Visual system, vestibular and auditory system
|
|
|
- Dustin McKenzie
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 BULBUS OCULI polus anterior polus posterior meridiani Visual system, vestibular and auditory system equator axis bulbi externus linea visus Optical power + 60 D MORPHOLOGY OF BULBUS OCULI Tunica fibrosa Sclera Cornea Tunica vasculosa Choroidea Corpus ciliare Iris Tunica interna Retina TUNICA FIBROSA - SCLERA limbus sclerae (vasa ciliaria ant.) sinus venosus sclerae (Schlemm s canal) lamina cribrosa sclerae (nn. ciliares breves, longi) vasa ciliaria post.) eguator (vv. vorticocae) spatium episclerale spatium perichoroidale TUNICA FIBROSA - CORNEA TUNICA VASCULOSA - CHOROIDEA Limbus corneae (sulcus sclerae) Facies ant. cornae (vertex cornae, polus ant.) Facies post. cornae Epithelium ant. cornae Substantia propria cornae Endothelium cornae circulus arteriosus iridis major circulus arteriosus iridis minor Optical power + 40 D Fibrotic tissue membrane pigment cells (dark chambre) vessels 1
2 TUNICA VASCULOSA CORPUS CILIARE Corona ciliaris processus ciliares, plicae ciliares Orbiculus ciliaris Zonula ciliaris fibrae zonulares Musculus ciliaris fibrae circulares, fibrae meridionales TUNICA VASCULOSA IRIS margo ciliaris margo pupillaris (pupilla) facies ant. iridis (anulus iridis major, minor) facies post. iridis STROMA IRIDIS m. sphincter pupillae (miosis, parasympaticus) m. dilataror pupillae (mydriasis, sympaticus) pigment (eye color) TUNICA INTERNA RETINA FUNDUS OCULI Pars caeca retinae pars ciliaris retinae pars iridica retinae Ora serrata ora serrata Pars optica fotoreceptors (coni, bacilli) Macula lutea fovea centralis (linea visus) Vasa centralia retinae (arteriolae et venulae maculares) Macula caeca discus n. optici, papilla n. optici, excavatio disci MORPHOLOGY OF RETINA Stratum pigmentosum Stratum neuroepitheliale coni (6-7 million, macula lutea) bacilli (130 million) Stratum ganglionare retinae bipolar neurons Stratum ganglionare n. optici external segment external segment multipolar neurons 2
3 OPTIC TRACT 1. neuron coni, bacilli 2. neuron bipolar cells 3. neuron multipolar cells 4. neuron corpus geniculatum laterale Area 17, 18, 19 LENS CRYSTALINA Facies anterior lentis (polus anterior lentis) Facies posterior lentis (polus posterior lentis) Equator lentis (fibrae zonulares) MORPHOLOGY Capsula lentis Substantia lentis (fibrae lentis) Epithelium lentis Cortex lentis Nucleus lentis ACCOMMODATION-LENS Optic power D a) Looking into the distance b) Near vision (m. ciliaris) CORPUS VITREUM Camera vitrea bulbi Membrana vitrea Stroma vitreum Humor vitreus Fossa hyaloidea Canalis hyaloideus a. hyaloidea) CAMERAE BULBI Camera oculi anterior Camera oculi posterior Camera vitrea Humor aquosus Angulus iridocornealis Lig. pectinatum anguli iridocornealis Spatia iridocornealia Sinus venosus sclerae Venulae aquosae MUSCULI BULBI m. rectus superior, inferior, medialis, lateralis m. obliquus superior, inferior m. levator palpebrae superioris 3
4 FASCIAE ORBITALES PALPEBRAE palpebra superior, inferior rima palpebrarum Periorbit (m. orbitalis) Vagina bulbi Spatium episclerale Corpus adiposum orbitae angulus oculi medialis, lateralis facies anterior, posterior palpebrae limbus palpebralis anterior (cilia, gll. sebacae, gl. ciliares) limbus palpebralis posterior rivus lacrimalis papilla lacrimalis (punctum lacrimale) EYELID MORPHOLOGY CONJUNCTIVA tunica conjunctiva palpebrarum tunica conjunctiva bulbi fornix conjunctivae sup., inf., saccus conjunctivae septum orbitale tarsus superior, inferior gl. tarsales (Meibomi) lig. palpebrale med., lat. m. tarsalis sup., inf. plica semilunaris conjunctivae lacus lacrimalis caruncula lacrimalis papilla lacrimalis punctum lacrimale m. orbicularis oculi APPARATUS LACRIMALIS Gl. lacrimalis (pars orbitalis a palpebralis) Ductuli exretorii (fornix conjunctivae sup.) Lacrimae Punta lacrimalis Canaliculi lacrimales (ampulla canaliculli lacrimalis) Saccus lacrimalis (fornix sacci lacrimalis) Ductus nasolacrimalis (meatus nasi inferior) Plica lacrimalis ARTERIA OPHTHALMICA a. centralis retinae a. lacrimalis (aa. palpebrales lat.) rr. musculares (a. ciliares ant.) a. ciliares posteriores breves et longi (circulus art. iridis major, minor) a. supraorbitalis a. ethmoidalis post. et ant. (a. meningea ant.) aa. palpebrales med. a. supratrochlearis a. dorsalis nasi 4
5 VENAE OPHTHALMICAE v. ophthalmica sup. v. nasofrontalis vv. palpebrales vv. ethmoidales ant., post., v. lacrimalis vv. vorticosae ORGANUM VESTIBULOCOCHLEARE Cochlear apparatus perception of sound Vestibular apparatus perception of position and movement of the head in space vv. ciliares v. centralis retinae v. ophthalmica inferior venous net on the bottom of orbit (fissura orbitalis sup., sinus cavernosus) (fissura orbitalis inf., plexus pterygoideus) Anastomosis with v. facialis (v. faciei profunda, v. angularis), Division of the organum vestibulocochleare I. Auris externa (external ear) catches sound waves and transport them to the tympanic cavity 1) Auricula 2) Meatus acusticus externus 3) Membrana tympani II. Auris media (middle ear) 1) Cavum tympani 2) Ossicula auditus and their ligg. and articulationes 3) Musculi ossiculorum auditus 4) Tunica mucosa cavi tympani 5) Tuba auditiva (auditory tube - Eustachian tube) 6) Cellulae mastoideae I. Auris externa (external ear) 1) Auricula lateral surface - cartilago auriculae, lobulus auriculae helix, crus helicis, scapha, anthelix, crura anthelicis, fossa triangularis, concha auriculae with cymba conchae, cavum conchae, porus acusticus externus, tragus, antitragus, incisura intertragica medial surface - eminentia scaphae, eminentia conchae, eminentia triangularis, fossa