EFFECTS OF RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING ON VENTILATION AND ENDURANCE PERFORMANCE OF ACTIVE MALE STUDENTS
|
|
|
- Arlene Melinda Phillips
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EFFECTS OF RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING ON VENTILATION AND ENDURANCE PERFORMANCE OF ACTIVE MALE STUDENTS *Mohammad Khazaei, Seyyed Amir Mousavi Mofakher, Naser Behpour and Ahmad Hematfar Department of Physical Education and Sports Science, Islamic Azad University, Boroojerd Branch, Boroojerd, Iran *Author for Correspondence ABSTRACT Respiratory system, including the lungs, respiratory muscles, and the nervous control, compound and complex physiological unit in order to survive in life, you have 24 hours a day and cycle through strictly controlled and coordinated work. s, unlike muscles in everyday life should be repeated, approximately 12 to 20 beats per minute contract. The essential function of the respiratory muscles, while promoting exercise routine observations should be respiratory muscle fatigue because it can precipitate or occur aggravate respiratory insufficiency or failure. If respiratory muscles are very weak, muscle strengthening exercises can be part of endurance. Improved outcome of respiratory muscle function, exercise performance, and exercise in relation to the whole body, there are many contradictory results and some studies have reported significant improvements and others have shown a slight improvement or no improvement in person s physical functioning reported that arises in this regard, this study is intended in a double-blind, placebo-controlled sham group exercises, effects of respiratory muscle on ventilation and endurance performance time trial performance is evaluated. Keywords: Respiratory Muscles, Ventilation Function, Endurance, Active Male Students INTRODUCTION s are responsible for breathing more work. At the rest, about 12 liters of air per minute enters into the body through the respiratory system, this amounts reaches to 150 liters per minute during intense exercise, and on elite athletes to even 220 liters per minute. So, obviously the respiratory system during exercise and sports activities, the pressure can be fairly large. for the first time since the late 1980s was proposed by Allison Mack O Connell, a doctor at the University of Birmingham, has attracted considerable attention. Understanding the effects of respiratory muscle on aerobic and anaerobic performance is very important in the physiology of human performance such supplementary may have the potential to improve the performance by improving lung volumes and capacities affected (28). This is also important from a clinical point because respiratory muscle in obstructive pulmonary disease often can be implemented as part of a treatment plan. Several recent studies in healthy subjects have shown that specialized of respiratory muscles and increase endurance performance, at least when in practice, functional test requires 70 to 80 percent of maximum capacity or slightly lower (2, 3, 16, 19, 20, 30, 31). Further studies have been studied the effect of exercise on respiratory muscle strength and endurance is very intense (85 to 95% of maximum capacity) (6, 13, 21, 37) and have not observed consistent effect on performance. Therefore, it may appear that while specialized to improve athletic performance and endurance of respiratory muscles, is leading to Intensity below 85% of the maximum capacity of the individual. Almost all of the above exercise test to assess the effects of respiratory muscle on endurance performance has used them, that were in constant workload and exhaustion was the criterion session (open ended). These exercises, which are related to the subjective sense of individual failure, Intensity range and repeat the test on the same subject, can produce variable results up to even 30% (14, 29). On the other hand, some researchers in the field of performance-based tests (performance oriented) have been used. These procedures are usually tried when (time trial) are implemented the subject with the maximum amount of work or a certain distance and speed might be doing. The big advantage of working is in a reproducible (coefficient of variation of one to four percent) (25, 26). Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1270
2 The Importance and Necessity of Research It is believed that the respiratory muscle can improve the performance of respiratory muscles in healthy subjects. And submaximal exercise performance is also boosted. For example, Mac O Connell, using techniques pioneered the IMT, has shown that using the device of Power Breathe Respiratory muscle strength as much as 30 to 50 percent, even with a lead of 30 breaths twice a day is effective. Although many studies in healthy subjects after respiratory muscle to improve endurance performance, whole-body (Butler and Pioko, 1992, Butler et al., 1992, Spengler et al., 1999; Makarov et al., 2001, Stosy et al., 2001) and the Extreme Trail of Time in short-term (Vilyanitis et al., 2001) have been reported, however, several studies also show that the ergogenic and efficient effects of this practice have failed (Morgan et al., 1987; Bellman and Gisero, 1988; Fierebarn et al., 1991, Hanel and Sacher, 1991, Kohl et al., 1997, Unbar et al., 2000; Sonnet et al., 2001). Perhaps the most remarkable thing about this is that most of previous studies of respiratory muscle to assess outcome focused on the performance and almost without exception, time to exhaustion at a fixed percentage of the workload and maximal oxygen consumption were examined. Such voluntary actions with endpoints (end the practice by saying voluntary exhaustion), to be competitive endurance performance cannot be accurately represented and reagent (low external validity) and not stable (Hopkins et al., 1999) have been criticized. Between individual differences in scale and size of area with a small sample size can be partially the report describes an improvement in exercise capacity but contribute reaching the level of significance in some studies (6, 10, and 29). Of these, some research on the use of matched control groups have not been successful in their experimental design (2, 3, and 30). In the studies that used a control group, similar exercises actual control group but there was no time to do (6, 16, 19, 21, and 31) and the intervention subjects were not applied in a blinded manner. A double-blind, placebo-controlled studies of the project have not low internal validity and potential of the subject and experimenter bias potential effects have been criticized. Given all the foregoing, and considering that the country has a study using IMT Threshold effects of respiratory muscle has not reviewed, the present study aims in a double-blind, placebo-controlled sham group exercises, the impact of such on ventilation and endurance performance time trial performance is evaluated. Research Aims Objective: The effects of respiratory muscle endurance on ventilation and endurance performance in healthy male university students activation. Research Hypotheses 1. endurance on maximum oxygen consumption has a significant impact on male students. 