Public Assessment Report
|
|
|
- Harry Barrett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed 6 Discussion 12 Conclusion 14 References 17 Glossary 21 1
2 Executive summary Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast media are used to enhance the contrast of images and to facilitate visualisation of abnormal structures or lesions in various parts of the body. In January, 2006, gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents were postulated to contribute to the development of a rare and sometimes fatal disorder called nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (NFD) or nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF). Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (NFD) was first recognised in the USA in 1997 as an idiopathic skin condition characterised by thickening and hardening of the skin of the extremities and sometimes of the trunk, with an increase in the number of dermal fibroblast-like cells associated with collagen remodelling and mucin deposition. Initially 20 cases of NSF from Denmark, and a further five cases from Austria were identified in which all patients had renal impairment and were noted to have received the MRI contrast agent gadodiamide (Omniscan) before development of the disorder. To date, there have been no reports of NSF in patients with normal kidney function. Since the 1980s, more than 200 million patients have been exposed to gadolinium-based contrast agents, more than 30 million of whom have received Omniscan. This issue was discussed at the Pharmacovigilance Working Party (PhVWP) of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) in June, Following this discussion, the marketing authorisation holder (MAH) for Omniscan sent a letter to radiologists and nephrologists in some EU member states to inform them of a possible association between gadodiamide with NSF i. Further data were discussed at the November, 2006, PhVWP meeting. 48 (validated) and 40 (under validation) cases of NSF were associated with gadodiamide (Omniscan), two possible cases were associated with gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist), and no cases were identified with other gadoliniumcontaining contrast agents. NSF and the role of gadolinium-based contrast agents is an emerging science. The exact disease mechanism has yet to be elucidated, but physicochemical properties of gadoliniumcontaining agents might affect their behaviour in the body and the amount of free gadolinium released in patients with renal impairment. Currently, there is no effective treatment for NSF; the most effective treatment options are related to improvement in renal impairment. Therefore, it is imperative that radiologists, nephrologists, and other relevant healthcare professionals receive guidance as to how to avoid this very debilitating and sometimes fatal disorder. This report discusses the current available data and summarises the advice of the Pharmacovigilance Working Party on appropriate regulatory action to provide guidance about this disorder to radiologists, nephrologists, and other healthcare professionals. i ocname=con &sstargetnodeid=221 2
3 1 Introduction 1.1 Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast agents MRI contrast media are used to enhance the contrast of images and to facilitate visualisation of abnormal structures or lesions in various parts of the body. Contrast media affect the relaxation times of protons in their vicinity. The most common MRI contrast media are based on paramagnetic compounds that contain metal ions from the transition or lanthanide series of the periodic table such as manganese, iron, and gadolinium. These metal ions have a large magnetic moment and can shorten the longitudinal (T1) and transversal (T2) relaxation times of protons in the water of tissues. The lanthanide metal ion gadolinium has the strongest effect of all elements on T1 relaxation time because it has seven unpaired electrons. To differentiate between normal and pathological structures, gadolinium selectively changes the signal intensity of protons in the vicinity of either normal or pathological tissues. Gadolinium alone is highly toxic in vivo because it distributes to bone and to the liver, where it rapidly produces liver necrosis. Therefore, all MRI products that contain gadolinium are based on chelates, which modify its bodily distribution to overcome toxicity while maintaining its contrast enhancement. Gadolinium chelates have different physical properties (see section 2.4). Unlike agents used to enhance x-rays, gadolinium chelates do not have a toxic effect on the kidneys. 1 Therefore, in recent years, patients with severe renal impairment or previous severe reactions to iodine-containing contrast media were recommended to receive gadoliniumbased MRI contrast agents instead of traditional radiographic contrast agents. 2 Gadodiamide (Omniscan) was the first agent to be associated with the disorder nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF). 3 Gadodiamide is a contrast medium used for cranial MRI, spinal MRI, and general MRI of the body; it is given intravenously. For cardiac MRI, gadodiamide is indicated for assessment of coronary artery disease (CAD). The recommended dose of gadodiamide for adults for imaging of the central nervous system, whole body, heart, and breasts is 0 1 mmol/kg bodyweight (equivalent to 0 2 ml/kg bodyweight) up to 100 kg. The recommended dose for assessment of cardiac perfusion is 0 15 mmol/kg bodyweight (equivalent to 0 3 ml/kg bodyweight) given as two separate doses of mmol/kg bodyweight at an interval of 10 minutes or longer (one at pharmacological stress followed by one at rest). Gadodiamide is also indicated for imaging of the central nervous system and whole body in children at a dose of 0 1 mmol/kg bodyweight. 3
4 1.2 Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (NFD) was first recognised in the USA in 1997 as an idiopathic skin condition characterised by thickening and hardening of the skin of the extremities and sometimes of the trunk, with an increase in the number of dermal fibroblastlike cells associated with collagen remodelling and mucin deposition. 4 In all of the first 15 cases of NFD, the patient had received, or was receiving, renal dialysis. A variant of NFD nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) has more prominent and visible effects on the skin than does NFD, and is associated with systemic involvement of other organs including the lungs, liver, muscles, and heart. 5 7 The International Center for Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy Research (ICNFDR, considers NSF as the preferred term to use over NFD because they think it reflects more accurately the current understanding of the disorder. Thus throughout this report, the term NSF will be used to denote NFD and NSF. NSF develops over a period of days to several weeks. The skin changes start as reddened or darkened patches, papules, or plaques. Over time, the skin feels woody, and the surface may have an appearance of texture of orange peel. Diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of specific histopathological features on skin biopsy thickened collagen bundles with surrounding clefts, mucin deposition, and proliferation of fibroblasts and elastic fibres without signs of inflammation. 8,9 Skin lesions are commonly symmetrical, with zones between the ankles and thighs; later lesions can develop between the wrist and upper arms. Patients may have burning, itching, or severe sharp pains in areas of involvement, and may have swelling of the hand and foot with blister-like lesions. Some patients have reported yellow papules or plaques on or near the eyes. Rapid, new-onset fluctuating hypertension of unknown cause has also been reported before onset of skin lesions. For many patients, the skin thickening inhibits the flexion and extension of joints, resulting in contractures. Those severely affected may be unable to walk or extend fully the arm, hand, leg, and feet joints; complaints of muscle weakness are common. Radiography might show calcification of soft tissue, and deep bone pain has been described in the hips and ribs. About 5% of patients have a rapidly progressive severe disease course. NSF might contribute to death by scarring of body organs (which impairs normal function), restriction of effective ventilation, or restriction of movement leading to an accidental fall that might be further exacerbated by fractures and clotting complications. Other patients have died as a result of renal disease or transplant surgery. 4