anthelicis III. Auris interna (internal ear) 1) Labyrinthus osseus (bone labyrinth) 2) Labyrinthus membranaceus (membranous labyrinth) 2) Meatus acusticus externus (about 3.5 cm long) Porus acusticus externus (med. 1/3 VM, middle 1/3 T, lat 1/3 VM) isthmus between bone and cartilagineous part lat. 2/3 cartilago meatus acustici externi (groove opened up and dorsally), med. 1/3 meatus acusticus externus osseus (pars tympanica, sulcus tympanicus, incisura tympanica, spina tympanica anterior and posterior Skin with glandulae ceruminosae (cerumen), tragi 3. Membrana tympani = (TM) (ear drum) (about 11x9 mm) Limbus membranae tympani, anulus fibrocartilagineus in sulcus tympanicus, umbo, stria mallearis, prominentia mallearis, plica mallearis anterior and posterior and between them pars flaccida (Schrapnell s membrane), rest of (TM) - pars tensa membranae tympani, light reflex Position: horizontal plane - 45 o (inclination of TM) Structure of (TM) Stratum fibrosum + anulus fibrocartilagineus, externally skin, internally mucosis. 5
6 CAVUM TYMPANI (TYMPANIC CAVITY=TC) Shape as a biconcave lens Lateral wall (paries membranaceus): membrana tympani, recessus epitympanicus and hypotympanicus Medial wall (paries labyrinthicus): promontorium (1st whorl of cochlea), fenestra cochleae (with membrana tympani secundaria), fenestra vestibuli (with basis of stapes), prominentia canalis semicircularis lateralis and prominentia canalis facialis, sulcus promontorii (for n. tympanicus), processus cochleariformis (turns here tendo of m. tensor tympani) Upper wall (paries tegmentalis): tegmen tympani, apertura tympanica canalis nervi petrosi minoris (=lesser petrosal nerve) Caudal wall (paries jugularis): apertura tympanica canaliculi tympanici Anterior wall (paries caroticus): canalis musculotubarius (semicanalis m. tensoris tympani and semicanalis tubae auditivae), canaliculi caroticotympanici, fissura petrotympanica (for chorda tympani) Posterior wall (paries mastoideus): antrum mastoideum, cellulae mastoideae, eminentia pyramidalis (for m. stapedius), apertura tympanica canaliculi chordae tympani Right tympanic cavity (view through paries membranaceus) paries tegmentalis paries mastoideus paries labyrinthicus paries caroticus paries jugularis Páč,L. (1995):Anatomie člověka III., Brno, p. 82 Ossicula auditus (malleus, incus, stapes) Malleus caput mallei, collum mallei, manubrium mallei (fuses with membrana tympani and forms stria mallearis), processus anterior (to the fissura petrotympanica), processus lateralis (fuses with membrana tympani and forms prominentia mallearis) proc.ant. proc.lat. Manubrium Incus corpus incudis, crus breve, crus longum with processus lenticularis (joins with head of stapes) Stapes caput stapedis, basis stapedis (located in fenestra vestibuli), crus anterius (straight) and crus posterius (curved) Ligaments: Lig. mallei anterius (through fissura petrotympanica to spina sphenoidalis) Lig. mallei superius (joins head of malleus to the tegmen of TC (= tympanic cavity) Lig. mallei laterale (to the edge of incisura tympanica) Lig. incudis superius (joins corpus incudis with tegmen of TC) Lig. incudis posterius (between crus breve incudis and dorsal wall of TC) Lig. anulare stapedis (joins basis stapedis and fenestra vestibuli) Membrana stapedis (between crura and basis stapedis) Joints: Articulatio incudomallearis (caput mallei + corpus incudis, sellar joint) Articulatio incudostapedia (processus lenticularis incudis + caput stapedis, spheroid joint but with minimal movements) s s l a Tendo m. tensoris tympani Joint incudomallearis p Tendo m. stapedis Lg anulare stapesdis 6
7 Muscles: M. tensor tympani (wall of upper part of musculotubar canal tendon around of processus cochleariformis manubrium mallei, V.) M. stapedius (eminentia pyramidalis crus posterius stapedis, VII., takes off stapes from the fenestra vestibuli) Mucosis: Plica mallearis anterior (covers processus anterior of malleus) Plica mallearis posterior (from collum mallei dorsally up and laterally recessus membranae tympani superior = Prusack s cavity /lat. pars flaccida MT, med. collum mallei, cran. lig. mall. lat, caud. continues to recessus MT posterior) BOTH MALLEAR PLICAE form PLICA CHORDAE TYMPANI (chorda passes between manubrium mallei and crus longum incudis) Plica incudis (from crus longum incudis to dorsal wall of TC) Plica stapedis (covers stapes and tendon of m. stapedis) Tuba auditiva (auditory tube, Eustachian tube) joins tympanic cavity with pharynx (baroperception) cm, ostium pharyngeum TA from here lat. + dors. + up and opens in TC to anterior wall as ostium tympanicum of TA. Lateral 1/3 is located in semicanalis TA = pars ossea TA, medial 2/3 = pars cartilaginea TA is opened caudally (with lamina membranacea), between bone and cartilaginous part is isthmus TA; mucosis continuation of nasopharynx mucosis and mucosis of TC, tonsilla tubaria Muscles: m. tensor veli palatini and m. levator veli palatini. Cellulae mastoideae (antrum mastoideum, mucosis continues from CT) Vessels and nerves of CT Arteries: A. tympanica inferior (from a. pharyngea ascendens - a. car. ext., canaliculus tympanicus) A. tympanica posterior (from a. stylomastoidea a.car.ext. to CT through canaliculus chordae tympani) A. tympanica superior (a. meningea media a.car.ext. through can. n. petrosi minoris) A. tympanica anterior (a. maxillaris a.car.ext. through fissura petrotympanica) Rr. carotici (a.car.int.) Veins: to the v. meningea media, sinus petrosus superior and plexus pterygoideus AURIS INTERNA I. Labyrinthus osseus 1) Vestibulum and canales semicirculares ossei 2) Cochlea 3) Perilympha II. Labyrinthus membranaceus 1) Labyrinthus vestibularis 2) Labyrinthus cochlearis 3) Endolympha Nerves: Sensory: Plexus tympanicus (n. tympanicus IX., nn. caroticotympanici sympathetic, + VII.) Motor: n. tensor tympani and n. stapedius Labyrinthus osseus I. Labyrinthus osseus 1. Vestibulum 2. Canales semicirculares ossei 3. Cochlea 4. Meatus acusticus internus 1. Vestibulum fenestra vestibuli (for basis stapedis) recessus utriculi=ellipticus with macula cribrosa superior (for n. utriculoampullaris) recessus sacculi=sphericus with macula cribrosa media (for n. saccularis) crista vestibuli with pyramis vestibuli recessus cochlearis for caecum vestibulare apertura interna aquaeductus vestibuli macula cribrosa posterior (n. ampullaris posterior) scala vestibuli cochleae 2. Canales semicirculares ossei Lateralis, anterior, posterior crus osseum simplex and commune, crus osseum ampullare 7
