Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen
|
|
|
- Barnaby Watson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document version below. Document Version Publisher's PDF, also known as Version of record Publication date: 2015 Link to publication in University of Groningen/UMCG research database Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen Copyright Other than for strictly personal use, it is not permitted to download or to forward/distribute the text or part of it without the consent of the author(s) and/or copyright holder(s), unless the work is under an open content license (like Creative Commons). Take-down policy If you believe that this document breaches copyright please contact us providing details, and we will remove access to the work immediately and investigate your claim. Downloaded from the University of Groningen/UMCG research database (Pure): For technical reasons the number of authors shown on this cover page is limited to 10 maximum. Download date:
2 GENERAL INTRODUCTION
3 CHAPTER 1 During the past decades, dental implant therapy has developed into a successful treatment option, both for partial and complete edentulism. The concept of osseointegration was developed in the 1960s by P.I. Brånemark ( ) and co-workers at the University of Göteborg. They were also the first to describe the use of osseointegrated dental implants for anchorage of dental prostheses (Brånemark et al. 1969). In the years thereafter, many different implant systems have been developed and the indications for their application have been gradually extended. Nowadays, the implant retained overdenture has even become the first choice of treatment for the edentulous mandible (Feine et al. 2002). In 2007 it was calculated by Statistics Netherlands that 8% of the Dutch population of fully edentulous patients have dental implants to support a full prosthesis. Overall, there were 800 thousand adults in the Netherlands (6.6% of the total adult population) with one or more dental implants and it is expected that this number will continuously increase. High survival rates of dental implants are generally reported (5-years survival rate 95.7%-97.1%; 10-years survival rate 89.8%-92.8%) (Pjetursson et al. 2012, Jung et al. 2012, Pjetursson et al. 2014). Yet, these survival rates do not surpass the longevity of natural teeth (Holm-Pedersen et al. 2007). Teeth surrounded by healthy periodontal tissues yield longevity of up to 99.5% over 50 years. Periodontally compromised teeth, that are treated and maintained regularly, or endodontically treated non-vital teeth still yield high survival and success rates: 10-year survival rate of 92-93% for periodontally compromised teeth, 10-year survival rate of > 90% for primary endodontically treated teeth as well as retreated teeth, 5-year survival rate < 80% for teeth with existing periapical pathology (Holm-Pedersen et al. 2007). It has therefore been stated that teeth should be given priority over dental implants whenever possible, unless multiple risks jeopardize their long-term prognosis (Lang et al. 2007). Implant failure and success In evaluating implant treatment, survival rate is often used as primary outcome. However, reporting on the clinical condition of surviving implants, i.e. implant success, is also important. To be considered successful, an implant-supported restoration has to meet certain criteria in terms of function (ability to chew), tissue physiology (absence of pain and other pathological processes) and user satisfaction (esthetics and absence of discomfort) (Esposito et al. 1998b). If the performance of an implant-supported restoration, measured in some quantitative way, falls below an acceptable level it is regarded a failure. Failures can be due to technical and biological complications. Technical complications are caused by mechanical damage of the implant, implant components or suprastructures. Biological complications refer to disturbances in the function of the implant characterized by biological processes affecting the tissues supporting the implant (Berglundh et al. 2002). According to occurrence in time biological complications can further be divided into early failures and late failures. In early failures osseointegration has not been sufficiently established and it represents an interference with the healing process. Late failures are characterized by a failure to maintain osseointegration and are caused by a process of loss of osseointegration (Esposito et al. 1998b). The main etiological factors for early dental implant failure are surgical trauma, impaired healing 10
4 ability, infection and insufficient bone volume and quality (Esposito et al. 1998a). In late dental implant failures peri-implant infections are considered to play the predominant role (Esposito et al. 1998a). Epidemiology of peri-implant infections Peri-implant infection results from a disturbance of the balance between the microbiological challenge and host response. Infection limited to the peri-implant mucosa is called peri-implant mucositis. Peri-implantitis is characterized by the additional loss of supporting bone (Zitzmann & Berglundh 2008). If peri-implant infection is left untreated it may ultimately lead to implant loss. The 10-years prevalence of peri-implant mucositis is estimated to be 63% on patient level (range , 95%CI ) and 30% on implant level (range , 95%CI ) (Atieh et al. 2013). The 10-years prevalence of peri-implantitis ranges from 6% to 47% on patient level (mean 18.8%, 95%CI ) and from 2% to 37% on implant level (mean 9.6%, 95%CI ) (Atieh et al. 2013). Based on these prevalence figures it can be concluded that peri-implant infection following dental implant placement is a frequently occurring complication. This is in line with observations on other permanent permucosal/percutaneous osseointegrated medical implants, for example implants for limb prosthesis fixation (Campoccia et al. 2013). Infection rates for this relatively new type of percutaneous devices range from 18% to 55% up to 5 years (Tillander et al. 2010, Tsikandylakis et al. 2014, Brånemark et al. 2014). Infection rates for totally internal osseointegrated implant devices, such as knee or hip prostheses are much lower, being approximately 2% within 2 years of functioning and about 0.5% between 2 and 10 years (Ong et al. 2009, Kurtz et al. 2010). The reason for this lower infection rate is that totally internal implants are placed in a sterile environment and are protected from exposure to external contaminations. Infections of these types of implants are usually caused by contamination of the implant surface before or during surgery or haematogenous seeding from a distant infected site (Campoccia et al. 2013). Permucosal/percutaneous implants on the other hand penetrate the protective body barriers, i.e. mucosal membranes and skin, and create conditions even for limited-aggressive opportunistic pathogens to gain access to and invade internal tissues (Campoccia et al. 2013). GENERAL INTRODUCTION Pathophysiology and etiology of peri-implant infections Plaque accumulation at dental implant-supported restorations induces an inflammatory response in the peri-implant mucosa (peri-implant mucositis), which is characterized by increased proportions of T- and B-cells in the infiltrated connective tissue area (Zitzmann et al. 2001). This host response to the bacterial challenge is similar to the development of gingivitis at teeth (Pontoriero et al. 1994, Zitzmann et al. 2001). Because it is expected that peri-implant mucositis proceeds peri-implantitis as gingivitis proceeds periodontitis, treatment of peri-implant mucositis has to be the pre-requisite for the prevention of peri-implantitis (Lang et al. 2011b). Failure to do so may result in gradual enlargement of the inflammatory cell infiltrate and increase in numbers of plasma cells, lymphocytes, neutrophil granulocytes and macrophages (Berglundh et al. 2011). The apical extension of the inflammatory cell infiltrate in peri-implantitis is 11
