A simple flow cytometric method to assess lipid accumulation in fat cells
|
|
|
- Karin Bates
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 A simple flow cytometric method to assess lipid accumulation in fat cells Ying-Hue Lee 1 *, Su-Yin Chen 1, Rudolf J. Wiesner 2 and Yi-Fong Huang 1 1 Laboratory of Molecular Pathology, Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan, and 2 Institute of Vegetative Physiology, University of Cologne, Germany. *Corresponding author: Institute of Molecular Biology Academia Sinica Nangang Taipei 115 Taiwan Tel/Fax: yinghue@gate.sinica.edu.tw
2 ABSTRACT Adipogenesis of pre-adipocytes in culture has been frequently used to study the molecular basis and effect of drugs on fat cell conversion. However, after adipogenic induction, cells respond to the inducing agent with various speeds of conversion and fat accumulation, which complicates direct molecular and biochemical analyses. Here we present a simple and sensitive method to detect and quantify fat accumulation inside cells by flow cytometry. Using this method, we detected elevated levels of cytoplasmic granularity that correlated well with an increased level of fat accumulated inside cells after adipogenic conversion. We further demonstrated the ability of this method to monitor and quantify fat cell maturation within a complex population of cells and to identify and collect the fat cells with similar fat storage for further analyses. Flow cytometry offers distinct advantages over existing detection systems for cytoplasmic lipid staining and lipid extraction and could represent a powerful analytical tool to monitor the effect of chemicals and biological molecules on fat cell conversion and maturation. Moreover, in combination with a cell sorting facility, our method offers a simple and efficient means of collecting fat cells of specific status for further analyses. Supplementary key words: Flow cytometry, Adipogenesis, Fat accumulation, Cytoplasmic granularity, Adipocyte 1
3 INTRODUCTION The prevalence of obesity and obesity-related disorders, such as diabetes and arthritis, has promoted much research in recent years into the prevention and treatment of obesity (1-3). Understanding the molecular mechanism underlying fat cell development has been one of the major focuses of many researchers in the field. Methods in use for the assessment of fat cell development and maturation after initiation of adipogenesis in cell culture include microscopic examination of cellular lipid droplet formation and cellular lipid staining by Oil-Red O (4). These methods, although excellent in detecting the presence of intracellular fat, are ineffective in objectively quantifying the degree of fat accumulation if not used in conjunction with other extraction and analytic systems. Particularly, during the process of adipogenesis of pre-adipocytes, it is observable that cells are heterogeneous in their response to adipogenic agents, in terms of speed of adipogenic conversion and degree of fat accumulation (5). This heterogeneity of response may cause difficulties when evaluating and comparing the effects of several treatments that target only fat cells of certain status, due to the masking influence of those nontargeted cells. Thus, an effective method to detect and classify cells with similar fat content will certainly increase analytical precision in monitoring fat cell development and the ability to quantify the effects of therapeutic agents. Currently, flow cytometry and FACS are extensively used in the analysis of hematological cells (6,7); we have explored the feasibility of using these methods to assess fat content during fat cell development and to group fat cells with similar fat content for more precise biochemical and molecular analyses. 2
4 METHODS 3T3-L1 cell culture and adipogenesis 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes were obtained from ATCC (CL173, ATCC) and maintained in culture according to the ATCC protocol. Adipogenesis was induced by adding insulin, 3-isobutyl-1-methyl-xanthine (IBMX) and dexamethasone to 2-day postconfluence cells (designated Day 0) at final concentrations of 10µg/ml, 0.5 mm and 1 µm, respectively, for 2 days (8). Cells were then maintained in culture media containing 5µg/ml of insulin until needed. Flow cytometry Adipogenically induced 3T3-L1 cells were analyzed and sorted in flow cytofluorometers (FACS calibur and FACS star plus, Becton Dickinson) using FACS (Fluorescence-Activated Cell Sorter) technology. Cells were briefly rinsed twice with pre-warmed 0.25% trypsin-edta and then incubated for 5 min at 37 o C. Cell were then gently resuspended in PBS, washed twice with PBS, re-suspended in cold PBS and kept on ice prior to flow cytometric analysis. For cell sorting, the sorted cells were collected directly into the culture medium and returned to the CO 2 incubator immediately after sorting. The cytofluorometer settings for both side (SSC) and forward (FSC) scatters to analyze fat cells were dependent on the analytic sensitivity of the machine. In general, the voltages and compensation between scatters were set to the degree so that the majority of control cells (Adipo 0D, non-induced) were, as shown in Fig. 1B, located below the scale of 200 for the SSC and between the scales of 200 and 800 for the FSC. RNA extraction and Northern blot analysis. 3
5 Cells were homogenized in TRIzol RNA reagent (GIBCO-BRL), and total RNA was isolated according to the manufacturer s protocol. Total RNA (5 µg) was denatured, electrophoresed, transferred to a nylon membrane, and probed with 32 P-labeled perilipin cdna probe using standard protocols. Oxygen consumption. Immediately prior to measurement, cells were harvested by trypsinization, washed twice in PBS and re-suspended in 0.2 ml PBS. Cells were then added to an Oxytherm oxygen electrode (HansaTech, UK) previously equilibrated and stabilized with air in a 0.5 ml oxygen buffer at 37 o C. Oxygen consumption was monitored for 10 min and calculated according to the manufacturer s instruction. The electrode buffer contained 0.3M mannitol, 10mM KCl, 5 mm MgCl 2, 10 mm KH 2 PO 4 and 1 mg/ml BSA (ph 7.4). Additional protocols. Mouse pre-adipocytes were isolated from male epidedylmal fat pads and cultured accordingly (9). Adipogenesis induction for the isolated pre-adipoctes was similar to that for 3T3-L1 cells. In addition, BRL49653C (Rosiglitazone, Smithkline Beecham, UK) was included in the induction media. To measure cellular lipid, cells were briefly homogenized in PBS using a Teflon homogenizer. After removal of cell debris, lipid levels were measured using a Triglyceride detection kit (Infinity, Sigma). For cytoplasmic lipid staining, cells were fixed in 70% isopropanol and stained in 0.2% Oil- Red O (4). Recombinant adenovirus carrying the GPF marker gene and a gene of interest was generated using the AdEasy vector system (Q-BIOgene). 4
