Cell Metabolism Assays. for. Immunology. Research
|
|
|
- Theresa Reed
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 the immunity-metabolism link Cell Metabolism Assays for Immunology Research
2 GOLD STANDARD ASSAYS FOR MEASURING METABOLIC RePROGRAMMING Metabolic Signatures Cell activation, amplification, and effector function are crucial aspects of the immune cell life cycle. Researchers are using XF technology to examine the cross-talk between immune cells and their metabolic signatures to gain insight into disease pathology, etiology, and possible treatment options. The XF Cell Mito Stress Test measures the key parameters of mitochondrial function: basal respiration, ATP-linked respiration, proton leak, maximal respiration, and spare respiratory capacity. The XF Glycolysis Stress Test measures the three key parameters of glycolytic function: glycolysis, glycolytic capacity, and glycolytic reserve FCCP Rotenone/ M M1 M2 (% mph/min) Glucose ** ** Uninfected HIV-infected (pmol/min/μg protein) Platelets Monocytes Lymphocytes Basal Neutrophils (mph/min/μg protein) Murine bone-derived macrophages Human s Human platelets and leukocytes Huang SC et al., (214) Nat Immunol. Hegedus A et al., (214) Retrovirology Kramer PA et al., (214) Redox Biol. XF Cell Mito Stress Test profiles metabolic signatures of activated bone marrow-derived macrophage subtypes. XF Assay reveals the role of glycolysis in HIV infection. XF Metabolic Switch Assay reveals distinct metabolic signatures in platelets and leukocytes. Metabolic reprogramming Signaling plays an important role in eliciting immunological response by coordinating immune cell communication and actions. Researchers are using XF technology to probe the signaling and metabolic programming of immune cells FCCP WT PBS WT Poly IC Rotenone/ ECAR IFNAR-/- Poly IC IFNAR-/- Poly PBS WT IFNAR -/ Inhibitor or DMSO α-cd3 and α-cd DMSO Events (% max) Activated Activated + PI(3)K inhibitor efluor 67 PI(3)K/Akt inhibitor ECAR Rapa 4 2 Unstim - - IL2/12 * + Murine dendritic cells Human s Murine natural killer cells Pantel A et al., (214) PLoS Biol. Gubser PM et al., (213) Nat Immunol. Donnelly RP et al., (214) J Immunol. XF Cell Mito Stress Test identifies IFNAR requirement for metabolic reprogramming. Real-time activation of memory s demonstrates a connection amongst signaling pathways, glycolysis, and proliferation. XF Assay reveals Natural Killer (NK) cell dependence on mtorc1 following stimulation of IL-2 and IL-12.
3 THE WORLD S MOST ADVANCED METABOLIC ANALYZERS Proven Technology for Cutting Edge Research There are over 2, references utilizing XF technology published in leading journals such as Nature and Cell. Scientists are embracing XF technology to identify metabolic phenotypes and reprogramming to target metabolic pathways for therapeutic purposes. Glucose Pyruvate Lactate IV III II I Mitochondrial Respiration Glycolysis ECAR (Extracellular Acidification Rate) OCR (Oxygen Consumption Rate) Metabolic Effect of Therapeutics The primary role of the immune system is to protect the host by targeting foreign antigens, controlling or clearing infections, and attacking cancerous cells. However, metabolic interventions present a largely untapped area of disease research. XF technology provides the necessary tools to understand the effects of therapeutic candidates on the antigen Baseline Induced αcd3/cd28 1 Control 6 ** 4 2 Th17 TGFβ1 Donor cells (per ml of blood) Th17IL1β 2 1 pmol O2/min 4 Exrtacellular Acicification Rate (ECAR) 6 8 Th17 TGFβ1 3 αcd3/cd28 FCCP Rotenone/ Control 4 1 Days 1 2 2, 1, *** Th17 2x1 1x1 3º Day 7 Recall FCCP 1º Day 7 Recall Rotenone 1 1, * 4x1 3x1 Tumor size (mm2) of interest, and on the immune system. IL1β 7 3º 1º Naive º Day Human s Murine T helper (Th) cells Murine s Yin Y et al., (21) Sci Transl Med. Chatterjee S et al., (214) Cancer Res. Fraser KA et al., (213) Immunity Real-time activation reveals metabolic signatures of lupus patient-derived CD4+ s. XF Assays reveal a metabolic switch which correlates to the antitumor ability of Th17IL1β cells. 12 3º Day 7 XF Assays reveal that tertiary immunization increases memory CD8+ recall.
