Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview
|
|
|
- Mark Snow
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University Hospital Paul-Brousse, AP-HP, 12, Avenue Paul Vaillant-Couturier, Villejuif Cedex, France Received 4 January 2008; received in revised form 4 January 2008; accepted 8 January 2008 Abstract Increasing use is made of extracellular MRI contrast agents that alter the image contrast following intravenous administration; they predominantly shorten the T1 relaxation time of tissues. The degree and location of these changes provide substantial diagnostic information. However gadoliniumbased contrast agents (Gd-CA) are not inert drugs. They may cause acute non-renal adverse reactions (e.g. anaphylactoid reactions), acute renal adverse reactions (e.g. contrast induced nephropathy), delayed adverse reactions (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis) and problems at the site of injection (e.g. local necrosis). This review describes the current status of Gd-CA, their mechanism of action, chemical structure, pharmacokinetics, dosage, elimination, nephrotoxicity and adverse events Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: Contrast agents; Gadolinium; Osmolality; Nephrotoxicity; Adverse reactions Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast agents (Gd-CA) are the most widely used contrast agents for MR imaging. Currently it is estimated that 40 50% of all MR studies performed worldwide are contrast-enhanced [1] and the degree of contrast utilization is expected to increase in the future [2]. Gd-CA are considered to have an excellent overall safety profile. However, both renal and non-renal adverse reactions have been reported in the last few years [3 11] following administration to patients with underlying kidney disease. Several recent reports have associated intravenous administration of Gd-CA with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), a rare, relatively new, devastating fibrosing disorder of the skin and other systemic organ, such as the liver, lungs, muscles and heart [4,9,12,13]. This disease has been reported exclusively in patients with renal insufficiency and is strongly associated with prior exposure to Gd-CA. At the time of this writing, the great majority (>90%) of published cases have been associated with the use of gadodiamide (Omniscan,GE Healthcare, Chalfont St. Giles, United Kingdom) and to a much lesser degree of gadopentetate (Magnevist, Bayer Schering, Berlin, Germany) and gadoversetamide (OptiMARK, Covidien, St. Louis, USA) in the USA (for further information please refer to the other papers in this issue of European Journal of Radiology on NSF). It is the radiologist s responsibility to understand Corresponding author. Tel.: ; fax: addresses: marie-france.bellin@pbr.aphp.fr, marie-france.bellin@u-psud.fr (M.-F. Bellin). the potential adverse effects of gadolinium chelates, to identify the special situations associated with a higher risk of occurrence, and to justify the use of Gd-CA. The purpose of this review is to discuss the chemical structure and the mechanism of action of Gd-CA, their dosage, elimination, and relevant aspects of their clinical pharmacology. 1. Toxicology of gadolinium All available Gd-CA are chelates that contain the gadolinium ion Gd 3+. Gadolinium belongs to the lanthanide group of elements. Free gadolinium is highly toxic. Its ionic radius (107.8 pm) is close to that of Ca 2+ (114 pm). Free gadolinium is an inorganic blocker of many types of voltage-gated calcium channels at nano- to micro-molar concentrations [14]. It inhibits the physiological processes which depend upon Ca 2+ influx as well as the activity of some enzymes. It may also depress the reticuloendothelial system [15] and has been found to increase the expression of hepatic cytokines. Chelation of gadolinium by appropriate ligands dramatically reduces its acute toxicity. 2. Chemical structure To date, nine intravenous Gd-CA have been approved, among which eight have been approved in Europe, and six in the United States (Table 1). Their generic names, brand names, acronyms and chemical characteristics are described X/$ see front matter 2008 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved. doi: /j.ejrad
2 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) Table 1 Approval status of gadolinium (Gd) chelates in clinical use Approved doses (mmol/kg) for children Approved doses (mmol/kg) for MR angiography Approved doses (mmol/kg) for CNS a imaging Gd chelate (trade name) Body region(s) approved Approval Approved doses (mmol/kg) for body imaging Gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist ) CNS a, whole body USA, EU, Japan b 0.1 Gadodiamide (Omniscan ) CNS a, whole body USA, EU, Japan From 6 months: 0.1 Gadoterate meglumine (Dotarem ) CNS a, whole body EU Gadoteridol (ProHance ) CNS a, whole body USA, EU, Japan Not approved From 2 years and above: 0.1, 6 months 2 years: caution, <6 months: contraindicated Gadobutrol (Gadovist ) CNS a EU Not approved Not approved Not approved Gadobenate dimeglumine (MultiHance ) CNS a, liver USA, EU Liver: Not approved Not approved <18 years Gadoversetamide (OptiMARK ) CNS a, liver USA Not approved Not approved <18 years Gadoxetic acid (Primovist ) (Europe), Eovist (USA) Liver USA, EU or Not approved Not approved Not approved <18 years 0.1 ml/kg Gadofosveset (Vasovist ) Abdominal and limb vessels EU Not approved Not approved MRA 0.03 Not approved <18 years a CNS: central nervous system. b Gadopentetate dimeglumine (Magnevist ) is approved for