6 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 3T3-L1 cells, grown to 2-day post-confluence in culture (designated Day 0, shown as Adipo 0D in Fig 1) were hormonally induced for adipogenesis (8), then dissociated and analyzed in a flow cytometer at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 days post-induction (Fig. 1A to 1B). The dot plot of cytometric FSC (shown as the X-axis in Fig. 1B and Fig. 2A) and SSC (shown as the Y-axis) scatters, reflecting the cell diameter and granular structures within the cell, respectively, showed that after adipogenic induction the cells had become increasingly heterogeneous in their cellular granularity (Fig. 1B). After adipogenic induction, the cells containing greater granular structure were markedly increased, and this increase in granularity positively correlated with the time of the postadipogenic induction (Fig. 1B to 1C). In general, the longer the period of induction, the greater the quantity of lipid a fat cell in culture can accumulate. Thus, to determine whether increasing the fat stored within a cell would result in the greater granularity seen in side scatter, eight days post-induction cells were gated for four regions as shown in Fig. 2A based on the full scale of SSC. The R1 region contains cells with a level of granularity similar to that seen in the control cells (non-induced), whereas R2 to R4 regions contain cells with increasing granularity. Cells in the gated regions were sorted and collected for further microscopic examination (Fig. 2B) and lipid content analysis (Fig. 2C). Indeed, both microscopic and lipid analyses of the sorted fat cells revealed that the granularity detected in the SSC correlated well with levels of fat storage within cells (Fig. 2B and 2C); the cells collected from the R4 region had the greatest intracellular granularity with the biggest lipid droplets and highest lipid content, whilst cells that exhibited lower granularity (R2, R3) contained fewer and smaller lipid droplets 5
7 and a lower lipid content (Fig. 2B). After sorting, cells collected from all regions were analyzed for their ability to re-attach to the surface of culture dished under culturing conditions (Fig. 2D). It was found that the degree of re-attachment was negatively correlated with the increased cellular granularity; more than 95% of the cells from the R1 region could re-attach, whilst less than 10% of cells from the R4 region could re-attach. Cells in the R1 region appeared to be not induced and could proliferate, whilst cells from other regions continued to accumulate fat as indicated by the growth of their cellular lipid pool (Fig. 2D). Nevertheless, our results indicate that the granularity of fat cells, as detected by flow cytometry, is an excellent indicator for cellular fat stored, and thus that the granularity of a fat cell can be easily distinguished via flow cytometric side-scatter. Quantification of distinct cell populations is one of the integral functions of flow cytometry. Thus, we next used flow cytometry to monitor and quantify 3T3-L1 cells based on their degree of fat accumulation at various stages of adipogenesis. Figure 3A summarizes and compares the R1, R2, R3 and R4 cell populations of 3T3-L1 cells at various stages of adipogenesis. Changes in cell distribution from low to higher granularity during the 10-day period of adipogenesis were clearly profiled by flow cytometry (Fig. 3A, upper panel). In comparison, cells at various stages of adipogenesis were also stained with Oil-Red O, which has been routinely used to monitor adipogenesis. Although the Oil-Red O staining clearly indicated the presence of lipid droplets within cells, by itself it did not provide any quantitive information regarding the lipid levels nor the heterogeneity of fat accumulation among cells, unlike flow cytometry (Fig. 3A, lower panel). Accordingly, we hypothesized that flow cytometry might be also more sensitive in detecting fat content when used to evaluate and compare the effect of 6
8 different factors on fat accumulation in fat cells. To examine this possibility, we isolated pre-adipocytes from mouse epidedymal fat pads and maintained them in culture for adipogenic conversion. To induce these cells to become fat cells, a PPAR ligand, BRL (10), was needed in addition to the insulin, IBMX and dexamethasone cocktail that were adequate to adipogenically induce 3T3-L1 cells. Thus, these isolated preadipocytes are ideal for used in evaluating the efect of PPAR ligands on adipogenic conversion. To evaluate the dosage effect of BRL on adipogenic conversion, isolated pre-adipocytes were cultured to confluency and induced for adipogenesis using the same system as used for 3T3-L1 cells, except that BRL 49653C was included in the inducing media. Eight days after induction, cells were analyzed for their granularity using flow cytometry (Fig. 3B). At concentrations of 0.5µM and higher, BRL 49653C significantly increased the cell populations in the R2 to R4 regions where cells contain greater granularity, suggesting that more cells were adipogenically induced to store fat. Although at the concentration of 5 µm, BRL did not further enhance the total level of adipogenesis (R2 to R4), the population of cells containing greater granularity (R4) increased relative to the cell populations from the R2 and R3 regions (Fig. 3B). As demonstrated above, despite under the same culturing condition, cells underwent adipogenesis at varying rates reflected by the degree of their fat accumulation. We were thus interested to see whether these fat cells with various degrees of fat storage differed in other physiological parameters associated or influenced by their cellular fat content. To test this, we analyzed and compared the expression levels of perilipin, a lipid droplet-specific protein that coats the surfaces of lipid droplets of adipocytes (11), and the oxygen consumption of fat cells with different levels of fat storage (the R2 to R4 7
9 regions). 3T3-L1 cells, eight days after adipogenic induction, were sorted and collected based on their granularity, similar to those cells shown in Figure 2A. The collected cells were monitored for their perilipin mrna levels and their oxygen consuming (Fig. 3C to 3D). We found that cells in the R1 region did not express perilipin mrna and consumed the least oxygen relative to the cells having higher granularity (R2 to R4). In addition, levels of perilipin mrna in cells from the R2 and R3 regions were found to be higher than in cells from the R4 region. Similarly, cells from the R2 and R3 regions consumed significantly more oxygen than those from the R4 region, indicating that fat cells with less fat stored are more active in oxidation when compared to those with higher fat storage. Lastly, to precisely analyze the effect of a treatment, such as over-expression of a gene in fat cells, we used flow cytofluorometer to identify and collect fat cells that were carrying similar fat stores and were subjected to treatments for further analysis. Here, we used recombinant adenoviral vector to deliver the GFP marker gene and the G alpha inhibitory subunit 2 (G i2 ) expression cassette into fat cells. 3T3-L1 cells, four days after adipogenic induction, were infected with the recombinant adenoviral vector Ad.Track carrying the GFP marker gene under the control of a CMV promoter (12) or the recombinant adenoviral vector carrying G i2 in addition to the GFP marker gene. Despite the use of the highly efficient adenoviral gene delivery system and a viral dosage of over 5 MOI, only a small number of fat-laden cells were found to express the GFP marker gene after 3 days of infection. To specifically select those fat cells that had similar fat content, we again used flow cytometric side scatter in combination with fluorescence detection. As shown in Fig. 3E, a group of GFP positive fat cells with 8
