Web: 1
|
|
|
- Laurence Simmons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Running head: Integrated systems in Aspergillus fumigatus. Interplay between Gliotoxin Resistance, Secretion and the Methyl/Methionine Cycle in Aspergillus fumigatus. Rebecca A. Owens 1, Grainne O Keeffe 1, Elizabeth B. Smith 1, Stephen K. Dolan 1, Stephen Hammel 1, Kevin J. Sheridan 1, David A. Fitzpatrick 1, Thomas M. Keane 2, Gary W. Jones 1,* and Sean Doyle 1,*. 1 Department of Biology, Maynooth University, Maynooth, Co. Kildare, Ireland. 2 The Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute, Hinxton, Cambridge CB10 1SA, UK. *Joint Corresponding Authors Professor Sean Doyle & Dr Gary W. Jones, Department of Biology, Maynooth University, Maynooth, Co. Kildare, Ireland. Tel: ; Fax: ; sean.doyle@nuim.ie Tel: ; Fax: ; gary.jones@nuim.ie Web: 1
2 Table S1. Aspergillus fumigatus strains used in the study. Strain Reference A. fumigatus ATCC A. fumigatus ATCC A. fumigatus Af293 Nierman et al. (1) A. fumigatus gliz Af293.1 Bok et al. (2) A. fumigatus metr AfS167 Amich et al. (3) A. fumigatus glit ATCC26933 Schrettl et al. (4) A. fumigatus glit ATCC46645 Schrettl et al. (4) A. fumigatus glik ATCC26933 Gallagher et al. (5) A. fumigatus glik ATCC46645 Gallagher et al. (5) A. fumigatus glig ATCC26933 Davis et al. (6) A. fumigatus gtma ATCC26933 Dolan et al. (7) A. fumigatus gtma:gtma ATCC26933 (gtma C ) Dolan et al. (7) A. fumigatus glia ATCC26933 This work A. fumigatus glia:glia ATCC26933 (glia C ) This work A. fumigatus gliz: glit Af293.1 This work A. fumigatus gliz: glit:: gliz Af293.1 This work 2
3 3
4 4
5 5
6 Continued.. 6
7 Continued.. 7
8 Figure S1 A. DIG ATCC26933 ΔgliA Ladder ATCC26933 Figure S1: A. Schematic representation of glia deletion and complementation strategy. B. PCR confirmation of glia presence (1629 bp) in A. fumigatus gliac. Expression analysis via RT-PCR of glia expression from cdna derived from wild-type, glia and gliac. C. glit expression is significantly elevated in A. fumigatus glia comapred to both wild-type and gliac. D. Generation of A. fumigatus ΔgliZ:ΔgliT and confirmation of glit deletion in A. fumigatus ΔgliZ293 (35) by Southern blot analysis. E. Reconstitution of gliz in A. fumigatus ΔgliZ:ΔgliT and confirmation by Southern blot analysis. F. RT-PCR confirms that gliz expression is restored in A. fumigatus ΔgliZ:ΔgliT::gliZ. G. Gliotoxin sensitivity of A. fumigatus AF293, gliz, glit, gliz:glit and gliz: glit::gliz. gliz complementation in A. fumigatus ΔgliZ:ΔgliT resulted 8 in wild-type like resistance to gliotoxin, possibly due to unexpected trans effects of this Zn(2)Cys(6) binuclear transcription factor.
9 Figure S1 B. (i) PCR (ii) RT-PCR L glia C L ΔgliA WT glia C 1629 bp 9
10 Figure S1 C. glit expression 10
11 Figure S1 D. DIG Ladder AF293 ΔgliZ ΔgliT ΔgliZΔgliT bp bp
12 Figure S1 E. DIG Ladder AF293 ΔgliZ ΔgliZΔgliT ΔgliZΔgliT::gliZ bp 3584 bp 2898 bp
13 Figure S1 F. AF293 ΔgliZ ΔgliZΔgliT ΔgliZΔgliT::gliZ Neg. ctrl gdna 186 bp AF293 ΔgliZ ΔgliZΔgliT ΔgliZΔgliT::gliZ Neg. ctrl gdna 617 bp 348 bp 13
14 Figure S1 G. [Gliotoxin] (µg/ml) Key: AF293 ΔgliZ ΔgliT::gliZ ΔgliZ ΔgliT ΔgliZ ΔgliT 14
15 Figure S2 A. ATCC ΔmetR 1 5 mm Met Gliotoxin (0 µg/ml) Gliotoxin (20 µg/ml) Figure S2: A. Phenotypic analysis for A. fumigatus ΔmetR sensitivity to gliotoxin (0-20 µg/ml) on AMM at 37 C for 72 h. A. fumigatus ΔmetR was supplemented with Met ( mm). Compared to wild-type, A. fumigatus ΔmetR was significant sensitivity to gliotoxin at concentrations > 10 µg/ml, regardless of Met concentration. B. qrt-pcr analysis of glit expression in A. fumigatus ATCC46645 and ΔmetR following 3 h gliotoxin or MeOH exposure. Significantly attenuated expression (p < 0.001) of glit in A. fumigatus ΔmetR is observed in response to gliotoxin. C. Phenotypic analysis of sensitivity to simultaneous gliotoxin and cystathionine exposure in ΔmetR grown on AMM at 37 C for 72 h. Gliotoxin (10 µg/ml) significantly sensitizes A. fumigatus ΔmetR to cystathionine (1.5 mm). 15
16 Figure S2 A. % Growth * * 100 ATCC metr (0.05 mm Met) metr (1 mm Met) metr (5 mm Met) Gliotoxin (µg/ml) 16
17 17 with MeOH with Gliotoxin Figure S2 B *** ATCC46645 metr Relative Ratio
18 Figure S2 30 ** ATCC46645 metr C. Radial Growth (mm) Cystathionine (mm) with 10 g/ml gliotoxin Cystathionine (mm)/gliotoxin (µg/ml) 0/10 0.5/10 1.0/10 1.5/10 ATCC46645 ΔmetR 18
19 Figure S3 GT CH6 GT CH2 gliz CH 3 gtma MtrA CH 3 -THF Hcy SahA 2 SAH CH 3 CH 2 -THF Methyl Cycle MetH Methionine Cycle GtmA NADH, CO 2, NH 3 GdcA THF NAD +, Gly Met ATP SasA 2 SAM PPi+Pi GliT NADP / O 2 ( ) Gliotoxin Biosynthetic Pathway Cell membrane/wall Intracellular [R]? GliA Extracellular 19 CH 3 CH 3
