecipitate pmol/mg Sphingomyelin 4200 ± 250 Not detected Monohexosylceramide 311 ± 18
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION doi:1.138/nature9814 a A SHARPIN FL B SHARPIN ΔNZF C SHARPIN T38L, F39V b His-SHARPIN FL -1xUb -2xUb -4xUb α-his c Linear 4xUb -SHARPIN FL -SHARPIN TF_LV -SHARPINΔNZF -SHARPIN
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells
 Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Supplementary Figure 1.TRIM33 binds β-catenin in the nucleus. a & b, Co-IP of endogenous TRIM33 with β-catenin in HT-29 cells (a) and HEK 293T cells (b). TRIM33 was immunoprecipitated, and the amount of
Mass Spectrometry. Mass spectrometer MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS. Basic components. Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector
 Mass Spectrometry MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS Mass spectrometer Basic components Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector 1 Principles of Mass Spectrometry Proteins are separated by mass to charge ratio (limit
Mass Spectrometry MALDI-TOF ESI/MS/MS Mass spectrometer Basic components Ionization source Mass analyzer Detector 1 Principles of Mass Spectrometry Proteins are separated by mass to charge ratio (limit
Nature Methods: doi: /nmeth Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Supplementary Figure 1 Subtiligase-catalyzed ligations with ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer biotinylated peptides. (a) General scheme for ligations between ubiquitin thioesters and 10-mer, biotinylated
Problem Set #5 4/3/ Spring 02
 Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
Question 1 Chloroplasts contain six compartments outer membrane, intermembrane space, inner membrane, stroma, thylakoid membrane, and thylakoid lumen each of which is populated by specific sets of proteins.
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS. Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of
 SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of cysteine and methionine and then treated with 10 μm puromycin in depletion medium
SUPPLEMENTAL MATERIALS AND METHODS Puromycin-synchronized metabolic labelling - Transfected HepG2 cells were depleted of cysteine and methionine and then treated with 10 μm puromycin in depletion medium
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes. Enzyme Engineering
 Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
Chapter 3. Structure of Enzymes Enzyme Engineering 3.1 Introduction With purified protein, Determining M r of the protein Determining composition of amino acids and the primary structure Determining the
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Expression constructs
 Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Gene expressed in bebe3 ZmBEa Expression constructs 35S ZmBEa Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S Pnos:Hygromycin r 35S ctp YFP Pnos:Hygromycin r B -1 Chl YFP- Merge Supplemental Figure S1: Constructs Used for the Expression
Supplementary Materials
 Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Supplementary Materials Supplementary Figure S1 Regulation of Ubl4A stability by its assembly partner A, The translation rate of Ubl4A is not affected in the absence of Bag6. Control, Bag6 and Ubl4A CRISPR
Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade
 058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
058PR-03 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Trypsin Mass Spectrometry Grade A Chemically Modified, TPCK treated, Affinity Purified
PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System
 Application Note LC/MS PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Purpose This application note describes an automated workflow
Application Note LC/MS PTM Discovery Method for Automated Identification and Sequencing of Phosphopeptides Using the Q TRAP LC/MS/MS System Purpose This application note describes an automated workflow
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Left, western blot analysis of ISGylated proteins in Jurkat T cells treated with 1000U ml -1 IFN for 16h (IFN) or left untreated (CONT); right, western
Materials and Methods , The two-hybrid principle.