10 similar fat content were effectively sorted and collected for further analysis to determine the effects of G i2 on the lipolytic activity of fat cells stimulated by the adrenergic receptor agonist, isoproterenol. The inhibitory effective of G i2 on the isoproterenolstimulated lipid release was not detected when the condition medium from the whole population of cells was analyzed (Fig. 3F). This could be due to the low infection rate of the adenoviral vector and/or the heterogeneous population of cells that contained close to 40% of cells failed to be adipogenically induced (Fig. 3A). However, a significant inhibitory effect of G i2 on the isoproterenol-stimulated lipid release was measured in the condition medium from the GFP-positive cells collected from the R3 region (Fig. 3F). This result further indicates the necessity to utilized an analytical system capable of monitoring, quantifying and selecting fat cells with different degrees of adipogenic conversion before an objective comparison among treatments can be made. In conclusion, this study demonstrates the feasibility of directly measuring the fat content of specific cells in a complex population of fat cells using flow cytometry. Not only is the system simple, sensitive and quantitative, but it also offers the advantage over existing methodology of being capable of monitoring the degree of intracellular fat accumulation in a precise, fast and selective manner. These results provide a basis for developing a variety of applications that including diagnostic and drug screening procedures to monitor fat cell development. 9
11 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This work was supported in part by the grant NSC B from the National Science Council and a fellowship (to YHL) from Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. 10
12 REFERECES 1. Kopelman, P.G. (2000) Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 404, Barsh, G.S., Farooqi, I.S., and O'Rahilly, S. (2000) Genetics of body-weight regulation. Nature 404, Valet, P., Tavernier, G., Castan-Laurell, I., Saulnier-Blache, J.S., and Langin, D. (2002) Understanding adipose tissue development from transgenic animal models. J Lipid Res. 43, von Goor, H., Gerrits, P.O. and Groud, J. (1986) The application of lipid-soluble stains in plastic-embedded sections. Histochemistry 85, Shigematsu, S., Miller, S.L., and Pessin, JE. (2001) Differentiated 3T3L1 adipocytes are composed of heterogenous cell population with distinct receptor tyrosin kinase signaling properties. J. Biol. Chem. 276, Peerschke, E.I. (2002) The laboratory evaluation of platelet dysfunction. Clin Lab Med. 22, Chianese, R., Brando, B. and Gratama, J.W. (2002) Diagnostic and prognostic value of flow cytometric immunophenotyping in malignant hematological diseases. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 16, Sadowski, H.B., Wheeler, T.T., and Young, D.A. (1992) Gene expression during 3T3-L1 adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 266, Zuk, P.A., Zhu, M., Mizuno H., Huang, J., Futrell, W., Katz, A.J., Benhaim, P., Lorenz, P., and Hedrick, M.H. (2001) Multilineage cells from Human adipose Tissue: Implications for cell-based therapies. Tissue Engineering 7, Lehmann, J.M., Moore, L.B., Smith-Oliver, T.A., Wilkison, W.O., Willson, T.M., 11
13 and Kliewer, S.A. (1995) An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem. 270, Greenberg, A.S., Egan, J.J., Wek, S.A., Garty, N.B.,Blanchette-Mackie, E. J., and Londos, C. (1991) Perilipin, a major hormonally regulated adipocytespecific phosphoprotein associated with the periphery of lipid storage droplets. J. Biol. Chem., 266, He, T.C., Zhou, S., da Costa, L.T., Yu, J., Kinzler K.W. and Vogelsterin, B. (1998) A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 95,
14 FIGURE LEGENDS Figure 1. Increased granularity and heterogeneity among 3T3-L1 cells during adipogenesis (A) Light microscopic examination of 3T3-L1 cells eight days after adipogenic induction. Arrowhead indicates the lipid droplets accumulated inside cells. (B) Dot plots of side scatter (SSC, x-axis) vs. forward scatter (FSC, y-axis) of 3T3-L1 cells generated from flow cytometric analysis of levels of granularity at different time points of adipogenesis. FSC represents the cell size, whereas SSC represents cytoplasmic granular intensity. Two-day post confluent 3T3-L1 cells (designated Day O, shown here as Adipo 0D) were hormonally induced for adipogenesis. Cells were dissociated and analyzed in a flow cytometer at 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 days after induction. (C) The overlay of cell distribution vs cellular granular intensity from five plots in 1B. Figure 2. Positive correlation between the cellular lipid content and granularity of 3T3- L1 cells after adipogenic induction (A) The regions gated for cell sorting. Scatter plot of 3T3-L1 cells eight days after adipogenic induction were gated into 4 regions based on their granularity distribution. The R1 region was gated to include the majority of control cells shown on the SSC scale. Regions R2 to R4 were gated to include the remaining range of SSC, and each region contained an equal range of SSC. Cells from these 4 regions were then collected separately. The x-axis, FSC, represents the cell size, whereas the y- axis, SSC, represents cytoplasmic granular intensity. (B) Light microscopy of the cultured 3T3-L1 cells collected from R1 and R3 regions. Arrowheads 13
15 indicate lipid droplets accumulated inside cells. (C) Comparison of the cellular lipid content of cells collected from each region in 2A. Cells were briefly homogenized in PBS in a Teflon homogenizer. The cytoplasmic fraction was collected and assayed for triglyceride levels. The value for each gated group is the mean of four sortings and is presented as a vertical bar in the figure. The standard error for each group is shown as a vertical line. (D) Light microscopy of the sorted 3T3-L1 cells from each region. After sorting, cells were collected from each region and re-cultured. Cell photographs were taken 1 day (1D) and 5 days (5D) after re-culturing. Arrowheads indicate lipid droplets accumulated inside cells. Figure 3. Use of flow cytometry in analyzing fat cell development (A) Quantification of fat cells during adipogenesis. Two-day post-confluent 3T3-L1 cells (designated 0D) were induced for adipogenesis and analyzed at different time points for both cytoplasmic granularity in flow cytometry (upper panel) and lipid storage via Oil-Red O staining (lower panel). For flow cytometric analysis, the value of granularity for a gated region at each time point was the mean of four samples, and the granularity (gated region) values for the same time point are displayed in a stacked column. (B) Analysis of the dosage effect of BRL49653C on adipogenesis in isolated mouse pre-adipocytes. Mouse preadipocytes isolated from male epidedymal fat pads were induced for adipogenesis two days post-confluence. Various concentrations of BRL49653C, as indicated, were added to the inducing medium. Eight days after induction, cells were analyzed for their scatter profile using flow 14