5 NSF occurs only in patients with renal impairment (see section 2.1), and the onset of this syndrome is associated with hypercoagulability, thrombotic events, recent vascular surgery, or recent renal transplant failure. 1.3 Regulatory action to date This issue discussed at a European level at the June, 2006 meeting of the Pharmacovigilance Working Party (PhVWP) of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP). All European marketing authorisation holders (MAHs) of gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents were requested to submit safety update reports to regulatory authorities to identify cases of NSF. In the UK, the Pharmacovigilance Expert Advisory Group (PEAG) of the Commission on Human Medicines (CHM) was informed of this issue in June, In August, 2006, a Dear Healthcare Professional letter was circulated to all UK radiologists and nephrologists to inform them of a possible association between gadodiamide with NSF ii. During the same period, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued preliminary guidance that physicians should be cautious when using gadolinium-containing contrast agents in patients with advanced renal failure. In December, 2006, the FDA issued a further update, informing physicians that they had received 90 reports of patients with moderate to end-stage renal disease who developed NSF after MRI or magnetic resonance angiography with a gadolinium-based contrast agent. Onset ranged from 2 days to 18 months after exposure to gadolinium, and the FDA identified Omniscan, Magnevist, and OptiMARK as the suspect products in these cases. The FDA considers that there is a potential for NSF to occur with use of any of the five gadolinium contrast agents licensed in the USA iii. Meanwhile in Europe, Member States assessed the safety update reports at the November, 2006, PhVWP meeting. 48 (validated) and 40 (under validation) cases of NSF were associated with gadodiamide (Omniscan), two possible cases were associated with gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist), and no cases were identified with other gadoliniumcontaining contrast agents. The PhVWP proposed further investigation to elucidate the mechanism by which gadolinium-containing contrast agents might cause NSF. ii ocname=con &sstargetnodeid=221 iii 5
6 2 Data assessed 2.1 Postulated triggers of NSF The cause of NSF has been the subject of great interest since it was first diagnosed in Because NSF is a newly diagnosed syndrome, several researchers suggest that a new agent or new examination technique might cause this syndrome. 5,7,8,10 Common factors of patients who develop NSF have been reviewed extensively. There seems to be no gender predisposition for development of NSF. Severe renal impairment is a common factor; however, neither the duration of renal disease nor its underlying causes seem to be related to development of NSF (see Other conditions that have been associated with NSF include coagulation abnormalities and deep venous thrombosis, recent surgery, failed kidney transplantation, and sudden-onset kidney disease with severe swelling of the extremities (see Patients with NSF have commonly had a vascular surgical procedure or have had a thrombotic episode about 2 weeks before the onset of skin changes. Several agents or contributory factors have been postulated to trigger this syndrome, including: dialysate fluid (or a contaminant), 5 erythropoietin, 11 inhibitors of angiotensinconverting enzyme, 12 and induced antibodies against phospholipids. 13 Cowper and Bucala suggested that circulating fibrocytes (bone-marrow derived, connectivetissue cells found in the peripheral circulation and mesenchymal tissue) may have a role in NSF. 14 These cells enter sites of inflammation and tissue repair, secrete growth factors and cytokines, and contribute to matrix production in connective tissue. 15 Mediators such as transforming growth factor β, a potent stimulus for production of type I collagen by some cell types and a mediator of interstitial fibrosis, can induce fibrocytes to differentiate into myofibroblasts cells that seem to represent a small proportion of spindle cells present in NSF. Other researchers have recorded increased levels of transforming growth factor β in the skin and muscle of some affected patients. 16 Cowper noted that development of NSF in many patients was associated temporally with vascular or thrombotic events, or with development of cancer. 10 Because many of these patients had received angiography that used a contrast agent (eg, for clot detection, surgery planning, and assessment of vascularity of brain neoplasms), Cowper and colleagues propose that radiographic contrast deposited in the peripheral circulation might be a target for circulating fibrocytes. 17 Evidence of this association was later shown in a pivotal study by Grobner (see section 2.3). 3 6
7 2.2 Current treatment options for NSF At present, there is no known effective treatment for NSF. Physical therapy or treatment with topical and systemic steroids has variable benefit; immunosuppressive therapy is ineffective. 3 Plasmapheresis, 18 photopheresis, 19 and thalidomide 20 have led to an improvement in some patients. Others have improved after restoration of normal renal function either spontaneously or as a result of a renal transplantation. 10 LeBoit proposes that a dose reduction in erythropoietin might improve NSF because recombinant erythropoietin has potential fibrogenic properties. 5 Maloo and colleagues suggest that calcineurin inhibitors and erythropoietin might play a part in NSF because both have profibrogenic potential through upregulation of transforming growth factor β. 21 Grobner (see section 2.3) gave two patients pentoxifylline, a substance with activity against tumour necrosis factor. 3 Skin changes in one patient who had late-stage disease seemed to slow or arrest; the second patient had stabilisation and a slight reversal of disease. Grobner adds that the role of vasodilation, with possible beneficial effects of renal perfusion and antifibrotic activity, in disease stabilisation is unclear. 2.3 Gadolinium as a trigger for NSF In January, 2006, a study in Austria suggested that a magnetic resonance contrast medium containing gadolinium might trigger NSF. 3 Five of nine patients with end-stage renal disease (mean age 58 years) who had magnetic resonance angiography with gadodiamide contrast medium developed NSF within 2 4 weeks. The five patients developed thickening and induration of the skin on the legs and feet, which eventually spread to the trunk and upper body. The five affected patients had signs of metabolic acidosis, whereas the unaffected patients had normal ph values and bicarbonate levels at the time of magnetic resonance angiography. Affected patients had a longer mean time of dialysis than did unaffected patients, but no other differences were found with respect to age, sex, medication, underlying renal disease, dialysis modalities, and comorbidities. A large study from Denmark reported an association between gadolinium-containing contrast agents and NSF. 22 Between August 2005 and May 2006, a review of case notes of all patients with NSF from a nephrology department in Copenhagen showed that all 13 patients with end-stage renal disease (mean age 50 years) with NSF had been exposed to gadodiamide before the first signs of NSF. 22 Seven patients developed severe disabilities, and one patient died 21 months after exposure; the remaining six patients were not as severely affected. Interestingly, six of the 13 patients were previously exposed to gadodiamide without any onset of NSF symptoms. 7
