Assessment of the Patient with Endocrine Dysfunction. Objective. Endocrine. Endocrine Facts. Physical Assessment 10/3/2013
|
|
|
- Willa Paul
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Objective Endocrine Jennifer MacDermott, MS, RN, ACNS BC, NP C, CCRN Clinical Nurse Specialist Surgical Intensive Care Unit Identify abnormal assessment finding sin a patient with endocrine dysfunction. Describe types of endocrine dysfunction. Describe the standards in caring for a patient undergoing endocrine surgery. Endocrine Facts Endocrine organ/gland manufactures and secretes hormones Body functions: reproduction; growth and development; maintenance of homeostasis; and energy production, utilization, and storage during metabolic processes Negative feedback loop Physical Assessment Assessment of the Patient with Endocrine Dysfunction Changes in skin texture (hypothyroidism/hyperthyroidism) Exophthalmos (hyperthyroidism) Changes in physical appearance Facial hair Moon face (Cushing s disease) Buffalo hump (Cushing s disease) Obesity of the trunk with thinness of extremities (Cushing s disease) Increased size of feet and hands (Cushing s disease) Edema Blood pressure Elevated (hyperfunction of adrenal cortex/hyperparathyroidism) Decreased (hypofunction of adrenal cortex) 1
2 Serum Laboratory Studies ADH Normal: 1 5 pg/ml Controls water resorption in kidney Glucose Normal: mg/dl Controlled by insulin and glucagon release Hyperglycemia Hypoglycemia Serum Laboratory Studies Sodium (Na + ) Normal: mg/dl Result of balance between dietary sodium intake and renal excretion; aldosterone, natriuretic hormone, and antidiuretic hormone all play a role Hypernatremia Hyponatremia Osmolality Normal: mosm/kg Measure of concentration of dissolved particles in blood Hyperosmolality Hypoosmolality Urine Laboratory Studies Glucose Normal: negative (random specimen) Abnormal result is a consequence of blood glucose levels that exceed the capability of renal threshold and results in glucose spilling into the urine Ketones Normal: negative Abnormal result occurs as a result of fatty acid catabolism Osmolality Normal: mosm/kg (random specimen) Evaluation of ability of kidney to concentrate urine Hyperosmolality Hypoosmolality Endocrine Dysfunction Acute Hypoglycemia Serum glucose <50 mg/dl High risk populations Diabetic patients taking insulin Children and pregnant women with type 1 diabetes Elderly patients with diabetes Causes Excess insulin or oral hypoglycemics Decreased exogenous insulin requirement Underproduction of glucose Rapid utilization of glucose Acute Hypoglycemia Clinical Manifestations Activation of Sympathetic Nervous System Nervousness/apprehension Tachycardia Palpitations Pallor Diaphoresis Dilated pupils Tremor Fatigue Weakness Headache Hunger Inadequate Glucose Supply to Neural Tissues Headache Restlessness Difficulty speaking/thinking Visual disturbances Parethesia Difficulty walking Altered consciousness Coma Convulsions Catatonia Acute paranoia 2
3 Acute Hypoglycemia Prolonged hypoglycemia may lead to irreversible brain damage and coma Mild hypoglycemia Blood glucose mg/dl Treatment: 15g carbohydrate by mouth (4 oz sweetened carbonated beverage, 4 oz fruit juice, 1 cup skim milk, 3 4 glucose tablets) Moderate hypoglycemia Blood glucose <60 mg/dl Treatment: 20g 30g carbohydrate by mouth Severe hypoglycemia Blood glucose <60 mg/dl Treatment: ½ amp D50 IV or 1mg glucagon SQ Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Affects patients with type 1 diabetes or type 2 diabetes in severe stress Develops quickly Factors leading to DKA Insulin deficiency Stress Infection Major acute illness, trauma, or surgery Pancreatitis Medications Other endocrine disorders: hyperthyroidism, Cushing s disease, pheochromocytoma Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Pathophysiology High glucose levels shift fluid out of cells to extracellular space (osmotic diuresis) urinary losses of water/electrolytes Serum glucose exceeds renal threshold glucose excreted via kidneys (glucosuria) Hyperosmolar state further impairs insulin secretion and promotes insulin resistance GFR as result of fluid volume deficit leading to reduced glucosuria serum glucose Liver breaks down protein stores to glucose and nitrogen to provide energy to the body Glucose cannot be used properly without insulin further serum glucose and osmotic diuresis Nitrogen accumulates in periphery BUN Absence/lack of insulin decomposition of fat (lipolysis) and impaired metabolism of ketones ketosis Increasing carbonic acid and impaired bicarb buffering metabolic acidosis Accumulation of lactic acid decreased perfusion to organs hypoxemia Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Clinical Manifestations Flushed, dry skin Dry mucous membranes skin turgor Tachycardia Hypotension Kussmaul respirations Acetone breath Altered level of consciousness Visual disturbances/ blurred vision Polydipsia ( thirst) Polyuria ( urination) Nausea and vomiting Anorexia Abdominal pain Weakness Headache Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Laboratory Studies Serum glucose mg/dl urine glucose level Arterial ph <7.30 serum bicarbonate (0 15 meq) Positive serum and urine ketones serum crea nine and azotemia Electrolytes vary with state of hydration Hyperkalemia/hypokalemia Serum hyperosomolality (average 330 mosm/kg) 3
4 Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Nonketotic Coma (HHNK) Inadequate insulin secretion or action and/or decreased utilization and/or increased production of glucose Most commonly seen in Type 2 Diabetes, but can be seen in patients without diabetes Mortality 10 40% Factors leading to HHNK High calorie parenteral or enteral feedings Decreased thirst mechanism Difficult access to fluids Medications HHNK Pathophysiology and Clinical Manifestations Pathophysiology Develops over weeks to months Hyperglycemia shift water to extracellular space profound dehydration Insulin levels prevent lipolysis and ketone formation Clinical manifestations Flushed, dry skin Dry mucous membranes skin turgor Tachycardia Hypotension Shallow respirations Altered level of consciousness HHNK Laboratory Studies Serum glucose mg/dl Arterial ph >7.30 Serum bicarbonate >15 meq/l Azotemia Electrolytes vary with state of dehydration, often hypernatremic Serum hyperosmolality > 350 mosm/kg Absence of significant ketosis Monitor vital signs and urine output q1hr Monitor ECG continuously for dysrhythmias Respiratory support Fluid replacement Typical water deficit 100 ml/kg Normal saline (0.9% NS) administration 1L NS bolus 10 to 20 ml/kg infusion 2 3 hours or until BP normalizes Hypotonic saline (0.45% NS) administration Goal: replacement ½ fluid deficit over first 8 hours and second ½ fluid deficit over next 16 hours therapy As blood glucose approach mg/dl, add 5% dextrose to fluid replacement (D5 0.45% NS) Insulin therapy IV bolus 0.15 units/kg regular insulin IV infusion 0.1 units/kg/hr Goal: steady decrease serum glucose mg/dl per hour Monitor blood glucose q1hr Electrolyte replacement Potassium replacement Phosphorus replacement Sodium bicarbonate administration Only use when serum ph <7.0 Only correct to serum ph 7.0 If necessary, should be added to hypotonic saline infusion and administered slowly Patient and family education 4
