Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
|
|
|
- Willis Flowers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria Tolls, MD; J. Curtis Nickel, MD Department of Urology, Queen s University, Kingston, ON, Canada Cite as: Can Urol Assoc J 2018;12(1):E Published online December 1, 2017 Abstract Introduction: We sought to determine if patients perceptions of success or failure of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/ BPS) therapies proposed in treatment guidelines align with the evidence from available clinical trial treatment data. Methods: A total of 1628 adult females with a self-reported diagnosis of IC completed a web-based survey in which patients described their perceived outcomes with the therapies they were exposed to. Previously published literature, used in part to develop IC/ BPS guidelines, provided the clinical trial data outcomes. Patientreported outcomes were compared to available clinical trial outcomes and published treatment guidelines. Results: Based on patient perceived outcomes (benefit:risk ratio), the most treatments were opioids, phenazopyridine, and alkalizing agents, with amitriptyline and antihistamines reported as moderately. The only surgical procedure with any ness was electrocautery of Hunner s lesions. In order of efficacy reported in the literature, the therapies for IC/BPS with predicted superior outcomes should be: cyclosporine A, amitriptyline, hyperbaric oxygen, pentosan polysulfate plus subcutaneous heparin, botulinum toxin A plus hydrodistension, and L-arginine. While some of the guideline s aligned with patientreported ness data, there was a general disconnect between guidelines and ness reported in clinical practice. Conclusions: There is a disconnect between real-world patient perceived ness of IC/BPS treatments compared to the efficacy reported from clinical trial data and subsequent guidelines developed from this efficacy data. Optimal therapy must include the best evidence from clinical research, but should also include real-life clinical practice implementation and ness. Introduction Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) is a urological pain condition associated with urinary storage symptoms that, once diagnosed, is managed with a variety of therapeutic strategies. Treatment has generally been empirical, but mostly based on theoretical and evidence-based considerations. The development of treatment guidelines, a strategy to improve outcomes by developing a standardized treatment approach, is shaped by clinical trial efficacy data. 1-5 In real-world practice, urologists are encouraged to employ efficacy data and guidelines to prescribe therapies and treatments for patients suffering from IC/BPS. There is, however, limited information on the ness of IC/BPS treatments and patients perceptions of these treatments in real-life clinical practice. The purpose of this study was to determine if treatments IC/BPS patients perceived to be in a web-based questionnaire aligned with clinical trial efficacy data and associated published guidelines in IC/BPS. Methods Clinical efficacy considerations were abstracted from a recent comprehensive review/meta-analysis performed by one of the authors (JCN) and colleagues 4 and guideline updates for the treatment of IC/BPS from the European Association of Urology (EAU), American Urological Association (AUA), Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists/British Society of Urogynecologists (RCOG/BSUG), and Canadian Urological Association (CUA). 1-4 Clinical ness was estimated from a patient-centred, web-based questionnaire. An initial analysis has been published and describes the diagnostic and therapeutic experience of the first 750 patients completing the survey. 6 The questionnaire was promoted by IC/BPS support groups and queried the impact of therapies (beneficial and deleterious effects) using a total of 202 unvalidated questions. Standard and common IC/ BPS therapies, such as oral medications, intravesical therapies, and surgery, were addressed and patients were asked whether symptoms were improved, deteriorated, or were unchanged. The questionnaire was designed and implemented by two of the authors (EK, KZ) and the collected data independently analyzed by the Queen s University group (AL, VT, JCN). Effectiveness was estimated based on 2018 Canadian Urological Association E1
