Interobserver and Test-Retest Reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 Measurements of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs by 3T Magnetic Resonance Imaging
|
|
|
- Alexander Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging pissn eissn Korean J Radiol 2016;17(6): Interobserver and Test-Retest Reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 Measurements of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs by 3T Magnetic Resonance Imaging Yeon Hwa Yoo, MD 1, Choon-Sik Yoon, MD, PhD 1, Na Lae Eun, MD 1, Moon-jung Hwang, PhD 2, Hanna Yoo, PhD 3, Robert D. Peters, PhD 4, Tae-Sub Chung, MD, PhD 1, Young Han Lee, MD, PhD 5, Jin-Suck Suh, MD, PhD 5, Sungjun Kim, MD, PhD 1 1 Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 06273, Korea; 2 GE Health Care, Seoul 06060, Korea; 3 Biostatistics Collaboration Lab, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea; 4 GE Health Care, Milwaukee, WI 53209, USA; 5 Department of Radiology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul 03722, Korea Objective: To investigate the interobserver and test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements of lumbar intervertebral discs using 3T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Materials and Methods: This study included a total of 51 volunteers (female, 26; male, 25; mean age, 54 ± 16.3 years) who underwent lumbar spine MRI with a 3.0 T scanner. Amongst these subjects, 40 underwent repeat T1ρ and T2 measurement acquisitions with identical image protocol. Two observers independently performed the region of interest measurements in the nuclei pulposi of the discs from L1 2 through L5 S1 levels. Statistical analysis was performed using intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) with a two-way random model of absolute agreement. Comparison of the ICC values was done after acquisition of ICC values using Z test. Statistical significance was defined as p value < Results: The ICCs of interobserver reproducibility were and for T1ρ and T2 mapping, respectively. The ICCs of test-retest reproducibility (40 subjects) for T1ρ and T2 measurements were and for observer A and and for observer B, respectively. In the comparison of the aforementioned ICCs, ICCs of interobserver and test-retest reproducibility for T1ρ mapping were significantly higher than T2 mapping (p < 0.001). Conclusion: The interobserver and test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ mapping were significantly higher than those of T2 mapping for the quantitative assessment of nuclei pulposi of lumbar intervertebral discs. Keywords: T1 rho; Intervertebral disc; Reproducibility; Magnetic resonance imaging; T2 mapping; Disc degeneration INTRODUCTION Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is the leading cause of low back pain worldwide (1). It is a complex Received May 10, 2016; accepted after revision July 15, Corresponding author: Sungjun Kim, MD, PhD, Department of Radiology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, 211 Eonju-ro, Gangnam-Gu, Seoul 06273, Korea. Tel: (822) Fax: (822) AGN70@yuhs.ac This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. multi-systemic disease with unclear etiology (2). The early changes in IDD are primarily associated with the loss of proteoglycan in the nucleus pulposus; the reduction in their water-binding capacity can cause alterations in the water content, leading to the loss of hydration and osmotic pressure (3). Currently, early detection of IDD has been an important issue for appropriate medical or surgical management of the disease in order to prevent further progression (4, 5). Therefore, a reliable quantitative parameter for the detection of early biochemical changes in IDD has been necessitated. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) has been the most important noninvasive diagnostic tool for the assessment of Copyright 2016 The Korean Society of Radiology 903
2 Yoo et al. IDD. Although T2-weighted MRI has been considered a wellestablished method for the semi-quantitative evaluation of disc degeneration according to the morphological grading system (6), conventional MRI technique has limited abilities in the quantification of early changes in IDD. Therefore, researchers have been focusing on the development of quantitative MRI techniques that can analyze the biochemical composition of intervertebral discs (7). More recently, several noninvasive quantitative MRI techniques such as T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences have emerged, which meet the expectations for detection of early biochemical changes in IDD; however, the targets of focus of these two techniques are different from each other. While quantitative T1ρ mapping (8) is sensitive to the proteoglycan content, quantitative T2 mapping (9) is sensitive to the water content and collagen fiber network of the intervertebral discs. However, the acquisition of accurate and clinically valuable quantitative data using T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences has been considered to be challenging. Therefore, the reproducibility of these two quantitative mapping techniques requires evaluation before application (10). To the best of our knowledge, there have been no studies on the evaluation of both interobserver and test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements in lumbar IDD by 3T MRI. Therefore, the purpose of our study was to investigate the interobserver and test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements of lumbar intervertebral discs measured from the corresponding mapping sequences using 3T MR Imaging. MATERIALS AND METHODS Study Participants This prospective study was approved by our institutional review board prior to patient recruitment, and written informed consent was obtained from each patient before enrollment in the study. A total of 51 patients (female, 26; male, 25; mean age, 54 ± 16.3 years; age range, years) were enrolled in this study between December 2013 and February The inclusion criteria were: 1) complaints of low back pain for more than 2 months and 2) agreement to participate in the study. The exclusion criteria were: 1) previous surgical history that might affect image quality, 2) claustrophobia, and 3) scoliosis of lumbar spine, which might cause geometrical variability during image acquisition. Intervertebral lumbar discs from L1 2 through L5 S1 levels were assessed in all the patients. A total of 51 patients underwent MR imaging with the T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences in the first scanning session, as detailed below. Of the 51 subjects, 40 patients who also agreed to undergo repeat imaging with the T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences for the evaluation of the test-retest reproducibility, underwent the repeat scanning session immediately after the first scanning session. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Acquisition All MR images were acquired using a 3.0 T MRI scanner (Discovery MR750, General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) with a spine matrix coil. Images of the lumbar spine including levels L1 2 through L5 S1 were acquired in the supine position between 10 A.M. and 2 P.M., considering diurnal variation (11). The study MRI protocol included the procedures followed in both the first and second scanning sessions. The MR protocol for the first scanning session included three different MR sequences: two-dimensional (2D) fast spin-echo (FSE) T2-weighted images were acquired in the sagittal plane; three-dimensional (3D) FSE pulse sequence with parallel imaging and long echo train, low flip angle, and low specific absorption rate acquisition (3D-CUBE) T1- weighted images were acquired in the sagittal plane for T1ρ mapping; and, finally, 2D-multisection FSE images were acquired in the sagittal plane for T2 mapping. The second scanning session involved image acquisition using just the two mapping sequences mentioned above, with the same parameters. The details of imaging parameters are as follows; 2D FSE protocol (Field of view [FOV] = 38 cm, repetition time [TR]/ echo time [TE] = 3973 ms/102 ms, acquisition matrix = 320 x 512, slice thickness; 3 mm, slice spacing; 4 mm, number of excitations [NEX] = 1, scan time = 1 minute 59 seconds). T1ρ protocol (Fat-saturated 3D CUBE, spin-lock pulse amplitude = 440 Hz [w1 = rb1/2], spin-lock pulse length [TSL] = 1, 10, 30, 60 ms, FOV = 28 cm, TR/TE = 1263 ms/60 ms, acquisition matrix = 192 x 288, bandwidth = 0.7 khz/pixel, slice thickness = 4 mm, NEX = 1, scan time = 7 minutes 6 seconds) and T2 map protocol (2D FSE protocol, FOV = 28 cm, TR = 1836 ms and TEs = 6.0, 12.4, 25.3, 38.1 ms, acquisition matrix = 192 x 288, slice thickness; 4 mm, slice spacing; 2 mm, NEX = 0.5, scan time = 5 minutes 34 seconds). The total scan time for first scanning session was 14 minutes 39 seconds and for second scanning session was 12 minutes 40 seconds. The imaging parameters are 904