4 MEASURING THE KEY PARAMETERS OF Immunometabolism Substrate Utilization, Flexibility & Dependency Each immune cell type has a specific function within the immune system. Cell fate decisions, activation, amplification, and effector function are driven by metabolism. To maintain the energy demands of the cell at each stage of its life cycle, the metabolic requirements for substrates or fuels that feed into the metabolic engines are altered. XF technology provides the capability to examine the effect of substrate utilization and dependency, yielding powerful metabolic data Glucose 2-DG Peg-BSA Peg-Arg I % s proliferating (CFSE) ***. 1 (μg/ml pegylated protein) 2 1 **** glucose ns + glucose Control Rapamycin Murine s Fletcher M et al., (21) Cancer Res. Murine s Goldberg EL, et al., (214) J Immol. XF Glycolysis Stress Test identifies L-Arginine dependence for proliferation in s. XF Assay reveals glucose-insensitivity of naïve s in the presence of rapamycin control or etomoxir PMA/ionomycin 1 1 B-ALL cell line #1 B-ALL cell line #2 B-ALL cell line #3 B cell line #1 B cell line #2 B cell line #3 No Fuel Glutamine Glutamine + Glucose Murine s Human B cells van der Windt GJ et al., (213) PNAS Liu T et al., (214) Cell Death Dis. XF Assay reveals a role of fatty acid oxidation in memory response. XF Assay reveals a glucose dependence in B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) cells.
5 Functional XF metabolic assays - THE intersection of immunology & metabolism XF Technology provides the tools TO MEASURE IMMUNOMETABOLISM Immunologists study how the innate and adaptive immune system recognizes and responds to insults. Whether the research focus is on a specific immune cell type, signaling pathway, or disease area, immunologists are actively exploring the mechanisms that drive and perpetuate antigen recognition and response. Immune system metabolism (referred to as immunometabolism ) has emerged as a key mechanism in understanding the connection between metabolic pathways and immune responses. Each immune cell type has a specialized role in an immune response, as well as a preferred metabolic pathway to generate energy required to maintain homeostasis. Research into metabolic changes provides insight into metabolic signature, signaling, and substrate preference. These metabolic choices are leading to new opportunities to modulate immunological response for therapeutic intervention. Signaling Pathways Cell Type Metabolism Disease Area XF technology is at the forefront, providing powerful and effective tools to explore the burgeoning field of immunometabolism. substrates and metabolism GLUCOSE FATTY ACID LACTATE PYRUVATE FATTY ACID CITRATE Cell LINEAGE and immunometabolism Acetyl-CoA TCA GLUTAMATE Naive Activated Fatty acid oxidation Effector Mitochondrial respiration (OCR) Glycolysis (ECAR) Memory GLYCOLYSIS (ECAR) ETC MITOCHONDRIAL RESPIRATION (OCR) GLUTAMINE
6 Gold Standard metabolic Assays MEASURING THE KEY PARAMETERS OF CELL METABOLISM XF Cell Mito Stress Test Profile Mitochondrial Respiration Basal Respiration ATP Production FCCP Rotenone & Maximal Respiration Proton Leak Non-mitochondrial Oxygen Consumption Spare Time (minutes) XF Cell Energy Phenotype Test Metabolic Phenotype & Potential Mitochondrial Respiration Aerobic Baseline Phenotype Quiescent Metabolic Potential Glycolysis Energetic Stressed Phenotype Glycolytic % GLC+GLN+FA Fuel Oxidation XF Glycolysis Stress Test Profile Glycolytic Function Glucose Glycolysis Glycolytic 2-DG Non-glycolytic Acidification Glycolytic Reserve Time (minutes) XF Mito Fuel Flex Test Profile Mitochondrial Function Dependency Flexibility Dependency Glucose Pathway Glutamine Pathway Fatty Acid Pathway Glucose Pathway Glutamine Pathway Fatty Acid Pathway Flexibility Dependency Corporate Headquarters European Headquarters Asia-Pacific Headquarters Seahorse Bioscience Inc. 16 Esquire Road North Billerica, MA 1862 US Phone: Seahorse Bioscience Europe Fruebjergvej 3 21 Copenhagen DK Phone: Seahorse Bioscience Asia 199 Guo Shou Jing Rd, Suite 27 Pudong, Shanghai 2123 CN Phone: Rev 3 21 All rights reserved. Seahorse Bioscience and the Seahorse logo are trademarks of Seahorse Bioscience Inc. The content in this brochure is for informational purposes only and may be subject to change without notice.