2. endurance on the 8-kilometer time trial in active male students, there were significant effects. 3. Endurance of respiratory muscles in active male students, there were significant effects on tidal volume. Theoretical Research Theoretical study includes fundamentals of breathing, respiratory assessment, lung volumes and capacities. Respiration Normal breathing is relaxed by contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostal. During exhalation, the diaphragm relaxes and slowly returns to its elastic state, chest wall and the lung-abdominal structures push the air out of there. Many factors can contribute to poor lung function, including smoking habits, history of surgery, accident risk, asthma, allergies, chronic pulmonary obstruction and obesity. The natural structure of the chest caused low gas exchange in circulation and respiration, excretion, as well as less carbon dioxide and less oxygen is absorbed. Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1271
3 Respiratory System A person can live even weeks without food, days without water but only minutes without oxygen. The respiratory system is redemptive to deliver oxygen to the body connection. It includes the diaphragm and chest muscles, nose, mouth, pharynx and trachea, and lungs Bronchiole. Function of Respiratory System Respiratory exchange, including the trachea, left and right lung and two in the bronchial airway branching and Bronchiole. The main purpose of the air navigation respiratory is to exchange between the external environment and the respiratory unit for allowing the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. Lung Lung is a unique organ not only a means of delivering oxygen from the air to the blood and removing carbon dioxide from the blood supply but it is also capable of metabolism and detoxify a wide range of materials, protection against infectious diseases and environmental pollution and certain key composition is like surface tension in the lungs and prostaglandins helps to keep the infectious interaction is important in practice. Pulmonary Function Test Pulmonary function test (PFT) consists of a number of direct and indirect measurements to describe the physiology of breathing. This plays an essential role in the recognition and measurement guidance in patients with respiratory disease or at risk for respiratory illness. Spirometric lung function test is the main element that directly exhaled the volume of air (exhaled) or tail by participants as a function of time as one of the most important measures and screening tools for lung disease and air flows, volumes and capacities expiratory pressure during one-lung measures. Types of Spirometric Tests 1) Ring size chart or flow (flow volume loop) 2) Push vital capacity (FVC) 3) Vital capacity (VC) 4) Maximum Voluntary Ventilation (MVV) Figure 2-1: Spiro grams or normal maximum breathing flow-volume curve Literature Given that this has not been discussed in the country studies, the present study suggests that the effect of respiratory muscle endurance on ventilation and endurance performance in healthy male students actively examine. External Investigations Goenteh et al., (2006) emphasized that the respiratory muscle has been an effective method to increase respiratory muscle strength and improve athletic performance, to evaluate the effects of respiratory muscle on time to exhaustion and cycling determine any potential effect of gender on this hypothesis, a similar improvement in maximal inspiratory pressure and cycling time lag to make men and women as a result of respiratory muscle put to the test. They conclude that the respiratory muscle, maximal inspiratory pressure increases and improves athletic performance but recovery is variable and there is no difference of opinion between men and women. Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1272
4 Inspiratory muscle significantly improved forced expiratory volume in one second strong inspiratory and expiratory volume in one second in vigorous exercise, which was higher than the results of dummy exercises. Significant improvements have been reported in the performance of ventilation, respiratory capacity, and ventilation threshold in both groups. A trend toward improvement (08/0 = p) in swim speed was observed after 12 weeks. The present study examines the effects of respiratory muscle on ventilation and endurance performance of the active male students. Sample The research students constitute the active male of those 24 student volunteers selected to complete the consent form and randomly divided into two groups of 12 experimental ( of respiratory muscles) or placebo control (sham exercise). MATERIALS AND METHODS Method Overview of the experimental design of the study is shown in the following figure: Figure 1: Overview of the research protocol Breathing Exercises Third session )1 Eight weeks of respiratory )2 muscle : day two 30 series of respiratory intensity of 50% maximal inspiratory pressure, with a ten minute break Recorded daily physical activity )2 test the function )1 of trial 8km Time Introduction to )2 the practice of respiratory muscles Second session 1) Learn how to perform the function of trial 8km Time 2) Introduction to the practice of respiratory muscles First session anthropometric )1 Breathing Survey )2 Measurement of )3 maximum oxygen consumption Statistical Methods To examine the differences between the two groups at pre-test and post-test, independent t test, and the difference between pre-test and post-test for each group of dependent groups T test was used. Deviation from pre-test to post-test among the groups will be discussed using independent t-tests. KS test for normal distribution of data and homogeneity of variances of the two groups will be determined by Levine test. 05/0 zero level benchmark test hypotheses and research where a significant difference, the smallest level of significance will be calculated and reported. Descriptive Analysis of Data View homogeneous groups of subjects and the results are shown in the following table: Table 4-1: Information about the homogeneity indices of body composition Significance level T observed mean ±SD Group 0/988 0/976 0/989 0/025 0/046 0/ /55± 5 / 65 83± 6 / /15± 1 / /83± 5 / /81± 4 / /16± 4 / 65 experimental control experimental control experimental control Variable Weight (kg) BFP Lean body weight (Kg) Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1273
