Introduction. Original Article
|
|
|
- Daniela Harrison
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Test-retest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient Symptom Scale instruments Marcella Lima Victal 1, Carlos Arturo Levi D Ancona 2, Roberto Gomes Junqueira 3, Daniel Carlos da Silva 2, Henrique Ceretta Oliveira 1, Maria Helena Baena de Moraes Lopes 1 1 School of Nursing, State University of Campinas, Campinas, Brazil; 2 Department of Urology, Clinical Hospital, State University of Campinas, Campinas, Brazil; 3 Departament of Urology, University of the Joinville Area, Joinville, Brazil Contributions: (I) Conception and design: ML Victal, MH de Moraes Lopes; (II) Administrative support: ML Victal, MH de Moraes Lopes, CA D Ancona, RG Junqueira; (II) Provision of study materials or patients: ML Victal, CA D Ancona, RG Junqueira, D Carlos da Silva; (IV) Collection and assembly of data: ML Victal; (V) Data analysis and interpretation: ML Victal, MH de Moraes Lopes, HC Oliveira; (VI) Manuscript writing: All authors; (VII) Final approval of manuscript: All authors. Correspondence to: Marcella Lima Victal. School of Nursing, State University of Campinas (UNICAMP), Street Tessália Vieira de Camargo, Cidade Universitária Zeferino Vaz Campinas, SP, Brazil. mavictal@hotmail.com. Background: The purpose is to evaluate the psychometric properties of reliability and discriminant validity of the Brazilian Portuguese versions of two instruments used in the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis (IC): The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index (The O Leary-Sant), and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/ Frequency (PUF) Patient Symptom Scale. Methods: Three groups of patients were examined: a study group (subjects with IC), control group 1 (individuals with at least one IC symptom), and control group 2 (subjects without IC symptoms). Test-retest stability was evaluated at intervals of 3 to 7 days in the study group. Discriminant validity was examined in all three groups. Results: The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) [95% confidence interval (CI)] results were 0.56 (range, ) for The O Leary-Sant Symptom Index, 0.48 (range, ) for The O Leary-Sant Problem Index, and 0.49 (range, ) for the PUF. To analyze discriminant validity between groups, we used Fisher s exact test and odd ratio (OR) to identify differences. We obtained a P value<0.0001, which indicated that the null hypothesis was rejected; in other words, there was evidence that at least two different groups were compared to the proportion of patients with IC. Conclusions: The analyzed instruments did not reach appropriate values for reliability. Future studies are needed to analyze the psychometric measures of these instruments on a larger sample of patients with IC. Keywords: Diagnosis; interstitial cystitis (IC); questionnaires; validation study Submitted Jul 23, Accepted for publication Aug 24, doi: /j.issn View this article at: Introduction Interstitial cystitis (IC) is characterized by painful urinary symptoms in the absence of a bacterial infection. It is diagnosed through clinical signs and the exclusion of other diseases (1). Symptoms of IC may include discomfort, pain, or pressure on the bladder extending to the pelvic area, associated with urgency and/or polyuria (2). Some authors include nocturia and pain during sexual intercourse as symptoms (2-8). Because of the difficulty of diagnosing IC,
2 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 4, No 6 December its exact prevalence remains unclear. In the United States, the reported prevalence ranges from 10 to 67 in 100,000 inhabitants (4). To our knowledge, no prevalence studies have been performed in Brazil. In 1987, the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) developed criteria for the diagnosis of IC. These criteria were designed to identity a homogenous subgroup of patients for epidemiological research and treatment protocols. The criteria required patients to have agglomerations and/or Hunner s ulcers on the cystoscopic exam, as well as pain in the bladder or urinary urgency (5). In 1999, the Interstitial Cystitis Database (ICDB) study group, financed by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), studied whether the NIDDK criteria were required to diagnose IC. The only difference between the ICDB and the NIDDK criteria was that the former did not necessarily require cystoscopic results for diagnosis. Even with rigorous application of the NIDDK criteria, two-thirds of patients who had strong indicators for IC by the ICDB criteria would still be excluded. According to the latter, IC may be characterized by painful vascular symptoms in the absence of infections or other identifiable clinical conditions (2). Diagnosing IC is a long and complex process that begins with a urologic or urogynecologic exam. Symptoms are evaluated from several perspectives, including whether they last for more than 3 months. The next step is to determine whether infections or other diseases are present that might cause the same symptoms. Results of cystoscopy, urodynamic exams, biopsy, and questionnaires support the exclusion other diseases and aid in determining the diagnosis (8-13). Questionnaires can be used to investigate the urinary, emotional, physical, and sexual aspects of the disease, as well as the patient s menstrual cycle and quality of life, leading to a precise diagnosis (9-13). However, no questionnaire related to the diagnosis of IC is available in Brazilian Portuguese. We translated The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index (The O Leary-Sant) and the Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient Symptom Scale instruments into Brazilian Portuguese and adapted them to Brazilian society. In this process, we followed all of the steps for cultural adaptation (i.e., translation, synthesis of the translations, back-translation, review by a committee of specialists, and pre-test) developed by the American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons. We adapted the content, obtaining Portuguese versions that were faithful to the original English versions (14). To use the instruments in research and clinical practice, we must first evaluate their psychometric properties to determine their validity and reliability. Thus, the goal of this study was to determine the psychometric properties of the Brazilian versions of these instruments, to judge their test-retest reliability (stability) and their discriminant (divergent) validity. Methods Authorization and ethical considerations This was a methodological study that aimed to evaluate the reliability and discriminant validity of The O Leary-Sant and PUF instruments. To perform the study, we made prior contact with the authors of the instruments and obtained formal authorization to translate and perform the cultural adaptation of the instruments. We observed all of the ethical principles involved in research with human subjects, with a positive report from the Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medical Sciences at UNICAMP (case No. 545/2010). All participants read and signed an informed consent form. Instruments for data collection Demographic information To define the population profile of the sample studied, we collected sociodemographic information, including age, income (value in Brazilian reais, R$), work activity, educational level ( no education to graduate studies ), and the results of previous exams performed to determine a diagnosis of IC. Verification list This instrument was used to evaluate exclusion criteria for IC (15). The O Leary-Sant The goal of this instrument is to evaluate and diagnose patients with IC. The O Leary-Sant instrument is comprised of a Symptom Index (score range: 0-20 points) and a Problem Index (score range: 0-16 points), each of which contains four questions related to urinary and pain symptoms. For each index, the score is calculated by summing the points for each item. On either index, a score 6 points indicates IC. The Symptom Index covers various areas, including: whether the patient feels the need to urinate with little or no warning, has to urinate more frequently than every