5 often more pronounced than in periodontitis and is in most cases located apical of the pocket epithelium and close to the alveolar bone (Berglundh et al. 2011). CHAPTER 1 Microbiology of peri-implant infections The microbiota associated with peri-implant infection varies from person to person and is in most cases dominated by a variety of Gram-negative anaerobic bacteria (Mombelli & Décaillet 2011, Kumar et al. 2012). The use of new molecular techniques such as polymerase chain reaction and pyrosequencing has revealed that the periodontal and peri-implant microflora is far more diverse than previously thought and harbors uncultivable species of which the potential pathogenic role in periodontal and peri-implant diseases is unknown (Kumar et al. 2003, Kumar et al. 2012). Nevertheless, several periodontal bacteria have been associated with peri-implant disease, such as Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, Porphyromonas gingivalis, Tannerella forsythia, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Prevotella intermedia (Mombelli et al. 1987, Leonhardt et al. 1999, Shibli et al. 2008, Kumar et al. 2012). However, there are also some marked differences between the periodontal and peri-implant microbiota. The diversity of peri-implant biofilms, in both health and disease, seems significantly lower than the diversity of subgingival biofilms (Kumar et al. 2012). Furthermore, several species, including previously unsuspected and unknown organisms, seem unique to the peri-implant niche, for example species belonging to the genera Anaerococcus, Anaerovorax, Exiguobacterium and Burkholderia (Kumar et al. 2012). Despite the fact that it has convincingly been demonstrated that micro-organisms are involved in the peri-implant disease process there is no proof that they are always the primary cause of the condition (Mombelli & Décaillet 2011). A suitable ecological environment is necessary to facilitate bacterial colonization and maturation of biofilms. Changes in local ecological conditions that favor the outgrowth of bacterial pathogens may be viewed as the true origin of peri-implant disease (Mombelli & Décaillet 2011). Risk factors of peri-implant infections Patients with a history of treated periodontitis have a significantly greater risk of developing peri-implantitis than patients without such a history (odds ratios ) (Heitz- Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009). This could be due to the fact that periodontitis patients generally harbor more putative periodontal pathogens in their oral cavity than nonperiodontitis patients (Van Winkelhoff et al. 2002, Kumar et al. 2003, Boutaga et al. 2006) and/or these patients may have a potentially higher genetic susceptibility to develop periodontal/peri-implant disease (Gruica et al. 2004, Laine et al. 2006). Smokers have a significantly higher risk for developing peri-implantitis than non-smokers (odds ratios ) and this association seems to be dose-related (Heitz-Mayfield 2008, Heitz-Mayfield & Huynh-Ba 2009). Furthermore there seems to be a synergistic effect between smoking and specific interleukin (IL-1) gene polymorphisms and a higher risk for peri-implantitis (Gruica et al. 2004, Laine et al. 2006). The third major risk factor for peri-implantitis is poor oral hygiene (Heitz-Mayfield 2008). Presence of plaque at > 30% of the sites is associated with increased risk for peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis (Ferreira et al. 2006). This association between full-mouth plaque score and peri-implant infection seems to be dose dependent. Ferreira et al. (2006) 12
6 found an odds ratio for very poor oral hygiene and peri-implantitis of 14.3 (95%CI ). Lack of accessibility for oral hygiene at implant sites, for example due to improper prosthetic reconstructions, has been related to presence of peri-implantitis (Serino & Ström 2009). Furthermore, progression from peri-implant mucositis to periimplantitis is significantly associated with lack of preventive maintenance (Costa et al. 2012). Attendance in a structured maintenance program seems to be strongly related to implant survival (Anner et al. 2010) and a lower prevalence of peri-implantitis (Atieh et al. 2013). Other factors that have been suggested as potential risk factors for development of peri-implant infection include absence of keratinized mucosa (Brito et al. 2014), alcohol consumption (Galindo-Moreno et al. 2005), diabetes (Ferreira et al. 2006), rough implant surface (Astrand et al. 2004) and implant brand (Derks et al. 2015). However, the evidence on these factors is limited and sometimes conflicting. Loose components, caused by fracture of the implant or abutment, or iatrogenic factors such as submucosal remnants of dental cement, implant malpositioning or illfitting suprastructures might also initiate peri-implant inflammation, by provoking a foreign body reaction and/or by creating local ecological conditions which facilitate undisturbed biofilm-formation (Wilson 2009). The role of implant overload on peri-implant bone loss and peri-implant infections is controversial and, due to limited available evidence, not clear. However, it has been suggested that the effect depends on the health status of the peri-implant mucosa (Naert et al. 2012). Supra-occlusal contacts acting in a non-inflamed peri-implant environment do not seem to negatively affect osseointegration, whereas supra-occlusal contacts in the presence of inflammation seem to increase the plaque-induced bone resorption (Naert et al. 2012). Titanium allergy and intolerance have also been suggested as possible initiating factors for peri-implant disease and causes for implant failure (Siddiqi et al. 2011). The prevalence of true titanium allergy seems to be low in dental implant patients (Sicilia et al. 2008), but debris-mediated titanium intolerance could play a more significant role in dental implant failure (Jacobi-Gresser et al. 2013). In fact, wear, or debris-mediated implant loosening, is the most common cause of failure in hip and knee arthroplasties (Landgraeber et al. 2014). Corrosion products of titanium implants may initiate macrophages, through phagocytosis of titanium particles, to produce inflammatory cytokines, leading to osteolysis and loosening of the implant. It has been shown that host factors, or the immune response to titanium particles, plays a significant role in this process. Particularly patients with risk genotypes of IL1A, IL1B, IL1RN and/or TNFA may be more susceptible to this type of dental implant failure than others (Taira et al. 2009, Jacobi-Gresser et al. 2013). GENERAL INTRODUCTION Diagnosis of peri-implant infections Essential in the diagnosis of peri-implant disease is probing of the peri-implant sulcus. An increase in probing pocket depth over time is associated with attachment loss and bone loss (Lang et al. 1993, Schou et al. 1993a, Schou et al. 1993b). Probing with a light force does not seem to damage the peri-implant tissues and is recommended for regular evaluation of peri-implant tissues (Heitz-Mayfield 2008). It has been shown 13
7 CHAPTER 1 that the mucosal attachment around implants after probing with a light force (0.25 N) is completely recovered within five days (Etter et al. 2002). Bleeding after gentle probing is a second valuable parameter for diagnosis of peri-implant infections (Heitz-Mayfield 2008). Bleeding on probing shows a high negative predictive value, i.e. absence of bleeding on probing is indicative for healthy peri-implant conditions (Jepsen et al. 1996, Luterbacher et al. 2000). Presence of bleeding on probing at more than half of the recall visits over a 2-year period is associated with progression of peri-implant disease (increase in probing pocket depth and/or bone loss) (Luterbacher et al. 2000). The presence of suppuration indicates presence of an inflammatory lesion and is most often related to a bacterial infection (Heitz-Mayfield 2008). Suppuration is associated with progressive bone loss (Roos-Jansåker et al. 2006, Fransson et al. 2008) and periimplantitis (Roos-Jansåker et al. 2006, Lang et al. 2011b) and is a frequent observation at implants with peri-implantitis (Lang et al. 2011a). Radiographs are required for evaluation of peri-implant bone levels and for distinguishing peri-implant mucositis from peri-implantitis (Heitz-Mayfield 2008). Progressive bone loss, as observed by comparing two consecutive radiographs, is indicative for presence of peri-implantitis. In the differential diagnosis of peri-implant disease it is important to include identification of possible underlying problems, even if suppuration or presence of a biofilm point to a bacterial infection (Mombelli & Décaillet 2011). In addition, peri-implant bone loss as a result of peri-implant infection should be distinguished from bone loss as a result of remodeling or overload. Physiological remodeling of peri-implant bone takes place during the first few months after implant placement when the biological width is created (Berglundh & Lindhe 1996, Sculean et al. 2014). The amount of physiological bone loss differs between implant systems and depends, amongst other factors, on implant positioning (Tatarakis et al. 2012). Initial bone loss might be more pronounced at implants that are placed too deep (Hämmerle et al. 1996) or to close to other structures (Tarnow et al. 2000). Implants