14. The nervous system mobilizes the body in response to stress; the nervous system controls the activities of the visceral organs under normal
|
|
|
- Anthony Hancock
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 02 Student: 1. Regulation of the autonomic nervous system occurs via the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. 2. The structures of the limbic system play an important role in emotion. 3. The endocrine system is responsible for fast-acting, short-duration responses to changes in the body. 4. Angina pectoris is most likely to occur when a clot has developed in a coronary vessel and blocks the flow of blood to the heart. 5. Statistics show a dramatic increase in the prevalence of allergic disorders including asthma in the past 20 to 30 years. 6. Hepatitis A is typically transmitted through food and water. 7. Menopause is a disorder of the reproductive system. 8. Genetic risks are magnified because they interact with environmental factors 9. Antigens are proteins produced in response to stimulation by antibodies. 10. Compared to women, men are at greater risk of contracting autoimmune disease. 11. The nervous system as a whole consists of the and the. A. brain; spinal cord B. central nervous system; peripheral nervous system C. somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system D. sensory nervous system; motor nervous system E. brain; central nervous system 12. The peripheral nervous system consists of the and the. A. brain; spinal cord B. central nervous system; peripheral nervous system C. somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system D. forebrain; hindbrain E. somatic nervous system; peripheral nervous system 13. The nervous system connects the central nervous system with all internal organs. A. peripheral B. automatic C. autonomic D. somatic E. sympathetic
2 14. The nervous system mobilizes the body in response to stress; the nervous system controls the activities of the visceral organs under normal conditions. A. parasympathetic; sympathetic B. sympathetic; parasympathetic C. somatic; autonomic D. autonomic; peripheral E. sympathetic; peripheral 15. Damage to the cerebellum is associated with impaired A. muscular coordination. B. respiration. C. speech. D. visual acuity. E. auditory acuity. 16. The is an important transition centre between the thoughts generated in the cerebral cortex of the brain and their impact on internal organs. A. forebrain B. hindbrain C. hypothalamus D. medulla E. primary somatic sensory cortex 17. Mark has been preparing for his graduate school entrance exam for several weeks and is very nervous about how he will perform. In addition to this stress, his girlfriend Jasmine is getting concerned that Mark has not been able to perform in the bedroom lately either. Mark's sexual difficulties due to stress are likely due to the involvement of his in the stress response. A. hypothalamus B. adrenal medulla C. limbic system D. pituitary gland E. parietal lobe 18. The prevalence of is expected to rise to affect over 100 million people worldwide by the year A. Alzheimer's disease B. Huntington's disease C. AIDS D. arthritis E. heart disease 19. Catecholamines are A. exogenes. B. neurotransmitters. C. telecystors. D. arterioles. E. receptors. 20. Secretion of catecholamines A. increases protein and fat mobilization. B. regulates sodium retention. C. increases heart rate and blood pressure. D. stimulates digestion.
3 21. is a chronic, nonprogressive disorder of the nervous system that is marked by lack of muscle control. A. Epilepsy B. Parkinson's disease C. Myasthenia gravis D. Cerebral palsy E. Multiple Sclerosis 22. The gene for has been identified. This allows for at-risk individuals to be tested to ascertain whether they are carriers of this hereditary disorder characterized by chronic physical and mental deterioration due to damaged brain cells. A. Epilepsy B. Myasthenia gravis C. Multiple sclerosis D. Parkinson's disease E. Huntington's disease 23. The nervous system is chiefly responsible for responses to changes in the body; whereas the endocrine system governs mainly responses. A. fast-acting, short-duration; slow-acting, long-duration B. slow-acting, long-duration; fast-acting, short-duration C. fast-acting, long-duration; slow-acting, short-duration D. complementary; antagonistic E. slow-acting, short-duration; fast-acting, long-duration 24. The release of steroids via the adrenal cortex is stimulated by A. epinephrine and norepinephrine. B. glucocorticoids. C. thyrotropic hormone (TSH). D. adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). E. vasopressin. 25. Type I diabetes A. typically occurs after age 40. B. is a condition that occurs when the body fails to produce enough insulin. C. is a condition that occurs when the body is not sufficiently responsive to insulin. D. is primarily managed through dietary and exercise regimens. E. disproportionately affects white males. 26. Conditions associated with diabetes include A. blindness. B. kidney failure. C. coronary heart disease. D. nervous system damage. 27. The carry blood from the heart to oxygenate organs and other tissues. A. arteries B. veins C. capillaries D. ventricles
4 28. is chest pain which occurs because the muscle tissue of the heart must continue its activity without a sufficient supply of oxygen or adequate removal of carbon dioxide and other waste products. A. Angina pectoris B. Myocardial infarction C. Phlebitis D. Arteriosclerosis E. Aneurysm 29. Atherosclerosis is A. associated with angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. B. characterized by a hardening and reduced elasticity of the arterial walls. C. a hereditary disease rather than a disease of lifestyle. D. a type of blood disorder. 30. During, blood is pumped out of the heart, and blood pressure. During, blood is taken into the heart, and blood pressure. A. diastole; increases; systole; decreases B. diastole; decreases; systole; increases C. systole; increases; diastole; decreases D. systole; decreases; diastole; increases E. diastole; decreases; systole; decreases 31. Hypertension is caused by A. high cardiac output. B. highly viscous blood. C. loss of elasticity of the arterial walls. D. too high a peripheral resistance. 32. Approximately 55% of blood volume is composed of A. platelets. B. white blood cells. C. red blood cells. D. plasma. E. hemoglobin. 33. Some individuals are unable to produce thromboplastin and fibrin. This condition is associated with a clotting disorder called A. arteriosclerosis. B. anemia. C. leukopenia. D. hemophilia. E. Erythrocytosis. 34. The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration occurs between the A. bronchi and the capillaries. B. alveoli and the capillaries. C. alveoli and the arteries. D. bronchioles and the alveoli. E. larynx and the bronchus.