3 596 Victal et al. Instruments for diagnosis of interstitial cystitis 2 hours, needs to get up during the night to urinate, and has pain in the bladder. The Problem Index evaluates other aspects, such as: urinary frequency during the day, urinary frequency at night, the need to urinate with little or no warning, and burning, pain, discomfort, or pressure on the bladder. Both indices evaluate the situation over the previous month. Pelvic pain and urgency/frequency (PUF) This instrument is another method for diagnosing IC. It consists of eight items that cover areas of pain, urgency, urinary frequency, and symptoms associated with sexual intercourse. Items 1, 2a, 4a, 5, 6, 7a, and 8a measure symptoms of IC. These items are related to urinary frequency during the day and night, as well as symptoms of pain during sexual intercourse or associated with the bladder or pelvis. Items 2b, 4b, 7b, and 8b relate to discomfort caused by IC. These items ask about the discomfort of nocturia and pain, as well as how often urinary urgency and dyspareunia negatively affect the respondent s life. The score ranges from 0 to 35 points. A score 5 points is considered to indicate IC. Study groups Three groups of patients participated in the study. The study group consisted of 30 patients who had a diagnosis of IC confirmed by clinical signs and biopsy. A verification list containing the exclusion criteria for IC was applied. Although it was not possible to evaluate these criteria, the clinical symptoms together with a positive biopsy exam for chronic or unspecific cystitis were sufficient to include the person in this group. Control group 1 consisted of 29 patients who had at least one symptom suggestive of IC (pelvic pain, urgency, polyuria, or nocturia). Control group 2 consisted of 14 patients who did not have any symptom suggestive of IC. Patients for the study group came from a private urology clinic located in Joinville, Santa Catarina, and from private clinics and a public hospital in the city of Campinas, São Paulo. Patients for control groups 1 and 2 came from a public hospital in the city of Campinas, São Paulo, and from a specialized medical walk-in clinic in the city of Limeira, São Paulo. Reliability The reliability of a research instrument is defined as the degree to which the instrument produces the same results in repeated measurements. It concerns coherence, precision, stability, equivalence, and homogeneity. A reliable measure will produce the same results if the behavior is measured again using the same scale (16). The coefficient of reliability ranges from 0 to 1, expressing the relationship between error variance, true variance, and the score observed. The closer the coefficient is to 1, the more reliable the instrument is (16). In this study, we used the test-retest reliability, which involves the administration of the same instrument to the same research subjects under similar conditions on two or more occasions. To evaluate this measurement, we used the patients from the study group. The questionnaires were applied at two different times at an interval of 3 to 7 days, before any factor (e.g., treatment) was applied that could influence the responses. Validity When a measurement instrument exactly measures what it should measure (i.e., truly reflects the concept that it is supposed to measure), then it is considered valid (16). This study evaluated the discriminant validity, also called the divergent validity, in which measurement approaches are used to differentiate one construct from others that may be similar to it (16). To evaluate this validity, we used the study group, control group 1, and control group 2. Treatment and data analysis The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) was determined with the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) program. An ICC 0.70 is considered adequate for indicating an instrument s reliability (16). Discriminant validity was evaluated by using the Chi-square test, as measured by the SAS 9.2 program. Results Analyses of test-retest reliability and discriminant validity were performed on the basis of the instruments calculated scores. Patients with a score 6 points on either index of The O Leary-Sant instrument or a score 5 points on the PUF instrument were considered to have a diagnosis of IC. In total, 73 patients (67 women, 6 men) participated in the study, with a mean overall age of 48 years. The mean age in each group was 45.2±11.9 years in the study group,
4 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 4, No 6 December Table 1 ICCs for The O Leary-Sant Index and the PUF scale Questionnaire ICC 95% CI P value The O Leary-Sant Symptom Index The O Leary-Sant Problem Index PUF ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; PUF, pelvic pain and urgency/frequency; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. Table 2 ICC by city for the tested instruments Variable City ICC 95% CI The O Leary-Sant Symptom Index Joinville Campinas The O Leary-Sant Problem Index Joinville Campinas PUF Joinville Campinas ICC, intraclass correlation coefficient; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval; PUF, pelvic pain and urgency/frequency. 50.9±12.6 years in control group 1, and 48.2±14.6 years in control group 2 (P=0.180 by Kruskal-Wallis test). The average monthly income for the three groups was R$1, The average monthly income was R$1,059.03± for control group 1 and R$1,528.57±1, for control group 2 (P=0.001 by Kruskal-Wallis test). The income in the study group was significantly higher than that of the control groups, but there was no difference between the control groups. There were no differences in terms of educational levels between the groups (P= by Fisher s exact test). In the study group, we observed a higher proportion of people with a middle school (36.67%) and high school education (33.33%); in the control groups 1 and 2, there was a greater concentration of elementary (57.14% and 35.71%, respectively) and middle school education (25% and 50%, respectively). Of the 30 patients who participated in the testretest, only 24 returned for the second application of the instrument. The main reason that subjects did not come back for the retest was that they could not miss work. The ICC was used to measure the test-retest reliability of The O Leary-Sant and PUF instruments (Table 1). The ICC for test-retest agreement for the O Leary-Sant and PUF instruments was compared between the cities of Joinville and Campinas (Table 2). The Chi-square test was used to evaluate the discriminant validity between the three groups (Tables 3-5). We analyzed the validity of both instruments, and obtained a P value of < Using a 5% significance value, we rejected the null hypothesis. Thus, the results indicated that there was evidence that at least two groups differed from each other with respect to the proportion of cases with IC. Discussion Differences in income and educational levels between the study group and the control groups might have occurred because the study group came from an area of Brazil with a higher per capita income than the other areas. The lower educational levels of patients in control groups 1 and 2 might have compromised the ability to obtain correct responses to the questions on the instruments, which, in turn, may have influenced the scores obtained. In this study, The O Leary Symptom Index and Problem Index were analyzed separately. The ICC of 0.56 for the Symptom Index and 0.48 for the Problem Index between the test and retest scores did not reach a value of 0.70, indicating insufficient reliability (15). We also calculated the ICC by city, because the interval of time between the test and retest differed between the cities of Joinville (3 days) and Campinas (7 days). This fact might have affected the agreement between the tests. The low values for the ICC in the city of Campinas for both instruments showed that the agreement between the test and retest was lower than
