THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL
|
|
|
- Gabriella McDowell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
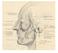
1 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, The British Association of Oral Surgeons X/81/ $02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A. ZIARAH, B.D.s., M.MED.SCI.~ and MARTIN E. ATKINSON, B.SC., PH.D.~* IDepartment of Dental Surgery, University of Shefield; adepartment of Human Biology and Anatomy, University of Shefield, Shefield SIO 2TN Summary. During the course of anatomical studies of the submandibular region, the presence of a strong fascial band running deep from the investing fascia to the fascia of the posterior belly of the digastric was repeatedly encountered. This angular tract is described in detail. Its position as a division between the submandibular gland and lower portion of the parotid gland suggests that the tract is potentially useful as a landmark and as protection for the glands and their contents in submandibular surgical approaches. Introduction In the course of anatomical studies of the nerves in the submandibular region (Ziarah & Atkinson, 1981a and b) we repeatedly observed a thick fascial band passing from the angle of the mandible to the hyoid bone. The position of this band makes it particularly important in the surgery of the submandibular gland and the submandibular region in general and therefore merits consideration. The fascial band we observed corresponds to the tractus angularis or pars angularis fasciae cervi as illustrated by Pernkopf (1963) and to the angular tract briefly mentioned by Seward (1968). Despite these previous references to its presence no detailed description has been made before and is presented below. Materials and methods Observations were made from 110 facial halves obtained from cadavers which had been hard-injected with a mixture of formalin, glycerine, alcohol and carbolic acid through the common carotid artery or femoral artery or both. Results As the outer lamina of the investing fascia of the neck is removed a thickened band of fascia is encountered on its deep surface (Fig. 1). The band runs obliquely in both the sagittal and coronal planes. It extends from the angle of the mandible above and runs downwards and backwards to the greater cornu of the hyoid bone below. The superficial edge blends with the investing fascia and the deep edge is placed more anteriorly and blends with the fascial sheaths of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle and stylohyoid muscle. The anterior surface which faces obliquely anterolaterally passes in its upper part behind and deep to the posterior pole of superficial lobe of the submandibular gland. The posterior surface which faces obliquely posteromedially overlies the lower pole of the parotid gland superiorly (Fig. 1). Essentially (Received 30 September 1980; accepted 18 October 1980) * For offprints. 116
2 SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE ANGULAR TRACT 117 FIG. 1. A dissection showing the angular tract (A). The platysma muscle (PM) and outer layer of the investing fascia (f) have been retracted postero-inferiorly. The facial artery (a) is indicated and the tip of the periosteal elevator lies over the gonion. P indicates the parotid compartment below the lower pole of the parotid gland (L) reflected superiorly. the thickened fascial band separates the two major salivary glands and their related structures in the neck (Fig. 2). The angular fascial band was present in every facial half examined as a tough fascial band. Discussion Following the precedent set by Pernkopf (1963) and Seward (1968) the most suitable name for this thickened deep extension of the investing fascia is the angular tract. When Seward (1968) mentioned the angular tract in connection with a submandibular approach to the submandibular gland he saw it as a surgical hazard with possibilities of instruments being deflected deeply by the tough fascia towards the external carotid artery and internal jugular vein. This is unlikely to happen due to its deep attachment to the fascial sheaths of the muscles which will protect the carotid sheath and its contents. Although bearing in mind Seward s (1968) warning we take an opposing view and see the angular tract as an aid to submandibular surgery and not a hindrance.
3 118 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ORAL SURGERY FIG. 2. Another dissection showing the angular tract (A) separating the parotid compartment (P) from the posterior part of the submandibular gland (S). The platysma muscle (PM) and investing fascia (f) have been reflected postero-inferiorly and the tip of the periosteal elevator lies over the gonion. Essentially the obliquely orientated angular tract divides the area immediately below the posterior part of the body of the mandible into an anterior submandibular compartment and a posterior parotid compartment. By dissecting anterior or posterior to the angular tract, as the individual case dictates, the other compartment can be left undisturbed and free from any damage. Access to the parotid compartment can best be achieved by incising the investing fascia immediately anterior to the sternocleidomastoid fascia, due consideration being taken of the course of the mandibular and cervical nerves during initial placement of the incision (Ziarah & Atkinson, 1981a and b). Once the investing fascia is incised posterior to the angular tract, a distinct surgical pocket is created (Fig. 2). The boundaries of this pocket are, Anteriorly. Above is the angle of the mandible and its associated musculature and from this and passing down to the hyoid bone is the angular tract. Posteriorly. The sternocleidomastoid fascia. Medially. The fascia covering the stylohyoid and posterior belly of the digastric muscles. Laterally. The parotid fascia on the deep side of the lower portion of the parotid gland and its contents and the investing layer of the deep cervical fascia.
