XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System
|
|
|
- Andrea Moore
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, USA Abstract Data normalization is required for any experiment to reach a valid conclusion, particularly when variation in sample quantity is involved. For real-time cellular metabolic analysis using Agilent Seahorse XF technology, the cell quantity per well is a commonly accepted reference value for data normalization. It can be assessed directly by cell counting or indirectly by measuring biomolecules such as total protein or genomic DNA. The Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization system integrates XF technology with a Cytation 1/5 Cell Imaging Multi-Mode reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc). In this configuration, the Cytation 1/5 is controlled by the new Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Cell Counting software, which provides a simplified, automated, and validated solution for microscopic image-based cell counting. This turnkey solution includes 1) in-situ administration of a cell membranepermeable nuclear staining compound (i.e. Hoechst 33342), 2) automated imaging and cell counting optimized for XF assays, and 3) synchronization of images and cell counts into XF result files in Wave software. This solution provides an efficient and reliable method of normalization with a seamless and rapid workflow for XF Analyzer users.
2 Introduction Cellular metabolic functions are measured as oxygen consumption rate (OCR) and extracellular acidification rate (ECAR) and further converted into values like proton efflux rate (PER) and ATP production rate by the Agilent Seahorse XF technology. Similar to other biological experiments, those data should be normalized to derive a valid conclusion if there is any variation in the cell quantity between wells and experiments. Variation in cell quantity can have many different causes including, but not limited to, differences in the proliferation or death rate. Technical errors during sample preparation can also be a possible cause of variation. Regardless of the cause, cell quantity per well should be the primary choice of denominator to normalize XF analysis data with any cell amount variation. The cell quantity per well can be counted directly or indirectly by measuring cellular components such as total protein and genomic DNA. For most users, the latter approach has been preferred to direct cell counting, which requires time and expertise. The Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization system provides an XF data normalization solution using an automated imaging and cell counting workflow. Here, the cell number per well is counted from microscopic images captured by the Cytation 1/5. For the identification of individual cells, cell nuclei are stained with Hoechst 33342, a cell-permeable DNA-binding fluorescent probe detected with a DAPI filter cube in the Cytation 1/5. The cell counts from the images are calculated and reported by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Cell Counting software. Subsequently, this data is imported into the Wave software to normalize XF data. The XF Imaging and Normalization system includes several unique features optimized for XF assays. First, each XF plate is registered by scanning its unique bar code, and subsequently, all image data, as well as the final cell counts, are automatically synchronized to the corresponding XF analysis file. All the information is documented in the Wave software for further review. Second, brightfield images can be obtained in the same workflow, and these images of the cell seeding condition in each well can be compared for data quality management. Third, as a default workflow, cell membranepermeable nuclear staining dye Hoechst is included in the last injection of any XF analysis. This not only simplifies the procedure but also reduces the chance of technical error during manual administration of the dye. The cells are stained during the last set of mix and measurement steps in the XF assay. These are then imaged in the Cytation 1/5 without any further washing or fixation step upon the completion of the XF assay. This workflow can be applied for most cell types cultured in vitro. Finally, this procedure is performed on living cells, thus any additional analysis is still possible. For example, the recommended XF Imaging and Normalization system workflow can be followed by protein assay or immunofluorescence staining to get additional or complimentary data. These tailored features, in combination with brightfield imaging, facilitate improved data interpretation for XF Analyzer users. 2
3 Experimental Normalization validation RAW264.7, HT29 and SKOV3 cells were cultured in high glucose DMEM (Gibco, ) base growth medium supplemented with 1 % FBS (HyClone, SH37.3), 2 mm L-glutamine (Corning, 25-5-CI), and 1 mm sodium pyruvate (Corning, 25--CI). A549 cells were cultured in DMEM:F12 (Corning, 1-9-CV) base growth medium supplemented with 1 % FBS and 2 mm GlutaMAX (Gibco, ). MCF7 cells were cultured in RPMI-164 (Gibco, 2187) with 1 % FBS and 1 mm sodium pyruvate. HepG2 cells were cultured in low glucose DMEM (Gibco, ) supplemented with 1 % FBS, 2 mm GlutaMAX, and 1 mm pyruvate. For XF96, cells were plated at five different cell densities that cover ± 5 % range of cell density recommended; 1 x 1 4 cells/well for HepG2, 2 x 1 4 cells/well for A549, HT29, MCF7 and SKOV3, and 3 x 1 4 cells/well for RAW For XF24, they were plated at three different cell densities ranging from ± 25 %; 2 x 1 4 cells/well for HepG2 and 4 x 1 4 cells/well for A549 and MCF7. Cells were cultured overnight and the metabolic phenotype measured by following the standard Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test protocol 1 except for a modification: 2 µm Hoechst (Thermo, 62249) was added to the oligomycin/fccp mix. Cells were counted by BioTek Cytation 1/5 using the XF Cell Imaging and Counting software 2 and data was normalized in Wave software. The data changes upon normalization were compared using the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Energy Phenotype Report Generator 3. All XF analysis was performed by using cells in Agilent Seahorse XF base medium without phenol red (Agilent Technologies, ) supplemented with 1 mm glucose, 2 mm L-glutamine, 1 mm sodium pyruvate, and 5 mm HEPES, ph 7.4 (Agilent Technologies, ). Macrophage activation RAW264.7 cells were plated at 2.5 x 1 4 cells/well and cultured overnight. Cells were further cultured for 16 h in the absence or presence of 1 ng/ml with or without 2 ng/ ml IFNγ, and the metabolic rates were analyzed by the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test, the Agilent Seahorse XF Glycolytic Rate Assay, or the Agilent Seahorse XF Real-Time ATP Rate Assay Kit according to the user manual 1,4. The last injection solution in each assay, rotenone/antimycin A or 2DG, includes 2 µm Hoechst for nuclear staining. XF