8 By contrast with Grobner s suggestion that acidosis might be an essential contributing factor in NSF, 3 Marckmann and colleagues found no evidence to support this idea. 22 Rather, they suggest that gadodiamide might be the causative factor: no further cases were observed after withdrawal of gadodiamide from their centre in March, Broome and colleagues have shown that patients on dialysis are at risk of NSF after gadodiamide administration from a review of 12 identified cases of NSF from 301 people exposed to gadodiamide exposed, compared with no cases of NSF from 258 people who were not exposed to gadodiamide (odds ratio for development of NSF after gadodiamide exposure 22 3 [95% CI ]). 23 Broome and colleagues noted that the risk was significantly higher when a dose twice the normal recommended dose of gadodiamide had been used. 23 In another study, seven of 254 patients with renal insufficiency developed NSF after administration of a gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agent an incidence of 3% for this population. 24 Moreover, prevalence of NSF in dialysis patients who were exposed to Omniscan was reported as 4% (odds ratio for NSF after Omniscan exposure 22 3 [95% CI ]). 23 Those who have received liver transplantation have also been identified as at risk of NSF. 18,21 Gadodiamide is almost exclusively excreted by the kidney, and it has a prolonged half-life in patients with impaired renal function: the half-life of gadodiamide in healthy volunteers is 1 3 hours, in patients with end-stage renal failure is 34 3 hours, in haemodialysis patients is 2 6 hours, and in patients having peritoneal dialysis is 52 7 hours. 22,25 Cowper and colleagues propose that NSF is the result of a combination of events that begin with renal disease, followed by deposition of allergens then circulating fibrocytes. Broome and colleagues speculate that if this idea is true, contrast media such as gadodiamide and gadoversetamide, which have different structures to other gadolinium-containing contrast agents, would be more likely to release free gadolinium (see section 2.4) Physicochemical properties of gadodiamide and other gadolinium-based agents All available gadolinium contrast agents are chelates that contain the gadolinium ion (Gd 3+ ). There are two structurally distinct categories of gadolinium chelates cyclic chelates (eg, gadoteridol and gadoterate meglumine), where Gd 3+ is caged in a cavity, and linear chelates (eg, gadodiamide and gadopentetate dimeglumine; figure 1). 26 Excess chelate is included in the contrast-agent preparation to ensure the absence of toxic free gadolinium (Gd 3+ ) in solution. High chelate concentration is an indirect marker of the likelihood that free gadolinium will be released more easily from the chelate complex. 2,26 8
9 Figure 1. Chemical Structures of cyclic chelates (ProHance [gadoteridol] and Dotarem [gadoterate meglumine]) and linear chelates (Omniscan [gadodiamide] and Magnevist [gadopentetate dimeglumine]) ProHance (gadoteridol) Omniscan (gadodiamide) Dotarem (gadoterate meglumine) Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine) Some gadolinium-based contrast media are more likely than others to release free Gd 3+ through a process called transmetallation with endogenous ions from the body. 27 These agents have the largest amount of excess chelate. Gadodiamide differs from other gadolinium-based contrast media, with the exception of gadoversetamide, 2 because it has an excess of chelate and is more likely to release free Gd 3+ compared with other agents. Cases of NSF in association with gadoversetamide have been reported in the USA. Table 1 (page 10) summarises the chemical structure and charge of the currently available marketed gadolinium contrast agents. Cyclic molecules offer better protection and binding to Gd 3+ compared with linear molecules. 2,26,28,29 Ionic cyclic chelates are least likely to release free Gd 3+ : they need no excess chelate, and have the longest dissociation half-life. Non-ionic linear gadolinium chelates (such as gadodiamide) are most likely to release free Gd 3+ in the body; they have the highest amount of excess chelate. 2,26,28,29 Furthermore, the charge of the molecule may increase the likelihood of release of free Gd through the available binding strength to the chelate. 29 9
10 Table 1: Currently marketed gadolinium contrast agents Brand name Generic name Acronym Chemical structure Charge Cases of NSF Omniscan gadodiamide Gd-DTPA-BMA Linear Non-ionic Yes OptiMARK* gadoversetamide Gd-DTPA-BMEA Linear Non-ionic Yes Magnevist MultiHance Primovist Vasovist gadopentetate dimeglumine gadobenate dimeglumine gadoxetic acid disodium salt gadofosveset trisodium Gd-DTPA Linear Ionic Yes Gd-BOPTA Linear Ionic No Gd-EOB-DTPA Linear Ionic No Gd-DTPA Linear Ionic No ProHance gadoteridol Gd-HP-DO3A Cyclic Non-ionic No Gadovist gadobutrol Gd-BT-DO3A Cyclic Non-ionic No Dotarem gadoterate meglumine Gd-DOTA Cyclic Ionic No *OptiMARK is not licensed in Europe, but is available in the USA Transmetallation releases free gadolinium through replacement of Gd 3+ in the chelate by cations such as zinc or copper. 2 Transmetallation occurs more easily with gadodiamide than with other gadolinium-based contrast media. 30 Moreover, transmetallation might occur more readily when a gadolinium contrast agent remains inside the body for a long period, such as in patients with renal failure. 27 Studies done in vitro, 26,31 34 in vivo, 26,35 41 and those involving human studies 42 lend support to these findings about the physicochemical properties of gadolinium-based contrast agents. 10
11 Human studies Puttagunta and colleagues showed that gadodiamide underwent more transmetallation than did two other gadolinium-containing contrast media (gadoteridol and gadopentetate dimeglumine) in healthy volunteers. 42 Gadoteridol was found to be the most inert of the three drugs tested. Moreover, Kimura and co-workers 39 showed that gadodiamide administration to patients resulted in the highest increase of zinc in urine (which suggests transmetallation) compared with two other gadolinium-containing contrast media (gadoterate meglumine and gadopentetate dimeglumine). Idée and colleagues reported transient increases in serum iron levels after injection of gadodiamide. 26 Gadodiamide interferes with the techniques of measurement of calcium in serum commonly used in hospitals. Cases of spurious hypocalcaemia have been reported with gadodiamide and gadoversetamide, which is caused by the formation of a complex between Gd 3+ and a reagent used in the measurement technique (o-cresol-phthalein, OCP) Gadolinium deposition occurs in human body tissues, 46,47 and has been identified in tissue samples of patients with NSF. High and colleagues 48 showed gadolinium deposition in four of 13 tissue samples from seven patients with NSF who were previously exposed to gadodiamide; Interestingly they were able to detect gadolinium in tissue samples up to 11 months after exposure. No gadolinium was identified in a tissue sample from a patient without NSF. Other metals found in the tissue of NSF patients included large deposits of iron, copper, and zinc. 23,48,49 High and colleagues speculate that gadolinium retained in tissue is phagocytosed by macrophages because the gadolinium in the tissue samples was associated with cell bodies. Intracellular gadolinium might increase the number of profibrotic cytokines or growth factors, leading to dermal or systemic fibrosis. 48 Boyd and colleagues also identified gadolinium deposition in patients with NSF, 50 which seemed to be restricted to areas where there was also deposition of calcium phosphate. The researchers conclude that cutaneous gadolinium deposition may have a role in the development of NSF. 11
12 3 Discussion In the past year, evidence to support a causal association between gadodiamide (Omniscan) and development of NSF has increased. Of the marketed gadolinium-based contrast agents, most cases of NSF have been associated with Omniscan, followed by OptiMARK (gadoversetamide, which is not licensed in Europe but is available in the USA), and a small number of cases have been reported with Magnevist (gadopentetate dimeglumine). The latest figures suggest that 90 cases of NSF associated with Omniscan, OptiMARK, or Magnevist have been reported to the US FDA. Elsewhere, more than 150 patients have developed NSF after exposure to a gadolinium-based contrast medium, more than 90% of which were exposed to Omniscan. 