5 598 Victal et al. Instruments for diagnosis of interstitial cystitis Table 3 Discriminant validity for The O Leary-Sant Symptom Index between groups Group No IC, n (%) IC, n (%) OR (95% CI) Study group 3 (10.0) 27 (90.0) ( ) Control group 1 7 (24.1) 22 (75.9) 1.00 Control group 2 20 (80.0) 5 (20.0) ( ) P< by Fisher s exact test. IC, interstitial cystitis; OR, odd ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. Table 4 Discriminant validity for The O Leary Problem Index between groups Group No IC, n (%) IC, n (%) OR (95% CI) Study group 5 (16.7) 25 (83.3) ( ) Control group 1 12 (41.4) 17 (58.6) 1.00 Control group 2 22 (88.0) 3 (12.0) ( ) P< by Fisher s exact test. IC, interstitial cystitis; OR, odd ratio; 95% CI, 95% confidence interval. Table 5 Discriminant validity for the PUF scale between groups Group No IC, n (%) IC, n (%) Study group 0 (0.0) 30 (100.0) Control group 1 1 (3.5) 28 (96.5) Control group 2 13 (52.0) 12 (48.0) P< by Fisher s exact test. PUF, pelvic pain and urgency/frequency; IC, interstitial cystitis. in the city of Joinville. This difference in the test and retest scores may stem from the fact that IC is an unstable disease, with continuously changing symptoms, which could have influenced the patients responses. Nevertheless, previous studies have found different results. In the study for the development and validation of The O Leary-Sant instrument (11), the test-retest reliability, as measured by the ICC, was higher than 0.90 for both indices, in a total of 45 patients. Subsequently, another study, evaluated only the Symptom Index in 67 people with IC. The testretest reliability, as measured by the ICC, was 0.80, indicating an excellent level of reproducibility (12). We obtained a value of 0.49 for the ICC of the PUF instrument, which is below the value of 0.70 proposed by another author (17). The lack of other studies of the test-retest reliability of this instrument makes it impossible to compare these findings. The analysis of discriminant validity of the Symptom and Problem Index of The O Leary-Sant instrument identified that the study group and control group 1 were very different from control group 2 in terms of the proportion of cases classified as IC; however, when we compared between them, this difference did not prove relevant. This result may stem from the fact that there were many people with urinary problems and symptoms characteristic of IC. However, because of the difficulty in diagnosing IC, these people might not have been treated properly. During the interview for inclusion in control group 2, we asked about symptoms of IC, so that only patients who denied having these symptoms were included. As shown in Table 4, the PUF instrument confirmed the presence of IC in 100% of patients classified with IC in the study group. However, in control group 1, the PUF instrument was not capable of discriminating between patients who only have some symptoms of the disease, but do not have a diagnosis of IC. A study concluded that The O Leary-Sant and PUF instruments are important ways to help diagnose IC, but neither alone is sufficient to guarantee the diagnosis (13). Moreover, a study stated that the PUF is not a rubric for diagnosis, but that it is essential to measure the disease s evolution and, consequently, develop proper treatment (18). The fact that the ICC values in both instruments did not reach a sufficient value for reliability probably reflects low case numbers. Other factors that might have interfered are inadequate understanding of the instruments or a change in the patient s clinical picture. These factors reinforce the importance of performing further validation studies on a larger sample of patients with IC to confirm or negate these findings.
6 Translational Andrology and Urology, Vol 4, No 6 December Conclusions Analyzing the test-retest stability for The O Leary-Sant and PUF instruments revealed below adequate levels for reliability. Analysis of the discriminant validity showed that there were differences in both instruments with respect to the proportion of subjects classified as having IC. Acknowledgements Funding: State of São Paulo Research Support Foundation (N. 10/ ) and the Research Teaching and Outreach Support Fund of the State University of Campinas (N Project 276/13) have supported this study. Footnote Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare. Ethical Statement: The study was approved by Research Ethics Committee of the Faculty of Medical Sciences at UNICAMP (case No. 545/2010). Written informed consent was obtained from the patients for publication of this article. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editor-in-chief of this journal. References 1. Kim SH, Oh SJ. Comparison of voiding questionnaires between female interstitial cystitis and female idiopathic overactive bladder. Int Neurourol J 2010;14: Nickel JC. Diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: another look. Rev Urol 2000;2: National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse. Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome. Available online: health-information/health-topics/urologic-disease/ interstitial-cystitis-painful-bladder-syndrome/pages/ facts.aspx 4. Warren JW, Brown J, Tracy JK, et al. Evidence-based criteria for pain of interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome in women. Urology 2008;71: Parsons CL, Dell J, Stanford EJ, et al. Increased prevalence of interstitial cystitis: previously unrecognized urologic and gynecologic cases identified using a new symptom questionnaire and intravesical potassium sensitivity. Urology 2002;60: Clemons JL, Arya LA, Myers DL. Diagnosing interstitial cystitis in women with chronic pelvic pain. Obstet Gynecol 2002;100: Macdiarmid SA, Sand PK. Diagnosis of interstitial cystitis/ painful bladder syndrome in patients with overactive bladder symptoms. Rev Urol 2007;9: Meijilink JM. Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome: Diagnosis & Treatment. Cited Mar 12, Available online: Diagnosis&Treatment_IPBF.pdf 9. Evans RJ, Sant GR. Current diagnosis of interstitial cystitis: an evolving paradigm. Urology 2007;69: Sirinian E, Azevedo K, Payne CK. Correlation between 2 interstitial cystitis symptom instruments. J Urol 2005;173: O'Leary MP, Sant GR, Fowler FJ Jr, et al. The interstitial cystitis symptom index and problem index. Urology 1997;49: Lubeck DP, Whitmore K, Sant GR, et al. Psychometric validation of the O'leary-Sant interstitial cystitis symptom index in a clinical trial of pentosan polysulfate sodium. Urology 2001;57: Kushner L, Moldwin RM. Efficiency of questionnaires used to screen for interstitial cystitis. J Urol 2006;176: Victal ML, Lopes MH, D'Ancona CA. Adaptation of the O'Leary-Sant and the PUF for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis for the Brazilian culture. Rev Esc Enferm USP 2013;47: Rebola J, Coelho MF. Cistite Intersticial: Etiopatogenia e atitudes terapêuticas. Acta Urológica 2003;20: LoBiondo-Wood G, Haber J. Pesquisa em enfermagem. Métodos, avaliação crítica e utilização. 4th ed. Rio de Janeiro: Guanabara Koogan, 2001: Streiner DL, Norman GR. Health measurement scales: a practical guide to their development and use. 3rd ed. New York: Oxford University Press, 2003: Brewer ME, White WM, Klein FA, et al. Validity of Pelvic Pain, Urgency, and Frequency questionnaire in patients with interstitial cystitis/painful bladder syndrome. Urology 2007;70: Cite this article as: Victal ML, D Ancona CA, Junqueira RG, Carlos da Silva D, Oliveira HC, de Moraes Lopes MH. Testretest reliability and discriminant validity for the Brazilian version of The Interstitial Cystitis Symptom Index and Problem Index and Pelvic Pain and Urgency/Frequency (PUF) Patient Symptom Scale instruments. Transl Androl Urol 2015;4(6): doi: /j.issn
In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective?
 Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
Original Article In what type of interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome is DMSO intravesical instillation therapy effective? Hikaru Tomoe Department of Urology and Pelvic Reconstructive Surgery, Tokyo
How does interstitial cystitis begin?
 Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
Original Article How does interstitial cystitis begin? C. Lowell Parsons Division of Urology, Department of Surgery, University of California, San Diego Medical Center, University of California, San Diego,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) MANAGEMENT About Interstitial Cystitis (IC) What is IC? IC is a chronic, yet manageable, bladder condition, characterized by bladder or pelvic pain, pain during or after sexual
In evaluating a patient with lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS), urologists
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS Interstitial Cystitis and Lower Urinary Tract Symptoms in Males and Females The Combined Role of Potassium and Epithelial Dysfunction C. Lowell Parsons, MD
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS. Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >60%
 DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
DELAYED DIAGNOSIS Mean time to diagnosis = 4-7 years Mean # of physicians = 8 NIDDK criteria underdiagnoses >6% 1 PREVALENCE 1,, 9,, 8,, 7,, 6,, 5,, 4,, 3,, 2,, 1,, NHS "Prostatitis" "Endometriosis" The
32 OBG Management July 2010 Vol. 22 No. 7 obgmanagement.com
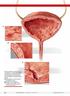 A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
A B C Although interstitial cystitis (IC) occurs in the absence of urinary tract infection or malignancy, some pathology may become apparent during cystoscopy with hydrodistention. Potential findings include:
INTRODUCTION. Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction. Aram Kim 1, Kyeong-Ok Hoe 2, Jung Hyun Shin 2, Myung-Soo Choo 2 1
 Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Original Article - Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction Investig Clin Urol 2017;58:353-358. pissn 2466-0493 eissn 2466-054X Evaluation of the incidence and risk factors associated with persistent frequency
Interstitial Cystitis:
 Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Diagnosis and Definition ESSIC approach Jørgen Nordling, chairman ESSIC Professor of Urology University of Copenhagen Denmark Interstitial Cystitis: A painful, potentially disabling, inflammatory disease
Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy
 Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
Review Article Interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome and glycosaminoglycans replacement therapy Mauro Cervigni Interstitial Cystitis Referral Center, Catholic University, Rome, Italy Correspondence
UroToday International Journal. Volume 2 - October 2009
 UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
UroToday International Journal Robert J. Evans, 1 Jeffrey Proctor, 2 Robert M. Moldwin 3 1 Alliance Urology Specialists, Greensboro, NC; 2 Georgia Urology, Cartersville, GA; 3 The Arthur Smith Institute
Cistite intersticial Diagnóstico Questionários Comparação transcultural
 Adaptation of the O Leary-Sant and the PUF, for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis for the brazilian culture * Adaptação à cultura brasileira dos questionários The O Leary-Sant e PUF, usados para cistite
Adaptation of the O Leary-Sant and the PUF, for the diagnosis of interstitial cystitis for the brazilian culture * Adaptação à cultura brasileira dos questionários The O Leary-Sant e PUF, usados para cistite
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence
 BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
BPS/IC: evolution of definition and prevalence ame in history Tic doloureux of the bladder 1836 Interstitial cystitis 1878 Cystitis parenchymatosa 197 unner s ulcer 1915 Panmural ulcerative cystitis 192
Urogynecology in EDS. Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018
 Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Urogynecology in EDS Joan L. Blomquist, MD Greater Baltimore Medical Center August 2018 One in three like me Voiding Issues Frequency/Urgency Urinary Incontinence neurogenic bladder Neurologic supply
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective. Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado
 Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Definitions of IC: U.S. perspective Edward Stanford MD MS FACOG FACS Western Colorado PURPOSE OF A DEFINITION? Identifies with specificity those patients who are most likely to have the disease. Identifies
Interstitial cystitis (IC), also
 Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
Interstitial cystitis: Algorithm to simplify diagnosis of chronic urinary symptoms By Anita L. Booth, DNP, FNP-BC and Jill Harpst Rodgers, DNP, FNP-BC This pre/post-test study was undertaken to determine
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC)
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS (IC) Painful Bladder Syndrome (PBS): THE BASIC FACTS ANDREW L. SIEGEL, M.D. Board-Certified Urologist and Urological Surgeon Specialty: Male and Female Incontinence, Voiding Dysfunction,
Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Effect of Low-Dose Amitriptyline Treatment for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Weiguo Chen 1, Donghua Xie 2, Guolu Liu 1, Yifan Chen 1, Zongqiang Cai 1 1 Department of Urology,
BLADDER HEALTH. Painful Bladder AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
 BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
BLADDER HEALTH Painful Bladder Interstitial Cystitis AUA FOUNDATION OFFICIAL FOUNDATION OF THE AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION Don t Let Interstitial Cystitis Keep You from Enjoying Life. many people have
Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores
 DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
DOI 10.1007/s10397-010-0587-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Endometriosis/adenomyosis is associated with more typical cystoscopic findings of interstitial cystitis in patients with elevated PUF scores Richard L. Heaton
Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome
 page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
page 1 Interstitial Cystitis/ Bladder Pain Syndrome Q: What is interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome (IC/BPS)? A: Interstitial cystitis (int-uhr-stishuhl siss-tyt-uhss) (IC), is a chronic pain condition
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis
 Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
Proof of Concept Trial of Tanezumab for the Treatment of Symptoms Associated With Interstitial Cystitis R. J. Evans,*, R. M. Moldwin, N. Cossons, A. Darekar, I. W. Mills and D. Scholfield From the Department
REVIEW. International Journal of Surgery
 International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
International Journal of Surgery 11 (2013) 233e237 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect International Journal of Surgery journal homepage: www.theijs.com Review The evil twin syndrome in
Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O. Talbott,* Josephine Davis and Lisa J. Regan
 Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Safety and Efficacy of the Use of Intravesical and Oral Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium for Interstitial Cystitis: A Randomized Double-Blind Clinical Trial Edward L. Davis, Samar R. El Khoudary, Evelyn O.