2 Lusty et al benefit:risk ratio (risk being defined as worsening of symptoms) reported by patients (benefit:risk ratio not = 1:1 or <1; mildly = >1:1 but <5:1; moderately = >5:1 but <10:1; markedly = >10:1). Informed consent was obtained online. Data was collected from Descriptive statistics were calculated to compare the efficacy, guideline s, and reallife ness of the various treatments. Results One thousand six hundred and twenty-eight women with a self-reported diagnosis of IC/BPS responded to the survey. Women reported from 48 different countries with a mean age of 39.6 years (standard deviation [SD] ± 12.8 years); 95.9% were Caucasian, 1.4% were African American, and 0.6% were Asian/Pacific Islander. Therapies achieving an improvement rate of over 50% included opioids (405/621; 65.2%), phenazopyridine (390/638; 61.1%), intravesical heparin (50/89; 56.2%), alkalinizing agents (365/660; 55.3%), and pentosan polysulfate (359/698; 51.4%); however, in order of ness (based on benefit:risk ratio), marked ness was only achieved with opioids (27:1), alkalinizing agents (22.8:1), and phenazopyridine (13.9:1). Moderate ness was reported for amitriptyline (9.2:1) and antihistamines (6.5:1). Cimetidine, intravesical heparin, and intravesical hyaluronic acid were associated with mild ness, while electrocautery, pentosan polysulfate, intravesical lidocaine, and dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO) showed mild but equivocal ness. Hydrodistension and antibiotics were not (although antibiotics were associated with a 49.4% improvement rate, they also had worsening of symptoms, reported by 47.1% of patients). Gabapentinoids, major surgery, and urethral dilation were not. Table 1 describes the number of patients exposed to each treatment, the improvement and worsening of symptoms reported, and the subsequent benefit:risk ratio for each reported treatment modality. Table 2 summarizes the interventions proven to be efficacious based on clinical trial data (the data was based on pain, frequency, urgency, and Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index [ICSI] symptoms). Table 2 also summarizes the s (and grade of ) for the EAU, AUA, RCOG/BSUG, and CUA guidelines compared to patient-perceived ness based on the benefit:risk ratio determined for each intervention. 1-4 Discussion The most recent and accepted definition of IC/BPS from the 2014 AUA guidelines states it is an unpleasant sensation (pain, pressure, discomfort), perceived to be related to the urinary bladder, associated with lower urinary tract Table 1. Patient-reported treatment ness Treatment Improved Worse Benefit:risk ratio Opioids 65.5% (405/621) 2.4% (15/621) 27:1 Alkalinizing 55.3% (365/660) 2.4% (16/660) 22.8:1 agents Phenazopyridine 61.1% (390/638) 4.4% (28/638) 13.9:1 Amitriptyline 45.5% (231/512) 4.9% (25/512) 9.2:1 Antihistamines 35.1% (203/579) 5.4% (31/579) 6.5:1 Cimetidine 27.6% (54/196) 8.7% (17/196) 3.2:1 56.2% (50/89) 19.1% (17/89) 2.9:1 heparin 31.9% (22/69) 14.5% (10/69) 2.2:1 hyaluronic acid Electrocautery 26.4% (31/121) 16.5% (20/121) 1.6:1 Pentosan 51.4 % 34.5% (241/698) 1.5:1 polysulfate (359/698) lidocaine 33.3% (6/18) 27.8% (5/18) 1.2:1 Antibiotics 49.4% (674/1364) DMSO 47.1% (642/1364)-N symptoms of more than six weeks duration, in the absence of infection or other identifiable cause. 2,4 IC/BPS is a disease complex that is diagnosed after the exclusion of an infectious or neoplastic process. 2,4 In reality, it appears to take a significant amount of time for patients to obtain a diagnosis. 4 Theoretically, once the diagnosis has been made, a strategy to flow patients through a treatment algorithm, such as those based on the EAU, AUA, RCOG/BSUG, or CUA guidelines, should be the optimal way to manage this condition. 1-4 This can only be predicted if the evidencebased efficacy data mirrors the actual ness seen in the real world. Clinical trial data would predict that the most beneficial therapies would include cyclosporine A, amitriptyline, hyperbaric oxygen, pentosan polysulfate plus subcutaneous heparin, botulinum toxin A plus hydrodistension, and L-arginine, in no particular order. 4 Guideline s from the EAU, AUA, RCOG/BSUG, and CUA follow as best they can with the clinical evidence modified by expert opinion. 1-4 Our survey of patients perceptions of what treatments they actually receive and how much benefit (or harm) they experience does not always align well with either the clinical trial efficacy data or the guideline s. 1:1 36.9% (148/401) 32.7% (131/401) 1.1:1 Hydrodistension 27.9% (218/780) 27.6% (215/780) 1:1 Gabapentanoids 26.1% (58/222) 4.6% (99/222) 0.6: 1 Major surgery 14.3% (28/196) 41.3% (81/196) 0.3:1 Urethral dilation 22.5% (115/512) 22.3% (114/512) 0.1:1 BoNT/A intravesical injection BoNT/A: botulinum toxin A; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide. N not sufficient N not sufficient N not sufficient E2