20 Figure S3. Integration of gliotoxin biosynthesis, self-protection and regulatory mechanisms into primary metabolism via gliotoxin bis-thiomethyltransferase (GtmA) activity. Exogenous, and endogenous, gliotoxin induces gli cluster (CH6; chromosome 6) and gtma (AFUA_2G11120 (CH2)) expression, and de novo gliotoxin biosynthesis (2, 4, 7, 8). Gliotoxin biosynthesis involves GliG-mediated bis-glutathionylation of an acyl imine intermediate (6) to form a bis-glutathionylated compound, which is subsequently processed via GliK, and additional enzymes to yield GT-(SH) 2. GliT oxidizes GT-(SH) 2 to gliotoxin followed by GliA-mediated secretion, or alternatively to attenuate gliotoxin biosynthesis, GtmA converts GT-(SH) 2 to BmGT, with concomitant consumption of 2 SAM molecules. Resultant SAH must be re-converted to SAM via the action of the methyl/methionine cycle. Absence of GliT activity, results in GT-(SH) 2 flux via GtmA to BmGT, which results in both SAM depletion and SAH overproduction. Thus, the negative regulation of gliotoxin biosynthesis via GtmA must be countered-balanced by GliT activity to avoid dysregulation of methyl/methionine cycle, SAM depletion and trans consequences of same on global cellular biochemistry in A. fumigatus. The differential proteomic impact of exogenous gliotoxin exposure on the GliT-mediated self-protection system of A. fumigatus in both A. fumigatus glig (no affect) and glik (attenuated), respectively, suggests that either BmGT presence, or interference with GSH homeostasis, also plays a role in enabling gliotoxin biosynthesis or self-regulation. 20
21 References 1. Nierman W.C., Pain A., Anderson M.J., Wortman J.R., Kim H.S. et al Genomic sequence of the pathogenic and allergenic filamentous fungus Aspergillus fumigatus. Nature 438: Bok J.W., Chung D., Balajee S.A., Marr K.A., Andes D. et al GliZ, a transcriptional regulator of gliotoxin biosynthesis, contributes to Aspergillus fumigatus virulence. Infect Immun 74: Amich J., Schafferer L., Haas H., Krappmann S Regulation of sulphur assimilation is essential for virulence and affects iron homeostasis of the human-pathogenic mould Aspergillus fumigatus. PLoS Pathog 9: e Schrettl M., Carberry S., Kavanagh K., Haas H., Jones G.W. et al Self-protection against gliotoxin-a component of the gliotoxin biosynthetic cluster, GliT, completely protects Aspergillus fumigatus against exogenous gliotoxin. PLoS Pathog 6:e Gallagher L., Owens R.A., O Keeffe G., Dolan S.K., Schrettl M. et al The Aspergillus fumigatus Protein GliK Protects Against Oxidative Stress and is Essential for Gliotoxin Biosynthesis. Eukaryot Cell 11: Davis C., Carberry S., Schrettl M., Singh I., Stephens J.C. et al The role of glutathione S- transferase GliG in gliotoxin biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. Chem Biol 18: Dolan S.K., Owens R.A., O Keeffe G., Hammel S., Fitzpatrick D.A. et al Regulation of Nonribosomal Peptide Synthesis: Bis-thiomethylation Attenuates Gliotoxin Biosynthesis in Aspergillus fumigatus. Chem Biol 21: O' Keeffe G., Hammel S., Owens R. A., Keane T. M., Fitzpatrick D. A., Jones G. W., Doyle S RNA-seq Reveals the Pan-Transcriptomic Impact of Attenuating the Gliotoxin Self-Protection Mechanism in Aspergillus fumigatus. BMC Genomics 15:
Boosting lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalga N. gaditana via genome engineering
 Boosting lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalga N. gaditana via genome engineering Imad Ajjawi, John Verruto, Moena Aqui, Eric Moellering and Robert Brown October 25th 216 Outline n Brief intro
Boosting lipid productivity of the oleaginous microalga N. gaditana via genome engineering Imad Ajjawi, John Verruto, Moena Aqui, Eric Moellering and Robert Brown October 25th 216 Outline n Brief intro
~PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY~ DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU
 ~PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY~ DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU OVERVIEW The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the hexose monophosphate shunt, or 6- phosphogluconate pathway) occurs in the cytosol
~PENTOSE PHOSPHATE PATHWAY~ DR. A. TARAB DEPT. OF BIOCHEMISTRY HKMU OVERVIEW The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the hexose monophosphate shunt, or 6- phosphogluconate pathway) occurs in the cytosol
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D.
 Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Pro-Oxidant Environmental Exposures: Implications of Redox Imbalance in Autism S. Jill James, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Autism Metabolic Genomics Laboratory Arkansas Children
Midterm 2. Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98. Standard Deviation: 17.7
 Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Midterm 2 Low: 14 Mean: 61.3 High: 98 Standard Deviation: 17.7 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Review of Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Synthesis of few amino acids Dietary
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids
 Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
Lecture 11 - Biosynthesis of Amino Acids Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Biosynthetic pathways for amino acids, nucleotides and lipids
0.5. Normalized 95% gray value interval h
 Normalized 95% gray value interval.5.4.3.2.1 h Supplemental Figure 1: Symptom score of root samples used in the proteomics study. For each time point, the normalized 95% gray value interval is an averaged
Normalized 95% gray value interval.5.4.3.2.1 h Supplemental Figure 1: Symptom score of root samples used in the proteomics study. For each time point, the normalized 95% gray value interval is an averaged
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines
 Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Oxidation and Methylation in Human Brain: Implications for vaccines 1 Life can be viewed through the perspective of oxidation and reduction, which involves the loss and gain of electrons, respectively.
Metabolism of. Sulfur Containing Amino Acids
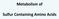 Metabolism of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids Methionine S CH 3 CH 2 cysteine CH 2 SH CH 2 CHNH 2 COOH CHNH 2 COOH Essential amino acid Non-polar amio acid Glucogenic amino acid Methionine IMPORTANCE: As
Metabolism of Sulfur Containing Amino Acids Methionine S CH 3 CH 2 cysteine CH 2 SH CH 2 CHNH 2 COOH CHNH 2 COOH Essential amino acid Non-polar amio acid Glucogenic amino acid Methionine IMPORTANCE: As
9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism
 9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism M.V. Martinov 1,V.M.Vitvitsky 1,E.V.Mosharov 2,R.Banerjee 2,F.I.Ataullakhanov 1 1 National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia 125167 2
9 Metabolic trigger: control of methionine metabolism M.V. Martinov 1,V.M.Vitvitsky 1,E.V.Mosharov 2,R.Banerjee 2,F.I.Ataullakhanov 1 1 National Research Center for Hematology, Moscow, Russia 125167 2
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers
 Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Analysis of Massively Parallel Sequencing Data Application of Illumina Sequencing to the Genetics of Human Cancers Gordon Blackshields Senior Bioinformatician Source BioScience 1 To Cancer Genetics Studies
Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems&
 Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems& Thursday, 5 June 2014 Course: Redox Regulation, Oxidative Stress, and Selenoproteins Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, 2-6 June 2014 Ed Schmidt, Professor Department
Mouse&Models&for&Studies&of&Redox&Systems& Thursday, 5 June 2014 Course: Redox Regulation, Oxidative Stress, and Selenoproteins Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, 2-6 June 2014 Ed Schmidt, Professor Department
Metabolic Dr Elizabeth Mumper
 MINDD Forum General Session Metabolic Elizabeth Mumper, MD Director of Medical Education Autism Research Institute May 2009 Vicious Cycles Food sensitivities Gut inflammation Malabsorption oxidative stress
MINDD Forum General Session Metabolic Elizabeth Mumper, MD Director of Medical Education Autism Research Institute May 2009 Vicious Cycles Food sensitivities Gut inflammation Malabsorption oxidative stress
Supplemental Figures 1-4 and Supplemental Table 1
 Supplemental Figures 1-4 and Supplemental Table 1 Contents Supplemental Figure 1: Hydrolytic enzyme activity profiles of the eight species... 2 Supplemental Figure 2: Laccase activity of the eight species...
Supplemental Figures 1-4 and Supplemental Table 1 Contents Supplemental Figure 1: Hydrolytic enzyme activity profiles of the eight species... 2 Supplemental Figure 2: Laccase activity of the eight species...
(A) Urea cycle (B) TCA cycle (C) Glycolysis (D) Pyruvate oxidation (E) Respiratory chain
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
 LAB #: Sample Report PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: SEX: Female DOB: 01/01/1985 AGE: 33 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Sample Doctor Doctors Data Inc 3755 Illinois Ave St. Charles, IL 60174 U.S.A.!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
LAB #: Sample Report PATIENT: Sample Patient ID: SEX: Female DOB: 01/01/1985 AGE: 33 CLIENT #: 12345 DOCTOR: Sample Doctor Doctors Data Inc 3755 Illinois Ave St. Charles, IL 60174 U.S.A.!!"#$%&'#()*+,-).(&"/+0&'12'
What systems are involved in homeostatic regulation (give an example)?
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS (Diabetes Mellitus Part 1): An Overview
Biochemistry. Metabolic pathways
 Biochemistry Metabolic pathways 07.11.2017 01.12.2017 Gerhild van Echten-Deckert Tel. 73 2703 E-mail: g.echten.deckert@uni-bonn.de www.limes-institut-bonn.de Objectives of the course: Energy metabolism
Biochemistry Metabolic pathways 07.11.2017 01.12.2017 Gerhild van Echten-Deckert Tel. 73 2703 E-mail: g.echten.deckert@uni-bonn.de www.limes-institut-bonn.de Objectives of the course: Energy metabolism
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function
 Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Introduction to Metabolism Cell Structure and Function Cells can be divided into two primary types prokaryotes - Almost all prokaryotes are bacteria eukaryotes - Eukaryotes include all cells of multicellular
Key knowledge base & conceptual questions
 Key knowledge base & conceptual questions Why is it said the pentose phosphate pathway is the major source of reducing power? What are the differences, in structure and in function, between NADH and NADPH?