Cell Metabolism Assays. for OMICS. Research
 Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Gene-Protein-metabolism links Cell Metabolism Assays for OMICS Research STANDARD Parameters of Functional METABOLIsm Genomics Cells use gene expression to synthesize proteins and other products that are
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction
 Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Agilent Technologies: Seahorse XF Introduction Tools for investigating cell metabolism diagnostic procedures. 1 The Engines Cells Generate Energy via Two Metabolic Pathways Glycolysis [ H + ] Respiration
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment
 Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Identifying Metabolic Phenotype Switches in Cancer Cells Using the Agilent Seahorse XF Analyzer in an Hypoxic Environment Application Note Introduction Decreased oxygen levels, or hypoxia, and hypoxic-mediated
Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer
 icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
icell Cardiomyocytes 2 Application Protocol Performing Bioenergetic Analysis: Seahorse XFe96 Analyzer Introduction The myocardium is the most metabolically active tissue in the body and is highly sensitive
Application Note. Introduction
 Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Simultaneously Measuring Oxidation of Exogenous and Endogenous Fatty Acids Using the XF Palmitate-BSA FAO Substrate with the Agilent Seahorse XF Cell Mito Stress Test Application Note Introduction The
Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology
 White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
White Paper Quantifying Cellular ATP Production Rate Using Agilent Seahorse XF Technology Authors Natalia Romero George Rogers Andy Neilson Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies, Inc., Lexington, MA, USA
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate
 Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Rapid Analysis of Glycolytic and Oxidative Substrate Flux of Cancer Cells in a Microplate Lisa S. Pike Winer, Min Wu* Seahorse Bioscience Inc., North Billerica, Massachusetts, United States of America
Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer. Bioenergetics and Metabolism
 7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
7/3/8 Metabolism and the extracellular flux bioanalyzer Jianhua Zhang Department of Pathology University of Alabama at Birmingham 8 Bioenergetics and Metabolism Neurodegeneration: Parkinson s, Huntington
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function
 Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Human induced pluripotent stem cell derived cardiomyocytes are a more relevant model for assessing drug-induced effects on mitochondrial function than H9C2 cells 16 January 2013 SLAS2013 Presentation Outline
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW macrophages
 Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Metabolism of Herpes Simplex Virus 1 infected RAW 264.7 macrophages A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science By Mary Kathryn Jenkins B.S., Bowling
Supplementary Figure 1
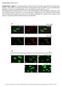 Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Supplementary Figure 1. (A) Representative confocal analysis of cardiac mesenchymal cells from nondiabetic (ND-CMSC) and diabetic (D-CMSC) immunostained with anti-h3k9ac and anti-h3k27me3 antibodies. Analysis
Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
 Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Cardiomyocyte function characterised through combined analysis of metabolic flux, beat rate and cellular oxygenation and its application in in vitro ischemia reperfusion modelling Ryan McGarrigle, Ph.D.
Supporting Information
 Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
Supporting Information van der Windt et al. 10.1073/pnas.1221740110 SI Materials and Methods Mice and Reagents. C57BL/6 and major histocompatibility complex class I-restricted OVA-specific T-cell receptor
XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System
 Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
Application Note Normalization XF Data Normalization by the Agilent Seahorse XF Imaging and Normalization System Authors Yoonseok Kam Kellie Chadwick Ned Jastromb Brian P. Dranka Agilent Technologies,
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY
 CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS FOR THE 21st CENTURY Seahorse XF Extracellular Flux Analyzers XF Extracellular Flux Analyzer PROVIDING A NEW WINDOW INTO CELLULAR BIOENERGETICS Before Seahorse developed With an
Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages
 Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages Jan Van den Bossche, PhD j.vandenbossche@amc.nl Departement of Medical Biochemistry Experimental Vascular Biology group Postdoc
Mitochondrial dysfunction prevents repolarization of inflammatory macrophages Jan Van den Bossche, PhD j.vandenbossche@amc.nl Departement of Medical Biochemistry Experimental Vascular Biology group Postdoc
Cellular Respiration Checkup Quiz. 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans?