4 SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF THE ANGULAR TRACT 119 The only contents in this pocket are one or two lrenae communicantes which may be dealt with by the standard surgical procedures. The submandibular gland, facial artery and anterior facial vein lie anterior to the angular tract and the cervical and mandibular branches of the facial nerve may be retracted within the fascia-muscle-skin flap. The angle of the mandible is exposed for manipulation or for further exposure by subperiosteal dissection (Fig, 3). There is no corresponding pocket in the submandibular compartment but access to the mandibular body and submandibular gland can be achieved by utilising a plane of dissection deep to the investing fascia and anterior to the angular tract. The facial artery and anterior facial vein are present in this plane but again can be dealt with using standard surgical techniques. The angular tract may be exposed by dividing the investing fascia from its attachment to the hyoid bone and providing dissection is carried out anterior to the tract the parotid gland and the emerging cervical and mandibular branches of the facial nerve are protected from damage. The nerves lie superficial to the plane of dissection and are therefore also protected (Ziarah & Atkinson, 198la and b). FIG. 3. The division, above the hyoid bone (H), of the neck into a parotid compartment and subman dibular compartment (S) by the angular tract (A). M indicates the mandibular body, V the IJed of the anterior facial vein and PM the platysma muscle reflected anteriorly.
5 120 BRITISH JOURNAL OF ORAL SURGERY If the whole hemimandible needs to be exposed the two compartments can be brought into continuity by detaching the angular tract from its inferior insertion into the hyoid bone and its deep insertion into the fascia of the stylohyoid and posterior belly of digastric. As the tract is reflected superiorly the lower pole of the parotid gland is carried with it by virtue of the obliquity of the angular tract and is safe from the field of operation. Thus the knowledge of the presence and precise relations of the angular tract has potential use in submandibular surgical approaches. We wish to thank Professor R. Barer for provision of facilities in the Department of Human Biology and Anatomy and Messrs G. Hibbard and D. Hinchliffe for technical assistance. We also thank Messrs R. Cousins and Mr Turton for preparation of the illustrations and Professor P. A. Bramley for his help and advice. Pernkopf, E. (1963). An atlas of topographic and applied human anatomy. Volume 1, Head and Neck. Philadelphia: Saunders. Seward, G. R. (1968). Anatomic surgery for salivary calculi. IV. Calculi in the intraglandular part of the submandibular duct. Oral Surgery, Oral Medicine and Oral Pathology, 25, 670. Ziarah, H. A. &Atkinson, M. E. (1981a). The surgical anatomy of the mandibular distribution of the facial nerve. British Journal of Oral Surgery, Vol. 19, No. 3 (in press). Ziarah, H. A. & Atkinson, M. E. (1981b). The surgical anatomy of the cervical distribution of the facial nerve. British Journal of Oral Surgery, Vol. 19, No. 3 (in press).
THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE. Biology and Anatomy, University of Shefield
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi
 Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Posterior Triangle of the Neck By Prof. Dr. Muhammad Imran Qureshi For the purpose of anatomical description the neck is sub divided into two major triangles, the Anterior and the Posterior by muscle bellies
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
 Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/ explanation Objectives: By the end of the lecture,
Lecture 01. The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands. By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018
 Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
Lecture 01 The Thyroid & Parathyroid Glands By: Dr Farooq Khan PMC Date: 12 th March. 2018 INTRODUCTION LAYERS OF THE NECK The neck has four major compartments or layer which are enclosed by an outer musculofascial
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Neck Ultrasound. Faculty Info: Amy Kule, MD
 Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
Neck Ultrasound Date: Friday, October 19, 2018 Time: 11:00 AM Location: SMALL GROUP LABORATORY SSOM L71 Watch: Ø Neck Ultrasound Scanning Protocol (4:00): https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zozd2x2ll4q Faculty
The Neck. BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat
 The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
The Neck BY: Lina Abdullah & Rahaf Jreisat Boundaries of the Neck: generally from base of the skull to root of the neck Superior margin :From superior nuchal line of occipital bone up to mastoid process
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
The Pharynx. Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D
 The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
The Pharynx Dr. Nabil Khouri MD. MSc, Ph.D Introduction The pharynx is the Musculo-fascial halfcylinder that links the oral and nasal cavities in the head to the larynx and esophagus in the neck Common
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
THYROID & PARATHYROID. By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy
 THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
THYROID & PARATHYROID By Prof. Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr. Sanaa Al-Sharawy 1 OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, the student should be able to: Describe the shape, position, relations and structure of
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES
 CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
CERVICAL LYMPH NODES (ANATOMY & EXAMINATION) Hemant (DTCD 1 st YEAR) 1. Lymphatic Tissues: A Type of connective tissue that contains large numbers of lymphocytes. 2. Lymphatic Vessels: Are Tubes that assist
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Head & Neck Contouring
 Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Head & Neck Contouring Presented by James Wheeler, MD Center for Cancer Care Goshen, IN 46526 September 12, 2014 Special Thanks to: Spencer Boulter, Director of Operations (AAMD) Adam Moore, RT(T), CMD
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland
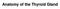 Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
Anatomy of the Thyroid Gland Introduction Nomenclature G, thyreos= shield, eidos= like Location Root of the neck ventrally (C5-T1) Function endocrine gland that secretes: Thyroxine (T4) T3 Calcitonin LWW,
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Página 1 de 6 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "37 - HIP DISLOCATIONS
Thyroid gland. importance. relations and connections. external laryngeal nerves. malformations.
 Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
Thyroid gland 1. Recognize and understand the coverings of the thyroid gland and their clinical importance. 2. Recognize and understand the main parts of the thyroid gland and their locations, relations
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate
 Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Unit 20: Prevertebral Region, Pharynx and Soft Palate Dissection Instructions: Step1 Step 2 Step 1: Insert your fingers posterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, vagus nerve, internal jugular vein,
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Over the past 18 years, numerous classifications have been proposed to distinguish
 ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
ORGNAL ARTCLE An maging-based Classification for the Cervical Nodes Designed as an Adjunct to Recent Clinically Based Nodal Classifications Peter M. Som, MD; Hugh D. Curtin, MD; Anthony A. Mancuso, MD
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Advanced Anatomy of the Neck
 AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
AACE 2018 Advanced Anatomy of the Neck Alex Tessnow, MD, MBA, FACE, ECNU University of Texas Southwestern Dallas, TX Content contributed by: H. Jack Baskin, Daniel Duick, Diana Dean, Robert A. Levine,
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus
 Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Outline of content Temporal fossa Infratemporal fossa Pterygopalatine fossa Terminal branches of external carotid artery Pterygoid venous plexus Boundary Content Communication Mandibular division of trigeminal
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip. Joseph H. Dimon
 Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
Surgical Anatomy of the Hip Joseph H. Dimon The hip joint is a deep joint surrounded by large and powerful muscles necessary for its proper function. Essential neurovascular structures lie in front and
APRIL
 APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
APRIL - 2003 OCTOBER - 2003 February 2009 [KU 652] Sub. Code : 4131 FIRST B.D.S DEGREE EXAMINATION (Modified Regulations III) Paper I HUMAN ANATOMY, HISTOLOGY AND EMBRYOLOGY Time : Three hours
Grossman, 1953), and there is little information so far concerning its function
 52 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 52-57 A SURGICAL APPROACH TO THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANGLION AND RELATED STRIJCTURES IN THE SHEEP BY THE LATE A. B. APPLETON* AND G. M. H. WAITES From the Zoological Society of
52 J. Physiol. (I957) I35, 52-57 A SURGICAL APPROACH TO THE SUPERIOR CERVICAL GANGLION AND RELATED STRIJCTURES IN THE SHEEP BY THE LATE A. B. APPLETON* AND G. M. H. WAITES From the Zoological Society of
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM
 REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
REVIEW/PREVIEW OF HEAD AND NECK ANATOMY FOR ENT EXAM - 2017 PALPATE CAROTID ARTERY: AT LEVEL OF CAROTID BIFURCATION VERTEBRAL LEVEL C4 Sternocleidomastoid Muscle INTERNAL CAROTID EXTERNAL CAROTID COMMON
Larynx. Rudimentary. Behind the posterior surface : -stylopharyngeus - salpingopharyngeus -platopharyngeus
 Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Larynx The larynx is an organ that provides a protective sphincter at the inlet of the air passages and is responsible for voice production. It extends from C3-C6: *Posterior: the pharynx *Lateral: the
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
The front of the thigh. Dr.Amjad shatarat
 The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
Neck of Condylar. Process. Anterior Border of Ramus. Mandibular. Foramen. Posterior Border of Ramus Incisive Fossa.
 Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
Learning Outcomes The Mandible Surface Anatomy Muscle Attachments The (FOM) Muscles of the FOM The Tongue Muscles of the Tongue The Submandibular Region Submandibular Gland Sublingual Gland Lingual The
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES
 PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
PLEURAE and PLEURAL RECESSES By Dr Farooq Aman Ullah Khan PMC 26 th April 2018 Introduction When sectioned transversely, it is apparent that the thoracic cavity is kidney shaped: a transversely ovoid space
Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper. Oral vestibule : is slit like space between.
 Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Oral cavity Oral cavity : consist of two parts: the oral vestibule and the oral cavity proper Oral vestibule : is slit like space between the teeth, buccal gingiva, lips, and cheeks 1 Oral cavity Oral
Mediastinum and pericardium
 Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Mediastinum and pericardium Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com The mediastinum: is the central compartment of the thoracic cavity surrounded by
Clinical evaluation. Imaging Surgical treatment
 Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands
 Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Head & Neck Surgery Course Surgical anatomy of thyroid and parathyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco PELLICCIA Pr Benjamin LALLEMANT Service ORL et CMF CHU de Nîmes CH de Arles Thyroid glands Dr Pierfrancesco
Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal bone Maxilla Nasal bone Palatine bone Vomer Zygomatic bone Mandible
 splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
splanchnocranium - Consists of part of skull that is derived from branchial arches - The facial bones are the bones of the anterior and lower human skull Bones Ethmoid bone Inferior nasal concha Lacrimal
A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):326-330 A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation Prasanna LC, Alva R, D Souza AS, Bhat KMR Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2013;3(2):326-330 A Rare Case of Bilateral Jugular Venous Malformation Prasanna LC, Alva R, D Souza AS, Bhat KMR Department of Anatomy, Kasturba Medical College, Manipal University,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle
 A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle Robert Lukavsky 1, Gary Linkov 2, Christopher Fundakowski 2,3 1 Department of General Surgery, Temple
A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle Robert Lukavsky 1, Gary Linkov 2, Christopher Fundakowski 2,3 1 Department of General Surgery, Temple
Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus.
 THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
THYROID GLAND 1 Lies in front and sides of the neck. Consists of two lobe connected anterior to the trachea by an isthmus. A small pyramidal lobe projects upwards from the left lobe in 40% of cases. The
Muscles of mastication [part 1]
![Muscles of mastication [part 1] Muscles of mastication [part 1]](/thumbs/76/73586850.jpg) Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Muscles of mastication [part 1] In this lecture well have the muscles of mastication, neuromuscular function, and its relationship to the occlusion morphology. The fourth determinant of occlusion is the
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi. E mail: a.al E. mail:
 Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Spinal nerves and cervical plexus Prof. Abdulameer Al Nuaimi E mail: a.al nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Branches of ophthalmic artery Muscles of face A spinal nerve Spinal
Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy
 Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Dr. Sami Zaqout Faculty of Medicine IUG
 Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Auricle External Ear External auditory meatus The Ear Middle Ear (Tympanic Cavity) Auditory ossicles Internal Ear (Labyrinth) Bony labyrinth Membranous labyrinth External Ear Auricle External auditory
Temporomandibular Joint. Dr Noman ullah wazir
 Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Temporomandibular Joint Dr Noman ullah wazir Type of Joint TMJ is a Synovial joint between : The condylar head of the mandible. The mandibular fossa of squamous part of temporal bone. The joint cavity
Defining the Fat Compartments in the Neck: A Cadaver Study
 526406AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14526406Aesthetic Surgery JournalLarson et al research-article2014 Facial Surgery Defining the Fat Compartments in the Neck: A Cadaver Study Jeffrey D. Larson, MD; William S.
526406AESXXX10.1177/1090820X14526406Aesthetic Surgery JournalLarson et al research-article2014 Facial Surgery Defining the Fat Compartments in the Neck: A Cadaver Study Jeffrey D. Larson, MD; William S.
