This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
|
|
|
- Shavonne Wood
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact No Incidence of Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis after Gadobenate Dimeglumine Administration in Patients Undergoing Dialysis or Those with Severe Chronic Kidney Disease 1 Original Research n Contrast Media Diego R. Martin, MD, PhD Bobby Kalb, MD Ankush Mittal, BS Khalil Salman, MD Srinivasan Vedantham, PhD Pardeep K. Mittal, MD 1 From the Department of Medical Imaging, University of Arizona College of Medicine, Banner University Medical Center, 1501 N Campbell Ave, PO Box Tucson, AZ (D.R.M., B.K., K.S., S.V.); and Department of Radiology and Imaging Sciences, Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta, Ga (A.M., P.K.M.). Received January 14, 2017; revision requested March 13; revision received April 16; final version accepted May 11. Address correspondence to D.R.M. ( dmartin@radiology.arizona.edu). q RSNA, 2017 Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion: To determine the incidence of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) in patients with severe chronic kidney disease (CKD) who underwent a uniform protocol for contrast material enhanced magnetic resonance (MR) imaging with a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). This retrospective, single-center, institutional review board approved, HIPAA-compliant study included 3819 patients with severe (stage 4 or 5) CKD who underwent gadobenate dimeglumine enhanced MR imaging as part of a preoperative evaluation for potential renal transplantation from January 2008 to February After undergoing, patients were assessed for NSF by means of clinical follow-up, including a full integumentary examination, with a minimum of 6 months between administration of the GBCA and clinical skin examination. Suspicious skin lesions were sampled with deep punch biopsy, and results of pathologic examination were reviewed and categorized. In addition, a search of the institution s pathology database during the time of the study was performed to identify any additional patients with NSF. The proportion of subjects who developed NSF after the administration of gadobenate dimeglumine was calculated, and Clopper-Pearson 95% confidence intervals were determined by using binomial proportions. The average length of follow-up for the patient population was 501 days (range, days). A total of 219 biopsies were performed, and none of the 3819 patients developed NSF after administration of gadobenate dimeglumine, resulting in a proportion of zero; the exact upper bound of 95% confidence interval was (0.0965%). None of the 3819 patients with severe CKD developed NSF after undergoing gadobenate dimeglumine enhanced MR imaging, which suggests that this GBCA may be safely administered in patients with severe CKD, with an immeasurable risk for the subsequent development of NSF. q RSNA, 2017 Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018 n radiology.rsna.org 113
2 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF) is a fibrosing disease of the skin and other soft tissues that is found in patients with advanced kidney disease. The histopathologic findings of NSF were first described in 2001 by Cowper et al (1), with historical first incidence noted to have occurred in In 2006, Grobner et al (2) and Thomsen et al (3) noted the correlation between NSF and previous magnetic resonance (MR) examination with a gadolinium-based contrast agent (GBCA). The first GBCA was introduced in 1987, 10 years before NSF was first diagnosed. It is presumed that the increasing use of contrast material enhanced MR imaging, particularly for MR angiography, led to sufficient overall population exposure in at-risk patients and, consequently, to the clinical appearance of NSF (4). A global NSF registry (5) has collected information regarding a total of 387 affected patients, with the incidence of NSF largely restricted to years 2000 to Most cases of NSF have been linked to the use of one of three different GBCAs (6,7) and have also been associated with higher doses of these agents as compared with a single dose at a level recommended for (8,9). There is little evidence to show risk of NSF in patients with stage 3 or higher kidney function (10), with most patients with NSF found to have been dependent on dialysis at the time of GBCA exposure (11,12). No cure for NSF is yet known, and the role of hemodialysis after GBCA exposure remains unproven, although the procedure is recommended (9). Advance in Knowledge nn Among 3819 patients with severe (stage 4 or 5) chronic kidney disease (CKD) who underwent gadobenate dimeglumine enhanced MR imaging, none developed nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF), resulting in a proportion of zero; the exact upper bound of 95% confidence interval was %. In 2006, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) announced an indiscriminate warning against the use of GBCAs in patients with kidney disease. In 2010, the FDA updated the warning to differentiate three of the agents found to be associated with NSF, stating that these GBCAs should never be used in patients with advanced acute or chronic kidney disease (CKD). The FDA further recommended that all other agents be used with caution in patients with kidney disease but did not give specific instruction on methodology (13). It has been presumed that the three agents most associated with NSF are chemically less stable than other ionic linear or macrocyclic agents with higher chemical chelate stability, leaving the gadolinium species more available for transmetallation (14). The common elimination pathway for GBCAs is through glomerular filtration. The role of alternative pathway elimination liver uptake and bile excretion noted with two of the linear agents (15) may also be protective. The American College of Radiology, in parallel with the FDA, has developed a risk stratification system for the different GBCAs (16), classifying the three agents most associated with NSF as group I. Other agents stratified as lower risk are classified as group II (linear agent, not associated with NSF, or macrocyclic agent). GB- CAs with limited data regarding NSF or that have only recently appeared on the market are classified as group III. Previous reports have shown an NSF incidence of 3% 5% in patients who are undergoing hemodialysis or Implications for Patient Care nn The risk of NSF to patients with severe CKD after the administration of gadobenate dimeglumine is immeasurably low. nn Commonly used methods of screening patients for contrastenhanced MR imaging (eg, estimated glomerular filtration rate) may be of low value when gadobenate dimeglumine is administered. peritoneal dialysis (patients who undergo dialysis have the highest risk for NSF) and have been exposed to a group I GBCA (9,17), although these reports do not address patients with a requirement for next dialysis within 24 hours. The current observed decrease in NSF incidence (18) presumably results from changed practices influenced by warnings and guidelines, including those issued by the FDA and the American College of Radiology. It was shown in a study of data from the Veterans Affairs Health Care System that practice patterns have changed and that has been avoided in patients suspected of having kidney disease (19). In a subset of university medical center practices, in which NSF had been reported previously, there has been subsequent published evidence of diminished incidence of NSF despite continued use of certain GBCAs for in at-risk patients (20 23). The absence of NSF in these patients has been attributed to changing the type of GBCA (from a grade I to a higherstability grade II or III agent). The outcomes of these two very different strategies avoidance versus continued use Content code: Radiology 2018; 286: Abbreviations: CKD = chronic kidney disease egfr = estimated glomerular filtration rate FDA = Food and Drug Administration GBCA = gadolinium-based contrast agent NSF = nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Author contributions: Guarantors of integrity of entire study, D.R.M., B.K., P.K.M.; study concepts/study design or data acquisition or data analysis/interpretation, all authors; manuscript drafting or manuscript revision for important intellectual content, all authors; manuscript final version approval, all authors; agrees to ensure any questions related to the work are appropriately resolved, all authors; literature research, D.R.M., B.K., K.S., P.K.M.; clinical studies, D.R.M., B.K., A.M., K.S., P.K.M.; statistical analysis, D.R.M., B.K., K.S., S.V.; and manuscript editing, D.R.M., B.K., K.S., S.V., P.K.M. Conflicts of interest are listed at the end of this article. See also the editorial by Prince and Weinreb in this issue. 114 radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018