 1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
1. Of the following products, which is produced by both anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration in humans? I. Pyruvate II. III. ATP Lactate A. I only B. I and II only C. I, II and III D. II and III
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author):
 Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): present a straightforward study using a novel BCAT1 inhibitor, complemented by sirna for BCAT using human monocyte-derived macs as well as murine
Reviewers' comments: Reviewer #1 (Remarks to the Author): present a straightforward study using a novel BCAT1 inhibitor, complemented by sirna for BCAT using human monocyte-derived macs as well as murine
Anaerobic Pathways. Glycolysis
 Anaerobic Pathways Glycolysis Glucose + 2 ATP 4 ATP + 2 Pyruvate No oxygen required Fairly low energy yield Lactate byproduct Resting levels low Tolerances 40 mmole/kg in humans, 200 mmole/kg in sea turtles
Anaerobic Pathways Glycolysis Glucose + 2 ATP 4 ATP + 2 Pyruvate No oxygen required Fairly low energy yield Lactate byproduct Resting levels low Tolerances 40 mmole/kg in humans, 200 mmole/kg in sea turtles
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.9 - RESPIRATION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
!! www.clutchprep.com CONCEPT: REDOX REACTIONS Redox reaction a chemical reaction that involves the transfer of electrons from one atom to another Oxidation loss of electrons Reduction gain of electrons
2/25/2015. Anaerobic Pathways. Glycolysis. Alternate Endpoints. Gluconeogenesis fate of end products
 Anaerobic Pathways Glycolysis Glucose + 2 ATP 4 ATP + 2 Pyruvate No oxygen required Fairly low energy yield Lactate byproduct Resting levels low Tolerances 40 mmole/kg in humans, 200 mmole/kg in sea turtles
Anaerobic Pathways Glycolysis Glucose + 2 ATP 4 ATP + 2 Pyruvate No oxygen required Fairly low energy yield Lactate byproduct Resting levels low Tolerances 40 mmole/kg in humans, 200 mmole/kg in sea turtles
The world's most advanced cell metabolism analyzer
 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + + H H + O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 The world's most advanced cell metabolism analyzer The Era of Cellular Bioenergetics Cellular Bioenergetics for the 21 st Century XF e 96 Analyzer
O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 + H H + + H H + + H H + O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 O 2 The world's most advanced cell metabolism analyzer The Era of Cellular Bioenergetics Cellular Bioenergetics for the 21 st Century XF e 96 Analyzer
Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 AP Biology Reading Guide Name: Date: Period Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take
AP Biology Reading Guide Name: Date: Period Chapter 9: Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Overview: Before getting involved with the details of cellular respiration and photosynthesis, take
Chapter 9 Notes. Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 Chapter 9 Notes Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Objectives Distinguish between fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the cell
Chapter 9 Notes Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Objectives Distinguish between fermentation and anaerobic respiration. Name the three stages of cellular respiration and state the region of the cell
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. Cellular Pathways In General
 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy A. Obtaining Energy and Electrons from Glucose Lecture Series 12 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy B. An Overview: Releasing Energy from Glucose
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux
 Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Cellular metabolism made easy: Microplate assays for mitochondrial function & glycolytic flux Convenient Microplate Based Analysis of Cell Metabolism Resuspend Add Reagent Measure A simple push-button
Introduction. Living is work. To perform their many tasks, cells must bring in energy from outside sources.
 Introduction Living is work. To perform their many tasks, cells must bring in energy from outside sources. In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. Light energy trapped in organic molecules is available
Introduction Living is work. To perform their many tasks, cells must bring in energy from outside sources. In most ecosystems, energy enters as sunlight. Light energy trapped in organic molecules is available
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
Respiration Practice Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following statements describes NAD+? A) NAD+ can donate
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research
 New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
New tools bring greater understanding to cellular metabolism research Mourad Ferhat, Ph.D, 7 Juin 2017 FDSS Users Meeting, Hamamatsu mourad.ferhat@promega.com Today s talk : focus on new cell-based assays
In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic
 Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
Glycolysis 1 In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate. If the pyruvate is reduced to lactate, the pathway does not require O 2 and is called anaerobic glycolysis. If this pyruvate is converted instead
7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY IN FOCUS URRY CAIN WASSERMAN MINORSKY REECE 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lecture Presentations by Kathleen Fitzpatrick and Nicole Tunbridge, Simon Fraser University SECOND EDITION
Concept 9.1: Catabolic pathways yield energy by oxidizing organic fuels Several processes are central to cellular respiration and related pathways
 Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the chimpanzee, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants Energy
Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the chimpanzee, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other organisms that eat plants Energy
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER
 AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
AWARD NUMBER: W81XWH-14-1-0255 TITLE: BIOENERGETICS OF STROMAL CELLS AS A PREDICTOR OF AGGRESSIVE PROSTATE CANCER PRINCIPAL INVESTIGATOR: Praveen K. Vayalil RECIPIENT: University of Alabama at Birmingham
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with
RESPIRATION Worksheet
 A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
A.P. Bio L.C. RESPIRATION Worksheet 1. In the conversion of glucose and oxygen to carbon dioxide and water a) which molecule becomes reduced? b) which molecule becomes oxidized? c) what happens to the
Acquired Immunity Cells are initially and require before they can work Responds to individual microbes