16 cytometry. The granularity value for each gated region at each concentration of BRL49653C was the mean of four samples, and the gated region values at the same time point are displayed in a stacked column. (C) Comparison of the levels of perilipin mrna in cells from each region. Five µg of total RNA from cells were electrophoresed, blotted onto a nylon membrane and probed with a 32 P-labelled perilipin cdna probe. (D) Comparison of oxygen consumption among fat cells gated for levels of fat storage. Four groups of cells were collected based on their SSC profile with regards to granularity as those shown in Fig. 2A and re-cultured for at least a further 12-hour in culture media prior to oxygen consumption measurement. The value for each gated group is the mean of four sortings and is presented as a vertical bar in the figure. The standard error for each group is shown as a vertical line. (E) Identification and collection of GFP-carrying adenovirus targeted fat cells displaying similar fat accumulation. Two days post-confluent 3T3-L1 cells were induced for adipogenesis. Four days after induction, recombinant adenoviruses carrying a GFP marker gene were added to the culture medium at the dosage of 5 MOI and incubated for 24 hours. Eight days after induction, cell were dissociated (upper panel) and analyzed in a flow cytometer. The cells that displayed a scatter profile in the R3 gated region (see Fig. 2A) and emitted green fluorescence were selected and collected for fluorescence microscopy (lower panel). (F) Lipolytic effect of isoproterenol on fat cells infected with adenovirus carrying the GFP marker gene and a gene encoding for G i2. Similar to the experiment described in 3E, cells were infected with 15
17 recombinant adenovirus carrying the G i2 expression cassette. Fat cells displaying a SSC profile in the R3 region and emitting green fluorescence were collected for re-culture. Isoproterenol was added to the culture media one day after re-culture. One day after the addition of isoproterenol, 100 µl of the condition media were removed for triglyceride measurement. The value for each gated group is the mean of four sortings and is presented as a vertical bar in the figure. The standard error for each group is shown as a vertical line. 16
18 17
19 18
20 19
ab Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab133102 Adipogenesis Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the study of induction and inhibition of adipogenesis in adherent cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Suppl Video: Tumor cells (green) and monocytes (white) are seeded on a confluent endothelial
 Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
Supplementary Information Häuselmann et al. Monocyte induction of E-selectin-mediated endothelial activation releases VE-cadherin junctions to promote tumor cell extravasation in the metastasis cascade
UNDERSTANDING THE BIOLOGY OF FAT METABOLISM is fundamental
 Image-Based High-Throughput Quantification of Cellular Fat Accumulation MIKE DRAGUNOW, 1,3 RACHEL CAMERON, 1 PRITIKA NARAYAN, 1,3 and SIMON O CARROLL 2 A number of biochemical methods are available for
Image-Based High-Throughput Quantification of Cellular Fat Accumulation MIKE DRAGUNOW, 1,3 RACHEL CAMERON, 1 PRITIKA NARAYAN, 1,3 and SIMON O CARROLL 2 A number of biochemical methods are available for
Supplemental Material:
 Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Supplemental Material: MATERIALS AND METHODS RNA interference Mouse CHOP sirna (ON-TARGETplus SMARTpool Cat# L-062068-00) and control sirna (ON-TARGETplus Control) were purchased from Dharmacon. Transfection
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol
 Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
Concentration Estimation from Flow Cytometry Exosome Data Protocol 1. STANDARD CURVE Create a standard curve for the target exosome by plotting the mean fluorescence (y axis) against the protein concentration
well for 2 h at rt. Each dot represents an individual mouse and bar is the mean ±
 Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Supplementary data: Control DC Blimp-1 ko DC 8 6 4 2-2 IL-1β p=.5 medium 8 6 4 2 IL-2 Medium p=.16 8 6 4 2 IL-6 medium p=.3 5 4 3 2 1-1 medium IL-1 n.s. 25 2 15 1 5 IL-12(p7) p=.15 5 IFNγ p=.65 4 3 2 1
Gladstone Institutes, University of California (UCSF), San Francisco, USA
 Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Fluorescence-linked Antigen Quantification (FLAQ) Assay for Fast Quantification of HIV-1 p24 Gag Marianne Gesner, Mekhala Maiti, Robert Grant and Marielle Cavrois * Gladstone Institutes, University of
Instructions for Use. APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests
 3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
3URGXFW,QIRUPDWLRQ Sigma TACS Annexin V Apoptosis Detection Kits Instructions for Use APO-AB Annexin V-Biotin Apoptosis Detection Kit 100 tests For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow
 SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA Supplementary Figure Legends Figure S1. PMVs from THP-1 cells expose phosphatidylserine and carry actin. A) Flow cytometry analysis of PMVs labelled with annexin-v-pe (Guava technologies)
In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay
 Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, in vitro suppression assay and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell suppression assay Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit
 Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Lipid (Oil Red O) staining Kit Catalog Number KA4541 1 Kit Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins
 Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Expressing Fluorescent Proteins www.vectalys.com/products/ Constitutive Reporter Lentiviral Vectors Catalog Number referring to this User Manual: 0008VCT; 0009VCT;
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL
 PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
PRODUCT INFORMATION & MANUAL Mitochondrial Extraction Kit NBP2-29448 Research use only. Not for diagnostic or therapeutic procedures www.novusbio.com P: 303.760.1950 P: 888.506.6887 F: 303.730.1966 technical@novusbio.com
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + CD127 dim/- regulatory T cell Workflow isolation, in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation
ab CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit
 ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab139485 CytoPainter Golgi/ER Staining Kit Instructions for Use Designed to detect Golgi bodies and endoplasmic reticulum by microscopy This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538
 Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Data Sheet TIGIT / NFAT Reporter - Jurkat Cell Line Catalog #60538 Background: TIGIT is a co-inhibitory receptor that is highly expressed in Natural Killer (NK) cells, activated CD4+, CD8+ and regulatory
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator. of the Interaction with Macrophages
 Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
Serum Amyloid A3 Gene Expression in Adipocytes is an Indicator of the Interaction with Macrophages Yohei Sanada, Takafumi Yamamoto, Rika Satake, Akiko Yamashita, Sumire Kanai, Norihisa Kato, Fons AJ van
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO
 Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Information p47 negatively regulates IKK activation by inducing the lysosomal degradation of polyubiquitinated NEMO Yuri Shibata, Masaaki Oyama, Hiroko Kozuka-Hata, Xiao Han, Yuetsu Tanaka,
Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary Materials and Methods
 Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
Silva et al. PTEN posttranslational inactivation and hyperactivation of the PI3K/Akt pathway sustain primary T cell leukemia viability Supplementary Table; Supplementary Figures and legends S1-S21; Supplementary
In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion
 - 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
- 1 - Human CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cell isolation, Workflow in vitro expansion and analysis In vitro human regulatory T cell expansion Introduction Regulatory T (Treg) cells are a subpopulation of T
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples.
 ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
ab14082 500X Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and
Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit)
 Product Insert QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit) Introduction About the Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit The homogeneous QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit from Molecular
Product Insert QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit) Introduction About the Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit The homogeneous QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit from Molecular
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
doi: 1.138/nature7221 Brown fat selective genes 12 1 Control Q-RT-PCR (% of Control) 8 6 4 2 Ntrk3 Cox7a1 Cox8b Cox5b ATPase b2 ATPase f1a1 Sirt3 ERRα Elovl3/Cig3 PPARα Zic1 Supplementary Figure S1. stimulates
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit
 Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
Annexin V-PE Apoptosis Detection Kit Catalog Number KA0716 100 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information...
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma
 Version 1 Last updated 25 May 2018 ab228565 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma For the isolation/detection of exosomes from human plasma, urine or cell culture media. This product
Version 1 Last updated 25 May 2018 ab228565 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Plasma For the isolation/detection of exosomes from human plasma, urine or cell culture media. This product
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Figures Supplementary Figure S1. Binding of full-length OGT and deletion mutants to PIP strips (Echelon Biosciences). Supplementary Figure S2. Binding of the OGT (919-1036) fragments with
Supplementary Information. Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose. neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization
 Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
Supplementary Information Glycogen shortage during fasting triggers liver-brain-adipose neurocircuitry to facilitate fat utilization Supplementary Figure S1. Liver-Brain-Adipose neurocircuitry Starvation
PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION
 Last Modified: April 2018 Last Review: October 2018 PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION Table of Contents 1. Brief Description 1 2. Materials and Reagents.1 3. Optimization
Last Modified: April 2018 Last Review: October 2018 PROTOCOL: OPTIMIZATION OF LENTIVIRAL TRANSDUCTION USING SPINFECTION Table of Contents 1. Brief Description 1 2. Materials and Reagents.1 3. Optimization
Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent
 ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
ab14143 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Reagent Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples This product is for research use only and is not
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Gene Expression Analysis: Immunoblot analysis: Immunohistochemistry:
 General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
General Laboratory methods Plasma analysis: Plasma insulin (Mercodia, Sweden), leptin (duoset, R&D Systems Europe, Abingdon, United Kingdom), IL-6, TNFα and adiponectin levels (Quantikine kits, R&D Systems
ab Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells
 ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
ab189819 Membrane fluidity kit Instructions for Use For the detection of membrane fluidity in cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version 1 Last Updated
Instructions. Fuse-It-mRNA easy. Shipping and Storage. Overview. Kit Contents. Specifications. Note: Important Guidelines
 Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
Membrane fusion is a highly efficient method for transfecting various molecules and particles into mammalian cells, even into sensitive and primary cells. The Fuse-It reagents are cargo-specific liposomal
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / CD81)
 Version 1 Last updated 26 September 2018 ab239682 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / For the isolation and analysis of exosome from cell culture. This product is
Version 1 Last updated 26 September 2018 ab239682 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell Culture (CD63 / For the isolation and analysis of exosome from cell culture. This product is
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells
 MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
MicroRNA sponges: competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells Margaret S Ebert, Joel R Neilson & Phillip A Sharp Supplementary figures and text: Supplementary Figure 1. Effect of sponges on
Life Sciences METABOLISM. Transform Your Metabolic Research
 METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of. PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
 Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Supplementary Materials and Methods Cell cycle analysis To determine the effect of over-expression and/or ligand activation of PPAR / on cell cycle, cell lines were cultured as described above until ~80%
Mamofillin New aesthetic perspective
 New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
New aesthetic perspective info@ White adipose tissue (WAT) White adipose tissue (WAT) is the prevalent type in human adults functioning as the major storage site for the lipids absorbed from daily intake
For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Glycerol in cell cultures.