imaging and normalization Brightfield and fluorescently labeled nuclear images were collected by the XF Cell Imaging and Counting software and the analyzed results were incorporated to XF analysis data in the Wave software as schematically described in Figure 7. Brightfield images were captured as the quality reference during the outgassing step while the cartridge was being calibrated 2. Cell number per well was measured by counting fluorescently labeled nuclei from images captured by Cytation 1/5. As described above, Hoechst was included in the last injection in the XF analysis protocol, with a rotenone/antimycin A injection in the XF Cell Mito Stress Test, 2DG injection in the XF Glycolysis Stress Test and the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay, and oligomycin/fccp injection in the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test. Data presentation XF data presented in this Application Note were prepared by using the GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software, Inc; Figure 1, 4, 5, and 6) or by the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test Report Generator (Figure 2 and 3) after a data export using the Wave software. 3
4 Results and Discussion Data normalization using cell counts from images As a validation model for data normalization, we plated various cell types at three to five different densities by assuming the two basal metabolic rates, OCR and ECAR, proportionally correlate to the cell quantity per well. This assumption is true only when cells don t have any biological response to the cell density change. Among the cell lines tested, most of the basal metabolic rates showed a good linear correlation to the cell density within the range of the standard plating density commonly recommended for XF analysis, with a few exceptions (data not shown). Figure 1 shows an example of how this data normalization solution works for the XF cell energy phenotype test 1. RAW264.7 macrophages were plated at four different cell densities one day prior to the assay and their metabolic phenotypes were analyzed by an Agilent Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer. The only difference from the standard XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test was to include cell-permeable Hoechst dye along with the oligomycin/fccp compounds in the same injection port (arrow). As shown in Figure 1A, OCR and ECAR increase proportionally to the seeding density. Upon completion of the XF analysis, fluorescence images were captured and counted by the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software as shown in Figure 1B. Figure 1C shows the data after normalization by dividing the metabolic rates by the cell numbers counted by the software. Both OCR and ECAR kinetic traces superimpose after applying the cell count normalization factor, particularly for the basal rates before the cells were stressed by oligomycin and FCCP. Notably, this data convergence by normalization happens only when there is no biological change occurring as a result of density differences. Therefore, data normalization can identify true biological change related to cell density difference. As shown in Figure 1C, the FCCP effect on OCR varied depending on cell density while the ECAR elevation by oligomycin was not affected by cell density even though the basal value of both rates converged well. A OCR (pmol/min) OCR Data B In situ Staining C OCR (pmol/min/1 Cells) Normalized OCR Data K 3K 38K 45K ECAR Data Nuclear Segmentation Normalized ECAR Data ECAR (mph/min) ECAR (mph/min/1 Cells) Figure 1. Normalization of the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test data using the XF Imaging and Normalization system. RAW264.7 cells were seeded at various cell densities, as indicated, a day prior to the assay. Hoechst (final 2 µm) was co-injected (arrow) with a oligomycin/fccp mixture in the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Assay; A) data before normalization; B) a representative image acquired and the corresponding nuclear segmentation result; C) normalization results. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 6 technical replicates. Cells growing in clumps are also identified and counted. 4
5 Before Normalization After Normalization Before Normalization After Normalization A549 dispersed A549 dispersed SKOV3 dispersed HepG2 moderately clustered HepG2 moderately clustered MCF7 highly clustered HT29 highly clustered Figure 3. Normalization of the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test data from multiple cancer cell lines on XF24 plates. Cell energy phenotypes of three different cell lines seeded at three different cell densities were obtained by using XF Cell Energy Phenotype Report Generator. The phenotype diagrams before (left column) and after (right column) normalization are compared for each cell line. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 6 technical replicates. MCF7 highly clustered MCF7 scattered Figure 2. Normalization of the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test data from multiple cancer cell lines on Agilent Seahorse XF96 Microplates. Cell energy phenotypes of six different cell lines seeded at five different cell densities were obtained by using the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Report Generator. The phenotype diagrams before (left column) and after (right column) normalization are compared for each cell line. This protocol and workflow was further validated by using different cell types exhibiting varied morphological characteristics in vitro. Up to 16 cell lines including RAW264.7 with various nuclear sizes and distribution were seeded at five different cell densities and the metabolic phenotypes were examined by employing the XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test. As described above, Hoechst was included in the oligomycin/fccp mixture. The data were normalized by the cell numbers calculated by the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software. Figure 2 shows a summary comparing the data from six representative cell lines before and after applying normalization. As shown, except for a few extreme cases, all basal metabolic rates converge well after applying the cell count normalization factor. A similar outcome was obtained from cells seeded on Agilent Seahorse XF24 Microplates at three different densities (Figure 3). 5