51 The reports, collated by the European Society of Urogenital Radiology (ESUR), showed that patients who developed NSF had received Omniscan a few weeks before. Four patients may have received another linear chelate (eg, OptiMARK and Magnevist), and for the remaining cases the causative agent is not known because several agents were given or because there is inadequate information about the case. 51 The Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) is aware of 21 cases of NSF associated with gadodiamide, five of which had a fatal outcome. The MAH for Magnevist has informed the UK of 13 non-uk cases of NSF associated with this agent. The causal role of Magnevist for some cases is unclear because several agents were given or because there is inadequate information about the case. However, for at least one case, in which the patient received high doses of Magnevist in a fairly short period, development of NSF seems related to Magnevist administration. To date, there have been no reports of NSF in patients with normal kidney function. Since the 1980s, more than 200 million patients have been exposed to gadolinium-based contrast agents, more than 30 million of whom have received Omniscan. Therefore, NSF does not appear to occur in association with gadolinium-based contrast agents in patients without renal impairment. 51 The population at risk are those with severely impaired renal function. Several researchers have suggested that liver transplant patients are prone to NSF. 18,21,23 Gadodiamide is almost exclusively excreted by the kidneys. Importantly, the half-life of gadodiamide in healthy volunteers is 1 3 hours, compared with 34 3 hours for those with endstage renal failure. 25 The different physicochemical properties of gadolinium-based contrast agents probably affect their behaviour in the body through the release of toxic free gadolinium (Gd 3+ ) (see section 2.4). Gadolinium-based contrast agents that consist of ionic cyclic chelate (see table 1, page 10) are least likely to release free Gd 3+ into the body. By contrast, gadolinium-based contrast agents that consist of non-ionic linear chelate (eg, Omniscan and OptiMARK; table 1) are most likely to release free Gd 3+ into the body. 2,26,28,29 12
13 Magnevist is a linear chelate, but it has an ionic charge that might lower the likelihood of release of Gd 3+ into the body. 28,29 In vitro and in vivo studies lend support to the idea that gadodiamide can release gadolinium ions through a process called transmetallation with endogenous ions from the body such as zinc, iron, calcium, and magnesium. In humans, gadodiamide interferes with measurement techniques of serum calcium that are commonly used in hospitals, which leads to spurious cases of hypocalcaemia Studies have shown that gadolinium deposition occurs in human body tissue ,50 Deposition of gadolinium in tissue has been postulated to stimulate development of NSF through various mechanisms such as involvement of circulating fibrocytes and transforming growth factor β. 14,16,52,53 NSF and the role of gadolinium-based contrast agents is an emerging science. The exact disease mechanism has yet to be elucidated, but physicochemical properties of gadoliniumcontaining agents might affect the amount of free gadolinium released in patients with renal impairment. Currently, there is no effective treatment for NSF; the most effective treatment options are related to improvement in renal impairment. Therefore, it is imperative that radiologists, nephrologists, and other relevant healthcare professionals receive guidance as to how to avoid this very debilitating and sometimes fatal disorder. In its recent communication of Dec 22, 2006, the US FDA does not differentiate between their five licensed gadolinium-based contrast agents and risk of NSF, although to date they have received only cases associated with Omniscan, OptiMARK, and Magnevist. The FDA recommends that treating physicians should assess carefully the benefits and risks associated with use of a gadolinium-based contrast agent in patients with moderate to endstage renal disease, and that an alternative imaging method or contrast agent should be used when possible. In addition, they propose prompt dialysis to remove gadolinium if used as a contrast agent is in these patients. However, some researchers have debated the benefits of dialysis of gadolinium. 23,26,52 For instance, daily dialysis for three consecutive days starting on the day of gadodiamide administration did not prevent development of NSF in three patients
14 4 Conclusion A review of the available data does not suggest that the risk of NSF in patients with advanced renal insufficiency is the same for all gadolinium-based contrast agents because distinct physiochemical properties affect their stabilities and thus the release of free gadolinium ions. The non-ionic linear chelates (Omniscan and OptiMARK) are associated with the highest risk of NSF; ionic cyclic chelates are associated with the lowest risk of NSF (Dotarem; see table 1, page 10). The ionic linear chelates (Magnevist, MultiHance, Vasovist and Primovist) and the non-ionic cyclic chelates (Gadovist and ProHance) have similar structures and these fall in between the other two groups. 4.1 UK regulatory position CHM and PEAG (see page 5) reviewed the issue of NSF and gadolinium-based contrast agents in January, With no known effective treatment for NSF and no effective method of removing free gadolinium ions from the body, the Commission advised that creatinine levels should be measured in all patients before use of a gadolinium-based contrast agent. CHM proposed a step-wise approach to restricting the use of gadolinium-based contrast agents in at-risk patients. They advised that Omniscan (and OptiMARK) should not be used in at-risk patients, and that ionic linear chelates (Magnevist, MultiHance, Vasovist and Primovist) or non-ionic cyclic chelates (Gadovist and ProHance) should not be used in at-risk patients unless regarded clinically essential. They advised that the standard recommended dose of these agents should not be exceeded, and their use should not be repeated at a time interval of less than 1 week. For the ionic cyclic agent Dotarem, CHM proposed a warning for its use in at-risk patients. CHM concluded that there is no robust evidence to suggest that haemodialysis is protective against NSF, and that dialysis in patients with severe renal impairment after gadoliniumcontaining contrast agent administration should not be recommended. CHM concluded that communications should be sent to relevant healthcare professionals (ie, radiologists, nephrologists, and all physicians who may request MRI radiological investigations in patients with severe renal impairment such as geriatricians and cardiologists) to inform them of these new recommendations. The advice of CHM informed the UK position during discussions of the European Pharmacovigilance Working Party (PhVWP, see section 4.2). 14
15 4.2 European regulatory position The PhVWP reviewed the issue of NSF and gadodiamide-based contrast agents in January, 2007 through data presented in an assessment report by the UK. On the basis of the current evidence, PhVWP concluded that there was strong suggestion of a causal association between gadodiamide and NSF in patients with severe renal failure. They noted that some gadolinium-containing products had been associated with few spontaneous reports of NSF, and some products had not been associated with any reports. PhVWP concluded that differences in the structure of gadolinium complexes may affect their propensity to trigger NSF. PhVWP concluded that the balance of risks and benefits of gadodiamide in patients with severe renal failure was negative, and that its use should be strictly contraindicated. PhVWP considered that dialysis after gadolinium administration was not beneficial in preventing NSF in patients with severe renal impairment. On a precautionary basis, PhVWP advised that a warning should be added to the product information about the use of gadodiamide in neonates because of their immature kidney function. 4.3 Proposed Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) wording for gadodiamide (Omniscan) Section 4.3 Contraindications Gadodiamide is contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR< 30 ml/min/1.73m 2 ), and those who have had or are undergoing liver transplantation (see section 4.4 for Special Warnings and Precautions). Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use Severe renal impairment and liver transplant patients: There have been reports of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) associated with use of gadodiamide and some other gadolinium-containing contrast agents in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR <30ml/min/1.73m 2 ) and those who have had or are undergoing liver transplantation. Therefore OMNISCAN should not be used in these populations (see section 4.3 for Contraindications). Neonates and Infants: Due to immature kidney function in neonates and infants up to 1 year of age, OMNISCAN should only be used in these patients after careful consideration. Section 4.8 Undesirable effects Cases of NSF have been reported with OMNISCAN. Box 1: Proposed SPC changes for gadodiamide (Omniscan) 15