3 Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Table 2. IC/BPS treatment: Efficacy, guidelines, and ness IC/BPS treatment s Efficacy* (effect) EAU grade of AUA grade and use Opioids NR Should be initiated with a multimodal therapy regimen RCOG/BSUG grade of CUA grade of Effectiveness** NR NR Markedly Alkalinizing agents NR NR NR NR Markedly Phenazopyridine NR NR NR NR Markedly Analgesics C 1 st line Recommended*** NR Amitriptyline Small-great (ICSI, pain, urgency, and **** Cimetidine Small (urgency + Hydroxyzine (±PPS) Small (ICSI + pain + urgency + A 2 nd line; B B Optional; B Moderately NR 2 nd line; B B Optional; B Mildly A 2 nd line; C Not recommended; B Optional; C (with allergic phenotype) heparin NR 2 nd line; C D Recommended; C Mildly B NR B Optional; C Mildly hyaluronic acid Electrocautery Recommended (for Hunner s lesion) 3 rd line; C Recommended*** Recommended; B (for Hunner s lesion) Mildly Pentosan polysulfate lidocaine (+ sodium bicarbonate) Small (pain)***** A 2 nd line; B Not recommended; A Optional; D Mildly Medium (urgency); NR 2 nd line; B B Recommended; B Mildly Small (ICSI + pain + Antibiotics Small ( NR NR Not NR Not recommended*** DMSO A 2 nd line; C C Recommended; B Not Hydrodistension Small (ICSI) C 3 rd line; C D Optional; C Not Gabapentanoids NR NR NR Optional; C (for Not neuropathic pain) Major surgery Inconclusive NR 6 th line; C D Optional; C Not (severe refractory/ last resort) Urethral dilation NR NR NR NR Not BoNT/A (+ hydrodistension) Great (pain); Medium (ICSI); Small ( Cyclosporine A Great (ICSI + pain + chondrointin sulfate Hyperbaric oxygen Small (ICSI + pain + Great (ICSI + pain); Medium (; Small (urgency) BCG Medium (ICSI + pain); Small (ICSI + pain + urgency + NR 4 th line; C B Optional; C A 5 th line; C D Optional; C (last resort with inflammation) B NR D Optional; D NR NR NR Optional; refractory to other options NR NR Not recommended*** Not recommended; B *Based on size of impact on specific symptoms. **Benefit:risk ratio=not (1:1 or <1); mildly (>1:1 but <5:1); moderately (>5:1 but <10:1); markedly (>10:1). ***Best practice based on the clinical experience of the guidelines development group. ****Efficacy dose dependent. *****Great (pain + when combined with subcutaneous heparin. BCG: Bacillus Calmette Guérin; BoNT/A: botulinum toxin A; DMSO: dimethylsulfoxide; ICSI: Interstitial Cystitis Symptoms Index; : insufficient data; NR: no. E3
4 Lusty et al In this study, the terms efficacy and ness are separate entities. Efficacy is defined as the power to produce a desired result and ness is the degree to which a treatment is successful in producing a desired result. 7 This study clearly shows there is a disconnect between real-world, patient-perceived ness of IC/BPS treatments compared to the efficacy clinical trial data. Patients perceived the following treatments to be : opioids, alkalinizing agents, phenazopyridine, amitriptyline, and antihistamines. heparin and pentosan polysulfate were associated with reports of high improvement rates, but also of worsening of symptoms, making them only moderately. Antibiotics were associated with almost half of the patients reporting improvement, but also half reporting worsening of symptoms and, therefore, based on our benefit:risk ratio, would be considered not. Based on benefit and risk, the other treatments examined showed either equivocal results or no ness. The only therapies that seem to align between this reported ness and published efficacy include amitriptyline (with the strongest alignment), pentosan polysulfate, hydroxyzine, and/or combinations. Most of the treatments noted to have the best efficacy from the review of published literature were associated with either equivocal patient-perceived ness or these therapies worsened patients symptoms. When comparing the patient-perceived ness to the most recent EAU, AUA, RCOG/BSUG, and CUA guidelines, hydroxyzine, amitriptyline, and pentosan polysulfate were included as Grade A s by the EAU and Grade B and C s by the AUA and CUA, respectively. 