Practice Problems on Lipids
|
|
|
- Kerry Gordon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Lipids.1 Practice Problems on Lipids 1. Which one of the following compounds has the structural pattern of the naturally occurring fats or oils? a) b) c) d) e) Which of the following compounds is least likely to be a natural fatty acid? a) b) c) d) e)
2 Lipids.2 3. Which of the following compounds is most likely to be a solid?
3 Lipids.3 4. Which of the following fatty acids is least likely to be found in a natural fat or oil? 5. Which of the following is most likely a natural fatty acid?
4 Lipids.4 6. Which of the following mechanistic steps are not part of the mechanism for the laisen condensation of methyl acetate ( 3 3 in 3 a/methanol)? I II III IV ) II ) III and IV ) II and III ) I and IV ) I and II
5 Lipids.5 7. Which one of the following is the normal product of the reaction sequence catalyzed by the fatty acid synthetase complex? a) S P b) S P c) S P d) S P e) S P 8. Which one of the following compounds would not be an intermediate in the biochemical synthesis of the compound below? SP SP SP SP SP
6 Lipids.6 9. Which one of the following is least likely to be involved in the biosynthesis of palmitic acid? SP SFS SP SP SP 10. Which one of the following processes is most likely to be involved in the mechanism of fatty acid synthase? In all cases "" or "" are part of an enzyme active site, and "R" is the rest of P 3 SP 3 SP 2 3 R 2 R SP SP SP R
7 Lipids Which one of the correctly shows the mechanism of a Michael ddition? ) u ) 2 ) u ) ) 12. When P acts as a reducing agent, which is transferred to the compound being reduced? (ircle correct ) 2 P 2 2 P 2
8 Lipids In fatty-acid biosynthesis, acetyl o is converted into malonyl o. Why is malonyl o synthesized? ) To incorporate another carbon from 2 into the growing chain ) To provide a catalytic group able to act as a base ) To make the laisen step favour product formation ) To make malonyl o more soluble in water ) To make malonyl o bind more strongly to fatty acid synthetase 14. To convert acetyl-o into 3 -( 2 ) 14 --S-R, how many equivalents of P must the cell use per equivalent of product formed? (Work out answer) 15. In nature, biotin is used as a: ) Reducing agent ) ehydrating agent ) arbonyl transfer agent ) xidizing agent ) ydrating agent
9 Lipids Palmitic acid with the carbon atoms numbered is shown below. Which - bond is formed by the laisen condensation between butyryl thiolester (a 4 carbon electrophile) and malonyl-p? ) ) 8 9 ) ) ) utanoic acid is biosynthesized by a route identical to the fatty acid biosynthetic pathway. If, during the biosynthesis of butanoic acid, all of the starting material (acetyl o) is isotope labelled at the methyl carbon atom as indicated by the asterisk, which atom(s) will be labelled in the product? ssume that the only organic carbon source is acetyl o. 3 * So 3 I II III IV ) I and III only ) I and II only ) II and IV only ) II and III only ) I only
10 Lipids Which one of the following compounds will most likely form micelles in water? a S 3 a S 3 a 19. Which one of the following would not act as a soap or detergent? ( 3 ) 3 l S 3 a a
11 Lipids arly settlers in anada prepared soap by boiling animal fat with wood ashes, a source of a and K. This technique can be seen at the Lower Fort Garry ational istoric Site in Manitoba. Which one of the following statements about this soap-making process is T correct? ) This process is called saponification ) fter the hydrolysis the soap is precipitated by al ) Soap made this way give precipitates with hard water ) Soaps made this way contain phosphates that bind metal ions ) Soaps made this way are readily biodegradable 21. ow many of the following are soluble in water? 3 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 16 2 K [ 3 ( 2 ) 4 =( 2 ) 7 2 ] 2 a 2 ( 2 ) 14 3 ( 2 ) 14 3 [ 3 ( 2 ) 12 2 S 3 ] 2 Mg 2 ( 2 ) Which one of the following is not an effective cleaning agent? 2 Mg 2+ S 3 2 a2+ K a S 3 a
12 Lipids Which one of the following detergents would not be a good laundry product when used with hard water? S 3 a S 3 a 2 a S 3 a S 3 a 24. Which one of the following is not likely to be a useful part of a detergent formulation? a) b) c) 2 P Si P P Si Si 2 2 d) e)
13 Lipids uring the synthesis of an alkylbenzenesulfonate detergent, the following transformation below is made. Which of 1-5 are involved in the correct mechanism? ) nly 2 and 3 ) nly 1 and 4 ) nly 2, 3, and 5 ) nly 1, 4, and 5 ) ll of the steps are involved
14 Lipids Which chemical step is least likely to occur? S 3 S 3 ) S 3 S 3 ) 2 2 S 3 S 3 ) 3 3 S 3 S 3 ) S 3 S 3 )
15 Lipids The following polymer can be synthesized by the acid-catalyzed polymerization of which building block? * * ) ) ) ) ) 28. Which one of the following is not biodegradable? S 3 a S 3 a ( 3 ) 3 l 2 a
16 Lipids Which one of the following statements best describes why phospholipids form bilayers whereas the metal salts of fatty acids form micelles in aqueous solution ) The aggregates formed in aqueous solution reflect a balance between maximizing the electrostatic attraction of the head groups and minimizing the contact of the lipophilic tail groups ) The repulsion between water and the tail groups of the metal salts of fatty acids is minimized in a micellular structure ) The aggregates formed in aqueous solution reflect a balance between maximizing hydrogen bonding between the head groups and maximizing the contact between the lipophilic tail groups. ) The aggregates formed in aqueous solution reflect a balance between minimizing the electrostatic replusion of the head groups and maximizing the contact of the lipophilic tail groups ) The electrostatic repulsion between the ionic head groups of metal salts of fatty acids is maximized in a micellular structure 30. PGF (shown below) is an extremely important prostaglandin that stimulates the contraction of smooth muscles. Which of the oxygen atoms in PGF from the cyclooxygenase-catalyzed reaction using oxygen molecules from the air? a e d b c ) a and b only ) a, b, and c only ) e and d only ) a and c only ) all except for e
17 Lipids Which one of the following statements about prostaglandins is incorrect? ) ccolate and Singular interfere with the action of prostaglandins. ) Vioxx, elebrex, and extra all inhibit the oxidation of arachidonic acid. ) Many prostaglandins are inflammatory agents. ) The enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid forms a 5-membered ring. ) Prostaglandins are synthesized primarily in the prostate gland. 32. Which one of the lipids would not be found as part of a biological membrane? 2 2 P P 2 2 ( 3 ) 3 l P 2 2 ( 3 ) 3 l
18 Lipids Which one of the following will form a bilayer by itself? P ( 3 ) 3 3 P ( 3 ) Which one of the following statements is not correct? ) The first step of prostaglandin synthesis from arachidonic acid involves the formation of a cyclopentane ring by the enzyme cyclooxygenase. ) Phospholipid bilayers are leaky and compounds can easily pass unassisted through the bilayer. ) In electrophilic aromatic substitution, electron-donating substituents on the aromatic ring are ortho/para directors. ) Phosphate compounds can be added to detergents to increase their performance in hard water. ) Micelles have a hydrophobic interior.