5 35. involves a condition in which the alveoli become dilated, atrophied, and thin so that elasticity is lost and exhalation becomes difficult. A. Bronchial pneumonia B. Pleurisy C. Tuberculosis D. Pulmonary emphysema E. Asthma 36. During the digestive process, the absorption of food takes place primarily in the A. stomach. B. duodenum. C. small intestine. D. large intestine. E. transverse colon. 37. Inflammatory bowel disease, A. rates are estimated to be the highest in Canada. B. includes ulcerative colitis. C. includes Crohn's disease. D. rates are highest in Alberta and Nova Scotia. 38. The regulate(s) bodily fluids by removing surplus water, surplus electrolytes, and the waste products generated by the metabolism of food. A. urethra B. bladder C. ureters D. renal system E. hepatic portal system 39. The female hormone, estrogen, A. is secreted by the anterior pituitary. B. is associated with lactation. C. is produced during the second half of the menstrual cycle. D. leads to the development of secondary sex characteristics in the female. 40. The male hormone, testosterone, A. is secreted by the anterior pituitary. B. brings about the primary sex characteristics in the male. C. is produced by the interstitial cells of the testes. D. is produced on a 14 day cycle E. All of these are characteristics of testosterone 41. Approximately percent of Canadian couples experience fertility problems. A. 3 B. 7 C. 10 D. 15 E Which of the following research methods are designed to investigate the relative importance of genetic and environmental factors that contribute to developing medical disorders? A. Studies of identical twins and fraternal twins. B. Studies of identical twins reared apart. C. Studies of adopted children. D. Family studies.
6 43. Prenatal diagnostic tests are currently available that help detect A. epilepsy. B. breast and colon cancer. C. Huntington's disease. D. cerebral palsy. 44. Jack and Jill had unprotected sexual intercourse while Jack had an outbreak of genital herpes. Jill has now also contracted genital herpes. This is an example of A. direct transmission of disease. B. indirect transmission of disease. C. biological transmission of disease. D. mechanical transmission of disease. E. physical transmission of disease. 45. The course of infection follows a specific sequence; that is A. incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, acute phase, period of decline. B. period of nonspecific symptoms, incubation period, acute phase, period of decline. C. acute phase, incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, period of decline. D. incubation period, acute phase, period of decline. E. incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, period of decline, recovery. 46. Lymphocytes play an important role in fighting infection and disease by A. secreting digesting enzymes that dissolve foreign particles. B. producing antibodies that destroy substances through the antigen-antibody reaction. C. secreting platelets that engulf foreign particles so they may be excreted. D. producing monoblasts that increase the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. E. carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. 47. A localized infection A. is confined to a particular site and does not spread. B. is confined to a particular area and sends toxins to other parts of the body. C. occurs when the body's resistance is lowered from fighting a primary infection. D. affects several different areas. 48. Nonspecific immunity may be mediated by the A. skin. B. phagocytes. C. inflammatory response. D. antimicrobial substances. 49. Humoral immunity is mediated by A. B cells. B. helper and suppressor T cells. C. B cells and helper and suppressor T cells. D. phagocytosis. 50. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by A. B cells. B. TC and TH cells. C. B cells and helper and suppressor T cells. D. interferon.
7 51. The spleen A. secretes insulin and bile into the bloodstream. B. produces neurotransmitters and corticosteroids. C. aids in the production of B and T cells and filters the blood. D. is primarily a vestigial organ. E. is a vermiform organ 52. Infectious disorders A. are acute problems that end when their course has run. B. that are kept in control through hygiene may have paradoxically increased the rates of these disorders. C. are not linked to the development of any chronic diseases D. attack only lymphatic tissue. E. All of these are traits of infectious disorders. 53. Autoimmunity A. involves the progressive, chronic enlargement of lymphatic tissue. B. is a viral disorder marked by an unusually large number of monocytes. C. is acquired through measures such as vaccination. D. is a condition in which a specific humoral or cell-mediated immune response attacks the body's own tissue. 54. Autoimmunity may be implicated in A. systemic lupus erythematosis. B. arthritis. C. multiple sclerosis. D. molecular mimicry. 55. Inflammation is also implicated in A. bowel disorders. B. cirrhosis of the liver. C. heart disease in men. D. asthma. 56. Describe the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Include in your answer the roles of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system in response to stress. 57. Describe the structure and function of the cardiovascular system. Include in your answer the internal and external factors influencing heart rate and the impact on heart functioning.