3 Reproducibility Comparison between T1ρ and T2 of Intervertebral Disc summarized in Table 1. Post-Processing of Magnetic Resonance Images The MR images were transferred to the Advantage Workstation (Version 4.5; General Electric Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA) for the calculation of the T1ρ and T2 relaxation times of the intervertebral discs using the Functool software (Version e). Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine images of each series were calculated pixel by pixel. The case-by-case threshold parameter was applied for each scan to remove trailing echoes that are of sufficiently low amplitude to be classified as noise. Subsequently, T1ρ maps were reconstructed by fitting the image intensity, pixel-by-pixel, to the equation below, using a mono-exponential non-negative least square fitting algorithm; S (TSL) = S0* exp (-TSL/T1ρ), where TSL is Time of spin-lock, and S is the signal intensity of T1ρweighted image with a given TSL. In the same manner, the mono-exponential fitting algorithm used in Functool iteratively estimated the relaxation parameter with a confidence level of The following equation was used for the reconstruction of T2 maps: S (TE) = S0* exp (-TE/ T2). Image Analysis and Region of Interest Measurement After the acquisition of mapping sequences, all image evaluations were performed by two radiologists, respectively. On the basis of the sagittal T2-weighted MR imaging findings, rectangular regions of interests were placed at the nuclei pulposi of lumbar discs from L1 2 through L5 S1 levels in the T1ρ mapping images of the discs excluding the annulus fibrosus (Fig. 1). Once region of interest (ROI) placement in the T1ρ mapping images was done for a nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc, simultaneous ROI placement at the corresponding disc portion in the T2 mapping images was automatically obtained, except in the cases with geometry mismatch; in such cases (7 out of 51 patients), the ROIs were manually placed at the most identical location as possible and simultaneously compared with the corresponding images. After randomization of the subjects, two radiologists placed the entire ROI measurements independently, blinded to clinical information as well as the result of Pfirrmann grading session. Rectangular ROIs were used for computing the average T1ρ and T2 relaxation times. The mean area of the ROIs was 23.3 ± 4.4 (range, ) mm 2. Thus, two ROI measurements for each of the mapping sequences were obtained for every pixel location at each level of lumbar discs from L1 2 through L5 S1. Discs classified as grade 5 based on the Pfirrmann grading system, as described below, were excluded because of the difficulty in accurate ROI placement within their nuclei pulposi owing to severely decreased disc height (12). In order to obviate bias due to recall memory, the observers analyzed the retest mapping images 2 weeks after the analysis of the first set of images (13). Lumbar intervertebral discs from L1 2 through L5 S1 levels were graded according to the Pfirrmann grading system (6) by a single observer, who did not participate in the T1ρ and T2 measurements. The discs were graded on the Table 1. Summary of Imaging Parameters for Study Protocol Imaging Parameters T2-Weighted 2D-FSE* Imaging in Sagittal Plane T1ρ-Weighted 3D-CUBE Imaging in Sagittal Plane for T1ρ Mapping T2-Weighted 2D-FSE* Imaging in Sagittal Plane for T2 Mapping Repetition time (ms) Echo time (ms) Number of echoes 1 4 (0, 10, 30, 60) 4 (6.0, 12.4, 25.3, 38.1) Number of excitations Matrix size 320 x x x 288 Field of view (cm) Acquisition pixel size (mm 2 ) x x x Section thickness (mm) Slice spacing Number of slices Fat suppression None Chemical fat saturation Chemical fat saturation Total scan time 1 min 59 s 7 min 6 s 5 min 34 s *2-dimensional fast spin-echo pulse sequence, Three-dimensional fast spin-echo pulse sequence with parallel imaging and long echo train, low flip angle, and low specific absorption rate image acquisition. 905
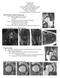
4 Yoo et al. basis of the sagittal T2-weighted MR images, which provide MR-based semi-quantitative evaluations of the discs. The discs were assigned into one of the two groups based on the grading non-degenerated (Pfirrmann grades 1, 2) or degenerated (Pfirrmann grades 3, 4) disc groups, in order to evaluate the significance of the differences between the normal/early and later stages of disc degeneration in terms of the T1ρ and T2 measurements (14, 15). Statistical Analysis All statistical analyses were performed using statistical software (SAS Institute, version 9.2, Cary, NC, USA and MedCalc Software, version , Ostend, Belgium). A total of 255 ROI measurements of 51 patients from the first scanning session and 200 ROI measurements of 40 patients from the second scanning session were assessed. To investigate the interobserver reproducibility between observer A and B in T1ρ and T2 measurements from each mapping sequence, we used the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) with a two-way random model of absolute agreement. This evaluation included 371 measurements, including the entire data from the first (255 measurements from 51 patients) and second (200 measurements from 40 patients) scanning sessions and excluded the data concerning grade 5 discs (n = 84). To determine the test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements from each mapping sequence for both observer A and B, we used ICC using 163 measurements A B C Fig. 1. Representative image of region of interest (ROI) placement in T1ρ and T2 maps. Eexample of region of placement (ROI) in T1ρ (B) and T2 (C) mapping images of 33-year-old female subject with low back pain. On basis of sagittal T2-weighted MR image (A), rectangular ROI was placed at nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc in T1ρ mapping image (B). Once ROI placement in T1ρ mapping images was done for nucleus pulposus of intervertebral disc, simultaneous ROI placement at corresponding disc portion in T2 mapping images was automatically obtained. Area of ROI was 30 mm 2. A. T2-weighted 2D-FSE (two-dimensional fast spin-echo) images acquired in sagittal plane. B. T1ρ mapping image acquired in sagittal plane (L1 2, L2 3, L3 4, L4 5, L5 S1). C. T2 mapping image acquired in sagittal plane (L1 2, L2 3, L3 4, L4 5, L5 S1). 906