8 Fundus meatus acustici interni sv 3. Cochlea Basis cochleae, cupula cochleae a) Canalis spiralis cochleae b) Modiolus c) Lamina spiralis ossea l.s.ossea st Tractus spiralis foraminosus modiolus Ad a) Canalis spiralis cochleae by scala vestibuli is joined with vestibulum, scala tympani passes under vestibulum, by fenestra cochleae opens to CT, ductus perilymphaticus Ad b) Modiolus basis modioli (tractus spiralis foraminosus), canales longitudinales modioli, canalis spiralis modioli (contents bodies of bipolar neurons ganglion spirale cochleae Ad c) Lamina spiralis ossea Scala vestibuli (opens to vestibulum), scala tympani (opens to CT membrana tympani secundaria), hamulus laminae spiralis, helicotrema Meatus acusticus internus Porus acusticus internus, fundus meatus acustici interni, crista transversa, area nervi facialis, area vestibularis superior (for n. utriculoampullaris), area vestibularis inferior (n. saccularis and foramen singulare for n. ampullaris posterior), area cochlearis with tractus spiralis foraminosus Vestibular ganglia II. Labyrinthus membranaceus Spatium perilymphaticum with perilymph, inside endolymph a) Labyrinthus vestibularis b) Labyrinthus cochlearis Ad II a) Labyrinthus vestibularis 1) Utriculus (on medial wall of vestibulum in recessus utriculi, from it pass 3 ductus semicirculares, by ductus utriculosaccularis is joined with sacculus) 2) Sacculus (on medial wall of vestibulum in recessus sacculi) Epithelium maculae staticae (macula utriculi is horizontal, macula sacculi is vertical, membrana statoconiorum with statoconia, ganglion vestibulare Ductus utriculosaccularis, ductus endolymphaticus aquaeductus vestibuli 8
9 3) Ductus semicirculares crus membranaceum ampullare, crus membranaceum simplex (lat. canal), crus membranaceum commune (ant. and post. canal), crista ampullaris, cupula ampullaris movement of endolymph, register movements of the head Ad II. B Labyrinthus cochlearis Ductus cochlearis with ceacum vestibulare and caecum cupulare, ductus reuniens (joins ductus cochlearis with sacculus). Ductus cochlearis divides bone cochlea into scala tympani and scala vestibuli helicotrema (for perilymph), membrana tympani secundaria in the fenestra cochleae end of scala tympani. Ductus cochlearis Lateral wall joins with periosteum of canalis spiralis cochleae, lig. spirale cochleae, lamina basilaris, prominentia spiralis with vas prominens. Tympanic wall forms bottom of DC and separates it from scala tympani, labium limbi vestibulare and tympanicum, foramina nervosa, lat. part of tympanic wall is formed by membrana basilaris (between labium limbi tympanicum and lig. spirale cochleae. Organum spirale Corti located on the membrana basilaris (two Corti s columnae cells with hairs), above this is membrana tectoria (medially is joined to labium limbi vestibulare, laterally is free), ganglion spirale cochleae (bipolar cells). Vestibular wall is formed by thin membrana vestibularis. Endolymph from plasma, ductus endolymphaticus to saccus and apertura externa aquaeductus vestibuli to subarachnoideal space. Scala vestibuli Perilymph in spatium perilymphaticum (between bone and membranaceous labytinth) through canaliculus cochleae to subarachnoideal space. Lamina tectoria Paries vestibularis (Reissner s) Arteries of the inner ear: a. labyrinthi (from a. basilaris aa. vertebrales) a. stylomastoidea (a. auricularis posterior) a. tympanica superior (a. meningea media) Corti s organ Scala tympani Ggl. cochleare b. Vv. labyrinthi to the sinus transversus and sinus petrosus superior and inferior c. No lymph (only perilymph and endolymph) d. N. vestibulocochlearis VIII. Hearing Sound waves are catched by auricula, to the meatus acusticus externus, to MT, by movement of ossicula auditis to fenestra vestibuli of inner ear to perilymph of scala vestibuli/tympani oscillation of endolymph basilar membrane and Corti s organ 1. neuron of auditory tract. 9
20 The ear (Vestibulo-acoustic Organs)
 20 The ear (Vestibulo-acoustic Organs) Median line Sella turcica Tuba auditiva Cavum tympani A. carotis int. Superior border of petrous part Membrana tympani Cochlea N. facialis Meatus acusticus internus
20 The ear (Vestibulo-acoustic Organs) Median line Sella turcica Tuba auditiva Cavum tympani A. carotis int. Superior border of petrous part Membrana tympani Cochlea N. facialis Meatus acusticus internus
Eye. iris. pupil. ciliary body
 Eye iris pupil ciliary body Eyeball Anterior segment Posterior segment Eyeball Procesus ciliares Corpus ciliare Pars caeca retinae Sclera Iris Cornea Eyebulb wall Tunica externa (fibrosa) Posterior segment
Eye iris pupil ciliary body Eyeball Anterior segment Posterior segment Eyeball Procesus ciliares Corpus ciliare Pars caeca retinae Sclera Iris Cornea Eyebulb wall Tunica externa (fibrosa) Posterior segment
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D.
 Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Bony and membranous labyrinth. Vestibular system. János Hanics M.D. The position of the inner ear The labyrinthes of the inner ear - Continuous cavity system in the petrous part of temporal bone - Cavity
Auditory and vestibular system. Auris, is = Us, oton
 Auditory and vestibular system Auris, is = Us, oton Auditory and vestibular system external ear (auris externa) middle ear (auris media) internal ear (auris interna) = organum vestibulocochleare External
Auditory and vestibular system Auris, is = Us, oton Auditory and vestibular system external ear (auris externa) middle ear (auris media) internal ear (auris interna) = organum vestibulocochleare External
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Organs of Special Senses
 8 The Organs of Special Senses Special senses are those other than touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception. Vision, hearing, and equilibrium are the special senses discussed in this chapter. The Eye
8 The Organs of Special Senses Special senses are those other than touch, pain, temperature, and proprioception. Vision, hearing, and equilibrium are the special senses discussed in this chapter. The Eye
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR
 Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Gross Anatomy of the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Professor of Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head
Auditory system. Organ of hearing
 Auditory system Organ of hearing Auditory systems is an engineering masterpiece Size of a pea Detects vibrations as small as the size of an atom Responds 1000 times faster than the visual photoreceptors
Auditory system Organ of hearing Auditory systems is an engineering masterpiece Size of a pea Detects vibrations as small as the size of an atom Responds 1000 times faster than the visual photoreceptors
AUDITORY APPARATUS. Mr. P Mazengenya. Tel 72204
 AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
AUDITORY APPARATUS Mr. P Mazengenya Tel 72204 Describe the anatomical features of the external ear Describe the tympanic membrane (ear drum) Describe the walls of the middle ear Outline the structures
Anatomy of the Ear Region. External ear Middle ear Internal ear
 Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
Ear Lecture Objectives Make a list of structures making the external, middle, and internal ear. Discuss the features of the external auditory meatus and tympanic membrane. Describe the shape, position,
The Senses. Chapter 10 7/8/11. Introduction
 Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Gross Anatomy of the. TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR. Assignment: Head to Toe Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
 Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
Gross Anatomy the TEMPORAL BONE, EXTERNAL EAR, and MIDDLE EAR M1 Gross and Developmental Anatomy 9:00 AM, December 11, 2008 Dr. Milton M. Sholley Pressor Anatomy and Neurobiology Assignment: Head to Toe
The Ear. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
The Ear Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology The Ear The ear consists of the external ear; the middle ear (tympanic cavity); and the internal ear (labyrinth), which contains
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The theme of the Eye-socket, bone nasal lesson cavity. bony palate
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 2 The theme of the Eye-socket, bone nasal lesson cavity. bony palate
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear
 Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
Unit VIII Problem 9 Anatomy of The Ear - The ear is an organ with 2 functions: Hearing. Maintenance of equilibrium/balance. - The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear. Middle ear (which is also known
The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Pearson Education, Inc.
 18 The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Introduction Sensory information arrives at the CNS Information is picked up by sensory receptors Sensory receptors are the interface between the nervous
18 The Nervous System: General and Special Senses Introduction Sensory information arrives at the CNS Information is picked up by sensory receptors Sensory receptors are the interface between the nervous
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab
 Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Activity 1: Anatomy of the Eye and Ear Lab 1. Launch the view! Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Eye and Ear Lab section. Launch Augmented Reality mode and scan the
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! Chapter 17 Part 2 Special Senses! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium!
 Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
Chapter 17, Part 2! The Special Senses! Hearing and Equilibrium! SECTION 17-5! Equilibrium sensations originate within the inner ear, while hearing involves the detection and interpretation of sound waves!
For this lab you will use parts of Exercise #18 in your Wise lab manual. Please be sure to read those sections before coming to lab
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise The Eye and Ear Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 17 For this lab you will use parts
Auditory and vestibular system
 Auditory and vestibular system Sensory organs on the inner ear inner ear: audition (exteroceptor) and vestibular apparatus (proprioceptor) bony and membranous labyrinths within the temporal bone (os temporale)
Auditory and vestibular system Sensory organs on the inner ear inner ear: audition (exteroceptor) and vestibular apparatus (proprioceptor) bony and membranous labyrinths within the temporal bone (os temporale)
Sensory system. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
Sensory system Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Sensory receptors Detect stimuli Classified by structure Origin Distribution Modality Structural Classification naked nerve endings
The eye (lens, vitreous body, chambers, accomodation)
 The eye (lens, vitreous body, chambers, accomodation) Zsuzsanna Tóth, PhD Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology- and Embryology Parts of the eye Core: Tunicae bulbi: Tunica fibrosa (fibrous
The eye (lens, vitreous body, chambers, accomodation) Zsuzsanna Tóth, PhD Semmelweis University, Department of Anatomy, Histology- and Embryology Parts of the eye Core: Tunicae bulbi: Tunica fibrosa (fibrous
Chapter 18. The Nervous System. General and Special Senses. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College
 Chapter 18 The Nervous System General and Special Senses Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction Every plasmalemma functions as a receptor for the cell Plasmalemma
Chapter 18 The Nervous System General and Special Senses Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction Every plasmalemma functions as a receptor for the cell Plasmalemma
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR.
