Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
|
|
|
- August Fitzgerald
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department of Urology, Wake Forest University, Winston-Salem, North Carolina (RJE), The Arthur Smith Institute for Urology, The North Shore-Long Island Jewish Healthcare System, New Hyde Park, New York (RMM), and Pfizer, Ltd., Sandwich, United Kingdom (NC, AD, IWM, DS) Abbreviations and Acronyms AE adverse event ECG electrocardiogram FAS full analysis set GRA global response assessment IC interstitial cystitis ICSI Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index IV intravenous MVV mean voided volume NGF nerve growth factor NRS numerical rating scale OA osteoarthritis PPS pentosan polysulfate sodium PVR post-void residual rfas restricted FAS Submitted for publication July 7, Study received institutional review board approval. Supported by Pfizer, Inc. Supplementary material for this article can be obtained at * Correspondence: Department of Urology, Wake Forest University, 140 Charlois Blvd., Winston-Salem, North Carolina (telephone: ; FAX: ; revans@ wfubmc.edu). Financial interest and/or other relationship with Pfizer, Ortho-McNeil, Watson, Allergan, Astellas and the Interstitial Cystitis Association. Financial interest and/or other relationship with Pfizer, Taris, Lipella and Ortho-McNeil. Financial interest and/or other relationship with Pfizer. For other articles on a related topic see pages 1946 and Purpose: In this randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled phase 2 study we investigated tanezumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that specifically inhibits nerve growth factor as a treatment for interstitial cystitis pain. Materials and Methods: Patients with interstitial cystitis received a single intravenous dose of 200 g/kg tanezumab or placebo. Patients recorded daily pain scores (on an 11-point numerical rating scale) 7 days before attending study visits and completed a urinary symptom diary for 3 of those days. Patients also completed the Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index questionnaire and a global response assessment. The primary end point was change in average daily numerical rating scale pain score from baseline to week 6. Secondary end points included global response assessment, Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index score, micturition and urgency episode frequency per 24 hours, and mean voided volume per micturition. The incidence of adverse events was also assessed. Results: A total of 34 patients received tanezumab and 30 received placebo. At week 6 tanezumab produced a significant reduction from baseline in average daily pain score vs placebo (treatment difference [LS mean, 90% CI] was 1.4 [ 2.2, 0.5]). A significantly higher proportion of patients on tanezumab responded as improved in the global response assessment and tanezumab also significantly reduced urgency episode frequency vs placebo. Tanezumab had no significant effect on Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index score, micturition frequency or mean voided volume per micturition. The most common adverse events were headache (tanezumab 20.6%, placebo 16.7%) and paresthesia (tanezumab 17.6%, placebo 3.3%). Conclusions: Tanezumab has shown preliminary efficacy in the treatment of pain associated with interstitial cystitis. Key Words: tanezumab; nerve growth factor; cystitis, interstitial; antibodies; pain INTERSTITIAL cystitis is characterized by increased urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia and chronic pain. 1,2 The Rand Interstitial Cystitis Epidemiology study estimated that 3 to 8 million women in the United States have IC symptoms, suggesting that IC may be a substantial burden on public health. 3 The etiology of IC is unknown but likely involves a process of bladder epithelial dysfunction, mast cell degranulation and neurogenic inflammation. 4 Studies have suggested that in IC there is a defect in the urothelium allowing irritants to leak into the bladder wall causing inflammation, tissue /11/ /0 Vol. 185, , May 2011 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION EDUCATION AND RESEARCH, INC. DOI: /j.juro
2 TANEZUMAB FOR TREATMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS 1717 irritation and injury, mast cell degranulation and afferent nerve depolarization. 5,6 Afferent nerve depolarization would result in the release of nociceptive neurotransmitters, leading to further mast cell degranulation and activation of nerve terminals. 4 During degranulation mast cells release proinflammatory agents including NGF. NGF is a neurotrophin which is essential for the differentiation and survival of sensory and sympathetic neurons during development. However, in adults it has been suggested that NGF, through the sensitization of nociceptive neurons, is important in the generation and potentiation of pain following tissue injury and inflammation. 