19 Lipids Which one of the following is not a terpene? 36. Which one of the following is not a terpene? a) b) c) d) e)
20 Lipids Which one of the following is not a terpene? 38. The enzyme catalyzed reaction between dimethylallyl pyrophosphate and isopentenyl pyrophosphate to give geranyl pyrophosphate is shown below. Which of the following arrows indicate where there is a significant build up of positive charge during the reaction? V 3 3 P 2 6 P 2 6 III IV isopentenyl pyrophosphate geranyl pyrophosphate P I II dimethylallyl pyrophosphate ) t carbons I, III, and V ) t carbons I, II, and V ) t carbons II and IV ) t carbons I, II, and V ) t carbons III and IV
21 Lipids Which compound is a terpene, based on obeying the isoprene rules? ) ) isohumulone - bitter tasting and found in beer bulnesol ) ) ( 2 ) 4 3 iso-germacrene tetrahydrocannabinol - found in plants ) humulone - from hops and found in beer
22 Lipids Terpenes are biosynthesized from dimethylallyl pyrophosphate and isopentenyl pyrophosphate. escribe, in words, and by writing a mechanism, how these two molecules are linked together to form geranyl pyrophosphate. PP imethylallyl pyrophosphate PP Isopentenyl pyrophosphate Geranyl pyrophosphate 41. Which one of the following carbon-carbon linkages was most likely to have been formed by a reductive dimerization reaction? 42. The reaction step shown occurs during the biosynthesis of terpenes and steroids. Which one of statements is correct? 3 nzyme 3 SR SR 2 SR ) The two thioester groups in the starting material differ in chemical reactivity. ) Production of a single enantiomer from an achiral starting material requires a chiral catalyst. ) The product retains a plane of symmetry. ) This reaction requires P. ) The carbonyl carbon of the remaining thiolester will subsequently be reduced and removed.
23 Lipids Which one of the following molecules is involved in terpene biosynthesis? P 2 P 3 P 2 P 3 P 2 P 3 P 2 P 3 P 2 P alculate the number of moles of TP needed to synthesize one mole of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate from three moles of acetyl o.
24 Lipids The tail of chlorophyll is comprised of a terpene alcohol, phytol. Phytol can be biosynthesized exclusively from acetyl o tagged with carbon-13 isotope as the carboxyl carbon atom and carbon-14 isotope as the methyl carbon atom, as shown on the right So Which one of shows phytol with the correct placement of atoms? The red colour of tomatoes is attributed to the antioxidant lycopene, the consumption of which has been suggested to reduce the risk of certain cancers. ow many head-to-tail linkages of the isoprene building block are present in lycopene, a 40 tetraterpene? ) 5 ) 3 ) 4 ) 7 ) 6
25 Lipids uring the synthesis of mevalonic acid, the reaction below takes place. Which one of statements is not correct? 3 2 SR + 3 SR 3 2 SR 2 SR ) This aldol reaction is the result of a nucleophilic attack by the enolate of the acetylthiolester on a -ketothiolester. ) The enolate of the acetylthiolester attacks the keto carbonyl rather than the thiolester carbonyl because the thiolester carbonyl is less electrophilic. ) This enzyme-catalyzed reaction results in the formation of only one enantiomer. ) It is not necessary to generate the enolate of the acetylthiolester by a decarboxylation since the thermodynamics of the aldol reaction are favourable. ) The -ketothiolester (the starting material) was formed in a modified laisen condensation between an acetyl thiolester and a malonyl thiolester. 48. Which one of the following is not a steroid? 2 a b c d e all are steroids
26 Lipids Which one of the following represents the folding of squalene oxide that is used for the enzyme-catalyzed cyclization to lanosterol? 50. holesterol is biosynthesized from the triterpene squalene, which has a single tail-to-tail (T-T) connection. Which bond in cholesterol corresponds to that T-T bond originally present in squalene? 51. Which one of the following compounds is least likely to be involved in the biosynthesis of cholesterol? P P P P P
27 Lipids Squalene epoxide is converted to lanosterol by two major processes. The first process is the carbon-carbon bond-forming reactions which form the characteristic steroid ring structure. The second process involves group and atom migrations and the elimination of a proton ultimately giving lanosterol. With respect to the first process only (the cyclization reactions), which atoms would bear some positive charge (even temporarily)? ) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ) 1, 9, 3, 4, 6 ) 1, 2, 3, 7 ) 10, 9, 2, 3, 8, 4 ) 10, 2, 8, 7 1
28 Lipids uring the biosynthesis of cholesterol, squalene oxide is converted to lanosterol as shown below. otice that one of the methyl groups in squalene oxide has been labeled with a star. Which one of the following methyl groups in lanosterol originated as the labeled methyl group in squalene oxide? squalene oxide lanosterol 54. Which one of the following statements about vitamin is not correct? ) Vitamin can form a resonance stabilized radical. ) Vitamin can form a hindered radical. ) Vitamin is a fat-soluble vitamin. ) Molecules with similar structural features as vitamin are used as antioxidants (preservatives) in foodstuffs. ) Vitamin is a triterpene.