3 of, but with a higher-stability GBCA remains unexplored but has potential significance: Avoidance of contrast-enhanced MR imaging may have unintended adverse outcomes through altered diagnostic results (24). Uncertainty regarding quantifiable risk of group II or III GBCA exposure in patients who undergo dialysis or those with severe CKD who are at high risk for NSF continues to influence practice patterns. Better measures of this risk may have an effect on future decisionsupport guidelines and practices. We have created a large single-center database for the evaluation of NSF risk in patients undergoing dialysis or those with severe CKD but who are not on dialysis, who have been exposed to a uniform institutional GBCA protocol for studies used for assessment of patients before they undergo renal transplant. The purpose of our study was to retrospectively determine the incidence of NSF in patients with severe CKD who underwent a uniform protocol for contrastenhanced MR imaging with the administration of gadobenate dimeglumine. Materials and Methods Patient Selection This single-center, retrospective study was approved by our institutional review board and compliant with the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. The study included electronic patient records filed between April 2008 and February We selected only patients with severe CKD who were at high risk for NSF and who were undergoing either peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis or those with stage 4 or 5 CKD but who were not undergoing dialysis by searching our electronic medical records (version ; Cerner, North Kansas City, Mo) and the institutional solid organ transplant patient care management software (version ; OTTR Chronic Care Solutions, Omaha, Neb) for all patients with severe CKD referred for transplant evaluation. A concurrent search of the electronic radiology information system was performed for all patients who had undergone during the study time window, and the results were cross-referenced with the list of patients referred for kidney transplant evaluation. This method produced a cohort of patients with severe CKD who had undergone at least one institutional protocol related contrast-enhanced MR examination. This cohort represented a continuation of our earlier report (12), in which patients from an earlier time window were selected (in the previous report, the last date of contrast material administration was March 2008). Other search criteria and selection filters were as follows: The electronic medical record of each patient was reviewed, with demographic and clinical data recorded for each patient, including age, sex, and estimated glomerular filtration rate (egfr) (for patients not undergoing dialysis) within 30 days of MR imaging based on both the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula and the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation (25). We did not specifically search for and categorize risk factors for NSF other than the presence of CKD. We documented the type of dialysis at the time of (classified as peritoneal dialysis, hemodialysis, or none). The date of the latest post MR imaging full integumentary examination was recorded, and only patients who underwent full integumentary examination at least 6 months after were included. The number of patients who did not undergo follow-up and documentation with our transplant service, including an integumentary follow-up examination, is unknown. GBCA Administration Per institutional protocol, patients referred for renal transplant evaluation underwent for pretransplant assessment of any potential underlying neoplasm and vascular disease. A single GBCA agent, gadobenate dimeglumine (Multihance; Bracco Diagnostics, Princeton, NJ), was administered according to weight, with a standard dose of 0.05 mmol/kg for MR imaging and 0.1 mmol/kg for MR angiography, followed by a 20-mL saline flush. The dose of gadobenate dimeglumine used for each patient was recorded in the electronic record. In addition, the number of contrast-enhanced MR examinations performed for each patient was recorded, and individual and cumulative doses were calculated. Our institutional protocol requires that, in patients undergoing hemodialysis scheduled for contrastenhanced MR imaging, the next dialysis session must be performed within 24 hours; patients did not undergo hemodialysis and contrast-enhanced MR imaging if they were not already undergoing hemodialysis before contrastenhanced MR imaging. Follow-up To identify patients who developed NSF after the administration of GBCA, the latest date and type of clinical follow-up that included a full integumentary examination were identified. Full integumentary examinations are protocol for our renal transplant patient evaluations and were documented for all patients included in this study cohort. Skin lesions that were suspicious on the basis of physical examination assessment underwent deep punch or excision biopsy, and the dermatopathologic results were recorded and categorized. A minimum follow-up of 6 months after GBCA administration was set as the threshold for inclusion in the study to ensure adequate time for symptom development. The number of days between the last contrast-enhanced MR examination and the follow-up clinic note and integumentary examination was calculated and recorded. In addition, a search was undertaken of pathologic information in the electronic medical records by using the search terms nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and NSF to find all histopathologic specimens of NSF in the pathologic information database. Any positive findings could then be crossreferenced with our patient cohort to Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018 n radiology.rsna.org 115
4 Study Cohort Characteristics Group Mean Age (y) No. of Patients Sex Race* M F Black White Asian Latino Average No. of Examinations Average Minimum Follow-up Interval (d) No. of Skin Biopsies Hemodialysis Peritoneal dialysis Combined dialysis No dialysis Total Note. The egfr was obtained in the patients who did not undergo dialysis. In those patients, the average egfr determined with the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease formula was 13.9 ml/ min/1.73 m 2, the average egfr determined with the Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equation was 9.2 ml/min/1.73 m 2, the average creatinine level was 4.6 mg/dl, and the average interval between egfr and MR imaging was 29 days. * Race was classified on the basis of available records for 3413 of the 3819 patients. aid in the identification of patients with a histologic diagnosis of NSF. Statistical Methods All analyses were performed by using software (version 9.3; SAS Institute, Cary, NC). A Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test was used to evaluate any difference in ages between male and female subjects in our study. The proportion of subjects who developed NSF after administration of GBCA and the exact (Clopper-Pearson) 95% confidence intervals were determined by using binomial proportions. Results Patients From January 2008 to February 2014, 3819 patients with severe CKD underwent per institutional pretransplant protocol and met inclusion and exclusion criteria. Our final study cohort consisted of 1587 female patients (average age, 50 years; age range, years) and 2232 male patients (average age, 51 years; age range, years); there was no significant difference in age between male and female patients (P =.185). Of the 3819 patients, 312 were also included at the end of a prior study (22), but now with longer follow-up. The detailed characteristics of our patient cohort are summarized in the Table. None of the 3819 patients developed NSF after the administration of gadobenate dimeglumine (resulting in a proportion of zero), and the exact upper bound of 95% confidence interval was %. GBCA Administration The average volume of gadobenate dimeglumine administered for each contrast-enhanced MR examination was 23 ml (range, 3 45 ml; dose of 0.05 mmol/kg for MR imaging and 0.1 mmol/kg for MR