7 Inhibition of NGF signaling reduces pain-like behavioral responses in a number of animal models of visceral pain Tanezumab is a humanized anti-ngf monoclonal antibody that binds with high affinity and specificity to NGF, preventing it from interacting with receptors on nociceptive neurons. We investigated the use of tanezumab for the treatment of moderate to severe IC pain in a phase 2 trial. The primary objective was to evaluate the efficacy, safety and tolerability of single dose 200 g/kg IV tanezumab for the treatment of IC pain, and the secondary objective was to evaluate tanezumab for the treatment of other IC symptoms. MATERIALS AND METHODS Study Population Participants had moderate to severe IC defined as scores of 13 or greater on the Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency symptom questionnaire 11 and 7 or more on the O Leary- Sant ICSI. 12 Exclusion criteria were IC symptoms for less than 6 months, PVR volume greater than 200 ml and history of allergic or anaphylactic reaction to mabs or IgG fusion proteins. Patients remained on existing nonprohibited oral medications as background therapy for IC symptoms provided these had been administered for 3 or more months before screening. In the event of inadequate pain relief or worsening IC symptoms patients were permitted to take acetaminophen. Study Design This study was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all International Conference on Harmonization Good Clinical Practice guidelines. The study protocol and amendments were reviewed and approved by the institutional review boards of each participating study center. Each subject provided written informed consent before study participation. This was a randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind, multicenter, parallel group, proof of concept study. The study was conducted between March 2008 and April 2009 in 23 study centers across the United States. After screening patients were enrolled in a 2-week run-in period during which they recorded daily pain scores (measured using a 0 to 10 NRS more than 7 days before the randomization visit) and daily urinary symptoms for 3 of those days. Patients who had completed 5 or more days of the daily symptom diary with a mean average daily pain NRS score of 4 or more and those with a mean micturition frequency of 8 or more per 24 hours were eligible for randomization. Patients were stratified according to baseline mean average daily pain score (4 to less than 7 and 7 or greater) and randomized using an automated tele-randomization system to receive a single IV dose of 200 g/kg tanezumab or placebo. Patients were followed for 16 weeks after treatment with study visits at weeks 2, 4, 6, 10 and 16. At each visit patients received a symptom diary and were instructed to record average daily NRS pain score each day for the 7 days before the subsequent study visit and urinary symptoms for 3 of those days. Efficacy Assessments The primary efficacy end point was the change from baseline to week 6 in average daily NRS pain score. Secondary efficacy end points included change in average daily NRS pain score at weeks 2, 4, 10 and 16, and GRA, ICSI score and micturition diary variables. The GRA questionnaire, measuring patient reported overall response to treatment compared with the start of the trial, was completed at weeks 6 and 16 or at early termination. Patients who responded as moderately or markedly improved were defined as treatment responders. The ICSI, a 4-question composite symptom score of urgency, frequency, nocturia and pain 12 was completed at all post-screening visits or at early termination. Micturition variables, including micturition and urinary urgency episode frequency per 24 hours and MVV per micturition, were derived from urinary symptom data collected at all post-screening visits. The dose of tanezumab and primary time for analysis were chosen by quantitative modeling of dose concentration response characteristics from a previously conducted trial of tanezumab in patients with OA. Although maximal efficacy was expected at week 6, the observation period of up to 16 weeks after treatment allowed the assessment of safety and tolerability over more than 5 half-lives for tanezumab clearance. Safety Assessments AEs were documented at each study visit. Safety assessments included vital signs and an ECG. Previous studies suggest that an anti-ngf antibody is unlikely to cross the blood-brain barrier and that the effects of tanezumab are limited to the peripheral nervous system. 13,14 A full neurological examination was performed by the study investigator at each study visit (including mental status, cranial nerves, motor, sensory, coordination, gait and reflexes). If an AE suggestive of new or worsening peripheral neuropathy or dysesthesia, paresthesia, allodynia, hypoesthesia or hyperesthesia was reported, or if the investigator detected clinically significant abnormalities, the patient was referred to a neurologist. PVR urine volume assessments were performed using a transabdominal ultrasound at visits 1, 3, 5 and 7. Statistical Analyses To achieve the planned sample size of 48 patients and accounting for a 25% estimated dropout rate, approximately 64 patients were to be recruited into the study. The
3 1718 TANEZUMAB FOR TREATMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS sample size was selected to provide a 90% CI of width 1.5 around the mean difference in the change in average daily pain score from baseline to week 6 for tanezumab vs placebo with 80% probability (assuming a SD of 2.8). As is suitable for an exploratory study, an estimation approach rather than a formal hypothesis testing approach was used as it requires fewer subjects while ensuring that appropriate efficacy conclusions can be made. Changes from baseline to week 6 in average daily pain score were analyzed using an ANCOVA model. Conclusions were based on adjusted mean treatment differences and corresponding CIs. A clinically significant treatment difference for the primary end point was considered to be a change from baseline in average daily NRS pain score of 1 or more point over placebo when the accompanying 90% CI does not overlap zero. Similar analyses were used to analyze ICSI score and the micturition