that are placed too deep generally also have deeper initial peri-implant pockets. This by its self might also be considered an initiating factor for peri-implant disease because pockets of 5 mm or more can be viewed as protected habitats for putative pathogens (Mombelli & Décaillet 2011). Treatment of peri-implant infections Once peri-implant infection has been diagnosed it is essential to initiate a prompt curative intervention in order to resolve the inflammatory lesion and prevent (further) bone loss. Mechanical non-surgical therapy can be effective for the treatment of periimplant mucositis, but non-surgical approaches for the treatment of peri-implantitis have shown to be unpredictable and, in most cases, not effective (Renvert et al. 2008, Esposito et al. 2012, Heitz-Mayfield & Mombelli 2014). If non-surgical therapy does not resolve the inflammatory lesion, it is recommended to perform access surgery (Lindhe et al. 2008), thus facilitating proper granulation tissue removal and debridement and decontamination of the implant surface. The removal of the biofilm on the implant surface may be compromised by the screw-shaped design of the implant and a rough implant surface. Because mechanical debridement alone may not be adequate to achieve sufficient biofilm removal, additional measures such as laser therapy, the use of antibiotics and/or the use of antiseptics such as hydrogen peroxide or chlorhexi- 14
8 dine are currently used. As of yet, a validated protocol for treatment of peri-implantitis is not available (for review see: Esposito et al. 2012, Heitz-Mayfield & Mombelli 2014). Currently used interventions may be effective, but it is unknown which interventions are most effective, and for the interventions having similar degrees of effectiveness it is unknown which one has less side effects, is easier and cheaper to use (Esposito et al. 2012, Heitz-Mayfield & Mombelli 2014). Objectives of this thesis Because the number of implants placed in everyday clinical practice is continuously increasing, it is reasonable to anticipate an increasing prevalence of peri-implant infections. This underlines the necessity for scientifically based clinical guidelines for prevention and treatment of peri-implant infections. The general aim of this thesis was to investigate epidemiological and microbiological aspects of peri-implant infections and to evaluate the effect of various protocols for treatment of peri-implantitis. Specific aims were: to compare peri-implant conditions between fully and partially edentulous implant patients and to investigate the prevalence of peri-implant diseases; to evaluate the peri-implant microflora in fully and partially edentulous subjects; to evaluate the effect of full-mouth tooth extraction on the composition of the oral microflora; to investigate the microflora associated with peri-implant health and peri-implantitis; to investigate the effect of implant surface decontamination using chlorhexidine solutions during surgical peri-implantitis treatment; to identify prognostic indicators for the outcome of surgical peri-implantitis treatment. GENERAL INTRODUCTION 15
9 CHAPTER 1 References Albrektsson T., Donos N. & Working Group 1. (2012) Implant survival and complications. The Third EAO consensus conference Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6, Anner R., Grossmann Y., Anner Y. & Levin L. (2010) Smoking, diabetes mellitus, periodontitis, and supportive periodontal treatment as factors associated with dental implant survival: a long-term retrospective evaluation of patients followed for up to 10 years. Implant Dentistry 19, Astrand P., Engquist B., Dahlgren S., Gröndahl K., Engquist E. & Feldmann H. (2004) Astra Tech and Brånemark system implants: a 5-year prospective study of marginal bone reactions. Clinical Oral Implants Research 15, Atieh M.A., Alsabeeha N.H., Faggion C.M.,Jr & Duncan W.J. (2013) The frequency of peri-implant diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Periodontology 84, Berglundh T., Zitzmann N.U. & Donati M. (2011) Are peri-implantitis lesions different from periodontitis lesions? Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38 Suppl 11, Berglundh T., Persson L. & Klinge B. (2002) A systematic review of the incidence of biological and technical complications in implant dentistry reported in prospective longitudinal studies of at least 5 years. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 29 Suppl 3, ; discussion Berglundh T. & Lindhe J.(1996) Dimension of the periimplant mucosa. Biological width revisited. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 23, Boutaga K., van Winkelhoff A.J., Vandenbroucke- Grauls C.M. & Savelkoul P.H. (2006) The additional value of real-time PCR in the quantitative detection of periodontal pathogens. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 33, Brånemark P.I., Adell R., Breine U., Hansson B.O., Lindström J. & Ohlsson A. (1969) Intra-osseous anchorage of dental prostheses. I. Experimental studies. Scandinavian Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 3, Brånemark R., Berlin O., Hagberg K., Bergh P., Gunterberg B. & Rydevik B. (2014) A novel osseointegrated percutaneous prosthetic system for the treatment of patients with transfemoral amputation: A prospective study of 51 patients. Bone and Joint Journal 96- B, Brito C., Tenenbaum H.C., Wong B.K., Schmitt C. & Nogueira-Filho G. (2014) Is keratinized mucosa indispensable to maintain peri-implant health? A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research. Part B, Applied Biomaterials 102, Campoccia D., Montanaro L. & Arciola C.R. (2013) A review of the clinical implications of anti-infective biomaterials and infection-resistant surfaces. Biomaterials 34, Costa F.O., Takenaka-Martinez S., Cota L.O., Ferreira S.D., Silva G.L. & Costa J.E. (2012) Peri-implant disease in subjects with and without preventive maintenance: a 5-year follow-up. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39, Derks J., Håkansson J., Wennström J.L., Tomasi C., Larsson M., Berglundh T. (2015) Effectiveness of implant therapy analyzed in a Swedish population: early and late implant loss. Journal of Dental Research 94 Suppl 3, Esposito M., Grusovin M.G. & Worthington H.V. (2012) Interventions for replacing missing teeth: treatment of peri-implantitis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, CD Esposito M., Hirsch J.M., Lekholm U. & Thomsen P. (1998a) Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (II). Etiopathogenesis. European Journal of Oral Sciences 106, Esposito M., Hirsch J.M., Lekholm U. & Thomsen P. (1998b) Biological factors contributing to failures of osseointegrated oral implants. (I). Success criteria and epidemiology. European Journal of Oral Sciences 106, Etter T.H., Håkanson I., Lang N.P., Trejo P.M. & Caffesse R.G. (2002) Healing after standardized clinical probing of the perlimplant soft tissue seal: a histomorphometric study in dogs. Clinical Oral Implants Research 13, Feine J.S., Carlsson G.E., Awad M.A., Chehade A., Duncan W.J., Gizani S., Head T., Lund J.P., MacEntee M., Mericske-Stern R., Mojon P., Morais J., Naert I., Payne A.G., Penrod J., Stoker G.T., Tawse-Smith A., Taylor T.D., Thomason J.M., Thomson W.M. & Wismeijer D. (2002) The McGill consensus statement on overdentures. Mandibular two-implant overdentures as first choice standard of care for edentulous patients. Montreal, Quebec, May 24-25, International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 17, 16