8 58. Describe the nature and symptoms of asthma. Discuss the factors that may contribute to the dramatic rise of asthma in recent years 59. Explain how a health psychologist might employ family studies and twins to study the genetic basis of a health disorder. 60. Compare and contrast nonspecific and specific immune mechanisms. Provide at least two examples of each.
9 1. (p. 23) 02 Key Regulation of the autonomic nervous system occurs via the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. TRUE 2. (p. 25) The structures of the limbic system play an important role in emotion. TRUE Taylor - Chapter 02 #1 3. (p. 23) 4. (p. 29) 5. (p. 32) Taylor - Chapter 02 #2 The endocrine system is responsible for fast-acting, short-duration responses to changes in the body. FALSE Learning Objective: 2 Taylor - Chapter 02 #3 Angina pectoris is most likely to occur when a clot has developed in a coronary vessel and blocks the flow of blood to the heart. FALSE Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #4 Statistics show a dramatic increase in the prevalence of allergic disorders including asthma in the past 20 to 30 years. TRUE 6. (p. 36) 7. (p. 39) 8. (p. 40) 9. (p. 43) Hepatitis A is typically transmitted through food and water. TRUE Menopause is a disorder of the reproductive system. FALSE Genetic risks are magnified because they interact with environmental factors TRUE Antigens are proteins produced in response to stimulation by antibodies. FALSE Learning Objective: 4 Taylor - Chapter 02 #5 Learning Objective: 6 Taylor - Chapter 02 #6 Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #7 Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #8 10. (p. 45) Compared to women, men are at greater risk of contracting autoimmune disease. FALSE Taylor - Chapter 02 #9 Taylor - Chapter 02 #10
10 11. (p. 23) 12. (p. 23) 13. (p. 23) 14. (p. 23) The nervous system as a whole consists of the and the. A. brain; spinal cord B. central nervous system; peripheral nervous system C. somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system D. sensory nervous system; motor nervous system E. brain; central nervous system Taylor - Chapter 02 #11 The peripheral nervous system consists of the and the. A. brain; spinal cord B. central nervous system; peripheral nervous system C. somatic nervous system; autonomic nervous system D. forebrain; hindbrain E. somatic nervous system; peripheral nervous system The nervous system connects the central nervous system with all internal organs. A. peripheral B. automatic C. autonomic D. somatic E. sympathetic The nervous system mobilizes the body in response to stress; the nervous system controls the activities of the visceral organs under normal conditions. A. parasympathetic; sympathetic B. sympathetic; parasympathetic C. somatic; autonomic D. autonomic; peripheral E. sympathetic; peripheral Taylor - Chapter 02 #12 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 24) Damage to the cerebellum is associated with impaired A. muscular coordination. B. respiration. C. speech. D. visual acuity. E. auditory acuity. Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 24) Taylor - Chapter 02 #15 The is an important transition centre between the thoughts generated in the cerebral cortex of the brain and their impact on internal organs. A. forebrain B. hindbrain C. hypothalamus D. medulla E. primary somatic sensory cortex Taylor - Chapter 02 #16
11 17. (p. 24) 18. (p. 25) Mark has been preparing for his graduate school entrance exam for several weeks and is very nervous about how he will perform. In addition to this stress, his girlfriend Jasmine is getting concerned that Mark has not been able to perform in the bedroom lately either. Mark's sexual difficulties due to stress are likely due to the involvement of his in the stress response. A. hypothalamus B. adrenal medulla C. limbic system D. pituitary gland E. parietal lobe Taylor - Chapter 02 #17 The prevalence of is expected to rise to affect over 100 million people worldwide by the year A. Alzheimer's disease B. Huntington's disease C. AIDS D. arthritis E. heart disease 19. (p. 25) 20. (p. 25) Catecholamines are A. exogenes. B. neurotransmitters. C. telecystors. D. arterioles. E. receptors. Secretion of catecholamines A. increases protein and fat mobilization. B. regulates sodium retention. C. increases heart rate and blood pressure. D. stimulates digestion. Taylor - Chapter 02 #18 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 25) Taylor - Chapter 02 #20 is a chronic, nonprogressive disorder of the nervous system that is marked by lack of muscle control. A. Epilepsy B. Parkinson's disease C. Myasthenia gravis D. Cerebral palsy E. Multiple Sclerosis Taylor - Chapter 02 #21
12 22. (p. 26) 23. (p. 26) The gene for has been identified. This allows for at-risk individuals to be tested to ascertain whether they are carriers of this hereditary disorder characterized by chronic physical and mental deterioration due to damaged brain cells. A. Epilepsy B. Myasthenia gravis C. Multiple sclerosis D. Parkinson's disease E. Huntington's disease Taylor - Chapter 02 #22 The nervous system is chiefly responsible for responses to changes in the body; whereas the endocrine system governs mainly responses. A. fast-acting, short-duration; slow-acting, long-duration B. slow-acting, long-duration; fast-acting, short-duration C. fast-acting, long-duration; slow-acting, short-duration D. complementary; antagonistic E. slow-acting, short-duration; fast-acting, long-duration 24. (p ) The release of steroids via the adrenal cortex is stimulated by A. epinephrine and norepinephrine. B. glucocorticoids. C. thyrotropic hormone (TSH). D. adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). E. vasopressin. Learning