diary variables. The GRA results were analyzed using proportional odds analysis. Odds ratios and corresponding 90% CIs of the estimated odds of patients responding after treatment with tanezumab vs placebo were calculated. The proportion of treatment responders based on a 30% or greater and 50% or greater reduction from baseline in average daily pain NRS score was also analyzed using logistic regression with the results presented as ORs and 90% CIs. Efficacy analyses were based on the rfas which included all randomized patients who had provided diary data for 4 or more days within the predefined diary windows at baseline and at the post-randomization visit. A sensitivity analysis was also conducted on the FAS, which only required diary data for 1 or more days after randomization. RESULTS Patient Disposition Overall 64 patients were randomized and received treatment. Of these patients 52 (81.3%) completed the study (fig. 1). Patients were mostly female (89%), 21 to 85 years old, with an average daily pain NRS score of 6.4 in the tanezumab group and 5.9 in the placebo group. Efficacy At week 6 tanezumab produced a clinically significant reduction from baseline in average daily pain score vs placebo (fig. 2). The upper limit of the 90% CI does not contain zero, implying statistical significance at the 1-sided 5% level of significance. Similar results were obtained from the analyses of the FAS. Overall 57% of patients on tanezumab vs 35% of those on placebo had a 30% or greater reduction in pain score from baseline, and 36% (tanezumab) vs 9% (placebo) had a 50% or greater reduction. Based on a definition of 50% or greater reduction from baseline in pain score, OR (90% CIs) showed that the odds of responding to treatment were more than 7-fold greater for patients on tanezumab vs placebo (7.6 [1.6, 36.0]). For the mean change from baseline to week 6 in ICSI score there was no significant difference for tanezumab vs placebo (mean difference [90% CIs] vs placebo, 1.5 [ 3.7, 0.8]). Figure 1 The GRA analysis showed that at week 6 a higher proportion of patients on tanezumab responded as improved compared with those on placebo (OR 5.1). In particular more patients on tanezumab responded as moderately and markedly improved (tanezumab 40.0% vs placebo 11.8%, table 1). At week 6 tanezumab produced a significant reduction from baseline in urgency episode frequency per 24 hours vs placebo (table 2). However, tanezumab had no significant effect vs placebo on mean change from baseline in micturition frequency per 24 hours or MVV per micturition. The number of patients who used acetaminophen during the study (48.4% vs 46.4%) and the number of acetaminophen doses per patient in the rfas (mean [SD] 11.7 [27.5] vs 9.7 [22.1]) was similar for tanezumab vs placebo. Safety Overall 23 (67.6%) patients on tanezumab and 18 (60.0%) on placebo experienced an AE. Two (5.9%) patients on tanezumab had a serious AE (vertigo, drug exposure during pregnancy) compared with 4 (13.3%) on placebo (cholelithiasis, ovarian mass, urosepsis and urinary tract infection, transient ischemic attack). Headache was the most frequently reported AE in the tanezumab group (20.6% vs placebo 16.7%). Paresthesia (tanezumab 17.6%, placebo 3.3%) and hyperesthesia (tanezumab 8.8%, placebo 0.0%) were the most common AEs of abnormal peripheral sensation reported for tanezumab. All of the abnormal peripheral sensation AEs were mild to moderate in severity and most had resolved by the end of the study. There were 3 patients on tanezumab and 2 on
4 TANEZUMAB FOR TREATMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS 1719 Figure 2. Data for rfas, adjusted for baseline pain severity score, amitriptyline, PPS and hydroxyzine use, age, gender and body mass index. Boldface indicates clinically significant results. placebo who had a clinically significant worsening from baseline in the neurological examination. Overall 3 patients (2 on tanezumab, 1 on placebo) with a clinically significant worsening from baseline in the neurological examination and/or an AE of abnormal peripheral sensation were examined by a Table 1. Summary of GRA analysis No. Placebo (%) No. Tanezumab (%) Wk 6:* Markedly improved 1 (5.9) 5 (20.0) Moderately improved 1 (5.9) 5 (20.0) Slightly improved 5 (29.4) 7 (28.0) No change 6 (35.3) 5 (20.0) Slightly worse 3 (17.6) 2 (8.0) Moderately worse 0 (0.0) 1 (4.0) Markedly worse 1 (5.9) 0 (0.0) OR (90% CI) 5.1 (1.7, 15.0) Wk 16: Markedly improved 0 (0.0) 4 (21.1) Moderately improved 2 (15.4) 5 (26.3) Slightly improved 5 (38.5) 2 (10.5) No change 5 (38.5) 5 (26.3) Slightly worse 0 (0.0) 1 (5.3) Moderately worse 1 (7.7) 2 (10.5) Markedly worse 0 (0.0) 0 (0.0) OR (90% CI) 2.7 (0.8, 9.8) Data for rfas. * Placebo group 17 patients, tanezumab group 25 patients. Placebo group 13 patients, tanezumab group 19 patients. neurologist. For all 3 patients the neurological consultation demonstrated that there was no evidence of new or worsened peripheral neuropathy. There were no apparent trends in vital signs and ECG assessments from weeks 1 to 16, at week 6 or in changes from baseline. In addition, no vital signs or ECG result was recorded as an AE. There were no clear trends in the PVR urine volume of patients on tanezumab or placebo. In addition, no patient in either treatment group reported urinary retention. Urinary tract infections were reported by 2 (6.7%) patients on placebo and 1 (2.9%) on tanezumab. DISCUSSION IC is a multifactorial condition in which patients have widely differing clinical phenotypes. Nickel et al proposed that the clinical phenotypes of patients with IC could be categorized into 6 domains (urological, psychosocial, organ specific, infection, neurological/systemic and tenderness). 15 Although there are several options for the treatment of IC targeted at 1 or more these domains, few address the core issue of IC related pain. Current therapies for IC including PPS, hydroxyzine and amitriptyline have demonstrated efficacy in clinical trials However, the response to these treatments varies. PPS produced low response rates for refractory cases in a trial funded by the National Institutes of Health, 20 sug-