10 Ferreira S.D., Silva G.L., Cortelli J.R., Costa J.E. & Costa F.O. (2006) Prevalence and risk variables for peri-implant disease in Brazilian subjects. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 33, Fransson C., Wennström J. & Berglundh T. (2008) Clinical characteristics at implants with a history of progressive bone loss. Clinical Oral Implants Research 19, Galindo-Moreno P., Fauri M., Avila-Ortiz G., Fernández-Barbero J.E., Cabrera-León A. & Sánchez- Fernández E. (2005) Influence of alcohol and tobacco habits on peri-implant marginal bone loss: a prospective study. Clinical Oral Implants Research 16, Gruica B., Wang H.Y., Lang N.P. & Buser D. (2004) Impact of IL-1 genotype and smoking status on the prognosis of osseointegrated implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research 15, Hämmerle C.H., Brägger U., Bürgin W. & Lang N.P. (1996) The effect of subcrestal placement of the polished surface of ITI implants on marginal soft and hard tissues. Clinical Oral Implants Research 7, Heitz-Mayfield L.J. & Mombelli A. (2014) The therapy of peri-implantitis: a systematic review. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 29 Suppl, Heitz-Mayfield L.J. & Huynh-Ba G. (2009) History of treated periodontitis and smoking as risks for implant therapy. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 24 Suppl, Heitz-Mayfield L.J. (2008) Peri-implant diseases: diagnosis and risk indicators. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35, Holm-Pedersen P., Lang N.P. & Müller F. (2007) What are the longevities of teeth and oral implants? Clinical Oral Implants Research 18 Suppl 3, Jacobi-Gresser E., Huesker K. & Schütt S. (2013) Genetic and immunological markers predict titanium implant failure: a retrospective study. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery 42, Jepsen S., Rühling A., Jepsen K., Ohlenbusch B. & Albers H.K. (1996) Progressive peri-implantitis. Incidence and prediction of peri-implant attachment loss. Clinical Oral Implants Research 7, Jung R.E., Zembic A., Pjetursson B.E., Zwahlen M. & Thoma D.S. (2012) Systematic review of the survival rate and the incidence of biological, technical, and aesthetic complications of single crowns on implants reported in longitudinal studies with a mean followup of 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6, Kumar P.S., Mason M.R., Brooker M.R. & O Brien K. (2012) Pyrosequencing reveals unique microbial signatures associated with healthy and failing dental implants. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 39, Kumar P.S., Griffen A.L., Barton J.A., Paster B.J., Moeschberger M.L. & Leys E.J. (2003) New bacterial species associated with chronic periodontitis. Journal of Dental Research 82, Kurtz S.M., Ong K.L., Lau E., Bozic K.J., Berry D. & Parvizi J. (2010) Prosthetic joint infection risk after TKA in the Medicare population. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 468, Laine M.L., Leonhardt Å., Roos-Jansåker A.M., Peña A.S., van Winkelhoff A.J., Winkel E.G. & Renvert S. (2006) IL-1RN gene polymorphism is associated with peri-implantitis. Clinical Oral Implants Research 17, Landgraeber S., Jäger M., Jacobs J.J. & Hallab N.J. (2014) The pathology of orthopedic implant failure is mediated by innate immune system cytokines. Mediators of Inflammation [Epub ahead of print] Lang N.P., Berglundh T. & Working Group 4 of Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. (2011a) Periimplant diseases: where are we now?--consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38 Suppl 11, Lang N.P., Bosshardt D.D. & Lulic M. (2011b) Do mucositis lesions around implants differ from gingivitis lesions around teeth? Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38 Suppl 11, Lang N.P., Müller F. & Working Group I. (2007) Epidemiology and oral function associated with tooth loss and prosthetic dental restorations. Consensus report of Working Group I. Clinical Oral Implants Research 18 Suppl 3, Lang N.P., Brägger U., Walther D., Beamer B. & Kornman K.S. (1993) Ligature-induced peri-implant infection in cynomolgus monkeys. I. Clinical and radiographic findings. Clinical Oral Implants Research 4, GENERAL INTRODUCTION 17
11 CHAPTER 1 Leonhardt Å., Renvert S. & Dahlén G. (1999) Microbial findings at failing implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research 10, Lindhe J., Meyle J. & Group D of European Workshop on Periodontology. (2008) Peri-implant diseases: Consensus Report of the Sixth European Workshop on Periodontology. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35, Luterbacher S., Mayfield L., Brägger U. & Lang N.P. (2000) Diagnostic characteristics of clinical and microbiological tests for monitoring periodontal and peri-implant mucosal tissue conditions during supportive periodontal therapy (SPT). Clinical Oral Implants Research 11, Mombelli A. & Décaillet F. (2011) The characteristics of biofilms in peri-implant disease. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 38 Suppl 11, Mombelli A., van Oosten M.A., Schurch E.,Jr & Land N.P. (1987) The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiology and Immunology 2, Naert I., Duyck J. & Vandamme K. (2012) Occlusal overload and bone/implant loss. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6, Ong K.L., Kurtz S.M., Lau E., Bozic K.J., Berry D.J. & Parvizi J. (2009) Prosthetic joint infection risk after total hip arthroplasty in the Medicare population. Journal of Arthroplasty 24, Pjetursson B.E., Asgeirsson A.G., Zwahlen M. & Sailer I. (2014) Improvements in implant dentistry over the last decade: comparison of survival and complication rates in older and newer publications. International Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Implants 29 Suppl, Pjetursson B.E., Thoma D., Jung R., Zwahlen M. & Zembic A. (2012) A systematic review of the survival and complication rates of implant-supported fixed dental prostheses (FDPs) after a mean observation period of at least 5 years. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6, Pontoriero R., Tonelli M.P., Carnevale G., Mombelli A., Nyman S.R. & Lang N.P. (1994) Experimentally induced peri-implant mucositis. A clinical study in humans. Clinical Oral Implants Research 5, Renvert S., Roos-Jansåker A.M. & Claffey N. (2008) Non-surgical treatment of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: a literature review. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35, Roos-Jansåker A.M., Renvert H., Lindahl C. & Renvert S. (2006) Nine- to fourteen-year follow-up of implant treatment. Part III: factors associated with peri-implant lesions. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 33, Scheuber S., Hicklin S. & Brägger U. (2012) Implants versus short-span fixed bridges: survival, complications, patients benefits. A systematic review on economic aspects. Clinical Oral Implants Research 23 Suppl 6, Schou S., Holmstrup P., Reibel J., Juhl M., Hjørting- Hansen E. & Kornman K.S. (1993a) Ligature-induced marginal inflammation around osseointegrated implants and ankylosed teeth: stereologic and histologic observations in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis). Journal of Periodontology 64, Schou S., Holmstrup P., Stoltze K., Hjørting-Hansen E. & Kornman K.S. (1993b) Ligature-induced marginal inflammation around osseointegrated implants and ankylosed teeth. Clinical Oral Implants Research 4, Sculean A., Gruber R. & Bosshardt D.D. (2014) Soft tissue wound healing around teeth and dental implants. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 41 Suppl 15, Serino G. & Ström C. (2009) Peri-implantitis in partially edentulous patients: association with inadequate plaque control. Clinical Oral Implants Research 20, Shibli J.A., Melo L., Ferrari D.S., Figueiredo L.C., Faveri M. & Feres M. (2008) Composition of supraand subgingival biofilm of subjects with healthy and diseased implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research 19, Sicilia A., Cuesta S., Coma G., Arregui I., Guisasola C., Ruiz E. & Maestro A. (2008) Titanium allergy in dental implant patients: a clinical study on 1500 consecutive patients. Clinical Oral Implants Research 19, Siddiqi A., Payne A.G., De Silva R.K. & Duncan W.J. (2011) Titanium allergy: could it affect dental implant integration? Clinical Oral Implants Research 22, Taira M., Nezu T., Sasaki M., Kimura S., Kagiya T., Harada H., Narushima T. & Araki Y. (2009) Gene expression analyses of human macrophage phagocytizing sub-micro titanium particles by allergy DNA chip (Genopal). Biomedical Materials and Engineering 19,
12 Tarnow D.P., Cho S.C. & Wallace S.S. (2000) The effect of inter-implant distance on the height of interimplant bone crest. Journal of Periodontology 71, Tatarakis N., Bashutski J., Wang H.L. & Oh T.J. (2012) Early implant bone loss: preventable or inevitable? Implant Dentistry 21, Tillander J., Hagberg K., Hagberg L. & Brånemark R. (2010) Osseointegrated titanium implants for limb prostheses attachments: infectious complications. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 468, Tsikandylakis G., Berlin O. & Brånemark R. (2014) Implant survival, adverse events, and bone remodeling of osseointegrated percutaneous implants for transhumeral amputees. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research 472, Van Winkelhoff A.J., Loos B.G., Van der Reijden W.A. & Van der Velden U. (2002) Porphyromonas gingivalis, Bacteroides forsythus and other putative periodontal pathogens in subjects with and without periodontal destruction. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 29, Wilson T.G.,Jr. (2009) The positive relationship between excess cement and peri-implant disease: a prospective clinical endoscopic study. Journal of Periodontology 80, GENERAL INTRODUCTION Zitzmann N.U. & Berglundh T. (2008) Definition and prevalence of peri-implant diseases. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 35, Zitzmann N.U., Hagmann E. & Weiger R. (2007) What is the prevalence of various types of prosthetic dental restorations in Europe? Clinical Oral Implants Research 18 Suppl 3, Zitzmann N.U., Berglundh T., Marinello C.P. & Lindhe J. (2001) Experimental peri-implant mucositis in man. Journal of Clinical Periodontology 28,