angiography). A fraction of our patient cohort underwent more than one contrast-enhanced MR examination during pretransplant work-up: 182 of the 3819 patients (5%) underwent two examinations, 16 (0.4%) underwent three examinations, and four (0.1%) underwent four examinations. Follow-up The average time between the initial MR examination and the most recent clinical examination was 501 days (range, days), with the follow-up intervals shown according to dialysis status in the Table. Biopsies were performed in a total of 219 patients at follow-up examination after MR imaging; Figure 1 summarizes dermatopathologic results, and Figure 2 summarizes the distribution of biopsies according to anatomic location. No patients were diagnosed with NSF at evaluation of biopsy specimens. Forty-six of the 219 biopsies (21%) revealed carcinomas, and the most common malignancy was squamous cell carcinoma (41 of 219 cases, 19%). The most common benign lesions were keratoid lesions (24 of 219 cases, 11%) and melanocytic nevi (23 of 219 cases, 10%). A search of the pathology database from January 2008 to February 2014 returned no pathologic specimens (biopsy or surgical excision) with a diagnosis of NSF. Discussion In our study, we found no patients with newly diagnosed NSF in a large population of patients who underwent with administration of a single GBCA (gadobenate dimeglumine). To our knowledge, our study represents the largest single-center study of patients with advanced kidney disease exposed to a uniform GBCA-enhanced MR imaging protocol and helps provide a foundation for individualized decisions weighing risk against benefit with regard to the use of in a patient with advanced CKD. Our study focused on patients at highest risk for NSF, including those with end-stage renal disease who are undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis or those with very low egfr (,30 ml/min/1.73 m 2 ) who were not yet undergoing dialysis. Moreover, in our study we required a clinical follow-up period of at least 6 months to ensure proper classification of patients with or patients without NSF. 116 radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018
5 Figure 1 Figure 1: Bar graph shows results of histologic examination of specimens from punch biopsy performed in patients with end-stage renal disease who had previously undergone. Numbers are numbers of cases. Our study results contribute to the body of evidence showing that the risk of NSF is related to the type of GBCA used and aligns with multiple previous reports suggesting that certain GBCAs may not be associated with the development of NSF even when administered to patients at the highest risk for development of NSF (stage 4 and stage 5 CKD) (10,21,26). Bruce et al (21) studied 1423 patients with an egfr of 30 ml/min/1.72 m 2 or lower who had undergone with gadobenate dimeglumine and also found that no patients developed NSF. Smorodinsky et al (27) evaluated 1167 patients with chronic liver disease who had been exposed to a variety of GBCAs, 843 of whom had some degree of renal insufficiency; none of these Figure 2 Figure 2: Bar graph shows location of biopsy relative to extremities, torso, or head and neck regions. Numbers are numbers of cases. Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018 n radiology.rsna.org 117
6 patients developed NSF. Our current findings represent an extension of previously reported relative risk from the same institution, as well as that reported by other centers (10,18,20,22,23). Together, these studies have collectively shown no new cases of NSF in thousands of patients with severe CKD who have undergone contrast-enhanced MR imaging with the administration of more stable group II gadolinium chelates (16). The American College of Radiology guidelines are based on the prediction that linear agents, as a subclass, are more likely to cause NSF. Whereas the three agents accounting for almost all reported patients with NSF are linear GBCAs, the linear agent used in this study (gadobenate dimeglumine) has no unconfounded reports associated with NSF. Reasons for this have yet to be fully determined. Gadobenate dimeglumine is reported to have a 3% clearance through the liver in patients with normal liver and kidney function, likely upregulated in patients with decreased kidney function (15,28). Although the liver clearance rate is relatively minor compared with the kidney pathway, it may represent a beneficial mechanism in patients with kidney disease who are at risk for NSF. Gadobenate dimeglumine is a higher-relaxivity GBCA, and some reports have shown effective diagnostic use at a lower dose (0.05 vs 0.1 mmol/kg) (29), which represents an additional potential factor in NSF risk management, through minimization of dose exposure. Similarly, gadoxetate disodium is another American College of Radiology group II linear GBCA that has a liver clearance of 50% in patients with normal liver and kidney function, a characteristic differentiating this agent from the group I linear agents associated with NSF, which do not have liver clearance; there are no published reports of NSF associated with gadoxetate disodium (30). It is interesting to note that our study does not provide additional insights into the role of dialysis in protecting patients from NSF. Institutional protocol requires that hemodialysis be performed within 24 hours of GBCA 10. Soulez G, Bloomgarden DC, Rofsky NM, et al. Prospective cohort study of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with stage 3 5 chronic kidney disease undergoadministration if the patient is already undergoing dialysis. However, it is estimated that at least three to five hemodialysis sessions are required to achieve a high level of contrast material elimination. Furthermore, peritoneal dialysis has been noted to effect limited contrast material clearance (31). In our cohort of patients with severe CKD, 10.6% (405 of 3819 patients) underwent only peritoneal dialysis and 30% (1149 of 3819 patients) did not undergo dialysis (either peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis). Those patients who did not undergo dialysis before MR imaging did not undergo hemodialysis after GBCA administration. As discussed previously, it may be that liver clearance plays a protective role for the agent used in our study or that other factors (yet to be determined) are responsible for the apparent differences in relative NSF risk between gadobenate dimeglumine and other linear agents with higher measured risk. Limitations of this study include a lack of information regarding GBCA tissue deposition, which we did not measure. The patients with kidney disease included in our study usually had multisystem disorders and required a contrast-enhanced study to obtain information that would affect clinical decisions (32). However, we did not directly assess the rationale for choosing over other methods, nor did we measure the relative clinical outcomes value of as compared with alternatives; these determinations were outside the scope of this study. In summary, our large single-center study demonstrates the safety of performing with gadobenate dimeglumine in patients with severe CKD, with no patients developing NSF at follow-up integumentary examinations. Our data show that the risk of NSF related to contrastenhanced MR imaging is sufficiently low to consider use of this diagnostic test when appropriately indicated, even in patients who are undergoing hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis or those with advanced CKD but who are not yet undergoing dialysis. Disclosures of Conflicts of Interest: D.R.M. Activities related to the present article: disclosed no relevant relationships. Activities not related to the present article: institution received an unrestricted training fund grant from Bracco Diagnostics. Other relationships: disclosed no relevant relationships. B.K. disclosed no relevant relationships. A.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. K.S. disclosed no relevant relationships. S.V. disclosed no relevant relationships. P.K.M. disclosed no relevant relationships. References 1. Cowper SE, Su LD, Bhawan J, Robin HS, LeBoit PE. Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy. Am J Dermatopathol 2001;23(5): Grobner T. Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Nephrol Dial Transplant 2006;21(4): Thomsen HS, Morcos SK, Dawson P. Is there a causal relation between the administration of gadolinium-based contrast media and the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)? Clin Radiol 2006;61(11): Gossner J. Is nephrogenic systemic fibrosis linked to the introduction of contrastenhanced MR angiography? Radiology 2009;251(2): ; author reply Girardi M, Kay J, Elston DM, Leboit PE, Abu-Alfa A, Cowper SE. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: clinicopathological definition and workup recommendations. J Am Acad Dermatol 2011;65(6): e7. 6. Thomsen HS, Marckmann P. Extracellular Gd-CA: differences in prevalence of NSF. Eur J Radiol 2008;66(2): Wertman R, Altun E, Martin DR, et al. Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: evaluation of gadolinium chelate contrast agents at four American universities. Radiology 2008;248(3): Khawaja AZ, Cassidy DB, Al Shakarchi J, McGrogan DG, Inston NG, Jones RG. Revisiting the risks of MRI with gadolinium based contrast agents: review of literature and guidelines. Insights Imaging 2015;6(5): Zou Z, Zhang HL, Roditi GH, Leiner T, Kucharczyk W, Prince MR. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: review of 370 biopsyconfirmed cases. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 2011;4(11): radiology.rsna.org n Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018