Interstitial Cystitis
 Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Clinical Communiqué Winter 2002 Interstitial Cystitis A Clinical Spectrum Jack Barkin, MD Chief of Urology, Humber River Regional Hospital, Toronto, Ontario Editorial Choosing the right treatment by J.
Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis
 Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Int Urogynecol J (2012) 23:1147 1153 DOI 10.1007/s00192-012-1686-2 REVIEW ARTICLE Intravesical treatment of painful bladder syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis P. K. Matsuoka & J. M. Haddad
Interstitial Cystitis
 Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Interstitial Cystitis Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder condition. Its symptoms are urinary urgency (the feeling that you need to urinate), frequent urination and/or pain anywhere between
Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis
 The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
The University of Toledo The University of Toledo Digital Repository Master s and Doctoral Projects Review of treatments for interstitial cystitis Lindsey Ann Miller The University of Toledo Follow this
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Interstitial Cystitis / Painful Bladder Syndrome National Kidney and Urologic Diseases Information Clearinghouse National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF
Translation and Linguistic Validation of the Korean Version of the Dysfunctional Voiding Symptom Score
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urology J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 400-404 Translation and Linguistic Validation of the Korean Version of the Dysfunctional Voiding Symptom Score Hahn-Ey Lee, 1 Walid Farhat, 2 and Kwanjin
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Urology J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29: 400-404 Translation and Linguistic Validation of the Korean Version of the Dysfunctional Voiding Symptom Score Hahn-Ey Lee, 1 Walid Farhat, 2 and Kwanjin
BJU International EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME
 EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
EFFECTS OF INTRAVESICAL HYALURONIC ACID/CHONDROITINE SULFATE IN PATIENTS WITH INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME Journal: Manuscript ID: Manuscript Type: Date Submitted by the Author: BJU-2007-1373
CommonKnowledge. Pacific University. Gina Clark Pacific University. Lauren Murphy Pacific University. Recommended Citation.
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge PT Critically Appraised Topics School of Physical Therapy 2012 The diagnostic accuracy of patient subjective history compared to the gold standard of urodynamic testing
INTERNATIONAL PROSTATE SYMPTOM SCORE IPSS - AUA AS DISCRIMINAT SCALE IN 400 MALE PATIENTS WITH LOWER URINARY TRACT SYMPTOMS (LUTS)
 Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology IPSS IN MALE PATIENTS WITH LUTS Vol. 30 (2): 135-141, March - April, 2004 INTERNATIONAL PROSTATE SYMPTOM
Urological Neurology International Braz J Urol Official Journal of the Brazilian Society of Urology IPSS IN MALE PATIENTS WITH LUTS Vol. 30 (2): 135-141, March - April, 2004 INTERNATIONAL PROSTATE SYMPTOM
Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vol. 41 (4): 739-743, July - August, 2015 doi: 10.1590/S1677-5538.IBJU.2014.0303 Urodynamic outcome of parasacral transcutaneous electrical neural stimulation for overactive bladder in
Mini-Reviews. Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review
 J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol (2004) 17:7 11 Mini-Reviews Interstitial Cystitis in Adolescents and Children: A Review T.F. Mattox, MD, FACOG Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Urogynecology,
Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol
 Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol Adilson Mendes 1 Luiza Hoga 1 Bruna Gonçalves 1 Pamela Silva 1 Priscilla Pereira 1 1. School of Nursing,
Adult women s experiences of urinary incontinence: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol Adilson Mendes 1 Luiza Hoga 1 Bruna Gonçalves 1 Pamela Silva 1 Priscilla Pereira 1 1. School of Nursing,
Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh Repair: A Prospective Study of 105 Cases
 International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
International Journal of Clinical Urology 2018; 2(1): 20-24 http://www.sciencepublishinggroup.com/j/ijcu doi: 10.11648/j.ijcu.20180201.14 Anatomical and Functional Results of Pelvic Organ Prolapse Mesh
Treatment effectiveness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines?
 original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
original research Treatment ness in interstitial cystitis/bladder pain syndrome: Do patient perceptions align with efficacy-based guidelines? Avril Lusty, MD; Elizabeth Kavaler, MD; Kay Zakariasen; Victoria
The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC
 CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS The Role of Pentosan Polysulfate in Treatment Approaches for Interstitial Cystitis Joel M.H. Teichman, MD, FRCSC Department of Surgery, Division of Urology,
4/30/2008. Campbell-Walsh Urology, 9 th edition, Pg
 INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
INTERSTITIAL CYSTITIS/ PAINFUL BLADDER SYNDROME: Advances in Diagnosis and Management Abhishek Seth PGY-3 Department of Urologic Sciences UBC Outline Definition Epidemiology Etiology Diagnosis Evidence
Infection/Inflammation. Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States
 Infection/Inflammation Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States Sra H. Berry,* Marc N. Elliott, Marika Suttorp, Laura M. Bogart, Michael
Infection/Inflammation Prevalence of Symptoms of Bladder Pain Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Among Adult Females in the United States Sra H. Berry,* Marc N. Elliott, Marika Suttorp, Laura M. Bogart, Michael
Addendum 1: International Consultation
 Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Reprinted with Permission of the International Consultation on Urological Diseases and the International Continence Society Hanno PM, Cervigni M, Dinis P, Lin A, Nickel JC, Nordling J, van Ophoven A, Ueda
Mr. GIT KAH ANN. Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur.
 Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Mr. GIT KAH ANN Pakar Klinikal Urologi Hospital Kuala Lumpur drgitka@yahoo.com 25 Jan 2007 HIGHLIGHTS Introduction ICS Definition Making a Diagnosis Voiding Chart Investigation Urodynamics Ancillary Investigations
Interstitial and chronic cystitis. Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall?
 Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Interstitial and chronic cystitis Have you heard about the 2-component protection for the bladder wall? What is special about Instillamed? 2-component protection for the bladder wall Instillamed is an
Voiding Diary. Begin recording upon rising in the morning and continue for a full 24 hours.
 Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Urodvnamics Your physician has scheduled you for a test called URODYNAMICS. This test is a series of different measurements of bladder function and can be used to determine the cause of a variety of bladder
Is Urethral Pain Syndrome Really Part of Bladder Pain Syndrome?
 Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Review ISSN 2465-8243(Print) / ISSN: 2465-8510(Online) https://doi.org/10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.22 Urogenit Tract Infect 2017;12(1):22-27 http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.14777/uti.2017.12.1.&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2017-04-25
Overactive Bladder: Prevalence and Implications in Brazil
 european urology 49 (2006) 1087 1092 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-Urology Overactive Bladder: Prevalence and Implications in Brazil Claudio Teloken
european urology 49 (2006) 1087 1092 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.europeanurology.com Neuro-Urology Overactive Bladder: Prevalence and Implications in Brazil Claudio Teloken
LILACS - JOURNAL SELECTION AND PERMANENCE CRITERIA
 LILACS - JOURNAL SELECTION AND PERMANENCE CRITERIA April/2010 LILACS - Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature, coordinated by BIREME, is a regional index that establishes the bibliographic
LILACS - JOURNAL SELECTION AND PERMANENCE CRITERIA April/2010 LILACS - Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature, coordinated by BIREME, is a regional index that establishes the bibliographic
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis
 Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
Bladder pain syndrome / Interstitial cystitis Terminology The term bladder pain syndrome/interstitial cystitis (BPS/IC) is defined as the presence of chronic pain, pressure, or pelvic discomfort lasting
DATA GATHERING METHOD
 DATA GATHERING METHOD Dr. Sevil Hakimi Msm. PhD. THE NECESSITY OF INSTRUMENTS DEVELOPMENT Good researches in health sciences depends on good measurement. The foundation of all rigorous research designs
DATA GATHERING METHOD Dr. Sevil Hakimi Msm. PhD. THE NECESSITY OF INSTRUMENTS DEVELOPMENT Good researches in health sciences depends on good measurement. The foundation of all rigorous research designs
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE?
 PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
PELVIC HEALTH PHYSICAL THERAPY AND THE NURSE PRACTITIONER: WHAT S GOING ON DOWN THERE? Kathy Curry, PT, DPT Physical Therapy Today Pelvic Health Physical Therapy () Objectives: Discuss components of pelvic
Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome?
 SCIENTIFIC PAPER Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome? Charles W. Butrick, MD ABSTRACT Background: Endometriosis and interstitial cystitis/painful
SCIENTIFIC PAPER Patients With Chronic Pelvic Pain: Endometriosis or Interstitial Cystitis/Painful Bladder Syndrome? Charles W. Butrick, MD ABSTRACT Background: Endometriosis and interstitial cystitis/painful
INJINTERNATIONAL. Original Article INTRODUCTION
 Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Official Journal of Korean Continence Society / Korean Society of Urological Research / The Korean Children s Continence and Enuresis Society / The Korean Association of Urogenital Tract Infection and
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Interstitial Cystitis
 J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
J Obstet Gynecol India Vol. 58, No. 1 : January/February 2008 pg 24-31 Review Article Interstitial Cystitis Satpathy Hemant K, Taylor Richert Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, CUMC, Omaha, NE, USA,
Infection/Inflammation. A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome
 Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
Infection/Inflammation A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Controlled Trial of Adalimumab for Interstitial Cystitis/Bladder Pain Syndrome Philip C. Bosch*, From the Department of Urology, Palomar Medical
The UNIVERSITY of NEWCASTLE
 The UNIVERSITY of NEWCASTLE R esearch C entre for G ender and H ealth Characteristics of Australian women with incontinence according to incontinence severity and treatment-seeking behaviour Results from
The UNIVERSITY of NEWCASTLE R esearch C entre for G ender and H ealth Characteristics of Australian women with incontinence according to incontinence severity and treatment-seeking behaviour Results from
Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio Region
 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiology Biostatistics and Public Health - 2016, Volume 13, Number 1 Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio
ORIGINAL ARTICLES Epidemiology Biostatistics and Public Health - 2016, Volume 13, Number 1 Reliability of the Columbia Impairment Scale (C.I.S.) for adolescents: Survey among an Italian sample in Lazio
BJUI. Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive bladder
 ; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
; 2010 Lower Urinary Tract PATIENT S PERCEPTION OF INTENSITY OF URGENCY SCALE IN OAB CARTWRIGHT ET AL. BJUI Validity and reliability of the patient s perception of intensity of urgency scale in overactive
Central Texas Myofascial Release New Patient Information Sheet P a g e 1
 P a g e 1 Welcome to our practice! Please help us serve you better by taking a few minutes to provide the following information. If a section does not apply please mark N/A. Name: Last Name First Name