5 As can be seen, of the lean body mass that can be a factor in making a difference in the performance and effectiveness of the participants, there was no significant difference between the two groups and all of the above are considered homogeneous groups. In this case, if the change occurs in the test results between the two groups, it can be more likely attributed to the effects of the independent variables. After ensuring the homogeneity of the two groups, and then apply the independent variables in the two groups, the statistical analysis was performed to test the hypothesis as follows. Inferential Analysis of Data To determine the appropriate statistical methods to compare the mean (parametric or nonparametric), normal distribution of data was checked using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test, if you are the preconditions to ensure the application of t-test, paired T test to compare means between groups of pre-test and post-test in both groups. And the independent samples of T test compare means between the two groups at pre-test and post-test should be used. The results of the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test for normal distribution data presented in the table below. Where the level was significantly higher than that of the normal distribution of data has 05/0: Table 4-2: Results of Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. α Z Stage Group 0/871 0/734 0/654 0/628 0/872 0/788 0/354 0/782 0/990 0/764 0/761 0/748 0/817 0/853 0/794 0/762 0/934 0/678 0/971 0/678 0/735 0/671 0/465 0/750 0/764 0/653 0/874 0/563 0/442 0/873 0/834 0/678 0/854 0/545 0/674 0/655 0/459 0/488 0/834 0/663 Measured factors Inspiratory muscle strength )Inches of water( Vital capacity )L( Tidal volume )L( Maximal oxygen consumption Ml per kilogram per ( )minute km time trial -8 performance )Min( Statistical Analysis of Hypotheses Hypothesis 1: endurance on maximal oxygen consumption did not significantly affect the active male students. The variations in the pre- and post-test results of the two groups are shown in the following table: Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1274
6 Table 4-3: The maximum oxygen consumption in the two groups Significance level T observed Group 0/71 1/ /58±2/ 84 46/1±2/9* 0/672 2/ 12 46/73±2/ 02 46/26±1/ 8 Dummy practice Maximal oxygen consumption (Ml kg per minute) * Mean ± standard deviation - 1/592 0 /812-1/767 0/764 T observed Significance level The results show that: A) The results of the pretest and posttest control group showed no significant difference. This means that the mock exercise, aerobic power, subjects had no significant change. B) The results of pre-test and post-test showed no significant difference in the respiratory muscle on respiratory muscle, aerobic power, and subjects had no significant change. C) Comparing pre- and post-test showed that no significant differences existed between the groups at any stage. The results are shown in the following figure. Figure 4-1: Aerobic capacity in the pre-test and post-test Hypothesis 2: The respiratory muscle endurance on the 8-kilometer time trial in healthy male university students activation is not significantly affected. Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1275
7 Table 4-4: The trial timeout of 8 km in the two groups Post- test Significance T Observed level T Group 0/786-0/ /12±1/ 73 37/33±1/82* 0/134-1/ /13±1/ 88 36/50±1/ 87 0/436 0/ 589 Dummy Practice T T observed Time travel 8 km )Min( * mean ± standard deviation 0/721 0/ 774 significance level The results show that: A) The results of the pre-test and post-test control group showed no significant difference. This means that a dummy, performance 8-kilometer time trial subjects had no significant change. B) The study of pre- and post- test results showed no significant difference between groups. This means that respiratory muscle, performance 8-kilometer time trial subjects had no significant change. C) Comparing pre- and post-test showed that no significant differences existed between the groups at any stage. The results are shown in the following figure. Figure 4-2: The 8-kilometer time trial in the pre-test and post-test Hypothesis 3: endurance on inspiratory muscle strength did not significantly affect the active male students. Table 4-5: Changes in blood lactate concentration at maximal test groups Significance T Group level observed 0/024 5/825 Respiratory 180 /24±0/ /15±2/26* muscle 0/651 1/223 * mean ± standard deviation. Practice Dummy 137/2±2/19 135/29±1/ 87 5/231 0/1377 obsrved T 0/03 0/675 Significance level I inspiratorymuscle e strength )Inches of water( Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1276
8 Figure 4-3: Inspiratory muscle strength in the pre-test and post-test The results show that: A) The results of the pretest and posttest control group showed no significant difference. This means that a dummy, inspiratory muscle strength in subjects is not significantly changed. B) To evaluate pre- and post-test results showed significant differences between groups. Inspiratory muscle on respiratory muscle strength increased significantly. C) Comparing pre- and post-test showed that although there was no significant difference between the two groups in the pre-test and post-test, the experimental group was significantly higher than inspiratory muscle strength dummy. The results are shown in the above diagram: Conclusion As we said, it does not seem that the athletic performance is limited by ventilation or respiratory muscle function, the incidence of respiratory muscle fatigue after submaximal and maximal exercise of short duration have been reported, somewhat suggests that ventilation system may be involved in limiting exercise performance. Statistical analysis and hypothesis testing showed that although the inspiratory muscle strength was significantly improved as a result of workout but has no significant change in tidal volume and vital capacity and exercises have significant influence on endurance performance was not subjects in 8km time trial. Based on the results of this research include tidal volume and ventilation function, there was no significant change in vital capacity was significantly increased, but the peak inspiratory muscles. Romer et al., (2002) in a double-blind study with a control scheme contrived by the group practice (as in the present study) found that over 16 trained cycling following respiratory muscle with a pressure threshold device (such as a device that is used in the present study) showed no significant change in ventilation function The dynamic performance is significantly improved in respiratory muscles. Research results have also been implicated in such effects. Research Suggestions 1. The simple breathing exercises and little time to devote to these exercises, considering the impact of the on respiratory function dynamically recommended minimum if athletes to improve their practice of these exercises are not used, minimum warm-up exercises apply to their specialized respiratory muscles. REFERENCES Belman MJ and Gaesser GA (1988). Ventilatory muscle in the elderly. Journal of Applied Physiology Boutellier U, Bachel R, Kunder A and Spengler C (1992). The respiratory system as an exercise limiting factor in normal trained subjects. European Journal of Applied Physiology Boutellier U and Piwko P (1992). The respiratory system as an exercise limiting factor in normal sedentary subjects.. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1277