7 ing MRI with injected gadobenate dimeglumine or gadoteridol. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2015;205(3): Bahrami S, Raman SS, Sauk S, et al. Tenyear experience with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: case-control analysis of risk factors. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2009;33(6): Lauenstein TC, Salman K, Morreira R, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: center case review. J Magn Reson Imaging 2007;26(5): U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Drug safety communication: new warnings for using gadolinium-based contrast agents in patients with kidney dysfunction. Silver Spring, Md: U.S. Food and Drug Administration, Morcos SK. Extracellular gadolinium contrast agents: differences in stability. Eur J Radiol 2008;66(2): Kirchin MA, Lorusso V, Pirovano G. Compensatory biliary and urinary excretion of gadobenate ion after administration of gadobenate dimeglumine (MultiHance) in cases of impaired hepatic or renal function: a mechanism that may aid in the prevention of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis? Br J Radiol 2015;88(1048): American College of Radiology. Manual on contrast media v10.1. Reston, Va: American College of Radiology, Thomsen HS. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: a serious adverse reaction to gadolinium: Part 1. Acta Radiol 2016;57(5): Zhang B, Liang L, Chen W, Liang C, Zhang S. An updated study to determine association between gadolinium-based contrast agents and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. PLoS One 2015;10(6):e Kim KH, Fonda JR, Lawler EV, Gagnon D, Kaufman JS. Change in use of gadoliniumenhanced magnetic resonance studies in kidney disease patients after U.S. Food and Drug Administration warnings: a cross-sectional study of Veterans Affairs Health Care System data from Am J Kidney Dis 2010;56(3): Amet S, Launay-Vacher V, Clément O, et al. Incidence of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients undergoing dialysis after contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents: the Prospective Fibrose Nephrogénique Systémique study. Invest Radiol 2014;49(2): Bruce R, Wentland AL, Haemel AK, et al. Incidence of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis using gadobenate dimeglumine in 1423 patients with renal insufficiency compared with gadodiamide. Invest Radiol 2016;51(11): Martin DR, Krishnamoorthy SK, Kalb B, et al. Decreased incidence of NSF in patients on dialysis after changing gadolinium contrast-enhanced MRI protocols. J Magn Reson Imaging 2010;31(2): Nandwana SB, Moreno CC, Osipow MT, Sekhar A, Cox KL. Gadobenate dimeglumine administration and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: is there a real risk in patients with impaired renal function? Radiology 2015;276(3): Martin DR, Semelka RC, Chapman A, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis versus contrast-induced nephropathy: risks and benefits of contrast-enhanced MR and CT in renally impaired patients. J Magn Reson Imaging 2009;30(6): Matsushita K, Mahmoodi BK, Woodward M, et al. Comparison of risk prediction using the CKD-EPI equation and the MDRD study equation for estimated glomerular filtration rate. JAMA 2012;307(18): Michaely HJ, Aschauer M, Deutschmann H, et al. Gadobutrol in renally impaired patients: results of the GRIP study. Invest Radiol 2017;52(1): Smorodinsky E, Ansdell DS, Foster ZW, et al. Risk of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is low in patients with chronic liver disease exposed to gadolinium-based contrast agents. J Magn Reson Imaging 2015;41(5): Swan SK, Lambrecht LJ, Townsend R, et al. Safety and pharmacokinetic profile of gadobenate dimeglumine in subjects with renal impairment. Invest Radiol 1999;34(7): Becker-Weidman DJ, Kalb B, Sharma P, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma lesion characterization: single-institution clinical performance review of multiphase gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging comparison to prior same-center results after MR systems improvements. Radiology 2011;261(3): Lauenstein T, Ramirez-Garrido F, Kim YH, et al. Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis risk after liver magnetic resonance imaging with gadoxetate disodium in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment: results of a prospective, open-label, multicenter study. Invest Radiol 2015;50(6): Perazella MA. Gadolinium-contrast toxicity in patients with kidney disease: nephrotoxicity and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis. Curr Drug Saf 2008;3(1): Winship B, Ramakrishnan S, Evans J, et al. A single-center analysis of abdominal imaging in the evaluation of kidney transplant recipients. Clin Transplant 2013;27(5): Radiology: Volume 286: Number 1 January 2018 n radiology.rsna.org 119
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018)
 Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Gadolinium Based Contrast Agent Recommendations (Revised 06/07/2018) Introduction: Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is the only known adverse health effect related to gadoliniumbased contrast agents (GBCAs).
Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects
 Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
Safety Forum: MR Safety Update - SMRT 2008 Sunday May 8, 2:25 p.m. Global reports and findings of NSF and its effects Tim Leiner, MD PhD Assistant Professor of Radiology, Department of Radiology, Maastricht
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research
 University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
University of Virginia Institutional Review Board - Health Sciences Research Guidelines for Researchers Using Gadolinium-Enhanced MRI in Research Page 1 of 16 Table of Contents New Information:... 3 IRB-HSR
Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions
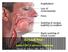 Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Source images Beyond NSF: Acute GBCA adverse reactions Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD, FACR Disclosures Patent Agreements: GE, Siemens, Philips, Hitachi, Toshiba, Bayer, Bracco, Mallinckrodt, Medrad, Nemoto,
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline
 Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Administration of Gadolinium Contrast in Adults Procedural Guideline This procedural guideline is designed to assist Radiologists by providing an analytical framework for the evaluation of gadolinium contrast
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, February 2014
Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges
 REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
REVIEW Review of Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents: Current Applications and Challenges Alex Frydrychowicz, M.D.*, The group of hepatobiliary contrast agents comprises two gadolinium-based contrast agents
Seeing is Believing... Look Beneath the Surface
 References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
References 1. Idee JM, Port C, Raynal I, et al. Clinical and geological consequences of transmetallation induced by contrast agents for magnetic resonance imaging: a review. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology.