5 Reproducibility Comparison between T1ρ and T2 of Intervertebral Disc from 40 patients who underwent both the first and second scan sessions, excluding grade 5 discs (n = 37). Values of ICC < 0.40 were considered as indicating poor reproducibility, those within the range of as indicating fair to good reproducibility, and those > 0.75 as indicating excellent reproducibility (16). Comparison of the ICC values were done using Z test after acquisition of ICC values of T1ρ and T2 measurements based on Fischer s method (17). The mean T1ρ and T2 measurements of the lumbar intervertebral discs were compared between the degenerative and non-degenerative discs according to Pfirrmann grading system. Student t test was used to assess whether there was a significant difference in the mean measurements between degenerative and non-degenerative discs from each mapping sequences. Values of p < 0.05 were considered as indicating statistical significance. The entire continuous data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation (SD), along with the range of the values. RESULTS Evaluation of the ICC values for interobserver reproducibility of both measurements from the first and second scanning sessions indicated excellent reproducibility in the T1ρ measurements (ICC = 0.951) and fair to good reproducibility in the T2 measurements (ICC = 0.672; Table 2). The overall ICC values for test-retest reproducibility of the T1ρ measurements indicated excellent reproducibility in the measurements of both observers A (ICC = 0.922) and B (ICC = 0.914), while those of the T2 measurements indicated fair to good reproducibility in the measurements of both observers A (ICC = 0.672) and B (ICC = 0.628). ICCs of interobserver and test-retest reproducibility for T1ρ mapping were significantly higher than T2 mapping (p < 0.001). Overall, a total of 255 discs of 51 patients from the first scanning session and 200 discs of 40 patients from the second scanning session were assessed (grade 1 = 87, grade 2 = 81, grade 3 = 77, grade 4 = 126, and grade 5 = 84). Since the T1ρ and T2 values for each disc were inherently different, we considered the number of discs for correlation analysis of the T1ρ and T2 measurements according to the Pfirrmann s grade as 455 (255 and 200 measurements from the first and second scanning sessions, respectively). Among the 455 intervertebral discs from the images, after excluding grade 5 discs (n = 84), the discs were categorized into degenerative disc group (grades 3, 4, n = 168) and non-degenerative disc group (grades 1, 2, n = 203). There were significant differences between the mean values of the T1ρ and T2 measurements, with the mean values of the degenerative intervertebral disc group (mean T1ρ; 94.6 ± 40.1 ms, mean T2; 70.0 ± 33.1 ms) being significantly lower as compared to those of the non-degenerative disc group (mean T1ρ; ± 41.6 ms, mean T2; 77.4 ± 35.0 ms) (p < 0.001) (Fig. 2). In addition, we could observe inverse correlation between the T1ρ and T2 values of the discs and Pfirrmann grades of the corresponding discs (Fig. 3, Table 3). DISCUSSION The main goal of this study was to evaluate the reproducibility of MRI-based quantitative measurements of the lumbar intervertebral discs using T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences with 3T MRI. Our results showed excellent reproducibility of T1ρ measurement in the assessment of the IDD using 3T MRI, which was significantly higher than the reproducibility of T2 measurement in terms of both interobserver and test-retest reproducibility. Several studies have explored the reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 Table 2. Intraclass Correlation Coefficient (ICC) for Each Observer and Test-Retest Reproducibility between Observers ICC* of two observers (371 discs including first scan and second scan) ICC of observer A (167 discs from second scan of 40 patients) ICC of observer B (167 discs from second scan of 40 patients) T1 rho Mapping T2 Mapping P ( ) ( ) < ( ) ( ) < ( ) ( ) < All data were expressed as ICC (95% CI). *ICC was used to evaluate reproducibility of measurement from each mapping sequences between two observers (observer A and observer B), ICC was used to evaluate reproducibility of measurement from each mapping sequences between first and second scan in observer A, ICC was used to evaluate reproducibility of measurement from each mapping sequences between first and second scan in observer B. 907
6 Yoo et al. measurements obtained from the images acquired using the corresponding mapping sequences in the assessment of IDD (18-20). One such study reported excellent reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements in the intervertebral discs, with higher ICC values as compared to those obtained in our study (20). However, the results of the previous study were based on ROI measurements in the axial plane using a 1.5 T scanner; additionally, there was no indication whether diurnal variation was considered in their evaluation. Another report recently revealed excellent ICC value for T1ρ and T2* measurements in nuclei pulposi of the intervertebral discs by 3T MRI; however, the results of this study were based on single-observer measurement (19). In addition, the prior reproducibility studies in articular cartilage of knee (21, 22) revealed excellent short-term reproducibility for T1ρ and T2 quantification on 3T MRI employing health volunteers. However, to the best of our knowledge, our study is the first to assess both interobserver and test-retest reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements obtained from images acquired using each of the mapping sequences with 3T MRI in patients with IDD. In this study, the T1ρ measurements exhibited superior reproducibility than the T2 measurements, which was consistent with previously reported results in the meniscus (23), hip cartilage (24), and knee cartilage (21, 22) using 3T MRI. Several previous reports have noted that, the wider dynamic range of T1ρ than T2 could be a possible explanation for higher reproducibility of T1ρ measurements as compared to that of T2 (22, 23). Meanwhile, the reproducibility of the T2 measurements was found to be fair to good in terms of both interobserver and test-retest reproducibility. Previous studies on intervertebral discs reported high levels of reproducibility for T2 measurements comparable to that of T1ρ measurements (20). In contrast, relatively low ICC values of T2 measurements were observed in our study, which may be due to several reasons as follows: to achieve higher reproducibility, patient immobilization is important along with proper image acquisition (24); since the T2 mapping images were acquired after the acquisition of the T1ρ T1 rho T2 Non-degenerated disc T1 rho T2 Degenerated disc A B Fig. 2. Bar graphs of T1ρ and T2 measurements of each observer according to severity of intervertebral disc degeneration graded according to Pfirrmann grading system. Bar graphs of mean values of T1ρ and T2 measurements of nuclei pulposi graded according to Pfirmann grading system, measured by observers (A, B). Grade 5 (n = 84) discs were excluded. Mean measurements of two mapping sequence are depicted in different colors. Graphs indicate significantly lower T1ρ and T2 value in degenerative discs group as compared to those in non-degenerated disc group (p < 0.05). 0 T1 rho T2 Non-degenerated disc T1 rho T2 Degenerated disc 908
7 Reproducibility Comparison between T1ρ and T2 of Intervertebral Disc mapping images in the present study, it is hypothesized that higher chances of motion artifacts might have influenced the reproducibility of the T2 values; in this context, since image acquisition was performed using a 3T MRI scanner, the increased noise, greater SD of T2 values, and/or possible greater magnetization transfer effects that might have been produced, could have made the motion-related loss of reproducibility (24-26); and another plausible explanation is that the TE for T2 mapping might not have been long enough for acquisition of long-te images, which would have resulted in the underestimation of the T2 values, thus potentially affecting reproducibility. Since this study focused on the evaluation of reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements, we excluded the annulus fibrosus from the ROI measurement for the acquisition of reliable quantitative data due to the reason that in the degenerated disc groups (Pfirrmann grades 3, 4), it can be hard to distinguish the nucleus pulposus from the annulus fibrosus, which might affect precise ROI placement. For the same reason, we did not include Pfirrmann grade 5 intervertebral discs for evaluation in the present study. Considering the technical challenges involved in ROI Table 3. Mean Measurements of T1ρ and T2 According to Pfirrmann Grading System Mean Measurements of T1ρ Mapping (ms) Mean Measurements of T2 Mapping (ms) Grade ± 34.3 ( ) 99.3 ± 31.4 ( ) Grade ± 29.6 ( ) 81.3 ± 22.5 ( ) Grade ± 24.1 ( ) 63.1 ± 17.6 ( ) Grade ± 17.8 ( ) 45.4 ± 24.8 ( ) All continuous data are expressed as mean values ± standard deviation (range) T1 rho T2 T1 rho T2 T1 rho T2 T1 rho T2 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 0 T1 rho T1 rho T1 rho T1 rho T2 T2 T2 T2 Grade 1 Grade 2 Grade 3 Grade 4 A Fig. 3. Bar graphs of T1ρ and T2 measurements according to severity of intervertebral disc degeneration graded according to Pfirrmann grading system. There was inverse correlation between mean values of T1ρ and T2 measurements of discs graded according to Pfirrmann grading system, measured by observers (A, B). B 909