5 Complications Cerebral edema Result of rapid fluid administration Result of reduction in serum glucose too quickly Seizures Coma Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH) Also known as vasopressin Synthesized by hypothalmus and stored in the posterior pituitary Release mediated by osmoreceptors in the hypothalmus ADH stimulation kidneys reabsorb water reduced urine output ADH suppression water excreted via kidneys increased urine output Diabetes Insipidus Disorder of posterior lobe of pituitary gland Pathophysiology Deficiency of ADH Results in large volumes of water to be excreted via kidneys Causes Idiopathic Intracranial tumors, metastatic disease, lymphoma Head trauma Surgical ablation or irradiation of pituitary gland CNS infections Chronic renal disease Medications causing suppression of ADH release: phenytoin, alcohol, α adrenergic agents DI Clinical Manifestations and Laboratory Studies Clinical manifestations Polyuria (excessive urination) and polydipsia (excessive thirst) Excessive ingestion of fluids Nocturia Dry mucous membranes, poor skin turgor, decreased saliva and sweat production Disorientation Seizures Laboratory studies Serum Na+ >145 meq/l Urine specific gravity to Low serum ADH level Diabetes Insipidus Identify and correct underlying pathology Adequate fluid replacement Replace ADH Vasopressin (Pitressin) Desmopressin (DDAVP) ADH (vasopressin tanate in oil) Thiazide diuretics, mild salt depletion, prostaglandin inhibitors (ibuprofen, aspirin) are used to treat nephrogenic DI Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) Disorder of posterior lobe of pituitary gland Pathophysiology Excessive ADH secretion from pituitary gland Unable to dilute urine retain fluids dilutional hyponatremia Causes Malignant lung tumors Tuberculosis or severe pneumonia Head injury Brain surgery or brain tumor Adrenal insufficiency Medications 5
6 Syndrome of Inappropriate Secretion of Antidiuretic Hormone (SIADH) Clinical manifestations Reduced urine output Weight gain Weakness, muscle cramps Fatigue Difficulty breathing Confusion, hemiparesis, seizures, coma Laboratory studies Na+ <135 meq/l Low hematocrit Low BUN Elevated urine osmolality Reduced serum osmolality SIADH Identify and correct underlying cause Monitoring intake/output, daily weight, urine and serum chemistries, neurological status Fluid restriction IV saline Diuretics Correction of hyponatremia (slowly) Endocrine Related Surgeries Endocrine Surgery Pre procedure care Informed consent Clotting studies Blood typing IV access Post operative care Vital sign assessment Respiratory effort Pain assessment and analgesic administration if necessary Assessment of surgical dressing, reinforcement if necessary Encourage ambulation Patient education Endocrine Surgeries Hypophysectomy Pituitary gland removal Patient education replacement therapy with corticosteroids and thyroid hormones Thyroidectomy or parathyroidectomy Thyroid removal or parathyroid removal Post operative assessment for hypocalcemia and respiratory difficulties Support of head during positioning to avoid tension on sutures Patient should avoid talking to reduce edema to vocal cords; MD should be notified of any voice changes Adrenalectomy Adrenal gland removal Post operative assessment for hypotension and hypoglycemia Patient education replacement therapy with corticosteroids if bilateral adrenalectomy Questions? 6
CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013
 A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
A & P Review CCRN/PCCN Review Course May 30, 2013 Endocrine Anterior pituitary Growth hormone: long bone growth Thyroid stimulating hormone: growth, thyroid secretion Adrenocorticotropic hormone: growth,
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017
 CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
CDE Exam Preparation Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE May 4, 2017 DKA at organ level 3 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Characteristics Ketones positive Anion Gap > 12 (High) Blood Sugar > 14 (High) Bicarbonate
9/11/2012. Chapter 11. Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. Endocrine Emergencies. Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes
 Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter 11 Endocrine Emergencies Learning Objectives Differentiate type 1 and type 2 diabetes Explain roles of glucagon, glycogen, and glucose in hypoglycemia Learning Objectives Discuss following medications
Chapter Goal. Learning Objectives 9/12/2012. Chapter 25. Diabetic Emergencies
 Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Chapter 25 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter Goal Use assessment findings to formulate field impression & implement treatment plan for patients with diabetic emergencies Learning Objectives Describe pathophysiology
Disorders of water and sodium homeostasis. Prof A. Pomeranz 2017
 Disorders of water and sodium homeostasis Prof A. Pomeranz 2017 Pediatric (Nephrology) Tool Box Disorders of water and sodium homeostasis Pediatric Nephrology Tool Box Hyponatremiaand and Hypernatremia
Disorders of water and sodium homeostasis Prof A. Pomeranz 2017 Pediatric (Nephrology) Tool Box Disorders of water and sodium homeostasis Pediatric Nephrology Tool Box Hyponatremiaand and Hypernatremia
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013
 Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
Emergency Medical Training Services Emergency Medical Technician Paramedic Program Outlines Outline Topic: Endocrine Revised: 11/2013 Endocrine system includes 8 major glands. 1. Pituitary (master gland)
AACN PCCN Review. Endocrine
 AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