9 Bye PT, Esau SA, Walley KR, Macklem PT and Pardy RL (1984). Ventilatory muscles during exercise in air and oxygen in normal men. Journal of Applied Physiology Fairbarn MS, Coutts KC, Pardy RL and McKenzie DC (1991). Improved respiratory muscle endurance of highly trained cyclists and the effects on maximal exercise performance. International Journal of Sports Medicine Geddes EL, Reid WD, Crow J, O Brien K and Brooks D (2005). Inspiratory muscle in adults with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a systematic review. Respiratory Medicine Gething AD, Williams M and Davies B (2044). Inspiratory resistive loading improves cycling capacity: a placebo controlled trial. British Journal of Sports Medicine Hanel B and Secher NH (1991). Maximal oxygen uptake and work capacity after inspiratory muscle : a controlled study. Journal of Sports Science Holm P, Sattler A and Fregosi F (2004). Endurance of respiratory muscles improves cycling performance in fit young cyclists. BMC Physiology 4 9. Hopkins WG, Hawley JA and Burke LM (1999). Design and analysis of research on sport performance enhancement. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise Inbar O, Weiner P, Azgad Y, Rotstein A and Weinstein Y (2000). Specific inspiratory muscle in well-trained endurance athletes. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise Jeukendrup A, Saris WH, Brouns F and Kester AD (1996). A new validated endurance performance test. Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise Klusiewicz A, Borkowski L, Zdanowicz R, Boros P and Wesolowski S (2008). The inspiratory muscle in elite rowers. Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness 48(3) Kohl J, Koller EA, Brandenberger M, Cardenas M and Boutellier U (1997). Effect of exercise induced hyperventilation on airway resistance and cycling endurance. European Journal of Applied Physiology and Occupational Physiology Leith DE and Bradley M (1976). Ventilatory muscle strength and endurance. Journal of Applied Physiology Loke J, Mahler DA and Virgulto JA (1982). fatigue after marathon running. Journal of Applied Physiology 52(4) Copyright 2014 Centre for Info Bio Technology (CIBTech) 1278
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
The effects of different inspiratory muscle training intensities on exercising heart rate and perceived exertion
 Eur J Appl Physiol (2004) 92: 50 55 DOI 10.1007/s00421-004-1044-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A. D. Gething Æ L. Passfield Æ B. Davies The effects of different inspiratory muscle training intensities on exercising
Eur J Appl Physiol (2004) 92: 50 55 DOI 10.1007/s00421-004-1044-2 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A. D. Gething Æ L. Passfield Æ B. Davies The effects of different inspiratory muscle training intensities on exercising
Breathing and pulmonary function
 EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
EXPERIMENTAL PHYSIOLOGY EXPERIMENT 5 Breathing and pulmonary function Ying-ying Chen, PhD Dept. of Physiology, Zhejiang University School of Medicine bchenyy@zju.edu.cn Breathing Exercise 1: Tests of pulmonary
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
The impact of hill training on middle and long distance athletes: with specific reference to oromia water works athletics club, Ethiopia
 International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 11, November 2017 287 The impact of hill training on middle and long distance athletes: with specific reference to oromia
International Journal of Scientific and Research Publications, Volume 7, Issue 11, November 2017 287 The impact of hill training on middle and long distance athletes: with specific reference to oromia
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
Effect of a 12-Week Awimming-Training on Spirometric parametersvariables in Teenage Females
 International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education Volume 1 Number 2 Article 2 5-1-2007 Effect of a 12-Week Awimming-Training on Spirometric parametersvariables in Teenage Females Maija Rumaka Riga
International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education Volume 1 Number 2 Article 2 5-1-2007 Effect of a 12-Week Awimming-Training on Spirometric parametersvariables in Teenage Females Maija Rumaka Riga
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Effects of Different Types of Respiratory Muscle Training on Exercise Performance in Runners
 MILITARY MEDICINE, 177, 5:559, 2012 Effects of Different Types of Respiratory Muscle Training on Exercise Performance in Runners Hiromi Uemura, MS*; Claes E.G. Lundgren, MD, PhD*; Andrew D. Ray, BS, MS,
MILITARY MEDICINE, 177, 5:559, 2012 Effects of Different Types of Respiratory Muscle Training on Exercise Performance in Runners Hiromi Uemura, MS*; Claes E.G. Lundgren, MD, PhD*; Andrew D. Ray, BS, MS,
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology
 Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
Asthma Management Introduction, Anatomy and Physiology University of Utah Center for Emergency Programs and The Utah Asthma Program Incidence, Impact and Goals of Asthma Management Prevalence, Morbidity
Overview. The Respiratory System. Chapter 18. Respiratory Emergencies 9/11/2012
 Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
Chapter 18 Respiratory Emergencies Slide 1 Overview Respiratory System Review Anatomy Physiology Breathing Assessment Adequate Breathing Breathing Difficulty Focused History and Physical Examination Emergency
#8 - Respiratory System
 Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
Page1 #8 - Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Equipment: Remember to bring photographic atlas. Figure 1. Structures of the respiratory system.
