CORE IDEAS CROSS CUTTING CONCEPTS
|
|
|
- Brianna Bryant
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Meet The Microbes! NGSS Alignment CORE IDEAS Core Idea LS1: From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes LS1.A: Structure and Function Core Idea LS2: Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics LS2.B: Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems Patterns Cause and effect: Mechanism and explanation Scale, proportion, and quantity Systems and system models Energy and matter: Flows, cycles, and conservation Structure and function Stability and change CROSS CUTTING CONCEPTS PRACTICES Asking questions (for science) and defining problems (for engineering) Developing and using models Planning and carrying out investigations Analyzing and interpreting data Using mathematics, information and computer technology, and computational thinking Constructing explanations (for science) and designing solutions (for engineering) Engaging in argument from evidence Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information Module 1 Meet The Microbes! 1
2 In this activity students will view different types of microbes using images provided (Student Handouts A and B). They will use their understanding of what microbes look like to create a microbe out of clay. Each student will decide whether their microbe is useful or harmful and should create a name for their microbe. Students will present their microbes to the class and should explain what features were selected and why they were chosen. Students should also be able to explain whether the microbe is helpful or harmful to humans or other organism. Time: 1 class period Materials: Images of microbes Petri dishes Clay (many colors) Student Handout A: What are Microbes? Student Handout B: Microbe Trivia Student Handout C: Make Your Microbe Polymer clay examples by Dan Bollinger - Own work. Licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - jpg#mediaviewer/file:polymer_clay_examples.jpg Microbe images by Module 1 Meet The Microbes! 2
3 Activity 2: Student Handout A: What Are Microbes? 1. Microbes are living organisms (except for viruses). 2. They are so small we need a microscope to see them. 3. They come in different shapes and sizes. What are microbes? 4. They are found EVERYWHERE! 5. Some microbes are useful or even good for us. 6. Some microbes can make us ill. The 3 types of microbes in order of size: Viruses Bacteria Fungi Viruses are the smallest, even smaller than bacteria, and can sometimes live INSIDE bacteria! Some viruses make us sick. Diseases like chickenpox and the flu are caused by viruses. Viruses can spread from one person to another but it depends on the type of virus. Spirals Rods Campylobacter Lactobacillus Balls Fungi are the largest of all microbes. Fungi can be found in the air, on plants and in water. Mold, which grows on bread, is a type of fungus. Some antibiotics are made by fungi! Influenza Staphylococcus They are so small that 1000 s of bacteria could fit on the period at the end of this sentence. Some bacteria are helpful in cooking, for example, making yogurt and cheese. Some bacteria are harmful and cause infection. Bacteria multiply very fast. There are three different types of bacteria: spirals, rods, and balls. Dermatophyte Penicillium Module 1 Meet The Microbes! 3
4 Activity 2: Student Handout B: Microbe Trivia There are 3 different types of microbe bacteria, viruses and fungi. From the pictures and descriptions below, can you work out which microbe is which? Staphylococcus Hint: Remember there are three types of bacteria: rods, spirals, and balls. I am round in shape and I like to live in your nose or armpits! If I live on your skin I can give you spots. If I get into your bloodstream I can make you ill! What kind of microbe am I? Influenza My friends call me the flu. I m very generous; I like to give people headaches and fever. I easily spread from one person to another through coughing and sneezing. People call me friendly because I change milk into yogurt! When you eat me in yogurt, I live in your guts and help you digest other food. Lactobacillus Penicillium You ll find me growing on old oranges or stale bread making them look moldy. Humans use me to make an antibiotic known as Penecillin, which can make them better, but only from bacterial infections! I like to live on your skin. I especially like living in damp places like between the toes on sweaty feet! When I live there I give people athlete s foot! Dermatophyte I have a pretty spiral shape and I like to live in chickens but if I get into your tummy I make you very ill I can give you diarrhea! Campylobacter Module 1 Meet The Microbes! 4
5 Activity 2: Student Handout C: Make Your Microbe Design a microbe of your choice with what you ve learned so far: either a bacterium, a virus, or a fungus, using materials provided. Decide if your microbe will be helpful or harmful. Viruses Bacteria Fungi Name Your Microbe: Helpful or Harmful? Module 1 Meet The Microbes! 5
Key Stage 2 Science PSHE English Estimated Teaching Time
 Key Stage 2 Science Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans (Upper KS2 only) PSHE Core Theme 1: Health and Wellbeing English Reading and Comprehension Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread
Key Stage 2 Science Working Scientifically Animals Including Humans (Upper KS2 only) PSHE Core Theme 1: Health and Wellbeing English Reading and Comprehension Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread
Germs. Grade Level: 1-2
 Germs Grade Level: 1-2 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Page pages 6 Practice Page page 7 Homework Page page 8-9 Answer Key page 10 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask: If you
Germs Grade Level: 1-2 Teacher Guidelines pages 1 2 Instructional Pages pages 3 5 Activity Page pages 6 Practice Page page 7 Homework Page page 8-9 Answer Key page 10 Classroom Procedure: 1. Ask: If you
MICROORGANISM NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS
 MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
MICROORGANISMS: NORMAL FLORA AND PATHOGENS BELL WORK- GO TO PAGE 468 IN NEW BOOK; READ THE GIVEN DEFINITIONS AND FIRST THREE PARAGRAPHS AND GIVE A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF THE FOLLOWING: MICROORGANISM PATHOGENIC
Section 1.3, Harmful Microbes, introduces students to the variety of health issues caused by harmful microbes.