8 Yoo et al. placement in the nuclei pulposi of severely degenerated discs, the quantitative measurements in the present study are less likely to have been affected by noise. In addition, we have demonstrated that both T1ρ and T2 measurements in patients with IDD differed significantly between the degenerated and non-degenerated disc groups, which are in accordance with the results of previous studies (27). The T1ρ and T2 measurements obtained in our study were consistent with previously reported values (11, 27) in the intervertebral discs. We have also shown that measurements obtained from both T1ρ and T2 mapping sequences were significantly and inversely correlated with the Pfirrmann grades of intervertebral discs (7). There are several limitations to this study. First, there were variations in the sizes of the individual ROIs. However, considering the variations in disc height, the placement of ROIs of variable sizes at the nuclei pulposi of intervertebral discs appears to be a more precise way of evaluation. Second, we did not correlate our study results of T1ρ and T2 measurements with glycosaminoglycan or collagen water content of the intervertebral disc, since we focused only on the reproducibility of T1ρ and T2 measurements. Further research supported by histological and biochemical findings will be helpful for the validation of the T1ρ and T2 measurements of intervertebral discs in patients with IDD. In conclusion, T1ρ mapping was significantly higher than T2 mapping in terms of interobserver and test-retest reproducibility in the quantitative assessment of the nuclei pulposi of lumbar intervertebral discs. Therefore, we consider T1ρ mapping as a more reliable tool than T2 mapping for the detection of early changes as well as for monitoring degenerative changes in the nucleus pulposus in IDD by 3T MRI. REFERENCES 1. Luoma K, Riihimäki H, Luukkonen R, Raininko R, Viikari- Juntura E, Lamminen A. Low back pain in relation to lumbar disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2000;25: Hadjipavlou AG, Tzermiadianos MN, Bogduk N, Zindrick MR. The pathophysiology of disc degeneration: a critical review. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2008;90: Cassinelli EH, Hall RA, Kang JD. Biochemistry of intervertebral disc degeneration and the potential for gene therapy applications. Spine J 2001;1: Carl A, Ledet E, Yuan H, Sharan A. New developments in nucleus pulposus replacement technology. Spine J 2004;4(6 Suppl):325S-329S 5. Urban JP, Roberts S. Degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther 2003;5: Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, Hodler J, Boos N. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2001;26: Auerbach JD, Johannessen W, Borthakur A, Wheaton AJ, Dolinskas CA, Balderston RA, et al. In vivo quantification of human lumbar disc degeneration using T(1rho)-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur Spine J 2006;15 Suppl 3:S338-S Wang L, Regatte RR. T1ρ MRI of human musculoskeletal system. J Magn Reson Imaging 2015;41: Liess C, Lüsse S, Karger N, Heller M, Glüer CC. Detection of changes in cartilage water content using MRI T2-mapping in vivo. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2002;10: Surowiec RK, Lucas EP, Ho CP. Quantitative MRI in the evaluation of articular cartilage health: reproducibility and variability with a focus on T2 mapping. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2014;22: Zhu T, Ai T, Zhang W, Li T, Li X. Segmental quantitative MR imaging analysis of diurnal variation of water content in the lumbar intervertebral discs. Korean J Radiol 2015;16: Zobel BB, Vadalà G, Del Vescovo R, Battisti S, Martina FM, Stellato L, et al. T1ρ magnetic resonance imaging quantification of early lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration in healthy young adults. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2012;37: Yi JS, Cha JG, Han JK, Kim HJ. Imaging of herniated discs of the cervical spine: inter-modality differences between 64-Slice multidetector CT and 1.5-T MRI. Korean J Radiol 2015;16: Antoniou J, Epure LM, Michalek AJ, Grant MP, Iatridis JC, Mwale F. Analysis of quantitative magnetic resonance imaging and biomechanical parameters on human discs with different grades of degeneration. J Magn Reson Imaging 2013;38: Zhou Z, Jiang B, Zhou Z, Pan X, Sun H, Huang B, et al. Intervertebral disk degeneration: T1ρ MR imaging of human and animal models. Radiology 2013;268: Lin LI. A concordance correlation coefficient to evaluate reproducibility. Biometrics 1989;45: Fischer RA. Statistical methods for research workers. Biological monographs and manuals, 5th ed. Edinburgh: Stechert/Oliver and Boyd, Wang YX, Zhao F, Griffith JF, Mok GS, Leung JC, Ahuja AT, et al. T1rho and T2 relaxation times for lumbar disc degeneration: an in vivo comparative study at 3.0-Tesla MRI. Eur Radiol 2013;23: Zhang X, Yang L, Gao F, Yuan Z, Lin X, Yao B, et al. Comparison of T1ρ and T2* relaxation mapping in patients with different grades of disc degeneration at 3T MR. Med Sci Monit 2015;21: Menezes-Reis R, Salmon CE, Carvalho CS, Bonugli GP, Chung CB, Nogueira-Barbosa MH. T1ρ and T2 mapping of the intervertebral disk: comparison of different methods of segmentation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2015;36:
9 Reproducibility Comparison between T1ρ and T2 of Intervertebral Disc 21. Jordan CD, McWalter EJ, Monu UD, Watkins RD, Chen W, Bangerter NK, et al. Variability of CubeQuant T1ρ, quantitative DESS T2, and cones sodium MRI in knee cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2014;22: Li X, Wyatt C, Rivoire J, Han E, Chen W, Schooler J, et al. Simultaneous acquisition of T1ρ and T2 quantification in knee cartilage: repeatability and diurnal variation. J Magn Reson Imaging 2014;39: Rauscher I, Stahl R, Cheng J, Li X, Huber MB, Luke A, et al. Meniscal measurements of T1rho and T2 at MR imaging in healthy subjects and patients with osteoarthritis. Radiology 2008;249: Carballido-Gamio J, Link TM, Li X, Han ET, Krug R, Ries MD, et al. Feasibility and reproducibility of relaxometry, morphometric, and geometrical measurements of the hip joint with magnetic resonance imaging at 3T. J Magn Reson Imaging 2008;28: Nishii T, Sugano N, Sato Y, Tanaka H, Miki H, Yoshikawa H. Three-dimensional distribution of acetabular cartilage thickness in patients with hip dysplasia: a fully automated computational analysis of MR imaging. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2004;12: Akella SV, Regatte RR, Wheaton AJ, Borthakur A, Reddy R. Reduction of residual dipolar interaction in cartilage by spinlock technique. Magn Reson Med 2004;52: Blumenkrantz G, Zuo J, Li X, Kornak J, Link TM, Majumdar S. In vivo 3.0-tesla magnetic resonance T1rho and T2 relaxation mapping in subjects with intervertebral disc degeneration and clinical symptoms. Magn Reson Med 2010;63:
Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping
 TR_002 Technical Reports Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping Min A Yoon 1,*, Suk-Joo Hong 1, Chang Ho Kang 2, Baek Hyun Kim 3 1 Korea University
TR_002 Technical Reports Knee Articular Cartilage in an Asymptomatic Population : Comparison of T1rho and T2 Mapping Min A Yoon 1,*, Suk-Joo Hong 1, Chang Ho Kang 2, Baek Hyun Kim 3 1 Korea University
RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE
 In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
In Practice RECENT ADVANCES IN CLINICAL MR OF ARTICULAR CARTILAGE By Atsuya Watanabe, MD, PhD, Director, Advanced Diagnostic Imaging Center and Associate Professor, Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Teikyo
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging
 Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Added value of MR myelography using 3D COSMIC sequence in the diagnosis of lumbar canal stenosis: comparison with routine MR imaging Poster No.: C-1099 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Scientific Exhibit
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration
 Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
Meniscus T2 Relaxation Time at Various Stages of Knee Joint Degeneration Richard Kijowski, Michael Fazio, Benjamin Beduhn, and Fang Liu Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin School of Medicine
With axial loading during MRI diurnal T2- value changes in lumbar discs are neglectable: a cross sectional study
 Torén et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:25 DOI 10.1186/s12891-018-1930-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE With axial loading during MRI diurnal T2- value changes in lumbar discs are neglectable: a cross sectional
Torén et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:25 DOI 10.1186/s12891-018-1930-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE With axial loading during MRI diurnal T2- value changes in lumbar discs are neglectable: a cross sectional
Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Assessing Cervical Spinal Canal Compression
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI Assessment of Cervical Spinal Canal Compression Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee-Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Eun-Chul Chung 1 So-Yeon
IVDD is a leading cause of lumbar spine related low back
 Published July 28, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2556 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Niu J. Yang R. Wang S. Dang E.X. Wu Y. Guo MR Imaging Assessment of Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Age-Related Changes: Apparent
Published July 28, 2011 as 10.3174/ajnr.A2556 ORIGINAL RESEARCH G. Niu J. Yang R. Wang S. Dang E.X. Wu Y. Guo MR Imaging Assessment of Lumbar Intervertebral Disk Degeneration and Age-Related Changes: Apparent
Further exploration of MRI techniques for liver T1rho quantification
 Original Article Further exploration of MRI techniques for liver T1rho quantification Feng Zhao 1, Jing Yuan 1,2, Min Deng 1, Pu-Xuan Lu 3, Anil T. Ahuja 1, Yi-Xiang J. Wang 1 1 Department of Imaging and
Original Article Further exploration of MRI techniques for liver T1rho quantification Feng Zhao 1, Jing Yuan 1,2, Min Deng 1, Pu-Xuan Lu 3, Anil T. Ahuja 1, Yi-Xiang J. Wang 1 1 Department of Imaging and
Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ORIGINAL ARTICLE SPINE SURGERY AND RELATED RESEARCH Signal intensity changes of the posterior elements of the lumbar spine in symptomatic adults Kosuke Sugiura, Toshinori Sakai, Fumitake Tezuka, Kazuta
ASJ. Magnification Error in Digital Radiographs of the Cervical Spine Against Magnetic Resonance Imaging Measurements. Asian Spine Journal
 Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
Asian Spine Journal Asian Spine Clinical Journal Study Asian Spine J 2013;7(4):267-272 Magnification http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.4.267 error in cervical spine 267 Magnification Error in Digital
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis
 In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
In vivo diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) of articular cartilage as a biomarker for osteoarthritis Jose G. Raya 1, Annie Horng 2, Olaf Dietrich 2, Svetlana Krasnokutsky 3, Luis S. Beltran 1, Maximilian F.
Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings
 Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings Poster No.: C-0539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Berg 1, O. Gjertsen 2, C. Hellum 2, G. F. Neckelmann 1, L. G. Johnsen 3, G. E. Eide
Reliability of change in lumbar MRI findings Poster No.: C-0539 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: L. Berg 1, O. Gjertsen 2, C. Hellum 2, G. F. Neckelmann 1, L. G. Johnsen 3, G. E. Eide
dgemric Effectively Predicts Cartilage Damage Associated with Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
Riccardo Lattanzi 1,2 Catherine Petchprapa 2 Daniele Ascani 1 Roy I. Davidovitch 3 Thomas Youm 3 Robert J. Meislin 3 Michael. Recht 2 1 The Bernard and Irene Schwartz Center for Biomedical Imaging, New
MRI of Cartilage. D. BENDAHAN (PhD)
 MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
MRI of Cartilage D. BENDAHAN (PhD) Centre de Résonance Magnétique Biologique et Médicale UMR CNRS 7339 Faculté de Médecine de la Timone 27, Bd J. Moulin 13005 Marseille France david.bendahan@univ-amu.fr
Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
 SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
SPINE Volume 26, Number 17, pp 1873 1878 2001, Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc. Magnetic Resonance Classification of Lumbar Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Christian W. A. Pfirrmann, MD,* Alexander
Sensitivity and Specificity in Detection of Labral Tears with 3.0-T MRI of the Shoulder
 Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
Magee and Williams MRI for Detection of Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Clinical Observations C M E D E N T U R I C L I M G I N G JR 2006; 187:1448 1452 0361 803X/06/1876 1448 merican Roentgen Ray
MAJOR PAPER. Introduction. Young Han Lee 1, Seok Hahn 1, Eunju Kim 2, and Jin-Suck Suh 1*
 Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 371 378, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2015-0055 MAJOR PAPER Introduction Fat-suppressed MR Imaging of the Spine for Metal Artifact Reduction at 3T: Comparison of STIR
Magn Reson Med Sci, Vol. 15, No. 4, pp. 371 378, 2016 doi:10.2463/mrms.mp.2015-0055 MAJOR PAPER Introduction Fat-suppressed MR Imaging of the Spine for Metal Artifact Reduction at 3T: Comparison of STIR
MRI DWI/ADC signal predicts shrinkage of lumbar disc herniation after O2 O3 discolysis
 Original article MRI DWI/ADC signal predicts shrinkage of lumbar disc herniation after O2 O3 discolysis The Neuroradiology Journal 0(00) 1 7! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
Original article MRI DWI/ADC signal predicts shrinkage of lumbar disc herniation after O2 O3 discolysis The Neuroradiology Journal 0(00) 1 7! The Author(s) 2015 Reprints and permissions: sagepub.co.uk/journalspermissions.nav
NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY
 A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
A-056 NEW SUBTRACTION ALGORITHMS FOR EVALUATION OF BREAST LESIONS ON DYNAMIC CONTRAST ENHANCED MR MAMMOGRAPHY So Hee Cho, M.D., Byung Gil Choi, M.D., Hak Hee Kim, M.D., Euy Neyng Kim, M.D., Bum-soo Kim,
Relationship of Facet Tropism with Degeneration and Stability of Functional Spinal Unit
 Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.624 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(5): 624-629, 2009 Relationship of Facet Tropism with Degeneration and Stability of Functional Spinal Unit
Original Article DOI 10.3349/ymj.2009.50.5.624 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 50(5): 624-629, 2009 Relationship of Facet Tropism with Degeneration and Stability of Functional Spinal Unit
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate
 Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
Quantitative Analysis of Vascular Canals in Vertebral Endplate Kristine Tan 1, Won C. Bae, PhD 1, Tomonori Yamaguchi, MS 1,2, Kelli Xu, BS 1, Iris Shieh, BS 1, Jade He, BS 1, Robert L. Sah, MD, ScD 1,
How Much Tesla Is Too Much?