P a g e 1 Welcome to our practice! Please help us serve you better by taking a few minutes to provide the following information. If a section does not apply please mark N/A. Name: Last Name First Name
Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
Painful Bladder Syndrome Department of Urology Patient Information What What is Painful is Painful Bladder Bladder Syndrome? Syndrome? Painful bladder syndrome also known as Interstitial Cystitis is a
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological disorder among premature ejaculation subjects
 (2007) 19, 321 325 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological
(2007) 19, 321 325 & 2007 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/07 $30.00 www.nature.com/ijir ORIGINAL ARTICLE Validation of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale and the psychological
Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****, Leite DRC *, Sousa TTS *, Ciconelli RM **,*** Abstract. Introduction
 ARTIGO ORIGINAL TRANSLATION INTO BRAZILIAN PORTUGUESE, CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATATION OF THE SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE ( SLEQOL) Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****,
ARTIGO ORIGINAL TRANSLATION INTO BRAZILIAN PORTUGUESE, CULTURAL ADAPTATION AND VALIDATATION OF THE SYSTEMIC LUPUS ERYTHEMATOSUS QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTIONNAIRE ( SLEQOL) Freire EAM *,**,***, Bruscato A ***,****,
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice
 Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Alan J. Wein Christopher Chapple Overactive Bladder in Clinical Practice Authors Alan J. Wein Division of Urology University of Pennsylvania Health System Philadelphia
Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis
 n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
n The Leeds Teaching Hospitals NHS Trust Painful Bladder Syndrome/Interstitial Cystitis Information for patients Leeds Centre for Women s Health Welcome to the Department of Urogynaecology Your consultant
CHRONIC PELVIC PAIN OF BLADDER ORIGIN:
 ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
ACCREDITATION This activity has been planned and implemented in accordance with the Essential Areas and policies of the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education through the joint sponsorship
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS)
 Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Interstitial Cystitis (IC)/Painful Bladder Syndrome(PBS) Ene G. George M.D., FACOG, FPMRS Kaiser Permanente Baldwin Park Division of Urogynecology Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology PBS/IC I have
Women s Health Development Unit, School of Medical Science, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia b
 The Malay Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC-QLQ C30): Reliability and Validity Study Yusoff N a, Low WY b and Yip CH c ORIGINAL
The Malay Version of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Quality of Life Questionnaire (EORTC-QLQ C30): Reliability and Validity Study Yusoff N a, Low WY b and Yip CH c ORIGINAL
Title: Reliability and validity of the adolescent stress questionnaire in a sample of European adolescents - the HELENA study
 Author's response to reviews Title: Reliability and validity of the adolescent stress questionnaire in a sample of European adolescents - the HELENA study Authors: Tineke De Vriendt (tineke.devriendt@ugent.be)
Author's response to reviews Title: Reliability and validity of the adolescent stress questionnaire in a sample of European adolescents - the HELENA study Authors: Tineke De Vriendt (tineke.devriendt@ugent.be)
Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial Cystitis: Pilot Study Combining Behavioral, Pharmacologic, and Endoscopic Therapies
 Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Neurourology Multimodal Therapy for Interstitial Cystitis: A Pilot Study International Braz J Urol Vol. 35 (4): 467-474, July - August, 2009 Multimodal Therapy for Painful Bladder Syndrome / Interstitial
Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery
 Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Medical History Questionnaire Name: Date: Age: D.O.B. Race: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical
Loyola University Medical Center Female Pelvic Medicine & Reconstructive Surgery Medical History Questionnaire Name: Date: Age: D.O.B. Race: What is the nature of your current gynecologic or urologic medical
Validity and reliability of a 36-item problemrelated distress screening tool in a community sample of 319 cancer survivors
 Validity and reliability of a 36-item problemrelated distress screening tool in a community sample of 319 cancer survivors Melissa Miller 1, Joanne Buzaglo 1, Kasey Dougherty 1, Vicki Kennedy 1, Julie
Validity and reliability of a 36-item problemrelated distress screening tool in a community sample of 319 cancer survivors Melissa Miller 1, Joanne Buzaglo 1, Kasey Dougherty 1, Vicki Kennedy 1, Julie
Cystoscopy and urethroscopy
 Page 1 of 5 Cystoscopy and urethroscopy Introduction This leaflet is provided to give you information about undergoing cystoscopy and/or urethroscopy. What is a cystoscopy? A cystoscopy is a procedure
Page 1 of 5 Cystoscopy and urethroscopy Introduction This leaflet is provided to give you information about undergoing cystoscopy and/or urethroscopy. What is a cystoscopy? A cystoscopy is a procedure
Measurement Properties of the Malay Version of the Golombok-Rust Inventory of Marital State (GRIMS) Among Urological Patients.
 ORIGINAL PAPER Measurement Properties of the Malay Version of the Golombok-Rust Inventory of Marital State (GRIMS) Among Urological Patients. Quek Kia Fatt, Low Wah Yun, And Hassan Razack, Loh Chit Sin,
ORIGINAL PAPER Measurement Properties of the Malay Version of the Golombok-Rust Inventory of Marital State (GRIMS) Among Urological Patients. Quek Kia Fatt, Low Wah Yun, And Hassan Razack, Loh Chit Sin,
flow resulting from damage to blood vessels can also contribute to sexual dysfunction.