6 A OCR (pmol/min) Oligomycin FCCP Hoechst Rot/AA Control B OCR (pmol/min/1 Cells) 12 Oligomycin 8 4 FCCP Hoechst Rot/AA Control Basal OxPhos SRC Basal OxPhos SRC OCR (pmol/min) OCR (pmol/min) OCR (pmol/min/1 Cells) OCR (pmol/min/1 Cells) Figure 4. Data normalization effect on the XF Cell Mito Stress Test results. RAW264.7 cells were cultured overnight in the presence of 1 ng/ml alone or together with 2 ng/ml IFNγ and mitochondrial function was analyzed by the XF Cell Mito Stress Test. A) before normalization; B) after normalization. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 5 technical replicates (ns, not significant; *, p <.5; **, p <.5; ***, p <.5;, p <.5). A glycoper (pmol/min) Rot/AA Hoechst Rot/AA Control B glycoper (pmol/min/1 Cells) Rot/AA Hoechst Rot/AA Control glycoper (pmol/min) Figure 5. Data normalization effect on the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay results. RAW264.7 cells were cultured overnight in the presence of 1 ng/ml alone or together with 2 ng/ml IFNγ and glycolytic activity changes upon macrophage activation were analyzed by the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay. The overall glycoper kinetic data as well as the basal and compensatory glycolytic rates were compared; A) before normalization; B) after normalization. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 5 technical replicates (ns, not significant; *, p <.5; **, p <.5; ***, p <.5;, p <.5) Basal Glycolysis Compensatory Glycolysis Basal Glycolysis Compensatory Glycolysis *** * glycoper (pmol/min) glycoper (pmol/min/1 Cells) ** glycoper (pmol/min/1 Cells) ns **
7 Data normalization leads to correct data interpretation A macrophage is a type of immune cell well known to exhibit metabolic plasticity and a dynamic metabolic phenotype switch that is associated with activation. RAW264.7 murine macrophage is widely used as a model for in vitro proinflammatory activation by pathogenic stimuli. In vitro exposure to bacterial lipopolysaccharide () and/or cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ) triggers an activation-associated metabolic change of RAW264.7 macrophages from an oxidative to a glycolytic phenotype. This is demonstrated by an increase in ECAR (or PER) and decrease in OCR 5. The metabolic rates, however, should be normalized for quantitative comparison because macrophage activation is tightly associated with proliferation rate change, with proliferation severely reduced upon activation. Figure 4 is an example of how data normalization affects the data interpretation of the XF Cell Mito stress test results 1. Figure 4A is the data summary before normalization, and both basal mitochondrial respiration and spare respiratory capacity (SRC) were severely suppressed either by alone or / IFNγ costimulation. However, the data interpretation turns out to be different when the data is normalized by cell number. Although alone suppressed mitochondrial respiration, the effect was rather specific to the SRC, while a significant amount of basal respiration was maintained. In contrast, / IFNγ costimulation suppressed mitochondrial function completely, including the basal respiration (Figure 4B). Interpretation of the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay 1 results was more dramatically affected by data normalization (Figure 5). Without normalization, the glycolytic rates of macrophages appeared to be downregulated slightly for the basal measurement and more severely for the compensatory activity upon activation (Figure 5A). By considering the XF Cell Mito Stress Test results shown in Figure 4A, the overall metabolic suppression seemed to happen without any significant phenotype switching. However, according to the normalized data shown in Figure 5B, the basal glycolysis was significantly up-regulated by stimulation and IFNγ costimulation maximized the basal glycolytic rate. Interestingly, the change in compensatory glycolysis was minimal even with complete suppression of mitochondrial respiration when treated with γ (Figure 4). Metabolic switching can be more precisely characterized by comparing the contribution of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis on ATP production. Figure 6 is an Agilent Seahorse XF Real-Time ATP Rate Assay 1,4 result showing that stimulation-made macrophages relied more on glycolytic ATP production, while γ co-stimulation-made macrophages were completely dependent on glycolysis. Without normalization, the total ATP production rates seemed to be suppressed upon activation. However, the data revealed that total ATP production rates per cell were kept stable, and it became evident that the cells exhibited an extremely glycolytic phenotype due to the mitochondrial downregulation. A ATP Production Rate (pmol/min) B ATP Production Rate (pmol/min/1 cells) ATP Production Rate ATP Production Rate Glyco ATP Mito ATP Glyco ATP Mito ATP Figure 6. Data normalization effect on ATP production rate comparison. The contributions of mitochondrial respiration and glycolysis on ATP production were compared after overnight activation of RAW264.7 macrophage; A) before normalization; B) after normalization. Data shown are mean ± SD, n = 5 technical replicates. 7
8 XF Cartridge Hydration Cell culture in XF Plate Cartridge Calibration By Wave Software Brightfield Imaging & CO 2 -free Incubation By XF Imaging and Cell Counting software Calibrate a cartridge loaded with reagents in injection ports The last injection includes Hoechst XF Assay Controlled by Wave software Fluorescent Imaging & Cell Counting By XF Imaging and Cell Counting software Data Analysis Imaging, cell counting and XF data analysis by Wave software Figure 7. A typical workflow of the XF Imaging and Normalization system 8
9 Cell counting and data normalization workflow Fluorescent staining of cell nuclei is a widely used method to identify individual cells, because it allows cells to be segmented into individual objects in a microscopic image for most two-dimensional cell cultures. Hoechst is the most commonly used membrane-permeable blue dye that can stain live cell nuclei, which can then be imaged and analyzed microscopically or counted by flow cytometry. In the recommended workflow, Hoechst is combined with the final reagent in an XF assay kits injection strategy. The dye is directly injected together with the kit reagent(s) for XF analysis (e.g. rotenone/antimycin A mix in the XF Cell Mito Stress Test and the XF Real-Time ATP Rate Assay, 2DG in the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay, etc.). The injected dye binds to nuclei during the last three to five measurement cycles. Because Hoechst labeled nuclei can be detected and identified without any additional washing step, cells can be imaged immediately by the Cytation 1/5 upon the completion of an XF assay. These cell numbers are calculated by the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software and used to transform XF data as accurate and reproducible normalization factors (Figure 7). Considerations for accurate cell counting Although the software provides an optimized cell counting solution for most cell types used for XF analysis by way of an automatic thresholding algorithm, there are several factors that should be considered to generate accurate cell counts for best normalization performance. It is critical to have detectable nuclear objects uniformly stained for better accuracy of cell counting. Reviewing the masked image in the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software is recommended. The masked image is