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES
 PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
PULMONARY FUNCTION. VOLUMES AND CAPACITIES The volume of air a person inhales (inspires) and exhales (expires) can be measured with a spirometer (spiro = breath, meter = to measure). A bell spirometer
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Respiratory System Mechanics
 M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
M56_MARI0000_00_SE_EX07.qxd 8/22/11 3:02 PM Page 389 7 E X E R C I S E Respiratory System Mechanics Advance Preparation/Comments 1. Demonstrate the mechanics of the lungs during respiration if a bell jar
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
The cardiovascular and respiratory system
 The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
The cardiovascular and respiratory system For this unit you need to be able to... Learning Outcomes: Covered? Confident? Understand and be able to give sporting examples of when each respiratory system
RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING
 RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING RESPIRATORY MUSCLE FATIGUE RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING During heavy exercise, breathing frequency rises to 40 to 50 breaths per minute. Tidal volume is 3 to 4 litres. This gives
RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING RESPIRATORY MUSCLE FATIGUE RESPIRATORY MUSCLE TRAINING During heavy exercise, breathing frequency rises to 40 to 50 breaths per minute. Tidal volume is 3 to 4 litres. This gives
Performance Enhancement. Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance
 Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Performance Enhancement Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems and Athletic Performance Functions of the Cardiovascular System Deliver oxygen & nutrients to body tissues Carry wastes from the cells Anatomy
Ch 16 A and P Lecture Notes.notebook May 03, 2017
 Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
Table of Contents # Date Title Page # 1. 01/30/17 Ch 8: Muscular System 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 02/14/17 Ch 9: Nervous System 12 03/13/17 Ch 10: Somatic and Special Senses 53 03/27/17 Ch 11: Endocrine System
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING. Purposes of Pulmonary Tests. General Categories of Lung Diseases. Types of PF Tests
 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTING Wyka Chapter 13 Various AARC Clinical Practice Guidelines Purposes of Pulmonary Tests Is lung disease present? If so, is it reversible? If so, what type of lung disease is present?
Repeated abdominal exercise induces respiratory muscle fatigue
 Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2009) 8, 543-547 http://www.jssm.org Research article Repeated abdominal exercise induces respiratory muscle fatigue Christopher L. Gomez, Lisa M. Strongoli and
Journal of Sports Science and Medicine (2009) 8, 543-547 http://www.jssm.org Research article Repeated abdominal exercise induces respiratory muscle fatigue Christopher L. Gomez, Lisa M. Strongoli and
Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men
 ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 8 (August-2014) pp. 85-90 www.ijcrar.com Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men M.Muralikrishna and P.V. Shelvam*
ISSN: 2347-3215 Volume 2 Number 8 (August-2014) pp. 85-90 www.ijcrar.com Effect of different intensities of aerobic training on vital capacity of middle aged obese men M.Muralikrishna and P.V. Shelvam*
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Humans:
 A. K. McConnell 1 Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Humans: L. M. Romer 2 Resolving the Controversy Abstract Specific respiratory muscle training offers the promise of improved exercise tolerance
A. K. McConnell 1 Respiratory Muscle Training in Healthy Humans: L. M. Romer 2 Resolving the Controversy Abstract Specific respiratory muscle training offers the promise of improved exercise tolerance
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
What is RESPIRATION?
 Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Respiration 1 What is RESPIRATION? Lung animation the production of energy (ATP) Definition-the exchange of CO2 and O2 AND it s also (it s NOT just breathing. It is also the release of energy by our cells!)
Cardiovascular Learners MUST KNOW R A G. Know the double- circulatory system (systemic and pulmonary)
 Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Please do the following 1. Read the Learners must know section (see below) 2. Watch the GCSE POD video 3. Attempt Exam Questions 4. Mark your answers 5. Reflect and repeat until you are successful and
Unit 14: The Respiratory System
 Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
Unit 14: The Respiratory System See what you already know! 1. Fill in the diagram on your own 2. Collaborate with your partner The Respiratory System The major function of the respiratory system is gas
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide
 RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
RESPIRATORY PHYSIOLOGY Pre-Lab Guide NOTE: A very useful Study Guide! This Pre-lab guide takes you through the important concepts that where discussed in the lab videos. There will be some conceptual questions
Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes
 Respiratory Exercise Response Chapter 11 Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes Submaximal (
Respiratory Exercise Response Chapter 11 Exercise Respiratory system Ventilation rate matches work rate Not a limiting factor Elite athletes Submaximal (
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
+ Asthma and Athletics
 + Asthma and Athletics Shaylon Rettig, MD, MBA Champion Sports Medicine + Financial Disclosure Dr. Shaylon Rettig has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. + Asthma
+ Asthma and Athletics Shaylon Rettig, MD, MBA Champion Sports Medicine + Financial Disclosure Dr. Shaylon Rettig has no relevant financial relationships with commercial interests to disclose. + Asthma
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
Chapter 3. Pulmonary Function Study Assessments. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
Chapter 3 Pulmonary Function Study Assessments 1 Introduction Pulmonary function studies are used to: Evaluate pulmonary causes of dyspnea Differentiate between obstructive and restrictive pulmonary disorders
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests
 6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
6- Lung Volumes and Pulmonary Function Tests s (PFTs) are noninvasive diagnostic tests that provide measurable feedback about the function of the lungs. By assessing lung volumes, capacities, rates of
PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS
 Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