Key knowledge base & conceptual questions Why is it said the pentose phosphate pathway is the major source of reducing power? What are the differences, in structure and in function, between NADH and NADPH?
I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation
 Epigenesis: Gene Regulation Epigenesis : Gene Regulation I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation (X chromosome inactivation or Lyonization) III) Regulation during
Epigenesis: Gene Regulation Epigenesis : Gene Regulation I) Development: tissue differentiation and timing II) Whole Chromosome Regulation (X chromosome inactivation or Lyonization) III) Regulation during
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions
 H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
H 2 S: Synthesis and functions 1 Signaling gas molecules: O 2, NO and CO Then, H 2 S - Fourth singling gas molecule after O 2, NO and CO 2 Nothing Rotten About Hydrogen Sulfide s Medical Promise Science
Supplementary figure legends
 Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Supplementary figure legends Fig. S1. Lineweaver-Burk plot of putrescine uptake by YeeF. An overnight culture of SK629 was inoculated in 100-mL LBG medium in 500-mL Erlenmeyer flasks. The medium was supplemented
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn
 Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Investigations of Pactamycin Biosynthesis Andrew Osborn Research Mentors: Dr. Taifo Mahmud, Dr. Kerry McPhail A Bioresource Research Thesis Seminar Presentation Streptomyces pactum produces the antitumor
Lecture 1- Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design. Introduction. Introduction. Introduction. Questions we will focus on this semester:
 Lecture 1- Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Questions we will focus on this semester: How does a cell
Lecture 1- Metabolism: Basic Concepts and Design Chem 454: Regulatory Mechanisms in Biochemistry University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire 1 Introduction Questions we will focus on this semester: How does a cell
Accessing and Using ENCODE Data Dr. Peggy J. Farnham
 1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
1 William M Keck Professor of Biochemistry Keck School of Medicine University of Southern California How many human genes are encoded in our 3x10 9 bp? C. elegans (worm) 959 cells and 1x10 8 bp 20,000
Midterm 2 Results. Standard Deviation:
 Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Midterm 2 Results High: Low: Mean: Standard Deviation: 97.5% 16% 58% 16.3 Lecture 17 Amino Acid Metabolism Urea Cycle N and S assimilation Last cofactors: THF and SAM Dietary (Exogenous) Proteins Hydrolyzed
Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis.
 ATP=cellular energy Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis. The reactions of energy extraction and energy use are called
ATP=cellular energy Cells extract energy from their environment and use the energy for a host of biological activities including biosynthesis. The reactions of energy extraction and energy use are called
HOST-PARASITE INTERPLAY
 HOST-PARASITE INTERPLAY Adriano Casulli EURLP, ISS (Rome, Italy) HOST-PARASITE INTERPLAY WP3 (parasite virulence vs human immunity) (Parasite) Task 3.1: Genotypic characterization Task 3.6: Transcriptome
HOST-PARASITE INTERPLAY Adriano Casulli EURLP, ISS (Rome, Italy) HOST-PARASITE INTERPLAY WP3 (parasite virulence vs human immunity) (Parasite) Task 3.1: Genotypic characterization Task 3.6: Transcriptome
Roles of Lipids. principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular
 Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
Roles of Lipids principal form of stored energy major constituents of cell membranes vitamins messengers intra and extracellular = Oxidation of fatty acids Central energy-yielding pathway in animals. O
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II
 BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
BIOL 158: BIOLOGICAL CHEMISTRY II Lecture 5: Vitamins and Coenzymes Lecturer: Christopher Larbie, PhD Introduction Cofactors bind to the active site and assist in the reaction mechanism Apoenzyme is an
Biochemistry: A Short Course
 Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 31 Amino Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 31 Outline Although the atmosphere is approximately 80% nitrogen,
Tymoczko Berg Stryer Biochemistry: A Short Course Second Edition CHAPTER 31 Amino Acid Synthesis 2013 W. H. Freeman and Company Chapter 31 Outline Although the atmosphere is approximately 80% nitrogen,
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice
 An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
An Unexpected Function of the Prader-Willi Syndrome Imprinting Center in Maternal Imprinting in Mice Mei-Yi Wu 1 *, Ming Jiang 1, Xiaodong Zhai 2, Arthur L. Beaudet 2, Ray-Chang Wu 1 * 1 Department of
Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury
 Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury Sophie S. Yuth Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Virginia
Role of Acid Sphingomyelinase Knockout Mice in Protection Against Hyperhomocystenimia Induced Glomerular Injury Sophie S. Yuth Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology Medical College of Virginia Virginia
Targeting MAT2A in MTAP-deleted Cancers
 Targeting MAT2A in MTAP-deleted Cancers Presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting, April 14-18, 2018, Chicago, IL, USA 1 Acknowledgements Agios 2017 Founders Day Retreat
Targeting MAT2A in MTAP-deleted Cancers Presented at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting, April 14-18, 2018, Chicago, IL, USA 1 Acknowledgements Agios 2017 Founders Day Retreat
Role of iron in invasive fungal infections
 Role of iron in invasive fungal infections Günter Weiss Department of Internal Medicine Clinical Immunology and Infectious Diseases Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria Iron at the host-pathogen-interface
Role of iron in invasive fungal infections Günter Weiss Department of Internal Medicine Clinical Immunology and Infectious Diseases Medical University of Innsbruck, Austria Iron at the host-pathogen-interface
Computational Biology I LSM5191
 Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Computational Biology I LSM5191 Aylwin Ng, D.Phil Lecture Notes: Transcriptome: Molecular Biology of Gene Expression II TRANSLATION RIBOSOMES: protein synthesizing machines Translation takes place on defined
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations. Lecture 9
 Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
c) Macrophages and B cells present antigens to helper T_-cells. (Fill in blanks.) 2 points
 Question 1 You are an immunologist who wants to make the big bucks. You decide to leave the world of science and get a job as a script-consultant on a new medical drama (ER-like) show. You test the writers
Question 1 You are an immunologist who wants to make the big bucks. You decide to leave the world of science and get a job as a script-consultant on a new medical drama (ER-like) show. You test the writers
Welcome to Class 14! Class 14: Outline and Objectives. Overview of amino acid catabolism! Introductory Biochemistry!
 Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
Welcome to Class 14 Introductory Biochemistry Class 14: Outline and Objectives Amino Acid Catabolism Fates of amino groups transamination urea cycle Fates of carbon skeletons important cofactors metabolic
Glutathione Regulation
 The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
The Virtual Free Radical School Glutathione Regulation Dale A. Dickinson 1, Henry Jay Forman 1 and Shelly C. Lu 2 1 University of California, Merced, School of Natural Sciences, P.O. Box 2039, Merced,
Relative Rates. SUM159 CB- 839-Resistant *** n.s Intracellular % Labeled by U- 13 C-Asn 0.
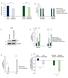 A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
A Relative Growth Rates 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 B Relative Rates 1.6 1.4 1.2 1.8.6.4.2 LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q-Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159 CB-839-Resistant LPS2 Parental LPS2 Q- Independent SUM159 Parental SUM159
Running title: Caspofungin and A. fumigatus. Key words: Aspergillus, Aspergillosis, Caspofungin, Hyphae, Oxidative stress response
 Lebda Medical Journal Vol. 4, Jun. 2018, p.140-147 Ahmed Eshwika, Received 4 Feb. 2018; accepted in revised form 24 Mar. 2018 Exposure of Aspergillus fumigatus to caspofungin induces an oxidative stress
Lebda Medical Journal Vol. 4, Jun. 2018, p.140-147 Ahmed Eshwika, Received 4 Feb. 2018; accepted in revised form 24 Mar. 2018 Exposure of Aspergillus fumigatus to caspofungin induces an oxidative stress
Regulation of Citric Acid Cycle
 Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 30 Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor UGC-CAS Department of Biosciences Saurashtra University, Rajkot-5
Paper : 04 Metabolism of carbohydrates Module : 30 Principal Investigator, Paper Coordinator and Content Writer Dr. Ramesh Kothari, Professor UGC-CAS Department of Biosciences Saurashtra University, Rajkot-5
Why Use Genetic Testing in Practice?
 Pure Encapsulations is committed to producing the most complete line of research-based nutritional supplements. Available through health professionals, finished products are pure and hypoallergenic to
Pure Encapsulations is committed to producing the most complete line of research-based nutritional supplements. Available through health professionals, finished products are pure and hypoallergenic to
number Done by Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb
 number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
number 23 Done by A. Rawajbeh Corrected by Doctor F. Al-Khateeb Ketone bodies Ketone bodies are used by the peripheral tissues like the skeletal and cardiac muscles, where they are the preferred source
What is the Warburg Effect
 What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
 Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
Many Forms of Cell-Cell Communication Regulate Tissue Function and Phenotype Physiological Functions of Gap Junctions Homeostasis buffering/sharing of ions, nutrients, and water Metabolic support nutrient
UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY
 1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
1 UNIVERSITY OF PNG SCHOOL OF MEDICINE AND HEALTH SCIENCES DIVISION OF BASIC MEDICAL SCIENCES DISCIPLINE OF BIOCHEMISTRY AND MOLECULAR BIOLOGY GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS An Overview WHAT IS HOMEOSTASIS? Homeostasis
Metabolism of amino acids. Vladimíra Kvasnicová
 Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
Metabolism of amino acids Vladimíra Kvasnicová Classification of proteinogenic AAs -metabolic point of view 1) biosynthesis in a human body nonessential (are synthesized) essential (must be present in
An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression
 www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
www.collaslab.com An epigenetic approach to understanding (and predicting?) environmental effects on gene expression Philippe Collas University of Oslo Institute of Basic Medical Sciences Stem Cell Epigenetics
LIPID METABOLISM. Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI
 LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
LIPID METABOLISM Sri Widia A Jusman Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Biology FMUI Lipid metabolism is concerned mainly with fatty acids cholesterol Source of fatty acids from dietary fat de novo
COO - l. H 3 N C a H l R 1
 COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
COO - l + H 3 N C a H l R 1 Amino acids There are 20 standard amino acids. All proteins are built from the same amino acids. The most important criteria for classification is affinity to water: hydrophilic
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln
 The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
The citric acid cycle Sitruunahappokierto Citronsyracykeln Ove Eriksson BLL/Biokemia ove.eriksson@helsinki.fi Metabolome: The complete set of small-molecule metabolites to be found in a cell or an organism.