Objective: 2 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 27) Type I diabetes A. typically occurs after age 40. B. is a condition that occurs when the body fails to produce enough insulin. C. is a condition that occurs when the body is not sufficiently responsive to insulin. D. is primarily managed through dietary and exercise regimens. E. disproportionately affects white males. Learning Objective: 2 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 27) Conditions associated with diabetes include A. blindness. B. kidney failure. C. coronary heart disease. D. nervous system damage. Learning Objective: 2 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 28) The carry blood from the heart to oxygenate organs and other tissues. A. arteries B. veins C. capillaries D. ventricles Learning Objective: 2 Taylor - Chapter 02 #26 Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #27
13 28. (p. 29) is chest pain which occurs because the muscle tissue of the heart must continue its activity without a sufficient supply of oxygen or adequate removal of carbon dioxide and other waste products. A. Angina pectoris B. Myocardial infarction C. Phlebitis D. Arteriosclerosis E. Aneurysm 29. (p. 29) Atherosclerosis is A. associated with angina pectoris and myocardial infarction. B. characterized by a hardening and reduced elasticity of the arterial walls. C. a hereditary disease rather than a disease of lifestyle. D. a type of blood disorder. Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 29) Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #29 During, blood is pumped out of the heart, and blood pressure. During, blood is taken into the heart, and blood pressure. A. diastole; increases; systole; decreases B. diastole; decreases; systole; increases C. systole; increases; diastole; decreases D. systole; decreases; diastole; increases E. diastole; decreases; systole; decreases 31. (p ) Hypertension is caused by A. high cardiac output. B. highly viscous blood. C. loss of elasticity of the arterial walls. D. too high a peripheral resistance. Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 30) Approximately 55% of blood volume is composed of A. platelets. B. white blood cells. C. red blood cells. D. plasma. E. hemoglobin. Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 30) Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #32 Some individuals are unable to produce thromboplastin and fibrin. This condition is associated with a clotting disorder called A. arteriosclerosis. B. anemia. C. leukopenia. D. hemophilia. E. Erythrocytosis. Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #33
14 34. (p. 31) The exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide during respiration occurs between the A. bronchi and the capillaries. B. alveoli and the capillaries. C. alveoli and the arteries. D. bronchioles and the alveoli. E. larynx and the bronchus. 35. (p ) Learning Objective: 4 Taylor - Chapter 02 #34 involves a condition in which the alveoli become dilated, atrophied, and thin so that elasticity is lost and exhalation becomes difficult. A. Bronchial pneumonia B. Pleurisy C. Tuberculosis D. Pulmonary emphysema E. Asthma 36. (p. 34) During the digestive process, the absorption of food takes place primarily in the A. stomach. B. duodenum. C. small intestine. D. large intestine. E. transverse colon. Learning Objective: 4 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 35) Inflammatory bowel disease, A. rates are estimated to be the highest in Canada. B. includes ulcerative colitis. C. includes Crohn's disease. D. rates are highest in Alberta and Nova Scotia. Learning Objective: 5 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 36) Learning Objective: 5 Taylor - Chapter 02 #37 The regulate(s) bodily fluids by removing surplus water, surplus electrolytes, and the waste products generated by the metabolism of food. A. urethra B. bladder C. ureters D. renal system E. hepatic portal system 39. (p. 37) The female hormone, estrogen, A. is secreted by the anterior pituitary. B. is associated with lactation. C. is produced during the second half of the menstrual cycle. D. leads to the development of secondary sex characteristics in the female. Learning Objective: 6 Taylor - Chapter 02 #38 Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #39
15 40. (p. 37) 41. (p. 38) 42. (p. 39) The male hormone, testosterone, A. is secreted by the anterior pituitary. B. brings about the primary sex characteristics in the male. C. is produced by the interstitial cells of the testes. D. is produced on a 14 day cycle E. All of these are characteristics of testosterone Approximately percent of Canadian couples experience fertility problems. A. 3 B. 7 C. 10 D. 15 E. 20 Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #40 Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #41 Which of the following research methods are designed to investigate the relative importance of genetic and environmental factors that contribute to developing medical disorders? A. Studies of identical twins and fraternal twins. B. Studies of identical twins reared apart. C. Studies of adopted children. D. Family studies. 43. (p. 40) Prenatal diagnostic tests are currently available that help detect A. epilepsy. B. breast and colon cancer. C. Huntington's disease. D. cerebral palsy. Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 41) 45. (p. 41) Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #43 Jack and Jill had unprotected sexual intercourse while Jack had an outbreak of genital herpes. Jill has now also contracted genital herpes. This is an example of A. direct transmission of disease. B. indirect transmission of disease. C. biological transmission of disease. D. mechanical transmission of disease. E. physical transmission of disease. The course of infection follows a specific sequence; that is A. incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, acute phase, period of decline. B. period of nonspecific symptoms, incubation period, acute phase, period of decline. C. acute phase, incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, period of decline. D. incubation period, acute phase, period of decline. E. incubation period, period of nonspecific symptoms, period of decline, recovery. Taylor - Chapter 02 #44 Taylor - Chapter 02 #45