an image layer that represents the algorithm s nuclei detection, which is superimposed on the raw fluorescence image and verifies that all valid objects are identified by the software. This review function is available after the completion of the postprocessing step of counting cells in the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software. If a significant number of cells are not identified in the masked images, users need to consider the options described in the following paragraphs to normalize the data. First, some cell types are not suitable for in situ nuclear staining. For example, Hoechst can be exported by ABCG2 transporter, which is expressed in hematopoietic stem cells and results in poor retention of the dye 6. For this kind of cell type, in-situ staining may not be applicable, and a staining after fixation may be preferred. The imaging and counting can still be performed in the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software and data can still be automatically linked to the corresponding XF data by utilizing the common bar code read in the database. Second, inconsistency in nuclear staining intensity can also affect nuclear identification. Similar to other DNA-binding dyes, Hoechst has a higher affinity to condensed chromosomes, which are commonly found in apoptotic cells 7. If the cell sample exhibits severe differences in fluorescence intensity between healthy cells and dying cells, the automatic thresholding algorithm may not work properly. Users may need to reanalyze the image data in the Gen5 software from BioTek Instruments and customize the cell counting parameters, including the threshold setting. The counting result obtained by Gen5 can be transferred manually to XF data in Wave. Third, the cell seeding condition is also a critical factor affecting normalization performance. Cells should be seeded subconfluently with an even distribution for accurate normalization and optimized XF assay performance. In contrast to brightfield imaging, which provides whole-well images, the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software uses a single image capturing the center portion of each well. The nuclei are counted within this image and then the software calculates the total number of cells per well by extrapolation. The imaged center portion closely overlaps with the area where oxygen and ph are measured most effectively. Thus, similar to the OCR and ECAR calculation, automatic cell counting is performed under the assumption that cells are evenly distributed across the entirety of each well. The cell seeding condition can be reviewed by using brightfield imaging and any error-prone wells can be identified and removed if necessary 2. Finally, any large foreign object in or under the well can affect the fluorescence images by scattering the excitation light. In situ staining can prevent the occurrence of foreign objects by eliminating exposure of the XF plate to an open environment during the staining. Also, any large object contamination can be reviewed by brightfield and fluorescence images in the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software as well as in the Wave software. Protocol modification The nuclear staining procedure can be modified depending on the user preference. Hoechst can be injected separately within the XF assay after the whole analysis, if there is an injection port available (e.g. Hoechst injection through port D after a standard running of the XF Cell Mito Stress Test). However, when an additional injection is added in the standard protocol, data compatibility needs to be verified if users want to run an XF Report Generator. For example, an additional injection of Hoechst after 2DG in the XF glycolytic rate assay is not compatible with the XF Glycolytic Rate Assay Report Generator, because it uses the last measurements as a reference value to assess the basal and compensatory glycolytic rates. 9
10 Conclusion The XF Imaging and Normalization system provides an easy, rapid, and seamless workflow to reproducibly generate cell counts per well for performing normalization of XF data, by running XFe96 or XFe24 Analyzers with the Cytation 1/5 through a single XF 64-bit controller. Cell images and counts are obtained by the XF Imaging and Cell Counting software and the data automatically synchronizes and is documented within the Wave XF result file. This enables users to more successfully perform XF assays with data integrity assurance for achieving the most optimized and valid data interpretation. References Scharenberg, C.W., Harkey, M.A. and Torok-Storb, B. (22) The ABCG2 transporter is an efficient Hoechst efflux pump and is preferentially expressed by immature human hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 99, Ellwart, J.W. and Dörmer, P. (199) Vitality measurement using spectrum shift in Hoechst stained cells. Cytometry 11,
11 11
12 For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. This information is subject to change without notice. Agilent Technologies, Inc. 218 Printed in the USA, June 21, EN
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer
 icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology
 White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction
 Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate
 Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Islet Assay Using the Agilent Seahorse XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Technical Overview Introduction Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached to
Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug
 1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
1 Islet Oxygen Consumption Assay using the XF24 Islet Capture Microplate Shirihai Lab and Seahorse Bioscience Aug 6 2009 XF Analyzers are most commonly used with an adherent monolayer of cells attached
Supplementary Figure 1
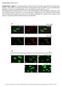 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Cell Metabolism Assays. for. Immunology. Research
 the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector
ab Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay
 Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
ROS Activity Assay Kit
 ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
ROS Activity Assay Kit Catalog Number KA3841 200 assays Version: 03 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General Information... 4 Materials
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW macrophages
 Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red)
 Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
Intracellular (Total) ROS Activity Assay Kit (Red) Catalog Number KA2525 200 assays Version: 04 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 General
ab Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay
 Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
 Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit
 Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit Item No. 500001 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Lipid Droplets Fluorescence Assay Kit Item No. 500001 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Cell Metabolism Assays. for OMICS. Research
 Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
ab Intracellular O 2 Probe
 ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab140101 Intracellular O 2 Probe Instructions for Use For the measurement of intracellular oxygen in populations of live mammalian cells This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM. Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator
 Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Cell Migration and Invasion Assays INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Real-time automated measurements of cell motility inside your incubator See the whole story Real-time cell motility visualization and
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate
 Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit
 Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Multi-Parameter Apoptosis Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1335 5 x 96 assays Version: 05 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function
 Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
MitoXpress FAO Assay. For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation
 MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux
 Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Item No. 10011125 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Rapid, Real-time Detection of T Cell Activation Using an Agilent Seahorse XFp Analyzer
 Rapid, Real-time etection of T ell ctivation Using an gilent Seahorse XFp nalyzer pplication Note uthors Pamela Swain, Yoonseok Kam, Kacey aradonna, George W. Rogers, and rian P. ranka bstract Immune cells
Rapid, Real-time etection of T ell ctivation Using an gilent Seahorse XFp nalyzer pplication Note uthors Pamela Swain, Yoonseok Kam, Kacey aradonna, George W. Rogers, and rian P. ranka bstract Immune cells
Speed - Accuracy - Exploration. Pathfinder SL
 Speed - Accuracy - Exploration Pathfinder SL 98000 Speed. Accuracy. Exploration. Pathfinder SL represents the evolution of over 40 years of technology, design, algorithm development and experience in the
Speed - Accuracy - Exploration Pathfinder SL 98000 Speed. Accuracy. Exploration. Pathfinder SL represents the evolution of over 40 years of technology, design, algorithm development and experience in the
Time after injection (hours) ns ns
 Platelet life span (% iotinylated platelets) 1 8 6 4 2 4 24 48 72 96 Time after injection (hours) 6 4 2 IgG GPIα GPIβ GPII GPVI Receptor expression (GeoMean, fluorescence inteity) Supplementary figure
Platelet life span (% iotinylated platelets) 1 8 6 4 2 4 24 48 72 96 Time after injection (hours) 6 4 2 IgG GPIα GPIβ GPII GPVI Receptor expression (GeoMean, fluorescence inteity) Supplementary figure
Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages
 Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages Jan Van den Bossche, PhD j.vandenbossche@amc.nl Departement of Medical Biochemistry Experimental Vascular Biology group Postdoc
Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages Jan Van den Bossche, PhD j.vandenbossche@amc.nl Departement of Medical Biochemistry Experimental Vascular Biology group Postdoc
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Introduction Kit Components Cat. # # of vials Reagent Quantity Storage
 Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
Human Pluripotent Stem Cell Cardiomyocyte Differentiation Kit (PSCCDK) Catalog #5901 Introduction Human pluripotent stem cells (hpsc), including embryonic stem cells (ESC) and induced pluripotent stem
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells.
 Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Supplemental Figure S1. RANK expression on human lung cancer cells. (A) Incidence and H-Scores of RANK expression determined from IHC in the indicated primary lung cancer subgroups. The overall expression
Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit)
 Product Insert QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit) Introduction About the Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit The homogeneous QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit from Molecular
Product Insert QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit Product # R8132 (Explorer Kit) R8133 (Bulk Kit) Introduction About the Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit The homogeneous QBT Fatty Acid Uptake Assay Kit from Molecular
Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells Exposed to Free Fatty Acids Image-Based Assay to Model Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
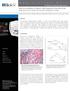 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells Exposed to Free Fatty Acids Image-Based Assay to Model Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Paul Held, Ph.D., Laboratory Manager, Applications
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Lipid Accumulation in HepG2 Cells Exposed to Free Fatty Acids Image-Based Assay to Model Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) Paul Held, Ph.D., Laboratory Manager, Applications
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY
 CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
ab LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
ab133127 LDL Uptake Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For the detection of LDL uptake into cultured cells. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use. Version
Comparison of Different Cell Types for Neutral Lipid Accumulation Using Image-Based Metrics to Quantify Lipid Accumulation in Cells
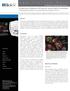 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Comparison of Different Cell Types for Neutral Lipid Accumulation Using Image-Based Metrics to Quantify Lipid Accumulation in Cells Paul Held, Ph.D., Laboratory Manager, Applications
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Comparison of Different Cell Types for Neutral Lipid Accumulation Using Image-Based Metrics to Quantify Lipid Accumulation in Cells Paul Held, Ph.D., Laboratory Manager, Applications
SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death
 SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death Andrea Glasauer, Laura A. Sena, Lauren P. Diebold, Andrew P. Mazar & Navdeep S. Chandel Inventory of Supplemental
SUPPLEMENTAL INFORMATION SOD1 inhibition reduces non-small cell lung cancer by inducing cell death Andrea Glasauer, Laura A. Sena, Lauren P. Diebold, Andrew P. Mazar & Navdeep S. Chandel Inventory of Supplemental
Supporting Information. Non-thermal plasma with 2-deoxy-D-glucose synergistically induces cell death by targeting glycolysis in blood cancer cells