 4, 5, 6, 7, 4, eveloping thinking, eveloping communication, ealth and emotional wellbeing: (1a), 1e). stimated eaching ime 50 minutes ection 1.3, armful icrobes, introduces students to the variety of health
4, 5, 6, 7, 4, eveloping thinking, eveloping communication, ealth and emotional wellbeing: (1a), 1e). stimated eaching ime 50 minutes ection 1.3, armful icrobes, introduces students to the variety of health
Warm Up. What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease?
 Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Warm Up What do you think the difference is between infectious and noninfectious disease? Infectious Diseases Chapter 14 Lesson 1: Types of Infectious Disease Infectious Diseases An infectious disease
Key Stage 2 / Science Years 5 & 6
 1 Key Stage 2 / Science Years 5 & 6 Contents 1 Curriculum Links... 3 2 Welcome to e-bug... 5 3 Partner Information... 7 4 Pack Content... 8 5 Microorganisms An Introduction... 9 6 Microorganisms Useful
1 Key Stage 2 / Science Years 5 & 6 Contents 1 Curriculum Links... 3 2 Welcome to e-bug... 5 3 Partner Information... 7 4 Pack Content... 8 5 Microorganisms An Introduction... 9 6 Microorganisms Useful
The invisible world of germs and cells
 DG3 DISCUSSION GUIDE 1 What is the smallest living thing that you can see with your naked eyes? DG1 OBJECTIVE: To introduce the of living microorganisms. 1. Ask: What is the smallest living thing that
DG3 DISCUSSION GUIDE 1 What is the smallest living thing that you can see with your naked eyes? DG1 OBJECTIVE: To introduce the of living microorganisms. 1. Ask: What is the smallest living thing that
2. Alcohol causes 2.5 million deaths in the world each year. In deaths of year olds, 9% of the time alcohol was involved.
 1 Drug classification Drugs change what is happening inside our bodies. Some drugs help our bodies to work properly. Some cause them damage. Draw lines to match each type of drug to some common names for
1 Drug classification Drugs change what is happening inside our bodies. Some drugs help our bodies to work properly. Some cause them damage. Draw lines to match each type of drug to some common names for
Microbiology. Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites
 Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Microbiology Bacteria Viruses Fungi Parasites On page C1: What do YOU think? What do you think 8.L.1 means? (look at your section tab) Choose 2 vocabulary words and write a definition and a drawing for
Communicable Diseases
 Lesson 5.1 Communicable Diseases By Carone Fitness You have probably been in a situation similar to Corry's. The common cold is a communicable disease. 1 Defined Communicable diseases are illnesses that
Lesson 5.1 Communicable Diseases By Carone Fitness You have probably been in a situation similar to Corry's. The common cold is a communicable disease. 1 Defined Communicable diseases are illnesses that
Section One: Background Material
 Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
Section One: Background Material What is the problem? Every day people all over the world get sick from the food they eat. This sickness is called foodborne disease and is caused by dangerous microorganisms
SEPUP ITEM BANK. Item Banks TR-253. Multiple choice. Circle the best answer.
 Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Item Banks Name: Teacher: School: Date: SEPUP ITEM BANK UNIT C: CELL BIOLOGY AND DISEASE Multiple choice. Circle the best answer. 1. Which of the following graphs best represents how an infectious disease
Infectious Diseases through Viruses. Obj. 3.c. & 3.g.
 Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Infectious Diseases through Viruses Obj. 3.c. & 3.g. Diseases Caused By Cells A disease is a condition that stops the body from functioning normally. Non-infectious diseases are not spread from person
Acute respiratory illness This is a disease that typically affects the airways in the nose and throat (the upper respiratory tract).
 Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Influenza glossary Adapted from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, US https://www.cdc.gov/flu/glossary/index.htm and the World Health Organization http://www.wpro.who.int/emerging_diseases/glossary_rev_sept28.pdf?ua=1
Immune System Review. 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes.
 Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
Name Immune System Review Date 1. State one way white blood cells protect the body from foreign microbes. 2. Cells of the immune system are able to respond to the presence of invading organisms because
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA
 OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
OPTIONAL GRADE 8 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.6.L.14.5 AA SC.6.L.14.5 AA Identify and investigate the general functions of the major systems of the human body (digestive, respiratory, circulatory, reproductive,
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L AA
 OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
OPTIONAL BIOLOGY 1 STUDY PACKET IMMUNE SYSTEM SC.912.L.14.52 AA SC.912.L.14.52 AA Explain the basic functions of the human immune system, including specific and nonspecific immune response, vaccines and
Infection, Detection, Prevention...
 Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Infection, Detection, Prevention... A disease is any change that disrupts the normal function of one or more body systems. Non infectious diseases are typically caused by exposure to chemicals or are inherited.
Biology. Slide 1 of 30. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Biology 1 of 30 2 of 30 What causes disease? 3 of 30 Disease A disease is any change, other than an injury, that disrupts the normal functions of the body. Disease-causing agents are called pathogens.
Infectious Disease. Unit 6 Lesson 1
 Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Infectious Disease Unit 6 Lesson 1 Reminder Getting Started Pick up your Infectious Disease Notes Objectives Identify five types of infectious agents Describe ways in which infections can spread Explain
Bacteria & Viruses. Biology Science Department
 Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
Bacteria & Viruses What do you already know? What are the differences between viruses and bacteria? Are all bacteria harmful? When you get a cold, should you take an antibiotic to help you get better?
About the Authors. Table of Contents. Learn more
 Ask A Biologist activity for classroom and home By Julie Dunlap, Esmeralda Manzano, Vanessa Vierkoetter, and Satina Sund Table of Contents Experiment Overview 2 Teaching Tips 4 Tree map 6 Cold and Flu
Ask A Biologist activity for classroom and home By Julie Dunlap, Esmeralda Manzano, Vanessa Vierkoetter, and Satina Sund Table of Contents Experiment Overview 2 Teaching Tips 4 Tree map 6 Cold and Flu
2 WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu?
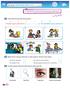 WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu? Joe and Sarah learn about flu. We are going to study flu too. Think about flu and order these pictures. 3 4 5 6 The easiest way to catch the flu The most difficult way to catch
WHAT do WE KNoW ABoUT flu? Joe and Sarah learn about flu. We are going to study flu too. Think about flu and order these pictures. 3 4 5 6 The easiest way to catch the flu The most difficult way to catch
Section 4, Treatment of Infection, explores the use of antibiotics and medicine in treating various illnesses and disease.
 P2 P7 SCN 1-13a SCN 2-20b HWB 1-15a, 2-15a HWB 1-16a, 2-16a HWB 1-17a, 2-17a Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes Section 4, Treatment of Infection, explores the use
P2 P7 SCN 1-13a SCN 2-20b HWB 1-15a, 2-15a HWB 1-16a, 2-16a HWB 1-17a, 2-17a Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes Section 4, Treatment of Infection, explores the use
8.L.1 Practice Questions
 Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name: Date: 1. Why should antibiotics be given to a person who is ill with a bacterial disease like strep throat, but not to a person who has a viral disease like flu?. ntibiotics kill bacteria but not
Name Date Germs Make Me Sick! by Melvin Berger Vocabulary Word Unscramble Unscramble the words. Use the words in the text box for help.
 Vocabulary Word Unscramble Unscramble the words. Use the words in the text box for help. germs ache bacteria viruses shapes microscope breathe harmful cells proteins antibodies multiply waste poisons damaged
Vocabulary Word Unscramble Unscramble the words. Use the words in the text box for help. germs ache bacteria viruses shapes microscope breathe harmful cells proteins antibodies multiply waste poisons damaged
Next, your teacher will ask everyone who is infected to raise their hand. How many people were infected?
 Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the
 Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Small living organism Not visible to the naked eye Must be viewed under a microscope Found everywhere in the environment, including on and in the human body Many Microorganisms are part of normal flora
Microbiology. Microbiology
 Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Microbiology Microbiology What are GERMS? What are GERMS? Microorganisms that make you sick (pathogens) There are many different types of microorganisms: Bacteria (strep throat, food poisoning like E.