29 Lipids Which one of the following statements is T correct? ) Vitamin is a fat-soluble vitamin. ) Vitamin K is required for the coagulation of blood. ) Polar bears store large amounts of Vitamin in their liver. ) Vitamin is a cholesterol derivative. ) The biosynthesis of vitamin requires light. 56. Which one of the following compounds would not be classified as a lipid? ( 3 ) P
30 Lipids Which one of the following steps is consistent with a nucleophilic acyl substitution mechanism? ) S S ) So So So So ) So So So So l l l l ) l 2 -R l 2 -R ) 2 2
31 Lipids The sequence of events listed below corresponds to which reaction mechanism? 1. Protonation of sp 2 oxygen 2. ucleophilic attack and formation of tetrahedral intermediate 3. Proton transfer 4. ollapse of tetrahedral intermediate, regeneration of sp 2 oxygen, and loss of leaving group 5. eprotonation ) lectrophilic aromatic substitution ) cid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition ) Saponification ) S 1 substitution ) cid-catalyzed nucleophilic acyl substitution 59. When detergents are dissolved in water, the p of the resulting solution is close to neutral, while soap solutions are alkaline. Which statement best explains this phenomenon? ) etergents contain less unsaturation than soaps. ) etergents are typically salts of strong acids. ) Soaps precipitate in the presence of a 2+. ) Soaps are carboxylic acids, which are soluble in bases. ) etergents are made from natural oils and fats, which are not basic. 60. dichloromethane solution containing 5% bromine by volume can be prepared by combining which one of the following? ) 95 ml of dichloromethane and 5 ml of bromine ) 95 g of water and 5 g of bromine that is dissolved in dichloromethane ) 95 ml of water and 5 ml of bromine dissolved in dichloromethane ) 95 g of dichloromethane and 5 g of bromine ) 95 ml of bromine and 5 ml of dichloromethane
32 Lipids Which one of the following shows the product(s) of the reaction of the glyceride (shown at right) with excess bromine? (o stereochemistry is implied by the structures) 2 ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) 8 3 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) r ( 2 ) 7 r ( 2 ) r ( 2 ) 7 r r ( 2 ) 8 3 r ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) 8 3 ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 r ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 r ( 2 ) 8 3 r 2 r ( 2 ) 7 + r r ( 2 ) 8 3 r 2 ( 2 ) 7 + ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) ( 2 ) 7 r ( 2 ) 8 3 r 2 + ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) r r ( 2 ) 7 + r r ( 2 ) 8 3 r r + ( 2 ) 7 ( 2 ) r + ( 2 ) 7 r ( 2 ) 8 3 r
33
4,5,9/99 Neuman Chapter 21
 21: Lipids Structures of Lipids Biosynthesis of Lipids Preview Lipids are biological molecules soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and ethers. They include fats, oils, waxes, terpenes, steroids,
21: Lipids Structures of Lipids Biosynthesis of Lipids Preview Lipids are biological molecules soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols and ethers. They include fats, oils, waxes, terpenes, steroids,
4,5,9/99 Neuman Chapter 21. Chapter 21 Lipids
 Chapter 21 Lipids from Organic Chemistry by Robert C. Neuman, Jr. Professor of Chemistry, emeritus University of California, Riverside orgchembyneuman@yahoo.com
Chapter 21 Lipids from Organic Chemistry by Robert C. Neuman, Jr. Professor of Chemistry, emeritus University of California, Riverside orgchembyneuman@yahoo.com
26.1 Acetyl Coenzyme A
 Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Lipids Lipids Lipids are naturally occurring substances grouped together on the basis of a common property they they are more soluble in nonpolar solvents than in water. Some of the most important
Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition. phospholipids. Sphingolipids. Cholesterol. db=books&itool=toolbar
 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez? db=books&itool=toolbar 1 The surface of a soap bubble is a bilayer formed by detergent molecules 2 Chapter 26 Biochemistry 5th edition phospholipids Sphingolipids
Naturally occurring compounds that are typically of low molecular weight and are hydrophobic (soluble in organic solvent).
 hapter 27. Biomolecules: Lipids aturally occurring compounds that are typically of low molecular weight and are hydrophobic (soluble in organic solvent). fatty acids and waxes essential oils many vitamins
hapter 27. Biomolecules: Lipids aturally occurring compounds that are typically of low molecular weight and are hydrophobic (soluble in organic solvent). fatty acids and waxes essential oils many vitamins
Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Chapter 17. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives
 Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chapter 17 suggested problems: 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 52, 54, 56, 62, 64, 66, 70 Class Notes I. Carboxylic acids (organic acids) and their derivatives A.
Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives Chapter 17 suggested problems: 36, 38, 40, 42, 44, 52, 54, 56, 62, 64, 66, 70 Class Notes I. Carboxylic acids (organic acids) and their derivatives A.