 U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services NATIONAL INSTITUTES OF HEALTH Troublesome bladder symptoms and changes in sexual function are common health problems as people age. Having diabetes can mean
Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
 ISRN Neurology, Article ID 167030, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/167030 Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Rebecca
ISRN Neurology, Article ID 167030, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/167030 Research Article Urinary Catheterization May Not Adversely Impact Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients Rebecca
Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial cystitis
 bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
bs_bs_banner International Journal of Urology (2014) 21 (Suppl 1), 43 47 doi: 10.1111/iju.12314 Review Article Hypersensitive bladder: A solution to confused terminology and ignorance concerning interstitial
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study
 Case Study Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study Melissa, a 28 year old veteran comes to your office complaining of lower abdominal pain for the past 6 months. She has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen but they
Case Study Chronic Pelvic Pain Case Study Melissa, a 28 year old veteran comes to your office complaining of lower abdominal pain for the past 6 months. She has tried acetaminophen and ibuprofen but they
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome
 Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
Interstitial Cystitis - Painful Bladder Syndrome Interstitial cystitis (in-tur-stish-ul sis-tie-tis) also called painful bladder syndrome is a chronic condition in which you experience bladder pressure,
2 Types of psychological tests and their validity, precision and standards
 2 Types of psychological tests and their validity, precision and standards Tests are usually classified in objective or projective, according to Pasquali (2008). In case of projective tests, a person is
2 Types of psychological tests and their validity, precision and standards Tests are usually classified in objective or projective, according to Pasquali (2008). In case of projective tests, a person is
Development of a self-reported Chronic Respiratory Questionnaire (CRQ-SR)
 954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
954 Department of Respiratory Medicine, University Hospitals of Leicester, Glenfield Hospital, Leicester LE3 9QP, UK J E A Williams S J Singh L Sewell M D L Morgan Department of Clinical Epidemiology and
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website:
 Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
Mrs Ami Shukla Consultant Gynaecologist and Obstetrician Lead Urogynaecologist, Northampton General Hospital Website: www.female-gynecologist.com What is Painful Bladder (PBS) or Interstitial Cystitis
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS.
 D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
D-MANNOSE, CRANBERRY AND VITAMIN C (CYSTOMAN 100MG) ARE EFFECTIVE IN PREVENTING URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS IN MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS SUBJECTS. Maria Laura Lopes De Carvalho, MD Guido Francavilla, MD Roberta
The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and after surgery for stress incontinence
 BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2003, Vol. 110, pp. 983 988 The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and
BJOG: an International Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology November 2003, Vol. 110, pp. 983 988 The development of a questionnaire to measure the severity of symptoms and the quality of life before and
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria. Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017
 Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Prostatitis: overview and assessment of pain outcomes and implications for inclusion criteria Michel Pontari IMMPACT-XX Meeting July 13, 2017 NIDDK Classification of Prostatitis 1 Type I: Acute Bacterial
Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis Scale (QOL-RA Scale)
 Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Advances in Medical Sciences Vol. 54(1) 2009 pp 27-31 DOI: 10.2478/v10039-009-0012-9 Medical University of Bialystok, Poland Validation of the Russian version of the Quality of Life-Rheumatoid Arthritis
Dr. Krithika Doshi. Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical?
 Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
Chronic Pelvic Pain: Headache in the Pelvis Pelvic Pain in Men- Are they all Noncyclical? Dr Kritika Doshi Introduction: Chronic pelvic and urogenital pain syndromes have recently been recognized as a
RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION SYMPTOM INDEX, PROSTATE VOLUME, PATIENTS WITH BENIGN PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA
 American Urological Association symptom index for BPH RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION SYMPTOM INDEX, PROSTATE VOLUME, AND DISEASE-SPECIFIC QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTION IN PATIENTS WITH
American Urological Association symptom index for BPH RELATIONSHIPS BETWEEN AMERICAN UROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION SYMPTOM INDEX, PROSTATE VOLUME, AND DISEASE-SPECIFIC QUALITY OF LIFE QUESTION IN PATIENTS WITH
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium
 Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
Evidence on Therapeutic Uses of Pentosan Polysulfate Sodium Excerpts from: Drugdex Monograph on Pentosan Edition: online URL: www.thomsonhc.com/home/dispatch Date Added: 29/04/2010 17:42:55 Source Notes:Evidence
5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France
 A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
A review of the 4 th INTERNATIONAL CONSULTATION ON INCONTINENCE 5-8 July, 2008, Palais des Congrès, Paris, France The 4 th International Consultation on Incontinence was held 5-8 July 2008 in Paris and
Citation for published version (APA): Bade, J. J. (1996). Interstitial cystitis: new clinical aspects Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Interstitial cystitis Bade, Jurjen Jacob IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults
 Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Diagnosis and Mangement of Nocturia in Adults Christopher Chapple Professor of Urology Sheffield Teaching Hospitals University of Sheffield Sheffield Hallam University UK 23 rd October 2015 Terminology
Describing the learning curve for bulbar urethroplasty
 Original Article Describing the learning curve for bulbar urethroplasty Marco Spilotros, Sachin Malde, Tamsin J. Greenwell Department of Urology, University College London Hospital, London, UK Contributions:
Original Article Describing the learning curve for bulbar urethroplasty Marco Spilotros, Sachin Malde, Tamsin J. Greenwell Department of Urology, University College London Hospital, London, UK Contributions:
Validity and reliability of measurements
 Validity and reliability of measurements 2 Validity and reliability of measurements 4 5 Components in a dataset Why bother (examples from research) What is reliability? What is validity? How should I treat
Validity and reliability of measurements 2 Validity and reliability of measurements 4 5 Components in a dataset Why bother (examples from research) What is reliability? What is validity? How should I treat
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH
 TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
TREATMENT OF OVERACTIVE BLADDER IN ADULTS FUGA 2016 KGH CONTENTS Overactive bladder (OAB) Treatment of OAB Beta-3 adrenoceptor agonist (Betmiga ) - Panacea? LASER treatment - a flash in the pan or the
Interstitial cystitis
 Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Interstitial cystitis Ilse Truter, PharmITCom Consulting Bladder Normal protective bladder lining Thinning of the protective bladder lining Pinpoint bleeding (glomerulations) on the bladder wall Hunner
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients
 Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Women s & Children s Directorate The TVT Operation - a guide for patients This leaflet was written for women who are considering having a TVT operation. If you have any questions that aren't answered by
Incontinence. Urinary. In Adults. THIS PUBLICATION IS OUT OF DATE. For most current information:
 Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Urinary Incontinence In Adults A Patient's Guide r I When you eat and drink, your body absorbs the liquid. The kidneys filter out waste products from the body fluids and make urine. Urine travels down
Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_
 207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
207 Alkalinized Lidocaine and Heparin Provide Immediate Relief of Pain and Urgency in Patients with Interstitial Cystitisjsm_2542 207..212 C. Lowell Parsons, MD,* Paul Zupkas, PhD,* Jeffrey Proctor, MD,