16 PhVWP advised that for all other gadolinium-containing contrast agents, strong warnings about potential NSF in patients with impaired renal function should be added to the product information. 4.3 Proposed SPC wording for all other gadolinium-containing contrast agents Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use There have been reports of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) associated with use of some gadolinium-containing contrast agents in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR <30mL/min/1 73m 2 ). As there is a possibility that NSF may occur with xxxx, it should only be used in these patients after careful consideration. Section 4.8 Undesirable effects (for those products where cases have been reported) Cases of NSF have been reported. Box 2: Proposed SPC wording for all other gadolinium-containing contrast agents PhVWP advised that appropriate wording should be added to the Patient Information Leaflets (PILs). PhVWP advised that healthcare professionals in the European Union should be informed of this new information promptly. 16
17 References 1 Runge VM. Safety of approved MR contrast media for intravenous injection. J Magn Reson Imaging 2000; 12: Thomsen HS ed. Contrast media. Safety issues and ESUR guidelines. Heidelberg: Springer Verlag: Grobner T. Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006; 21: Erratum Cowper SE, Robin HS, Steinberg SM, et al. Scleromyxoedema-like cutaneous diseases in renal-dialysis patients. Lancet 2000; 356: LeBoit PE. What nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy might be. Arch Dermatol 2003; 139: Ting WW, Stone MS, Madison KC, Kurtz K. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy with systemic involvement. Arch Dermatol 2003; 139: Daram SR, Cortese CM, Bastani B. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: report of a new case with literature review. Am J Kidney Dis 2005; 46: Cowper SE, Su LD, Bhawan J, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. Am J Dermatopathol 2001; 23: McNeill AM, Barr RJ. Scleromyxedema-like fibromucinosis in a patient undergoing hemodialysis. Int J Dermatol 2002; 41: Cowper SE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: the first 6 years. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2003; 15: Swaminathan S, Ahmed I, McCarthy JT, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and high-dose erythropoietin therapy. Ann Intern Med 2006; 145: Fazeli A, Lio PA, Liu V. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: are ACE inhibitors the missing link? Arch Dermatol 2004; 140: Mackay-Wiggan JM, Cohen DJ, Hardy MA, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy (scleromyxedema-like illness of renal disease). J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 48: Cowper SE, Bucala R. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy: suspect identified, motive unclear. Am J Dermatopathol 2003; 25: Quan TE, Cowper SE, Bucala R. The role of circulating fibrocytes in fibrosis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2006; 8: Jimenez SA, Artlett CM, Sandorfi N, et al. Dialysis-associated systemic fibrosis (nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy): study of inflammatory cells and transforming growth factor beta1 expression in affected skin. Arthritis Rheum 2004; 50: Cowper SE, Bucala R, LeBoit PE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis setting the record straight. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2006; 35: Baron PW, Cantos K, Hillebrand DJ, Hu KO, et al. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy after liver transplantation successfully treated with plasmapheresis. Am J Dermatopathol; :
18 19 Gilliet M, Cozzio A, Burg G, Nestle FO. Successful treatment of three cases of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy with extracorporeal photopheresis. Br J Dermatol 2005; 152: Moschella SL, Kay J, Mackool BT, Liu V. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case A 68-year-old man with end stage renal disease and thickening of the skin. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: Maloo M, Abt P, Kashvap R, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis among liver transplant recipients: a single institution experience and topic update. Am J Transplant 2006; 6: Marckmann P, Skov L, Rossen K, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: suspected causative role of gadodiamide used for contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Soc Nephrol 2006; 17: Broome DR, Girguis MS, Baron PW, Cottrell AC, et al. Gadodiamide-associated nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: why radiologists should be concerned. MR Imaging (In press). AJR Am J Roentgenol 2007; 188: Sadowski E, Bennett L, Chang M, Wentland A, et al. Gadolinium and Nephrogenic Fibrosing Dermopathy. RSNA 2006; E353B. 25 Joffe P, Thomsen HS, Meusel M. Pharmacokinetics of gadodiamide injection in patients with severe renal insufficiency and patients undergoing hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Acad Radiol 1998; 5: Idée JM, Port M, Schaefer M, et al. Clinical and biological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2006; 20: Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, Dawson P. Is there a causal relation between the administration of gadolinium based contrast media and the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)? Clin Radiol 2006; 61: Dawson P. Gadolinium chelates: chemistry. In: Dawson P, Cosgrove DO, Grainger RG, eds. Textbook of contrast media. Oxford: Isis Medical Media, 1999: Desreux JF, Gilsoul D. Chemical synthesis of paramagnetic complexes. In: Thomsen HS, Muller RN, Mattrey, eds. Trends in contrast media. Heildelberg: Springer Verlag, 1999: Behra-Miellet J, Gressier B, Brunet C, et al. Free Gadolinium and gadodiamide, a gadolinium chelate used in magnetic resonance imaging: evaluation of their in vitro effects on human neutrophil viability. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 1996; 18: Tweedle MF. Physicochemical properties of gadoteridol and other magnetic resonance contrast agents. Invest Radiol 1992; 27 (suppl 1): S Tweedle MF, Hagan JJ, Kumar K, et al. Reaction of gadolinium chelates with endogenously available ions. Magn Reson Imaging 1991; 9: Laurent S, Elst LV, Copoix F, Muller RN. Stability of MRI paramagnetic contrast media: a proton relaxometric protocol for transmetallation assessment. Invest Radiol 2001; 36: Corot C, Idée JM, Hentsch AM, Santus R, et al. Structure-activity relationship of macrocyclic and linear gadolinium chelates: investigation of transmetallation effect on the 18
19 zinc-dependent metallopeptidase angiotensin-converting enzyme. J Magn Reson Imaging 1998; 8: Spencer A, Wilson S, Batchelor J, et al. Gadolinium chloride toxicity in the rat. Toxicol Pathol 1997; 25: Spencer A, Wilson S, Harpur E. Gadolinium chloride toxicity in the mouse. Hum Exp Toxicol. 1998; 17: Tweedle MF, Wedeking P, Kumar K. Biodistribution of radiolabeled, formulated gadopentetate, gadoteridol, gadoterate, and gadodiamide in mice and rats. Invest Radiol 1995; 30: Idée JM, Berthommier C, Goulas V, Corot C, et al. Haemodynamic effects of macrocyclic and linear gadolinium chelates in rats: role of calcium and transmetallation. Biometals 1998; 11: Kimura J, Ishiguchi T, Matsuda J, Ohno R, et al. Human comparative study of zinc and copper excretion via urine after administration of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Radiat Med 2005; 23: Harpur ES, Worah D, Hals PA, et al. Preclinical safety assessment and pharmacokinetics of gadodiamide injection, a new magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent. Invest Radiol 1993; 28 (suppl 1): S Wible JH, Troup CM, Hynes MR, et al. Toxicological assessment of gadoversetamide injection (OptiMARK), a new contrast-enhancement agent for use in magnetic resonance imaging. Invest Radiol 2001; 36: Puttagunta NR, Gibby WA, Smith GT. Human in vivo comparative study of zinc and copper transmetallation after administration of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. Invest Radiol 1996; 31: Emerson J, Kost G. Spurious hypocalcemia after Omniscan- or OptiMARK-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging: an algorithm for minimizing a false-positive laboratory value. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004; 128: Moore CD, Newman RC, Caridi JG. Spurious hypocalcemia after gadodiamideenhanced magnetic resonance imaging: a case report and review of the literature. Rev Urol 2006; 8: Zhang HL, Ersoy H, Prince MR. Effects of gadopentetate dimeglumine and gadodiamide on serum calcium, magnesium, and creatinine measurements. J Magn Reson Imaging 2006; 23: Gibby WA, Gibby KA, Gibby WA. Comparison of Gd DTPA-BMA (Omniscan) versus Gd HP-DO3A (ProHance) retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy. Invest Radiol 2004; 39: White GW, Gibby WA, Tweedle MF. Comparison of Gd (DTPABMA) (Omniscan) versus Gd (HP-DO3A) (ProHance) relative to gadolinium retention in human bone tissue by inductively coupled plasma mass spectroscopy. Invest Radiol 2006; 41: High WA, Avers RA, Chandler J, et al. Gadolinium is detectable within the tissue of patients with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56:
20 49 Vorobiov M, Basok A, Tovbin D, et al. Iron-mobilizing properties of the gadolinium- DTPA complex: clinical and experimental observations. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2003; 18: Boyd AS, Zic JA, Abraham JL. Gadolinium deposition in nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. J Am Acad Dermatol 2007; 56: Thomsen HS. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious late adverse reaction to gadodiamide. Eur Radiol 2006; 16: Galan A, Cowper SE, Bucala R. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy). Curr Opin Rheumatol 2006; 18: Morcos SK. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis following the administration of extracellular gadolinium based contrast agents: Is the stability of the contrast agent molecule an important factor in the pathogenesis of this condition? (In press). 20
21 Glossary Antifibrotic Events or factors that prevent the laying down of fibrous scar tissue Bicarbonate A bodily substance that controls the acidity of blood; levels are regulated by the kidney Bone marrow The spongy component of blood that produces blood cells Brain neoplasm New growth of cells in the brain, which may develop into cancer Calcification The process by which bodily tissues become hard due to deposition of calcium Calcineurin inhibitors Agents that block the binding protein calcineurin Cation A positively charged atom or molecule Central nervous system The nerves of the brain and spinal cord Chelate A metal that is complexed with other molecules, sometimes in a ring Coagulation The process of blood clotting Collagen (type I) The protein component of connective tissue, it is also present in skin, bone, cartilage, and ligaments Comorbidities Presence of more than one disease or disorder in a person at the same time Contractures Resistance to the stretch of a muscle Cranial Relating to the skull Creatinine A bodily waste product that is passed in urine, which can be used to measure kidney function Cutaneous Relating to the skin Cytokines Proteins that circulate in the body that have a signalling and regulatory role Deep vein thrombosis Blood clotting in the legs Dermal Relating to the skin Dialysate fluid The mixture of fluid that flows during kidney dialysis 21
22 Dialysis A process of filtering waste products from the body Electrons Negatively charged particle End-stage renal disease A patient with impaired liver function who requires kidney dialysis Endogenous Developing or originating in an organism Erythropoietin A bodily substance that regulates production of red blood cells in the bone marrow Fibroblast A cell present in connective tissue Fibrocyte A cell present in connective tissue that can form collagen and has an important role in wound healing Fibrogenic Events or factors that promote the laying down of fibrous tissue Glomerular filtration rate A measure of the ability of the kidneys to filter waste Haemodialysis The process of filtering products from the blood Half-life The time taken by a substance to decrease to half its value Histopathological Signs of disease that are evident through a microscope Hypercoagulability A bodily state of heightened ability of the blood to clot Hypocalcaemia Low concentration of calcium in the blood, which can cause muscular problems such as cramp Idiopathic Of unknown cause Immunosuppressive An agent that decreases that activity of the immune system Induration Hardening Inert Unreactive, stable Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme Drugs that block the activity of an enzyme that has role in the regulation of blood pressure Intracellular Inside cells 22
23 In vitro Experiments or studies done in an artificial environment such as a test tube In vivo Experiments or studies done with a living organism Ionic A substance that separates into ions Ions Atoms that carry a positive or negative charge Liver necrosis Death of cells in the liver Macrophages Important cells of the body s immune system that engulf and kill some foreign bodies such as bacteria Magnetic resonance angiography A non-invasive method of imaging blood vessels Magnetic resonance imaging A non-invasive method of imaging bodily structures Marketing Authorisation Holder An organisation that holds a licence for a medicine (a pharmaceutical company) Matrix A meshwork in which cells are embedded Mean Average Mesenchymal tissue Connective tissue that describes a developmental pathway in the embryo that leads to the formation of connective tissue Metabolic acidosis An abnormal level of acidity in the blood, which can lead to symptoms such as dehydration and shock Mucin A component of mucous Myofibroblast A fibroblast cell that contains muscle filaments such that they may contract Non-ionic A substance that does not separate into ions Odds ratio A measure of the risk or likelihood of an event occurring; a 95% CI (confidence interval) estimates the precision of this measurement Paramagnetic A substance with magnetic properties Pathological A diseased state 23
24 Peripheral circulation The blood supply to the extremities of the body such as the arms and legs Peritoneal Relating to the lining of the abdomen ph The scale that measures acidity Phagocytose The process by which a macrophage engulfs foreign bodies Pharmacological Relating to the action of medicines Phospholipids A type of fatty molecules that have an important role in cell membranes Photophoresis Destruction of cells by use of ultra-violet light, which activates a drug Plasmapheresis Separation of blood into the a cellular component and a plasma component Protons Positively charged particles Topical An agent applied to the skin Radiographic Relating to the procedure of taking x-rays Renal Relating to the kidneys Serum The clear portion of bodily fluid or of blood Skin biopsy A method of measuring the cellular components of a skin sample Systemic Relating to the whole body Thalidomide A drug that is able to modulate the immune system Thrombotic Agents or events that promote blood clotting or thrombus formation Transforming growth factor β A bodily substance that stimulates the growth of some cells Transmetallation A chemical reaction, in which one metal attached to other molecules is substituted for another Tumour necrosis factor A bodily substance that promotes inflammation Vasodilation Widening of blood vessels 24
Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects
 Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research
 University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
 Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates
 Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 1104 1108 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfk062 Advance Access publication 23 January 2006 Interesting Case Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 1104 1108 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfk062 Advance Access publication 23 January 2006 Interesting Case Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (marketed as Magnevist, MultiHance, Omniscan, OptiMARK, ProHance)
 Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018)
 Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies
 Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
NSF Coming and Going
 NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions
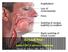 Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline
 Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Imaging in the time of NFD/NSF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency?
 DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR
 William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
Figure 1 Figure 1: Energy diagram illustrates formation of a chelate (ML) created by combining two chemicals free Gd 3 (M), which is a metal ion, and
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the product information
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist and Magnevist below.
 August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS
 DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: Possible Association with a Predisposing Infection
 MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
Summary. Correspondence Jerrold L. Abraham. Accepted for publication 17 September 2007
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA.
 ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents
 Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. DOTAREM mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid)
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media
 HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing theory
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist, Eovist and Magnevist on the following pages.
 Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7
 PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
Policy #: 291 Latest Review Date: February 2013
 Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document. Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013
 FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice?
 Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Chapter 9 A 65-Year-Old Woman with Hardened Skin, Joint Contractures, and Yellow Scleral Plaques
 Chapter 9 A 65-Year-Old Woman with Hardened Skin, Joint Contractures, and Yellow Scleral Plaques Jonathan Kay Keywords Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Chronic kidney disease Contrast media Gadolinium Gadolinium
Chapter 9 A 65-Year-Old Woman with Hardened Skin, Joint Contractures, and Yellow Scleral Plaques Jonathan Kay Keywords Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Chronic kidney disease Contrast media Gadolinium Gadolinium
Annex II. Scientific conclusions
 Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
INTRODUCTION CLINICAL EXPERIENCE CLINICAL EFFICACY PEDIATRIC EXPERIENCE DOSING SUMMARY
 1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be used
 Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Update. Drug Safety. Welcome to the first issue of the newly launched Drug Safety Update. This
 Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance
 Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Report on the Investigation Results
 This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
Gadolinium in Humans: A Family of Disorders
 Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Safety of Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) as a Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
Complications of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis following repeated exposure to gadolinium in a man with hypothyroidism: a case report
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Complications of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis following repeated exposure to gadolinium in a man with hypothyroidism: a case report Arpita Aggarwal
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Complications of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis following repeated exposure to gadolinium in a man with hypothyroidism: a case report Arpita Aggarwal
Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
 Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Scientific Paper. Authors: E. De Kerviler 1, S. Gaillard 2 ; 1 Paris/FR, 2 Villepinte/FR
 Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
PRAC recommendations on signals for update of the product information
 Thursday 22 January 2015 EMA/PRAC/62352/2015 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee PRAC recommendations on signals for update of the product information Adopted at the 6-9 January 2015 PRAC 1. Atorvastatin,
Thursday 22 January 2015 EMA/PRAC/62352/2015 Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee PRAC recommendations on signals for update of the product information Adopted at the 6-9 January 2015 PRAC 1. Atorvastatin,
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM. (gadoterate meglumine) Injection. For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern
 Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are significantly
 Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Package Leaflet: Information for the user. MAGNEVIST 2 mmol/l solution for injection dimeglumine gadopentetate
 Due to regulatory changes, the content of the following Patient Information Leaflet may vary from the one found in your medicine pack. Please compare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' towards the end
Due to regulatory changes, the content of the following Patient Information Leaflet may vary from the one found in your medicine pack. Please compare the 'Leaflet prepared/revised date' towards the end
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
 Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE
 CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
CHRONIC KIDNEY FAILURE Overview Chronic kidney disease, also called chronic kidney failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function. Your kidneys filter wastes and excess fluids from your blood,
During the past decade, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 Low Risk for Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Nondialysis Patients Who Have Chronic Kidney Disease and Are Investigated with Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Constantina Chrysochou,* Albert
Low Risk for Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis in Nondialysis Patients Who Have Chronic Kidney Disease and Are Investigated with Gadolinium-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging Constantina Chrysochou,* Albert
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. 1.1 Central Nervous System. 1.2 Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues. 1.3 Body
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
October 23, Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs. Dear Dr. Hamburg:
 October 23, 2012 Commissioner Margaret A. Hamburg, M.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue WO Bldg. 1, Room 2217 Silver Springs, MD 20993 Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs Dear
October 23, 2012 Commissioner Margaret A. Hamburg, M.D. U.S. Food and Drug Administration 10903 New Hampshire Avenue WO Bldg. 1, Room 2217 Silver Springs, MD 20993 Re: Gadolinium Toxicity from GBCAs Dear
Biologic Effects of Diagnostic Imaging Modalities
 Biologic Effects of Diagnostic Imaging Modalities Gerald R. Aben, MD FACR Department of Radiology College of Osteopathic Medicine 6/12/2012 DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY 1 Biologic Effects 6/12/2012 DEPARTMENT
Biologic Effects of Diagnostic Imaging Modalities Gerald R. Aben, MD FACR Department of Radiology College of Osteopathic Medicine 6/12/2012 DEPARTMENT OF RADIOLOGY 1 Biologic Effects 6/12/2012 DEPARTMENT
London Strategic Clinical Networks. My AKI. Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury
 London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
London Strategic Clinical Networks My AKI Guidance for patients with, or recovering from, acute kidney injury Supporting the delivery of equitable, high quality AKI care through collaboration www.londonaki.net
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 and 46 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended
 Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 and 46 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Gadopentetic acid (Gadopentate) Magnevist UK/W/049/pdWS/001 Rapporteur:
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 and 46 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Gadopentetic acid (Gadopentate) Magnevist UK/W/049/pdWS/001 Rapporteur:
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended.
 Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Omniscan UK/W/063/pdWS/001 Rapporteur UK Finalisation procedure (day 20)
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Omniscan UK/W/063/pdWS/001 Rapporteur UK Finalisation procedure (day 20)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. flow rate of approximately 2 ml/second for adults and 1-2 ml/second for pediatric
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology
 VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Indication: Treatment of blood clots Blood clots in the large veins of the legs, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are a common
VI.2 VI.2.1 Elements for a Public Summary Overview of disease epidemiology Indication: Treatment of blood clots Blood clots in the large veins of the legs, known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), are a common
Special Articles Original Research
 Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia
 Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia What other foods in the diet cause edema?. The veins in the legs are responsible for transporting blood up to the veins of the torso, where it is then returned to the
Bumex vs lasix in hypoalbuminemia What other foods in the diet cause edema?. The veins in the legs are responsible for transporting blood up to the veins of the torso, where it is then returned to the
Introduction What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease? How Do Doctors Treat Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 9
 Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
Patient Information Table of Contents Introduction... 3 What is Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 5 What Are Some of the Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease?... 7 What Causes Peripheral Vascular Disease?...
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1652 1656, November/December 2002 Contrast between Scar and Recurrent Herniated Disk on Contrast-Enhanced MR Images Victor Haughton, Ken Schreibman, and Arthur De Smet BACKGROUND
Gadolinium Retention in the Dentate Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Is Dependent on the Class of Contrast Agent 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
Pro-enkephalin and Renal Disease. Alan H. Wu, Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco 12 th Annual UCSD Biomarkers of Cardiac Disease
 Pro-enkephalin and Renal Disease Alan H. Wu, Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco 12 th Annual UCSD Biomarkers of Cardiac Disease The presenter has received relevant grants and /or consulting
Pro-enkephalin and Renal Disease Alan H. Wu, Ph.D. University of California, San Francisco 12 th Annual UCSD Biomarkers of Cardiac Disease The presenter has received relevant grants and /or consulting
Histopathology: healing
 Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
Histopathology: healing These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2003) 18 [Suppl 8]: viii2 viii6 DOI: 10.1093/ndt/gfg1083 Left ventricular hypertrophy: why does it happen? Gerard M. London Department of Nephrology and Dialysis, Manhes Hospital,
VI.2 ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY (VOLUVEN 10%)
 VI.2 ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY (VOLUVEN 10%) VI.2.1 OVERVIEW OF DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY Hypovolaemia is a state of decreased or reduced circulating blood volume which can be caused by a number of medical
VI.2 ELEMENTS FOR A PUBLIC SUMMARY (VOLUVEN 10%) VI.2.1 OVERVIEW OF DISEASE EPIDEMIOLOGY Hypovolaemia is a state of decreased or reduced circulating blood volume which can be caused by a number of medical
Chronic kidney disease in cats
 Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Chronic kidney disease in cats What is chronic kidney disease (CKD)? Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the name now used to refer to cats with kidney failure (or chronic kidney failure). CKD is one of the
Incidence of Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions
 Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST. gadoxetate disodium injection mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml)
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
CONTRAINDICATIONS History of severe hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI
 11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
Excipients with known effect: Each gramme of gel contains 1 mg methyl parahydroxybenzoate (E-218) and 0.5 mg propyl parahydroxybenzoate (E-216).
 VENOSMIL 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT VENOSMIL 200 mg hard capsules VENOSMIL 20 mg/g gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENOSMIL 200 mg hard capsules Each capsule contains 200 mg hidrosmin.
VENOSMIL 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT VENOSMIL 200 mg hard capsules VENOSMIL 20 mg/g gel 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION VENOSMIL 200 mg hard capsules Each capsule contains 200 mg hidrosmin.
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS
 INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
INTRODUCTION TO HAEMODIALYSIS Why do I need dialysis? What is dialysis? How does haemodialysis work? Where will I have my treatment? Will dialysis cure my kidney failure? Will dialysis keep me well? I
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL. Living well with Kidney Disease
 HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
HEALTHYSTART TRAINING MANUAL Living well with Kidney Disease KIDNEY DISEASE CAN AFFECT ANYONE! 1 HEALTHYSTART PROGRAMME HEALTHYSTART is a lifestyle management programme to assist you to remain healthy
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM. Gadoterate meglumine injection. (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and
 CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
CHAPTER 4 Study of different tissues Abnormal cells and tissues can be compared to normal tissues to identify disease, such as cancer Being able to know and recognize normal tissues under the microscope
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for injection contains
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for injection contains
T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents in Human Whole Blood at 1.5, 3, and 7 T
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
Make an appointment with your doctor if you have any signs or symptoms of acute kidney failure.
 Acute Kidney Failure Acute kidney failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes
Acute Kidney Failure Acute kidney failure occurs when your kidneys suddenly become unable to filter waste products from your blood. When your kidneys lose their filtering ability, dangerous levels of wastes
Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents Produce Analytic Interference in Multiple Serum Assays
 Clinical Chemistry / GDOLINIUM CONTRST GENT INTERFERENCE Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Contrast gents Produce nalytic Interference in Multiple Serum ssays Kerry.S. Proctor, MD, 1 Lokinendi V. Rao, PhD,
Clinical Chemistry / GDOLINIUM CONTRST GENT INTERFERENCE Gadolinium Magnetic Resonance Contrast gents Produce nalytic Interference in Multiple Serum ssays Kerry.S. Proctor, MD, 1 Lokinendi V. Rao, PhD,
What Your Kidneys Do
 UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
UW MEDICINE PATIENT EDUCATION What Your Kidneys Do And what happens with kidney disease Class Goals 1. Understand what kidneys do. 2. Understand symptoms of uremia. 3. Know the common causes of kidney