 The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
The Ear The ear consists of : 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR 2-THE MIDDLE EAR, OR TYMPANIC CAVITY 3-THE INTERNAL EAR, OR LABYRINTH 1-THE EXTERNAL EAR Made of A-AURICLE B-EXTERNAL AUDITORY MEATUS A-AURICLE It consists
Chapter 10. The Senses
 Chapter 10 The Senses 1 Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Chapter 10 The Senses 1 Introduction A. Sensory receptors detect changes in the environment and stimulate neurons to send nerve impulses to the brain. B. A sensation is formed based on the sensory input.
Ear. Utricle & saccule in the vestibule Connected to each other and to the endolymphatic sac by a utriculosaccular duct
 Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
Rahaf Jreisat *You don t have to go back to the slides. Ear Inner Ear Membranous Labyrinth It is a reflection of bony labyrinth but inside. Membranous labyrinth = set of membranous tubes containing sensory
The cochlea: auditory sense. The cochlea: auditory sense
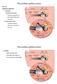 Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Inner ear apparatus 1- Vestibule macula and sacculus sensing acceleration of the head and direction of gravity 2- Semicircular canals mainly for sensing direction of rotation of the head 1 3- cochlea in
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION
 SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
SPECIAL SENSES PART I: OLFACTION & GUSTATION 5 Special Senses Olfaction Gustation Vision Equilibrium Hearing Olfactory Nerves Extend through cribriform plate into nasal cavity on both sides of nasal septum
Anatomy of the ear: Lymphatics
 Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Anatomy of the ear: 1. External ear which consist of auricle and external auditory canal. The auricle has a framework of cartilage except the lobule, the skin is closely adherent to perichonderium at the
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Al Balqa Applied University. Collage of Medicine. Anatomy Lab Check List
 Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Orbit, Eye and Ear Lab Objectives: Recgnize individual structures related
Al Balqa Applied University Cllage f Medicine Anatmy Lab Check List Blck: Nervus System and Special Senses (31500311) Lab Title: Orbit, Eye and Ear Lab Objectives: Recgnize individual structures related
1 Eyelids. Lacrimal Apparatus. Orbital Region. 3 The Orbit. The Eye
 1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
1 1 Eyelids Orbital Region 2 Lacrimal Apparatus 3 The Orbit 4 The Eye 2 Eyelids The eyelids protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure. The upper eyelid is larger and more mobile
The orbit-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
The orbit-2 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Eyelids The eyelids (act like the curtains) protect the eye from injury and excessive light by their closure The upper eyelid
Essential questions. What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2
 Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
Essential questions What are the structures of the sensory system? 3.03 Remember the structures of the sensory system 2 The Senses Eyes Sight Ears Hearing Nose Smell Tongue Taste Skin Touch 3.03 Remember
The sebaceous glands (glands of Zeis) open directly into the eyelash follicles, ciliary glands (glands of Moll) are modified sweat glands that open
 The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
The Orbital Region The orbits are a pair of bony cavities that contain the eyeballs; their associated muscles, nerves, vessels, and fat; and most of the lacrimal apparatus upper eyelid is larger and more
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball
 Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Unit VIII Problem 8 Anatomy: Orbit and Eyeball - The bony orbit: it is protecting our eyeball and resembling a pyramid: With a base directed: anterolaterally. And an apex directed: posteromedially. Notes:
Structure, Energy Transmission and Function. Gross Anatomy. Structure, Function & Process. External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer Ear
 Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
Gross Anatomy Structure, Energy Transmission and Function IE N O ME 1 Structure, Function & Process 4 External Auditory Meatus or Canal (EAM, EAC) Outer third is cartilaginous Inner 2/3 is osseous Junction
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY. Department of human anatomy
 BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline дисципліна HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 12 The theme of the lesson Course Sphenoid and temporal
BOGOMOLETS NATIONAL MEDICAL UNIVERSITY Department of human anatomy GUIDELINES Academic discipline дисципліна HUMAN ANATOMY Module 1 Content module 12 The theme of the lesson Course Sphenoid and temporal
GNK485 The eye and related structures. Prof MC Bosman 2012
 GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
GNK485 The eye and related structures Prof MC Bosman 2012 Surface anatomy Bony orbit Eyeball and Lacrimal apparatus Extra-ocular muscles Movements of the eye Innervation Arterial supply and venous drainage
The Special Senses: Part A
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Janice Meeking, Mount Royal College CHAPTER 15 The Special Senses: Part A Warm Up What is the function of the eyeball? List any structures of the eyeball that you
Special Senses. Accessory Structures of the Eye. The Eye and Vision. Accessory Structures of the Eye. Accessory Structures of the Eye
 8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
8 PART A Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Senses General senses
Head: Special Senses. Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance
 Head: Special Senses Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance TASTE: how does it work? Taste buds on tongue on fungiform papillae ( mushroom-like projections) Each bud contains several cell types in microvilli
Head: Special Senses Taste Smell Vision Hearing/Balance TASTE: how does it work? Taste buds on tongue on fungiform papillae ( mushroom-like projections) Each bud contains several cell types in microvilli
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit
 Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
Major Anatomic Components of the Orbit 1. Osseous Framework 2. Globe 3. Optic nerve and sheath 4. Extraocular muscles Bony Orbit Seven Bones Frontal bone Zygomatic bone Maxillary bone Ethmoid bone Sphenoid
The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the:
 Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Scrub In The white of the eye and the part that maintains its shape is know n as the: a. Cornea b. Pupil c. Retina d. Sclera The structure that is found in the ear and contains the organ of hearing is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium
 Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