CH 3. Lipids CHAPTER SUMMARY
 H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
H 3 C H 3 C 15 H 3 C H Views of Cholesterol APTER SUMMARY 15.1 The Nature of can best be defined as biomolecules which are soluble to a great extent in solvents. In contrast to carbohydrates, proteins
Chapter 26: Lipids. Hydrophobic (non-polar, soluble in organic solvent), typically of low molecular compound or organic origin
 hapter 26: Lipids. ydrophobic (non-polar, soluble in organic solvent), typically of low molecular compound or organic origin fatty acids and waxes essential oils many vitamins hormones (non-peptide) components
hapter 26: Lipids. ydrophobic (non-polar, soluble in organic solvent), typically of low molecular compound or organic origin fatty acids and waxes essential oils many vitamins hormones (non-peptide) components
Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react. methyl pentanoate. Name the type of reaction used to make an ester
 1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
1 Name the ester produced when methanol and pentanoic acid react methyl pentanoate 2 Name the type of reaction used to make an ester condensation reaction 3 Name the by-product of the reaction used to
Chem 60 Takehome Test 2 Student Section
 Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Multiple choice: 1 point each. Mark only one answer for each question. 1. are composed primarily of carbon and hydrogen, but may also include oxygen, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus, and a few other elements.
Lipids and Classification:
 Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Lipids and Classification: Lipids: Biological lipids are a chemically diverse group of organic compounds which are insoluble or only poorly soluble in water. They are readily soluble in non-polar solvents
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
 arboxylic Acid Derivatives The most important derivatives of carboxylic acids are l " ' ' acid halide acid anhydride an ester an amide Although not direct derivatives, nitriles, -, are related to carboxylic
arboxylic Acid Derivatives The most important derivatives of carboxylic acids are l " ' ' acid halide acid anhydride an ester an amide Although not direct derivatives, nitriles, -, are related to carboxylic
Chapter 18. Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
Chapter 18 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition-Elimination at the Acyl Carbon Carboxylic Acids Organic compounds characterized by their acidity Contains COOH group (must be at
3.1.3 Lipids. Source: AQA Spec
 alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
alevelbiology.co.uk SPECIFICATION Triglycerides and phospholipids are two groups of lipid. Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol and three molecules of fatty acid. A
Biomolecules. Unit 3
 Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
Biomolecules Unit 3 Atoms Elements Compounds Periodic Table What are biomolecules? Monomers vs Polymers Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Minerals Vitamins Enzymes Triglycerides Chemical Reactions
What is the intermolecular force present in these molecules? A) London B) dipole-dipole C) hydrogen bonding D) ion-dipole E) None. D.
 REVIEW SHEET CHP 7, FRST AND DEAL 1. (7.1) Types of Attractive Forces (Intermolecular forces (IMF)). IMF s are attractive forces between molecules due to electrostatic attraction. Therefore a molecule
REVIEW SHEET CHP 7, FRST AND DEAL 1. (7.1) Types of Attractive Forces (Intermolecular forces (IMF)). IMF s are attractive forces between molecules due to electrostatic attraction. Therefore a molecule
Lecture 19. Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Y - + X - Y X R C X. April 2, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 19 Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution X Y - - Y X X - Y April 2, 2019 hemistry 328N Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) H H 3 H H H 2 H 3 Please study the mechanism hemistry
Lecture 19 Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution X Y - - Y X X - Y April 2, 2019 hemistry 328N Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) H H 3 H H H 2 H 3 Please study the mechanism hemistry
Functions of Lipids. - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g).
 Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Chapter 8: Lipids Functions of Lipids - Storage Fats are long term energy (9 kcal/g) while carbohydrates are quick energy (4 kcal/g). - Membrane Components Lipid barriers keep water out. - Messengers Hormones
Lipids and Membranes
 Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Lipids and Membranes Presented by Dr. Mohammad Saadeh The requirements for the Pharmaceutical Biochemistry I Philadelphia University Faculty of pharmacy Lipids and Membranes I. overview Lipids are related
Chemistry 1506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Section 8: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons. Outline
 hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
hemistry 1506 Dr. unter s lass Section 8 Notes - Page 1/21 hemistry 1506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 Section 8: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons utline SETIN 8.1 INTRDUTIN...2 SETIN SETIN SETIN 8.2
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*)
 NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
NOTE: For studying for the final, you only have to worry about those with an asterix (*) (*)1. An organic compound is one that: a. contains carbon b. is slightly acidic c. forms long chains d. is soluble
A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH
 1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
1.6 Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Fats Carboxylic Acids A carboxylic acid is an organic compound that contains a carboxyl group, COOH These compounds are weak acids. Citrus fruits, crabapples, rhubarb,
Chemistry 506: Allied Health Chemistry 2. Chapter 17: Lipids. Biochemical Esters and Hydrocarbons
 hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
hemistry 506 Dr. unter s lass hapter 17. hemistry 506: Allied ealth hemistry 2 1 hapter 17: Lipids Biochemical Esters and ydrocarbons Introduction to General, rganic & Biochemistry, 5 th Edition by Bettelheim
Physical properties: C L = L. Cl, NH 2, OCH 3, OH, OCR O O O NH 2 CH 3 N(CH 3 ) 2. Sol. in H 2 O
 Lecture Notes hem 51 S. King hapter 22 arboxylic Acids and their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution I. Structure and Physical Properties: Type 2 carbonyl compounds (carboxylic acids and derivatives)
Lecture Notes hem 51 S. King hapter 22 arboxylic Acids and their Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution I. Structure and Physical Properties: Type 2 carbonyl compounds (carboxylic acids and derivatives)
ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY
 P. GERGELY Department os Medical Chemistry Medical and Health Science Center University of Debrecen ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY FÓR MEDICAL STUDENTS THIRD EDITION University of Debrecen Medical and
P. GERGELY Department os Medical Chemistry Medical and Health Science Center University of Debrecen ORGANIC AND BIOORGANIC CHEMISTRY FÓR MEDICAL STUDENTS THIRD EDITION University of Debrecen Medical and
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives. Carboxylic Acids: RCOOH (RCO 2 H)
 Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Chapter 10 Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Naming Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic Acids: RCH (RC 2 H) The functional group of a carboxylic acid is a carboxyl group (carbonyl & hydroxyl group)
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions
 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Dr. Ayad Kareem Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Collage of Pharmacy Al-Mustansiriyah University (2017-2018). Closely related
Carboxylic Acid Derivatives: Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Reactions Dr. Ayad Kareem Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Collage of Pharmacy Al-Mustansiriyah University (2017-2018). Closely related
Oxidative Phosphorylation
 Oxidative Phosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation - In Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, we ve made a lot of reduced cofactors NADH and FADH 2 - In oxidative phosphorylation, we use the energy generated
Oxidative Phosphorylation Oxidative Phosphorylation - In Glycolysis and the citric acid cycle, we ve made a lot of reduced cofactors NADH and FADH 2 - In oxidative phosphorylation, we use the energy generated
The four levels of protein structure are: primary structure, secondary structure, tertiary structure, and quaternary structure.
 Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
Proteins Proteins are organic complex nitrogenous compounds of high molecular weight, formed of C, H, O and N. They are formed of a number of amino acids linked together by peptide linkage [-CO-NH-]. Proteins
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON
 CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR DERIVATIVES: NUCLEOPHILIC ADDITION-ELIMINATION AT THE ACYL CARBON RED ANT WAS SOURCE OF FORMIC ACID (RCOOH) Lecture 8 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY 2 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO
2.2 Properties of Water
 2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
2.2 Properties of Water I. Water s unique properties allow life to exist on Earth. A. Life depends on hydrogen bonds in water. B. Water is a polar molecule. 1. Polar molecules have slightly charged regions
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
28 09/16/2013 17:44:40 Page 415 APTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents
15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids. Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
Chapter 15 Lipids 15.1 Lipids 15.2 Fatty Acids Copyright 2009 by Pearson Education, Inc. 1 Lipids Lipids are biomolecules that contain fatty acids or a steroid nucleus. soluble in organic solvents, but
OBJECTIVE. Lipids are largely hydrocarbon derivatives and thus represent
 Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Paper 4. Biomolecules and their interactions Module 20: Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, Nomenclature of fatty acids and Essential and non-essential fatty acids OBJECTIVE The main aim of this module
Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
Chapter 12 Chemistry 1050 Exam 3 Study Guide 12.1 a) Identify alkenes, alkynes and aromatics as unsaturated hydrocarbons. Determine the number of hydrogen atoms needed to complete an alkene structure.
Macromolecules. The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1.
 Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
Macromolecules The four groups of biomolecules or macromolecules found in living things which are essential to life are: 1. PROTEINS 1. CARBOHYDRATES 1. LIPIDS 1. NUCLEIC ACIDS Carbon Compounds All compounds
For questions 1-4, match the carbohydrate with its size/functional group name:
 Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
Chemistry 11 Fall 2009 Examination #5 ANSWER KEY For the first portion of this exam, select the best answer choice for the questions below and mark the answers on your scantron. Then answer the free response
1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing?
 Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing? 2. Label each picture either a Carbohydrate, Protein, Nucleic Acid, or Fats(Lipid). a.
Exam 1 Review Bio 212: 1. Describe the difference between covalent and ionic bonds. What are the electrons doing? 2. Label each picture either a Carbohydrate, Protein, Nucleic Acid, or Fats(Lipid). a.
Introduction to the Study of Lipids
 Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
Introduction to the Study of Lipids Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12
 BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
BIOB111_CHBIO - Tutorial activity for Session 12 General topic for week 6 Session 12 Lipids Useful Links: 1. Animations on Cholesterol (its synthesis, lifestyle factors, LDL) http://www.wiley.com/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cholesterol/cholesterol.htm
PAPER No. : 16 Bioorganic and biophysical chemistry MODULE No. : 25 Coenzyme-I Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and biotin
 Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 16, Bio organic and Bio physical chemistry 25, Coenzyme-I : Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and CHE_P16_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Subject Paper No and Title Module No and Title Module Tag 16, Bio organic and Bio physical chemistry 25, Coenzyme-I : Coenzyme A, TPP, B12 and CHE_P16_M25 TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Learning Outcomes 2. Introduction
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
 Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) 1 High energy bonds ATP adenosine triphosphate N NH 2 N -O O P O O P O- O- O O P O- O CH 2 H O H N N adenine phosphoanhydride bonds (~) H OH ribose H OH Phosphoanhydride bonds
cholesterol structure Cholesterol FAQs Cholesterol promotes the liquid-ordered phase of membranes Friday, October 15, 2010
 cholesterol structure most plasma cholesterol is in the esterified form (not found in cells or membranes) cholesterol functions in all membranes (drives formation of lipid microdomains) cholesterol is
cholesterol structure most plasma cholesterol is in the esterified form (not found in cells or membranes) cholesterol functions in all membranes (drives formation of lipid microdomains) cholesterol is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2.
 BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES REVIEW-UNIT 1 1. The factor being tested in an experiment is the A. data. B. variable. C. conclusion. D. observation. 2. A possible explanation for an event that occurs in nature is
Chapter Three (Biochemistry)
 Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Chapter Three (Biochemistry) 1 SECTION ONE: CARBON COMPOUNDS CARBON BONDING All compounds can be classified in two broad categories: organic compounds and inorganic compounds. Organic compounds are made
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles. Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry
 Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
Carboxylic Acids and Nitriles Chapters 20, 21 Organic Chemistry, 8th Edition John McMurry 1 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives 2 Carboxylic Acid Derivatives nitrile R = CH 3 acetonitrile 3 Structure and Bonding
BCM 221 LECTURES OJEMEKELE O.
 BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
BCM 221 LECTURES BY OJEMEKELE O. OUTLINE INTRODUCTION TO LIPID CHEMISTRY STORAGE OF ENERGY IN ADIPOCYTES MOBILIZATION OF ENERGY STORES IN ADIPOCYTES KETONE BODIES AND KETOSIS PYRUVATE DEHYDROGENASE COMPLEX
13. Carboxylic Acids (text )
 2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 13.1 13. Carboxylic Acids (text 14.1 14.9) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carboxylic acid functional group results from the connection
2009, Department of Chemistry, The University of Western ntario 13.1 13. Carboxylic Acids (text 14.1 14.9) A. Structure and Nomenclature The carboxylic acid functional group results from the connection
Org/Biochem Final Lec Form, Spring 2012 Page 1 of 6
 Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Page 1 of 6 Missing Complete Protein and Question #45 Key Terms: Fill in the blank in the following 25 statements with one of the key terms in the table. Each key term may only be used once. Print legibly.
Acid/Base chemistry. NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 Review problems for the first exam. Complete the following sentences
 1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
1 NESA Biochemistry Fall 2001 eview problems for the first exam Acid/Base chemistry 1. 2 3 is a weak acid. 2. The anion of a weak acid is a weak base 3. p is the measure of a solutions acidity. 4. 3 and
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide
 Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Chemistry 1120 Exam 2 Study Guide Chapter 6 6.1 Know amines are derivatives of ammonia, which is not an amine. Classify amines as primary, secondary or tertiary. Master Tutor Section 6.1 Review Section
Biochemistry Worksheet
 Biology 138 Name Section 3.1 Properties of Water Biochemistry Worksheet 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water
Biology 138 Name Section 3.1 Properties of Water Biochemistry Worksheet 1. Why is water such an important molecule to living things? 2. Describe the chemical make up and type of bonding found in water
From Atoms to Cells: Fundamental Building Blocks. Models of atoms. A chemical connection
 From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids
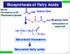 Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Biosynthesis of Fatty Acids CH 511 ource b-oxidation of FA Glycolysis of glucose n H CoA Acetyl CoA CoA Malonyl CoA Carboxylation of acetyl CoA H 3 C CH 2 CH 2 n-1 CoA aturated thioesters aturated fatty
Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds.
 Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Lipids Lipids Lipids fatty, oily, or waxy hydrophobic organic compounds. u long hydrocarbon chain u composed of CHO Diverse group u fats u oils u waxes u steroids Do not form polymers u big molecules made
Organic molecules highly hydrophobic and water insoluble.
 UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
UNIT 5. LIPIDS OUTLINE 5.1. Introduction. 5.2. Fatty acids. 5.3. Eicosanoids. 5.4. Triacylglycerols = Triglycerides. 5.5. Waxes. 5.6. Membrane lipids: glycerophospholipids and sphingolipids. 5.7. Isoprenoids
Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I
 2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
2302272 Org Chem II Part I Lecture 5 Carboxylic Acids and their Derivatives I Instructor: Dr. Tanatorn Khotavivattana E-mail: tanatorn.k@chula.ac.th Recommended Textbook: Chapter 20 in Organic Chemistry,
and hydrophilic and how they relate to solubility.
 o o o and hydrophilic and how they relate to solubility. o o o o o o o o Page 1: Introduction Page 2: 1. Hydrocarbons are referred to as organic molecules with a "backbone." Take a snapshot of the hydrocarbon
o o o and hydrophilic and how they relate to solubility. o o o o o o o o Page 1: Introduction Page 2: 1. Hydrocarbons are referred to as organic molecules with a "backbone." Take a snapshot of the hydrocarbon
Will s Pre-Test. (4) A collection of cells that work together to perform a function is termed a(n): a) Organelle b) Organ c) Cell d) Tissue e) Prison
 Will s Pre-Test This is a representative of Exam I that you will take Tuesday September 18, 2007. The actual exam will be 50 multiple choice questions. (1) The basic structural and functional unit of the
Will s Pre-Test This is a representative of Exam I that you will take Tuesday September 18, 2007. The actual exam will be 50 multiple choice questions. (1) The basic structural and functional unit of the
CHAPTER 28 LIPIDS SOLUTIONS TO REVIEW QUESTIONS
 HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
HAPTER 28 LIPIDS SLUTINS T REVIEW QUESTINS 1. The lipids, which are dissimilar substances, are arbitrarily classified as a group on the basis of their solubility in fat solvents and their insolubility
Carbonyl Chemistry VI + C O C. 1pm In Geology Room 112. Exam is Monday 11am-1pm. Chemistry /06/02
 arbonyl hemistry VI Ō - + hemistry 391 11/06/02 Exam is Monday 11am-1pm 1pm In Geology Room 112 The Dibasic Acids h - My - Such - hemistry 391 11/06/02 Good- Apple- Pie- Fischer Esterification Esters can
arbonyl hemistry VI Ō - + hemistry 391 11/06/02 Exam is Monday 11am-1pm 1pm In Geology Room 112 The Dibasic Acids h - My - Such - hemistry 391 11/06/02 Good- Apple- Pie- Fischer Esterification Esters can
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules
 Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
Factors to Consider in the Study of Biomolecules What are the features of the basic building blocks? (ex: monosaccharides, alcohols, fatty acids, amino acids) 1) General structure and functional groups
1/3/2011. Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic Addition- Elimination at the Acyl Carbon
 Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
Introduction The carboxyl group (-CO 2 H) is the parent group of a family of compounds called acyl compounds or carboxylic acid derivatives Chapter 17 Carboxylic Acids and Their Derivatives. Nucleophilic
BIOCHEMISTRY. How Are Macromolecules Formed? Dehydration Synthesis or condensation reaction Polymers formed by combining monomers and removing water.
 BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
BIOCHEMISTRY Organic compounds Compounds that contain carbon are called organic. Inorganic compounds do not contain carbon. Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent bonds with as
Lipid Metabolism. Catabolism Overview
 Lipid Metabolism Pratt & Cornely, Chapter 17 Catabolism Overview Lipids as a fuel source from diet Beta oxidation Mechanism ATP production Ketone bodies as fuel 1 High energy More reduced Little water
Lipid Metabolism Pratt & Cornely, Chapter 17 Catabolism Overview Lipids as a fuel source from diet Beta oxidation Mechanism ATP production Ketone bodies as fuel 1 High energy More reduced Little water
Chapter 3. Table of Contents. Section 1 Carbon Compounds. Section 2 Molecules of Life. Biochemistry
 Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Biochemistry Table of Contents Section 1 Carbon Compounds Section 2 Molecules of Life Section 1 Carbon Compounds Objectives Distinguish between organic and inorganic compounds. Explain the importance of
Nebal Al - Gallab. Shatha Al - Jabri. Mamoon Ahram
 10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
10 Nebal Al - Gallab Shatha Al - Jabri Mamoon Ahram Note: the doctor showed extra examples, they were in the slides, you can refer to them... Naming of Fatty Acids - 1 st Method ( IUPAC system ) We start
Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide
 Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Chapter 7 Chemistry 107 Exam 3 Study Guide 7.1 Recognize the aldehyde, ketone and hydroxyl (-OH) functional groups found in carbohydrates. Differentiate between mono-, di-, and polysaccharides. Master
Lipids are used to store and excess energy from extra carbohydrates in animals
 Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Lipids Lipids are a major source of energy used by cells, however lipids are more difficult for your body to break down. They produce nearly twice the amount of energy than proteins or carbohydrates. Lipids
Chapter 20 Carboxylic Acids. Introduction
 hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
hapter 20 arboxylic Acids Introduction arbonyl (-=) and hydroxyl (-H) on the same carbon is carboxyl group. arboxyl group is usually written -H or 2 H. Aliphatic acids have an alkyl group bonded to -H.
R O R' Acid anhydride. Acid halide. Carboxylic acid. Ester O O O O. Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester. Amide
 Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic acid X Acid halide ' Acid anhydride Ester ' P N 2 C N S' Amide Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester The common structural feature of all these compounds
Chapter 10. Carboxylic Acids and Derivatives Carboxylic acid X Acid halide ' Acid anhydride Ester ' P N 2 C N S' Amide Nitrile Acyl phosphate Thioester The common structural feature of all these compounds
SAM Teachers Guide Lipids and Carbohydrates
 SAM Teachers Guide Lipids and Carbohydrates Overview Students will explore the structure and function of two of the four major macromolecules, lipids and carbohydrates. They will look specifically at the
SAM Teachers Guide Lipids and Carbohydrates Overview Students will explore the structure and function of two of the four major macromolecules, lipids and carbohydrates. They will look specifically at the
Fatty acid breakdown
 Fatty acids contain a long hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxylate group. Most contain between 14 and 24 carbon atoms. The chains may be saturated or contain double bonds. The complete oxidation of
Fatty acids contain a long hydrocarbon chain and a terminal carboxylate group. Most contain between 14 and 24 carbon atoms. The chains may be saturated or contain double bonds. The complete oxidation of
4 Types of Organic Polar Reactions
 Objective 12 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 1: Alkenes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product 4 Types of Organic
Objective 12 Apply Reactivity Principles to Electrophilic Addition Reactions 1: Alkenes Identify structural features (pi bond) and electrophiles Use curved arrows to predict product 4 Types of Organic
Lecture 20. Herman Emil Fischer Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines. April 4, Chemistry 328N
 Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
Lecture 20 April 4, 2019 Herman Emil Fischer 1852-1919 Nobel Prize 1902 Sugars, Esters and Purines Acid-catalyzed Esterification (also called Fischer esterification) CH CH 3 H H H 2 CCH 3 Please study
Biochemistry. 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds.
 Biochemistry Carbon compounds Section 3-1 1. What is an organic compound? 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds. 3. Carbon dioxide, CO 2, is NOT an organic compound.
Biochemistry Carbon compounds Section 3-1 1. What is an organic compound? 2. Besides carbon, name 3 other elements that make up most organic compounds. 3. Carbon dioxide, CO 2, is NOT an organic compound.
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18
 Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Good Afternoon! 11/30/18 1. The term polar refers to a molecule that. A. Is cold B. Has two of the same charges C. Has two opposing charges D. Contains a hydrogen bond 2. Electrons on a water molecule
Lipids Definition. Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups)
 Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Lipids Definition Definition: Water insoluble No common structure (though generally large R groups) Water Solubility (Hydrophilic) What makes molecules water soluble (hydrophilic)? Like dissolves like
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2
 Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Chapter 2 The Chemistry of Life Part 2 Carbohydrates are Polymers of Monosaccharides Three different ways to represent a monosaccharide Carbohydrates Carbohydrates are sugars and starches and provide
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1)
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 7. CARBOXYLIC ACIDS AND THEIR
3150:112 SAMPLE TEST 2. Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck!
 SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
SAMPLE TEST 2 3150:112 Print out a copy Answer the questions on your own. Check the answers at GOBC Ans.pdf. Good Luck! QUESTIONS 1-3 REFER TO TE FOLLOWING: A. C 2 O O B. C 2 O O O C 2 O C. O C 2 O 1.