16 46. (p. 43) Lymphocytes play an important role in fighting infection and disease by A. secreting digesting enzymes that dissolve foreign particles. B. producing antibodies that destroy substances through the antigen-antibody reaction. C. secreting platelets that engulf foreign particles so they may be excreted. D. producing monoblasts that increase the amount of hemoglobin in the blood. E. carrying oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. 47. (p. 42) 48. (p. 43) 49. (p. 43) 50. (p. 43) 51. (p. 44) A localized infection A. is confined to a particular site and does not spread. B. is confined to a particular area and sends toxins to other parts of the body. C. occurs when the body's resistance is lowered from fighting a primary infection. D. affects several different areas. Nonspecific immunity may be mediated by the A. skin. B. phagocytes. C. inflammatory response. D. antimicrobial substances. Humoral immunity is mediated by A. B cells. B. helper and suppressor T cells. C. B cells and helper and suppressor T cells. D. phagocytosis. Cell-mediated immunity is mediated by A. B cells. B. TC and TH cells. C. B cells and helper and suppressor T cells. D. interferon. The spleen A. secretes insulin and bile into the bloodstream. B. produces neurotransmitters and corticosteroids. C. aids in the production of B and T cells and filters the blood. D. is primarily a vestigial organ. E. is a vermiform organ Taylor - Chapter 02 #46 Taylor - Chapter 02 #47 Taylor - Chapter 02 #48 Taylor - Chapter 02 #49 Taylor - Chapter 02 #50 Taylor - Chapter 02 #51
17 52. (p. 44) 53. (p. 45) Infectious disorders A. are acute problems that end when their course has run. B. that are kept in control through hygiene may have paradoxically increased the rates of these disorders. C. are not linked to the development of any chronic diseases D. attack only lymphatic tissue. E. All of these are traits of infectious disorders. Taylor - Chapter 02 #52 Autoimmunity A. involves the progressive, chronic enlargement of lymphatic tissue. B. is a viral disorder marked by an unusually large number of monocytes. C. is acquired through measures such as vaccination. D. is a condition in which a specific humoral or cell-mediated immune response attacks the body's own tissue. 54. (p. 45) 55. (p. 45) Autoimmunity may be implicated in A. systemic lupus erythematosis. B. arthritis. C. multiple sclerosis. D. molecular mimicry. Inflammation is also implicated in A. bowel disorders. B. cirrhosis of the liver. C. heart disease in men. D. asthma. Taylor - Chapter 02 #53 Taylor - Chapter 02 # (p. 23) Taylor - Chapter 02 #55 Describe the functioning of the autonomic nervous system. Include in your answer the roles of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system in response to stress. Answers may vary. 57. (p ) Gradable: manual Taylor - Chapter 02 #56 Describe the structure and function of the cardiovascular system. Include in your answer the internal and external factors influencing heart rate and the impact on heart functioning. Answers may vary. Gradable: manual Learning Objective: 3 Taylor - Chapter 02 #57
18 58. (p. 32) Describe the nature and symptoms of asthma. Discuss the factors that may contribute to the dramatic rise of asthma in recent years Answers may vary. 59. (p ) Gradable: manual Learning Objective: 4 Taylor - Chapter 02 #58 Explain how a health psychologist might employ family studies and twins to study the genetic basis of a health disorder. Answers may vary. 60. (p. 43) Gradable: manual Learning Objective: 7 Taylor - Chapter 02 #59 Compare and contrast nonspecific and specific immune mechanisms. Provide at least two examples of each. Answers may vary. Gradable: manual Taylor - Chapter 02 #60
19 Category # of Questions 55 Gradable: manual 5 15 Learning Objective: 2 5 Learning Objective: 3 9 Learning Objective: 4 4 Learning Objective: 5 2 Learning Objective: 6 2 Learning Objective: Taylor - Chapter Summary
Full file at
 02 Student: 1. Regulation of the autonomic nervous system occurs via the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. True False 2. The structures of the limbic system play an important
02 Student: 1. Regulation of the autonomic nervous system occurs via the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system. True False 2. The structures of the limbic system play an important
CHAPTER 2 THE SYSTEMS OF THE BODY
 CHAPTER 2 THE SYSTEMS OF THE BODY Learning Objectives 1 Describe the Function of the Nervous System 2 Explain How the Endocrine System Operates 3 Identify How the Cardiovascular System Works 4 Describe
CHAPTER 2 THE SYSTEMS OF THE BODY Learning Objectives 1 Describe the Function of the Nervous System 2 Explain How the Endocrine System Operates 3 Identify How the Cardiovascular System Works 4 Describe
Health Psychology. Health Psychology. Health Psychology. Health Psychology. What is Health Psychology? Biobehavioural aspects of health
 Health Psychology Health Psychology Psychology 46.339 (01) Summer 2007 Instructor: Dr. Fuschia Sirois Wednesday July 4: Introduction & Lecture 1 Taylor text, 6 th ed. Lecture slides in pdf format on course