Investigation of Genomic Imprinting in the X- linked Transketolase-like Protein 1 (TKTL1) in Human and the Implications for Autism
 University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-1-2015 Investigation of Genomic Imprinting in the X- linked Transketolase-like Protein 1 (TKTL1) in
University of Connecticut DigitalCommons@UConn Honors Scholar Theses Honors Scholar Program Spring 5-1-2015 Investigation of Genomic Imprinting in the X- linked Transketolase-like Protein 1 (TKTL1) in
#16 made by Nour omar corrected by laith sorour date 17/11
 Lipid metabolism 2 #16 made by Nour omar corrected by laith sorour date 17/11 Keton Bodies Ketone bodies: acetone, -hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate formed principally in the liver mitochondria. can be
Lipid metabolism 2 #16 made by Nour omar corrected by laith sorour date 17/11 Keton Bodies Ketone bodies: acetone, -hydroxybutyrate, and acetoacetate formed principally in the liver mitochondria. can be
Acetyl-CoA or BC acyl-coa. Int1-ACP. FabH. FabF. Anti-FabF Platensimycin ACP. Fak
 Initiation Acetyl-CoA AccBCDA FabZ Int-ACP Elongation [N+] FabG Int1-ACP Acetyl-CoA or BC acyl-coa FabH FabD CoA Malonyl-ACP Malonyl CoA ACP Anti-FabI Triclosan AFN-15 FabI acyl-acp PlsX PlsY Pls C Lipoic
Initiation Acetyl-CoA AccBCDA FabZ Int-ACP Elongation [N+] FabG Int1-ACP Acetyl-CoA or BC acyl-coa FabH FabD CoA Malonyl-ACP Malonyl CoA ACP Anti-FabI Triclosan AFN-15 FabI acyl-acp PlsX PlsY Pls C Lipoic
Nature Genetics: doi: /ng Supplementary Figure 1. Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Figure 1 Immunofluorescence (IF) confirms absence of H3K9me in met-2 set-25 worms. IF images of wild-type (wt) and met-2 set-25 worms showing the loss of H3K9me2/me3 at the indicated developmental
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
Supplementary Information HBV maintains electrostatic homeostasis by modulating negative charges from phosphoserine and encapsidated nucleic acids Authors: Pei-Yi Su 1,2,3, Ching-Jen Yang 2, Tien-Hua Chu
CHEM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Monday, 24 October 2005
 CHEM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Monday, 24 October 2005 Name Dr. H. White - Instructor There are 8 pages to this examination including this page. In addition, you will get a metabolic
CHEM-643 Biochemistry Mid-term Examination 8:00 10:00, Monday, 24 October 2005 Name Dr. H. White - Instructor There are 8 pages to this examination including this page. In addition, you will get a metabolic
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways
 Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
Chapter 5: Major Metabolic Pathways David Shonnard Department of Chemical Engineering 1 Presentation Outline: Introduction to Metabolism Glucose Metabolism Glycolysis, Kreb s Cycle, Respiration Biosysthesis
INTEGRATION OF GENERAL AMINO ACID CONTROL AND TOR REGULATORY PATHWAYS IN NITROGEN ASSIMILATION IN YEAST
 INTEGRATION OF GENERAL AMINO ACID CONTROL AND TOR REGULATORY PATHWAYS IN NITROGEN ASSIMILATION IN YEAST Kirk A. Staschke 1, Souvik Dey 1, John M. Zaborske 2, Lakshmi Reddy Palam 1, Jeanette N. McClintick
INTEGRATION OF GENERAL AMINO ACID CONTROL AND TOR REGULATORY PATHWAYS IN NITROGEN ASSIMILATION IN YEAST Kirk A. Staschke 1, Souvik Dey 1, John M. Zaborske 2, Lakshmi Reddy Palam 1, Jeanette N. McClintick
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209. Petr Tůma Eva Samcová
 Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Coenzymes, vitamins and trace elements 209 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová History and nomenclature of enzymes 1810, Gay-Lussac made an experiment with yeats alter saccharide to ethanol and CO 2 Fermentation From
Supplementary Figures and Tables
 Supplementary Figures and Tables Supplementary Figure 1. Study design and sample collection. S.japonicum were harvested from C57 mice at 8 time points after infection. Total number of samples for RNA-Seq:
Supplementary Figures and Tables Supplementary Figure 1. Study design and sample collection. S.japonicum were harvested from C57 mice at 8 time points after infection. Total number of samples for RNA-Seq:
6. How Are Fatty Acids Produced? 7. How Are Acylglycerols and Compound Lipids Produced? 8. How Is Cholesterol Produced?
 Lipid Metabolism Learning bjectives 1 How Are Lipids Involved in the Generationand Storage of Energy? 2 How Are Lipids Catabolized? 3 What Is the Energy Yield from the xidation of Fatty Acids? 4 How Are
Lipid Metabolism Learning bjectives 1 How Are Lipids Involved in the Generationand Storage of Energy? 2 How Are Lipids Catabolized? 3 What Is the Energy Yield from the xidation of Fatty Acids? 4 How Are
Gene polymorphisms and Folate metabolism as maternal risk factors for Down syndrome child
 Nutrition is a fundamental pillar of human life, health and development across the entire life span. From the earliest stages of fetal development, at birth, through infancy, childhood, adolescence and
Nutrition is a fundamental pillar of human life, health and development across the entire life span. From the earliest stages of fetal development, at birth, through infancy, childhood, adolescence and
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15
 Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Lecture Sixteen: METABOLIC ENERGY: [Based on GENERATION Chapter 15 AND STORAGE Berg, (Figures in red are for the 7th Edition) Tymoczko (Figures in Blue are for the 8th Edition) & Stryer] Two major questions
Microbial Metabolism Microbial nutrients, growth and cultivation
 1 Microbial Metabolism Microbial nutrients, growth and cultivation Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Hall, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw 2 Microbial Nutrition Purpose To