Infectious Disease Learning Packet 3. Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention
 Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
Name Infectious Disease: Causes and Prevention Objective #3: The students will be able to identify one or more infectious diseases and their cause(s). The students will be able to list at least 3 ways
Microorganisms. 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell?
 Name: ate: 1. How does a virus cause a person to develop a common cold? 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell? A. invades the host cell to reproduce.
Name: ate: 1. How does a virus cause a person to develop a common cold? 3. Which of the following is one important difference between a virus and a bacterial cell? A. invades the host cell to reproduce.
Immune System. Before You Read. Read to Learn
 Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Immune System 37 section 1 Infectious Diseases Biology/Life Sciences 10.d Students know there are important differences between bacteria and viruses with respect to their requirements for growth and replication,
Certificate in Understanding Common Childhood Illnesses
 CACHE Level 2 Certificate in Understanding Common Childhood Illnesses LE SPREAD OF INFECTION POLICIES AND PROCEDURES M P HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS SA SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Workbook 1 ALLERGIES ACUTE AND CHRONIC
CACHE Level 2 Certificate in Understanding Common Childhood Illnesses LE SPREAD OF INFECTION POLICIES AND PROCEDURES M P HEALTHY ENVIRONMENTS SA SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS Workbook 1 ALLERGIES ACUTE AND CHRONIC
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C
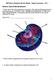 2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
2018 Science Olympiad: Microbe Mission - Sample Tournament Div C Section A: Types of cells and their parts 1. Please state if the cell is prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Then label the following molecular components
CHAPTER AT A GLANCE. Science Class (SA-II)- IX
 13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
13 CHAPTER AT A GLANCE Health is a general condition of a preson s mind and body. According to WHO (World Health Organisation) health is a state of physical, metal and social well-being of a person. To
What Is This Module About? What Will You Learn From This Module?
 What Is This Module About? Have you ever experienced feeling well one day then suddenly being taken ill the next? Do you know why this happens? This module will address this question. It is about germs
What Is This Module About? Have you ever experienced feeling well one day then suddenly being taken ill the next? Do you know why this happens? This module will address this question. It is about germs
2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria?
 STATION 1: 1) Explain the benefit of saprotrophic bacteria/fungi. 2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria? 3) When transitioning from a low power to a higher power on a microscope, describe
STATION 1: 1) Explain the benefit of saprotrophic bacteria/fungi. 2) In what two ways do Archaea differ from true bacteria? 3) When transitioning from a low power to a higher power on a microscope, describe
Chapter 39 Viruses. Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium.
 Chapter 39 Viruses Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium. They are not made of cellsand cannot reproduceon their own. Therefore they are not alive according to our rules.
Chapter 39 Viruses Viruses are tiny. They are much smaller (50 times) than a bacterium. They are not made of cellsand cannot reproduceon their own. Therefore they are not alive according to our rules.
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 12: Simple Organisms NC Essential Standard: 1.2.3 Explain how specific cell adaptations help cells survive in particular environments 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms
Communicable and Noncommunicable. Diseases
 Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable
S. Jett, NBCT Montevallo Middle School
 S. Jett, NBCT Montevallo Middle School 1 Create a pamphlet/brochure about resistance skills. 2 Write a commercial about abstinence. 3 Find the location and phone number for the local red cross. 1 explain
S. Jett, NBCT Montevallo Middle School 1 Create a pamphlet/brochure about resistance skills. 2 Write a commercial about abstinence. 3 Find the location and phone number for the local red cross. 1 explain
The Chain of Infection
 The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
The Chain of Infection As healthcare professionals, it is important to understand two facts about infection: 1.The various ways infection can be transmitted. 2. The ways the infection chain can be broken.
Next, your teacher will ask everyone who is infected to raise their hand. How many people were infected?
 Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Some Similarities between the Spread of an Infectious Disease and Population Growth by Jennifer Doherty and Dr. Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2007 1 How Does an Infectious
Our Heart Rate. Measuring our heart rate at rest and after physical exercise
 Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Our Heart Rate USA Standards Correlation FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 The Dimension I practices listed below
Dimension 2 Cross Cutting Concepts Dimension 1 Science and Engineering Practices Our Heart Rate USA Standards Correlation FRAMEWORK FOR K-12 SCIENCE EDUCATION 2012 The Dimension I practices listed below
Lesson 3: Immunizations
 K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
K-W-L Graphic Organizer K (Know) What do you know about W (Want) What do you want to know about L (Learned) What did you learn about Glossary 1. antibodies: proteins created by the immune system to fight
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE
 NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
NOTES OF CH 13 WHY DO WE FALL ILL CLASS 9TH SCIENCE Topics in the Chapter Introduction Health Community Health Differences between Being Healthy and Disease-free Disease and its cases Types of diseases
How to Become a Flu Fighter
 How to Become a Flu Fighter Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 6-8 1 Lesson One Understanding the Flu Virus 2 Five Codes of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand the flu virus Code 2: Know what
How to Become a Flu Fighter Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 6-8 1 Lesson One Understanding the Flu Virus 2 Five Codes of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand the flu virus Code 2: Know what
Airborne Viruses, Mold, and Bacteria
 Airborne Viruses, Mold, and Bacteria A Basic Understanding of Airborne Hazards for the Code Enforcement Officer in Georgia Student Performance Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of airborne viruses,
Airborne Viruses, Mold, and Bacteria A Basic Understanding of Airborne Hazards for the Code Enforcement Officer in Georgia Student Performance Objectives 1. Have a deeper understanding of airborne viruses,
Germs! Germs! Everywhere!
 Germs! Germs! Everywhere! Introduction Microorganisms, sometimes called microbes, are tiny living creatures that cannot be seen without a microscope. There are microscopic animals, plants, and fungi, as
Germs! Germs! Everywhere! Introduction Microorganisms, sometimes called microbes, are tiny living creatures that cannot be seen without a microscope. There are microscopic animals, plants, and fungi, as
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease
 The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
The Immune System: Your Defense Against Disease Terms: Immune System: body s primary defense against disease-causing microorganisms. Immune: condition in which a body is able to permanently fight a disease.
What are Germs? Click on the germ to find out more.
 Click here to start What are Germs? Germs are tiny organisms that cause disease. Germs can make you ill if they get into your stomach or your lungs. You need a microscope to see germs. Germs are carried
Click here to start What are Germs? Germs are tiny organisms that cause disease. Germs can make you ill if they get into your stomach or your lungs. You need a microscope to see germs. Germs are carried
Do First: Answer in your DFAD
 Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer each question with a short answer. Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card 1. What body system does HIV attack? 2. What cells does HIV attack? 3. Is HIV a virus or
Do First: Answer in your DFAD Answer each question with a short answer. Haveouts Guided Notes Pen/pencil CAV Card 1. What body system does HIV attack? 2. What cells does HIV attack? 3. Is HIV a virus or
Max s hand washing school
 Hand hygiene Max s hand washing school Max s hand washing school What is this brochure about? This brochure will teach children facts regarding hand hygiene and why it is so important. This material is
Hand hygiene Max s hand washing school Max s hand washing school What is this brochure about? This brochure will teach children facts regarding hand hygiene and why it is so important. This material is
What is HIV? Shoba s story. What is HIV?
 1 What is HIV? Shoba s story What is HIV? The immune system HIV inside a cell Medicines against HIV The future Answering Shoba s questions Shoba s story Shoba is a fifteen-year-old student in Pakistan.
1 What is HIV? Shoba s story What is HIV? The immune system HIV inside a cell Medicines against HIV The future Answering Shoba s questions Shoba s story Shoba is a fifteen-year-old student in Pakistan.
Chapter 13. Preventing Infectious Diseases. Copyright by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
 Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Preventing Infectious Diseases Preventing Infectious Diseases Contents Section 1 What Are Infectious Diseases? Section 2 Protecting Yourself from Infectious Diseases Section 3 Common Infectious Diseases
Microbes: Friend or Foe?
 Microbes: Friend or Foe? A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Book Word Count: 1,658 LEVELED BOOK U Written by Lisa Ing Illustrated by Cende Hill U W Z Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Microbes: Friend or Foe? A Reading A Z Level U Leveled Book Word Count: 1,658 LEVELED BOOK U Written by Lisa Ing Illustrated by Cende Hill U W Z Visit www.readinga-z.com for thousands of books and materials.