AACN PCCN Review Endocrine Presenter: Carol A. Rauen, RN, MS, CCNS, CCRN, PCCN, CEN Independent Clinical Nurse Specialist & Education Consultant rauen.carol104@gmail.com Endocrine I. INTRODUCTION Disorders
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM. Objectives A & P 8/11/2011
 PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
PROBLEMS WITH REGULATION AND METABOLISM Lemone and Burke Chapters 18-20 Objectives Review A & P Recall age related changes Identify diagnostic tests Describe etiology, pathophysiology, clinical manifestation,
Calcium (Ca 2+ ) mg/dl
 Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Quick Guide to Laboratory Values Use this handy cheat-sheet to help you monitor laboratory values related to fluid and electrolyte status. Remember, normal values may vary according to techniques used
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Diabetic Ketoacidosis Definition: Diabetic Ketoacidosis is one of the most serious acute complications of diabetes. It s more common in young patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus. It s usually characterized
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes
 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Chapter 22 Basic Fluid and Electrolytes Introduction Infants and young children have a greater need for water and are more vulnerable to alterations in fluid and electrolyte
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27
 Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
Medical-Surgical Nursing: An Integrated Approach - Chapter 27 NURSING CARE OF THE CLIENT: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM NVOC 22C Eliza Rivera-Mitu Mitu,, RN, MSN A Unique System The endocrine system is unique in that
CCRN Review - Renal. CCRN Review - Renal 10/16/2014. CCRN Review Renal. Sodium Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l
 CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
CCRN Review Renal Leanna R. Miller, RN, MN, CCRN-CMC, PCCN-CSC, CEN, CNRN, CMSRN, NP Education Specialist LRM Consulting Nashville, TN Sodium 136-145 Critical Value < 120 meq/l > 160 meq/l Sodium Etiology
Diabetic Emergencies: Ketoacidosis and the Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State. Adam Bursua, Pharm.D., BCPS
 Diabetic Emergencies: Ketoacidosis and the Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Adam Bursua, Pharm.D., BCPS Objectives Describe the epidemiology of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
Diabetic Emergencies: Ketoacidosis and the Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State Adam Bursua, Pharm.D., BCPS Objectives Describe the epidemiology of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar
10. ACUTE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS
 10. ACUTE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS Prof. Oren Zinder, Ph.D. Rambam Medical Center, and the Technion Faculty of Medicine, Haifa, Israel 1.1. Hypoglycaemia Hypoglycaemia is a lowered blood glucose
10. ACUTE COMPLICATIONS OF DIABETES MELLITUS Prof. Oren Zinder, Ph.D. Rambam Medical Center, and the Technion Faculty of Medicine, Haifa, Israel 1.1. Hypoglycaemia Hypoglycaemia is a lowered blood glucose
IV Fluids. I.V. Fluid Osmolarity Composition 0.9% NaCL (Normal Saline Solution, NSS) Uses/Clinical Considerations
 IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
IV Fluids When administering IV fluids, the type and amount of fluid may influence patient outcomes. Make sure to understand the differences between fluid products and their effects. Crystalloids Crystalloid
The Metabolic System. Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs. The Endocrine System
 Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
Physiologic Integrity and Therapeutic Nursing Interventions for Patients With Endocrine Needs Black, J.M. & Hawks, J.H. (2005) Chapters 44, (pp 1154-1189) Baptist Health School of Nursing NSG 4037: Adult
5/18/2017. Specific Electrolytes. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium. Sodium
 Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Specific Electrolytes Hyponatremia Hypervolemic Replacing water (not electrolytes) after perspiration Freshwater near-drowning Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH Secretion (SIADH) Hypovolemic GI disease (decreased
Water (Dysnatremia) & Sodium (Dysvolemia) Disorders Ahmad Raed Tarakji, MD, MSPH, PGCertMedEd, FRCPC, FACP, FASN, FNKF, FISQua
 Water (Dysnatremia) & Sodium (Dysvolemia) Disorders Ahmad Raed Tarakji, MD, MSPH, PGCertMedEd, FRCPC, FACP, FASN, FNKF, FISQua Assistant Professor Nephrology Unit, Department of Medicine College of Medicine,
Water (Dysnatremia) & Sodium (Dysvolemia) Disorders Ahmad Raed Tarakji, MD, MSPH, PGCertMedEd, FRCPC, FACP, FASN, FNKF, FISQua Assistant Professor Nephrology Unit, Department of Medicine College of Medicine,
Wales Critical Care & Trauma Network (North) Management of Hyponatraemia in Intensive Care Guidelines
 Wales Critical Care & Trauma Network (North) Management of Hyponatraemia in Intensive Care Guidelines Author: Richard Pugh June 2015 Guideline for management of hyponatraemia in intensive care Background
Wales Critical Care & Trauma Network (North) Management of Hyponatraemia in Intensive Care Guidelines Author: Richard Pugh June 2015 Guideline for management of hyponatraemia in intensive care Background
I have no financial disclosures
 Athina Sikavitsas DO Children's Emergency Services University of Michigan Discuss DKA Presentation Assessment Treatment I have no financial disclosures 1 6 Y/O male presents with vomiting and abdominal
Athina Sikavitsas DO Children's Emergency Services University of Michigan Discuss DKA Presentation Assessment Treatment I have no financial disclosures 1 6 Y/O male presents with vomiting and abdominal
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University
 Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Dr. Dafalla Ahmed Babiker Jazan University objectives Overview Definition of dehydration Causes of dehydration Types of dehydration Diagnosis, signs and symptoms Management of dehydration Complications
Chapter 50 4/9/2015. Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder. Endocrine Glands and Hormones. Endocrine Glands and Hormones cont d
 Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
Chapter 50 Care of the Patient with an Endocrine Disorder All items and derived items 2015, 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an imprint of Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved. Endocrine Glands and Hormones Pituitary
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!!
 Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
Diabetic Ketoacidosis: When Sugar Isn t Sweet!!! W Ricks Hanna Jr MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics University of Tennessee Health Science Center LeBonheur Children s Hospital Introduction Diabetes
DOWNLOAD OR READ : SYNDROME OF INAPPROPRIATE SECRETION OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN MALIGNANCY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : SYNDROME OF INAPPROPRIATE SECRETION OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN MALIGNANCY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in malignancy
DOWNLOAD OR READ : SYNDROME OF INAPPROPRIATE SECRETION OF ANTIDIURETIC HORMONE IN MALIGNANCY PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 syndrome of inappropriate secretion of antidiuretic hormone in malignancy
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES
 Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Amjad Bani Hani Ass.Prof. of Cardiac Surgery & Intensive Care FLUIDS AND ELECTROLYTES Body Water Content Water Balance: Normal 2500 2000 1500 1000 500 Metab Food Fluids Stool Breath Sweat Urine
Diabetic Emergencies. Chapter 15
 Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
Diabetic Emergencies Chapter 15 Diabetes- is a disorder of glucose metabolism or difficulty metabolizing carbohydrates, fats and proteins Full name is diabetes mellitus which refers to the presence of
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) K E M I A D E Y E R I, P G Y - 1
 DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) K E M I A D E Y E R I, P G Y - 1 QUESTION # 1 7 year old boy comes to the ER with a 2 week history of abdominal pain and weight loss. Further history reveals polyuria and polydipsia,
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS (DKA) K E M I A D E Y E R I, P G Y - 1 QUESTION # 1 7 year old boy comes to the ER with a 2 week history of abdominal pain and weight loss. Further history reveals polyuria and polydipsia,
Diabetes mellitus - diagnosis, classification and acute complications. David Karásek 3rd Department of Internal Medicine University Hospital Olomouc
 Diabetes mellitus - diagnosis, classification and acute complications David Karásek 3rd Department of Internal Medicine University Hospital Olomouc Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases, characterized
Diabetes mellitus - diagnosis, classification and acute complications David Karásek 3rd Department of Internal Medicine University Hospital Olomouc Diabetes mellitus is a group of metabolic diseases, characterized
Guidelines for management of. Hyponatremia
 Guidelines for management of Hyponatremia Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith by the authors reviewing available
Guidelines for management of Hyponatremia Children s Kidney Centre University Hospital of Wales Cardiff CF14 4XW DISCLAIMER: These guidelines were produced in good faith by the authors reviewing available
Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com
 1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
1 Purchase the complete book on Amazon.com 2 Disclaimer Medicine and nursing are continuously changing practices. The author and publisher have reviewed all information in this book with resources believed
1/3/2008. Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown. Medical-Surgical Nursing Care, 2e Karen Burke, Priscilla LeMone, and Elaine Mohn-Brown
 Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Medical-Surgical Nursing Care Second Edition Karen Burke Priscilla LeMone Elaine Mohn-Brown Chapter 7 Caring for Clients with Altered Fluid, Electrolyte, or Acid-Base Balance Water Primary component of
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Dextran 40 (Gentran 40)
 Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
Assess for presence/history of hypovolemia, shock, venous thrombosis. Assess vital signs: Hypovolemic shock secondary to surgery, burns, hemorrhage, other serious condition PT and PTT abnormalities Venous
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts:
 Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Objectives / Learning Targets: The learner who successfully completes this course will be able to demonstrate understanding of the following concepts: Insulin s function in the body. The basics of diabetes
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance
 Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Chapter 26 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid- Base Balance 1 Body Water Content Infants: 73% or more water (low body fat, low bone mass) Adult males: ~60% water Adult females: ~50% water (higher fat content,
Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances
 Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances Pediatric emergency PICU division Pediatric department Medical faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, Electrolyte disturbances and acid-base imbalances Pediatric emergency PICU division Pediatric department Medical faculty, University of Sumatera Utara H. Adam Malik Hospital 1 Hypoglycemia
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM
 WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
WATER, SODIUM AND POTASSIUM Attila Miseta Tamás Kőszegi Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2016 1 Average daily water intake and output of a normal adult 2 Approximate contributions to plasma osmolality
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE
 UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
UNIT VI: ACID BASE IMBALANCE 1 Objectives: Review the physiological mechanism responsible to regulate acid base balance in the body i.e.: Buffers (phosphate, hemoglobin, carbonate) Renal mechanism Respiratory
diabetes in adults Metabolic complications of
 Metabolic complications of diabetes in adults Dimitri MARGETIS MD ICU St ANTOINE PARIS Definition Diabetic acidoketosis Serious complication in type I diabetes : Hyperglycemia Metabolic acidosis Acidic
Metabolic complications of diabetes in adults Dimitri MARGETIS MD ICU St ANTOINE PARIS Definition Diabetic acidoketosis Serious complication in type I diabetes : Hyperglycemia Metabolic acidosis Acidic
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter
 Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