 ab185433 Lipolysis Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Glycerol in cell cultures. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab185433 Lipolysis Assay Kit (Colorimetric) Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Glycerol in cell cultures. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab Hepatic Lipid Accumulation/ Steatosis Assay Kit
 ab133131 Hepatic Lipid Accumulation/ Steatosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For evaluating steatosis risk of drug candidates using Oil Red O to stain neutral lipids in hepatocytes. This product is for
ab133131 Hepatic Lipid Accumulation/ Steatosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For evaluating steatosis risk of drug candidates using Oil Red O to stain neutral lipids in hepatocytes. This product is for
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
Influenza A H1N1 HA ELISA Pair Set for H1N1 ( A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 ) HA Catalog Number : SEK11684 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the
MULTI-GENERATIONAL STOMACH SLIMMING SOLUTION. be inspired. reveal
 observe PHEOSLIM & PERILIPIN: MULTI-GENERATIONAL STOMACH SLIMMING SOLUTION be inspired reveal NEW PHEOSLIM & PERILIPIN: MULTI-GENERATIONAL STOMACH SLIMMING SOLUTION BE INSPIRED A slimming agent for everyone.
observe PHEOSLIM & PERILIPIN: MULTI-GENERATIONAL STOMACH SLIMMING SOLUTION be inspired reveal NEW PHEOSLIM & PERILIPIN: MULTI-GENERATIONAL STOMACH SLIMMING SOLUTION BE INSPIRED A slimming agent for everyone.
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer. Application Note
 Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
Analysis of small RNAs from Drosophila Schneider cells using the Small RNA assay on the Agilent 2100 bioanalyzer Application Note Odile Sismeiro, Jean-Yves Coppée, Christophe Antoniewski, and Hélène Thomassin
ab Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture
 Version 1 Last updated 14 March 2018 ab228564 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture For the measurement of human exosomes in cell culture. This product is for research use only
Version 1 Last updated 14 March 2018 ab228564 Exosome Isolation and Analysis Kit - Flow Cytometry, Cell culture For the measurement of human exosomes in cell culture. This product is for research use only
FOCUS SubCell. For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions. (Cat. # ) think proteins! think G-Biosciences
 169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
169PR 01 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name FOCUS SubCell For the Enrichment of Subcellular Fractions (Cat. # 786 260) think
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well
 Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
Optimization of the Fuse-It-mRNA Protocol for L929 Cells in the µ-plate 24 Well 1. General Information... 1 2. Background... 1 3. Material and Equipment Required... 2 4. Experimental Procedure and Results...
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative. breast cancer patients
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION CXCR4 inhibitors could benefit to HER2 but not to Triple-Negative breast cancer patients Lefort S. 1,2, Thuleau A. 3, Kieffer Y. 1,2, Sirven P. 1,2, Bieche I. 4, Marangoni E.
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit with SYTOX
 ab14086 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit with SYTOX Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in living cells. This product is for research use only and
ab14086 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit with SYTOX Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in living cells. This product is for research use only and
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Supplementary Information Supplementary Figure 1. CD4 + T cell activation and lack of apoptosis after crosslinking with anti-cd3 + anti-cd28 + anti-cd160. (a) Flow cytometry of anti-cd160 (5D.10A11) binding
Instructions. Fuse-It-Color. Overview. Specifications
 Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Membrane fusion is a novel and highly superior method for incorporating various molecules and particles into mammalian cells. Cargo-specific liposomal carriers are able to attach and rapidly fuse with
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonates Exhibit Higher Activity towards Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Signaling Pathways than Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Chuan-Hai
Supporting Information Chlorinated Polyfluorinated Ether Sulfonates Exhibit Higher Activity towards Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Signaling Pathways than Perfluorooctane Sulfonate Chuan-Hai
Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis
 PR072 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE-403) think proteins!
PR072 G-Biosciences 1-800-628-7730 1-314-991-6034 technical@gbiosciences.com A Geno Technology, Inc. (USA) brand name Biodiversity Study & Biomass Analysis Teacher s Guidebook (Cat. # BE-403) think proteins!
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS
 SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS Histological analysis. Colonic tissues were collected from 5 parts of the middle colon on day 7 after the start of DSS treatment, and then were cut into segments, fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde,
NEW PHYTOCHEMICAL BASED COCKTAIL FOR IN VITRO ADIPOCYTES DIFFERENTIATION. Resources Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Skudai, Johor.