Chapter 15 Hearing & Equilibrium ANATOMY OF THE OUTER EAR EAR PINNA is the outer ear it is thin skin covering elastic cartilage. It directs incoming sound waves to the EXTERNAL AUDITORY CANAL, which is
THE SPECIAL SENSES. Introduction Vision
 THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable complexity RECEPTORS: GENERAL PROPERTIES Transducers Receptor Potential Generator Potential RECEPTORS
THE SPECIAL SENSES Introduction Vision RECEPTORS Structures designed to respond to stimuli Variable complexity RECEPTORS: GENERAL PROPERTIES Transducers Receptor Potential Generator Potential RECEPTORS
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to:
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 13 The Special Senses. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 13-1 through 13-24. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 13-1. Identify functions of structures
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 13 The Special Senses. LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 13-1 through 13-24. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 13-1. Identify functions of structures
The Special Senses. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 17 The Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Special Senses Five Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation 3. Vision
17 The Special Senses PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris An Introduction to the Special Senses Five Special Senses 1. Olfaction 2. Gustation 3. Vision
4. Which letter in figure 9.1 points to the fovea centralis? Ans: b
 Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Chapter 9: The Sensory System 1. Proprioceptors are involved in the sense of A) pain. B) temperature. C) pressure. D) movement of limbs. 2. Which are chemoreceptors? A) taste B) olfactory C) proprioceptors
Biology 218 Human Anatomy
 Chapter 22 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Special Senses 1. Olfaction: Sense of Smell (p. 672) i. The olfactory epithelium is located in the superior portion of the nasal cavity and
Chapter 22 Adapted form Tortora 10 th ed. LECTURE OUTLINE A. Special Senses 1. Olfaction: Sense of Smell (p. 672) i. The olfactory epithelium is located in the superior portion of the nasal cavity and
Bi 121 Lab OLFACTION. olfactory bulb, olfactory nerve (=cranial nerve I), olfactory foramina, olfactory epithelium
 Bi 121 Lab Week 9: THE SPECIAL SENSES The special senses include smell, taste, vision, hearing, and balance. In this laboratory exercise, we will look at many of the structures that provide for these senses.
Bi 121 Lab Week 9: THE SPECIAL SENSES The special senses include smell, taste, vision, hearing, and balance. In this laboratory exercise, we will look at many of the structures that provide for these senses.
1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC.
 PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
PA IAC SSC A 1. Axial view, left temporal bone. Plane through the upper antrum (A), superior semicircular canal (SSC) and IAC. IAC VII M I LSC Plane through the IAC, malleus head and incus and the lateral
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing
 Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Anatomy and Physiology of Hearing The Human Ear Temporal Bone Found on each side of the skull and contains the organs for hearing and balance Divided into four major portions: - squamous - mastoid - tympanic
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno
 Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Introduction to biophysics of receptors Biophysics of hearing and vestibular sense 1 Lecture outline
Lectures on Medical Biophysics Department of Biophysics, Medical Faculty, Masaryk University in Brno Introduction to biophysics of receptors Biophysics of hearing and vestibular sense 1 Lecture outline
Special Senses. The Senses. General senses. Special senses. Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
 8 Special Senses Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Senses General senses Touch Pressure Pain Temperature Proprioception Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium
8 Special Senses Yong Jeong, MD, PhD Department of Bio and Brain Engineering The Senses General senses Touch Pressure Pain Temperature Proprioception Special senses Smell Taste Sight Hearing Equilibrium
Introduction. Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups. General senses Special senses
 Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
Introduction Senses our perception of what is out there 2 groups General senses Special senses Central Processing and Adaptation Adaptation the loss of sensitivity after continuous stimulation Tonic receptors
THE CRANIAL NERVES(nervi craniales)
 THE CRANIAL NERVES(nervi craniales) I. Nervus olfactorius the olfactory nerve II. Nervus opticus the optic nerve III. Nervus oculomotorius the oculomotor nerve IV. Nervus trochlearis the trochlear nerve
THE CRANIAL NERVES(nervi craniales) I. Nervus olfactorius the olfactory nerve II. Nervus opticus the optic nerve III. Nervus oculomotorius the oculomotor nerve IV. Nervus trochlearis the trochlear nerve
Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar
 Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar 1 Human Ear For Anatomical description, Ear is divided into Auricle (or pinna) The external auditory canal The Middle Ear and its derivatives The Inner
Anatomy of External and Middle ear. Dr Sai Manohar 1 Human Ear For Anatomical description, Ear is divided into Auricle (or pinna) The external auditory canal The Middle Ear and its derivatives The Inner
The Orbit. The Orbit OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION 9/25/2014. The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? Openings in the orbit
 The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
The eye is a 23 mm organ...how difficult can this be? OCULAR ANATOMY AND DISSECTION JEFFREY M. GAMBLE, OD COLUMBIA EYE CONSULTANTS OPTOMETRY & UNIVERSITY OF MISSOURI DEPARTMENT OF OPHTHALMOLOGY CLINICAL
THE SPECIAL SENSES (1) THE CHEMICAL SENSES: TASTE (GUSTATION) AND SMELL (OLFACTION)
 THE SPECIAL SENSES Senses allow the body to maintain homeostasis by constantly receiving information regarding internal and external environmental changes. There are many ways we sense things, but there
THE SPECIAL SENSES Senses allow the body to maintain homeostasis by constantly receiving information regarding internal and external environmental changes. There are many ways we sense things, but there
Special Senses Sight Smell Taste Hearing and balance. Touch, not special, and not here (Ch 13)
 Special Senses Sight Smell Taste Hearing and balance Touch, not special, and not here (Ch 13) Eye, matey. Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all body sensory receptors are in the eye About half of the
Special Senses Sight Smell Taste Hearing and balance Touch, not special, and not here (Ch 13) Eye, matey. Eye and Associated Structures 70% of all body sensory receptors are in the eye About half of the
7/24/2018. Special Senses. Special sensory receptors. Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium.