whole body imaging and for doses of mmol/kg but does not have a trial based approval for MR angiography. in Table 2. They include non-specific extracellular gadolinium chelates (gadopentetate, gadoterate, gadoteridol, gadodiamide, gadobutrol and gadoversetamide), two liver specific contrast agents (gadobenate and gadoxetate), and one contrast agent specifically designed for MR angiography (gadofosveset). After bolus injection, liver specific Gd-CA combine established features of extracellular contrast agents during the first minutes following injection with the advantages of hepatocyte specificity and biliary excretion in the delayed phase [16 18]. Gadofosveset, a new blood pool contrast agent designed for vascular imaging, is a gadolinium-based compound that binds reversibly to albumin in the blood [19]. This contrast agent gives both an increased signal intensity compared with that of other extracellular agents and persistent intravascular image enhancement for at least 1 h. Blood pool agents can provide dynamic images, such as those available with existing extracellular agents, and a longer steady-state phase to image the vasculature. The price is that the T 1/2 is much longer (18 h in patients with normal renal function) than that of the pure extracellular agent. Of course the excretion time is also longer in patients with reduced renal function. The advantage of the lower dose may be obviated by the much prolonged body exposure. Extracellular Gd-CA are distributed within the extracellular interstitial space. They are formed by chelation of gadolinium to organic ligands. Chelation serves to eliminate heavy metal toxicity by preventing the cellular uptake of free gadolinium ion Gd 3+ which has high toxicity. Chelation maintains the biodistribution of gadolinium chelates within the extracellular space and enhances renal filtration, resulting in a biological half life of approximately h in patients with normal renal function. However in patients with renal kidney disease, renal elimination is decreased and delayed toxic effects of gadolinium may occur. There are two structurally distinct categories of Gd-CA: the macrocyclic molecules where Gd 3+ is caged in the preorganized cavity of the ligand and linear molecules (Fig. 1). The stability of extracellular contrast agents depends on their kinetic, thermodynamic and conditional stability. These parameters are not directly related to the molecular structure although macrocyclic contrast media have a much higher stability than linear (Table 2). The commercially available contrast agent with the lowest thermodynamic stability is the linear, non-ionic gadodiamide, which has been associated with the great majority of NSF reported cases. In addition, because of their relatively low stability, the pharmaceutical solutions of some gadolinium complexes (e.g. gadodiamide and gadoversetamide) include excess chelate to ensure the absence of toxic free Gd 3+ cations in the pharmaceutical solutions over their shelf lives. Cyclic chelates need no excess chelate to ensure the absence of toxic Gd 3+ in solution and are least likely to release free from the gadolinium complex through a process called transmetallation with endogenous ions from the body [13,14]. 3. Stability of MRI contrast media 3.1. Transmetallation Please refer to the chapter written by SK Morcos.
3 162 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) Table 2 Physicochemical characteristics of gadolinium-based MR contrast agents Gadofosveset Gadoxetic acid Gadoteridol Gadodiamide Gadobutrol Gadoversetamide Gadobenate dimeglumine Gadoterate meglumine Generic name Gadopentetate dimeglumine Brand name Magnevist Dotarem ProHance Omniscan Gadovist OptiMARK MultiHance Primovist Vasovist Gd-DTPA Gd-DTPA-BMEA Gd-BOPTA Gd-EOB- DTPA Acronym Gd-DTPA Gd-DOTA Gd-HP-DO3A Gd-DTPA-BMA Gd-BT- DO3A Bayer Schering Pharma Tyco Bracco Bayer Schering Pharma Guerbet Bracco GE Healthcare Bayer Schering Pharma Manufacturer Bayer Schering Pharma Characteristic 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.5 mol/l 0.25 mol/l 0.25 mol/l Molecular structure Linear Cyclic Cyclic Linear Cyclic Linear Linear Linear Linear Charge Ionic Ionic Nonionic Nonionic Nonionic Nonionic Ionic Ionic Ionic N/A Thermodynamic stability constant (log Keq) Osmolality (Osm/kg) Viscosity (mpa s at 37 C) T1 relaxivity (L/mmol s 1 ) blood Kobs (s 1 ) h 35 s 90 min 18 h min h 29 min T1/2 10 min 9 h, 60 h, >1 month 4. Osmolality Logically, the ionic complexes have a higher osmolality then the so-called non-ionic complexes (Table 2). Non-ionic complexes with low osmolality were developed to improve tolerance and allow the use of higher doses [20,21]. Because of the low amounts of compounds injected for MR imaging, the ionic charge of the Gd complexes is not a crucial factor, as the increased plasma osmolality following administration of Gd chelates is very low, unlike what is observed with iodinated contrast media. Low osmolarity chelates could be advantageous when higher doses are required. In addition, it has been shown in a rat model that the extravasation of ionic gadopentetate was associated with higher incidences of necrosis, hemorrhage and edema than non-ionic gadoteridol [22].The first commercially available agents had a 0.5 M osmolarity. Manufacturers now provide 1 M solutions (Table 2) in order to increase the quality of bolus injection and to reduce the volume of injected solution. 