 How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
How Much Tesla Is Too Much? Johnny U. V. Monu, MB, BS; MSc Professor of Radiology and Orthopedics University of Rochester School of Medicine Rochester, New York Historical Timeline Clinical Imaging 1970
T1rho and T2 relaxation times of the normal adult knee meniscus at 3T: analysis of zonal differences
 Takao et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:202 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1560-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access T1rho and T2 relaxation times of the normal adult knee meniscus at 3T: analysis of zonal
Takao et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2017) 18:202 DOI 10.1186/s12891-017-1560-y RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access T1rho and T2 relaxation times of the normal adult knee meniscus at 3T: analysis of zonal
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison between Pre-Contrast and Post-Contrast Images
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/.3348/kjr.14.15.1.123 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 05-83 Korean J Radiol 14;15(1):123-129 T2 Values of Femoral Cartilage of the Knee Joint: Comparison
The Clinical Correlation of a New Practical MRI Method for Grading Cervical Neural Foraminal Stenosis Based on Oblique Sagittal Images
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Park et al. MRI for Grading Cervical Foraminal Stenosis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Hee Jin Park 1,2 Sam Soo Kim 2 Chul Hee Han 1 So Yeon Lee 1 Eun
Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative MRI
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2016;20:224-230 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2016.20.4.224 Fatty Degeneration and Atrophy of Rotator Cuffs: Comparison of Immediate Postoperative MRI with Preoperative
The effects of acute loading on T1rho and T2 relaxation times of tibiofemoral articular cartilage
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1557e1563 The effects of acute loading on T1rho and T2 relaxation times of tibiofemoral articular cartilage R.B. Souza yz *, C. Stehling x, B.T. Wyman k, M.-P. Hellio
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage 18 (2010) 1557e1563 The effects of acute loading on T1rho and T2 relaxation times of tibiofemoral articular cartilage R.B. Souza yz *, C. Stehling x, B.T. Wyman k, M.-P. Hellio
Correspondence should be addressed to Zhihua Han; and Chun Chen;
 Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2018, Article ID 6843053, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6843053 Research Article Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluation
Hindawi BioMed Research International Volume 2018, Article ID 6843053, 7 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/6843053 Research Article Apparent Diffusion Coefficient of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Evaluation
Classification of intervertebral disk degeneration using quantitative T2 relaxation time measurements
 Classification of intervertebral disk degeneration using quantitative T2 relaxation time measurements Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. A. Nagy 1, I. Juhasz 1,
Classification of intervertebral disk degeneration using quantitative T2 relaxation time measurements Poster No.: C-1685 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. A. Nagy 1, I. Juhasz 1,
UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works
 UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works Title High-resolution morphologic and ultrashort time-to-echo quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7670k1rf
UC San Diego UC San Diego Previously Published Works Title High-resolution morphologic and ultrashort time-to-echo quantitative magnetic resonance imaging of the temporomandibular joint Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7670k1rf
of the lumbar facet joints there
 Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Skeletal Radiol (1999) 28:215±219 International Skeletal Society 1999 A R T I C L E Dominik Weishaupt Marco Zanetti Norbert Boos Juerg Hodler MR imaging and CT in osteoarthritis of the lumbar facet joints
Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging in Pediatric Bell s Palsy
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2015;19:162-167 http://dx.doi.org/10.13104/imri.2015.19.3.162 Quantitative Analysis of the Facial Nerve Using Contrast-Enhanced Three Dimensional FLAIR-VISTA Imaging
Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR Imaging
 Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Provläsningsexemplar / Preview TECHNICAL REPORT ISO/TR 16379 First edition 2014-03-01 Tissue-engineered medical products Evaluation of anisotropic structure of articular cartilage using DT (Diffusion Tensor)-MR
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35124 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Wokke, Beatrijs Henriette Aleid Title: Muscle MRI in Duchenne and Becker muscular
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Effects of Music intervention on Functional connectivity. Supplemental Information
 Yang et al. 0 The Effects of Music intervention on Functional connectivity strength of Brain in Schizophrenia Supplemental Information Mi Yang,#, Hui He #, Mingjun Duan,, Xi Chen, Xin Chang, Yongxiu Lai,
Yang et al. 0 The Effects of Music intervention on Functional connectivity strength of Brain in Schizophrenia Supplemental Information Mi Yang,#, Hui He #, Mingjun Duan,, Xi Chen, Xin Chang, Yongxiu Lai,
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Evaluation of normal ankle cartilage by MRI T1ρ mapping
 Evaluation of normal ankle cartilage by MRI T1ρ mapping Ryuhei Katsui 1 MD Akira Taniguchi 2 MD, Ph. D Munehiro Ogawa 2 MD, Ph. D Hiroaki Kurokawa 2 MD Norihiro Samoto 3 MD, Ph. D Yasuhito Tanaka 2 MD,
Evaluation of normal ankle cartilage by MRI T1ρ mapping Ryuhei Katsui 1 MD Akira Taniguchi 2 MD, Ph. D Munehiro Ogawa 2 MD, Ph. D Hiroaki Kurokawa 2 MD Norihiro Samoto 3 MD, Ph. D Yasuhito Tanaka 2 MD,
Research Paper: Measuring Dimensions of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs in Normal Subjects
 Research Paper: Measuring Dimensions of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs in Normal Subjects Seyed Mohammad Hadi Mirab 1, Mohammad Barbarestani 1, Seyyed Mohammad Tabatabaei 2, Soodeh Shahsavari 3, Mohammad
Research Paper: Measuring Dimensions of Lumbar Intervertebral Discs in Normal Subjects Seyed Mohammad Hadi Mirab 1, Mohammad Barbarestani 1, Seyyed Mohammad Tabatabaei 2, Soodeh Shahsavari 3, Mohammad
Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point Using the Cricoid Cartilage as Landmark Through X-ray Review
 Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Original Article Korean J Pain 2011 September; Vol. 24, No. 3: 141-145 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2011.24.3.141 Estimation of Stellate Ganglion Block Injection Point
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
MRI of Bucket-Handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1
 MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
MRI of ucket-handle Te a rs of the Meniscus of the Knee 1 Joon Yong Park, M.D., Young-uk Lee M.D., Eun-Chul Chung M.D., Hae-Won Park M.D., E u n - Kyung Youn M.D., Shin Ho Kook, M.D., Young Rae Lee, M.D.