1,2,4 The RCOG/BSUG endorsed amitriptyline with a Grade B ; however, did not advise hydroxyzine or pentosan polysulfate treatments, with Grade B and A s, against both treatments, respectively. 3 The intravesical therapies that patients perceived to have equivocal results, including intravesical DMSO, lidocaine and bladder hydrodistension, were listed as Grade A and B s in the EAU, but Grade C and D s in the AUA and CUA guidelines 1,2,4 and ranged from B, C, and D s in the RCOG/BSUG guidelines. 3 This highlights not only the differences between guidelines based on the same available efficacy data, but also some disconnect between patient-perceived ness and the s that major urological associations promote. The most glaring example of this disconnect is with opioid therapy. It is certainly interesting that opioids are not only one of the most prescribed medications for IC/BPS, but also perceived to be one of the most according to patients exposed to this treatment. Opioids are not recommended in the EAU guidelines, while the AUA guidelines suggest that opioid therapy can be considered for multimodal pain therapy and list six essential principles that should be followed if/ when a narcotic is prescribed to a patient for pain management. 1,2 The RCOG/BSUG suggests opioids should be used with caution in patients with long-term chronic pain and early referral to a pain clinic for patients with refractory symptoms, while the CUA guidelines do not discuss opioid treatment. 3,4 Opioid therapy in IC/BPS, which has been very poorly studied, needs to be rigorously evaluated to determine its role for pain management. Why is there such a disconnect between efficacy (and guideline s based on efficacy) and ness? Most of the therapies evaluated in large, randomized, placebo-controlled trials are performed on promising approaches that industry hopes to commercialize. These studies have very rigid inclusion and exclusion criteria that typically enrol only a very small percentage of patients who are screened. The efficacy data may be appropriate in the population studied, but may not reflect the actual patient population in clinical practice. Those treatments that are deemed successful are sometimes financially out of reach for the average patient. Similarly, some treatments recommended in the guidelines (e.g., neuromodulation) are not in general use or available in the real world. The therapies most often used by clinicians are usually generic and funding for evaluating such treatments is almost non-existent. Some of the best approaches include conservative management, such as diet manipulation, 8 exercise, 9 improving coping skills, and even cognitive behavioural therapy; 9 all treatments never rigorously evaluated. One recent exception is pelvic floor physiotherapy in which the benefits suggested by early, small, uncontrolled studies have now been confirmed by NIH randomized, controlled trials. 10,11 Physiotherapy is now being prescribed more frequently for IC/BPS patients with pelvic floor dysfunctional pain and we would like to believe that a contemporary survey would show a correlation between patients perceived ness and clinical trial efficacy. 10,11 We cannot abandon our evidence-based approach to developing treatment algorithms and guidelines. We certainly cannot develop these strategies based on uncontrolled data collection of patients perceptions; however, to be truly, there must be some alignment between what we determine in our limited clinical trials and what the patients are actually telling us. We must incorporate patient input of what they value in terms of treatments and outcomes in future treatment algorithm development. To accomplish this, we must try and collect real-life clinical data in this difficult condition using validated real-life clinical practice methodology, including prospective, observational, and/or registry trials. The limitations to this study are fairly obvious. We are comparing apples (efficacy) and oranges (ness) with the guidelines attempting to provide a balance between the two (expert opinion). The web-based questionnaire included questions that were never validated and was based on E4