5 1720 TANEZUMAB FOR TREATMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Table 2. Mean changes from baseline to week 6 Placebo Group Tanezumab Group No. pts Urgency episodes/24 hrs: Mean change (SE) 1.1 (1.6) 1.0 (1.5) Difference vs placebo (90% CI) 2.1 ( 4.3, 0.0) Micturitions/24 hrs: Mean change (SE) 0.1 (1.3) 0.7 (1.2) Difference vs placebo (90% CI) 0.6 ( 1.1, 2.3) MVV (ml): Mean change (SE) 3.2 (17.9) 0.4 (15.6) Difference vs placebo (90% CI) 2.8 ( 25.9, 20.3) Data for rfas. gesting that it may not be effective in many patients with IC, particularly those with severe symptoms. In addition, PPS can take 6 to 9 months before symptom relief is noted. Hydroxyzine has produced inconsistent response rates and has sedative properties which can restrict its use. 20,21 Amitriptyline has been associated with an increased incidence of side effects related to its anticholinergic activity. 22 In this study tanezumab demonstrated preliminary efficacy in reducing pain in patients with moderate to severe IC who were continuing to take their preexisting IC medications. An analysis of treatment response demonstrated that the odds of having a 50% or greater reduction from baseline in pain were more than 7 times higher for patients on tanezumab vs placebo. The improvement in pain symptoms was reflected in the GRA, which showed 5 times higher odds of improvement for tanezumab vs placebo. In addition, tanezumab significantly reduced urgency episode frequency but had no significant effect on the other micturition end points. Tanezumab also had no significant effect on ICSI score vs placebo, which may relate to the ICSI questionnaire containing 2 frequency related questions and, thus, is consistent with the results for the diary measure of frequency (micturition frequency per 24 hours). Tanezumab was generally safe with no discontinuations due to AEs. One patient experienced a serious AE (exposure during pregnancy) that the investigator considered treatment related. AEs of abnormal peripheral sensation were more common with tanezumab than placebo, but all of these AEs were mild to moderate in severity and most had resolved by the end of the study. For the patients who underwent neurological evaluation none of the AEs were considered related to peripheral neuropathy. There were no clear trends in PVR for patients on tanezumab vs placebo and no reports of urinary retention in either group. Limitations of this study were the small sample size for assessing secondary end points, limited exposure of patients to tanezumab (single dose) and short followup (16 weeks). These factors were particularly limiting in assessing the effect of tanezumab on the micturition end points, which have a large behavioral component that may not have been impacted during the 6-week period. Further analysis in a longer, multiple dose, dose ranging study would enable a more thorough investigation of the effects of tanezumab on urinary symptoms associated with IC. Through May 24, 2010, 16 subjects participating in 1 of 13 phase 3 studies of OA of the hip or knee experienced progressively worsening OA associated with radiographic evidence of bone necrosis that required total joint replacements. The affected joints included the knee, hip or shoulder (predominately unilateral involvement) with more than half of the cases occurring in a joint other than the index joint under evaluation in the study. These 16 events led the Food and Drug Administration to put the OA clinical program for tanezumab on clinical hold on June 22, 2010 until more information can be obtained to determine the true incidence and causality of these events. On July 19, 2010 the Food and Drug Administration also added phase 2 studies with tanezumab in chronic low back pain and diabetic peripheral neuropathy to the clinical hold. CONCLUSIONS This study has demonstrated positive proof of concept for the treatment of pain associated with IC following a single dose of 200 g/kg IV tanezumab. Furthermore, tanezumab reduced urgency episode frequency and provided overall patient reported treatment benefit. Additional multiple dose studies are required to fully understand the effect of tanezumab on IC symptoms. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS Editorial support provided by Michelle Jenvey, UBC Scientific Solutions, and funded by Pfizer, Inc. REFERENCES 1. Driscoll A and Teichman JM: How do patients with interstitial cystitis present? J Urol 2001; 166: Metts JF: Interstitial cystitis: urgency and frequency syndrome. Am Fam Physician 2001; 64: Berry SH, Stoto MA, Elliott M et al: Prevalence of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome in the United States. J Urol 2009; 181: Evans RJ: Treatment approaches for interstitial cystitis: multimodality therapy. Rev Urol 2002; 4: S Lilly JD and Parsons CL: Bladder surface glycosaminoglycans is a human epithelial permeability barrier. Surg Gynecol Obstet 1990; 171: Parsons CL: The role of the urinary epithelium in the pathogenesis of interstitial cystitis/prostatitis/urethritis. Urology 2007; 69: 9.