Chapter 16 Nutrition, Fluids and Electrolytes, and Acid-Base Balance Nutrition Nutrients Water o Functions Promotes metabolic processes Transporter for nutrients and wastes Lubricant Insulator and shock
DIABETES AND PREGNANCY. CDE Exam Preparation March 22 & 27, 2018 Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE Mentor
 DIABETES AND PREGNANCY CDE Exam Preparation March 22 & 27, 2018 Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE Mentor OBJECTIVES Describe targets for blood glucose in pregnancy Discuss the risks to baby if blood glucose
DIABETES AND PREGNANCY CDE Exam Preparation March 22 & 27, 2018 Presented by Wendy Graham RD CDE Mentor OBJECTIVES Describe targets for blood glucose in pregnancy Discuss the risks to baby if blood glucose
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION
 Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Hyperglycaemic Emergencies GRI EDUCATION LEARNING OUTCOMES Develop and describe your system of blood gas interpretation and recognise common patterns of acid-base abnormality. Describe the pathophysiology
Chapter 2. Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances
 Chapter 2 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances Review of Concepts and Processes The major component of the body is water. Water is located in these compartments: Intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment
Chapter 2 Fluid, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Imbalances Review of Concepts and Processes The major component of the body is water. Water is located in these compartments: Intracellular fluid (ICF) compartment
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1
 Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
Major intra and extracellular ions Lec: 1 The body fluids are solutions of inorganic and organic solutes. The concentration balance of the various components is maintained in order for the cell and tissue
The Endocrine System. Lipid-Soluble Hormones. Bio217 Sp14 Unit 5. Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow
 Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Bio217: Pathophysiology Class Notes Professor Linda Falkow Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Unit V: Endocrine System Disorders Chapter 17 Chap. 17: Mechanisms of Hormonal Regulation Chap. 18: Alterations
Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone
 Adrenal gland Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Cortex 80 % Glucocorticoids Cortisol Sex hormones Androgen Medulla 20% Catecholamines E, NE 1 2 Adrenal cortex hormones Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoids
Adrenal gland Adrenal Hormone Mineralocorticoids Aldosterone Cortex 80 % Glucocorticoids Cortisol Sex hormones Androgen Medulla 20% Catecholamines E, NE 1 2 Adrenal cortex hormones Glucocorticoid Mineralocorticoids
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines. Hyponatraemia in Adults
 Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyponatraemia in Adults Purpose of Guideline The investigation and management of adult patients with newly diagnosed hyponatraemia. Hyponatraemia can
Southern Derbyshire Shared Care Pathology Guidelines Hyponatraemia in Adults Purpose of Guideline The investigation and management of adult patients with newly diagnosed hyponatraemia. Hyponatraemia can
Wk 10. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus
 Wk 10. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 2. Acute complications of DM 1) Hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis Hyperglycemia: glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis 1) Etiology and Risk Factors Taking
Wk 10. Management of Clients with Diabetes Mellitus 2. Acute complications of DM 1) Hyperglycemia and diabetic ketoacidosis Hyperglycemia: glycogenolysis gluconeogenesis 1) Etiology and Risk Factors Taking
With Dr. Sarah Reid and Dr. Sarah Curtis
 5. Headaches 6. Known diabetes 7. Specific high risk groups (ie. Teenagers, children on insulin pumps and those from lower socio-economic status). Episode 63 Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis With Dr. Sarah
5. Headaches 6. Known diabetes 7. Specific high risk groups (ie. Teenagers, children on insulin pumps and those from lower socio-economic status). Episode 63 Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis With Dr. Sarah
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders
 CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM Disorders molecular formula C12H22O11 Major index which describes metabolism of carbohydrates, is a sugar level in blood. In healthy people it is 4,4-6,6 mmol/l (70-110 mg/dl)
DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol. Glycemic Task Force September 2014
 DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol Glycemic Task Force September 2014 Hyperglycemic Crises: Pathophysiology DKA HHS Hyperglycemia DKA HHS Umpierrez, In Shoemaker,
DKA : Diabetic Ketoacidosis & HHS: Hyperlgycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome Protocol Glycemic Task Force September 2014 Hyperglycemic Crises: Pathophysiology DKA HHS Hyperglycemia DKA HHS Umpierrez, In Shoemaker,
Fluids and electrolytes
 Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Body Water Content Fluids and electrolytes Infants have low body fat, low bone mass, and are 73% or more water Total water content declines throughout life Healthy males are about 60% water; healthy females
Pare. Blalock. Shires. shock caused by circulating toxins treatment with phlebotomy. shock caused by hypovolemia treatment with plasma replacement
 Pare shock caused by circulating toxins treatment with phlebotomy Blalock shock caused by hypovolemia treatment with plasma replacement Shires deficit in functional extracellular volume treatment with
Pare shock caused by circulating toxins treatment with phlebotomy Blalock shock caused by hypovolemia treatment with plasma replacement Shires deficit in functional extracellular volume treatment with
The Urinary System 15PART B. PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Urinary System 15PART B Ureters Slender tubes attaching the kidney to the bladder Continuous with
Monitor patient s ability to self-administer insulin. (To evaluate safe administration of drug.)
 Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Nursing Process Focus: Patients Receiving Regular Insulin (Humulin, Novolin) Assessment Prior to administration: Assess any patient allergies. Older forms of insulin are made from beef and pork and may
Endocrine System. Regulating Blood Sugar. Thursday, December 14, 17
 Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Endocrine System Regulating Blood Sugar Stress results in nervous and hormonal responses. The adrenal glands are located above each kidney. Involved in stress response. Stress Upsets Homeostasis Stress
Pathology of pituitary gland. By: Shifaa Qa qa
 Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Pathology of pituitary gland By: Shifaa Qa qa Sella turcica Adenohypophysis (80%): - epithelial cells - acidophil, basophil, chromophobe - Somatotrophs, Mammosomatotrophs, Corticotrophs, Thyrotrophs, Gonadotrophs
Faculty version with model answers
 Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
Faculty version with model answers Urinary Dilution & Concentration Bruce M. Koeppen, M.D., Ph.D. University of Connecticut Health Center 1. Increased urine output (polyuria) can result in a number of
The Mentally Altered Diabetic Diagnosis and Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome Christy Michael, BVMS, MBA
 The Mentally Altered Diabetic Diagnosis and Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome Christy Michael, BVMS, MBA Introduction When a mentally altered patient arrives on the scene at any veterinary
The Mentally Altered Diabetic Diagnosis and Management of Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Syndrome Christy Michael, BVMS, MBA Introduction When a mentally altered patient arrives on the scene at any veterinary
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + )
 Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration in body fluids Precise regulation of ph at
Diabetes Mellitus Case Study
 COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Diabetes Mellitus Case Study Medical Nutrition Therapy By: Emily Lancaster 9/28/2012 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the
COLORADO STATE UNIVERSITY Diabetes Mellitus Case Study Medical Nutrition Therapy By: Emily Lancaster 9/28/2012 [Type the abstract of the document here. The abstract is typically a short summary of the
ADVOCATE CHRIST MEDICAL CENTER DKA (DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS) TREATMENT GUIDELINES
 ADVOCATE CHRIST MEDICAL CENTER DKA (DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS) TREATMENT GUIDELINES DEFINITION -Glucose >250 mg/dl*, anion gap > 16, + ketones * Glucose < 250 does not exclude DKA especially if anion gap >
ADVOCATE CHRIST MEDICAL CENTER DKA (DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS) TREATMENT GUIDELINES DEFINITION -Glucose >250 mg/dl*, anion gap > 16, + ketones * Glucose < 250 does not exclude DKA especially if anion gap >
ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING
 ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING Metabolic Alkalosis 2 factors are responsible for generation and maintenance of metabolic alkalosis this includes a process that raises serum bicarbonate and a process that
ELECTROLYTES RENAL SHO TEACHING Metabolic Alkalosis 2 factors are responsible for generation and maintenance of metabolic alkalosis this includes a process that raises serum bicarbonate and a process that
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences. Endocrinology. (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine
 Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Endocrinology (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine Presented by: Dr. Mona Arekat Prepared by: Ali Jassim Alhashli Case (1):
Kingdom of Bahrain Arabian Gulf University College of Medicine and Medical Sciences Endocrinology (Review) Year 5 Internal Medicine Presented by: Dr. Mona Arekat Prepared by: Ali Jassim Alhashli Case (1):
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE
 Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
Chapter 27: WATER, ELECTROLYTES, AND ACID-BASE BALANCE I. RELATED TOPICS Integumentary system Cerebrospinal fluid Aqueous humor Digestive juices Feces Capillary dynamics Lymph circulation Edema Osmosis
DIABETES MELLITUS. IAP UG Teaching slides
 DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
DIABETES MELLITUS 1 DIABETES MELLITUS IN CHILDREN Introduction, Definition Classification, pathogenesis Clinical features Investigations and diagnosis Therapy and follow up Complications Carry home message
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine. Amal Alamri
 Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Instrumental determination of electrolytes in urine Amal Alamri What is the Electrolytes? Electrolytes are positively and negatively chargedions, Found in Within body's cells extracellular fluids, including
Composition of Body Fluids
 Water and electrolytes disturbances Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances Hao, Chuan-Ming MD Huashan Hospital Sodium balance Hypovolemia Water balance Hyponatremia Hypernatremia Potassium balance Hypokelemia
Water and electrolytes disturbances Fluid and Electrolyte Disturbances Hao, Chuan-Ming MD Huashan Hospital Sodium balance Hypovolemia Water balance Hyponatremia Hypernatremia Potassium balance Hypokelemia
Hyponatraemia- Principles, Investigation and Management. Sirazum Choudhury Biochemistry
 Hyponatraemia- Principles, Investigation and Management Sirazum Choudhury Biochemistry Contents Background Investigation Classification Normal Osmolality General management and SIADH Cases Background Relatively
Hyponatraemia- Principles, Investigation and Management Sirazum Choudhury Biochemistry Contents Background Investigation Classification Normal Osmolality General management and SIADH Cases Background Relatively
HYPONATRAEMIA: NUH GUIDELINE FOR INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT.