5 Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome patient self-identified diagnosis, with all the sampling bias that this carries with it (including selection bias and lack of control patients). We were unable to provide clinical confirmation regarding diagnosis, clinical phenotyping (e.g., Hunner s lesion), treatment actually prescribed, or therapeutic response, but rather relied on self-diagnosis and patients perception of response. Some of the results are difficult to interpret, as few patients received some treatments listed (for example, botulinum toxin A and cyclosporine A), resulting in a small sample size. The questionnaire is dated and may influence this disconnect between patient perceptions and the more recent guidelines, but would not overly influence the comparison to efficacy since most data presented was available at the time of the questionnaire. We also have no information as to how the various treatments were applied in clinical practice (e.g., duration or order of treatment modalities in individual patients); however, real-life clinical practice in this enigmatic condition is messy and does not follow the niceties of recommended algorithms. We believe that this questionnaire, with its acknowledged limitations, reflects the IC/BPS patients real-life experience with the treatments we, as clinicians, regularly administer. Conclusion There is a disconnect between IC/BPS treatment guidelines based on clinical trial data efficacy and ness in realworld clinical practice. Optimal therapy must include the best evidence from clinical trial research, but should also include patient experience from real-life practice. Competing interests: Dr. Nickel has been a consultant for Astellas, Auxillium, Eli Lilly, Farr Labs, Ferring, GSK, Pfizer, Taris Biomedical, Tribute, and Trillium Therapeutics; a lecturer for Astellas and Eli Lilly; and has participated in clinical trials supported by Eli Lilly, GSK, J&J, Pfizer, and Taris Biomedical. The remaining authors report no competing personal or financial interests. This paper has been peer-reviewed. References 1. Fall M, Baranowski AP, Elneil S, et al. EAU guidelines on chronic pelvic pain. Eur Urol 2010;57: Hanno PM, Erickson DA, Moldwin RM, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: AUA guideline amendment. J Urol 2015;193: juro Tirlapur SA, Birch JV, Carberry CL, et al. Management of bladder pain syndrome. BJOG 2016;124:e Cox A, Golda N, Nadeau G, et al. CUA guideline: Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/ bladder pain syndrome. Can Urol Assoc J 2016;10: Giannantoni A, Bini V, Dmochowski R, et al. Contemporary management of the painful bladder: A systematic review. Eur Urol 2012;61: Hill JR, Isom-Batz G, Panagopoulos G, et al. Patient perceived outcomes of treatments used for interstitial cystitis. Urology 2007;7: Merriam-Webster. Available at Accessed March 22, Friedlander JI, Shorter B, Moldwin RM. Diet and its role in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS) and comorbid conditions. BJU Int 2012;109: Whitmore KE. Complementary and alternative therapies as treatment approaches for interstitial cystitis. Rev Urol 2002;4:S FitzGerald MP, Anderson RU, Potts J, et al. Randomized, multicentre feasibility trial of myofascial physical therapy for the treatment of urological chronic pelvic pain syndromes. J Urol 2013;189:S FitzGerald MP, Payne CK, Lukacz ES, et al. Randomized, multicentre clinical trial of myofascial physical therapy in women with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome and pelvic floor tenderness. J Urol 2012;187: Correspondence: Dr. J. Curtis Nickel, Department of Urology, Queen s University, Kingston, ON, Canada; jcn@queensu.ca E5
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
1 of 8 3/2/15 9:22 PM
 Close window Guideline Title Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Bibliographic Source(s) Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, FitzGerald MP, Forrest
Close window Guideline Title Diagnosis and treatment of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome. Bibliographic Source(s) Hanno PM, Burks DA, Clemens JQ, Dmochowski RR, Erickson D, FitzGerald MP, Forrest
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines
 Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Review Article Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines Amita Jain To cite: Jain A. Bladder Pain Syndrome Current Concepts and Management Guidelines. Pan Asian J Obs Gyn 2018;1(1):18-23.