NSF Coming and Going
 NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
NSF Coming and Going Martin R. Prince, MD, PhD Cornell and Columbia Universities Patent agreements: GE, Philips, Siemens, Hitachi, Medrad, Epix, Lantheus, Bayer, Bracco, Nemoto, Mallinckrodt and Topspins
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders
 Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
Information for Healthcare Professionals and other Stakeholders NEPHROGENIC SYSTEMIC FIBROSIS: AN UNCOMMON AND DEBILITATING DISEASE POSSIBLY ASSOCIATED WITH GADOLINIUM CHELATES Villepinte, April 2013 Any
MR Contrast Agents. Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? US Agents. Understanding and Embracing Change
 Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Why Use Contrast Agents in MRI? Improve disease detection and characterization Increase sensitivity to extent of disease MR Contrast Agents Understanding and Embracing Change Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging (marketed as Magnevist, MultiHance, Omniscan, OptiMARK, ProHance)
 Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Information for Healthcare Professionals Page 1 of 5 FDA ALERT [6/2006, updated 12/2006 and 5/23/2007: This updated Alert highlights FDA s request for addition of a boxed warning and new warnings about
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies
 Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Protocol for iv. iodine and gadolinium contrast studies Royal College of Radiologists Standard The individual administering the contrast agent must ensure that the patient understands that it is to be
Clinical Study Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis Risk and Liver Disease
 International Nephrology, Article ID 679605, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/679605 Clinical Study Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis Risk and Liver Disease Robert F. Hanna, 1 Lee A. Finkelstone, 1 Daniel
International Nephrology, Article ID 679605, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/679605 Clinical Study Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis Risk and Liver Disease Robert F. Hanna, 1 Lee A. Finkelstone, 1 Daniel
Special Articles Original Research
 Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Special Articles Original Research Soulez et al. NSF in Patients With Stage 3 5 CKD Undergoing MRI With GBCA Special Articles Original Research Gilles Soulez 1 Daniel C. Bloomgarden 2,3 Neil M. Rofsky
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media
 Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
Gadolinium-Based Contrast Media Wm. Faulkner, B.S.,R.T.(R)(MR)CT, FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, R.T.(R)(MR), MRSO (MRSC TM ) Gadolinium ( 64 Gd) 7 un-paired electrons chelate, any of a class
A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates
 Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
Control # 1029 A Safety Update on the Gadolinium Chelates Val M. Runge, MD Universitätsinstitut für Diagnostische, Interventionelle und Pädiatrische Radiologie University Hospital Bern Allergic Reactions
PLEASE SCROLL DOWN FOR ARTICLE
 This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
This article was downloaded by:[danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] [Danish Veterinary and Agricultural Library] On: 24 June 2007 Access Details: [subscription number 773444395] Publisher: Informa
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist and Magnevist below.
 August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
August 15 th, 2018 Dear Valued Customer: Thank you for your continued patience over the last several months as we have worked to resolve our contrast supply interruption. The purpose of this letter is
Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media
 HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
HOSPITAL CHRONICLES 2012, 7(4): 208 214 Review Side Effects and Complications of Magnetic Resonance Contrast Media Ekaterini Tavernaraki, MD, PhD, Anna Skoula MD, Stylianos Benakis, MD, Dimitrios Exarhos
SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA.
 ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
ASSESSMENT OF PATIENTS: IMAGING SERVICES Policy #: 300.02 Effective Date: 6/29/09 Last Revision Date: 10/07 Page 1 of 5 SUBJECT: ASSESSMENT OF LAB RESULTS PRIOR TO INJECTING GADOLINIUM-BASED CONTRAST MEDIA
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS
 DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
DIVISION OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND HEMATOLOGY PRODUCTS MEMORANDUM TO THE FILE i. NDA: 20-123, 22-066 Product: Omniscan ii. NDA: 19-596, 21-037 Product: Magnevist iii. NDA: 20-976, 20-937,20-975 Product: OptiMARK
Please see Important Safety Information, including Boxed Warnings for Gadavist, Eovist and Magnevist on the following pages.
 Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Dear Valued Customer: As a valued partner we want to inform you that a technical issue occurred at our Berlin manufacturing center where final formulation and packaging of Bayer MRI (Magnetic Resonance
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents
 Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Important Update - Availability of Bayer s MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Contrast agents Certain batches of pharmaceutical products from our company s Supply Center in Berlin where final formulation
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 0.35 T 35/1600
Annex III. Amendments to relevant sections of the product information
 Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Annex III Amendments to relevant sections of the product information Note: These amendments to the relevant sections of the product information are the outcome of the referral procedure. The product information
Instructions for the safe administration of gadolinium based contrast agents (GBCA). 1. PREADMINISTRATION PRECAUTIONS:
 POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
POLICY NUMBER: RM 6-18 CATEGORY: Patient Care DATE: June 2016 NEXT REVIEW DATE: April 2017 SUBJECT: PURPOSE: POLICY: Intravenous Gadolinium Based Contrast Administration To prevent complications associated
Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice?
 Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
Safety considerations in contrast enhanced procedures Carlo Catalano Sapienza University of Rome Contrast-enhanced MRI: how do changing EU regulations impact daily practice? CE MRI: EU regulations - Initial
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact Purpose: Materials and Methods: Results: Conclusion:
 This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
This copy is for personal use only. To order printed copies, contact reprints@rsna.org Original Research n Pediatric Imaging Pediatric Brain: Repeated Exposure to Linear Gadolinium-based Contrast Material
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document. Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee. Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013
 FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
FDA Advisory Committee Briefing Document Medical Imaging Drugs Advisory Committee Meeting to be held on February 14, 2013 New Drug Application 204-781 Gadoterate meglumine Injection (Dotarem ), sponsored
Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis: Possible Association with a Predisposing Infection
 MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
MR Imaging Original Research MR Imaging Original Research Lauren Parks Golding 1,2 James M. Provenzale 3 Golding LP, Provenzale JM Keywords: connective tissue disorders, contrast media, dialysis, infections,
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans are significantly
 Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
Mini-Review Current Status of Gadolinium Toxicity in Patients with Kidney Disease Mark A. Perazella Department of Medicine, Section of Nephrology, Yale University School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR
 William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor of Radiology Chair, Dept of Radiology University of California, San Diego Medical Center San Diego, California Learning Objectives Identify emerging safety
Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 160 167 Extracellular gadolinium-based contrast media: An overview Marie-France Bellin, Aart J. Van Der Molen University Paris-Sud 11, Department of Radiology, University
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents
 Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Gadolinium-Based MR Contrast Agents Magnetic Resonance Imaging, Vol 3, pp27-35, 1985 Wm. Faulkner, BS,RT(R)(MR)(CT), FSMRT, MRSO (MRSC ) Kristan Harrington, MBA, RT(R)(MR) ARRT, MRSO (MRSC ) 0.35 T 0.35
Index. mri.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Angiogenesis, and cancer of prostate, 689 690 Angiography, MR. See MR angiography. Apoptosis, MR imaging of, 637 Apparent diffusion coefficient,
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Angiogenesis, and cancer of prostate, 689 690 Angiography, MR. See MR angiography. Apoptosis, MR imaging of, 637 Apparent diffusion coefficient,
Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be used
 Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Contrast vs Non-Contrast When to Order Stephen McManus, M.D. Contrast media Purpose of using contrast Contrast reaction Nephrotoxicity from contrast Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis When should contrast be
Objectives. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Pre-dialysis CKD: The Problem. Objectives
 The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
The Role of the Primary Physician and the Nephrologist in the Management of Chronic Kidney Disease () By Brian Young, M.D. Assistant Clinical Professor of Medicine David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA
Public Assessment Report
 Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
Public Assessment Report Increased risk of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy/nephrogenic systemic fibrosis and gadolinium-containing MRI contrast agents Executive summary 2 Introduction 3 Data assessed
Effective Health Care Program
 Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 143 Effective Health Care Program Techniques for the Diagnosis and Staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Executive Background and Objectives Hepatocellular carcinoma
Comparative Effectiveness Review Number 143 Effective Health Care Program Techniques for the Diagnosis and Staging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Executive Background and Objectives Hepatocellular carcinoma
Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern
 Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Editorial Gadolinium Use in Patients with Kidney Disease: A Cause for Concern Mark A. Perazella* and Roger A. Rodby *Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Yale University School of Medicine, New
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With Over half of patients from the Medicare 5% sample (restricted to age 65 and older) have a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease (), cardiovascular disease,
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI
 Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
Hepatobiliary Contrast Agents for Liver MRI Scott B. Reeder, MD, PhD International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Sociedad Mexicana de Radiologia e Imagen (SMRI) Mexico City June 4, 2014 Department
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM. (gadoterate meglumine) Injection. For Intravenous Use
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH DOTAREM (gadoterate meglumine) Injection For Intravenous Use Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent For Use with Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Guerbet LLC Date: August 26, 2013 120 W. 7 th
Gadolinium in Humans: A Family of Disorders
 Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Residents Section Clinical Perspective Semelka et al. Gadolinium in Humans Residents Section Clinical Perspective Residents inradiology Richard C. Semelka 1 Miguel Ramalho 1,2 Mamdoh AlObaidy 1,3 Joana
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population
 Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Chapter 1: CKD in the General Population Overall prevalence of CKD (Stages 1-5) in the U.S. adult general population was 14.8% in 2011-2014. CKD Stage 3 is the most prevalent (NHANES: Figure 1.2 and Table
Frequency and Severity of Acute Allergic-Like Reactions to Gadolinium-Containing IV Contrast Media in Children and Adults
 Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
Reactions to Gadolinium- Containing Contrast Media MR Imaging Original Research Jonathan R. Dillman 1 James H. Ellis 1 Richard H. Cohan 1 Peter J. Strouse 2 Sophia C. Jan 1 Dillman JR, Ellis JH, Cohan
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
 Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Gadolinium Deposition in the Brain: Summary of Known Science and Recommendations from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine Vikas Gulani, MD, PhD 1-4*, Fernando Calamante, PhD 5,6,
Shuma Hirashio 1,2, Shigehiro Doi 1 and Takao Masaki 1*
 Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
Hirashio et al. Renal Replacement Therapy (2018) 4:24 https://doi.org/10.1186/s41100-018-0164-9 CASE REPORT Open Access Magnetic resonance imaging is effective for evaluating the therapeutic effect of
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST. gadoxetate disodium injection mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml)
 PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
PRODUCT MONOGRAPH PRIMOVIST gadoxetate disodium injection 181.43 mg/ml (0.25 mmol/ml) Intravenous contrast enhancement agent for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) For Professional Use Only Distributed and
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
White Rose Research Online URL for this paper: Version: Accepted Version
 This is a repository copy of Accuracy of staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: should incisional biopsy be done before or after magnetic resonance imaging?. White Rose Research Online
This is a repository copy of Accuracy of staging of oral squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: should incisional biopsy be done before or after magnetic resonance imaging?. White Rose Research Online
Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization
 JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
JOURNAL OF APPLIED CLINICAL MEDICAL PHYSICS, VOLUME 16, NUMBER 5, 2015 Using lesion washout volume fraction as a biomarker to improve suspicious breast lesion characterization Jie Huang, a Sarah M. Schafer,
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD
 Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients with CKD Over half of patients in the Medicare 5% sample (aged 65 and older) had at least one of three diagnosed chronic conditions chronic kidney disease
Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis
 mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
mini review http://www.kidney-international.org & 2007 International Society of Nephrology Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis T Grobner 1 and FC Prischl 2 1 2nd Department of Medicine/Nephrology,
St. Michael s Hospital, Department of Medical Imaging invites you to join us for a live conference and live webinar: 4 th Annual MRI Symposium
 2017 St. Michael s Hospital, Department of Medical Imaging invites you to join us for a live conference and live webinar: 4 th Annual MRI Symposium September 16, 2017 MRI for Oncology Program This event
2017 St. Michael s Hospital, Department of Medical Imaging invites you to join us for a live conference and live webinar: 4 th Annual MRI Symposium September 16, 2017 MRI for Oncology Program This event
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES. M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly
 LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
LIVER IMAGING TIPS IN VARIOUS MODALITIES M.Vlychou, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor of Radiology University of Thessaly Hepatocellular carcinoma is a common malignancy for which prevention, screening, diagnosis,
Update in Nephrology. Case: Question 1. Case presentation. Acute Kidney Injury. For her hypertension management, you decide to:
 Update in Nephrology Chronic Kidney Disease Renoprotection and Proteinuria, ACE and/or ARB Anemia management Update in Nephrology Renal artery stenosis Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Division of Nephrology
Update in Nephrology Chronic Kidney Disease Renoprotection and Proteinuria, ACE and/or ARB Anemia management Update in Nephrology Renal artery stenosis Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis Division of Nephrology
FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.
![FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA. FULL PAPER. reported in 200 articles in the peer-reviewed literature, the vast majority of which [595/815 (73.0%)] were observed in the USA.](/thumbs/77/75534485.jpg) Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
Received: 1 August 2014 Revised: 28 January 2015 Accepted: 3 February 2015 doi: 10.1259/bjr.20140526 2015 The Authors. Published by the British Institute of Radiology under the terms of the Creative Commons
Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know
 Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know Presented By Tom Wadsworth PharmD, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor UAA/ISU Doctor of Pharmacy Program Idaho State University College of
Assessing Renal Function: What you Didn t Know You Didn t Know Presented By Tom Wadsworth PharmD, BCPS Associate Clinical Professor UAA/ISU Doctor of Pharmacy Program Idaho State University College of
CURRENTLY IN THE United States, 431,284
 Increased Breast Calcifications in Women With ESRD on Dialysis: Implications for Breast Cancer Screening Mario Castellanos, MD, Seema Varma, MD, Kathleen Ahern, PhD, RN, Sue-Jane Grosso, MD, Shalom Buchbinder,
Increased Breast Calcifications in Women With ESRD on Dialysis: Implications for Breast Cancer Screening Mario Castellanos, MD, Seema Varma, MD, Kathleen Ahern, PhD, RN, Sue-Jane Grosso, MD, Shalom Buchbinder,
Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 2 diabetic patients?
 Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 3, 2008 The MCQ equation in DM2 patients Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration
Diabetes Care Publish Ahead of Print, published online October 3, 2008 The MCQ equation in DM2 patients Is the new Mayo Clinic Quadratic (MCQ) equation useful for the estimation of glomerular filtration
Renal cell carcinoma of the native kidney in a renal transplant recipient
 www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Renal cell carcinoma of the native kidney in a renal transplant recipient Vikrampal Bhatti, Ananthalaxmi Vangapalli, Deepti Bhattacharya,
www.edoriumjournals.com CLINICAL IMAGES PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Renal cell carcinoma of the native kidney in a renal transplant recipient Vikrampal Bhatti, Ananthalaxmi Vangapalli, Deepti Bhattacharya,
Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting
 European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
European Journal of Radiology 66 (2008) 230 234 Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis associated with gadolinium based contrast agents: A summary of the medical literature reporting Dale R. Broome Department of
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI
 Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Innovations in HCC Imaging: MDCT/MRI Anthony E. Cheng, M.D. Cardinal MRI Center Cardinal Santos Medical Center, Wilson Street, San Juan Innovations in HCC Imaging: Goals/Objectives MDCT/MRI Learn the diagnostic
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a common complication of chronic liver disease with increasing incidence worldwide ( 1,2 ). Liver trans plantation r
 Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Note: This copy is for your personal, non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Neuroradiology Original Research
 MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
MRI of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Neuroradiology Original Research Ender Uysal 1 Sukru Mehmet Erturk 1 Hakan Yildirim 1 Feray Seleker 2 Muzaffer Basak 1 Uysal E, Erturk SM, Yildirim H, et al. Keywords:
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance
 Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Safety and clinical usefulness of gadoteric acid including post-marketing surveillance MRI is an essential diagnostic tool in making definite diagnoses and determining therapeutic strategies. Extracellular
Report on the Investigation Results
 This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
This English version is intended to be a reference material for the convenience of users. In the event of inconsistency between the Japanese original and this English translation, the former shall Report
Imaging in the time of NFD/NSF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency?
 DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
DI 10.1007/s10334-007-0071-5 EDITRIAL REVIEW Imaging in the time of FD/SF: do we have to change our routines concerning renal insufficiency? Georg Bongartz Accepted: 7 March 2007 ESMRMB 2007 Abstract To
The Incidence Of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Or Radiocontrast Nephropathy
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 The Incidence Of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Or Radiocontrast Nephropathy K O Kragha Citation K O Kragha. The Incidence Of Contrast-Induced
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 18 Number 1 The Incidence Of Contrast-Induced Nephropathy Or Radiocontrast Nephropathy K O Kragha Citation K O Kragha. The Incidence Of Contrast-Induced
REVISITING THE PHARMACOKINETICS IN PATIENTS
 REVISITING THE PHARMACOKINETICS IN PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION IN THE LIGHT OF THE LATEST FDA AND EMA GUIDELINES 3 RD CONFERENCE OF EUROPEAN PHARMACOLOGICAL SOCIETIES EUROPEAN COMPETITIVENESS
REVISITING THE PHARMACOKINETICS IN PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION IN THE LIGHT OF THE LATEST FDA AND EMA GUIDELINES 3 RD CONFERENCE OF EUROPEAN PHARMACOLOGICAL SOCIETIES EUROPEAN COMPETITIVENESS
Annex II. Scientific conclusions
 Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Annex II Scientific conclusions 31 Scientific conclusions In accordance with Article 107k of Directive 2001/83/EC, the CHMP considered the PRAC recommendation adopted on 6 July 2017. Overall summary of
Incidence of Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions
 Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Prince et al. Immediate Gadolinium Contrast Media Reactions Health Care Policy and Quality Original Research Martin R. Prince 1 Honglei Zhang Zhitong Zou
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009
 The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
The Diabetes Kidney Disease Connection Missouri Foundation for Health February 26, 2009 Teresa Northcutt, RN BSN Primaris Program Manager, Prevention - CKD MO-09-01-CKD This material was prepared by Primaris,
Lucia Cea Soriano 1, Saga Johansson 2, Bergur Stefansson 2 and Luis A García Rodríguez 1*
 Cea Soriano et al. Cardiovascular Diabetology (2015) 14:38 DOI 10.1186/s12933-015-0204-5 CARDIO VASCULAR DIABETOLOGY ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Open Access Cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in
Cea Soriano et al. Cardiovascular Diabetology (2015) 14:38 DOI 10.1186/s12933-015-0204-5 CARDIO VASCULAR DIABETOLOGY ORIGINAL INVESTIGATION Open Access Cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality in
Multiparametric T1, T2 and T2* MR Imaging
 Multiparametric T1, T2 and T2* MR Imaging Kate Hanneman MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate family members
Multiparametric T1, T2 and T2* MR Imaging Kate Hanneman MD Assistant Professor of Radiology Joint Department of Medical Imaging, University of Toronto Disclosure Neither I nor my immediate family members
Policy #: 291 Latest Review Date: February 2013
 Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
Effective for dates of service on or after April 1, 2013, refer to: https://www.bcbsal.org/providers/policies/carecore.cfm Name of Policy: Magnetic Resonance Angiography (MRA) of the Chest (excluding the
A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Predicting Risk. William McClellan, MD, MPH Emory University Atlanta
 A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Predicting Risk William McClellan, MD, MPH Emory University Atlanta Goals Understand the limitations and uses of creatinine based measures of kidney function
A New Approach for Evaluating Renal Function and Predicting Risk William McClellan, MD, MPH Emory University Atlanta Goals Understand the limitations and uses of creatinine based measures of kidney function
MRI Research Safety Form for IRB Approval
 MRI Research Safety Form for IRB Approval Please complete and e-mail to Julie Hanlon and Vera Kimbrell jahanlon@partners.org ;vkimbrell@partners.org Study Name: Contact: Anticipated Start Date: The MRI
MRI Research Safety Form for IRB Approval Please complete and e-mail to Julie Hanlon and Vera Kimbrell jahanlon@partners.org ;vkimbrell@partners.org Study Name: Contact: Anticipated Start Date: The MRI
Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver Metastases
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 10:165 169 (1999) Original Research Common Occurrence of Benign Liver Lesions in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Breast Cancer Investigated by MRI for Suspected Liver
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7
 PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
PATIENT CARE AND MRI SAFETY Module 7 1 Biological Considerations There are no reported adverse biological effects of extended exposure to MRI. However, several inconsequential and reversible effects of
Summary of Recommendation Statements Kidney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi: /kisup
 http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
http://www.kidney-international.org & 2013 DIGO Summary of Recommendation Statements idney International Supplements (2013) 3, 5 14; doi:10.1038/kisup.2012.77 Chapter 1: Definition and classification of
Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Shimauchi, H. Abe, N. Mori, H. Ota, K. Takase, S.