13
Please visit the C.E. Pavilion to validate your course attendance Or If There s a Line Go cdapresents.com
 UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
UCLA Innovations 2016 CDA Presents in Anaheim Tara Aghaloo, DDS, MD, PhD Dean Ho, MS, PhD Jay Jayanetti Eric C. Sung, DDS David T. W. Wong, DMD, DMSc Benjamin M. Wu, DDS, PhD Saturday, May 14, 2016 8:00
As an increasing number of
 LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
LITERATURE REVIEWS Understanding Peri-implantitis: A Strategic Review Preetinder Singh, MDS* The high survival rate of osseointegrated dental implants is well documented, but it is becoming increasingly
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of
 Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Persson GR, Salvi GE, Heitz-Mayfield LJA et al. Antimicrobial therapy using a local drug delivery system (Arestin) in the treatment of peri-implantitis I: microbiological outcomes. Clin Oral Imp Res 2006;
Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study
 Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Clin Oral Invest (2017) 21:717 724 DOI 10.1007/s00784-016-1941-x ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bacterial colonization of the peri-implant sulcus in dentate patients: a prospective observational study M. A. Stokman
Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis
 Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Martin Saaby Eva Karring Søren Schou Flemming Isidor Factors influencing severity of periimplantitis Authors affiliations: Martin Saaby, Søren Schou, Section for Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery and Oral
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Abstract Purpose: Materials and methods Results:
 Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Evaluation of peri-implant tissue response according to the presence of keratinized mucosa Bum-Soo Kim 1, Young-Kyun Kim 1, Pil-Young Yun 1, Yang-Jin Lee 2, Hyo-Jeong Lee 3, Su-Gwan Kim 4 1Department of
Case Presentation. Overall Health. Oral Hygiene. Chief Complaint. I hate my upper denture. I can t taste food. I want an implant solution
 Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Case Presentation Medical History Age & Gender 62 years old female Peri-implant Osteitis Overall Health Good Hx of Smoking 5 cigarets per day (Peri-implantitis) Oral Hygiene Fair Systemic Disease Osteoarthritis
Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology
 Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
Article Periimplant diseases: where are we now? Consensus of the Seventh European Workshop on Periodontology LANG, Niklaus P, BERGLUNDH, Tord, MOMBELLI, Andrea Abstract Peri-implant diseases present in
Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y
 Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2329
Periodontal conditions in patients Title dental implant treatment. Ito, T; Yasuda, M; Norizuki, Y; Sas Author(s) S; Furuya, Y; Kato, T; Yajima, Y Journal Bulletin of Tokyo Dental College, 5 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10130/2329
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
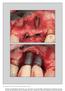 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 699 A Classification System for Peri-implant Diseases and Conditions Hector L. Sarmiento, DMD, MSc 1 Michael R. Norton, BDS, FDS, RCS(Ed)
Correlations between clinical parameters in implant maintenance patients: analysis among healthy and history-of-periodontitis groups
 Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
Seki et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:45 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0108-0 International Journal of Implant Dentistry RESEARCH Correlations between clinical parameters in implant
Straumann SmartOne. Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance. Step 2 Maintenance visit
 Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
Stage 4 Af terc are and maintenance Step 2 Maintenance visit Overview Assessment and treatment planning Step 1 Patient's expectations, history and examination Step 2 Treatment planning Step 3 Consultation
University of Groningen. Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella
 University of Groningen Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen Implant treatment for patients with severe hypodontia Filius, Marieke Adriana Pieternella IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if
University of Groningen. Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke
 University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
University of Groningen Dental implants in maxillofacial prosthodontics Korfage, Anke DOI: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2014.05.013 10.1016/j.ijom.2013.04.003 10.1002/hed.24053 IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy.
 Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
Mechanical and technical risks in implant therapy. Salvi GE, Brägger U. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2009;24 Suppl:69-85. Department of Periodontology, School of Dental Medicine, University of Bern,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 3 Influence of the 3-D Bone-to-Implant Relationship on Esthetics Ueli Grunder, DMD* Stefano Gracis, DMD** Matteo Capelli, DMD** There are
Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease?
 C L I N I C A L Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: A. Monje, L. Aranda, K.T. Diaz,
C L I N I C A L Is peri-implant maintenance therapy (PIMT) important for preventing peri-implant disease? Johan Hartshorne 1 A critical appraisal of a systematic review: A. Monje, L. Aranda, K.T. Diaz,
Primary prevention of periimplantitis: peri-implant mucositis S152
 J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
J Clin Periodontol 2015; 42 (Suppl. 16): S152 S157 doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12369 Primary prevention of periimplantitis: Managing peri-implant mucositis Jepsen S, Berglundh T, Genco R, Aass AM, Demirel K, Derks
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry
 Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Creating emergence profiles in immediate implant dentistry AUTHORS Dr. Daniel Capitán Maraver Dr. Manuel Fuentes Ortiz Visiting lecturers in the Master s Degree in Clinical Practice in Implantology and
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
 Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Risk of Implant Failure and Marginal Bone Loss in Subjects with a History of Periodontitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Syarida H. Safii, DDS [Correction added after online publication 1 June
Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen
![Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen Citation for published version (APA): de Waal, Y. C. M. (2015). Peri-implant infections [Groningen]: University of Groningen](/thumbs/82/86452679.jpg) University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Peri-implant infections de Waal, Yvonne IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Peri-implant marginal bone loss: What is the current concensus? an academic controversy or a clinical challenge?
 Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Peri-implant marginal bone loss; What is the current concensus? Bjorn.Klinge@mah.se Peri-implant marginal bone loss: an academic controversy or a clinical challenge? Björn Klinge Eur J Oral Implantol 2012;5
Detection of predominant subgingival periopathogens around submerged and non submerged hydroxy apatite implants
 [Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
[Downloaded free from http://www.jdionline.org on Sunday, January 26, 2014, IP: 201.22.186.203] Click here to download free Android application for this journa ORIGINAL ARTICLE Detection of predominant
Outcome of dental implants in patients with a history of periodontitis
 Joint Degree Master Program of the International Medical College and the Universities Dresden, Essen, Saarland, Leipzig, Szeged and Bangkok Scientific director: Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Dr. med. dent. Dr.
Joint Degree Master Program of the International Medical College and the Universities Dresden, Essen, Saarland, Leipzig, Szeged and Bangkok Scientific director: Univ.-Prof. Dr. med. Dr. med. dent. Dr.