 1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
3. Distinguish between aerobic and anaerobic in terms of cell respiration. Outline the general process of both.
 3.7 Cell Respiration 1. Define cell respiration. Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration.
3.7 Cell Respiration 1. Define cell respiration. Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic molecules in cells to form ATP. 2. State the equation for the process of cell respiration.
Unit 2: Metabolic Processes
 How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
How is energy obtained biologically? Recall: Red Ox Reactions Unit 2: Metabolic Processes Oxidation Is the chief mechanism by which chemical potential energy is released This energy comes from reduced
Name Class Date. 1. Cellular respiration is the process by which the of "food"
 Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
Name Class Date Cell Respiration Introduction Cellular respiration is the process by which the chemical energy of "food" molecules is released and partially captured in the form of ATP. Carbohydrates,
LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable to Energy Stress Induced by ATP Depletion
 Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 12-2014 LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable
Texas Medical Center Library DigitalCommons@TMC UT GSBS Dissertations and Theses (Open Access) Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences 12-2014 LKB1 Deficient Non-small Cell Lung Cancer Cells are Vulnerable
glucose glucose 6-phospho fructose 6-phosphate fructose 1,6-bisphosphate glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate 3-phosphoglycerate
 Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Cells glucose glucose glucose 6-phospho glycogen pentose phosphate T 1-phosphate 6-phosphate gluconate CC T CC+PD-1 pathway Isobar: fructose 1,6-diphosphate; glucose 1,6-diphosphate DHAP lactate fructose
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation*
 Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
Chapter 7 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. Life Is Work
Manipulating the Tumor Environment
 Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Manipulating the Tumor Environment Vincenzo Bronte Verona University Hospital vincenzo.bronte@univr.it Escape from immune control can be viewed as one of the «Hallmarks of Cancer» D. Hanahan and R. A.
Chapter 9. Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Living cells require energy from outside sources Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy Living cells require energy from outside sources Energy flows into an ecosystem as sunlight and leaves as heat Photosynthesis generates O 2 and
How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7. Respiration
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms classified on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on organic compounds
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I
 Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration part 1I Agenda I. Overview (Big Pictures) of Photosynthesis & Cellular Respiration II. Making Glucose - Photosynthesis III. Making ATP - Cellular
Class XI Chapter 14 Respiration in Plants Biology. 1. It is a biochemical process. 1. It is a physiochemical process.
 Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.)
 This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
This is an example outline of 3 lectures in BSC 2010. (Thanks to Dr. Ellington for sharing this information.) Topic 10: CELLULAR RESPIRATION (lectures 14-16) OBJECTIVES: 1. Know the basic reactions that
HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells
 Hegedus et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:98 RESEARCH Open Access HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells Andrea Hegedus, Maia Kavanagh
Hegedus et al. Retrovirology 2014, 11:98 RESEARCH Open Access HIV-1 pathogenicity and virion production are dependent on the metabolic phenotype of activated CD4+ T cells Andrea Hegedus, Maia Kavanagh
7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy
 7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of Glucose Metabolism? How Is Energy Harvested
7 Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of Glucose Metabolism? How Is Energy Harvested
Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Respiration Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs:
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration
 Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration Learning Objectives Know the relationship between photosynthesis & cellular respiration Know the formulae of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis
Harvesting energy: photosynthesis & cellular respiration Learning Objectives Know the relationship between photosynthesis & cellular respiration Know the formulae of the chemical reactions for photosynthesis
Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories
 Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories Organ Glucose/ Glycogen Triacyl Glycerols* Liver 400 450 400 Brain 8 0 0 Mobile Proteins Muscle 1,200 450 24,000 Adipose Tissue 80 135,000
Energy stores in different organs for a 155 lb male, in Calories Organ Glucose/ Glycogen Triacyl Glycerols* Liver 400 450 400 Brain 8 0 0 Mobile Proteins Muscle 1,200 450 24,000 Adipose Tissue 80 135,000
 Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Question 1: Differentiate between (a) Respiration and Combustion (b) Glycolysis and Krebs cycle (c) Aerobic respiration and Fermentation (a) Respiration and combustion Respiration Combustion 1. It is a
Reading Assignments. A. Energy and Energy Conversions. Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy. gasoline) or elevated mass.
 Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Lecture Series 9 Cellular Pathways That Harvest Chemical Energy Reading Assignments Review Chapter 3 Energy, Catalysis, & Biosynthesis Read Chapter 13 How Cells obtain Energy from Food Read Chapter 14
Chemical Energy. Valencia College
 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Valencia College 9 Pathways that Harvest Chemical Energy Chapter objectives: How Does Glucose Oxidation Release Chemical Energy? What Are the Aerobic Pathways of
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.
 Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
Investigating the Effect of Energy Substrates and LPS-activation on the In Vitro Energy Metabolism of BV-2, RAW264.7 and VM-M3 Cells Author: Ashley Kaye Brown Persistent link: http://hdl.handle.net/2345/bc-ir:106811
3.2 Aerobic Respiration
 3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
3.2 Aerobic Respiration Aerobic Cellular Respiration Catabolic pathways Breaks down energy-rich compounds to make ATP Requires oxygen Occurs in different parts of the cell C 6 H 12 O 6 (s) + 6O 2 (g) 6CO
NOTES: Ch 9, part & Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration
 NOTES: Ch 9, part 4-9.5 & 9.6 - Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration 9.5 - Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen Cellular respiration requires O 2 to produce
NOTES: Ch 9, part 4-9.5 & 9.6 - Fermentation & Regulation of Cellular Respiration 9.5 - Fermentation enables some cells to produce ATP without the use of oxygen Cellular respiration requires O 2 to produce
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 27 Monday 5 Apr. 1 Review Metabolic Pathways and Processes that Participate in Respiration - Glycolysis Occurs in the cytoplasmic matrix - Pyruvate dehydrogenase - Krebs Cycle
Yoshifusa Abe, 1,2 Toru Sakairi, 3 Craig Beeson, 4 and Jeffrey B. Kopp 2 1
 Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 35: F1477 F149, 13. First published September 18, 13; doi:1.1152/ajprenal.182.13. TGF- 1 stimulates mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and generation of reactive oxygen
Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 35: F1477 F149, 13. First published September 18, 13; doi:1.1152/ajprenal.182.13. TGF- 1 stimulates mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and generation of reactive oxygen
Organic Acids Part 2 Dr. Jeff Moss
 Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part II Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
Using organic acids to resolve chief complaints and improve quality of life in chronically ill patients Part II Jeffrey Moss, DDS, CNS, DACBN jeffmoss@mossnutrition.com 413-530-08580858 (cell) 1 Summer
WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT?
 CHAPTER 3 ESSENTIALS OF METABOLISM WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? It is important to have a basic understanding of metabolism because it governs the survival and growth of microorganisms The growth of microorganisms
CHAPTER 3 ESSENTIALS OF METABOLISM WHY IS THIS IMPORTANT? It is important to have a basic understanding of metabolism because it governs the survival and growth of microorganisms The growth of microorganisms
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department
 Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
Medical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology department Cardiac Fuels [Sources of energy for the Cardiac muscle] Intended learning outcomes of the lecture: By the end of this lecture you would be able to:-
(A) Urea cycle (B) TCA cycle (C) Glycolysis (D) Pyruvate oxidation (E) Respiratory chain
 Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Biochemistry - Problem Drill 15: Citric Acid Cycle No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements is not a metabolic pathway involved in carbohydrate catabolism and ATP production. (A) Urea cycle (B)
Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes
 Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299: C464 C476, 2010. First published May 5, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00563.2009. Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes Yoshifusa Abe, 1,2 Toru Sakairi, 1 Hiroshi
Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 299: C464 C476, 2010. First published May 5, 2010; doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00563.2009. Bioenergetic characterization of mouse podocytes Yoshifusa Abe, 1,2 Toru Sakairi, 1 Hiroshi
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular
 III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
III. 6. Test. Respiració cel lular Chapter Questions 1) What is the term for metabolic pathways that release stored energy by breaking down complex molecules? A) anabolic pathways B) catabolic pathways
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS
 MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following statements concerning anabolic reactions is FALSE? A. They are generally endergonic. B. They usually require ATP. C. They are part of metabolism. D.