 The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
The enzymatic activity of an unknown protein which cleaves the phosphodiester bond between the tyrosine residue of a viral protein and the 5 terminus of the picornavirus RNA Introduction Every day there
Carotenoid Oxygenases from Camellia sinensis, Osmanthus fragrans, and Prunus persica nucipersica
 Carotenoid Oxygenases from Camellia sinensis, Osmanthus fragrans, and Prunus persica nucipersica - Kinetics and Structure - Von der Fakultatfur Lebenswissenschaften der Technischen Universitat Carolo-Wilhelmina
Carotenoid Oxygenases from Camellia sinensis, Osmanthus fragrans, and Prunus persica nucipersica - Kinetics and Structure - Von der Fakultatfur Lebenswissenschaften der Technischen Universitat Carolo-Wilhelmina
Double charge of 33kD peak A1 A2 B1 B2 M2+ M/z. ABRF Proteomics Research Group - Qualitative Proteomics Study Identifier Number 14146
 Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Abstract The 2008 ABRF Proteomics Research Group Study offers participants the chance to participate in an anonymous study to identify qualitative differences between two protein preparations. We used
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB
 Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Structural Characterization of Prion-like Conformational Changes of the Neuronal Isoform of Aplysia CPEB Bindu L. Raveendra, 1,5 Ansgar B. Siemer, 2,6 Sathyanarayanan V. Puthanveettil, 1,3,7 Wayne A. Hendrickson,
Rabbit Polyclonal antibody to NFkB p65 (v-rel reticuloendotheliosis viral oncogene homolog A (avian))
 Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Datasheet GeneTex, Inc : Toll Free 1-877-GeneTex (1-877-436-3839) Fax:1-949-309-2888 info@genetex.com GeneTex International Corporation : Tel:886-3-6208988 Fax:886-3-6208989 infoasia@genetex.com Date :
Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure 1. Comparative analysis of thermal denaturation of enzymatically synthesized polyubiquitin chains of different length. a, Differential scanning calorimetry traces
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
Figure S1. Silver staining and immunoblotting of the purified TAK1 kinase complex. The TAK1 kinase complex was purified through tandem affinity methods (Protein A and FLAG), and aliquots of the purified
PROTEINS. Building blocks, structure and function. Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties
 PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
PROTEINS Building blocks, structure and function Aim: You will have a clear picture of protein construction and their general properties Reading materials: Compendium in Biochemistry, page 13-49. Microbiology,
MALDI-TOF. Introduction. Schematic and Theory of MALDI
 MALDI-TOF Proteins and peptides have been characterized by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or SDS PAGE by generating peptide maps. These peptide maps have been used as fingerprints of protein
MALDI-TOF Proteins and peptides have been characterized by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC) or SDS PAGE by generating peptide maps. These peptide maps have been used as fingerprints of protein
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
a c e doi:10.1038/nature10407 b d f Supplementary Figure 1. SERCA2a complex analysis. (a) Two-dimensional SDS-PAGE gels of SERCA2a complexes. A silver-stained SDSPAGE gel is shown, which reveals a 12 kda
ab Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions.
 ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab139409 Membrane Fractionation Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid and simple separation of membrane, cytosolic and nuclear cellular fractions. This product is for research use only and is not intended
N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis
 JOURNAL OF PROTEOMICS 74 (2011) 431 441 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/jprot N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis Masahiro Kamita
JOURNAL OF PROTEOMICS 74 (2011) 431 441 available at www.sciencedirect.com www.elsevier.com/locate/jprot N α -Acetylation of yeast ribosomal proteins and its effect on protein synthesis Masahiro Kamita
TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer
 Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Supplementary Information TRAF6 ubiquitinates TGFβ type I receptor to promote its cleavage and nuclear translocation in cancer Yabing Mu, Reshma Sundar, Noopur Thakur, Maria Ekman, Shyam Kumar Gudey, Mariya
Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit
 Agilent 5188-2749 Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Instructions Kit Contents The Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit includes sufficient reagents for approximately
Agilent 5188-2749 Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Agilent Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit Instructions Kit Contents The Protein In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit includes sufficient reagents for approximately
condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1%
 FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig 1 (A) sumoylation pattern detected under denaturing condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1% SDS in the presence and absence
FIGURE LEGENDS Supplementary Fig 1 (A) sumoylation pattern detected under denaturing condition. Left panel, the HCT-116 cells were lysed with RIPA buffer containing 0.1% SDS in the presence and absence
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS
 SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
SUPPLEMENTAL FIGURE LEGENDS Supplemental Figure S1: Endogenous interaction between RNF2 and H2AX: Whole cell extracts from 293T were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-rnf2 or anti-γ-h2ax antibodies
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis
 Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. PD-L1 is glycosylated in cancer cells. (a) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in breast cancer cells. (b) Western blot analysis of PD-L1 in ovarian cancer cells. (c) Western blot analysis
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry
 Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
Development of a Human Cell-Free Expression System to Generate Stable-Isotope-Labeled Protein Standards for Quantitative Mass Spectrometry Ryan D. omgarden 1, Derek aerenwald 2, Eric Hommema 1, Scott Peterman
Appendix. Table of Contents
 Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
Appendix Table of Contents Appendix Figures Figure S1: Gp78 is not required for the degradation of mcherry-cl1 in Hela Cells. Figure S2: Indel formation in the MARCH6 sgrna targeted HeLa clones. Figure
CONVENTIONAL VACCINE DEVELOPMENT
 CONVENTIONAL VACCINE DEVELOPMENT PROBLEM Lethal germ Dead mouse LIVE VACCINES Related but harmless germ gives protection against lethal pathogen. Examples are the original pox vaccine and some TB vaccines
CONVENTIONAL VACCINE DEVELOPMENT PROBLEM Lethal germ Dead mouse LIVE VACCINES Related but harmless germ gives protection against lethal pathogen. Examples are the original pox vaccine and some TB vaccines
Rosanna Coppo has documented that she has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve.