Chapter 4 PULMONARY FUNCTION TESTS M.G.Rajanandh, Department of Pharmacy Practice, SRM College of Pharmacy, SRM University. OBJECTIVES Review basic pulmonary anatomy and physiology. Understand the reasons
#7 - Respiratory System
 #7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
#7 - Respiratory System Objectives: Study the parts of the respiratory system Observe slides of the lung and trachea Perform spirometry to measure lung volumes Define and understand the lung volumes and
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science. Learning Outcomes
 IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
IB Sports, Exercise and Health Science Learning Outcomes 1 TOPIC 1: ANATOMY 1.1. THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1.1.1 Distinguish anatomically between the axial and appendicular skeleton. 1.1.2 Distinguish between
Respiratory System. Student Learning Objectives:
 Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
Respiratory System Student Learning Objectives: Identify the primary structures of the respiratory system. Identify the major air volumes associated with ventilation. Structures to be studied: Respiratory
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan
 Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning How can the cardio-respiratory system aid the human body in physical activity
Year 10 Physical Education LC1 Medium Term Plan Overarching challenge question Exam board links Line of enquiry s Home learning How can the cardio-respiratory system aid the human body in physical activity
COMPREHENSIVE RESPIROMETRY
 INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
INTRODUCTION Respiratory System Structure Complex pathway for respiration 1. Specialized tissues for: a. Conduction b. Gas exchange 2. Position in respiratory pathway determines cell type Two parts Upper
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
Chapter 13. The Respiratory System.
 Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
Chapter 13 The Respiratory System https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hc1ytxc_84a https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9fxm85fy4sq http://ed.ted.com/lessons/what-do-the-lungs-do-emma-bryce Primary Function of Breathing
MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE:
 MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE: WHAT IS HEALTHY ACTIVE LIVING? Before starting off on a journey, you need to know what your starting point is. This exercise will
MY SPORTFOLIO ISM PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND FITNESS TEACHER: BLOCK: GRADE: WHAT IS HEALTHY ACTIVE LIVING? Before starting off on a journey, you need to know what your starting point is. This exercise will
Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology
 Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Title: Spirometry Teacher : Dorota Marczuk Krynicka, MD., PhD. Coll. Anatomicum, Święcicki Street no. 6, Dept. of Physiology I. Measurements of Ventilation Spirometry A. Pulmonary Volumes 1. The tidal
Station A: YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament. Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5.
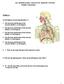 YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
GAS EXCHANGE IB TOPIC 6.4 CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM. Terminal bronchiole Nasal cavity. Pharynx Left lung Alveoli.
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts
 Pulmonol. 2018;24(4):219-223 www.journalpulmonology.org BRIEF COMMUNICATION Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts B. Lazovic a,f,, M. Zlatkovic-Svenda b,f,
Pulmonol. 2018;24(4):219-223 www.journalpulmonology.org BRIEF COMMUNICATION Comparison of lung diffusing capacity in young elite athletes and their counterparts B. Lazovic a,f,, M. Zlatkovic-Svenda b,f,
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2
 Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Aerobic and Anaerobic Respiration Revision 2 65 minutes 65 marks Page of 23 Q. A person did five different activities in turn. These activities needed increasing amounts of energy. For each activity two
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review
 Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
Unit 2 7 th Science NCFE Review. How are cells organized? Ø Complex living things are organized into 5 levels. Ø Cells carry on the processes that keep us alive. Examples: Red Blood Cells Muscle Cells
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE
 IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
IB TOPIC 6.4 GAS EXCHANGE CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM CARDIOPULMONARY SYSTEM Branch from the pulmonary artery (oxygen-poor blood) Branch from the pulmonary vein (oxygen-rich blood) Terminal bronchiole Nasal
Chapter 14: Improving Aerobic Performance
 Chapter 14: Improving Aerobic Performance Thought Questions Why would aerobic athletes perform resistance training exercises? What are advantages and disadvantages of Fartlek training? What are advantages
Chapter 14: Improving Aerobic Performance Thought Questions Why would aerobic athletes perform resistance training exercises? What are advantages and disadvantages of Fartlek training? What are advantages
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION
 Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
Overview of COPD INTRODUCTION Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a common lung disease that affects millions of people, and it is the fourth leading cause of death in the United States. It
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY
 Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
Biology 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Unit Quiz Preparation KEY Learning Goals: 1. I will be able to explain the role of acids, bases and bases in the body 2. I will be able to explain the structures and functions
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
BURNOUT The Overtraining Syndrome in Swimming
 BURNOUT The Overtraining Syndrome in Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Introduction There are numerous terms associated with a state of poor or diminished sporting performance; burnout, staleness, chronic fatigue,
BURNOUT The Overtraining Syndrome in Swimming Dr Ralph Richards Introduction There are numerous terms associated with a state of poor or diminished sporting performance; burnout, staleness, chronic fatigue,
Understanding Breathing Muscle Weakness
 Understanding Breathing Muscle Weakness A N D R E A L. K L E I N P R E S I D E N T / F O U N D E R B R E A T H E W I T H M D w w w.facebook.com/ b r e a t h e w i t h m d h t t p : / / w w w. b r e a t
Understanding Breathing Muscle Weakness A N D R E A L. K L E I N P R E S I D E N T / F O U N D E R B R E A T H E W I T H M D w w w.facebook.com/ b r e a t h e w i t h m d h t t p : / / w w w. b r e a t
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
ATHLETES, YOGIS AND INDIVIDUALS WITH SEDENTARY LIFESTYLES; DO THEIR LUNG FUNCTIONS DIFFER?