1 Microbial Metabolism Microbial nutrients, growth and cultivation Ching-Tsan Huang ( 黃慶璨 ) Office: Agronomy Hall, Room 111 Tel: (02) 33664454 E-mail: cthuang@ntu.edu.tw 2 Microbial Nutrition Purpose To
Amino acid metabolism I
 Amino acid metabolism I Jana Novotná Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Metabolic relationship of amino acids DIETARY PROTEINS GLYCOLYSIS
Amino acid metabolism I Jana Novotná Department of the Medical Chemistry and Clinical Biochemistry The 2nd Faculty of Medicine, Charles Univ. Metabolic relationship of amino acids DIETARY PROTEINS GLYCOLYSIS
In Vitro Interactions of Antifungal agents and Tacrolimus against Aspergillus Biofilms
 AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 24 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01510-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 In Vitro Interactions
AAC Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 24 August 2015 Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. doi:10.1128/aac.01510-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 In Vitro Interactions
Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells. Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010
 Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010 Introduction The Warburg Effect Cancer cells metabolize glucose differently Primarily
Evidence for an Alternative Glycolytic Pathway in Rapidly Proliferating Cells Matthew G. Vander Heiden, et al. Science 2010 Introduction The Warburg Effect Cancer cells metabolize glucose differently Primarily
LAST LECTURE. 1. Things the course missed 2. Things you might be tested on
 LAST LECTURE 1. Things the course missed 2. Things you might be tested on Things I didn t tell you that might make more sense now that you have had BIS105 From Regulation of Cellular Metabolism by Protein
LAST LECTURE 1. Things the course missed 2. Things you might be tested on Things I didn t tell you that might make more sense now that you have had BIS105 From Regulation of Cellular Metabolism by Protein
Information transmission
 1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
1-3-3 Case studies in Systems Biology Goutham Vemuri goutham@chalmers.se Information transmission Fluxome Metabolome flux 1 flux flux 3 Proteome metabolite1 metabolite metabolite3 protein 1 protein protein
Energy metabolism - the overview
 Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Energy metabolism - the overview Josef Fontana EC - 40 Overview of the lecture Important terms of the energy metabolism The overview of the energy metabolism The main pathways of the energy metabolism
Coupled, interconnecting reactions
 Metabolism: Basic concepts Hand-out for the CBT version November 2011 This module is based on 'Biochemistry' by Berg, Tymoczko and Stryer, seventh edition (2011), Chapter 15: Metabolism: Basic Concepts
Metabolism: Basic concepts Hand-out for the CBT version November 2011 This module is based on 'Biochemistry' by Berg, Tymoczko and Stryer, seventh edition (2011), Chapter 15: Metabolism: Basic Concepts
RESISTANCE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN PLATINUM AND PARP-INHIBITORS IN OVARIAN CANCER.
 RESISTANCE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN PLATINUM AND PARP-INHIBITORS IN OVARIAN CANCER. Britta Stordal 1, Yidong Chen 2, Angela Farrelly 3, Danielle Gallagher 3, Steven Busschots 1, Mattia Cremona 3, Mark Carey
RESISTANCE RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN PLATINUM AND PARP-INHIBITORS IN OVARIAN CANCER. Britta Stordal 1, Yidong Chen 2, Angela Farrelly 3, Danielle Gallagher 3, Steven Busschots 1, Mattia Cremona 3, Mark Carey
Glucose is the only source of energy in red blood cells. Under starvation conditions ketone bodies become a source of energy for the brain
 Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
Glycolysis 4 / The Text :- Some Points About Glucose Glucose is very soluble source of quick and ready energy. It is a relatively stable and easily transported. In mammals, the brain uses only glucose
EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN
 EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN Financial Disclosure: Consultant to DaVinci Labs AGENDA Overview of the following: Methylation Telomere
EVERYDAY CLINICAL APPLICATION OF TELOMERE AND AGING SUPPORT PRESENTED BY: Fred Pescatore, MD, MPH, CCN Financial Disclosure: Consultant to DaVinci Labs AGENDA Overview of the following: Methylation Telomere
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester
 BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
BBSG 501 Section 4 Metabolic Fuels, Energy and Order Fall 2003 Semester Section Director: Dave Ford, Ph.D. Office: MS 141: ext. 8129: e-mail: fordda@slu.edu Lecturers: Michael Moxley, Ph.D. Office: MS
CELLS. Cells. Basic unit of life (except virus)
 Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Basic unit of life (except virus) CELLS Prokaryotic, w/o nucleus, bacteria Eukaryotic, w/ nucleus Various cell types specialized for particular function. Differentiation. Over 200 human cell types 56%
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Supplementary information Human Cytomegalovirus MicroRNA mir-us4-1 Inhibits CD8 + T Cell Response by Targeting ERAP1 Sungchul Kim, Sanghyun Lee, Jinwook Shin, Youngkyun Kim, Irini Evnouchidou, Donghyun
Complexity DNA. Genome RNA. Transcriptome. Protein. Proteome. Metabolites. Metabolome
 DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
DNA Genome Complexity RNA Transcriptome Systems Biology Linking all the components of a cell in a quantitative and temporal manner Protein Proteome Metabolites Metabolome Where are the functional elements?