5. Viscosity It is a measure of the amount of internal friction within a fluid. Increasing viscosity results in increased resistance to flow. The viscosity of water is 1 cp (centipoise) at 20 C, and those of plasma and whole blood are 1.5 and 3 cp at 37 C. The viscosities of the first-generation intravenous Gd agents at 37 C range from 1.3 to 2.9 cp, with these figures increasing by approximately 50% at room temperature [1]. At the standard doses and injection rates the viscosity of current Gd-CA is not a significant concern. However, viscosity should be taken into account when dealing with high-flow-rate applications and small catheters. 6. Dosage The recommended dose of nonspecific gadolinium chelate for the majority of clinical indications is 0.1 mmol/kg of body weight and the recommended injection rate is 2 3 ml/s (0.5 mmol/ml). However, higher doses ( mmol/kg), may also be required for MR angiography and CNS imaging (Table 1). Liver specific contrast agent gadobenate is approved for a dose of 0.05 mmol/kg while gadoxetate is approved for a dose of 25 mol/kg. For MR angiography gadodiamide and gadopentetate are approved for a dose up to 0.3 mmol/kg, while gadoterate for a dose up to 0.2 mmol/kg. The blood pool agent gadofosveset is approved for MR angiography of the abdominal and limb vessels for a dose up to 0.03 mmol/kg. All nonspecific gadolinium chelates except gadobutrol are available in a concentration of 0.5 mmol/ml; gadobutrol is available in a concentration of 1 mmol/ml. To date, no cumulative dose beyond which NSF (or any other adverse event) may occur has been established. However, it seems that most NSF cases were reported in patients with end stage renal disease who received large amounts of gadolinium chelates as a result of serial MR examinations.
4 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) Mechanism of action Gd-CA of small molecular weight are extracellular space markers. They are highly paramagnetic because gadolinium has seven unpaired electrons. They shorten the T1, T2, and T2 * relaxation time constants of adjacent water protons in tissues. Furthermore, the chemical structure of the chelate also influences the number of available sites for interaction between water molecules and Gd 3+, which conditions the paramagnetic efficacy of the contrast agents. These relaxation effects tend to produce signal enhancement on T1-weighted MR images and signal loss on T2- and T2 * -weighted MR images. One exception is short inversion time inversion recovery (STIR) sequences with gadolinium accumulation leading to signal loss as a result of T1 shortening. Most applications of contrast-enhanced MRI and MRA rely on shortening of T1 and images are acquired after a bolus injection of Gd with short repetition times (TRs) and short echo times (TEs). Gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA) is an octodentate chelate of the paramagnetic ion gadolinium, with a distribution phase followed by an elimination phase. In addition it produces transient, weak protein binding. It is distributed not Fig. 1. Examples of the structures of the organic ligands of gadolinium chelates approved for clinical use.
5 164 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) Fig. 1. (Continued ).
6 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) only to the extracellular space, but is also selectively taken up by functioning hepatocytes and excreted into bile by canalicular multispecific organic anion transporter shared with bilirubin. The biliary excretion rate is only 3 5% in humans, but is sufficient to bring about specific, long lasting enhancement of the normal liver parenchyma. Gd-EOB-DTPA is a paramagnetic hepatobiliary contrast agent with a non-specific extracellular phase followed by a hepatocellular uptake via the anionictransporter protein. It is excreted almost equally by the kidneys and biliary system, while about 2% enters the enterohepatic circulation. It has a higher T1 relaxivity in human plasma than gadopentetate dimeglumine. With these two hepatobiliary agents, post contrast imaging includes rapid dynamic T1-weighted images followed by T1- weighted delayed images. 8. Pharmacokinetics 8.1. Biodistribution Nonspecific extracellular gadolinium chelates (gadopentetate, gadoterate, gadodiamide, gadoteridol, gadobutrol) have pharmacokinetics similar to those of iodinated radiographic contrast agents and are excreted almost exclusively by passive glomerular filtration through the kidneys, without secretion nor reabsorption (elimination is complete in h). For gadofosveset 84% of the injected dose is eliminated after 14 days. They are hydrophilic complexes that do not bind to proteins or receptors and are excreted unmetabolized in urine. Gadolinium chelates have low molecular masses (around 500 Da). Because of their small size, they are rapidly cleared from the intravascular space into the interstitial space, and therefore their biodistribution is non-specific. In patients with normal renal function about 98% of these agents are excreted within 24 h of injection. Biobistribution of four commercially available Gd-CA has been studied in mice and rats using a radiolabeling technique [23]. The macrocyclic chelates, gadoterate and gadoteridol, had the lowest residual Gd in rodents. The lowest-to-highest order of residual whole body gadolinium at 14 days was: gadoteridol gadoterate = gadopentetate gadodiamide [23]. Gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd-BOPTA), gadoxetic acid disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA), and gadofosveset (Gd-DTPA) are eliminated through both the renal and hepatobiliary pathways [19,24 27]. Hepatic uptake represents 2 4% of the injected dose of gadobenate (kidney pathway: 96 98%), 50% of the injected dose of gadoxetic acid disodium (kidney pathway: 50%), and 9% of the injected dose for gadofosveset (kidney pathway: 91%). 