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2017
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Basing a Treatment Strategy on Randomized Placebo Controlled Trials 2012
 Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Basing a Treatment Strategy on Randomized Placebo Controlled Trials 2012 J. Curtis Nickel Professor of Urology, Queen s University Canada CIHR Canada Research
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome: Basing a Treatment Strategy on Randomized Placebo Controlled Trials 2012 J. Curtis Nickel Professor of Urology, Queen s University Canada CIHR Canada Research
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails
 Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence?
 Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Functional Bladder Problems
 european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
european urology supplements 6 (2007) 710 716 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Functional Bladder Problems Emmanuel Chartier-Kastler * Department of Urology,
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. February 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC)
 Article ID: WMC002428 ISSN 2046-1690 Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC) Corresponding Author: Dr. Daniele Porru, Consultant Urologist, Divisione Urologia, IRCCS
Article ID: WMC002428 ISSN 2046-1690 Results of Omalizumab in Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis (BPS/IC) Corresponding Author: Dr. Daniele Porru, Consultant Urologist, Divisione Urologia, IRCCS
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015
 International Journal of Urology (2016) 23, 542--549 doi: 10.1111/iju.13118 Guideline Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015 Yukio Homma, 1 Tomohiro Ueda,
International Journal of Urology (2016) 23, 542--549 doi: 10.1111/iju.13118 Guideline Clinical guidelines for interstitial cystitis and hypersensitive bladder updated in 2015 Yukio Homma, 1 Tomohiro Ueda,
Interstitial Cystitis and Pelvic Pain: Looking Beyond the Bladder
 Interstitial Cystitis and Pelvic Pain: Looking Beyond the Bladder Kenneth M. Peters, MD Professor and Chairman of Urology Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Royal Oak, Michigan Disclosures
Interstitial Cystitis and Pelvic Pain: Looking Beyond the Bladder Kenneth M. Peters, MD Professor and Chairman of Urology Oakland University William Beaumont School of Medicine Royal Oak, Michigan Disclosures
Management of Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Management of ladder Pain Syndrome Green-top Guideline No. 70 RCOG/SUG Joint Guideline ecember 2016 Please cite this paper as: Tirlapur SA, irch JV, Carberry CL, Khan KS, Latthe PM, Jha S, Ward KL, Irving
Management of ladder Pain Syndrome Green-top Guideline No. 70 RCOG/SUG Joint Guideline ecember 2016 Please cite this paper as: Tirlapur SA, irch JV, Carberry CL, Khan KS, Latthe PM, Jha S, Ward KL, Irving
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA Injections for Refractory Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
Toxins 2015, 7, 2860-2871; doi:10.3390/toxins7082860 Article OPEN ACCESS toxins ISSN 2072-6651 www.mdpi.com/journal/toxins O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Predicts the Treatment Outcome for OnabotulinumtoxinA
2018 Canadian Urological Association guideline for Peyronie s disease and congenital penile curvature
 2018 Canadian Urological Association guideline for Peyronie s disease and congenital penile curvature Anthony J. Bella, Jay C. Lee, Ethan D. Grober, Serge Carrier, Francois Benard, Gerald B. Brock Originally
2018 Canadian Urological Association guideline for Peyronie s disease and congenital penile curvature Anthony J. Bella, Jay C. Lee, Ethan D. Grober, Serge Carrier, Francois Benard, Gerald B. Brock Originally
LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke
 LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke Department of Urology Global Congress on LUTD, Rome, 26 th June 2015 Disclosures Consultant, speaker, trial participant and/or research grants
LUTS after TURP: How come and how to manage? Matthias Oelke Department of Urology Global Congress on LUTD, Rome, 26 th June 2015 Disclosures Consultant, speaker, trial participant and/or research grants
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease Jefferies Healthcare Conference
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease 2016 Jefferies Healthcare Conference Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease 2016 Jefferies Healthcare Conference Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Intravesical Botox Injections
 Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
Intravesical Botox Injections Department of Urology Patient Information What What is is Botox? Botox? Botox or Botulinum Type-A is toxin produced by bacteria called Clostridium Botulinum. It is given intravesically
WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS?
 Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
Patient Information WHAT IS INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS? Interstitial Cystitis (IC) is a condition resulting in recurring discomfort or pain in the bladder and the surrounding pelvic region. Its cause is unknown,
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE?
 PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
Treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome
 International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 31S (2008) S112 S116 Treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome J. Curtis Nickel Department of Urology, Queen s University, Kingston General
International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 31S (2008) S112 S116 Treatment of chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome J. Curtis Nickel Department of Urology, Queen s University, Kingston General
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria. Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017
 Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN SYNDROME. Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Assistant Professor, University of Calgary
 CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN SYNDROME Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Assistant Professor, University of Calgary Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN SYNDROME Jay Lee, MD, FRCSC Clinical Assistant Professor, University of Calgary Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU)
 SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
SOCIETY FOR URODYNAMICS & FEMALE UROLOGY (SUFU) SUFU 2010 Winter Meeting, 23-27 February 2010 Tampa-St. Petersburg, Florida, USA Reviewer: Jane Meijlink This year s SUFU Winter Meeting included many interesting
Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review
 eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
eau-ebu update series 4 (2006) 47 61 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Efficacy of Interstitial Cystitis Treatments: A Review Gilles Karsenty, Walid AlTaweel,
Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain. Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital
 Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital What is PPP? Chronic Pelvic Pain Pelvic Pain Pelvic Floor/ Pelvic Pain Syndrome Pelvic
Role of Physiotherapy in the Management of Persistent Pelvic Pain Brigitte Fung Physiotherapist Kwong Wah Hospital What is PPP? Chronic Pelvic Pain Pelvic Pain Pelvic Floor/ Pelvic Pain Syndrome Pelvic
Vague symptoms. Unexpected flares.
 PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION We need to expand the differential diagnosis for chronic pelvic pain to include pelvic myofascial pain Amie Kawasaki, MD Dr. Kawasaki is Fellow in the Division of Female Pelvic
PELVIC FLOOR DYSFUNCTION We need to expand the differential diagnosis for chronic pelvic pain to include pelvic myofascial pain Amie Kawasaki, MD Dr. Kawasaki is Fellow in the Division of Female Pelvic
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, March 2008, Milan, Italy
 A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
A review of the 23 rd Congress of the European Association of Urology, 26-29 March 2008, Milan, Italy by Jane Meijlink The 23 rd congress of the EAU was an unprecedented success with some 14,000 participants,
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Interstitial Cystitis
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
Management of High Grade, T1 Bladder Cancer Douglas S. Scherr, M.D.
 Management of High Grade, T1 Bladder Cancer Douglas S. Scherr, M.D. Assistant Professor of Urology Clinical Director, Urologic Oncology Weill Medical College-Cornell University Estimated new cancer cases.
Management of High Grade, T1 Bladder Cancer Douglas S. Scherr, M.D. Assistant Professor of Urology Clinical Director, Urologic Oncology Weill Medical College-Cornell University Estimated new cancer cases.
Investor & Analyst Event. February 9, 2018 David Main President & CEO
 Investor & Analyst Event February 9, 2018 David Main President & CEO Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that
Investor & Analyst Event February 9, 2018 David Main President & CEO Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that
Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis
 Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
Review Article Review of intravesical therapies for bladder pain syndrome/ interstitial cystitis Kristina Cvach 1, Anna Rosamilia 2 1 Mercy Hospital for Women, Melbourne, Australia; 2 Monash Medical Centre,
Mapping of Pain Phenotypes in Female Patients with Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis and Controls
 EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 1188 1194 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Pelvic Pain Mapping of Pain Phenotypes in Female Patients with Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial
EUROPEAN UROLOGY 62 (2012) 1188 1194 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Pelvic Pain Mapping of Pain Phenotypes in Female Patients with Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial
Original Article - Infection/Inflammation. Ömer Gülpınar, Ahmet Hakan Haliloğlu 1, Mehmet İlker Gökce, Nihat Arıkan
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354 Original Article - Infection/Inflammation http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.4111/kju.2014.55.5.354&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2014-05-16
Dr. Krithika Doshi. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical?
 Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
Minimally Invasive Therapies for Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome
 Curr Urol Rep (2010) 11:276 285 DOI 10.1007/s11934-010-0120-x Minimally Invasive Therapies for Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Salim A. Wehbe & Jennifer Y. Fariello & Kristene Whitmore Published online: 7
Curr Urol Rep (2010) 11:276 285 DOI 10.1007/s11934-010-0120-x Minimally Invasive Therapies for Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome Salim A. Wehbe & Jennifer Y. Fariello & Kristene Whitmore Published online: 7
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
Diagnosis and classification of CPP
 GUIDELINEs ON Chronic Pelvic Pain (Text update March 2009) M. Fall (chairman), A.P. Baranowski, S. Elneil, D. Engeler, J. Hughes, E. J. Messelink, F. Oberpenning, A.C. de C. Williams 218 Chronic Pelvic
GUIDELINEs ON Chronic Pelvic Pain (Text update March 2009) M. Fall (chairman), A.P. Baranowski, S. Elneil, D. Engeler, J. Hughes, E. J. Messelink, F. Oberpenning, A.C. de C. Williams 218 Chronic Pelvic
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Novel research approaches for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: thinking beyond the bladder
 Review Article Novel research approaches for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: thinking beyond the bladder Chris Mullins, Tamara Bavendam, Ziya Kirkali, John W. Kusek National Institute of Diabetes
Review Article Novel research approaches for interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: thinking beyond the bladder Chris Mullins, Tamara Bavendam, Ziya Kirkali, John W. Kusek National Institute of Diabetes
University of Bristol - Explore Bristol Research
 Drake, M., Lewis, A. L., & Lane, A. (2016). Urodynamic Testing for Men with Voiding Symptoms Considering Interventional Therapy: The Merits of a Properly Constructed Randomised Trial. European Urology,
Drake, M., Lewis, A. L., & Lane, A. (2016). Urodynamic Testing for Men with Voiding Symptoms Considering Interventional Therapy: The Merits of a Properly Constructed Randomised Trial. European Urology,
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information
 Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Interstitial Cystitis (Chronic Pelvic Pain) Consultation Information Round Rock Jollyville Westlake Central office: Phone 512-231-1444 Fax 512-231-1470 www.urologyteam.com Rev June 2017 What is Interstitial
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
Inflammation Pathways
 Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Inflammation Pathways Siam Oottamasathien, MD FAAP FACS Associate Professor of Surgery and Pediatric Urology Research Associate Professor of Medicinal Chemistry Director of Pediatric Urology Basic Science
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS
 The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS Frank Van der Aa Leuven, Belgium This symposium is supported by Astellas Pharma Europe Ltd., including speaker honoraria and production of materials the slides
The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS Frank Van der Aa Leuven, Belgium This symposium is supported by Astellas Pharma Europe Ltd., including speaker honoraria and production of materials the slides
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
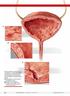 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
ESSIC 2008 Annual Meeting Rome
 Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
Bladder Pain Syndrome Developing a History Protocol Normal Bladder Function Depends on Suzy, Arul, Andrei, Arvind Integrity of the macroscopic and microscopic anatomy of the bladder Central nervous system
REVIEW. International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome
 Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Review Article Role of cystoscopy and hydrodistention in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome Gisela Ens, Gustavo L. Garrido Voiding Dysfunction and Urodynamic Section, Division
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males
 Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Lower Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) in Males Clinical presentation For patients in care homes see UTI in adults where IV Antibiotics in the community may be appropriate (under development) History and
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also
 Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
FROM THE EDITOR - Peter de Jong
 SAUGA NEWSLETTER SA UROGYNAECOLOGICAL SOCIETY AUTUMN 2014 V O L U M E 2 I S S U E 2 FROM THE EDITOR - Peter de Jong Female genital cosmetic surgery : what is it all about? In this issue we examine the
SAUGA NEWSLETTER SA UROGYNAECOLOGICAL SOCIETY AUTUMN 2014 V O L U M E 2 I S S U E 2 FROM THE EDITOR - Peter de Jong Female genital cosmetic surgery : what is it all about? In this issue we examine the
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome and Male Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis: How Are They Related?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.15 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):15-21 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Introduction. Original Article
 Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