Five Features of Fighting the Flu
 Five Features of Fighting the Flu Public Health Emergency Preparedness Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 9-12 1 Day One Understand the Flu Virus 2 Five Features of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand
Five Features of Fighting the Flu Public Health Emergency Preparedness Pandemic Influenza Prevention Curriculum Grades 9-12 1 Day One Understand the Flu Virus 2 Five Features of Flu Fighting Code 1: Understand
Christmas Infection Jingle
 Christmas Infection Jingle Here are a few thoughts to think about with your children when you have watched our video. Christmas Infection Jingle Dashing to the loo I feel too ill to play I wish I d washed
Christmas Infection Jingle Here are a few thoughts to think about with your children when you have watched our video. Christmas Infection Jingle Dashing to the loo I feel too ill to play I wish I d washed
Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed
 Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed This table reflects the cumulative weekly total number of seasonal influenza vaccine doses distributed in the US as reported to CDC by influenza
Table of Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Total Doses Distributed This table reflects the cumulative weekly total number of seasonal influenza vaccine doses distributed in the US as reported to CDC by influenza
Coughs, Colds & Pneumonia
 Coughs, colds and pneumonia affect millions of people worldwide and can kill. Older children can learn how to avoid coughs or colds, stop them spreading and prevent them developing. They can learn about
Coughs, colds and pneumonia affect millions of people worldwide and can kill. Older children can learn how to avoid coughs or colds, stop them spreading and prevent them developing. They can learn about
Bacteria. Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles)
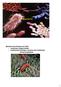 Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
Bacteria Bacteria and Archaea are both: unicelluar (single-celled) prokaryotes (lacking a nucleus and membrane bound organelles) 1 Grouped by their need for oxygen obligate anaerobes are poisoned by oxygen
Pathogens!! What are Pathogens? 12/7/14. Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens
 Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Pathogens!! Copyright 2011. PEER.tamu.edu Infectious Diseases are Caused by Pathogens What are Pathogens? Pathogens are microbes (microscopic living organisms) or other agents that cause diseases. Ex:
Science Home Learning Task. Year 9. GCSE Keeping healthy
 Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Keeping healthy Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 18 April Hand in: Monday 25 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment Target Investigating science Welcome
Science Home Learning Task Year 9 GCSE Keeping healthy Name Tutor Group Teacher Given out: Monday 18 April Hand in: Monday 25 April Parent/Carer Comment Staff Comment Target Investigating science Welcome
Bacteria and Viruses
 CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
CHAPTER 13 LESSON 3 Bacteria and Viruses What are viruses? Key Concepts What are viruses? How do viruses affect human health? What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree
Bacteriology Virology Mycology Parasitology Immunology Pathology Epidemiology. Microbe alternate terms Germs, microorganisms, pathogens, agents, bugs
 1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
1 BIO 205 Microbiology for Health Professionals The study of microscopic agents as they relate to human health The causes of infectious disease. The control of infectious disease. Host defenses against
Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc.
 The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
The Immune System Disease: any change, other than an injury, that disrupts homeostasis. Pathogen: disease-causing agent such as bacteria, virus, etc. Infectious disease- caused by pathogen Germ theory
Vaccines for Children
 Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
Vaccines for Children 12 24 old Our goal is to offer your family the best care possible, which includes making sure your child is up to date on all vaccines. DTaP (Diptheria, Tetanus, Pertussis) Vaccine
DISEÑO DEL SERVICIO. GUÍAS Página 1 de 6
 GUÍAS Página 1 de 6 REINFORCEMENT PLAN Date: Day 27 Month 04 Year 2018 TERM: I COMPREHENSION GOAL: The student will develop understanding about living things, the classification of living things, nutrition
GUÍAS Página 1 de 6 REINFORCEMENT PLAN Date: Day 27 Month 04 Year 2018 TERM: I COMPREHENSION GOAL: The student will develop understanding about living things, the classification of living things, nutrition
Name Class Date. Infection in which a virus inserts its nucleic acid into the DNA of the host cell and is duplicated with the cell s DNA
 Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Name Class Date 20.1 Viruses Lesson Objectives Explain how viruses reproduce. Explain how viruses cause infection. BUILD Vocabulary A. The chart below shows key terms from the lesson with their definitions.
Infection Agents: Agent Icky
 Infection Agents: Agent Icky 1.1 Welcome Welcome to Infectious Agents: Agent Icky an online Science tutorial for students in 6th grade. 1.2 Objective Hi, I m Agent Icky, and I used to be an infectious
Infection Agents: Agent Icky 1.1 Welcome Welcome to Infectious Agents: Agent Icky an online Science tutorial for students in 6th grade. 1.2 Objective Hi, I m Agent Icky, and I used to be an infectious
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease
 Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
Chapter 6: Fighting Disease Lesson 1: Infectious Disease How Do Pathogens Cause Disease? Ancient times, people had different ideas about what caused disease. - Evil spirits - Swamp air - Imbalance of four
SNEEZE ZONE BACKGROUND INFORMATION MATERIALS TO RUN THE ACTIVITY. Teacher s notes
 BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many diseases are airborne and can spread in tiny droplets of water or aerosols that people cough or sneeze into the air. Aerosols in a sneeze can travel at more than 100 kilometres
BACKGROUND INFORMATION Many diseases are airborne and can spread in tiny droplets of water or aerosols that people cough or sneeze into the air. Aerosols in a sneeze can travel at more than 100 kilometres
It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
 A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
A Publication of the National Center for Farmworker Health Let s Learn about Respiratory Infections It is very common to get symptoms like cough, sore throat, runny nose and watery eyes. Usually when you
Starting with MICROBIOLOGY
 Starting with MICROBIOLOGY Micro means very small and biology is the study of living things. Microbes are the oldest form of life on Earth. They've been here for 3.8 billion years! Microbes live everywhere.