9. Acute renal adverse reactions (contrast induced nephropathy) The guidelines of the Safety Committee of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology indicate that, for MR examinations, the risk of nephrotoxicity is very low when Gd-CA are used in approved doses [28]. They also indicate that Gd-CA should not be used for radiographic examinations in patients with renal impairment and that for radiographic examinations, Gd-CA are more nephrotoxic than iodinated contrast in equivalent X-ray attenuating doses. Nephrotoxicity of the Gd-CA has now been documented in both man and animals. The use of high doses (>0.3 mmol/kg bw) of Gd-CA in patients with impaired renal function is clearly contraindicated. In 2003, Sam et al. [29] reported that in 3.5% of 195 patients with abnormal creatinine clearance levels, acute renal failure developed after Gd-CA. For MR angiography the incidence was 1.9% and for digital subtraction angiography 9.5%. Dialysis was required in three of the seven patients who developed acute renal failure. The doses of gadolinium-dtpa ranged from 0.31 to 0.41 mmol/kg for MR angiography and from 0.27 to 0.42 mmol/kg for digital subtraction angiography. In an experimental study investigating whether Gd-CA were less nephrotoxic than iodine media in X-ray arteriography of a kidney made temporarily ischemic by arterial balloon occlusion, Elmståhl et al. [6] found in 2004 that 0.5 M Gd-CA were more nephrotoxic than both equal-attenuating (70 mg I/mL) and equimolar (190 mg I/mL) concentrations of the iodine media. Using the same ischemic porcine model, they found in 2007 that the histomorphological changes caused by Gd-CA were similar to those caused by iodine media [5]. Vacuolation appeared to be independent of the osmolality and viscosity of the contrast medium, and did not seem to be an indicator of renal impairment. In a retrospective study that included 473 patients with stage 3 and 4 renal failure who received 0.2 ml/kg of gadolinium contrast medium, Ergun et al. [8] found that risk factors for acute renal failure after Gd-CA included diabetic nephropathy and low GFR. In addition, Briguori et al. [3] showed in prospective study that the strategy of Gd-CA administration does not seem to reduce the rate of contrast induced nephropathy, as compared to the iodinated iso-osmolality contrast agents in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. 10. Delayed adverse reactions This rare and devastating reaction (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis) is described in details in the following chapters. 11. Acute non-renal adverse reactions General adverse events may be seen following injection of Gd-CA with a frequency much lower than that observed with iodinated contrast media. The most frequently reported adverse events include transient headache, nausea, and emesis [11]. Other adverse events have been observed, but at frequencies of less than 1%. The incidence of moderate and severe reactions is well below 1% [30,31]. A post marketing surveillance study [32] of 24,308 patients who were intravenously injected with gadolinium DOTA for various diagnostic examinations reported that the incidence of adverse events was 0.4%; most of them were rated as minor, such as feeling of warmth or taste alteration. Anaphylactoid reactions, involving respiratory, cardiovascular, cutaneous, gastrointestinal and/or genitourinary manifestations have been reported but are anecdotal. Their true prevalence appears to be between 1/100,000 and 1/500,000 [11]. Most patients who experienced anaphylactoid reactions had a past history of respiratory difficulties or respiratory allergic dis-
7 166 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) ease. In 1991, Neindorf et al. [30] reported that the risk of adverse reactions to gadopentetate dimeglumine was 3.7 times higher in patients with a prior history of reaction to iodinated contrast media. Regarding the safety of higher unapproved dosages, the number of published studies is too small to draw any conclusions. One of the reasons for the lower prevalence of adverse reactions after Gd-CA than iodine-based contrast agents is the much lower dose of the agent used for MRI than for radiography, i.e., the molar dose for enhanced MRI of the brain is on average 8 times lower than the molar dose for CT of the brain 12. Pregnancy and lactating women A teratogenic effect of gadolinium chelates has been documented in animal studies, but no controlled studies have been performed. In rabbits, gadolinium can be detected in the fetus the 60 min after it has been given intravenously to the mother [33]. There are relatively few clinical reports of the effects on neonates of giving gadolinium agents to the pregnant mother. Due to the lack of knowledge it is recommended that Gd- CA should be avoided in the first trimester and used later in pregnancy only when needed to establish a critical diagnosis that will significantly impact patient care [34]. In those cases a stable macrocyclic agent is recommended [13] in order to leave the smallest amount (if any) of the gadolinium ion in the fetus. Denying a clinically justified examination may cause more harm to the mother and hereby the fetus than the examination itself. Only small amounts of gadolinium contrast media reach the milk after intravenous administration of a purely extracellular