 Indian 76 Prakash J Physiol et Pharmacol al 2007; 51 (1) : 76 80 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2007; 51(1) ATHLETES, YOGIS AND INDIVIDUALS WITH SEDENTARY LIFESTYLES; DO THEIR LUNG FUNCTIONS DIFFER? SHIVESH
Indian 76 Prakash J Physiol et Pharmacol al 2007; 51 (1) : 76 80 Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 2007; 51(1) ATHLETES, YOGIS AND INDIVIDUALS WITH SEDENTARY LIFESTYLES; DO THEIR LUNG FUNCTIONS DIFFER? SHIVESH
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
The Respiratory System Learning Intention What will I know? 1. The function of the respiratory system. 2. The difference between respiration and the breathing. Success Criteria What can I do? 1. State
Analysis of Lung Function
 Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
Computer 21 Spirometry is a valuable tool for analyzing the flow rate of air passing into and out of the lungs. Flow rates vary over the course of a respiratory cycle (a single inspiration followed by
Ventilatory functions response to breathing training versus aerobic training in asthmatic children
 Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012;10(1):33-37. Original article Ventilatory functions response to breathing training versus aerobic training in asthmatic children Background: There is worldwide public
Egypt J Pediatr Allergy Immunol 2012;10(1):33-37. Original article Ventilatory functions response to breathing training versus aerobic training in asthmatic children Background: There is worldwide public
Year 12 BTEC L3 Sport ( )
 Programme of Study Teacher A UNIT 5- Application of Fitness Testing UNIT 5- Application of fitness ing Unit introduction A1: Validity of fitness s Understand what validity means and the application to
Programme of Study Teacher A UNIT 5- Application of Fitness Testing UNIT 5- Application of fitness ing Unit introduction A1: Validity of fitness s Understand what validity means and the application to
AEROBIC METABOLISM DURING EXERCISE SYNOPSIS
 SYNOPSIS This chapter begins with a description of the measurement of aerobic metabolism by direct calorimetry and spirometry and proceeds with a discussion of oxygen drift as it occurs in submaximal exercise
SYNOPSIS This chapter begins with a description of the measurement of aerobic metabolism by direct calorimetry and spirometry and proceeds with a discussion of oxygen drift as it occurs in submaximal exercise
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
The Effects of Simulated Altitude Training on Aerobic Capacity and Function
 International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 6, No. 2; June 2016 The Effects of Simulated Altitude Training on Aerobic Capacity and Function Matthew T. Maher, MS, CEP William Paterson University
International Journal of Applied Science and Technology Vol. 6, No. 2; June 2016 The Effects of Simulated Altitude Training on Aerobic Capacity and Function Matthew T. Maher, MS, CEP William Paterson University
The Respiratory System
 Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Respiration and Excretion Name Date Class The Respiratory System This section describes the parts of the respiratory system and how they work to help you breathe and speak. Use Target Reading Skills As
Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics
 8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
8 Study of pulmonary functions in Yoga performing group and non-yogics Dr. Nilay A. Kapadia*, Dr. Ashok Goswami**, Dr. Prakash Chaudhari*, Dr. Kalpan Desai*Dr Janardan V Bhatt @ *P.G.Student, Department
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE
 GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE Content Title: The Long Term Effects of Exercise on the Body Key points Adaptations to the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems. Practical Application/Explanation
GCE PHYSICAL EDUCATION PE2 UNIT GUIDE Content Title: The Long Term Effects of Exercise on the Body Key points Adaptations to the cardiovascular, respiratory and muscular systems. Practical Application/Explanation
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
EFFECTS OF OXYGEN BREATHING ON INSPIRATORY MUSCLE FATIGUE DURING RESISTIVE LOAD IN CYCLING MEN
 JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, Suppl 5, 111-115 www.jpp.krakow.pl M.O. SEGIZBAEVA, N.P. ALEKSANDROVA EFFECTS OF OXYGEN BREATHING ON INSPIRATORY MUSCLE FATIGUE DURING RESISTIVE LOAD IN
JOURNAL OF PHYSIOLOGY AND PHARMACOLOGY 2009, 60, Suppl 5, 111-115 www.jpp.krakow.pl M.O. SEGIZBAEVA, N.P. ALEKSANDROVA EFFECTS OF OXYGEN BREATHING ON INSPIRATORY MUSCLE FATIGUE DURING RESISTIVE LOAD IN
NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ]
![NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ]](/thumbs/76/73199826.jpg) s@lm@n NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] https://certkill.com NBRC RPFT : Practice Test Question No : 1 Using a peak
s@lm@n NBRC Exam RPFT Registry Examination for Advanced Pulmonary Function Technologists Version: 6.0 [ Total Questions: 111 ] https://certkill.com NBRC RPFT : Practice Test Question No : 1 Using a peak
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Anatomy and Physiology
 Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory Diagnostic Procedures 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Bell Work Complete cost of smoking exercise. We will go over this together! (Don t worry)!
Anatomy and Physiology Respiratory Diagnostic Procedures 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. Bell Work Complete cost of smoking exercise. We will go over this together! (Don t worry)!