Starting with MICROBIOLOGY Micro means very small and biology is the study of living things. Microbes are the oldest form of life on Earth. They've been here for 3.8 billion years! Microbes live everywhere.
HEALTH EDUCATION CURRICULUM GUIDE
 GRADE 4 Human Body Revised 6/16 4.1 The student will explain how nutrition and other health-enhancing behaviors affect personal health and academic achievement. Responsible for Teaching The student will
GRADE 4 Human Body Revised 6/16 4.1 The student will explain how nutrition and other health-enhancing behaviors affect personal health and academic achievement. Responsible for Teaching The student will
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine)
 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM Chapter 40 (Miller & Levine) 40 1 Infectious Disease A. How Diseases Are Spread 1. Vectors animals that carry disease-causing organisms from person to person (ticks, mosquitos, other
How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness?
 3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
3.7 Investigate 3.7 Investigate How Does the Digestive System React to Illness and Help Spread Illness? The respiratory and circulatory systems work together to move oxygen around your body. You read in
Pathogens and disease
 Pathogens and disease Task 1: Have a go at completing the exam questions for 35 minutes. Task 2: Review the mark scheme and touch up on the areas we need to work on. Pathogens and disease Pathogens: Microorganisms
Pathogens and disease Task 1: Have a go at completing the exam questions for 35 minutes. Task 2: Review the mark scheme and touch up on the areas we need to work on. Pathogens and disease Pathogens: Microorganisms
KILLS FOUR. Watch Informative Video
 Watch Informative Video 1 KILLS FOUR Virus Bacteria Mold Fungus After a decade of testing Inspired TEC s Cluster Ion Technology emerges as a formidable strategy to combat many of the biological, chemical
Watch Informative Video 1 KILLS FOUR Virus Bacteria Mold Fungus After a decade of testing Inspired TEC s Cluster Ion Technology emerges as a formidable strategy to combat many of the biological, chemical
bacteria review 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria?
 Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Name: Date: 1. Which of the following structures is not found in bacteria? 5. How do human diseases caused by bacteria and diseases caused by viruses react to antibiotics? A. ribosome B. cytoplasm C. cell
Year 9 Science 9B5: Microbes, disease and drugs Home-Learning Challenge
 Year 9 Science 9B5: Microbes, disease and drugs Home-Learning Challenge Name: Form: 9B5 Module Overview and Home-Learning Subject: Science - Biology Year: 9 Half-Term: 1, 2 or 3 Topic: Microbes, disease,
Year 9 Science 9B5: Microbes, disease and drugs Home-Learning Challenge Name: Form: 9B5 Module Overview and Home-Learning Subject: Science - Biology Year: 9 Half-Term: 1, 2 or 3 Topic: Microbes, disease,
Infection Prevention Prevention and Contr
 Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
Infection Prevention and Control o What is an infection? An infection is an illness caused by microorganisms A disease producing micro organism is called a pathogen Most microorganisms are classified as:
Effective January 1, 2003
 Effective January 1, 2003 Because children are more susceptible to communicable diseases and illnesses it is important that staff and parents follow strict control practices. As a result we have created
Effective January 1, 2003 Because children are more susceptible to communicable diseases and illnesses it is important that staff and parents follow strict control practices. As a result we have created
4. Which sentence is a
 1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
1 Read the text and then answer the questions. Your body does a lot of things amazingly well. But as incredible as your body is, it can still be attacked by germs. Germs can invade your body, and until
P2 P7 SCN 1-13a HWB 1-15a, 2-15a HWB 1-16a, 2-16a HWB 1-17a, 2-17a Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes
 P2 P7 SCN 1-13a HWB 1-15a, 2-15a HWB 1-16a, 2-16a HWB 1-17a, 2-17a Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread of Infection section aims to teach students how poor
P2 P7 SCN 1-13a HWB 1-15a, 2-15a HWB 1-16a, 2-16a HWB 1-17a, 2-17a Unit of Study Unit 6 Micro-organisms Estimated Teaching Time 50 minutes The Spread of Infection section aims to teach students how poor
UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS immunize.ca
 UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS Understanding the correct answers Question 1: Vaccination is... (information adapted from Your Child s Best Shot, 3rd edition, page 10) Vaccination (or immunization) is