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter
 THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
THE PERIODONTAL ASPECT OF IMPLANT THERAPY Prof. Dr. Windisch Péter Periodontal aspects of implant therapy 1) Comprehensive perioprosthodontic treatment by utilizing implants on perio-patients. 2) Anatomical
The majority of the early research concerning
 Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Gingival Recession Around Implants: A 1-Year Longitudinal Prospective Study Paula N. Small, DDS, MPH 1 /Dennis P. Tarnow, DDS 2 A longitudinal study was performed, which measured the soft tissue around
Porous titanium granules in the treatment of peri-implant osseous defects a 7-year follow-up study
 Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
Andersen et al. International Journal of Implant Dentistry (2017) 3:50 DOI 10.1186/s40729-017-0106-2 International Journal of Implant Dentistry SHORT REPORT Open Access Porous titanium granules in the
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry
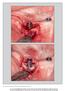 The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 729 Resective Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years Emmanuel Englezos, DDS, MSc 1 Jan Cosyn,
The International Journal of Periodontics & Restorative Dentistry 729 Resective Treatment of Peri-implantitis: Clinical and Radiographic Outcomes After 2 Years Emmanuel Englezos, DDS, MSc 1 Jan Cosyn,
Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N
 ADI GUIDELINES On Peri-implant Monitoring and Maintenance Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N Scope of the Problem: During the last two decades implant treatment
ADI GUIDELINES On Peri-implant Monitoring and Maintenance Ucer, C; Wright, S; Scher E; West, N; Retzepi, M; Simpson, S; Slade, K; Donos, N Scope of the Problem: During the last two decades implant treatment
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys
 The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
The Influence of Controlled Occlusal Overload on Peri-implant Tissue. Part 3: A Histologic Study in Monkeys Takashi Miyata, DDS, DDSc 1 /Yukinao Kobayashi, DDS 2 /Hisao Araki, DDS, DDSc 3 / Takaichi Ohto,
Implant osseointegration and successful restoration
 Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Prosthodontic Complications in a Prospective Clinical Trial of Single-stage Implants at 36 Months Jacqueline P. Duncan, DMD, MDSc 1 /Elena Nazarova, DMD, PhD 2 /Theodora Vogiatzi, DDS 1 / Thomas D. Taylor,
Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report
 CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
CASE REPORT J Korean Dent Sci. 2013;6(1):27-33 http://dx.doi.org/10.5856/jkds.2013.6.1.27 ISSN 2005-4742 Overcoming and Preventing Dental Implant Complications: Abutment Fracture Case Report Se Hoon Kahm
Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology
 143 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 56, No. 2, 143-150, 2014 Original Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology Miguel A. de Araújo Nobre
143 Journal of Oral Science, Vol. 56, No. 2, 143-150, 2014 Original Associations of clinical characteristics and interval between maintenance visits with peri-implant pathology Miguel A. de Araújo Nobre
Peri-implantitis susceptibility as it relates to periodontal therapy and supportive care
 Bjarni E. Pjetursson Christoph Helbling Hans-Peter Weber Giedre Matuliene Giovanni E. Salvi Urs Brägger Kurt Schmidlin Marcel Zwahlen Niklaus P. Lang Peri-implantitis susceptibility as it relates to periodontal
Bjarni E. Pjetursson Christoph Helbling Hans-Peter Weber Giedre Matuliene Giovanni E. Salvi Urs Brägger Kurt Schmidlin Marcel Zwahlen Niklaus P. Lang Peri-implantitis susceptibility as it relates to periodontal
G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM
 American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons 2013 Dental Implant Conference December 5 7, 2013 Sheraton Chicago Hotel & Towers G03: Complications 12/7/2013 8:00AM 4:30PM Prosthetic Complications
Volume 2 Issue
 Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
Volume 2 Issue 2 2017 Page 333 to 340 Research Article Oral Health and Dentistry ISSN: 2573-4989 The Anti-Inflammatory Actions of an Intra-Oral Adhesive Patch Containing Botanical Extracts Exert Inhibitory
What You Should Know About Dental Implants: The Process of Care Applies
 Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
Learn how the process of care model can apply to dental implants and empower decisions for providing quality care for clients. Starting with assessing the need for implants, the process covers documentation,
2017 WORLD WORKSHOP. Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March DOI: /jcpe.12957
 Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12957 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017
Received: 20 December 2017 Revised: 6 February 2018 Accepted: 1 March 2018 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12957 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES
 Braz J Periodontol - September 2014 - volume 24 - issue 03 CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES Rachel de Queiroz Ferreira Rodrigues
Braz J Periodontol - September 2014 - volume 24 - issue 03 CEMENT-RETAINED PROSTHESES INCREASE RISK OF PERI-IMPLANTITIS WHEN COMPARED TO SCREW- RETAINED PROSTHESES Rachel de Queiroz Ferreira Rodrigues
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases Louropoulou, A. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases Louropoulou, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Louropoulou, A. (01). Prevention and treatment
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases Louropoulou, A. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Louropoulou, A. (01). Prevention and treatment
The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up
 Original article The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up Alessandro Quaranta, DDS, PhD 1 Bartolomeo Assenza,
Original article The impact of smoking and previous periodontal disease on peri-implant microbiota and health: a retrospective study up to 7-year follow-up Alessandro Quaranta, DDS, PhD 1 Bartolomeo Assenza,
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) Peri-implantitis
 Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 661 676 Peri-implantitis Bjo rn Klinge, DDS, Odont Dr a, *, Margareta Hultin, DDS, Odont Dr a, Tord Berglundh, DDS, Odont Dr b a Karolinska Institutet, Institute of Odontology,
Dent Clin N Am 49 (2005) 661 676 Peri-implantitis Bjo rn Klinge, DDS, Odont Dr a, *, Margareta Hultin, DDS, Odont Dr a, Tord Berglundh, DDS, Odont Dr b a Karolinska Institutet, Institute of Odontology,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy
 Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Consensus Statements and Recommended Clinical Procedures Regarding Risk Factors in Implant Therapy David L. Cochran, DDS, MS, PhD, MMSci 1 /Søren Schou, DDS, PhD, Dr Odont 2 / Lisa J. A. Heitz-Mayfield,
Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease
 Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Clinical Multidisciplinary treatment planning for patients with severe periodontal disease Josselin Lethuillier, 1 Sébastien Felenc, 2 Philippe Bousquet 3 Abstract Periodontally compromised patients usually
Osseointegrated dental implant treatment generally
 Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Placement of Dental Implants Without Flap Surgery: A Clinical Report Bader H. Al-Ansari, BDS, MScD*/Robert R. Morris, DMD** Traditionally, the procedure of implant placement requires a surgical periosteal
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study
 Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Influence of Patient Age on the Success Rate of Dental Implants Supporting an Overdenture in an Edentulous Mandible: A 3-year Prospective Study Henny J. A. Meijer, DDS, PhD 1 /Rutger H. K. Batenburg, DDS,
Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers?
 412 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no6a5 Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers? 2018 Theme Article: Oral manifestations of systemic disease SADJ July 2018, Vol 73
412 > http://dx.doi.org/10.17159/2519-0105/2018/v73no6a5 Peri-implant diseases at a glance do we have all the answers? 2018 Theme Article: Oral manifestations of systemic disease SADJ July 2018, Vol 73
A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive. maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years.
 Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Original Article A retrospective study on separate single-tooth implant restorations to replace two or more consecutive maxillary posterior teeth up to 6 years follow up Myat Nyan Department of Prosthodontics,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo. Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
 Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Immediate implant placement in the Title central incisor region: a case repo Author(s) Sekine, H; Taguchi, T; Yamagami, M; Alternative Takanashi, T; Furuya, K Journal Journal of prosthodontic research,
Peri-implantitis Review
 1 2 Aro n J. Saf f er D DS M S Di pl omate o f th e Ame ric an Bo ard of P eri od o n tol og y A quarterly review of the latest publications related to the study of Peri-implant inflammation and bone loss
1 2 Aro n J. Saf f er D DS M S Di pl omate o f th e Ame ric an Bo ard of P eri od o n tol og y A quarterly review of the latest publications related to the study of Peri-implant inflammation and bone loss
University of Groningen. Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten
 University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Immediate dental implant placement in the aesthetic zone Slagter, Kirsten IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy
 The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
The Endodontic / Implant Controversy Innovations in Endodontics Series Robert Handysides DDS Associate Professor and Chair Department of Endodontics Loma Linda University School of Dentistry Endodontic
Peri-Implant Mucositis and Peri-Implantitis: A Current Understanding of Their Diagnoses and Clinical Implications*
 Volume 84 Number 4 Peri-Implant Mucositis and Peri-Implantitis: A Current Understanding of Their Diagnoses and Clinical Implications* The American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) periodically publishes
Volume 84 Number 4 Peri-Implant Mucositis and Peri-Implantitis: A Current Understanding of Their Diagnoses and Clinical Implications* The American Academy of Periodontology (AAP) periodically publishes
Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function
 Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Young-Il Kang* Dong-Won Lee* Kwang-Ho Park Ik-Sang Moon Effect of thread size on the implant neck area: preliminary results at 1 year of function Authors affiliations: Young-Il Kang*, Dong-Won Lee*, Ik-Sang
Brånemark System Facts & Figures
 Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Brånemark System Facts & Figures Brånemark System is synonymous with the revolution in dental care by the introduction of safe and effective implants. Professor Brånemark, its inventor, always put the
Tae-Hyung Kim. The Graduate School. Yonsei University. Department of Dental Science
 Influence of early cover screw exposure on the crestal bone loss around implants: comparison between exposed and non-exposed implants in identical subjects Tae-Hyung Kim The Graduate School Yonsei University
Influence of early cover screw exposure on the crestal bone loss around implants: comparison between exposed and non-exposed implants in identical subjects Tae-Hyung Kim The Graduate School Yonsei University
Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
 Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
Case Reports in Dentistry Volume 2015, Article ID 217895, 10 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/217895 Case Report Immediate, Early, and Conventional Implant Placement in a Patient with History of Periodontitis
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review
 The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
The Effects of Anti-infective Preventive Measures on the Occurrence of Biologic Implant Complications and Implant Loss: A Systematic Review Giovanni E. Salvi, DMD, Prof Dr Med Dent 1 /Nicola U. Zitzmann,
University of Groningen. Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant
 University of Groningen Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
University of Groningen Soft tissue development in the esthetic zone Patil, Ratnadeep Chandrakant IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite
BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
 Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Mechanics and Materials in Design, Editors: J.F. Silva Gomes & S.A. Meguid, P.Delgada/Azores, 26-30 July 2015 PAPER REF: 5734 BIOMECHANICS AND OVERDENTURES
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang.
 Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Implantology without Periodontology is like Yin without Yang. NIWOP: The systematic and evidence-based workflow #niwop wh.com No Implantology without Periodontology NIWOP 1 Pretreatment Optimal periodontal
Case study 2. A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant
 Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Case study 2 A Retrospective Multi-Center Study on the Spiral Implant Benny Karmon DMD, Jerry Kohen DMD, Ariel Lor DMD, Yiftach Gratciany DMD, Zvi Laster DMD, Gideon Hallel DMD MPA, Tsvia Karmon A Retrospective
Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report
 Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Case report AODMR Use of Implant Retained Overdenture in Atrophic Mandible - A Case Report Sheren Fatima 1, Rajarshi Basu 2, Neelkamal Hallur 3, Aaisha Siddiqua 4, Syed Zakaullah 4, Sumaiyya 2, Chaitanya
Interest in and studies on osseointegration
 CASE REPORT A Two-Stage Surgical Approach to the Treatment of Severe Peri-Implant Defect: A 30-Month Clinical Follow- Up Report Jong-Eun Kim, DDS, MSD 1 Ha-Young Kim, DDS, MSD 1 Jung-Bo Huh, DDS, MSD,
CASE REPORT A Two-Stage Surgical Approach to the Treatment of Severe Peri-Implant Defect: A 30-Month Clinical Follow- Up Report Jong-Eun Kim, DDS, MSD 1 Ha-Young Kim, DDS, MSD 1 Jung-Bo Huh, DDS, MSD,
T he survival of an implant involves
 KU ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER 3 2016 1 Explaining the Red Fluorescence Evident on the Surface of Failed Dental Implants: Case Reports Hye-Min Ku, RDH,* Mi-Kyoung Jun, RDH, MSD,* Jee-Hwan
KU ET AL IMPLANT DENTISTRY / VOLUME 25, NUMBER 3 2016 1 Explaining the Red Fluorescence Evident on the Surface of Failed Dental Implants: Case Reports Hye-Min Ku, RDH,* Mi-Kyoung Jun, RDH, MSD,* Jee-Hwan
Parodontitis versus Peri-Implantitis: Klinische und mikrobiologische Diagnose?
 Parodontitis versus Peri-Implantitis: Klinische und mikrobiologische Diagnose? Arndt Güntsch & Bernd W. Sigusch Parodontologie Nachrichten 1/2010 Literaturverzeichnis (1) Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Marinello
Parodontitis versus Peri-Implantitis: Klinische und mikrobiologische Diagnose? Arndt Güntsch & Bernd W. Sigusch Parodontologie Nachrichten 1/2010 Literaturverzeichnis (1) Berglundh T, Lindhe J, Marinello
The Microbial Etiology and Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis
 The Microbial Etiology and Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis Liqaa Shallal Farhan Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, University of Anbar, Iraq Abstract Patients with moderate Perimplantitis
The Microbial Etiology and Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis Liqaa Shallal Farhan Department of Maxillofacial Surgery, College of Dentistry, University of Anbar, Iraq Abstract Patients with moderate Perimplantitis
Peri implantitis. Frank Schwarz 1* Jan Derks 2* Alberto Monje 3,4 Hom Lay Wang 4. Abstract 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP
 Received: 6 June 2016 Revised: 14 September 2017 Accepted: 24 September 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12954 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implantitis Frank Schwarz 1* Jan Derks 2* Alberto Monje 3,4 Hom Lay Wang 4
Received: 6 June 2016 Revised: 14 September 2017 Accepted: 24 September 2017 DOI: 10.1111/jcpe.12954 2017 WORLD WORKSHOP Peri implantitis Frank Schwarz 1* Jan Derks 2* Alberto Monje 3,4 Hom Lay Wang 4
The surgical placement of dental implants has
 Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Flapless Implant Surgery: A 10-year Clinical Retrospective Analysis Luis Dominguez Campelo, DDS 1 /Jose R. Dominguez Camara, MD, DDS 2 Purpose: This article is a retrospective clinical analysis of implants
Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated by GTR.
 Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Cortellini P, Tonetti M. Long-term tooth survival following regenerative treatment of intrabony defects. J Periodontol 2004; 75:672-8. (28 Refs) Purpose: To assess the long term survival of sites treated
Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta
 Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta Long-term results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients: 10-year data around sandblasted and
Mario Roccuzzo Luca Bonino Paola Dalmasso Marco Aglietta Long-term results of a three arms prospective cohort study on implants in periodontally compromised patients: 10-year data around sandblasted and
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr.
 Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
Failures in implant therapy. Biological and mechanical complications. Their prevention management. Dr. Katalin Csurgay Dr. Tatiana Shkolnik Complications could be: Doctor related Patient related Early
4. What about age? There is no age limit. After puberty, anyone can get dental implants.
 Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Dental Implants 1. What are Osseointegrated implants? Osseointegrated implants are a new generation of dental implants in Rio de Janeiro, introduced in the 1960 s, they come in different shapes and sizes.
Failures in Endosseous Dental Implants A Literature review
 Eswaran Arumugam et al/ International Journal of Biomedical Research 2015; 6(10): 756-762. 756 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print) Journal DOI: 10.7439/ijbr
Eswaran Arumugam et al/ International Journal of Biomedical Research 2015; 6(10): 756-762. 756 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print) Journal DOI: 10.7439/ijbr
The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration
 IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
IJOI 27 INTERDISCIPLINARY TREATMENT The 2B-3D rule for implant planning, placement and restoration 1. What is biologic width? Is there a golden rule for implant planning, placement and restoration as the
 Wittneben JG, Kern M: Imitation der Rot-Weiß-Ästhetik im Frontzahnbereich Literatur: 1 Buser D, Sennerby L, De Bryn H: Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current
Wittneben JG, Kern M: Imitation der Rot-Weiß-Ästhetik im Frontzahnbereich Literatur: 1 Buser D, Sennerby L, De Bryn H: Modern implant dentistry based on osseointegration: 50 years of progress, current
The concept of prosthetic restoration based on implants with retention resulting both from screwing and cementing clinical case report
 The concept of prosthetic restoration based on implants with retention resulting both from screwing and cementing clinical case report Andrzej Bożyk 1, Grzegorz Michalczewski 1, Leszek Szalewski 1, Agata
The concept of prosthetic restoration based on implants with retention resulting both from screwing and cementing clinical case report Andrzej Bożyk 1, Grzegorz Michalczewski 1, Leszek Szalewski 1, Agata
Interrelationship between Periodontitis and Peri-Implantitis: Myth or Reality?
 REVIEW ARTICLE Rashmi Paramashivaiah 1, *, Prabhuji M.L.V 2 1 Reader, 2 Professor& HOD, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore-562157 *Corresponding Author: Email: rashparams2005@yahoo.co.in
REVIEW ARTICLE Rashmi Paramashivaiah 1, *, Prabhuji M.L.V 2 1 Reader, 2 Professor& HOD, Krishnadevaraya College of Dental Sciences, Bangalore-562157 *Corresponding Author: Email: rashparams2005@yahoo.co.in
PERI-IMPLANTITIS A PROBLEM.