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
FOLLOW-UP MEDICAL CARE OF SERVICE MEMBERS AND VETERANS CARDIOPULMONARY EXERCISE TESTING
 Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Chapter 13 FOLLOW-UP MEDICAL CARE OF SERVICE MEMBERS AND VETERANS CARDIOPULMONARY EXERCISE TESTING WILLIAM ESCHENBACHER, MD* INTRODUCTION AEROBIC METABOLISM ANAEROBIC METABOLISM
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Chapter 13 FOLLOW-UP MEDICAL CARE OF SERVICE MEMBERS AND VETERANS CARDIOPULMONARY EXERCISE TESTING WILLIAM ESCHENBACHER, MD* INTRODUCTION AEROBIC METABOLISM ANAEROBIC METABOLISM
2015 PHYSICAL EDUCATION
 1 2015 PHYSICAL EDUCATION External Examination 2015 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 16 pages, 7 questions RE-MARKED Thursday 12
1 2015 PHYSICAL EDUCATION External Examination 2015 FOR OFFICE USE ONLY SUPERVISOR CHECK ATTACH SACE REGISTRATION NUMBER LABEL TO THIS BOX QUESTION BOOKLET 1 16 pages, 7 questions RE-MARKED Thursday 12
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. 1. Label the following parts of the respiratory system:
 RSPIRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the respiratory system: 2. In the diagram below, label the types of air volumes with the following terms: tidal volume, vital capacity, residual volume,
RSPIRTORY SYSTM 1. Label the following parts of the respiratory system: 2. In the diagram below, label the types of air volumes with the following terms: tidal volume, vital capacity, residual volume,
Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health
 UNIT 5 Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health The Health Effects of Air Pollution ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION The first part of this activity introduces students to the human respiratory system. Using provided posters
UNIT 5 Our Lungs, Our Air, Our Health The Health Effects of Air Pollution ACTIVITY DESCRIPTION The first part of this activity introduces students to the human respiratory system. Using provided posters
Exercise Stress Testing: Cardiovascular or Respiratory Limitation?
 Exercise Stress Testing: Cardiovascular or Respiratory Limitation? Marshall B. Dunning III, Ph.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine & Physiology Medical College of Wisconsin What is exercise? Physical activity
Exercise Stress Testing: Cardiovascular or Respiratory Limitation? Marshall B. Dunning III, Ph.D., M.S. Professor of Medicine & Physiology Medical College of Wisconsin What is exercise? Physical activity
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Exercise physiology and sports performance
 Klinikum rechts der Isar Technische Universität München Exercise physiology and sports performance Axel Preßler Lehrstuhl und Poliklinik für Prävention, Rehabilitation und Sportmedizin Klinikum rechts
Klinikum rechts der Isar Technische Universität München Exercise physiology and sports performance Axel Preßler Lehrstuhl und Poliklinik für Prävention, Rehabilitation und Sportmedizin Klinikum rechts
International Journal of Physical Education, Fitness and Sports
 INVESTIGATION OF VARIED INTENSITY INTERVAL SPRINT TRAINING AND DETRAINING IMPACT ON SELECTED SPEED PARAMETERS Y. Wise Blessed Singh a,* a Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Annamalai
INVESTIGATION OF VARIED INTENSITY INTERVAL SPRINT TRAINING AND DETRAINING IMPACT ON SELECTED SPEED PARAMETERS Y. Wise Blessed Singh a,* a Department of Physical Education and Sports Sciences, Annamalai
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision
 Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
Year 7 End of Year Exam Revision Physical Education https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=el1_enlemka Starter Video The Exam The exam you will sit is out of 40 marks. 25 of these are multiple choice, 7 are short
SPIROMETRY METHOD. COR-MAN IN / EN Issue A, Rev INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark
 SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
SPIROMETRY METHOD COR-MAN-0000-006-IN / EN Issue A, Rev. 2 2013-07 INNOVISION ApS Skovvænget 2 DK-5620 Glamsbjerg Denmark Tel.: +45 65 95 91 00 Fax: +45 65 95 78 00 info@innovision.dk www.innovision.dk
BEFORE YOU BEGIN. Endurance activities have major positive effects on health, and focus on enhancing the way our cardio-respiratory AIMS
 ENDURANCE BEFORE YOU BEGIN Endurance is a physical ability to withstand exercises that take a long time, whether they are sports or everyday activities, without becoming too tired. Endurance activities
ENDURANCE BEFORE YOU BEGIN Endurance is a physical ability to withstand exercises that take a long time, whether they are sports or everyday activities, without becoming too tired. Endurance activities
Effects of concurrent inspiratory and expiratory muscle training on respiratory and exercise performance in competitive swimmers
 Eur J Appl Physiol (2005) 94: 527 540 DOI 10.1007/s00421-005-1375-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gregory D. Wells Æ Michael Plyley Æ Scott Thomas Len Goodman Æ James Duffin Effects of concurrent inspiratory and expiratory
Eur J Appl Physiol (2005) 94: 527 540 DOI 10.1007/s00421-005-1375-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gregory D. Wells Æ Michael Plyley Æ Scott Thomas Len Goodman Æ James Duffin Effects of concurrent inspiratory and expiratory
B. Correct! As air travels through the nasal cavities, it is warmed and humidified.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 20: The Respiratory System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the portion of the respiratory system labeled in the image below is correct? Question