Gd-CA to the mother, less than 0.04% of the intravenous dose was excreted into the milk over 24 h according to Kubik- Huch et al. [35]. The amount transferred to a nursing infant would be more than 100 times less than the permitted IV dose (200 mol/kg) for neonates. Furthermore only a very small portion of the ingested agent is taken up from the gut. The Contrast Media Safety Committee of the European Society of Urogenital Radiology indicates that breast feeding may be continued normally when gadolinium agents are given to the mother [34]. Whether there is a higher transfer of the protein bound agents (the high relaxivity agents) than of the purely extracellular Gd-CA to milk remains unknown. Therefore a stability (macrocyclic) agent should be for a lactating mother. References [1] Lin SP, Brown JJ. MR contrast agents: physical and pharmacologic basics. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007;25: [2] Burns M. The US market for medical imaging contrast media. Las Vegas, NV: Bio-tech Systems, Inc.; [3] Briguori C, Colombo A, Airoldi F, Melzi G, et al. Gadolinium-based contrast agents and nephrotoxicity in patients undergoing coronary artery procedures. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2006;67: [4] Grobner T, Prischl FC. Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Kidney Int 2007;72: [5] Elmståhl B, Leander P, Grant D, et al. Histomorphological changes after renal X-ray arteriography using iodine and gadolinium contrast media in an ischemic porcine model. Acta Radiol 2007;23:1 11. [6] Elmståhl B, Nyman U, Leander P, Chai CM, Frennby B, Almen T. Gadolinium contrast media are more nephrotoxic than a low osmolar iodine medium employing doses with equal X-ray attenuation in renal arteriography: an experimental study in pigs. Acad Radiol 2004;11: [7] Elmståhl B, Nyman U, Leander P, et al. Gadolinium contrast media are more nephrotoxic than iodine media. The importance of osmolality in direct renal artery injections. Eur Radiol 2006;16: [8] Ergun I, Keven K, Uruç I, et al. The safety of gadolinium in patients with stage 3 and 4 renal failure. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21: [9] Mendichovszky IA, Marks SD, Simcock CM, Olsen OE. Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: time to tighten practice. Pediatr Radiol 2007;(October (18)) [Epub ahead of print]. [10] Thomsen HS, Marckmann P, Logager VB. Enhanced computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging: a choice between contrast medium-induced nephropathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Acta Radiol 2007: [11] Shellock FG, Kanal E. Safety of magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents. J Magn Reson Imaging 1999;10: [12] Thomsen HS, Marckmann P, Logager V. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF): a late adverse reaction to some of the gadolinium based contrast agents. Cancer Imaging 2007;7: [13] Thomsen HS. ESUR guideline: gadolinium-based contrast media and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Eur Radiol 2007;17: [14] Idee JM, Port M, Raynal I, Schaefer M, Le Greneur S, Corot C. Clinical and biological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 2006;20: [15] Evans CH. Biochemistry of the lanthanides. New York: Plenum Press; [16] Gandhi SN, Brown MA, Wong JG, Aguirre DA, Sirlin CB. MR contrast agents for liver imaging: what, when, how. RadioGraphics 2006;26: [17] Bellin MF. MR contrast agents: the old and the new. Eur J Radiol 2006: [18] Bellin MF, et al. Safety of MR liver specific contrast media. Eur Radiol 2005;15: [19] Rapp JH, Wolff SD, Quinn SF, et al. Aortoiliac occlusive disease in patients with known or suspected peripheral vascular disease: safety and efficacy of gadofovsveset-enhanced MR angiography Multicenter comparative phase III study. Radiology 2005;236:71 8. [20] Tweedle MF. The prohance story: the making of a novel MRI contrast agent. Eur Radiol 1997;7(suppl 5):S [21] Olukotun AY, Parker JR, Meeks MJ, Lucas MA, Fowler DR, Lucas TR. Safety of gadoteridol injection: US clinical trial experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 1995;5: [22] Cohan RH, Leder RA, Herzberg AJ, et al. Extravascular toxicity of two magnetic resonance contrast agents: preliminary experience in the rat. Invest Radiol 1991;26: [23] Tweedle MF, Wedeking P, Krishan K. Biodistribution of radiolabeled, formulated gadopentetate, gadoteridol, gadoterate, and gadodiamide in mice and rats. Invest Radiol 1995;30: [24] Kirchin MA, Pirovano GP, Spinazzi A. Gadobenate dimeglumine (Gd- BOPTA): an overview. Invest Radiol 1998;33: [25] Spinazzi A, Lorusso V, Pirovano G, Kirchin M. Safety, tolerance, biodistribution and MR imaging enhancement of the liver with Gd-BOPTA: results of clinical pharmacologic and pilot imaging studies in non-patient and patient volunteers. Acad Radiol 1999;6: [26] Hamm B, Staks T, Mühler A, et al. Phase I clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB- DTPA as a hepatobiliary MR contrast agent: safety, pharmacokinetics, and MR imaging. Radiology 1995;195: [27] Reimer P, Rummeny EJ, Shamsi K, et al. Phase II clinical evaluation of Gd-EOB-DTPA: dose, safety aspects, and pulse sequence. Radiology 1996;199: [28] Thomsen HS. How to avoid CIN: guidelines from the European Society of Urogenital Radiology. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2005;20(Suppl 1):i [29] Sam II AD, Morasch MD, Collins J, Song G, Chen R, Pereles FS. Safety of gadolinium contrast angiography in patients with chronic renal insufficiency. J Vasc Surg 2003;38:313 8.