 Rosanna Coppo has documented that she has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Symposium Immune Mediated Disorders New drugs entering in portfolio of treatments
Rosanna Coppo has documented that she has no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflict of interest to resolve. Symposium Immune Mediated Disorders New drugs entering in portfolio of treatments
William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti, Patricia Cogswell, Lewis C. Cantley, and Albert S. Baldwin
 Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Molecular Cell, Volume 45 Supplemental Information p85 SH2 Domain Phosphorylation by IKK Promotes Feedback Inhibition of PI3K and Akt in Response to Cellular Starvation William C. Comb, Jessica E. Hutti,
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/6/283/ra57/dc1 Supplementary Materials for JNK3 Couples the Neuronal Stress Response to Inhibition of Secretory Trafficking Guang Yang,* Xun Zhou, Jingyan Zhu,
7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002
 RECITATION TA: NAME: 7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002 This is an open book exam and you are allowed access to books, notes, and calculators. Please limit your answers to the spaces allotted after
RECITATION TA: NAME: 7.06 Cell Biology Exam #3 April 23, 2002 This is an open book exam and you are allowed access to books, notes, and calculators. Please limit your answers to the spaces allotted after
Mass Spectrometry. - Introduction - Ion sources & sample introduction - Mass analyzers - Basics of biomolecule MS - Applications
 - Introduction - Ion sources & sample introduction - Mass analyzers - Basics of biomolecule MS - Applications Adapted from Mass Spectrometry in Biotechnology Gary Siuzdak,, Academic Press 1996 1 Introduction
- Introduction - Ion sources & sample introduction - Mass analyzers - Basics of biomolecule MS - Applications Adapted from Mass Spectrometry in Biotechnology Gary Siuzdak,, Academic Press 1996 1 Introduction
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements.
 Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Table S1. Sequence of human and mouse primers used for RT-qPCR measurements. Ca9, carbonic anhydrase IX; Ndrg1, N-myc downstream regulated gene 1; L28, ribosomal protein L28; Hif1a, hypoxia inducible factor
Cellular functions of protein degradation
 Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Protein Degradation Cellular functions of protein degradation 1. Elimination of misfolded and damaged proteins: Environmental toxins, translation errors and genetic mutations can damage proteins. Misfolded
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system
 Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
Recombinant Protein Expression Retroviral system Viruses Contains genome DNA or RNA Genome encased in a protein coat or capsid. Some viruses have membrane covering protein coat enveloped virus Ø Essential
MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY
 1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
1 Lodish Berk Kaiser Krieger scott Bretscher Ploegh Matsudaira MOLECULAR CELL BIOLOGY SEVENTH EDITION CHAPTER 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Copyright 2013 by W. H. Freeman and Company
Key Concept B F. How do peptides get loaded onto the proper kind of MHC molecule?
 Location of MHC class I pockets termed B and F that bind P and P9 amino acid side chains of the peptide Different MHC alleles confer different functional properties on the adaptive immune system by specifying
Location of MHC class I pockets termed B and F that bind P and P9 amino acid side chains of the peptide Different MHC alleles confer different functional properties on the adaptive immune system by specifying
B F. Location of MHC class I pockets termed B and F that bind P2 and P9 amino acid side chains of the peptide
 Different MHC alleles confer different functional properties on the adaptive immune system by specifying molecules that have different peptide binding abilities Location of MHC class I pockets termed B
Different MHC alleles confer different functional properties on the adaptive immune system by specifying molecules that have different peptide binding abilities Location of MHC class I pockets termed B
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible ProteasMAX Surfactant
 Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Improve Protein Analysis with the New, Mass Spectrometry- Compatible Surfactant ABSTRACT Incomplete solubilization and digestion and poor peptide recovery are frequent limitations in protein sample preparation
Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience. Analytical 2-D. Electrophoresis.
 electrophoresis tech note 2859 Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience Pia Davidsson, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Experimental Neuroscience
electrophoresis tech note 2859 Combination of 2-D Gel and Liquid-Phase Electrophoretic Separations as Proteomic Tools in Neuroscience Pia Davidsson, Department of Clinical Neuroscience, Experimental Neuroscience
Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for
 Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for 15 min at 37 C and replaced with fresh complete medium.