UNDERSTANDING THE CORRECT ANSWERS Understanding the correct answers Question 1: Vaccination is... (information adapted from Your Child s Best Shot, 3rd edition, page 10) Vaccination (or immunization) is
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System
 Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
Grade 2: Historical Lesson Lesson 8: Louis Pasteur, Andrew Taylor Still, and the Digestive System Objectives: Students will obtain information about the discoveries and contribution made by Louis Pasteur
U.S. Human Cases of Swine Flu Infection (As of April 29, 2009, 11:00 AM ET)
 Swine Flu Call Center Script 4/29/2009 3:00 PM SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks
Swine Flu Call Center Script 4/29/2009 3:00 PM SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks
Infection Prevention for everyday life. Farhana Saeed RN, MHSA, CIC
 Infection Prevention for everyday life By Farhana Saeed RN, MHSA, CIC Handwashing How this can keep you healthy Germs are everywhere, and can get into your body through your eyes, nose and mouth and can
Infection Prevention for everyday life By Farhana Saeed RN, MHSA, CIC Handwashing How this can keep you healthy Germs are everywhere, and can get into your body through your eyes, nose and mouth and can
Thank you for not chewing gum!
 March 25 th, 2015 What do I need today? 1. Pencil 2. Science Notebook 3. Epidemiology note sheet Learning Target: Today we will continue to learn about the fascinating world of disease and epidemiology
March 25 th, 2015 What do I need today? 1. Pencil 2. Science Notebook 3. Epidemiology note sheet Learning Target: Today we will continue to learn about the fascinating world of disease and epidemiology
Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL
 In-Home Aides Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL 2016-1 Infection Control and the In-home Aide s Role Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or
In-Home Aides Part ners in Quality Care - APRIL 2016-1 Infection Control and the In-home Aide s Role Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or
Operated by Public Health England. Key Stage 3 / Science
 Operated by Public Health England Key Stage 3 / Science h 1 2 Welcome to e-bug 2 e-bug has been designed to bring the world of microbes and antibiotics to life for children in the school environment. The
Operated by Public Health England Key Stage 3 / Science h 1 2 Welcome to e-bug 2 e-bug has been designed to bring the world of microbes and antibiotics to life for children in the school environment. The
How many students at St. Francis Preparatory School in New York City have become ill or been confirmed with swine flu?
 Swine Flu Call Center Script SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks of swine flu happen
Swine Flu Call Center Script SWINE FLU QUESTIONS What is swine flu? Swine Influenza, also called swine flu, is a respiratory disease of pigs caused by type A influenza viruses. Outbreaks of swine flu happen
DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD?
 DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD? Starter: How is your body like a castle? Our skin is like the castle walls but microbes can enter through gaps in the defences AIM Can use simple physical models to show
DISEASE HOW ARE DISEASES SPREAD? Starter: How is your body like a castle? Our skin is like the castle walls but microbes can enter through gaps in the defences AIM Can use simple physical models to show
Immune System and Disease. Chapter 31
 Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Immune System and Disease Chapter 31 31.1 PATHOGENS AND HUMAN ILLNESS Key Concept Germs cause many diseases in humans Microogranisms (microscopic particles) cause certain diseases proposed by Louis Pasteur
Downloaded from
 Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
Class IX: Biology Chapter: Why do we fall ill Chapter Notes Key learnings: 1) Our body s well-being is dependent on the proper functioning of its cells and tissues. 2) All our body parts and activities
H1N1 FLU H1N1 Influenza (Flu) 2009 H1N1 Flu in People. What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? Why is 2009 H1N1 flu sometimes called swine flu?
 2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
2009 H1N1 Influenza (Flu) What is 2009 H1N1 flu swine flu? 2009 H1N1 (also known as swine flu ) is a new flu virus that makes people sick. The 2009 H1N1 flu spreads from person to person like seasonal
2009 H1N1 Influenza A Virus EHS&RM
 2009 H1N1 Influenza A Virus What is 2009 H1N1 (swine flu)? 2009 H1N1 (sometimes called swine flu ) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This virus was originally referred to as swine flu
2009 H1N1 Influenza A Virus What is 2009 H1N1 (swine flu)? 2009 H1N1 (sometimes called swine flu ) is a new influenza virus causing illness in people. This virus was originally referred to as swine flu