Health Psychology Health Psychology Psychology 46.339 (01) Summer 2007 Instructor: Dr. Fuschia Sirois Wednesday July 4: Introduction & Lecture 1 Taylor text, 6 th ed. Lecture slides in pdf format on course
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Objectives. Objectives 9/11/2012. Chapter 7 Body Systems. Define term connective tissue. Identify five body cavities
 Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Chapter 7 Body Systems Objectives Define term connective tissue Identify five body cavities Define terms joints, cartilage, ligaments, tendons Identify two major divisions of skeletal system and describe
Body Systems Overview
 Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Body Systems Overview Body Systems work together: If you damage one system, you may damage several for example, smoking irritates the lungs and destroys the cells of the immune system Levels of Organization
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Organs and Systems Organ: System:
 3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
3.2 Organ Systems Organs and Systems Organ: a combination of several types of tissues working together to perform a specific function System: a group of tissues and organs that perform specific functions
Chapter 16. Human Anatomy
 Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16 Human Anatomy Each System we will examine: Structures types Problems or health concerns How to care for that system Skeletal System Made up of bones, joints, connective tissue Is the frame for
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Unit 3 - Homeostasis in the Human Body
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) Key Concepts What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels
Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages )
 Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Section 37 1 The Circulatory System (pages 943 950) What are the structures of the circulatory system? What are the three types of blood vessels in the circulatory
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1. INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM: skin is the largest system.
 Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
Chapter 7 Body Structure and Function Cell: Tissue: Examples: lining of the nose, mouth, stomach, muscle tissue Organs: Example: heart, brain, liver, lungs, kidneys Systems: organs that work together to
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Warm Up Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells?
 Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
Body Systems Warm Up 4-4-16 1. Where in a flower would you find xylem and phloem? 2. Where in a flower would you find palisade cells? 3. Where in a flower would you find root hair cells? 4. What organelle
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
How is an organism made up? (Use the levels or organization and explain their relationship to each other.)
 Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Unit 11 Test Review Chapter 28 a. List and describe the systems of the body and their functions (Respiratory, circulatory, digestive, immune, reproductive, excretory, nervous, integumentary, muscular,
Chapter 15. Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems
 Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 15 Cardiovascular, Respiratory, Digestive Systems Cardiovascular/Respiratory Systems Cardiovascular System Blood is pumped to the body 24/7 Heart s tasks: Carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System
 Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Major Endocrine Organs Hypothalamus Pineal Gland Pituitary Gland Thyroid Gland Thymus Gland Adrenal Glands Pancreas Ovaries (Female) Testis (Male) Chapter 8.2 The Endocrine System The endocrine system
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY
 Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Name: Period: Review for Animal Systems Test II - KEY Questions 1-9: Write the main functions of the following body s in the spaces below. Then, write the levels of organization for each body. Give specific
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to:
 Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Outcomes: By the end of this session the student will be able to: Discuss the cardiovascular system Identify the normal changes that occur with ageing Explain the nurses role in the care of residents with
Chapter 17. Nervous System Nervous systems receive sensory input, interpret it, and send out appropriate commands. !
 Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Chapter 17 Sensory receptor Sensory input Integration Nervous System Motor output Brain and spinal cord Effector cells Peripheral nervous system (PNS) Central nervous system (CNS) 28.1 Nervous systems
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
RESPIRATION- Life function. Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily
 HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
HUMAN BODY SYSTEMS RESPIRATION- Life function Humans convert the chemical energy stored in foods so the cells can use it more easily Breathing: A. Nasal cavity- -Series of channels which the outside air
Animal Structure and Function
 Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Name Period Date Animal Structure and Function Structure 1. What is the definition of a tissue? What are the four general categories of animal tissues. (p.415) 2. List the six types of connective tissues.
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended.
 BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
BIO 116 Practice Assignment 1 The Endocrine System and Blood This is not a required assignment but it is recommended. 1. Match the following glands of the endocrine system with the appropriate label 1.