Live cell imaging of trafficking of the chaperone complex vaccine to the ER. BMDCs were incubated with ER-Tracker Red (1 M) in staining solution for 15 min at 37 C and replaced with fresh complete medium.
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS)
 Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Supplementary Figure S1. Venn diagram analysis of mrna microarray data and mirna target analysis. (a) Western blot analysis of T lymphoblasts (CLS) and their exosomes (EXO) in resting (REST) and activated
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR
 Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
Figure S1. (A) SDS-PAGE separation of GST-fusion proteins purified from E.coli BL21 strain is shown. An equal amount of GST-tag control, LRRK2 LRR and LRRK2 WD40 GST fusion proteins (5 µg) were loaded
1. endoplasmic reticulum This is the location where N-linked oligosaccharide is initially synthesized and attached to glycoproteins.
 Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Biology 4410 Name Spring 2006 Exam 2 A. Multiple Choice, 2 pt each Pick the best choice from the list of choices, and write it in the space provided. Some choices may be used more than once, and other
Nature Immunology doi: /ni.3268
 Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
Supplementary Figure 1 Loss of Mst1 and Mst2 increases susceptibility to bacterial sepsis. (a) H&E staining of colon and kidney sections from wild type and Mst1 -/- Mst2 fl/fl Vav-Cre mice. Scale bar,
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry. Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013
 The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
The Immunoassay Guide to Successful Mass Spectrometry Orr Sharpe Robinson Lab SUMS User Meeting October 29, 2013 What is it? Hey! Look at that! Something is reacting in here! I just wish I knew what it
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells
 Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
Immune surveillance: The immune system can recognize and destroy nascent malignant cells Control Escape APC T C T H B NKT NK Innate Tumor T cells are believed to play a major role in controlling tumor
Complexity DNA. Genome RNA. Transcriptome. Protein. Proteome. Metabolites. Metabolome
 DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
Cytosolic targeting of macromolecules using a ph-dependent fusogenic peptide in. combination with cationic liposomes
 Cytosolic targeting of macromolecules using a ph-dependent fusogenic peptide in combination with cationic liposomes Sachiko Kobayashi, Ikuhiko Nakase, Noriko Kawabata, Hao-hsin Yu, Silvia Pujals, Miki
Cytosolic targeting of macromolecules using a ph-dependent fusogenic peptide in combination with cationic liposomes Sachiko Kobayashi, Ikuhiko Nakase, Noriko Kawabata, Hao-hsin Yu, Silvia Pujals, Miki
Practice Exam 2 MCBII
 1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
1. Which feature is true for signal sequences and for stop transfer transmembrane domains (4 pts)? A. They are both 20 hydrophobic amino acids long. B. They are both found at the N-terminus of the protein.
There are approximately 30,000 proteasomes in a typical human cell Each proteasome is approximately 700 kda in size The proteasome is made up of 3
 Proteasomes Proteasomes Proteasomes are responsible for degrading proteins that have been damaged, assembled improperly, or that are of no profitable use to the cell. The unwanted protein is literally
Proteasomes Proteasomes Proteasomes are responsible for degrading proteins that have been damaged, assembled improperly, or that are of no profitable use to the cell. The unwanted protein is literally
Protein methylation CH 3
 Protein methylation CH 3 methionine S-adenosylmethionine (SAM or adomet) Methyl group of the methionine is activated by the + charge of the adjacent sulfur atom. SAM S-adenosylhomocysteine homocysteine
Protein methylation CH 3 methionine S-adenosylmethionine (SAM or adomet) Methyl group of the methionine is activated by the + charge of the adjacent sulfur atom. SAM S-adenosylhomocysteine homocysteine
Problem Set 5, 7.06, Spring of 13
 Problem Set 5, 7.06, Spring 2003 1 of 13 1. In order to please your demanding thesis advisor, you've completed an extensive fractionation and biochemical purification of proteins localized to the mitochondria,
Problem Set 5, 7.06, Spring 2003 1 of 13 1. In order to please your demanding thesis advisor, you've completed an extensive fractionation and biochemical purification of proteins localized to the mitochondria,
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes
 Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Antigen Presentation to T lymphocytes Immunology 441 Lectures 6 & 7 Chapter 6 October 10 & 12, 2016 Jessica Hamerman jhamerman@benaroyaresearch.org Office hours by arrangement Antibodies and T cell receptors
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine
 Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Protein sorting (endoplasmic reticulum) Dr. Diala Abu-Hsasan School of Medicine dr.abuhassand@gmail.com An overview of cellular components Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) It is a network of membrane-enclosed
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting
 Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Molecular Cell Biology Problem Drill 16: Intracellular Compartment and Protein Sorting Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. Which of the following statements about the nucleus is correct? Question #01 A. The
Supplementary Figure 1
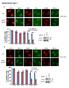 Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
Supplementary Figure 1 a γ-h2ax MDC1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1 U2OS Cells sgrna-1 ** 60 sgrna 40 20 0 % positive Cells (>5 foci per cell) b ** 80 sgrna sgrna γ-h2ax MDC1 γ-h2ax RNF8 FK2 MDC1 BRCA1 RNF8 FK2 BRCA1
SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES
 1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking
 5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking In the quest of the omics sciences for holistic schemes, the identification of binding partners of proteins
5 Identification of Binding Partners of the Annexin A2 / P11 Complex by Chemical Cross-Linking In the quest of the omics sciences for holistic schemes, the identification of binding partners of proteins
Schwarz et al. Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis
 Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
Schwarz et al Activity-Dependent Ubiquitination of GluA1 Mediates a Distinct AMPAR Endocytosis and Sorting Pathway Supplemental Data Supplemental Fie 1: AMPARs undergo activity-mediated ubiquitination
In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit
 INSTRUCTIONS In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit 3747 N. Meridian Road P.O. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 89871 1468.2 Number Description 89871 In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit, sufficient reagents for approximately
INSTRUCTIONS In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit 3747 N. Meridian Road P.O. Box 117 Rockford, IL 61105 89871 1468.2 Number Description 89871 In-Gel Tryptic Digestion Kit, sufficient reagents for approximately
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University
 Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University matthias.trost@ncl.ac.uk previously Peptide fragmentation Hybrid instruments 117 The Building Blocks of Life DNA RNA Proteins
Mass Spectrometry and Proteomics - Lecture 4 - Matthias Trost Newcastle University matthias.trost@ncl.ac.uk previously Peptide fragmentation Hybrid instruments 117 The Building Blocks of Life DNA RNA Proteins
The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein
 THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
THESIS BOOK The functional investigation of the interaction between TATA-associated factor 3 (TAF3) and p53 protein Orsolya Buzás-Bereczki Supervisors: Dr. Éva Bálint Dr. Imre Miklós Boros University of
Isolation and Structural Characterization of Cap-Binding Proteins from Poliovirus-Infected HeLa Cells
 JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1985. p. 515-524 0022-538X/85/050515-10$02.00/0 Copyright C 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 54, No. 2 Isolation and Structural Characterization of Cap-Binding Proteins
JOURNAL OF VIROLOGY, May 1985. p. 515-524 0022-538X/85/050515-10$02.00/0 Copyright C 1985, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 54, No. 2 Isolation and Structural Characterization of Cap-Binding Proteins
Cell Lysis Buffer. Catalog number: AR0103
 Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Cell Lysis Buffer Catalog number: AR0103 Boster s Cell Lysis Buffer is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction of total soluble protein in nondenatured state
Trypsin Digestion Mix
 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name 239PR Trypsin Digestion Mix Provides optimal buffered conditions for in gel trypsin digestion
G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name 239PR Trypsin Digestion Mix Provides optimal buffered conditions for in gel trypsin digestion
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems. Expressway Mini Cell-Free Expression System
 Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
Overview of the Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems The Expressway Cell-Free Expression Systems use an efficient coupled transcription and translation reaction to produce up to milligram quantities
crossmark Ca V subunits interact with the voltage-gated calcium channel
 crossmark THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 291, NO. 39, pp. 20402 20416, September 23, 2016 Author s Choice 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in
crossmark THE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY VOL. 291, NO. 39, pp. 20402 20416, September 23, 2016 Author s Choice 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc. Published in
RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh-
 1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
1 a b Supplementary Figure 1. Effects of GSK3b knockdown on poly I:C-induced cytokine production. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing control shrna (Con) or GSK3b-specific shrna (sh- GSK3b) were stimulated
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody
 Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Anti-Lamin B1/LMNB1 Picoband Antibody Catalog Number:PB9611 About LMNB1 Lamin-B1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LMNB1 gene. The nuclear lamina consists of a two-dimensional matrix of proteins
Coenzyme Q 10. R. JÜRGEN DOHMEN Institute for Genetics, University of Cologne, Germany