8 M.-F. Bellin, A.J. Van Der Molen / European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) [30] Niendorf HP, Haustein J, Cornelius I, Alhassan A, Clauss W. Safety of gadolinium-dtpa: extended clinical experience. Magn Reson Med 1991;22: [31] Thomsen HS. Frequency of acute adverse events to a non-ionic lowosmolar contrast medium: the effect of verbal interview. Pharmacol Toxicol 1997;80: [32] Herborn CU, Honold E, Wolf M, et al. Clinical safety and diagnostic value of the gadolinium chelate gadoterate meglumine (Gd-DOTA). Invest Radiol 2007;42: [33] Novak Z, Thurmond AS, Ross PL, Jones MK, Thornburg KL, Katzberg RW. Gadolinium-DTPA transplacental transfer and distribution in fetal tissue in rabbits. Invest Radiol 1993;28: [34] Webb JA, Thomsen HS, Morcos SK. The use of iodinated and gadolinium contrast media during pregnancy and lactation. Eur Radiol 2005;15: [35] Kubik-Huch RA, Gottstein-Aalame NM, Frenzel T, et al. Gadopentetate dimeglumine excretion into human breast milk during lactation. Radiology 2000;216:555 8.
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
 Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects
 Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018)
 Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates
 Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline
 Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
INTRODUCTION CLINICAL EXPERIENCE CLINICAL EFFICACY PEDIATRIC EXPERIENCE DOSING SUMMARY
 1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies
 Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7
 PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents
 Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research
 University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist and Magnevist below.
 August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist, Eovist and Magnevist on the following pages.
 Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice?
 Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
NSF Coming and Going
 NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Figure 1 Figure 1: Energy diagram illustrates formation of a chelate (ML) created by combining two chemicals free Gd 3 (M), which is a metal ion, and
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, use the Radiology Reprints form at the end of this article.
Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions
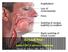 Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document. Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013
 FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the product information
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern
 Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM. (gadoterate meglumine) Injection. For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
Annex II. Scientific conclusions
 Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Public Assessment Report
 Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide. flow rate of approximately 2 ml/second for adults and 1-2 ml/second for pediatric
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR
 William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 2013
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
Safety of Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) as a Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST. gadoxetate disodium injection mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml)
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media
 HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Frequency and Severity of Acute Allergic-Like Reactions to Gadolinium-Containing IV Contrast Media in Children and Adults
 Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
CONTRAINDICATIONS History of severe hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Scientific Paper. Authors: E. De Kerviler 1, S. Gaillard 2 ; 1 Paris/FR, 2 Villepinte/FR
 Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
Pharmacovigilance based on spontaneous adverse event reporting of meglumine gadoterate (Gd-DOTA) after 15 million administrations and 20 years of clinical use Poster No.: B-229 Congress: ECR 2011 Type:
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION. 1.1 Central Nervous System. 1.2 Extracranial/Extraspinal Tissues. 1.3 Body
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
Imaging in the time of NFD/NSF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency?
 DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance
 Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are significantly
 Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Bayer Inc. Date
Incidence of Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions
 Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET. DOTAREM mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid)
 PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
PATIENT INFORMATION LEAFLET DOTAREM 279.32 mg/ml, solution for injection (Gadoteric acid) Read all this leaflet carefully before you start using this medicine because it contains important information
flow rate of approximately 2 ml/second for adults and 1-2 ml/second for pediatric patients. The dose is delivered by manual or power injection.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
PRIMOVIST 5 ml, 7,5 ml, 10 ml
 REGISTERED PACKAGE INSERT SCHEDULING STATUS S4 PROPRIETARY NAMES AND DOSAGE FORMS PRIMOVIST 5 ml, 7,5 ml, 10 ml Solution for injection COMPOSITION 1 ml of the MRI contract agent Primovist contains 181,43
REGISTERED PACKAGE INSERT SCHEDULING STATUS S4 PROPRIETARY NAMES AND DOSAGE FORMS PRIMOVIST 5 ml, 7,5 ml, 10 ml Solution for injection COMPOSITION 1 ml of the MRI contract agent Primovist contains 181,43
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
 Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Report on the Investigation Results
 This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
Reference ID:
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
CONTRAINDICATIONS Clinically important hypersensitivity reactions to DOTAREM. (4)
 M120177AB HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
M120177AB HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DOTAREM. DOTAREM (gadoterate
Gadolinium Retention in the Dentate Nucleus and Globus Pallidus Is Dependent on the Class of Contrast Agent 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Alexander Radbruch,
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (marketed as Magnevist, MultiHance, Omniscan, OptiMARK, ProHance)
 Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM. Gadoterate meglumine injection. (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH INCLUDING PATIENT MEDICATION INFORMATION DOTAREM Gadoterate meglumine injection (376.9 mg/ml, equivalent to 0.5 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance
T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents in Human Whole Blood at 1.5, 3, and 7 T
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2015 T1 Relaxivities of Gadolinium-Based Magnetic Resonance Contrast Agents
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0. gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH GADOVIST 1.0 gadobutrol injection 604 mg/ml (1.0 mmol/ml) For Intravenous Use Contrast Enhancement Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Bayer Inc. 77 Belfield Road Toronto, ON M9W