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine
 Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Supplementary Information Titles Journal: Nature Medicine Article Title: Corresponding Author: Supplementary Item & Number Supplementary Fig.1 Fig.2 Fig.3 Fig.4 Fig.5 Fig.6 Fig.7 Fig.8 Fig.9 Fig. Fig.11
Chem 454, Spring Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = kcal/mol V
 Name Chem 454, Spring 2003 - Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = 23.06 kcal/mol V 1. Analysis of electron transport pathway in a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium reveals the presence of six electron transport
Name Chem 454, Spring 2003 - Exam II F, Faraday's constant, = 23.06 kcal/mol V 1. Analysis of electron transport pathway in a pathogenic gram-negative bacterium reveals the presence of six electron transport
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria
 Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Chapter 19: The Genetics of Viruses and Bacteria What is Microbiology? Microbiology is the science that studies microorganisms = living things that are too small to be seen with the naked eye Microorganisms
Walter: Treatment rapidly alters the physiologic state of Mtb in sputum. 2/24/16- Advances in the Science
 Treatment rapidly alters the physiologic state of M tuberculosis in sputum Nicholas Walter, MD, PhD Denver Veterans Affairs Medical Center Colorado School of Public Health National Jewish Health Makerere
Treatment rapidly alters the physiologic state of M tuberculosis in sputum Nicholas Walter, MD, PhD Denver Veterans Affairs Medical Center Colorado School of Public Health National Jewish Health Makerere
Physiological Adaptation. Microbial Physiology Module 4
 Physiological Adaptation Microbial Physiology Module 4 Topics Coordination of Metabolic Reactions Regulation of Enzyme Activity Regulation of Gene Expression Global Control, Signal Transduction and Twocomponent
Physiological Adaptation Microbial Physiology Module 4 Topics Coordination of Metabolic Reactions Regulation of Enzyme Activity Regulation of Gene Expression Global Control, Signal Transduction and Twocomponent
Integrative Metabolism: Significance
 Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Integrative Metabolism: Significance Energy Containing Nutrients Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Catabolism Energy Depleted End Products H 2 O NH 3 ADP + Pi NAD + NADP + FAD + Pi NADH+H + NADPH+H + FADH2 Cell
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment. Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein
 Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Gene Ontology and Functional Enrichment Genome 559: Introduction to Statistical and Computational Genomics Elhanan Borenstein The parsimony principle: A quick review Find the tree that requires the fewest
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):
 Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
Role of metabolism in Drug-Induced Liver Injury (DILI) Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 Drug Metab Rev. 2007;39(1):159-234 A schematic representation of the most relevant
Biochemistry - I SPRING Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) Lecture 16. Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat
 Biochemistry - I Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) SPRING 2017 Lecture 16 Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat 1 Catabolism of Di- and Polysaccharides Catabolism (digestion) begins
Biochemistry - I Mondays and Wednesdays 9:30-10:45 AM (MR-1307) SPRING 2017 Lecture 16 Based on Profs. Kevin Gardner & Reza Khayat 1 Catabolism of Di- and Polysaccharides Catabolism (digestion) begins
Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway
 Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway Gustavo H. Goldman Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil Calcineurin is a calmodulin/ca +2 dependent
Factors influencing the Aspergillus fumigatus survival into the host mediated by the calcineurin pathway Gustavo H. Goldman Universidade de São Paulo, Brazil Calcineurin is a calmodulin/ca +2 dependent
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International
 Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
Cysteine Peptide Scientific Review, Dr. S. Dudek, DMV International Ethanol and Glutathione Reduced glutathione plays a critical role in cellular detoxification processes including the metabolism of peroxides,
Red Blood Cell s Metabolism: HMP Pathway
 Click to edit Master title style Edit Master text styles Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Red Blood Cell s Metabolism: HMP Pathway Prof. Samar Kassim Prof. Reem Sallam 2017-2018 1. Recognize
Click to edit Master title style Edit Master text styles Second level Third level Fourth level Fifth level Red Blood Cell s Metabolism: HMP Pathway Prof. Samar Kassim Prof. Reem Sallam 2017-2018 1. Recognize
Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status
 Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status Dr. Attila Bezzegh Semmelweis Medical University, Instutute for Laboratory Medicine, Budapest, Hungary 2017 Vitamin B12
Vitamin B12 and folate metabolism: their role in the regulation of the lipid status Dr. Attila Bezzegh Semmelweis Medical University, Instutute for Laboratory Medicine, Budapest, Hungary 2017 Vitamin B12
1. Epistasis Analysis Reveals Distinct Roles of Non-homologous End Joining Factors in Human HAP1 Cells Mengtan Xing, NTNU
 Posters you find at the NORBIS meeting 1. Epistasis Analysis Reveals Distinct Roles of Non-homologous End Joining Factors in Human HAP1 Cells Mengtan Xing, NTNU 2. Copy Number Variation detection tool
Posters you find at the NORBIS meeting 1. Epistasis Analysis Reveals Distinct Roles of Non-homologous End Joining Factors in Human HAP1 Cells Mengtan Xing, NTNU 2. Copy Number Variation detection tool
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses
 Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
Under the Radar Screen: How Bugs Trick Our Immune Defenses Session 7: Cytokines Marie-Eve Paquet and Gijsbert Grotenbreg Whitehead Institute for Biomedical Research HHV-8 Discovered in the 1980 s at the
BCH Graduate Survey of Biochemistry
 BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 44 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
BCH 5045 Graduate Survey of Biochemistry Instructor: Charles Guy Producer: Ron Thomas Director: Marsha Durosier Lecture 44 Slide sets available at: http://hort.ifas.ufl.edu/teach/guyweb/bch5045/index.html
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids. Amino acid metabolism
 Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Catabolism of Carbon skeletons of Amino acids Amino acid metabolism Carbon skeleton Carbon Skeleton a carbon skeleton is the internal structure of organic molecules. Carbon Arrangements The arrangement
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site.
 Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Find this material useful? You can help our team to keep this site up and bring you even more content consider donating via the link on our site. Still having trouble understanding the material? Check
Krebs cycle Energy Petr Tůma Eva Samcová
 Krebs cycle Energy - 215 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová Overview of Citric Acid Cycle Key Concepts The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) is a multistep catalytic process that converts acetyl groups derived from carbohydrates,
Krebs cycle Energy - 215 Petr Tůma Eva Samcová Overview of Citric Acid Cycle Key Concepts The citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) is a multistep catalytic process that converts acetyl groups derived from carbohydrates,