 Coenzyme Q 10 Ubiquitin is a small protein of 76 residues that is conjugated posttranslationally to other proteins. It is ubiquitously present in all eukaryotes, hence its name, and is one of the most
Coenzyme Q 10 Ubiquitin is a small protein of 76 residues that is conjugated posttranslationally to other proteins. It is ubiquitously present in all eukaryotes, hence its name, and is one of the most
Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli
 Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli Hye Soon Won Dept. of Chem. Eng. Chungnam National University INTRODUCTION Human interleukin-2(hil-2) - known as T Cell Growth
Purification of Glucagon3 Interleukin-2 Fusion Protein Derived from E. coli Hye Soon Won Dept. of Chem. Eng. Chungnam National University INTRODUCTION Human interleukin-2(hil-2) - known as T Cell Growth
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent
 Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent Catalog number: AR0101 Boster s Mammalian Tissue Protein Extraction Reagent is a ready-to-use Western blot related reagent solution used for efficient extraction
Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Dr. Daniel Hebert
 Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Massachusetts, USA 1 Intracellular protein trafficking Plasma membrane
Glycoprotein Maturation and Quality Control in the Endoplasmic Reticulum Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology University of Massachusetts, USA 1 Intracellular protein trafficking Plasma membrane
Chemical Biology, Option II Mechanism Based Proteomic Tagging Case History CH1
 Proteome Wide Screening of Serine Protease Activity Proc Natl Acad Sci 1999, 97, 14694; Proteomics 2001, 1, 1067; Proc Natl Acad Sci 2002, 99, 10335; Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4005; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,
Proteome Wide Screening of Serine Protease Activity Proc Natl Acad Sci 1999, 97, 14694; Proteomics 2001, 1, 1067; Proc Natl Acad Sci 2002, 99, 10335; Biochemistry 2001, 40, 4005; J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2005,
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS
 BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
BabyBio IMAC columns DATA SHEET DS 45 655 010 BabyBio columns for Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography (IMAC) are ready-to-use for quick and easy purification of polyhistidine-tagged (His-tagged)
293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell extracts were subjected
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1. Formation of a complex between Slo1 and CRL4A CRBN E3 ligase. (a) HEK 293T cells were transfected with indicated expression vectors and the whole-cell
Ubiquitinated proteins promote the association of proteasomes with the deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14 and the ubiquitin ligase Ube3c
 Ubiquitinated proteins promote the association of proteasomes with the deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14 and the ubiquitin ligase Ube3c Chueh-Ling Kuo a and Alfred Lewis Goldberg a,1 a Department of Cell Biology,
Ubiquitinated proteins promote the association of proteasomes with the deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14 and the ubiquitin ligase Ube3c Chueh-Ling Kuo a and Alfred Lewis Goldberg a,1 a Department of Cell Biology,
Supplementary information. MARCH8 inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins
 Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
Supplementary information inhibits HIV-1 infection by reducing virion incorporation of envelope glycoproteins Takuya Tada, Yanzhao Zhang, Takayoshi Koyama, Minoru Tobiume, Yasuko Tsunetsugu-Yokota, Shoji
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL 0.4 micron for Overall Exosome Isolation (Cell Media) NBP2-49826 For research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. www.novusbio.com - P: 303.730.1950 - P:
Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g.
 Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g., casein more interestingly, in most other cases, it is a transient
Phosphorylation of proteins Steve Barnes Feb 19th, 2002 in some cases, proteins are found in a stable, hyperphosphorylated state, e.g., casein more interestingly, in most other cases, it is a transient
Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles
 13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Review the Concepts 1. In eukaryotes, protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane is most commonly cotranslational; it can also
13 Moving Proteins into Membranes and Organelles Review the Concepts 1. In eukaryotes, protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) membrane is most commonly cotranslational; it can also
Amino acids. Side chain. -Carbon atom. Carboxyl group. Amino group
 PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
PROTEINS Amino acids Side chain -Carbon atom Amino group Carboxyl group Amino acids Primary structure Amino acid monomers Peptide bond Peptide bond Amino group Carboxyl group Peptide bond N-terminal (
Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis
 Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
Supplementary information Tyrosine phosphorylation and protein degradation control the transcriptional activity of WRKY involved in benzylisoquinoline alkaloid biosynthesis Yasuyuki Yamada, Fumihiko Sato