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic
 Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
Answer the bell work questions. Write the underline portion of the state standard for your class. Follow the directions given for the graphic organizer and take notes for each of the body systems. Copy
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite
 Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Date Revised: 1980 Date Revised: 1985 Date Revised: 1985, 1998, 2002 BIO 202 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY II BIO 201 Prefix No. Course Title Prerequisite Credit Hours: 4 Contact Hours: Lecture 3 Lab 2
Human Anatomy & Physiology
 Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
Human Anatomy & Physiology Hey I thought those were the same thing! Nope they ain t Anatomy-Where everything is and to what it is connected. Physiology-How all that stuff works to keep you alive! Morphology-How
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Circulation and Respiration
 Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Lesson 10 Circulation and Respiration Introduction to Life Processes - SCI 102 1 Circulatory System: Features and Functions All circulatory systems have three major parts The heart: a pump that keeps blood
Anatomy & Physiology Student Edition. 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex?
 Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Name: Date: 1. Which list shows different levels or organization within a population ordered from least to most complex? A. organ systems, organs, organelles, organisms B. organelles, organs, organ systems,
Cardiovascular System Notes
 Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
Cardiovascular System Notes Cardiovascular System a transportation system that carries needed substances to cells and waste products away from cells. Functions Transports nutrients to cells Transports
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide Subject: Anatomy and Physiology
 RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
RCPS Curriculum Pacing Guide 2013 2014 Subject: Anatomy and Physiology Week of: SOL # Unit Bloom s Objectives Throughout All units the course During field trip Throughout the course A+P1 Collecting, analyzing,
Chapter 3. Biological Processes
 Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
Biological Processes Psychology, Fifth Edition, James S. Nairne What s It For? Biological Solutions Communicating internally Initiating and coordinating behavior Regulating growth and other internal functions
The Human Body. The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course.
 The Human Body The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course. Circulatory - Immune Respiratory - Digestive Musculoskeletal - Nervous Urinary - Endocrine THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.0
The Human Body The human body is composed of many systems. We have covered 8 in this course. Circulatory - Immune Respiratory - Digestive Musculoskeletal - Nervous Urinary - Endocrine THE NERVOUS SYSTEM.0
Summary The Circulatory System Blood and the Lymphatic System. Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall.
 Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
Name Class Date Chapter 37 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Summary 37-1 The Circulatory System The human circulatory system consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. Together with the respiratory
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Chapter 24. Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill.
 Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
Chapter 24 Lecture Outline Enger, E. D., Ross, F. C., & Bailey, D. B. (2012). Concepts in biology (14th ed.). New York: McGraw- Hill. 1 24-1 Exchanging Materials: Basic Principles Large, multicellular
3. A process that occurs in the human body is represented in the diagram below.
 1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
1. Molecules in a certain medication attach to receptors on nerve cells. This prevents the normal chemical signal from binding to the receptor. One immediate result of taking this medication might be a
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body
 Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Body Systems The Digestive System: to convert food particles into simpler micro molecules that can be absorbed into the bloodstream and used by the body Major Organs and their Functions: Mouth to chew
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 6.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11, 15, 17, 26, 27, 31, 33, 37, 40 42, 44, 45, 51, 58 6.2 Describe the basic roles and structures
The Endocrine System. Lab Exercise 31. Objectives. Introduction
 Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Lab Exercise The Endocrine System Objectives - Become familiar with the major endocrine glands and their location. - Learn some of the hormones produced by each gland. - Become familiar with the anatomy
Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view
 Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Human Body Systems Regulation and Homeostasis in the Human Body: Quick view Eleven Body Systems work together to maintain homeostasis. 1. Nervous System 2. Endocrine System 3. Lymphatic System 4. Circulatory
Body Systems Notes. Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive
 Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Body Systems Notes Nervous, Integumentary, Immune/Lymphatic, Circulatory, Skeletal, Respiratory, Digestive, Excretory, Endocrine, Reproductive Homeostasis: maintaining a balance. Examples: temperature,
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Visualizing Psychology
 Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Visualizing Psychology by Siri Carpenter & Karen Huffman PowerPoint Lecture Notes Presentation Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Biological Foundations Siri Carpenter, Yale University Karen Huffman, Palomar
Anatomy and Physiology 2
 Anatomy and Physiology 2 The Nervous System Nerves allows organisms to detect and respond to stimuli by transmitting electrical impulses cell to cell. Can send info at high speeds! Neurons are the smallest
Anatomy and Physiology 2 The Nervous System Nerves allows organisms to detect and respond to stimuli by transmitting electrical impulses cell to cell. Can send info at high speeds! Neurons are the smallest
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Langara College Spring archived
 COURSE DETAILS Department of Human Kinetics and Recreation Human Kinetics 1191 Anatomy & Physiology II Term: 2007-10 Sections: 001, 002, 003 Lecture/Seminar/Lab Hrs: 2: 0: 2 Credits: 3 Schedule: Section
COURSE DETAILS Department of Human Kinetics and Recreation Human Kinetics 1191 Anatomy & Physiology II Term: 2007-10 Sections: 001, 002, 003 Lecture/Seminar/Lab Hrs: 2: 0: 2 Credits: 3 Schedule: Section
CATEGORY Endocrine System Review. Provide labels for the following diagram CHAPTER 13 BLM
 CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.1 CATEGORY Endocrine System Review Provide labels for the following diagram. 1. 6. 2. 7. 3. 8. 4. 9. 5. 10. CHAPTER 13 BLM 13.1.2 OVERHEAD Glands and Their Secretions Endocrine gland
Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2
 The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
The Endocrine System: Anatomy & Physiology Final Exam Study Guide Semester 2 1) List the major processes controlled by hormones. 2) Under normal conditions, how are hormone concentrations in the blood
Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I
 Intended Learning Outcomes Circulatory System: Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I 1. Explain the concept of homeostasis and its critical nature of living things. 2. Explain the importance
Intended Learning Outcomes Circulatory System: Biology 2201 Unit III: Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium I 1. Explain the concept of homeostasis and its critical nature of living things. 2. Explain the importance
Nervous System. Skeletal System. Muscular System. Reproductive System. Circulatory System. Endocrine System. Respiratory System. Integumentary System
 The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
The Human Body Skeletal System Muscular System Circulatory System Respiratory System Digestive System Nervous System Reproductive System Endocrine System Integumentary System Excretory System Lymphatic/Immune
Introduction to Human Body Systems
 The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Human Organism: Introduction to Human Body Systems By Deanne Erdmann, MS Levels of Organization in the Body Cells Tissues Epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous Organs Examples include stomach,
The Endocrine System ( PART II) Individual Endocrine glands and their hormones
 The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
The Endocrine System ( PART I) Hormone Describe the major endocrine organs, list their main locations and functions. Indicate important differences between hormonal and neural controls of body functioning.