 Special Senses Special sensory receptors Distinct, localized receptor cells in head Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium Sense of Vision Ora serrata Ciliary body
Special Senses Special sensory receptors Distinct, localized receptor cells in head Vision - 70% of body's sensory receptors in eye Taste Smell Hearing Equilibrium Sense of Vision Ora serrata Ciliary body
TEXTBOOK REFERENCE & NOTES
 ACTIVITY 8: SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, SENSORY ORGANS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 16 and 19, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. You can also
ACTIVITY 8: SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, SENSORY ORGANS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 16 and 19, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. You can also
The Special Senses. Smell, taste, vision, hearing and equilibrium Housed in complex sensory organs
 The Special Senses Smell, taste, vision, hearing and equilibrium Housed in complex sensory organs Chemical Senses Interaction of molecules with receptor cells Olfaction (smell) and gustation (taste) Both
The Special Senses Smell, taste, vision, hearing and equilibrium Housed in complex sensory organs Chemical Senses Interaction of molecules with receptor cells Olfaction (smell) and gustation (taste) Both
Physiology of human perception
 Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
Physiology of human perception Vision Hearing Thermal and tactile sensations Basic introduction and the list and description of the tasks to be carried out Visible light: 400-700 nm. Vision or sight Anatomy
 Question 1: Briefly describe the structure of the following: (a) Brain (b) Eye (c) Ear (A) Brain: Brain is the main coordinating centre of the body. It is a part of nervous system that controls and monitors
Question 1: Briefly describe the structure of the following: (a) Brain (b) Eye (c) Ear (A) Brain: Brain is the main coordinating centre of the body. It is a part of nervous system that controls and monitors
Olfaction. The Special Senses. The Special Senses. Olfaction. The Ethmoid. Olfactory Receptors. The five special senses are
 The Special Senses The Special Senses Chapter 14 in Open Stax Chapter 17 in Martini The five special senses are Olfaction Gustation Equilibrium Hearing Vision Olfaction Olfaction The sense of smell, or
The Special Senses The Special Senses Chapter 14 in Open Stax Chapter 17 in Martini The five special senses are Olfaction Gustation Equilibrium Hearing Vision Olfaction Olfaction The sense of smell, or
Special Senses. Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others
 Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Special Senses Mechanoreception Electroreception Chemoreception Others Recall our receptor types Chemically regulated: Respond to particular chemicals Voltage regulated: respond to changing membrane potential
Histology of Ear. Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008
 Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
Histology of Ear Histology Department Medical Faculty University of Sumatera Utara 2008 References: Gartner LP, Hiatt JL. Color textbook of histology. 2 nd ed. Philadelphia. WB Saunders company. 2001 Kierszenbaum
AT THIS POINT, STUDENTS ARE RESPONSIBLE FOR THE SPECIFIC SENSORY FUNCTIONS AND MUSCLES INNERVATED BY EACH PERIPHERAL NERVE LISTED.
 ACTIVITY 8: SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, SENSORY ORGANS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 16 and 19, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. You can also
ACTIVITY 8: SPINAL CORD, SPINAL NERVES, SENSORY ORGANS OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapter 16 and 19, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. You can also
Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and. physiology of auditory analyzer. Study 1
 Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and physiology of auditory analyzer Study 1 Auditory analyzer consists of: Auricle Middle ear Inner ear Peripheral Part Transmitting
Methods and technique of endoscopic research of ENTorgans. Clinical anatomy and physiology of auditory analyzer Study 1 Auditory analyzer consists of: Auricle Middle ear Inner ear Peripheral Part Transmitting
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric
 Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Ocular Anatomy for the Paraoptometric Minnesota Optometric Association Paraoptometric CE Friday September 30, 2016 Lindsay A. Sicks, OD, FAAO Assistant Professor, Illinois College of Optometry lsicks@ico.edu
Theme 6. Temporal bone. Its canals and tubules.
 Theme 6. Temporal bone. Its canals and tubules. The Temporal Bone (Os Temporale) is situated at the sides and base of the skull. Each consists of the squama, the petrous (pyramid) with mastoid process
Theme 6. Temporal bone. Its canals and tubules. The Temporal Bone (Os Temporale) is situated at the sides and base of the skull. Each consists of the squama, the petrous (pyramid) with mastoid process
Review Anatomical Features Ossicular Cattle and Pigs, with Special Reference to Morfometric Characteristics Bule Tympani
 Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 06/05/2014 Accepted on : 30/05/2014 Published : 05/06/2014 Review Anatomical Features Ossicular Cattle and Pigs, with Special Reference to Morfometric
Manuscript Processing Details (dd/mm/yyyy) : Received : 06/05/2014 Accepted on : 30/05/2014 Published : 05/06/2014 Review Anatomical Features Ossicular Cattle and Pigs, with Special Reference to Morfometric
ATLAS OF THE SENSORY ORGANS
 ATLAS OF THE SENSORY ORGANS ATLAS OF THE SENSORY ORGANS FUNCTIONAL AND CLINICAL ANATOMY ANDRÁS CSILLAG, MD, PhD, DSc Department of Anatomy, Histology, and Embryology Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary
ATLAS OF THE SENSORY ORGANS ATLAS OF THE SENSORY ORGANS FUNCTIONAL AND CLINICAL ANATOMY ANDRÁS CSILLAG, MD, PhD, DSc Department of Anatomy, Histology, and Embryology Semmelweis University, Budapest, Hungary
Unit 8: The Special Senses
 Unit 8: The Special Senses I. The Senses A. General senses of touch 1. Temperature 2. Pressure 3. Pain B. Special senses 1. Smell 2. Taste 3. Sight 4. Hearing 5. Equilibrium II. The Eye and Vision A. 70%
Unit 8: The Special Senses I. The Senses A. General senses of touch 1. Temperature 2. Pressure 3. Pain B. Special senses 1. Smell 2. Taste 3. Sight 4. Hearing 5. Equilibrium II. The Eye and Vision A. 70%
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing
 20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
20-20,000 Hertz range of human hearing accommodation automatic adjustment in focal length of the lens of the eye; changing the shape of the lens aqueous humor Watery fluid in the anterior chambers of the
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 15 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr.