6 TANEZUMAB FOR TREATMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Hefti FF, Rosenthal A, Walicke PA et al: Novel class of pain drugs based on antagonism of NGF. Trends Pharmacol Sci 2006; 27: Delafoy L, Raymond F, Doherty AM et al: Role of nerve growth factor in the trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid-induced colonic hypersensitivity. Pain 2003; 105: Lamb K, Kang YM, Gebhart GF et al: Nerve growth factor and gastric hyperalgesia in the rat. Neurogastroenterol Motil 2003; 15: Jaggar SI, Scott HC and Rice AS: Inflammation of the rat urinary bladder is associated with a referred thermal hyperalgesia which is nerve growth factor dependent. Br J Anaesth 1999; 83: Parsons CL, Dell J, Stanford EJ et al: Increased prevalence of interstitial cystitis: previously unrecognized urologic and gynecologic cases identified using a new symptom questionnaire and intravesical potassium sensitivity. Urology 2002; 60: O Leary MP, Sant GR, Fowler FJ Jr et al: The interstitial cystitis symptom index and problem index. Urology 1997; 49: Halvorson KG, Kubota K, Sevcik MA et al: A blocking antibody to nerve growth factor attenuates skeletal pain induced by prostate tumor cells growing in bone. Cancer Res 2005; 65: Lane NE, Schnitzer TJ, Birbara CA et al: Tanezumab for the treatment of pain from osteoarthritis of the knee. N Engl J Med 2010; 363: Nickel JC, Shoskes D and Irvine-Bird K: Clinical phenotyping of women with interstitial cystitis/ painful bladder syndrome: a key to classification and potentially improved management. J Urol 2009; 182: Theoharides TC and Sant GR: Hydroxyzine therapy for interstitial cystitis. Urology 1997; 49: van Ophoven A, Pokupic S, Heinecke A et al: A prospective, randomized, placebo controlled, double-blind study of amitriptyline for the treatment of interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2004; 172: Mulholland SG, Hanno P, Parsons CL et al: Pentosan polysulfate sodium for therapy of interstitial cystitis. A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical study. Urology 1990; 35: Parsons CL, Benson G, Childs SJ et al: A quantitatively controlled method to study prospectively interstitial cystitis and demonstrate the efficacy of pentosanpolysulfate. J Urol 1993; 150: Sant GR, Propert KJ, Hanno PM et al: A pilot clinical trial of oral pentosan polysulfate and oral hydroxyzine in patients with interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2003; 170: Dimitrakov J, Kroenke K, Steers WD et al: Pharmacologic management of painful bladder syndrome/interstitial cystitis: a systematic review. Arch Intern Med 2007; 167: van Ophoven A and Hertle L: Long-term results of amitriptyline treatment for interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2005; 174: 1837.
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
Study No. 178-CL-008 Report Final Version, 14 Dec 2006 Reissued Version, 18 Jul 2011 Astellas Pharma Europe B.V. Page 13 of 122
 Page 13 of 122 3 SYNOPSIS Title of study: (International) Study No: A randomized, double-blind, parallel group, proof-of-concept study of in comparison with placebo and tolterodine in patients with symptomatic
Page 13 of 122 3 SYNOPSIS Title of study: (International) Study No: A randomized, double-blind, parallel group, proof-of-concept study of in comparison with placebo and tolterodine in patients with symptomatic
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB?
 What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
What is on the Horizon in Drug Therapy for OAB? K-E Andersson, MD, PhD Wake Forest Institute for Regenerative Medicine Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston Salem, North Carolina Disclosures
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Infection/Inflammation. Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States
 Infection/Inflammation Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States Sra H. Berry,* Marc N. Elliott, Marika Suttorp, Laura M. Bogart, Michael
Infection/Inflammation Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States Sra H. Berry,* Marc N. Elliott, Marika Suttorp, Laura M. Bogart, Michael
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Results The Authors. BJU Int 2017; 120:
 Functional Urology Efficacy and safety of combinations of mirabegron and solifenacin compared with monotherapy and placebo in patients with overactive bladder (SYNERGY study) Sender Herschorn*, Christopher
Functional Urology Efficacy and safety of combinations of mirabegron and solifenacin compared with monotherapy and placebo in patients with overactive bladder (SYNERGY study) Sender Herschorn*, Christopher
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2
 Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Office based non-oncology urology trials Richard W. Casey, MD, 1 Jack Barkin, MD 2 1 The Male Health Centre, Oakville, Ontario, Canada 2 Humber River Regional Hospital, University of Toronto, Toronto,
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment of bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis
 Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Received: 17 December 2016 Accepted: 26 February 2017 DOI: 10.1002/nau.23284 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Clinical comparison of intravesical hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulfate therapies in the treatment
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS.
 D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
Interstitial Cystitis. Dr. Gerard Testa
 Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Interstitial Cystitis Dr. Gerard Testa Auto Immune Disease Infection Glycosaminoglycan layer deficiency Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy? Hereditary Classification of Interstitial Cystitis Ulcerative Non Ulcerative
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
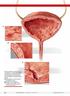 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
Voiding Dysfunction. Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan H. Kaufmann, David D. Chancellor, Michael B. Chancellor and Hann-Chorng Kuo,k
 Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Voiding Dysfunction Bladder Instillation of Liposome Encapsulated OnabotulinumtoxinA Improves Overactive Bladder Symptoms: A Prospective, Multicenter, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial Yao-Chi Chuang,* Jonathan
Mirabegron 50 mg once-daily for the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder: An overview of efficacy and tolerability over 12 weeks and 1 year
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21, 960 967 doi: 10.1111/iju.12568 Review Article Mirabegron 50 mg once-daily for the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder: An overview of efficacy
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21, 960 967 doi: 10.1111/iju.12568 Review Article Mirabegron 50 mg once-daily for the treatment of symptoms of overactive bladder: An overview of efficacy
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder
 Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Intravesical Drug Delivery for Dysfunctional Bladder Yao-Chi Chuang Professor and Chief, Division of Urology, Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan 成長於台南 建興國中 台南一中 2 Yao-Chi Chuang In connection
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology
 Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
Botulinum Toxin: Applications in Urology Dr. Lee Jonat, PGY-4 Department of Urologic Sciences University of British Columbia Outline Mechanism of Action Technical Considerations Adverse Events Neurogenic
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW?
 NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
NEW EVIDENCE FOR EXOGENOUS GLYCOSAMINOGLYCANS TREATMENT OF CYSTITIS : IS THE FUTURE NOW? *Massimo Lazzeri, 1 Philip Van Kerrebroeck 2 1. Department of Urology, Istituto Clinico Humanitas IRCCS, Humanitas
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome?
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome? Charles W. Butrick, MD ABSTRACT Background: Endometriosis and interstitial cystitis/painful
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome? Charles W. Butrick, MD ABSTRACT Background: Endometriosis and interstitial cystitis/painful
A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS)
 31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
31 Review Article A Review on Interstitial Cystitis Syndrome (ICS) M Sushma*, TVV Vidyadhar, R Mohanraj, M Babu Department of Pharmacy Practice, Raghavendra Institute of Pharmaceutical Education & Research
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation Policy Number: Original Effective Date: MM.02.025 01/01/2015 Lines of Business: Current Effective Date: HMO; PPO; QUEST Integration 02/01/2015 Section: Medicine Place(s)
Consequences of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Symptoms on Women s Work Participation and Income: Results from a National Household Sample
 Consequences of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Symptoms on Women s Work Participation and Income: Results from a National Household Sample Megan K. Beckett,* Marc N. Elliott, J. Quentin Clemens, Brett
Consequences of Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Symptoms on Women s Work Participation and Income: Results from a National Household Sample Megan K. Beckett,* Marc N. Elliott, J. Quentin Clemens, Brett
Introduction. Original Article
 Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
PENTOSAN POLYSULFATE SODIUM FOR THERAPY OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study
 OFHA eol0e PENTOSAN POLYSULFATE SODIUM FOR THERAPY OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study S. GRANT MULHOLLAND, M.D. PHILLIP HANNO, M.D. C. LOWELL PARSONS, M.D. GRANNUM
OFHA eol0e PENTOSAN POLYSULFATE SODIUM FOR THERAPY OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study S. GRANT MULHOLLAND, M.D. PHILLIP HANNO, M.D. C. LOWELL PARSONS, M.D. GRANNUM
Neurogenic bladder. Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder.
 Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
Definition: Neurogenic bladder Neurogenic bladder is a type of dysfunction of the bladder due to neurological disorder. Types: Nervous system diseases: Congenital: like myelodysplasia like meningocele.
A SURVEY ON LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS (LUTS) AMONG PATIENTS WITH BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH) IN HOSPITAL UNIVERSITI SAINS MALAYSIA (HUSM)
 Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 14, No. 2, July 2007 (67-71) SHORT COMMUNICATION A SURVEY ON LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS (LUTS) AMONG PATIENTS WITH BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH) IN HOSPITAL
Malaysian Journal of Medical Sciences, Vol. 14, No. 2, July 2007 (67-71) SHORT COMMUNICATION A SURVEY ON LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS (LUTS) AMONG PATIENTS WITH BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA (BPH) IN HOSPITAL
The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence?
 Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Rev Article CHRONIC PROSTATITIS THERAPY NICKEL The three As of chronic prostatitis therapy: antibiotics, a-blockers and anti-inflammatories. What is the evidence? J. CURTIS NICKEL Department of Urology,
Mini-Reviews. Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review
 J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 May 01.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2014 May ; 191(5): 1294 1299. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.11.099. Segmental Hyperalgesia to Mechanical Stimulus in Interstitial
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: J Urol. 2014 May ; 191(5): 1294 1299. doi:10.1016/j.juro.2013.11.099. Segmental Hyperalgesia to Mechanical Stimulus in Interstitial
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS
 The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS Frank Van der Aa Leuven, Belgium This symposium is supported by Astellas Pharma Europe Ltd., including speaker honoraria and production of materials the slides
The patient, your co-pilot in assessing LUTS Frank Van der Aa Leuven, Belgium This symposium is supported by Astellas Pharma Europe Ltd., including speaker honoraria and production of materials the slides
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain
 Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Neuroanatomy, Neurophysiology and Clinical Presentation of Visceral Urological Pain Prof Dr K. Everaert Functional urology Department of Urology Ghent University Hospital Gent, Belgium Chronic pelvic pain
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria. Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017
 Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Original Research Article Exploring the Role of Tanezumab as a Novel Treatment for the Relief of Neuropathic Pain
 Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1163 1176 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. NEUROPATHIC PAIN SECTION Original Research Article Exploring the Role of Tanezumab as a Novel Treatment for the Relief of Neuropathic Pain Candace
Pain Medicine 2015; 16: 1163 1176 Wiley Periodicals, Inc. NEUROPATHIC PAIN SECTION Original Research Article Exploring the Role of Tanezumab as a Novel Treatment for the Relief of Neuropathic Pain Candace
Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo in Reducing Pain in Patients with Osteoarthritis?
 Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine DigitalCommons@PCOM PCOM Physician Assistant Studies Student Scholarship Student Dissertations, Theses and Papers 2018 Is Tanezumab More Effective than a Placebo
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion
 Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
Management of Pain related to Spinal Cord Lesion A Neurologist s Perspective Vincent Mok, MD Associate Professor Division of Neurology Department of Medicine and Therapeutics The Chinese University of
s r e t n I sititsyc laititsret ystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis In itial Ctsretn IC I sititsyc laititsretni PRODUCT MONOGRAPH
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Intersti t i a l Cystitis Interstitial Cystitis Inters IC CONTENTS Interstitial Cystitis: An Overview Introduction... Epidemiology of
Objectives. Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
URINARY INCONTINENCE: EVALUATION AND CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Lisa S Pair, MSN, CRNP Division of Urogynecology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology University of Alabama
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
LONG-TERM SAFETY AND EFFICACY OF TAMSULOSIN FOR THE TREATMENT OF LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS ASSOCIATED WITH BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA
 0022-5347/03/1702-0498/0 Vol. 170, 498 502, August 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000076140.68657.fd LONG-TERM SAFETY
0022-5347/03/1702-0498/0 Vol. 170, 498 502, August 2003 THE JOURNAL OF UROLOGY Printed in U.S.A. Copyright 2003 by AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION DOI: 10.1097/01.ju.0000076140.68657.fd LONG-TERM SAFETY
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment
 Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Overactive Bladder: Diagnosis and Approaches to Treatment A Hidden Condition* Many Many patients self-manage by voiding frequently, reducing fluid intake, and wearing pads Nearly Nearly two-thirds thirds
Summary. Neuro-urodynamics. The bladder cycle. and voiding. 14/12/2015. Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics
 Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Neuro-urodynamics Summary Neural control of the LUT Initial assessment Urodynamics Marcus Drake, Bristol Urological Institute SAFETY FIRST; renal failure, dysreflexia, latex allergy SYMPTOMS SECOND; storage,
Aquinox Q2 /2015 Conference Call: LEADERSHIP Secondary Endpoint Update - AQX-1125 in BPS/IC. August 6, 2015
 Aquinox Q2 /2015 Conference Call: LEADERSHIP Secondary Endpoint Update - AQX-1125 in BPS/IC August 6, 2015 Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary
Aquinox Q2 /2015 Conference Call: LEADERSHIP Secondary Endpoint Update - AQX-1125 in BPS/IC August 6, 2015 Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond
 Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Interstitial cystitis: bladder pain and beyond Review 1. Introduction 2. Methods 3. Presentation 4. Other invasive approaches 5. Conclusion 6. Expert opinion Theoharis C Theoharides, Kristine Whitmore,
Innovations in Childhood Incontinence: Neurogenic and Functional Bladder Disorders
 TNe 10 Innovations in Childhood Incontinence: Neurogenic and Functional Bladder Disorders Stuart B. Bauer, MD President, ICCS Department of Urology Children s Hospital Boston Professor of Urology Harvard
TNe 10 Innovations in Childhood Incontinence: Neurogenic and Functional Bladder Disorders Stuart B. Bauer, MD President, ICCS Department of Urology Children s Hospital Boston Professor of Urology Harvard
Sacral neuromodulation (SNM), using permanent foramen S3 electrode, Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
ORIGINAL RESEARCH Early versus late treatment of voiding dysfunction with pelvic neuromodulation Magdy M. Hassouna, MD, PhD; Mohamed S. Elkelini, MD See related article on page 111 Abstract Introduction:
UV-2005/01. Chronic Prostatitis and Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrom (CP/CPPS) Karl-Bickleder-Str. 44C Straubing - Germany
 SYNOPSIS UV-2005/01 Title: Short Title: Indication: Phase: Study Code: Study Director Co-ordinating Investigator: Study Centres: Multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study
SYNOPSIS UV-2005/01 Title: Short Title: Indication: Phase: Study Code: Study Director Co-ordinating Investigator: Study Centres: Multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. February 2018
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease February 2018 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
 www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
www.kjurology.org http://dx.doi.org/10.4111/kju.2013.54.10.682 Voiding Dysfunction/Female Urology Effect of Transurethral Resection With Hydrodistention for the Treatment of Ulcerative Interstitial Cystitis
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration and Results System (PRS) Receipt Release Date: 10/11/2013. ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT
 ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration and Results System (PRS) Receipt Release Date: 10/11/2013 ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT00168454 Study Identification Unique Protocol ID: 191622-077 Brief Title: A
ClinicalTrials.gov Protocol Registration and Results System (PRS) Receipt Release Date: 10/11/2013 ClinicalTrials.gov ID: NCT00168454 Study Identification Unique Protocol ID: 191622-077 Brief Title: A
VOIDING DYSFUNCTION IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS
 Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (3): 315-320, May - June, 2000 VOIDING DYSFUNCTION IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CEYHUN OZYURT, ÇAG
Urological Neurology Brazilian Journal of Urology Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology Vol. 26 (3): 315-320, May - June, 2000 VOIDING DYSFUNCTION IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS CEYHUN OZYURT, ÇAG
NGF the TrkA to successful pain treatment
 NGF the TrkA to successful pain treatment The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
NGF the TrkA to successful pain treatment The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation Published Version Accessed
Rawal Medical Journal
 Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Original Article Role of alpha blockers
Rawal Medical Journal An official publication of Pakistan Medical Association Rawalpindi Islamabad branch Established 1975 Volume 36 Number 4 October - December 2011 Original Article Role of alpha blockers