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTIONS 1. Which of the following statements concerning anabolic reactions is FALSE? A. They are generally endergonic. B. They usually require ATP. C. They are part of metabolism. D.
Respiration. Respiration. Respiration. How Cells Harvest Energy. Chapter 7
 How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
How Cells Harvest Energy Chapter 7 Organisms can be classified based on how they obtain energy: autotrophs: are able to produce their own organic molecules through photosynthesis heterotrophs: live on
ab Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay
 Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Version 3 Last updated 22 June 2017 ab217602 Fatty Acid Oxidation Assay For the convenient measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation (FAO) in live cells when used in combination with Extracellular Oxygen Consumption
Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
Integration Of Metabolism
 Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Integration Of Metabolism Metabolism Consist of Highly Interconnected Pathways The basic strategy of catabolic metabolism is to form ATP, NADPH, and building blocks for biosyntheses. 1. ATP is the universal
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations. Lecture 9
 Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
Metabolic engineering some basic considerations Lecture 9 The 90ties: From fermentation to metabolic engineering Recruiting heterologous activities to perform directed genetic modifications of cell factories
MitoXpress FAO Assay. For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation
 MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
MitoXpress FAO Assay For the measurement of Fatty Acid Oxidation Companion Kit to be used in combination with Luxcel s MitoXpress Xtra - Oxygen Consumption Assay ILLUMINATING DISCOVERY TABLE OF CONTENTS
ab Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay
 Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
Version 1 Last updated 12 July 2017 ab222945 Glycolysis Stress Test Companion Assay For the characterization of glycolytic stress in live cells when used in combination with Glycolysis Assay [Extracellular
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology. Abstract
 Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reduced glycolytic reserve in isolated natural killer cells from Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients: A preliminary
Asian Pacific Journal of Allergy and Immunology ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reduced glycolytic reserve in isolated natural killer cells from Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome patients: A preliminary
Chapter 8. Metabolism. Topics in lectures 15 and 16. Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Chapter 8 Topics in lectures 15 and 16 Metabolism Chemical foundations Catabolism Biosynthesis 1 Metabolism Chemical Foundations Enzymes REDOX Catabolism Pathways Anabolism Principles and pathways 2 Enzymes
Glycolysis Introduction to Metabolism Regulation of Metabolism Overview of Glycolysis Reactions of Glycolysis
 Glycolysis Introduction to Metabolism Regulation of Metabolism Overview of Glycolysis Reactions of Glycolysis Suggested Reading: Lippincot s Ilustrated reviews: Biochemistry Glycolysis, an example of metabolic
Glycolysis Introduction to Metabolism Regulation of Metabolism Overview of Glycolysis Reactions of Glycolysis Suggested Reading: Lippincot s Ilustrated reviews: Biochemistry Glycolysis, an example of metabolic
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Sources of cellular ATP 2. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular work (ATP) 3. Importance of electrons and
Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes
 Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
Topics Microbial Metabolism Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis 2 Metabolism Catabolism Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Breakdown of complex organic molecules in order to extract energy and dform simpler
The Immune System. A macrophage. ! Functions of the Immune System. ! Types of Immune Responses. ! Organization of the Immune System
 The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
The Immune System! Functions of the Immune System! Types of Immune Responses! Organization of the Immune System! Innate Defense Mechanisms! Acquired Defense Mechanisms! Applied Immunology A macrophage
A cell has enough ATP to last for about three seconds.
 Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
Energy Transformation: Cellular Respiration Outline 1. Energy and carbon sources in living cells 2. Sources of cellular ATP 3. Turning chemical energy of covalent bonds between C-C into energy for cellular
What is the Warburg Effect
 What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
What is the Warburg Effect Roles nutrients play in the biochemistry of a cell Thus, proliferating cells must acquire more nutrients, convert them into biosynthetic building blocks, and coordinate the reactions
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine
 Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Innate immune regulation of T-helper (Th) cell homeostasis in the intestine Masayuki Fukata, MD, Ph.D. Research Scientist II Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Medicine, F. Widjaja Foundation,
Growth. Principles of Metabolism. Principles of Metabolism 1/18/2011. The role of ATP energy currency. Adenosine triphosphate
 Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth Principles of Metabolism Cells (including your own) must: Synthesize new components (anabolism/biosynthesis) Harvest energy and convert it to a usable form (catabolism)
Metabolism: Fueling Cell Growth Principles of Metabolism Cells (including your own) must: Synthesize new components (anabolism/biosynthesis) Harvest energy and convert it to a usable form (catabolism)
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms.