 HYPONATRAEMIA: NUH GUIDELINE FOR INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT. HYPONATRAEMIA: SODIUM < 130 MMOL/L SIGNIFICANT. Symptoms/signs usually only occur when sodium < 125 mmol/l. Acute hyponatraemia is less
HYPONATRAEMIA: NUH GUIDELINE FOR INITIAL ASSESSMENT AND MANAGEMENT. HYPONATRAEMIA: SODIUM < 130 MMOL/L SIGNIFICANT. Symptoms/signs usually only occur when sodium < 125 mmol/l. Acute hyponatraemia is less
Hormones by location
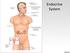 Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
Endocrine System Hormones by location Pineal Gland: Melatonin Feeling of sleepiness Hypothalamus: Hormones that stimulate or inhibit pituitary Temp., hunger, parenting attachment, thirst Pituitary Gland:
For more information about how to cite these materials visit
 Author(s): Roger Grekin, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Author(s): Roger Grekin, M.D., 2009 License: Unless otherwise noted, this material is made available under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Noncommercial Share Alike 3.0 License: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/
Extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment volume control
 Water Balance Made Easier Joon K. Choi, DO. Extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment volume control Humans regulate ECF volume mainly by regulating body sodium content. Several major systems work together
Water Balance Made Easier Joon K. Choi, DO. Extracellular fluid (ECF) compartment volume control Humans regulate ECF volume mainly by regulating body sodium content. Several major systems work together
Name: Oasis: Questions EPCP. Professional Development: Diabetes
 EPCP Professional Development: Diabetes Name: Oasis: Questions 1) Type 1 diabetes in characterized by which of the following: 1) adult onset, obesity 2) juvenile onset, lean build 3) auto-immune beta cell
EPCP Professional Development: Diabetes Name: Oasis: Questions 1) Type 1 diabetes in characterized by which of the following: 1) adult onset, obesity 2) juvenile onset, lean build 3) auto-immune beta cell
Unit 8 Problems of Regulation and Metabolism. Function of the Endocrine system. Example of Negative feedback control. Hormones are controlled by:
 Unit 8 Problems of Regulation and Metabolism Function of the Endocrine system Hormones are controlled by: Negative feedback control Circadian rhythms Stress Example of Negative feedback control Another
Unit 8 Problems of Regulation and Metabolism Function of the Endocrine system Hormones are controlled by: Negative feedback control Circadian rhythms Stress Example of Negative feedback control Another
Vinaya Simha, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Endocrinology
 Vinaya Simha, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Endocrinology Faculty photo will be placed here Simha.aj@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Diabetic Ketoacidosis a few pearls Mayo School of Continuous Professional
Vinaya Simha, M.D. Assistant Professor, Division of Endocrinology Faculty photo will be placed here Simha.aj@mayo.edu 2015 MFMER 3543652-1 Diabetic Ketoacidosis a few pearls Mayo School of Continuous Professional
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Acid-Base Balance Dr. Gary Mumaugh Introduction Acid-base balance is one of the most important of the body s homeostatic mechanisms Acid-base balance refers to regulation of hydrogen ion (H + ) concentration
Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus
 Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Acute Effects of Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: Early Stages Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus:
Chapter 24 Diabetes Mellitus Classification of Diabetes Mellitus Acute Effects of Diabetes Mellitus Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus: Early Stages Chronic Complications of Diabetes Mellitus:
Hyponatraemia: confident diagnosis, effective treatment and avoiding disasters. Dr James Ahlquist Endocrinologist Southend Hospital
 Hyponatraemia: confident diagnosis, effective treatment and avoiding disasters Dr James Ahlquist Endocrinologist Southend Hospital Hyponatraemia: a common electrolyte disorder Electrolyte disorder Prevalence
Hyponatraemia: confident diagnosis, effective treatment and avoiding disasters Dr James Ahlquist Endocrinologist Southend Hospital Hyponatraemia: a common electrolyte disorder Electrolyte disorder Prevalence
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences
 Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S -Regular
Technical University of Mombasa Faculty of Applied and Health Sciences DEPARTMENT OF MEDICAL SCIENCES UNIVERSITY EXAMINATION FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF MEDICAL LABORATORY SCIENCES BMLS 12S -Regular
Scrub In. TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of:
 Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Scrub In TSH is secreted by the pituitary and acts on the: a. Pancreas b. Testes c. Thymus gland d. Thyroid gland Parathormone tends to increase the concentration of: a. Calcium in the blood b. Endorphins
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN
 Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
Acid Base Balance by: Susan Mberenga RN, BSN, MSN Acid Base Balance Refers to hydrogen ions as measured by ph Normal range: 7.35-7.45 Acidosis/acidemia: ph is less than 7.35 Alkalosis/alkalemia: ph is
Basic approach to: Hyponatremia Adley Wong, MHS PA-C
 2016 Topics in Acute and Ambulatory Care CAPA Conference 2018 for Advanced Practice Providers Basic approach to: Hyponatremia Adley Wong, MHS PA-C Goals Physiology of hyponatremia Why we care about hyponatremia
2016 Topics in Acute and Ambulatory Care CAPA Conference 2018 for Advanced Practice Providers Basic approach to: Hyponatremia Adley Wong, MHS PA-C Goals Physiology of hyponatremia Why we care about hyponatremia
Type 1 Diabetes. Insulin
 Type 1 Diabetes Introduction Type 1 diabetes prevents the body from removing sugar from the blood stream normally. Diabetes can lead to serious health problems if it is not treated. Currently, there is