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Infratemporal fossa: Tikrit University college of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck Anatomy 2 nd y.
 Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Infratemporal fossa: This is a space lying beneath the base of the skull between the lateral wall of the pharynx and the ramus of the mandible. It is also referred to as the parapharyngeal or lateral pharyngeal
Learning Outcomes. The Carotid 20/02/2013. Scalp, Face, Parotid. Layers of the Scalp. The Parotid Gland. The Scalp. The Carotid The Facial Artery
 Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Learning Outcomes The Scalp Layers of the Scalp Bleeding from the Scalp The Carotid The Facial Artery Major Muscles of the Face and Jaw(s) Muscles of Mastication Muscles of Facial Expression The Parotid
Subdivided into Vestibule & Oral cavity proper
 Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
Extends from the lips to the oropharyngeal isthmus The oropharyngeal isthmus: Is the junction of mouth and pharynx. Is bounded: Above by the soft palate and the palatoglossal folds Below by the dorsum
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
Clarification of Terms The Spine, Spinal Column, and Vertebral Column are synonymous terms referring to the bony components housing the spinal cord Spinal Cord = made of nervous tissue Facet = a small,
LECTURE -I. Intercostal Spaces & Its Content. BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai. Date:
 LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
LECTURE -I Intercostal Spaces & Its Content BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Date: 18.04.18 Layers of IC space: Following are the layers of the thoracic region: Skin Subcutaneous CT External IC muscle and membrane
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy. Raleigh E. Lingeman
 Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Chapter 84: Surgical Anatomy Raleigh E. Lingeman Surgeons doing head and neck surgery must first master the surgical anatomy and technique of doing neck dissection. Neck dissection is either the classic
Tor Chiu. Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161
 18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
18 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap Tor Chiu Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap 161 Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap FLAP TERRITORY The deep inferior epigastric
Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies
 Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies Prof.Mohamed Hesham Alexandria Faculty of Medicine Alexandria, Egypt Emberyological Basis Branchial Clefts 1st 2nd Pinna EAC 3rd 4th 4th 6th Cervical sinus Branchial
Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies Prof.Mohamed Hesham Alexandria Faculty of Medicine Alexandria, Egypt Emberyological Basis Branchial Clefts 1st 2nd Pinna EAC 3rd 4th 4th 6th Cervical sinus Branchial
Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System. SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable
 L O W E R E X T R E M I T Y T E C H N I Q U E G U I D E Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable Versatility and Control SafeView is
L O W E R E X T R E M I T Y T E C H N I Q U E G U I D E Endoscopic Soft Tissue Release System SafeViewTM 360 Panoramic Visualization Sterile Packaged Fully Disposable Versatility and Control SafeView is
Definition of Anatomy. Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts.
 Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Definition of Anatomy Anatomy is the science of the structure of the body and the relation of its parts. Basic Anatomical Terms Anatomical terms for describing positions: Anatomical position: Supine position:
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space
 Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Bony orbit Roof The orbital plate of the frontal bone Lateral wall: the zygomatic bone and the greater wing of the sphenoid
 Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
Bony orbit Roof: Formed by: The orbital plate of the frontal bone, which separates the orbital cavity from the anterior cranial fossa and the frontal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere Lateral wall: Formed
1. Thyroxine (inactive form) also called T4 (90% of the secretion). 2. Triiodothyronine (active form) also called T3 (10% of the secretion).
 A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
A Introduction The nomenclature of the thyroid gland comes from its close relation to the thyroid cartilage (the thyroid cartilage was named like this because thyroid means shield and it is shielding the
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity RADIUS AND ULNA right
 11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
11 CHAPTER 2 Levels of the anatomical cuts of the upper extremity AND right CUT 1 CUT 4 1 2 3 4 5 6 Isolated fixation of the radius is difficult at this level because of the anterolateral vessels and the
Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
 Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery. John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe. Chapter 1: The Neck
 Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
Anatomical Complications in General Surgery John E. Skandalakis, Stephen W. Gray, Joseph S. Rowe Chapter 1: The Neck The human neck is so designed that the swelling of a normal structure or the presence
EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System
 Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Bones of the Skull Lateral View
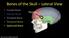 Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Bones of the Skull Lateral View Frontal Bone Parietal Bone Occipital Bone Temporal Bone Sphenoid Bone Pterion Sutures of the Skull Lateral View Coronal Suture Lambdoid Suture Squamous Suture Sutures of
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