 Supporting Information Non-thermal plasma with 2-deoxy-D-glucose synergistically induces cell death by targeting glycolysis in blood cancer cells Neha Kaushik, 1 Su Jae Lee, 2 Tae Gyu Choi 3, Ku Youn Baik,
Supporting Information Non-thermal plasma with 2-deoxy-D-glucose synergistically induces cell death by targeting glycolysis in blood cancer cells Neha Kaushik, 1 Su Jae Lee, 2 Tae Gyu Choi 3, Ku Youn Baik,
ab MitoTox Complex I OXPHOS Activity Microplate Assay
 ab109903 MitoTox Complex I OXPHOS Activity Microplate Assay Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex I activity in Bovine samples This product is for research use only and is not
ab109903 MitoTox Complex I OXPHOS Activity Microplate Assay Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex I activity in Bovine samples This product is for research use only and is not
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology
 Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
Next-Gen Analytics in Digital Pathology Cliff Hoyt, CTO Cambridge Research & Instrumentation April 29, 2010 Seeing life in a new light 1 Digital Pathology Today Acquisition, storage, dissemination, remote
Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation
 Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
Laboratory Hematology 8:85-90 2002 Carden Jennings Publishing Co.. Ltd. Abbott Cell-Dyn Reticulocyte Method Comparison and Reticulocyte Normal Reference Range Evaluation T. SCHISANO, L. VAN HOVE Abbott
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL
 DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
DEVELOPMENTAL VALIDATION OF SPERM HY-LITER EXPRESS Jennifer Old, Chris Martersteck, Anna Kalinina, Independent Forensics, Lombard IL Background and Introduction SPERM HY-LITER is the first immunofluorescent
Determination of Copper in Green Olives using ICP-OES
 Application Note Food and Agriculture Determination of Copper in Green Olives using ICP-OES Intelligent Rinse function reduced analysis time by 60%, saving 191.4 L of argon Authors Ryley Burgess, Agilent
Application Note Food and Agriculture Determination of Copper in Green Olives using ICP-OES Intelligent Rinse function reduced analysis time by 60%, saving 191.4 L of argon Authors Ryley Burgess, Agilent
Carnitine / Acylcarnitines Dried Blood Spots LC-MS/MS Analysis Kit User Manual
 Page 1 / 14 Carnitine / Acylcarnitines Dried Blood Spots LC-MS/MS Analysis Kit User Manual ZV-3051-0200-15 200 Page 2 / 14 Table of Contents 1. INTENDED USE... 3 2. SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 3 3. TEST
Page 1 / 14 Carnitine / Acylcarnitines Dried Blood Spots LC-MS/MS Analysis Kit User Manual ZV-3051-0200-15 200 Page 2 / 14 Table of Contents 1. INTENDED USE... 3 2. SUMMARY AND EXPLANATION... 3 3. TEST
Features & Benefits of the Oris Cell Migration Assay
 Adherent cell migration without cell culture inserts The Oris Cell Migration Assay* is designed with a unique cell seeding stopper, detection mask, and stopper tool. There is no Transwell membrane insert
Adherent cell migration without cell culture inserts The Oris Cell Migration Assay* is designed with a unique cell seeding stopper, detection mask, and stopper tool. There is no Transwell membrane insert
Fluorescence Microscopy
 Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
Fluorescence Microscopy Imaging Organelles Mitochondria Lysosomes Nuclei Endoplasmic Reticulum Plasma Membrane F-Actin AAT Bioquest Introduction: Organelle-Selective Stains Organelles are tiny, specialized
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms.
 1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
Dako IT S ABOUT TIME. Interpretation Guide. Agilent Pathology Solutions. ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis)
 INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
INTERPRETATION Dako Agilent Pathology Solutions IQFISH Interpretation Guide ALK, ROS1 and RET IQFISH probes (Dako Omnis) MET IQFISH probe (Dako Omnis) IT S ABOUT TIME For In Vitro Diagnostic Use ALK, ROS1,
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening
 Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
Protocol for A-549 VIM RFP (ATCC CCL-185EMT) TGFβ1 EMT Induction and Drug Screening Introduction: Vimentin (VIM) intermediate filament (IF) proteins are associated with EMT in lung cancer and its metastatic
SUPPORTING INFORMATION
 SUPPORTING INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles. Tests were conducted on the separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles added in excess to BEGM (A)
SUPPORTING INFORMATION SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE LEGENDS Fig. S1. Separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles. Tests were conducted on the separation of non-dissolved nanoparticles added in excess to BEGM (A)
Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Author: Jeanine Hinterneder, PhD PerkinElmer Inc. Hopkinton, MA Measuring PD-L1 Expression in Breast Cancer Cell Lines with AlphaLISA Introduction In the tumor microenvironment,
Detection. personal. Now, you can optimize your personal workflow. Promega instruments and reagents integrate easily.
 personal Detection Now, you can optimize your personal workflow. Promega instruments and reagents integrate easily. An ultra-sensitive, versatile, and affordable single tube luminometer for Life Science
personal Detection Now, you can optimize your personal workflow. Promega instruments and reagents integrate easily. An ultra-sensitive, versatile, and affordable single tube luminometer for Life Science
ab Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit
 ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
ab133078 Lysosome/Cytotoxicity Dual Staining Kit Instructions for Use For studying lysosome function at the cellular level. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic use.
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer
 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay on the XF24 Analyzer Mitochondria oxidize a variety of fuels to generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation. Cells can utilize fatty acid, glucose and amino acids as their
Nature Protocols: doi: /nprot Supplementary Figure 1. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA (10 um) upon addition of GSH in HEPES (10 mm, ph = 7.4) containing 10% DMSO. Each spectrum was recorded
Supplementary Figure 1 Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA. Fluorescent titration of probe CPDSA (10 um) upon addition of GSH in HEPES (10 mm, ph = 7.4) containing 10% DMSO. Each spectrum was recorded
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving Function of the xcelligence System to Optimize Endpoint Viability and
Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis
 icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
icell Skeletal Myoblasts Application Protocol Modulating Glucose Uptake in Skeletal Myotubes: Insulin Induction with Bioluminescent Glucose Uptake Analysis Introduction The skeletal muscle is one of the
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.
 Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented
 Supplemental Materials Figure S1. Cultured BMDCs express CD11c BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented with 15 ng/ml GM-CSF. Media was changed and fresh
Supplemental Materials Figure S1. Cultured BMDCs express CD11c BMDCs were generated in vitro from bone marrow cells cultured in 10 % RPMI supplemented with 15 ng/ml GM-CSF. Media was changed and fresh
Assays for Immuno-oncology Research Real-time automated measurements of immune and tumor cell dynamics within your incubator
 INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Assays for Immuno-oncology Research Real-time automated measurements of immune and tumor cell dynamics within your incubator See what your cells are doing and when they
INCUCYTE LIVE-CELL ANALYSIS SYSTEM Assays for Immuno-oncology Research Real-time automated measurements of immune and tumor cell dynamics within your incubator See what your cells are doing and when they
Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays
 Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays 2 Automated and Standardized Colony Counting Table of Contents 4 Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assays for Mouse Bone Marrow 5 Automated Assay
Automated and Standardized Counting of Mouse Bone Marrow CFU Assays 2 Automated and Standardized Colony Counting Table of Contents 4 Colony-Forming Unit (CFU) Assays for Mouse Bone Marrow 5 Automated Assay
Cellular Respiration Guided Notes
 Respiration After you hear word 'respiration', you may now think about breathing. During breathing, the is entered with each inhale and is released with each exhale. You may have noticed that breathing
Respiration After you hear word 'respiration', you may now think about breathing. During breathing, the is entered with each inhale and is released with each exhale. You may have noticed that breathing
effect on the upregulation of these cell surface markers. The mean peak fluorescence intensity
 SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
SUPPLEMENTARY FIGURE 1 Supplementary Figure 1 ASIC1 disruption or blockade does not effect in vitro and in vivo antigen-presenting cell activation. (a) Flow cytometric analysis of cell surface molecules
Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint
 APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
APPLICATION NOTE AlphaLISA Technology Authors: Matthew Marunde Stephen Hurt PerkinElmer, Inc. Hopkinton, MA Utilizing AlphaLISA Technology to Screen for Inhibitors of the CTLA-4 Immune Checkpoint Introduction
Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival
 Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
Supplementary Information for Proteomic profiling of small-molecule inhibitors reveals dispensability of MTH1 for cancer cell survival Tatsuro Kawamura 1, Makoto Kawatani 1, Makoto Muroi, Yasumitsu Kondoh,
HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells
 Hegedus et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:98 RESEARCH Open Access HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells Andrea Hegedus, Maia Kavanagh
Hegedus et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:98 RESEARCH Open Access HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells Andrea Hegedus, Maia Kavanagh
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Plus
 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Plus User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis (Cat#: 68FT-AnnVP-) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent upport And ervice
RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Detection Kit Plus User Manual Version 1.0 May 25, 2014 RayBio Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis (Cat#: 68FT-AnnVP-) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent upport And ervice
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
ab SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based)
 ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ab133114 SREBP-2 Translocation Assay Kit (Cell-Based) Instructions for Use For analysis of translocation of SREBP-2 into nuclei. This product is for research use only and is not intended for diagnostic
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES. Bratislav M. Janjic
 ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
ANALYSIS OF THE LEVEL OF OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION IN BREAST CANCER CELL TYPES by Bratislav M. Janjic Diplom in Biology, Univerziteta u Beogradu, Yugoslavia, 1996 Submitted to the Graduate Faculty of the
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay
 Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
Challenges in Development and Validation of an Intracellular Cytokine Staining assay Jenny Hendriks, Crucell Hatching @ EBF, Brussels, June 202 www.crucell.com Vaccines vs Protein therapeutics Protein
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT. Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx
 WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
WHO Prequalification of In Vitro Diagnostics PUBLIC REPORT Product: Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect WHO reference number: PQDx 0226-032-00 Alere q HIV-1/2 Detect with product codes 270110050, 270110010 and 270300001,
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop
 BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
BD CBA on the BD Accuri C6: Bringing Multiplexed Cytokine Detection to the Benchtop Maria Dinkelmann, PhD Senior Marketing Applications Specialist BD Biosciences, Ann Arbor, MI 23-14380-00 Cellular Communication
ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA
 ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
ANDROVISION - MORE THAN CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research
 New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
AbsoluteIDQ p150 Kit. Targeted Metabolite Identifi cation and Quantifi cation. Bringing our targeted metabolomics expertise to your lab.
 AbsoluteIDQ p150 Kit Targeted Metabolite Identifi cation and Quantifi cation Bringing our targeted metabolomics expertise to your lab. The Biocrates AbsoluteIDQ p150 mass spectrometry Assay Preparation
AbsoluteIDQ p150 Kit Targeted Metabolite Identifi cation and Quantifi cation Bringing our targeted metabolomics expertise to your lab. The Biocrates AbsoluteIDQ p150 mass spectrometry Assay Preparation
Unsupervised Identification of Isotope-Labeled Peptides
 Unsupervised Identification of Isotope-Labeled Peptides Joshua E Goldford 13 and Igor GL Libourel 124 1 Biotechnology institute, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108 2 Department of Plant Biology,
Unsupervised Identification of Isotope-Labeled Peptides Joshua E Goldford 13 and Igor GL Libourel 124 1 Biotechnology institute, University of Minnesota, Saint Paul, MN 55108 2 Department of Plant Biology,
The Journal of Physiology
 J Physiol 594.24 (216) pp 7197 7213 7197 TECHNIQUES FOR PHYSIOLOGY Development of a high-throughput method for real-time assessment of cellular metabolism in intact long skeletal muscle fibre bundles Rui
J Physiol 594.24 (216) pp 7197 7213 7197 TECHNIQUES FOR PHYSIOLOGY Development of a high-throughput method for real-time assessment of cellular metabolism in intact long skeletal muscle fibre bundles Rui
Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000
 GE Healthcare Application note 28-9673-96 AA IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Key words: IN Cell Analyzer online
GE Healthcare Application note 28-9673-96 AA IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Use of online cell counting for micronucleus and neurite outgrowth assays on IN Cell Analyzer 2000 Key words: IN Cell Analyzer online
Life Sciences METABOLISM. Transform Your Metabolic Research
 METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
METABOLISM Transform Your Metabolic Research COMPREHENSIVE TOOLS FOR ADVANCING YOUR METABOLIC RESEARCH Metabolism refers to a set of chemical reactions which are responsible for transforming carbohydrates,
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
 EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric) Base Catalog # PLEASE READ THIS ENTIRE USER GUIDE BEFORE USE Uses: The EpiQuik Circulating Acetyl Histone H3K18 ELISA Kit (Colorimetric)
ABSTRACT INTRODUCTION
 /, 2017, Vol. 8, (No.50), pp: 87860-87877 Extracellular ATP, as an energy and phosphorylating molecule, induces different types of drug resistances in cancer cells through ATP internalization and intracellular
/, 2017, Vol. 8, (No.50), pp: 87860-87877 Extracellular ATP, as an energy and phosphorylating molecule, induces different types of drug resistances in cancer cells through ATP internalization and intracellular
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
LDL Uptake Flow Cytometry Assay Kit Item No. 601470 www.caymanchem.com Customer Service 800.364.9897 Technical Support 888.526.5351 1180 E. Ellsworth Rd Ann Arbor, MI USA TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL INFORMATION
Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the
 Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the nuclear export inhibitor, selinexor Joshua M. Marcus 1, Russell T. Burke 1, John A. DeSisto 1, Yosef Landesman
Longitudinal tracking of single live cancer cells to understand cell cycle effects of the nuclear export inhibitor, selinexor Joshua M. Marcus 1, Russell T. Burke 1, John A. DeSisto 1, Yosef Landesman
Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum...1. Trademarks: HiLyte Fluor (AnaSpec, Inc.)
 Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
Table of Contents Fluor TM Labeling Dyes Superior Fluorescent Labeling Dyes Spanning the Full Visible Spectrum....1 Fluor TM 405 Dye, an Excellent Alternative to Alexa Fluor 405 & DyLight 405....2 Fluor
ab Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit
 ab109908 Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex II activity in samples from Human, Rat, Mouse and Cow This product is for research
ab109908 Complex II Enzyme Activity Microplate Assay Kit Instructions for Use For the quantitative measurement of Complex II activity in samples from Human, Rat, Mouse and Cow This product is for research
Focus Application. Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity
 xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
xcelligence System Real-Time Cell Analyzer Focus Application Compound-Induced Cytotoxicity For life science research only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Featured Study: Using the Time Resolving
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Supporting Information Identification of Novel ROS Inducers: Quinone Derivatives Tethered to Long Hydrocarbon Chains Yeonsun Hong,, Sandip Sengupta,, Wooyoung Hur, *, Taebo Sim,, * KU-KIST Graduate School
Nature Biotechnology: doi: /nbt Supplementary Figure 1. Diagram of BBB and brain chips.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
Supplementary Figure 1 Diagram of BBB and brain chips. (a) Schematic of the BBB Chip demonstrates the 3 parts of the chip, Top PDMS channel, membrane and Bottom PDMS channel; (b) Image of 2 BBB Chips,
20X Buffer (Tube1) 96-well microplate (12 strips) 1
 PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
PROTOCOL MitoProfile Rapid Microplate Assay Kit for PDH Activity and Quantity (Combines Kit MSP18 & MSP19) 1850 Millrace Drive, Suite 3A Eugene, Oregon 97403 MSP20 Rev.1 DESCRIPTION MitoProfile Rapid Microplate
Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon
 Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE BIOLOGY F214/01 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy *F210040113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
Friday 11 January 2013 Afternoon A2 GCE BIOLOGY F214/01 Communication, Homeostasis and Energy *F210040113* Candidates answer on the Question Paper. OCR supplied materials: None Other materials required:
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit
 RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
RayBio Annexin V-Cy5 Apoptosis Detection Kit User Manual Version 1.0 Mar 20, 2014 (Cat#: 68C5-AnnV-S) RayBiotech, Inc. We Provide You With Excellent Support And Service Tel:(Toll Free)1-888-494-8555 or
ECHOLAB. Screening and Clinical Modality. User Programmable Protocols. Otoacoustic Emissions System TEOAE - DPOAE - ABR - AABR
 ECHOLAB Otoacoustic Emissions System - DPOAE - ABR - AABR Screening and Clinical Modality User Programmable Protocols ECHOLAB Otoacoustic Emissions System - DPOAE - ABR - AABR All of Labat s technology
ECHOLAB Otoacoustic Emissions System - DPOAE - ABR - AABR Screening and Clinical Modality User Programmable Protocols ECHOLAB Otoacoustic Emissions System - DPOAE - ABR - AABR All of Labat s technology
Stimulation of IL-2 Secretion in Human Lymphocytes
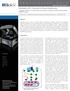 A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Stimulation of IL-2 Secretion in Human Lymphocytes Using the Lionheart LX Automated Microscope to Image and Analyze Silver-stained ELISPOT Assays Paul Held, Ph.D., Lab Manager,
A p p l i c a t i o n N o t e Stimulation of IL-2 Secretion in Human Lymphocytes Using the Lionheart LX Automated Microscope to Image and Analyze Silver-stained ELISPOT Assays Paul Held, Ph.D., Lab Manager,
Computerized semen analysis. Product features. Basic system
 AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
AndroVision - more than CASA AndroVision CASA system with Zeiss AxioScope optics and automated ScanStage Computerized semen analysis AndroVision is a highly precise CASA* system for standardised, interactive
Cellometer Image Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis
 Cellometer Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis Importance of Cell Cycle Research Oncology: Since cancer cells often undergo abnormal cell division and proliferation, it is important to understand the cell
Cellometer Cytometry for Cell Cycle Analysis Importance of Cell Cycle Research Oncology: Since cancer cells often undergo abnormal cell division and proliferation, it is important to understand the cell
Assay Name: Transwell migration using DAPI
 Assay Name: Transwell migration using DAPI Assay ID: Celigo_04_0001 Table of Contents Experiment: Identification of cells which have migrated through the membrane of a transwell insert....2 Celigo Setup...2
Assay Name: Transwell migration using DAPI Assay ID: Celigo_04_0001 Table of Contents Experiment: Identification of cells which have migrated through the membrane of a transwell insert....2 Celigo Setup...2