Type 1 Diabetes Introduction Type 1 diabetes prevents the body from removing sugar from the blood stream normally. Diabetes can lead to serious health problems if it is not treated. Currently, there is
LOW BLOOD GLUCOSE (Hypoglycemia)
 Section Four DAILY CRISES In this section, you will learn about: Low blood glucose High blood glucose Diabetic Ketoacidosis Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome LOW BLOOD GLUCOSE (Hypoglycemia)
Section Four DAILY CRISES In this section, you will learn about: Low blood glucose High blood glucose Diabetic Ketoacidosis Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic Nonketotic Syndrome LOW BLOOD GLUCOSE (Hypoglycemia)
Metabolism of water and electrolytes. 2. Special pathophysiology disturbances of intravascular volume and
 Metabolism of water and electrolytes 1. Physiology and general pathophysiology Compartments of body fluids Regulation of volume and tonicity (osmolality) Combinations of volume and osmolality disorders
Metabolism of water and electrolytes 1. Physiology and general pathophysiology Compartments of body fluids Regulation of volume and tonicity (osmolality) Combinations of volume and osmolality disorders
Body fluids. Lecture 13:
 Lecture 13: Body fluids Body fluids are distributed in compartments: A. Intracellular compartment: inside the cells of the body (two thirds) B. Extracellular compartment: (one third) it is divided into
Lecture 13: Body fluids Body fluids are distributed in compartments: A. Intracellular compartment: inside the cells of the body (two thirds) B. Extracellular compartment: (one third) it is divided into
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis
 Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Kidneys in regulation of homeostasis Assoc. Prof. MUDr. Markéta Bébarová, Ph.D. Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University This presentation includes only the most important terms
Acid-Base Balance 11/18/2011. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulation of Potassium Balance. Regulatory Site: Cortical Collecting Ducts.
 Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Influence of Other Hormones on Sodium Balance Acid-Base Balance Estrogens: Enhance NaCl reabsorption by renal tubules May cause water retention during menstrual cycles Are responsible for edema during
Diseases of the Adrenal gland
 Diseases of the Adrenal gland Adrenal insufficiency Cushing disease vs syndrome Pheochromocytoma Hyperaldostronism What are the layers of the adrenal gland?? And what does each layer produce?? What are
Diseases of the Adrenal gland Adrenal insufficiency Cushing disease vs syndrome Pheochromocytoma Hyperaldostronism What are the layers of the adrenal gland?? And what does each layer produce?? What are
** TMP mean page 340 in 12 th edition. Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2:
 QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
QUESTION Questions 1 and 2 Use the following clinical laboratory test results for questions 1 and 2: Urine flow rate = 1 ml/min Urine inulin concentration = 100 mg/ml Plasma inulin concentration = 2 mg/ml
Hypoglycemia, Sick Days/DKA and Hospitalization
 Hypoglycemia, Sick Days/DKA and Hospitalization General survival skills for your client with diabetes at home and in Hospital Diabetes Canada guidelines for your client with diabetes while they are in
Hypoglycemia, Sick Days/DKA and Hospitalization General survival skills for your client with diabetes at home and in Hospital Diabetes Canada guidelines for your client with diabetes while they are in
Diabetes Mellitus. Raja Nursing Instructor. Acknowledgement: Badil 09/03/2016
 Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Diabetes Mellitus Raja Nursing Instructor 09/03/2016 Acknowledgement: Badil Objective: Define Diabetes Mellitus (DM) & types of DM. Understand the pathophysiology of Type-I & II DM. List the clinical features
Endocrine System. Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs
 Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
Endocrine System Overview Hormones Endocrine Organs Endocrine vs. Exocrine Gland Secretes hormones sweat & saliva Ductless gland has ducts Injects tissue duct is filled Chemistry of Hormones & Physiology
EXCRETION QUESTIONS. Use the following information to answer the next two questions.
 EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
EXCRETION QUESTIONS Use the following information to answer the next two questions. 1. Filtration occurs at the area labeled A. V B. X C. Y D. Z 2. The antidiuretic hormone (vasopressin) acts on the area
Endocrine System. Chapter 9
 Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Endocrine System Chapter 9 Endocrine Organs Hormones Chemical messengers that are released from one tissue and transported through blood to a target tissue. Chemical classification: amino acids, steroids,
Nothing to disclose. Disclosure
 Nothing to disclose. Disclosure Inpatient Management of Diabetes Mellitus Cindy Chin, MD Pediatrics in the Red Rocks 2015 Objectives Name 3 diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus. Understand and apply
Nothing to disclose. Disclosure Inpatient Management of Diabetes Mellitus Cindy Chin, MD Pediatrics in the Red Rocks 2015 Objectives Name 3 diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus. Understand and apply
1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 09/07/16 Ch 1: Intro to Human A & P 1 2. 09/19/16 Ch 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base Balance 5 i 1 09/19/16 Chapter 18: Water, Electrolyte, and Acid-Base
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
 October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
October 2015 Michael T. McDermott MD Director, Endocrinology and Diabetes Practice University of Colorado Hospital Case History HPI: 24 yo man with recent 8 lb. weight loss, increased thirst and frequent
Diuretic Agents Part-2. Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia
 Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
Diuretic Agents Part-2 Assistant Prof. Dr. Najlaa Saadi PhD Pharmacology Faculty of Pharmacy University of Philadelphia Potassium-sparing diuretics The Ion transport pathways across the luminal and basolateral