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS
 DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be used
 Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
ARTICLE IN PRESS European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx
 European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Tolerability and diagnostic value
European Journal of Radiology xxx (2011) xxx xxx Contents lists available at ScienceDirect European Journal of Radiology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ejrad Tolerability and diagnostic value
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, 2 july 2008
Clinical MRI of the Abdomen
 Clinical MRI of the Abdomen Why,How,When Bearbeitet von Nicholas C. Gourtsoyiannis 1. Auflage 2011. Buch. xi, 750 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 85688 7 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 26 cm Gewicht: 2103 g Weitere
Clinical MRI of the Abdomen Why,How,When Bearbeitet von Nicholas C. Gourtsoyiannis 1. Auflage 2011. Buch. xi, 750 S. Hardcover ISBN 978 3 540 85688 7 Format (B x L): 19,3 x 26 cm Gewicht: 2103 g Weitere
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml (for multiple use) solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml (for multiple use) solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for injection contains
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT DOTAREM 0.5 mmol/ml solution for injection in vials 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION 1 ml solution for injection contains
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents SCBT/MR Annual Meeting Salt Lake City September 21, 2016 Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD Department of Radiology University of Wisconsin Madison, WI Disclosures University of Wisconsin-Madison
Renal Tolerance of a Neutral Gadolinium Chelate (gadobutrol) in Patients with Chronic Renal Failure: Results of a Randomized Study 1
 Contrast Media Bernd Tombach, MD Christoph Bremer, MD Peter Reimer, MD Klaus Kisters, MD Roland M. Schaefer, MD Viviane Geens, MD Walter Heindel, MD Index terms: Gadolinium Kidney, failure, 81.699 Kidney,
Contrast Media Bernd Tombach, MD Christoph Bremer, MD Peter Reimer, MD Klaus Kisters, MD Roland M. Schaefer, MD Viviane Geens, MD Walter Heindel, MD Index terms: Gadolinium Kidney, failure, 81.699 Kidney,
Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges
 REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work?
 Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
Contrast Materials Patient Safety: What are contrast materials and how do they work? Which imaging exams use contrast materials? How safe are contrast materials? How should I prepare for my imaging procedure
IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI
 11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
11-12 Maggio 2018 Rimini IL PROBLEMA DEL GADOLINIO OGGI Il punto di vista del Neuroradiologo pediatrico Dott.ssa Camilla Rossi Espagnet U.O. Neuroradiologia, Dipartimento Immagini, Ospedale Pediatrico
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC
 DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively.
DOTAREMÂ - gadoterate meglumineâ injectionâ Guerbet LLC ---------- HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DOTAREM safely and effectively.
Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA)
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinical Safety and Diagnostic Value of the Gadolinium Chelate Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) Christoph U. Herborn, MD,* Elmar Honold, MD, Michael Wolf, Jörn Kemper, MD, Sonja Kinner,
Gadolinium in Humans: A Family of Disorders
 Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA.
 ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI
 Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Special Articles Original Research
 Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient
 Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient About DOTAREM: DOTAREM is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain
Radiology Reimbursement Information Setting: Hospital Outpatient About DOTAREM: DOTAREM is a gadolinium-based contrast agent indicated for intravenous use with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in brain
CONTRAINDICATIONS History of severe hypersensitivity reaction to EOVIST (4)
 HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
HIGHLIGHTS F PRESCRIBING INFRMATIN These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EVIST Injection. EVIST (gadoxetate
Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
 Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Instructions for the safe administration of gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCA). 1. PREADMINISTRATION PRECAUTIONS:
 POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
Each ml contains 0.25 mmol gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA disodium), equivalent to mg gadoxetate disodium.
 1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Primovist 0.25 mmol/ml, solution for injection, pre-filled syringe 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml contains 0.25 mmol gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT Primovist 0.25 mmol/ml, solution for injection, pre-filled syringe 2. QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITATIVE COMPOSITION Each ml contains 0.25 mmol gadoxetate disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA
Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing theory
 Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
Thomas Jefferson University Jefferson Digital Commons Scleroderma Center Faculty Papers Scleroderma Center of Thomas Jefferson University 11-2009 Mechanism of NSF: New evidence challenging the prevailing
PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM
 PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM NAME OF THE MEDICINE DOTAREM (gadoteric acid) paramagnetic contrast medium for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The structural formula of gadoteric acid is shown below: The
PRODUCT INFORMATION DOTAREM NAME OF THE MEDICINE DOTAREM (gadoteric acid) paramagnetic contrast medium for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). The structural formula of gadoteric acid is shown below: The
Update. Drug Safety. Welcome to the first issue of the newly launched Drug Safety Update. This
 Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
Latest advice for medicines users The monthly newsletter from the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency and its independent advisor the Commission on Human Medicines Volume 1, Issue 1 August
PRODUCT INFORMATION NAME OF THE MEDICINE DESCRIPTION. GADOVIST 1.0 (gadobutrol) Physico-chemical properties
 PRODUCT INFORMATION GADOVIST 1.0 (gadobutrol) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Gadovist 1.0 injection is a 1.0 mmol/ml solution of 10-(2,3-Dihydroxy-1- hydroxymethylpropyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triacetic
PRODUCT INFORMATION GADOVIST 1.0 (gadobutrol) NAME OF THE MEDICINE Gadovist 1.0 injection is a 1.0 mmol/ml solution of 10-(2,3-Dihydroxy-1- hydroxymethylpropyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7-triacetic
Reference ID: MultiHance Injection, NDA , SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov _CLEAN.