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Year 6 ENT SMC Otitis Media (Dr. Jalal Almarzooq) - Anatomy of the ear: The ear is divided into 3 parts: External ear.
Cranial nerves.
 Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
Cranial nerves eaglezhyxzy@163.com Key Points of Learning Name Components Passing through Peripheral distribution Central connection Function Cranial nerves Ⅰ olfactory Ⅱ optic Ⅲ occulomotor Ⅳ trochlear
SKULL / CRANIUM BONES OF THE NEUROCRANIUM (7) Occipital bone (1) Sphenoid bone (1) Temporal bone (2) Frontal bone (1) Parietal bone (2)
 Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
Important! 1. Memorizing these pages only does not guarantee the succesfull passing of the midterm test or the semifinal exam. 2. The handout has not been supervised, and I can not guarantee, that these
CHAPTER 17 LECTURE OUTLINE
 CHAPTER 17 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Receptors for the special senses - smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium - are housed in complex sensory organs. B. Ophthalmology is the science that
CHAPTER 17 LECTURE OUTLINE I. INTRODUCTION A. Receptors for the special senses - smell, taste, vision, hearing, and equilibrium - are housed in complex sensory organs. B. Ophthalmology is the science that
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 17 The Special Senses Olfaction: Sense of Smell Smell and taste are chemical senses. The human nose contains 10 million to 100 million receptors
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 17 The Special Senses Olfaction: Sense of Smell Smell and taste are chemical senses. The human nose contains 10 million to 100 million receptors
Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways
 Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways Dr. Gabriella Kékesi 74. Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests.
Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests. The auditory pathways Dr. Gabriella Kékesi 74. Hearing: the function of the outer, the middle and inner ear. Hearing tests.
Histology of the Eye
 Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
Histology of the Eye Objectives By the end of this lecture, the student should be able to describe: The general structure of the eye. The microscopic structure of:»cornea.»retina. EYE BULB Three coats
GENERAL REFLEX ARC. Sense Organs. Lecture Overview. Senses. Melissa Gonzales McNeal 1
 Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sense Organs One definition of man is an intelligence served by organs Ralph Waldo Emerson Brain Spinal Cord Cranial Nerves Anatomical Classification
Nervous System Central Nervous System Peripheral Nervous System Sense Organs One definition of man is an intelligence served by organs Ralph Waldo Emerson Brain Spinal Cord Cranial Nerves Anatomical Classification
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD February 23, 2012 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea
Specialists in the Field Ophthalmology:
 The Eye and Ear Outline of class lecture After studying this chapter you should be able to: 1. List and describe the accessory structures of the eye. 2. Describe the structures and functions of the fibrous
The Eye and Ear Outline of class lecture After studying this chapter you should be able to: 1. List and describe the accessory structures of the eye. 2. Describe the structures and functions of the fibrous
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE Scalp 2. Cranium. 13. Superior sagittal sinus
 TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
TRANSVERSE SECTION PLANE 1 1. Scalp 2. Cranium 3. Superior sagittal sinus 4. Dura mater 5. Falx cerebri 6. Frontal lobes of the cerebrum 7. Middle meningeal artery 8. Cortex, grey matter 9. Cerebral vessels
Eye Movements. Geometry of the Orbit. Extraocular Muscles
 Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Eye Movements Geometry of the Orbit The eye (oculus) is located in the anterior aspect of the orbit: the equator of the eye (defined by a coronal plane passing through its middle) lies at the margin of
Presentation On SENSATION. Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur
 Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Presentation On SENSATION Prof- Mrs.Kuldeep Kaur INTRODUCTION:- Sensation is a specialty area within Psychology that works at understanding how are senses work and how we perceive stimuli in the environment.
Special Senses. Chapter 17
 Special Senses Chapter 17 Overview of Special Senses Special senses: Sense of smell.olfaction. Sense of taste.gustation. Sense of sight.vision. Sense of hearing and balance.auditory and equilibrium. Visual
Special Senses Chapter 17 Overview of Special Senses Special senses: Sense of smell.olfaction. Sense of taste.gustation. Sense of sight.vision. Sense of hearing and balance.auditory and equilibrium. Visual
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE
 REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
REVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK CRANIAL NERVES AND EVERYTHING ELSE OLFACTORY NERVE CN I ANTERIOR CRANIAL FOSSA CRISTA GALLI OF ETHMOID OLFACTORY FORAMINA IN CRIBIFORM PLATE OF ETHMOID BONE CN I OLFACTORY NERVE
o A cushion of fat surrounds most of the eye
 Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Name Period SPECIAL SENSES The Senses of touch o Temperature o Pressure o Pain o Smell o Taste o Sight o Hearing o Equilibrium The Eye and Vision are in the eyes has over a o Most of the eye is enclosed
Bony orbit. Lateral wall: Formed by : the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
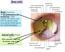 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Unit 8 - The Special Senses 1
 Unit 8 - The Special Senses 1 I. Unit 8: The Special Senses A. The Senses 1. General senses a) Light touch (1) Meissner's corpuscles b) Temperature c) Pressure (1) Pacinian corpuscles; also called lamellar
Unit 8 - The Special Senses 1 I. Unit 8: The Special Senses A. The Senses 1. General senses a) Light touch (1) Meissner's corpuscles b) Temperature c) Pressure (1) Pacinian corpuscles; also called lamellar
THE COCHLEA AND AUDITORY PATHWAY
 Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
Dental Neuroanatomy Suzanne S. Stensaas, PhD April 14, 2010 Reading: Waxman, Chapter 16, Review pictures in a Histology book Computer Resources: http://www.cochlea.org/ - Promenade around the Cochlea HyperBrain