Lecture'22:'April'30,'2013 Ch.%29:%Metabolism,%catabolism,%anabolism Metabolic%energy%&%ATP%Coupling Glycolysis%and%the%Link%ReacDon
 CM'224' 'rganic'chemistry'ii pring'2013,'des'laines' 'rof.'chad'landrie 2 2 2 Gº' = -7.3 + + + Lecture'22:'April'30,'2013 Ch.%29:%Metabolism,%catabolism,%anabolism Metabolic%energy%&%AT%Coupling Glycolysis%and%the%Link%ReacDon
CM'224' 'rganic'chemistry'ii pring'2013,'des'laines' 'rof.'chad'landrie 2 2 2 Gº' = -7.3 + + + Lecture'22:'April'30,'2013 Ch.%29:%Metabolism,%catabolism,%anabolism Metabolic%energy%&%AT%Coupling Glycolysis%and%the%Link%ReacDon
KMnO 4 1 O 4'' Apigenin. 1 In the following reactions draw the structures of products B and C. 1. NaH/DMF 2. excess MeI. acetic anhydride(excess)
 Problem 26: hemical and Stereochemical Structure of oniine oniine is a toxic compound found in the plant hemlock (conium maculatum), with which the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates was poisoned. oniine
Problem 26: hemical and Stereochemical Structure of oniine oniine is a toxic compound found in the plant hemlock (conium maculatum), with which the ancient Greek philosopher Socrates was poisoned. oniine
Chapter 20 Lipids. Organic and Biochem
 Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Chapter 20 Lipids rganic and Biochem 20.1 Introduction Found in living organisms Insoluble in water but Soluble in non-polar substances Example of Lipid Solvent: diethyl ether Polar groups in lipids are
Ahmad Ulnar. Faisal Nimri ... Dr.Faisal
 24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
24 Ahmad Ulnar Faisal Nimri... Dr.Faisal Fatty Acid Synthesis - Occurs mainly in the Liver (to store excess carbohydrates as triacylglycerols(fat)) and in lactating mammary glands (for the production of
Chapter 8. Functions of Lipids. Structural Nature of Lipids. BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes. Slide 1. Slide 2.
 BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
BCH 4053 Spring 2001 Chapter 8 Lecture Notes 1 Chapter 8 Lipids 2 Functions of Lipids Energy Storage Thermal Insulation Structural Components of Membranes Protective Coatings of Plants and Insects Hormonal
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought
 Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Chapter 11 Nutrition: Food for Thought Do you think about the food that goes into your body and how it affects you? How can you interpret the various nutrition information found in the press? What are
Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids
 The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
The Structure of Carboxylic Acids Prelab 6: Carboxylic Acids Carboxylic acids contain a carboxyl functional group attached to a hydrocarbon (alkyl group) part. Carboxyl groups contain both a carbonyl group,
Problem 19: Lipids CH 2 OH N + CH 3 CH 3 H C H 2 C CH 2 O CH O P O - OH O
 Problem 19: Lipids Lipids are important components of our nutrition, and they fulfill a variety of important roles in the body - although we do not always want to be reminded of their presence! Lipids
Problem 19: Lipids Lipids are important components of our nutrition, and they fulfill a variety of important roles in the body - although we do not always want to be reminded of their presence! Lipids
Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites
 Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Secondary Metabolism Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction. Secondary metabolites are those chemical
Biosynthesis of Secondary Metabolites Secondary Metabolism Secondary metabolism, metabolic pathways that are not essential for growth, development or reproduction. Secondary metabolites are those chemical
Hind Abu Tawileh. Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh. Ma moun
 26 Hind Abu Tawileh Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh... Ma moun Cofactors are non-protein compounds, they are divided into 3 types: Protein-based. Metals: if they are bounded tightly (covalently) to the enzyme
26 Hind Abu Tawileh Moh Tarek & Razi Kittaneh... Ma moun Cofactors are non-protein compounds, they are divided into 3 types: Protein-based. Metals: if they are bounded tightly (covalently) to the enzyme
Radicals. Structure and Stability of Radicals. Radicals are formed from covalent bonds by adding energy in the form of heat (Δ) or light (hν).
 Radicals Chapter 15 A small but significant group of reactions involve radical intermediates. A radical is a reactive intermediate with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond.
Radicals Chapter 15 A small but significant group of reactions involve radical intermediates. A radical is a reactive intermediate with a single unpaired electron, formed by homolysis of a covalent bond.
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids
 Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids are compounds in which the OH of a carboxyl group has been replaced by CI, OOCR, NH2, or OR'to convert acid chlorides,anhydrides,
Functional Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids Derivatives of Carboxylic Acids are compounds in which the OH of a carboxyl group has been replaced by CI, OOCR, NH2, or OR'to convert acid chlorides,anhydrides,
Carboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl Chlorides
 R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
R hemistry A 432 arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic Acids, Esters and Acyl hlorides arboxylic acids contain the functional group, attached to an alkyl stem. They are widely found in nature,
Biology 12. Biochemistry. Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds.
 Biology 12 Biochemistry Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds. Electrons in these bonds spend more time circulating around the larger Oxygen atom than the smaller Hydrogen
Biology 12 Biochemistry Water - a polar molecule Water (H 2 O) is held together by covalent bonds. Electrons in these bonds spend more time circulating around the larger Oxygen atom than the smaller Hydrogen
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
CHAPTER 2 FUNDAMENTAL CHEMISTRY FOR MICROBIOLOGY WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? An understanding of chemistry is essential to understand cellular structure and function, which are paramount for your understanding
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review
 Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
Bio 12 Chapter 2 Test Review 1.Know the difference between ionic and covalent bonds In order to complete outer shells in electrons bonds can be Ionic; one atom donates or receives electrons Covalent; atoms
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life. Chapter 3
 The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
The Chemical Building Blocks of Life Chapter 3 Biological Molecules Biological molecules consist primarily of -carbon bonded to carbon, or -carbon bonded to other molecules. Carbon can form up to 4 covalent