 MultiHance Injection, NDA 21-357, SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov-18-2010_CLEAN.doc HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
MultiHance Injection, NDA 21-357, SAFETY LABELING CHANGES UNDER 505(o)(4) MultiHance PI to FDA_Revised Nov-18-2010_CLEAN.doc HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended.
 Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Omniscan UK/W/063/pdWS/001 Rapporteur UK Finalisation procedure (day 20)
Public Assessment Report for paediatric studies submitted in accordance with Article 45 of Regulation (EC) No1901/2006, as amended Omniscan UK/W/063/pdWS/001 Rapporteur UK Finalisation procedure (day 20)
Contrast controversies and confusion
 Contrast controversies and confusion Mariya Kobi 1 ; Meir H Scheinfeld 1 ; Seymour Sprayregen 1 ; R Joshua Dym 2 * 1 Department of Radiology, Montefiore Medical Center, USA 2 Department of Radiology, Rutgers
Contrast controversies and confusion Mariya Kobi 1 ; Meir H Scheinfeld 1 ; Seymour Sprayregen 1 ; R Joshua Dym 2 * 1 Department of Radiology, Montefiore Medical Center, USA 2 Department of Radiology, Rutgers
Clinical guidelines to reduce the risk of contrast induced nephropathy
 Nephrology Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Consultation: Clinical guidelines to reduce the risk of contrast induced nephropathy To implement all possible measures to reduce the risk of nephropathy from
Nephrology Subject: Objective: Prepared by: Consultation: Clinical guidelines to reduce the risk of contrast induced nephropathy To implement all possible measures to reduce the risk of nephropathy from
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use MAGNEVIST safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for MAGNEVIST. MAGNEVIST (gadopentetate
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
ASCI CCT & CMR Guideline Working Group Masahiro Jinzaki Kakuya Kitagawa I-Chen Tsai Carmen Chan Wei Yu Hwan Seok Yong Byoung Wook Choi
 Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2010) 26:203 212 DOI 10.1007/s10554-010-9691-3 ORIGINAL PAPER ASCI 2010 contrast media guideline for cardiac imaging: a report of the Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging cardiac
Int J Cardiovasc Imaging (2010) 26:203 212 DOI 10.1007/s10554-010-9691-3 ORIGINAL PAPER ASCI 2010 contrast media guideline for cardiac imaging: a report of the Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging cardiac
Quantifying differences in hepatic uptake of the liver specific contrast agents Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-BOPTA: a pilot study
 Quantifying differences in hepatic uptake of the liver specific contrast agents Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-BOPTA: a pilot study Olof Dahlqvist Leinhard, Nils Dahlström, Johan Kihlberg, Per Sandström, Torkel Brismar,
Quantifying differences in hepatic uptake of the liver specific contrast agents Gd-EOB-DTPA and Gd-BOPTA: a pilot study Olof Dahlqvist Leinhard, Nils Dahlström, Johan Kihlberg, Per Sandström, Torkel Brismar,
Summary. Correspondence Jerrold L. Abraham. Accepted for publication 17 September 2007
 CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
CLINICAL AND LABORATORY INVESTIGATIONS DOI 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2007.08335.x Dermal inorganic gadolinium concentrations: evidence for in vivo transmetallation and long-term persistence in nephrogenic systemic
Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece
 Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece Hepatospecificcontrast agents Gadobenate dimeglumine (Multihance) Gadoxeticacid (Primovist) 3-5% liver uptake 50% liver uptake Hepatobiliary
Evangelos Chartampilas Bioclinic Hospital Thessaloniki, Greece Hepatospecificcontrast agents Gadobenate dimeglumine (Multihance) Gadoxeticacid (Primovist) 3-5% liver uptake 50% liver uptake Hepatobiliary
PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN
 AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
AZEARLY Tablets Each Tablet Contains Azilsartan 20/40/80 mg PHARMACEUTICAL INFORMATION AZILSARTAN Generic name: Azilsartan Chemical name: 2-Ethoxy-1-{[2'-(5-oxo-2,5-dihydro-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4-biphenylyl]methyl}-
FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.
![FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA. FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.](/thumbs/77/75534485.jpg) Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