 NEW PHYTOCHEMICAL BASED COCKTAIL FOR IN VITRO ADIPOCYTES 1 DIFFERENTIATION F.A. ABDUL MAJID 1*, M. TAHER 1 AND M.R. SARMIDI 2 1 Department of Bioprocess, 2 Chemical Engineering Pilot Plant, Faculty of
NEW PHYTOCHEMICAL BASED COCKTAIL FOR IN VITRO ADIPOCYTES 1 DIFFERENTIATION F.A. ABDUL MAJID 1*, M. TAHER 1 AND M.R. SARMIDI 2 1 Department of Bioprocess, 2 Chemical Engineering Pilot Plant, Faculty of
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) p24 / Capsid Protein p24 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11695 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14142 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended
ab14142 Annexin V-Cy3 Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of apoptosis in various samples. This product is for research use only and is not intended
Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154+CD4+ T cell Rapid antigen-specific T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central role
T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells
 A complete workflow for cell preparation, isolation, polarization and analysis T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells Introduction Workflow CD4 + T helper (T H) cells play a
A complete workflow for cell preparation, isolation, polarization and analysis T H 1, T H 2 and T H 17 polarization of naïve CD4 + mouse T cells Introduction Workflow CD4 + T helper (T H) cells play a
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set
 Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Human Immunodeficiency Virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp120 / Glycoprotein 120 ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11233 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2*
 Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Ex vivo Human Antigen-specific T Cell Proliferation and Degranulation Willemijn Hobo 1, Wieger Norde 1 and Harry Dolstra 2* 1 Department of Laboratory Medicine - Laboratory of Hematology, Radboud University
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Supplementary Information GADD34-deficient mice develop obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic carcinoma and insulin resistance Naomi Nishio and Ken-ichi Isobe Department of Immunology, Nagoya
Research Article Inhibitory Effects of 4-(4-Methylbenzamino)benzoate on Adipocyte Differentiation
 Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 171570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/171570 Research Article Inhibitory Effects of 4-(4-Methylbenzamino)benzoate on Adipocyte Differentiation Jin Taek Hwang,
Chemistry Volume 2015, Article ID 171570, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/171570 Research Article Inhibitory Effects of 4-(4-Methylbenzamino)benzoate on Adipocyte Differentiation Jin Taek Hwang,
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
doi:10.1038/nature12652 Supplementary Figure 1. PRDM16 interacts with endogenous EHMT1 in brown adipocytes. Immunoprecipitation of PRDM16 complex by flag antibody (M2) followed by Western blot analysis
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Nuclear Extraction Kit Catalog Number KA1346 50 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Principle of the Assay... 3 General Information... 4
Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays
 Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Supplemental methods Detailed step-by-step operating procedures for NK cell and CTL degranulation assays Materials PBMC isolated from patients, relatives and healthy donors as control K562 cells (ATCC,
Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread
 Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Supplementary Information Influenza virus exploits tunneling nanotubes for cell-to-cell spread Amrita Kumar 1, Jin Hyang Kim 1, Priya Ranjan 1, Maureen G. Metcalfe 2, Weiping Cao 1, Margarita Mishina 1,
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit
 Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Annexin V-APC/7-AAD Apoptosis Kit Catalog Number KA3808 100 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h)
 Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
Online Appendix Material and Methods: Pancreatic RNA isolation and quantitative real-time (q)rt-pcr. Mice were fasted overnight and killed 1 hour (h) after feeding. A small slice (~5-1 mm 3 ) was taken
ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit
 ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate detection of Cytochrome c translocation from Mitochondria into Cytosol during Apoptosis in
ab65311 Cytochrome c Releasing Apoptosis Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate detection of Cytochrome c translocation from Mitochondria into Cytosol during Apoptosis in
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of basophils after reconstitution of SCID mice
 Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Supplementary figure legends Supplementary Figure 1. Characterization of after reconstitution of SCID mice with CD4 + CD62L + T cells. (A-C) SCID mice (n = 6 / group) were reconstituted with 2 x 1 6 CD4
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit
 ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
ab14085 Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Instructions for Use For the rapid, sensitive and accurate measurement of Apoptosis in living cells (adherent and suspension). View kit datasheet: www.abcam.com/ab14085
Supplemental Data Figure S1 Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells.
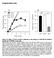 Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Supplemental Data Figure S1. Effect of TS2/4 and R6.5 antibodies on the kinetics of CD16.NK-92-mediated specific lysis of SKBR-3 target cells. (A) Specific lysis of IFN-γ-treated SKBR-3 cells in the absence
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Supplementary Figure 1 Traditional electronic gating strategy for analysing cell death based on A5-FITC and 7-AAD. a, Flow cytometry analysis showing the traditional two-stage electronic gating strategy
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
Influenza A H7N9 (A/Anhui/1/2013) Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK40103 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay
VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization
 Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Cell Reports, Volume 9 Supplemental Information VEGFR2-Mediated Vascular Dilation as a Mechanism of VEGF-Induced Anemia and Bone Marrow Cell Mobilization Sharon Lim, Yin Zhang, Danfang Zhang, Fang Chen,
Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit
 PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
PROTOCOL Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit DESCRIPTION Mitochondrial Trifunctional Protein (TFP) Protein Quantity Microplate Assay Kit Sufficient materials
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes
 A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
A protocol for enhancement of the AAV-mediated expression of transgenes Hiroaki Mizukami, Takeharu Kanazawa, Takashi Okada, and Keiya Ozawa Division of Genetic Therapeutics, Center for Molecular Medicine,
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION EXPERIMENTAL PROCEDURES Tryptic digestion protection experiments - PCSK9 with Ab-3D5 (1:1 molar ratio) in 50 mm Tris, ph 8.0, 150 mm NaCl was incubated overnight at 4 o C. The
SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric*
 SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72171 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect Cathepsin K activity. Enhanced Value: Ample
SensoLyte 520 Cathepsin K Assay Kit *Fluorimetric* Catalog # 72171 Kit Size 100 Assays (96-well plate) Optimized Performance: This kit is optimized to detect Cathepsin K activity. Enhanced Value: Ample
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Complete but curtailed T-cell response to very-low-affinity antigen Dietmar Zehn, Sarah Y. Lee & Michael J. Bevan Supp. Fig. 1: TCR chain usage among endogenous K b /Ova reactive T cells. C57BL/6 mice
Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice.
 Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Supplementary Figures: Supplementary Figure S I: Effects of D4F on body weight and serum lipids in apoe -/- mice. Male apoe -/- mice were fed a high-fat diet for 8 weeks, and given PBS (model group) or
Validation & Assay Performance Summary
 Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Validation & Assay Performance Summary LanthaScreen IGF-1R GripTite Cells Cat. no. K1834 Modification Detected: Phosphorylation of Multiple Tyr Residues on IGF-1R LanthaScreen Cellular Assay Validation
Supplementary information
 Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Supplementary information Lipid peroxidation causes endosomal antigen release for cross-presentation Ilse Dingjan 1, Daniëlle RJ Verboogen 1, Laurent M Paardekooper 1, Natalia H Revelo 1, Simone P Sittig
Supplementary Material and Methods
 Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Online Supplement Kockx et al, Secretion of Apolipoprotein E from Macrophages 1 Supplementary Material and Methods Cloning of ApoE-GFP Full-length human apoe3 cdna (pcdna3.1/zeo + -apoe) was kindly provided
Immature organoids appear after hours.
 THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED Allison Ruchinskas, B.S., and James Clinton, Ph.D. ATCC Cell Systems, Gaithersburg, MD INTRODUCTION Figure 1. Mouse small intestinal organoid
THE ESSENTIALS OF LIFE SCIENCE RESEARCH GLOBALLY DELIVERED Allison Ruchinskas, B.S., and James Clinton, Ph.D. ATCC Cell Systems, Gaithersburg, MD INTRODUCTION Figure 1. Mouse small intestinal organoid
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set
 Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Influenza B Hemagglutinin / HA ELISA Pair Set Catalog Number : SEK11053 To achieve the best assay results, this manual must be read carefully before using this product and the assay is run as summarized
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in
 Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Data 1. Alanine substitutions and position variants of APNCYGNIPL. Applied in Supplementary Fig. 2 Substitution Sequence Position variant Sequence original APNCYGNIPL original APNCYGNIPL
Supplementary Materials for
 www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
www.sciencesignaling.org/cgi/content/full/8/407/ra127/dc1 Supplementary Materials for Loss of FTO in adipose tissue decreases Angptl4 translation and alters triglyceride metabolism Chao-Yung Wang,* Shian-Sen
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE)
 Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Direct ex vivo characterization of human antigen-specific CD154 + CD4 + T cells Rapid antigen-reactive T cell enrichment (Rapid ARTE) Introduction Workflow Antigen (ag)-specific T cells play a central
Nuclear Extraction Kit
 Nuclear Extraction Kit Item No. 10009277 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
Nuclear Extraction Kit Item No. 10009277 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION 3 Materials
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION FOR Liver X Receptor α mediates hepatic triglyceride accumulation through upregulation of G0/G1 Switch Gene 2 (G0S2) expression I: SUPPLEMENTARY METHODS II: SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURES
Impact factor: Reporter:4A1H0019 Chen Zi Hao 4A1H0023 Huang Wan ting 4A1H0039 Sue Yi Zhu 4A1H0070 Lin Guan cheng 4A1H0077 Chen Bo xuan
 Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Curcumin Protects Neonatal Rat Cardiomyocytes against High Glucose-Induced Apoptosis via PI3K/Akt Signalling Pathway Wei Yu,1,2 Wenliang Zha,1 Zhiqiang Ke,1 Qing Min,2 Cairong Li,1 Huirong Sun,3 and Chao
Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay
 TECHNICAL MANUAL Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay Instructions for Use of Products J1341, J1342, and J1343 Revised 2/17 TM467 Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
TECHNICAL MANUAL Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay Instructions for Use of Products J1341, J1342, and J1343 Revised 2/17 TM467 Glucose Uptake-Glo Assay All technical literature is available at: www.promega.com/protocols/
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a
 Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
Supplementary Figure 1. BMS98662 enhances human T cell activation in vitro in a concentration-dependent manner. Jurkat T cells were activated with anti-cd3 and anti-cd28 antibody in the presence of titrated
genome edited transient transfection, CMV promoter
 Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Supplementary Figure 1. In the absence of new protein translation, overexpressed caveolin-1-gfp is degraded faster than caveolin-1-gfp expressed from the endogenous caveolin 1 locus % loss of total caveolin-1-gfp
Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range
 Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Product Name: DynaMarker Protein MultiColor Stable, Low Range Code No: DM670L Lot No: ******* Size: 200 μl x 3 (DM670 x 3) (120 mini-gel lanes) Storage: 4 C Stability: 12 months at 4 C Storage Buffer:
Kit for assay of thioredoxin
 FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
FkTRX-02-V2 Kit for assay of thioredoxin The thioredoxin system is the major protein disulfide reductase in cells and comprises thioredoxin, thioredoxin reductase and NADPH (1). Thioredoxin systems are
Flow Cytometry Based Exosome Detection and Analysis Using the ZE5 Cell Analyzer
 Flow Cytometry ased Exosome Detection and nalysis Using the ZE5 Cell nalyzer Yasha Talaga, Elizabeth Dreskin, Joyce Lee io-rad Laboratories, Inc. 2000 lfred Nobel Drive, Hercules C 94547 Flow Cytometry
Flow Cytometry ased Exosome Detection and nalysis Using the ZE5 Cell nalyzer Yasha Talaga, Elizabeth Dreskin, Joyce Lee io-rad Laboratories, Inc. 2000 lfred Nobel Drive, Hercules C 94547 Flow Cytometry
CD14 + S100A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
 CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
CD14 + S1A9 + Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells and Their Clinical Relevance in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Po-Hao, Feng M.D., Kang-Yun, Lee, M.D. Ph.D., Ya-Ling Chang, Yao-Fei Chan, Lu- Wei, Kuo,Ting-Yu