H6D-MC-LVHR Clinical Study Report Synopsis Page LVHR Synopsis (LY450190)
 H6D-MC-LVHR Clinical Study Report Synopsis Page 1 2. LVHR Synopsis H6D-MC-LVHR Clinical Study Report Synopsis Page 2 Clinical Study Report Synopsis: Study H6D-MC-LVHR Title of Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind,
H6D-MC-LVHR Clinical Study Report Synopsis Page 1 2. LVHR Synopsis H6D-MC-LVHR Clinical Study Report Synopsis Page 2 Clinical Study Report Synopsis: Study H6D-MC-LVHR Title of Study: A Randomized, Double-Blind,
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena Petta, Francesco Sciobica, Patrizio Pasqualetti, Stefania Musco and Pierluigi Bove
 Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation Effects on Detrusor Overactivity Incontinence are Not Due to a Placebo Effect: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena
Percutaneous Tibial Nerve Stimulation Effects on Detrusor Overactivity Incontinence are Not Due to a Placebo Effect: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial Enrico Finazzi-Agrò,*, Filomena
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails
 Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Chronic pelvic pain-when surgery fails Sherif Tawfeek FRANZCOG, FRCOG, FICS, MSc, Dip-Endoscopy Consultant in Obstetrics and Gynaecology Senior lecturer at University of Otago Objectives Identify the common
Clinical Study Synopsis
 Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Clinical Study Synopsis This Clinical Study Synopsis is provided for patients and healthcare professionals to increase the transparency of Bayer's clinical research. This document is not intended to replace
Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Review Article Interstitial cystitis intravesical therapy Tanya Ha, Jie Hua Xu Urology Department, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia Contributions: (I) Conception and design: All authors; (II) Administrative
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction
 Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction Corporate Medical Policy File name: Posterior Tibial Nerve Stimulation for Voiding Dysfunction File code: UM.NS.05 Origination: 8/2011 Last Review:
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only.
 The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
The clinical trial information provided in this public disclosure synopsis is supplied for informational purposes only. Please note that the results reported in any single trial may not reflect the overall
La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici
 La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
La Prostata nel Mirino Napoli, 1 dicembre 2016 La vescica iperattiva: dalla diagnosi ai nuovi approcci terapeutici Giorgio Annoni Cattedra e Scuola di Specializzazione in Geriatria Università degli Studi
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease. June 2017
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease June 2017 1 Forward Looking Statements/ Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking statements that involve
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve
 Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
Neuromodulation and the pudendal nerve Stefan De Wachter, MD, PhD, FEBU Professor of Urology University of Antwerpen, Belgium Chairman dept of Urology, UZA Disclosures Consultant speaker: Astellas, Medtronic,
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline.
 Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Diagnosis and treatment of overactive bladder (non-neurogenic) in adults: AUA/SUFU guideline. TARGET POPULATION Eligibility Decidable (Y or N) Inclusion Criterion non-neurogenic OAB Exclusion Criterion
Case L.M. Question 1 4/17/2013. Sumana Koduri, MD Associate Professor, Ob/gyn and Urology Medical College of Wisconsin
 Sumana Koduri, MD Associate Professor, Ob/gyn and Urology Medical College of Wisconsin Case L.M. L.M. is a 46 yo G0 woman who presents with a 3 year history of worsening pelvic pain. She has a h/o endometriosis
Sumana Koduri, MD Associate Professor, Ob/gyn and Urology Medical College of Wisconsin Case L.M. L.M. is a 46 yo G0 woman who presents with a 3 year history of worsening pelvic pain. She has a h/o endometriosis
Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome
 Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Int Urogynecol J (2011) 22:395 400 DOI 10.1007/s00192-010-1252-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Treatment choice, duration, and cost in patients with interstitial cystitis and painful bladder syndrome Jennifer T. Anger
Sponsor. Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation Generic Drug Name. Agomelatine Therapeutic Area of Trial. Major depressive disorder Approved Indication
 Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation Generic Drug Name Therapeutic Area of Trial Major depressive disorder Approved Indication Investigational drug Study
Clinical Trial Results Database Page 1 Sponsor Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation Generic Drug Name Therapeutic Area of Trial Major depressive disorder Approved Indication Investigational drug Study
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis
 Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urinary nerve growth factor levels could be a biomarker for overactive bladder symptom: a meta-analysis H.C. Qu, S. Yan, X.L. Zhang, X.W. Zhu, Y.L. Liu and P. Wang Department of Urological Surgery, The
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider
 Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Urinary Incontinence for the Primary Care Provider Diana J Scott FNP-BC https://youtu.be/gmzaue1ojn4 1 Assessment of Urinary Incontinence Urge Stress Mixed Other overflow, postural, continuous, insensible,
Dr. Aso Urinary Symptoms
 Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Haematuria The presence of blood in the urine (haematuria) is always abnormal and may be the only indication of pathology in the urinary tract. False positive stick tests and the discolored urine caused
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults
 Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease Jefferies Healthcare Conference
 Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease 2016 Jefferies Healthcare Conference Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking
Targeted Therapeutics for Inflammatory Disease 2016 Jefferies Healthcare Conference Forward Looking Statements / Safe Harbor This presentation and the accompanying oral commentary contain forward-looking