 1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
1 Respiration is a vital process in living organisms. All organisms carry out glycolysis. The Krebs cycle also occurs in some organisms. (a) The diagram below shows some of the stages in glycolysis, using
Age-Related Changes in Immune System Function. Professor Justin Hall October 12, 2010
 Age-Related Changes in Immune System Function Professor Justin Hall October 12, 2010 Immune Function: Effect of Aging and Exercise Why study this? INCREASED RISK for infectious diseases, tumorigenesis,
Age-Related Changes in Immune System Function Professor Justin Hall October 12, 2010 Immune Function: Effect of Aging and Exercise Why study this? INCREASED RISK for infectious diseases, tumorigenesis,
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources
 Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other
Chapter 9 Cellular Respiration Overview: Life Is Work Living cells require energy from outside sources Some animals, such as the giant panda, obtain energy by eating plants, and some animals feed on other
FILE // ATP LEVELS IN CANCER CELLS
 02 March, 2018 FILE // ATP LEVELS IN CANCER CELLS Document Filetype: PDF 346.71 KB 0 FILE // ATP LEVELS IN CANCER CELLS It is not good enough to measure absolute levels of ATP in cells since this will
02 March, 2018 FILE // ATP LEVELS IN CANCER CELLS Document Filetype: PDF 346.71 KB 0 FILE // ATP LEVELS IN CANCER CELLS It is not good enough to measure absolute levels of ATP in cells since this will
4. Which step shows a split of one molecule into two smaller molecules? a. 2. d. 5
 1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
1. Which of the following statements about NAD + is false? a. NAD + is reduced to NADH during both glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. b. NAD + has more chemical energy than NADH. c. NAD + is reduced
Metabolism. Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism. Metabolic balancing act. Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes. Topics. Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis
 Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 1 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism and anabolism simple model Catabolism Enzymes
Chapter 8 Microbial Metabolism Topics Metabolism Energy Pathways Biosynthesis Catabolism Anabolism Enzymes Metabolism 1 2 Metabolic balancing act Catabolism and anabolism simple model Catabolism Enzymes
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush OMM: permeable to small molecules (MW
Chapter 9 Overview. Aerobic Metabolism I: The Citric Acid Cycle. Live processes - series of oxidation-reduction reactions. Aerobic metabolism I
 n n Chapter 9 Overview Aerobic Metabolism I: The Citric Acid Cycle Live processes - series of oxidation-reduction reactions Ingestion of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids Provide basic building blocks for
n n Chapter 9 Overview Aerobic Metabolism I: The Citric Acid Cycle Live processes - series of oxidation-reduction reactions Ingestion of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids Provide basic building blocks for
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis
 Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis Mitochondria and ATP Synthesis 1. Mitochondria are sites of ATP synthesis in cells. 2. ATP is used to do work; i.e. ATP is an energy source. 3. ATP hydrolysis releases energy
10/25/2010 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION. Life is Work. Types of cellular respiration. Catabolic pathways = oxidizing fuels
 CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Life is Work Living cells require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform their many tasks: Chemical work Transport work Mechanical work Energy stored in the
CHAPTER 9 CELLULAR RESPIRATION Life is Work Living cells require transfusions of energy from outside sources to perform their many tasks: Chemical work Transport work Mechanical work Energy stored in the
Cellular Respiration
 Cellular Respiration The breakdown of glucose for cellular energy. happens in all living cells. is exothermic H atoms and e are removed from glucose (oxidization) and added to oxygen (reduction) excess
Cellular Respiration The breakdown of glucose for cellular energy. happens in all living cells. is exothermic H atoms and e are removed from glucose (oxidization) and added to oxygen (reduction) excess
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy CHAPTER 9
 Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy CHAPTER 9 9.1 Metabolic pathways that release energy are exergonic and considered catabolic pathways. Fermentation: partial degradation of sugars that occurs
Cellular Respiration: Harvesting Chemical Energy CHAPTER 9 9.1 Metabolic pathways that release energy are exergonic and considered catabolic pathways. Fermentation: partial degradation of sugars that occurs
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration
 Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
Ch 9: Cellular Respiration Cellular Respiration An overview Exergonic reactions and catabolic pathway Energy stored in bonds of food molecules is transferred to ATP Cellular respiration provides the energy