 MRI- Detected Breast Masses: Are CAD-Measured Kinetic Diversity Analyses Useful for Differential Diagnosis? A New Approach with Whole Lesion Curve Distribution Analysis. Poster No.: C-1901 Congress: ECR
MRI- Detected Breast Masses: Are CAD-Measured Kinetic Diversity Analyses Useful for Differential Diagnosis? A New Approach with Whole Lesion Curve Distribution Analysis. Poster No.: C-1901 Congress: ECR
Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
 Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
Reiter et al. Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance 2012, 14:31 REVIEW Open Access Minimizing Risk of Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Theresa Reiter 1*, Oliver
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM
 USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
USRDS UNITED STATES RENAL DATA SYSTEM Chapter 2: Identification and Care of Patients With CKD Over half of patients from the Medicare 5 percent sample have either a diagnosis of chronic kidney disease
Safety of Gadoterate Meglumine (Gd-DOTA) as a Contrast Agent for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Drugs R D 2010; 10 (3): 133-145 1179-6901/10/0003-0133 ª 2010 Ishiguchi & Takahashi, publisher and licensee Adis Data Information BV. This is an open access article published
Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin as a Biomarker of Acute Kidney Injury in Patients with Morbid Obesity Who Underwent Bariatric Surgery
 Published online: October 31, 213 1664 5529/13/31 11$38./ This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3. Unported license (CC BY-NC) (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Published online: October 31, 213 1664 5529/13/31 11$38./ This is an Open Access article licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution- NonCommercial 3. Unported license (CC BY-NC) (www.karger.com/oa-license),
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 10
 Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Diagnostic performance of automated breast volume scanner (ABVS) versus hand-held ultrasound (HHUS) as second look for breast lesions detected only on magnetic resonance imaging. Poster No.: C-1701 Congress:
Kidney Transplant: Functional Assessment with Diffusion-Tensor MR Imaging at 3T 1
 Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Note: This copy is for your personal non-commercial use only. To order presentation-ready copies for distribution to your colleagues or clients, contact us at www.rsna.org/rsnarights. Original Research
Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis?
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 1104 1108 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfk062 Advance Access publication 23 January 2006 Interesting Case Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2006) 21: 1104 1108 doi:10.1093/ndt/gfk062 Advance Access publication 23 January 2006 Interesting Case Gadolinium a specific trigger for the development of nephrogenic fibrosing
INTRODUCTION CLINICAL EXPERIENCE CLINICAL EFFICACY PEDIATRIC EXPERIENCE DOSING SUMMARY
 1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
1 2 DOTAREM Administered Doses 3 Molecular Structure of DOTAREM DOTAREM offers high thermodynamic and kinetic stability provided by its macrocyclic and ionic structure* 3 *The clinical significance of
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript World J Urol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 February 1.
 NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Published in final edited form as: World J Urol. 2011 February ; 29(1): 11 14. doi:10.1007/s00345-010-0625-4. Significance of preoperative PSA velocity in men with low
Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page:
 Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
Synopsis Abbott Laboratories Name of Study Drug: Paricalcitol Capsules (ABT-358) (Zemplar ) Name of Active Ingredient: Paricalcitol Individual Study Table Referring to Part of Dossier: Volume: Page: (For
Dialysis Initiation and Optimal Vascular Access: Outcomes and Mortality
 Dialysis Initiation and Optimal Vascular Access: Outcomes and Mortality Shannon H. Norris, BSN, RN June 6, 2018 Dialysis Initiation and Optimal Vascular Access: Outcomes and Mortality DISCUSSION: End Stage
Dialysis Initiation and Optimal Vascular Access: Outcomes and Mortality Shannon H. Norris, BSN, RN June 6, 2018 Dialysis Initiation and Optimal Vascular Access: Outcomes and Mortality DISCUSSION: End Stage
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD
 Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Primary Care Approach to Management of CKD This PowerPoint was developed through a collaboration between the National Kidney Foundation and ASCP. Copyright 2018 National Kidney Foundation and ASCP Low
Handheld Radiofrequency Spectroscopy for Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Margins During Breast-Conserving Surgery
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Last Review Status/Date: December 2014 Page: 1 of 6 Intraoperative Assessment of Surgical Description Breast-conserving surgery as part of the treatment of localized breast cancer is optimally achieved
Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates
 Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates Georgeta Mihai, PhD, DABR Medical Physicist, BIDMC, Boston Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston Disclosures None Acknowledgments: Da
Contrast Enhanced Spectral Mammography (CESM) Updates Georgeta Mihai, PhD, DABR Medical Physicist, BIDMC, Boston Assistant Professor, Harvard Medical School, Boston Disclosures None Acknowledgments: Da
Long-term prognosis of BK virus-associated nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients
 Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
Original Article Kidney Res Clin Pract 37:167-173, 2018(2) pissn: 2211-9132 eissn: 2211-9140 https://doi.org/10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.2.167 KIDNEY RESEARCH AND CLINICAL PRACTICE Long-term prognosis of BK