Introduction to Medical Careers. Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12
 Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Introduction to Medical Careers Cardiovascular & Circulatory Systems Chapters 11-12 CHAPTER 11 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM I will be able to: 1. Define at least eight terms referring to the cardiovascular system.
Chapter 20 Endocrine System
 Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
Chapter 20 Endocrine System The endocrine system consists of glands and tissues that secrete Hormones are chemicals that affect other glands or tissues, many times far away from the site of hormone production
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism. Cells: the smallest unit of life.
 Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems Organism Cells: the smallest unit of life. The Circulatory Systems brings oxygen, nutrients and hormones to cells; fights infections; removes cell wastes; regulates
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Open Circulatory System. Closed Circulatory System
 General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
General Types of Circulatory Systems -All circulatory systems exchange gases, nutrients, and wastes at the cellular level -Although all animals need to do this, they do so in a variety of ways: -Two types
THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: RESULTS/SCORES FROM LEARNING ASSESSMENTS
 MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
MAP MASTERY Unit 7: Anatomy and Physiology THESE ARE THE IMPORTANT CONCEPTUAL UNDERSTANDINGS I NEED TO MASTER FOR THIS UNIT: A. Demonstrates an understanding of the of the circulatory system. Identify
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Chapter 11. The Cardiovascular System. Clicker Questions Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Clicker Questions Oxygen-poor blood is pumped through the venae cavae to the right side of the heart, and then through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs and back
Heal a th t y h y B o B dy d Systems
 Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Chapter 16 Healthy Body Systems The Cell The smallest unit of structure in a living organism Robert Hooke Identified & coined the term Cell when he saw cork under the microscope He used a compound microscope
Cardiovascular System
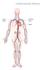 Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Cardiovascular System Cardiovascular System - Function The cardiovascular system transports, from one part of the body to another: nutrients, oxygen, ions, proteins, hormones and other signaling molecules,
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Tissues: systems of cells working together to perform specialized tasks. Ex muscles, nerves, blood
 Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The
 Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Copyright Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Name Date Class Circulation 33 Chapter 19 Circulation Section 1 The Circulatory System A. Your system includes the blood, heart,
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Cardiovascular and Circulatory System The Heart and Blood Vessels Circulatory Learning Outcomes 1. Identify and explain the functions of the vessels of the Circulatory system. 2. Explain the functions
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y
 n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
n A m I 8 I A U n I V ER SI TV"Y OF SCIEnCE AnD TECHnOLOGY3Y FACULTY OF HEALTH AND APPLIED SCIENCES DEPARTMENT OF HEALTH SCIENCES QUALIFICATION: BACHELOR OF BIOMEDICAL SCIENCES QUALIFICATION CODE: SOBBMS
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
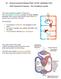 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species
 Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
Testosterone and Male Aggression Testosterone and other male hormones seem to be related to aggressive behavior in some species In the fish species Oreochromis mossambicus, elevated levels have been found
SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL
 Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
Winnipeg Adult Education Centre SCIENCE LEARNING JOURNAL BIOLOGY 30S: HUMAN BIOLOGY Scientist: 1 *inside cover* 2 Contents COURSE OBJECTIVES: SELF ANALYSIS... 5 Unit 1: Wellness and Homeostasis - Specific
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours)
 PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
PNUR 101: ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (48 Hours) COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is an introduction to the anatomy and physiology of the human body. Learners will explore the structure and function of the major
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science
 CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
CAYUGA COMMUNITY COLLEGE Division of Computer Science, Mechanical Technology, Electrical Technology, GIS, Math, Nursing, Science Anatomy and Physiology II - Biology 204 4 Credit Hours CATALOG DESCRIPTION