Original Policy Date
 MP 6.01.39 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Medical Policy Section Radiology Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
MP 6.01.39 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Medical Policy Section Radiology Issue 12:2013 Original Policy Date 12:2013 Last Review Status/Date Reviewed with literature search/12:2013 Return to Medical
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping
 The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
The Characteristic Findings to Assess Meniscal Healing Status After Meniscal Repair on MRI-T2 Mapping Shinya Yamasaki, MD, PhD 1,2, Yusuke Hashimoto, MD, PhD 2, Takuya Kinoshita, MD 2, Kazuya Nishino,
Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status
 # 154134 Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status Jun-Gu Park, Seong-Il Bin, Jong-Min Kim, Bum Sik Lee Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical
# 154134 Survivorship After Meniscal Allograft Transplantation According To Articular Cartilage Status Jun-Gu Park, Seong-Il Bin, Jong-Min Kim, Bum Sik Lee Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Asan Medical
Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils
 Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
Clinical Orthopedic Imaging Musculoskeletal Imaging at 3T with Simultaneous Use of Multipurpose Loop Coils Elena Ferrer 1 ; Rafael Coronado Santos 2 1 Radiology Department, Clínica Creu Blanca, Barcelona,
A Method to Monitor Local Changes in MR Signal Intensity in Articular Cartilage: A Potential Marker for Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis
 A Method to Monitor Local Changes in MR Signal Intensity in Articular Cartilage: A Potential Marker for Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis Josephine H. Naish 1, Graham Vincent 2, Mike Bowes 2, Manish
A Method to Monitor Local Changes in MR Signal Intensity in Articular Cartilage: A Potential Marker for Cartilage Degeneration in Osteoarthritis Josephine H. Naish 1, Graham Vincent 2, Mike Bowes 2, Manish
High Field MR of the Spine
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego 3T for MR Applications Advantages High Field MR of the Spine Increased signal-to-noise Better fat suppression Increased enhancement with gadolinium
High Resolution T1r Mapping of In Vivo Human Knee Cartilage at 7T
 High Resolution T1r Mapping of In Vivo Human Knee Cartilage at 7T Anup Singh 1,2 *, Mohammad Haris 1,3, Kejia Cai 1,4, Feliks Kogan 1, Hari Hariharan 1, Ravinder Reddy 1 1 CMROI, Department of Radiology,
High Resolution T1r Mapping of In Vivo Human Knee Cartilage at 7T Anup Singh 1,2 *, Mohammad Haris 1,3, Kejia Cai 1,4, Feliks Kogan 1, Hari Hariharan 1, Ravinder Reddy 1 1 CMROI, Department of Radiology,
High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 1, pp 38~42, 2007 High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History Kun-Woo Park*, Kwang-Sup Song, Jae Yoon Chung*, Jin-Man Choi*,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 1, pp 38~42, 2007 High-Intensity Zone on L-spine MRI: Clinical Relevance and Association with Trauma History Kun-Woo Park*, Kwang-Sup Song, Jae Yoon Chung*, Jin-Man Choi*,
Repeatability of 2D FISP MR Fingerprinting in the Brain at 1.5T and 3.0T
 Repeatability of 2D FISP MR Fingerprinting in the Brain at 1.5T and 3.0T Guido Buonincontri 1,2, Laura Biagi 1,3, Alessandra Retico 2, Michela Tosetti 1,3, Paolo Cecchi 4, Mirco Cosottini 1,4,5, Pedro
Repeatability of 2D FISP MR Fingerprinting in the Brain at 1.5T and 3.0T Guido Buonincontri 1,2, Laura Biagi 1,3, Alessandra Retico 2, Michela Tosetti 1,3, Paolo Cecchi 4, Mirco Cosottini 1,4,5, Pedro
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging
 Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
Effect of intravenous contrast medium administration on prostate diffusion-weighted imaging Poster No.: C-1766 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit J. Bae, C. K. Kim, S.
T2, T2*, ute. Yeo Ju Kim. Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
 SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
SY28-1 T2, T2*, ute Yeo Ju Kim Radiology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea T2 relaxation times relate to the rate of transverse magnetization decay, caused by the loss of phase coherence induced
Personalized Solutions. MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides
 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides 2 Personalized Solutions MRI Protocol for PSI and Signature Guides Purpose and Summary This protocol is applicable for the Zimmer Biomet
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Outline Coils, Patient Positioning Acquisition Parameters, Planes and Pulse Sequences Knee Arthrography Normal
Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff Tears: Comparison with Standard Oblique Sagittal Images
 Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Journal of Magnetics 22(3), 519-524 (2017) ISSN (Print) 1226-1750 ISSN (Online) 2233-6656 https://doi.org/10.4283/jmag.2017.22.3.519 Modified Oblique Sagittal Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Rotator Cuff
Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Description
 Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Subject: Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Page: 1 of 6 Last Review Status/Date: June 2015 Positional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Description Positional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows imaging
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee:
 Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
Why Talk About Technique? MRI of the Knee: Part 1 - Imaging Techniques Mark Anderson, M.D. University of Virginia Health Sciences Center Charlottesville, Virginia Always had an interest teach our fellows
This presentation is the intellectual property of the author. Contact them at for permission to reprint and/or distribute.
 MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
MRI of the Knee Jennifer Swart, M.D. Musculoskeletal Radiology South Texas Radiology Group Financial Disclosure Dr. Jennifer Swart has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose.
High-Resolution 3D Cartilage Imaging with IDEAL SPGR at 3 T
 Siepmann et al. Knee MRI with IDEL SPGR Musculoskeletal Imaging Technical Innovation David. Siepmann 1 Jeff McGovern 2 Jean H. rittain 3 Scott. Reeder 1,4 Siepmann D, McGovern J, rittain JH, Reeder S Keywords:
Siepmann et al. Knee MRI with IDEL SPGR Musculoskeletal Imaging Technical Innovation David. Siepmann 1 Jeff McGovern 2 Jean H. rittain 3 Scott. Reeder 1,4 Siepmann D, McGovern J, rittain JH, Reeder S Keywords:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22: (2005)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 22:788 793 (2005) Original Research STIR vs. T1-Weighted Fat-Suppressed Gadolinium- Enhanced MRI of Bone Marrow Edema of the Knee: Computer-Assisted Quantitative Comparison
Association between Sacral Slanting and Adjacent Structures in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 17;9:57-62 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.17.9.1.57 Association between Sacral Slanting and Adjacent Structures in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 17;9:57-62 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.17.9.1.57 Association between Sacral Slanting and Adjacent Structures in Patients with Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
21 year-old collegiate rower: R/O labral tear
 Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
Hip MRI Primer AOSSM 2014 Hollis G. Potter, MD Chair, Department of Radiology & Imaging The Coleman Chair, MRI Research Hospital for Special Surgery Professor of Radiology Weill Medical College of Cornell
A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 3, NUMBER 2, SPRING 2002 A quality control program for MR-guided focused ultrasound ablation therapy Tao Wu* and Joel P. Felmlee Department of Radiology,
6/23/2009. Inversion Recovery (IR) Techniques and Applications. Variations of IR Technique. STIR, FLAIR, TI and TI Null. Applications of IR
 The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
The Anatomy of Basic R Pulse Sequences Inversion Recovery () Techniques and Applications Chen Lin, PhD Indiana University School of edicine & Clarian Health Partners agnetization Preparation Section Chemical
Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience
 African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
African Journal of Nephrology (2009) 13: 26-30 Original Article AJN Diffusion weighted MRI in evaluation of transplanted kidney: Preliminary clinical experience Mohamed Abou El-Ghar; M.D, Huda Refaie;
1Pulse sequences for non CE MRA
 MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
MRI: Principles and Applications, Friday, 8.30 9.20 am Pulse sequences for non CE MRA S. I. Gonçalves, PhD Radiology Department University Hospital Coimbra Autumn Semester, 2011 1 Magnetic resonance angiography
Diagnosis of Disc Herniation Based on Classifiers and Features Generated from Spine MR Images
 Diagnosis of Disc Herniation Based on Classifiers and Features Generated from Spine MR Images Jaehan Koh, Vipin Chaudhary a and Gurmeet Dhillon, MD b a Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University
Diagnosis of Disc Herniation Based on Classifiers and Features Generated from Spine MR Images Jaehan Koh, Vipin Chaudhary a and Gurmeet Dhillon, MD b a Department of Computer Science and Engineering, University
High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1881 1886, November/December 2001 Technical Note High-Sensitivity Coil Array for Head and Neck Imaging: Technical Note Roland G. Henry, Nancy J. Fischbein, William P. Dillon, Daniel
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Oak foundation for donating the 3T Siemens Verio scanner. Board of directors BBH and Frh Hospitals for supporting the
 Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Knee pain and inflammation in the infrapatellar fat pad estimated by conventional and dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a crosssectional study
Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Basics of MRI in practice. Generation of MR signal. Generation of MR signal. Spin echo imaging. Generation of MR signal
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Protons aligned with B0 magnetic filed Longitudinal magnetization - T1 relaxation Transverse magnetization - T2 relaxation Signal measured in the transverse plane Basics of MRI
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans
 Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
Assessment of Adipose Tissue from Whole Body 3T MRI Scans Ting Song 1, Jing An 2, Qun Chen 2, Vivian Lee 2, Andrew Laine 1 1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Columbia University, New York, NY, USA
International Cartilage Repair Society
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) 17, 12e18 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Osteoarthritis Research Society International. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.05.016 T1r relaxation time of the meniscus and
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2009) 17, 12e18 Published by Elsevier Ltd on behalf of Osteoarthritis Research Society International. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2008.05.016 T1r relaxation time of the meniscus and
T2 Mapping issues of the knee articular cartilage at 3 Tesla
 Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 6(7) pp. 71-79 July 2017 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full Length
Basic Research Journal of Medicine and Clinical Sciences ISSN 2315-6864 Vol. 6(7) pp. 71-79 July 2017 Available online http//www.basicresearchjournals.org Copyright 2015 Basic Research Journal Full Length
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending
 A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
A Computational Model of Annulus Fiber Deformation in Cervical Discs During In Vivo Dynamic Flexion\Extension, Rotation and Lateral Bending William Anderst, Mara Palmer, Joon Lee, William Donaldson, James
Usefulness of Unenhanced MRI and MR Arthrography of the Shoulder in Detection of Unstable Labral Tears
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Unenhanced MRI and MR rthrography for Unstable Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Thomas 1,2 T Keywords: labral tear, MRI, shoulder DOI:10.2214/JR.14.14262
Prevalence of Meniscal Radial Tears of the Knee Revealed by MRI After Surgery
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.207.114 on 12/22/17 from IP address 46.3.207.114. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Thomas Magee 1 Marc Shapiro David Williams Received
Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee
 Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Skeletal Radiol (2009) 38:761 769 DOI 10.1007/s00256-009-0683-0 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Comparative study of imaging at 3.0 T versus 1.5 T of the knee Scott Wong & Lynne Steinbach & Jian Zhao & Christoph Stehling
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment
 Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Kinematic Cervical Spine Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Low-Impact Trauma Assessment 1 Seminars in Ultrasound, CT, and MRI June 2009; Volume 30; Number 3; pp. 168-173 Vincenzo Giuliano, MD, Antonio Pinto,
Methods of MR Fat Quantification and their Pros and Cons
 Methods of MR Fat Quantification and their Pros and Cons Michael Middleton, MD PhD UCSD Department of Radiology International Workshop on NASH Biomarkers Washington, DC April 29-30, 2016 1 Disclosures
Methods of MR Fat Quantification and their Pros and Cons Michael Middleton, MD PhD UCSD Department of Radiology International Workshop on NASH Biomarkers Washington, DC April 29-30, 2016 1 Disclosures
144 Gübitz R et al. Influence of Age, Fortschr Röntgenstr 2018; 190: Schlussfolgerung Steigendes Alter korrelierte signifikant.
 Musculoskeletal System Influence of Age, BMI, Gender and Lumbar Level on T1ρ Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Lumbar Discs in Healthy Asymptomatic Adults Einfluss von Alter, Geschlecht, BMI und lumbalem Level
Musculoskeletal System Influence of Age, BMI, Gender and Lumbar Level on T1ρ Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Lumbar Discs in Healthy Asymptomatic Adults Einfluss von Alter, Geschlecht, BMI und lumbalem Level
Liver Fat Quantification
 Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Liver Fat Quantification Jie Deng, PhD, DABMP Department of Medical Imaging May 18 th, 2017 Disclosure Research agreement with Siemens Medical Solutions 2 Background Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) WCPCG 2014
 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences 159 ( 2014 ) 743 748 WCPCG 2014 Differences in Visuospatial Cognition Performance and Regional Brain Activation
Preliminary Experience with 3-Tesla MRI and Cushing s Disease
 TECHNICAL NOTE Preliminary Experience with 3-Tesla MRI and Cushing s Disease LouisJ.Kim,M.D., 1 Gregory P. Lekovic, M.D., Ph.D., J.D., 1 William L.White, M.D., 1 and John Karis, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT Because
TECHNICAL NOTE Preliminary Experience with 3-Tesla MRI and Cushing s Disease LouisJ.Kim,M.D., 1 Gregory P. Lekovic, M.D., Ph.D., J.D., 1 William L.White, M.D., 1 and John Karis, M.D. 2 ABSTRACT Because
Does T2 mapping of the posterior annulus fibrosus indicate the presence of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation? A 3.0 Tesla magnetic resonance study
 Eur Spine J (2017) 26:877 883 DOI 10.1007/s00586-016-4873-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does T2 mapping of the posterior annulus fibrosus indicate the presence of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation? A 3.0 Tesla
Eur Spine J (2017) 26:877 883 DOI 10.1007/s00586-016-4873-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Does T2 mapping of the posterior annulus fibrosus indicate the presence of lumbar intervertebral disc herniation? A 3.0 Tesla
Low back pain is the leading cause of disability worldwide,
 SPINE Volume 43, Number 1, pp E592 E6 ß 218 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. ll rights reserved. Cartilage Endplate Thickness Variation Measured by Ultrashort Echo-Time MRI Is ssociated With djacent Disc Degeneration
SPINE Volume 43, Number 1, pp E592 E6 ß 218 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. ll rights reserved. Cartilage Endplate Thickness Variation Measured by Ultrashort Echo-Time MRI Is ssociated With djacent Disc Degeneration
Differentiation of Osteophytes and Disc Herniations in Spinal Radiculopathy Using Susceptibility-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differentiation of Osteophytes and Disc Herniations in Spinal Radiculopathy Using Susceptibility-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Yvonne Yi-Na Bender, MD,* Gerd Diederichs, MD,* Thula
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Differentiation of Osteophytes and Disc Herniations in Spinal Radiculopathy Using Susceptibility-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging Yvonne Yi-Na Bender, MD,* Gerd Diederichs, MD,* Thula
Magic angle artifact in MRI of the patellar ligament: preliminary comparison between conventional and weightbearing
 Magic angle artifact in MRI of the patellar ligament: preliminary comparison between conventional and weightbearing MRI Poster No.: C-1017 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Piccazzo
Magic angle artifact in MRI of the patellar ligament: preliminary comparison between conventional and weightbearing MRI Poster No.: C-1017 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Piccazzo
Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine
 NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular Volumetry in Late Postoperative Patients with Tetralogy of Fallot
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:71-77 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.71 Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:71-77 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.71 Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular
imri 2017;21:
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2017;21:154-161 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2017.21.3.154 Diagnostic Performance of Diffusion- Weighted Steady-State Free Precession in Differential Diagnosis of
New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis
 Original Article New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/30862:2366 Radiology Section BINOJ VARGHESE v, ARUN C BABU ABSTRACT Introduction:
Original Article New Magnetic Resonance Imaging Grading System for Lumbar Neural Foramina Stenosis DOI: 10.7860/IJARS/2018/30862:2366 Radiology Section BINOJ VARGHESE v, ARUN C BABU ABSTRACT Introduction:
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 07 Page July 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i7.84 Anatomical Differences Between T2 WI FSE
Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the
 Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
Supplementary Methods Materials & Methods Subjects Twelve right-handed subjects between the ages of 22 and 30 were recruited from the Dartmouth community. All subjects were native speakers of English,
Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal Cord without Evidence of Spinal Cord Herniation or an Intradural Mass
 Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
Original Article Musculoskeletal Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.733 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):733-738 Focal Anterior Displacement of the Thoracic Spinal