 PERI-IMPLANTITIS A PROBLEM. Infections around implants are stubborn. What can help? What doesn t? How can infections be prevented? Geistlich News 02 2014 5 Illustration: Büro Haeberli How prevalent is
PERI-IMPLANTITIS A PROBLEM. Infections around implants are stubborn. What can help? What doesn t? How can infections be prevented? Geistlich News 02 2014 5 Illustration: Büro Haeberli How prevalent is
Peri-implant pathology has been described as
 Microleakage at the Abutment-Implant Interface of Osseointegrated Implants: A Comparative Study Martin Gross, BDS, LDS, MSc*/Itzhak Abramovich, DMD**/Ervin I. Weiss, DMD*** Microleakage can occur at the
Microleakage at the Abutment-Implant Interface of Osseointegrated Implants: A Comparative Study Martin Gross, BDS, LDS, MSc*/Itzhak Abramovich, DMD**/Ervin I. Weiss, DMD*** Microleakage can occur at the
There is overwhelming evidence that implant-retained
 CLINICAL Two-Year Success Rate of Implant-Retained Mandibular Overdentures by Novice General Dentistry Residents Hans Malmstrom, DDS 1 * Jin Xiao, DDS, MS, PhD 1 Georgios Romanos, DDS, PhD 1,2 Yan-Fang
CLINICAL Two-Year Success Rate of Implant-Retained Mandibular Overdentures by Novice General Dentistry Residents Hans Malmstrom, DDS 1 * Jin Xiao, DDS, MS, PhD 1 Georgios Romanos, DDS, PhD 1,2 Yan-Fang
Prevalence of peri-implant disease on platform switching implants: a cross-sectional pilot study
 Original Research Implantodontology Prevalence of peri-implant disease on platform switching implants: a cross-sectional pilot study Andrés Duque DUQUE (a) Astrid Giraldo ARISTIZABAL (a) Susana LONDOÑO
Original Research Implantodontology Prevalence of peri-implant disease on platform switching implants: a cross-sectional pilot study Andrés Duque DUQUE (a) Astrid Giraldo ARISTIZABAL (a) Susana LONDOÑO
ASSESSMENT OF THE PROGNOSIS OF PRESERVATION OR EXTRACTION OF PERIODONTOPATHIC TEETH FOR IMPLANT DECISIONS
 Parodontology ASSESSMENT OF THE PROGNOSIS OF PRESERVATION OR EXTRACTION OF PERIODONTOPATHIC TEETH FOR IMPLANT DECISIONS Atamna Hussein Magde 1, Mâr]u Silvia 2 1. PhD Student, Gr.T.Popa U.M.Ph Iasi, Romania,
Parodontology ASSESSMENT OF THE PROGNOSIS OF PRESERVATION OR EXTRACTION OF PERIODONTOPATHIC TEETH FOR IMPLANT DECISIONS Atamna Hussein Magde 1, Mâr]u Silvia 2 1. PhD Student, Gr.T.Popa U.M.Ph Iasi, Romania,
Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3)
 B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
B. Klinge Thomas F. Flemmig Consensus Report Tissue augmentation and esthetics (Working Group 3) Members of working group: Matteo Chiapasco Jan-Eirik Ellingsen Ronald Jung Friedrich Neukam Isabella Rocchietta
A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years
 REVIEW S155 Lars Hjalmarsson, Maryam Gheisarifar, Torsten Jemt A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years Key words 10-year
REVIEW S155 Lars Hjalmarsson, Maryam Gheisarifar, Torsten Jemt A systematic review of survival of single implants as presented in longitudinal studies with a follow-up of at least 10 years Key words 10-year
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION. By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur
 COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
COMBINED PERIODONTAL-ENDODONTIC LESION By Dr. P.K. Agrawal Sr. Prof and Head Dept. Of Periodontia Govt. Dental College, Jaipur Differential diagnosis For differential diagnostic purposed the endo-perio
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS
 INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
INTRODUCTION TO DENTAL IMPLANTOLOGY HISTORY OF DENTAL IMPLANTS EUGENIA PROKOPETS, DDS LSU PERIODONTICS Thank you Dr. Simmons BEFORE THE COMMON ERA 16TH AND 17TH CENTURIES Archeological records from China
Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior Region Along with Soft and Hard Tissue Grafting- A Case Report.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 10 Ver. XII (October. 2016), PP 68-73 www.iosrjournals.org Implant Placement in Maxillary Anterior
Safety and esthetics with
 Safety and esthetics with dental implants A guide for patients Dear reader, Implant restorations follow nature's example. You can have the functions of natural teeth completely restored and thus maintain
Safety and esthetics with dental implants A guide for patients Dear reader, Implant restorations follow nature's example. You can have the functions of natural teeth completely restored and thus maintain
Complication incidence of two implant systems up to six years: a comparison between internal and external connection implants
 Complication incidence of two implant systems up to six years: a comparison between internal and external connection implants Sung-Wook Chae 1, Young-Sung Kim 1,2, Yong-Moo Lee 3, Won-Kyung Kim 1, Young-Kyoo
Complication incidence of two implant systems up to six years: a comparison between internal and external connection implants Sung-Wook Chae 1, Young-Sung Kim 1,2, Yong-Moo Lee 3, Won-Kyung Kim 1, Young-Kyoo
The notable success of dental implants. Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing RESEARCH
 RESEARCH Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing João Gustavo Oliveira de Souza 1 Marco Aurélio Bianchini, PhD, MSc 2 Cimara Fortes Ferreira, PhD, MSc 3 * The objective of this study was to
RESEARCH Relationship Between Smoking and Bleeding on Probing João Gustavo Oliveira de Souza 1 Marco Aurélio Bianchini, PhD, MSc 2 Cimara Fortes Ferreira, PhD, MSc 3 * The objective of this study was to
With the establishment of evaluation
 J Periodontol December 2009 Comparative Analysis of Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss Based on Microthread Location: A 1-Year Prospective Study After Loading Dong-Wook Song,* Dong-Won Lee,* Chong-Kwan Kim,
J Periodontol December 2009 Comparative Analysis of Peri-Implant Marginal Bone Loss Based on Microthread Location: A 1-Year Prospective Study After Loading Dong-Wook Song,* Dong-Won Lee,* Chong-Kwan Kim,
Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2014) 55(4): 217 224 Case Report Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Periodontal Regeneration and Different Types of Prosthesis: A 2-year Follow-up Report Takashi
Improvement of Systemic Symptoms after Dental Implant Removal
 Open Journal of Stomatology, 2016, 6, 37-46 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2016.62005 Improvement of Systemic Symptoms after
Open Journal of Stomatology, 2016, 6, 37-46 Published Online February 2016 in SciRes. http://www.scirp.org/journal/ojst http://dx.doi.org/10.4236/ojst.2016.62005 Improvement of Systemic Symptoms after
Periodontitis & Implants
 Objectives Periodontitis & Implants Dr Simon Hinckfuss D.C.D (Melb), Cert.Perio, MS (Minn, USA) Diplomat of the American Board of Periodontology Diagnose common types of periodontal disease Describe the
Objectives Periodontitis & Implants Dr Simon Hinckfuss D.C.D (Melb), Cert.Perio, MS (Minn, USA) Diplomat of the American Board of Periodontology Diagnose common types of periodontal disease Describe the
Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report
 Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Bull Tokyo Dent Coll (2013) 54(4): 243 250 Case Report Longitudinal Supportive Periodontal Therapy for Severe Chronic Periodontitis with Furcation Involvement: A 12-year Follow-up Report Akiyo Komiya-Ito,
Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis
 Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
Clin Dent Rev (2017) 1:3 https://doi.org/10.1007/s41894-017-0004-2 TREATMENT Evidence-based decision making in periodontal tooth prognosis Carlos Ernesto Nemcovsky 1 Received: 12 April 2017 / Accepted:
EFFECTIVE DATE: 04/24/14 REVISED DATE: 04/23/15, 04/28/16, 06/22/17, 06/28/18 POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Dental
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: DENTAL IMPLANTS PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including an Essential
