Case Report Multi-slice computed tomography diagnosis of left paraduodenal hernia in an adult complicated by volvulus: a case report
|
|
|
- Georgiana Bailey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11): /ISSN: /IJCEM Case Report Multi-slice computed tomography diagnosis of left paraduodenal hernia in an adult complicated by volvulus: a case report Haifei Li 1, Xia Wang 2, Keping Tan 1, Gaofeng Yi 1, Peiyuan Wang 1,3 1 Department of Radiology, Yantai Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, PR China; 2 Department of Pathology, 3 Medical Imaging Research Institute, Binzhou Medical University, Yantai, PR China Received July 22, 2016; Accepted September 18, 2016; Epub November 15, 2016; Published November 30, 2016 Abstract: Internal hernia is an uncommon cause of intestinal obstruction, of which paraduodenal hernias are the most common. It is difficult to diagnose this entity clinically, as symptoms tend to be nonspecific; computed tomography (CT), however, is diagnostic. A case of 29-year-old female with 11 hours of progressive, severe, and sharp left sided abdominal pain was retrospectively studied. The diagnostic value of preoperative multi-slice computed tomography (MSCT) was evaluated. On MSCT, a cluster of small bowel loops to the left of the fourth portion of the duodenum, within the fossa of Landzert was demonstrated. And a reverse C-shaped significant expansion loop, filled with fluid and a small amount of air was shown on multiplanar reformation imaging (MPR). The distal afferent, proximal efferent and both sides of the C-shaped loop were concentrated to a point and showed irregular blind ends. The first jejunal arterial branch was in drumstick congestion with twisted terminal branches on MPR and CT angiography images. The CT diagnosis of left paraduodenal hernia and volvulus with obstruction was made, and confirmed by laparotomy. With regards to the patients presenting with intestinal obstruction, focus should be made on the changes around the herniation, including supplying vessels, as well as afferent and efferent loops anatomy using the multi post-processing technique, to determine the etiology of the obstruction and to plan the surgical approach. Keywords: Internal hernias, intestinal obstruction, multi-slice computed tomography, paraduodenal hernias, volvulus Introduction Internal hernia is an uncommon cause of intestinal obstruction. Paraduodenal hernias, the most common type of internal hernia, account for approximately 53% of all cases [1, 2]. Paraduodenal hernias are rare congenital anomalies in which the small intestine is completely or partially trapped beneath the mesentery of the developing colon. Nearly 75% occur on the left and the majority involves the paraduodenal fossa of Landzert [3, 4]. The clinical signs and symptoms of left paraduodenal hernias lack specific characteristics and may vary from asymptomatic to acute or chronic small bowel obstruction. Due to their high mortality rate (approximately 20%, as a result of complete obstruction, strangulation, bowel ischemia and volvulus), accurate and prompt preoperative diagnosis is critical [5]. Multi-slice computed tomo- graphy (MSCT) plays an important role in the diagnostic workup of these hernias. Herein, we reported a case of intestinal obstruction complicated by volvulus, secondary to a left paraduodenal hernia, and diagnosed preoperatively by MSCT with intravenous contrast. Case presentation A 29-year-old female with 11 hours of progressive, severe, and sharp left sided abdominal pain presented to the emergency room. The pain was associated with non-bilious vomiting and purulent bloody diarrhea. She was not distended, nor did the pain radiate. She had no history of previous abdominal surgery or trauma, and had never had this type of pain in the past. On physical examination, her abdomen was flat with weak bowel sounds; moderate tenderness
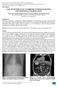
2 Figure 1. Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography shows a cluster of dilated small bowel loops (B) to the left of the fourth portion of duodenum, behind the stomach (S), below the pancreas, and anterior to the left kidney (LK). A small amount of exudation could be seen between loops (arrow). Figure 2. Oblique-coronal MPR shows a reverse C shaped (arrow) clearly dilated loop (diameter 3.5 cm) filled with fluid. The distal afferent, proximal efferent, and bilateral C shaped loops (star) were concentrated to a point and showed irregular blind ends. without rebound was appreciated in the left upper abdomen. There was no abdominal mass. On laboratory investigation, she was found to have a normal leukocyte count with increased neutrophil granulocytes (81.9%) and no other abnormal findings. A small air-fluid level in the left mid-abdomen indicated a proximal small bowel obstruction on plain radiographs and a small amount of lower abdominal intraluminal air. There was no evidence of perforation. Figure 3. Axial MPR image shows the first jejunal arterial branch from the superior mesenteric artery extending laterally and posteriorly to the sac with a drumstick appearing, congested trunk (arrowhead) and twisting shape of the terminal branches (arrow). Abdominal MSCT was performed before and after intravenous injection of nonionic contrast. On MSCT, a cluster of small bowel loops to the left of the fourth portion of the duodenum (retrogastric and retropancreatic, anterior to the left kidney) was demonstrated (Figure 1). The small bowel loops caused mild to moderate displacement of the posterior wall of the stomach and the anterior pancreatic body and tail. The mass had a sharp and smooth, left convex lateral border within the fossa of Landzert, and showed a reverse C-shaped significant expansion loop (diameter 3.5 cm), filled with fluid and a small amount of air on multiplanar reformation (MPR) imaging (Figure 2), and a small amount of exudation between loops. The computed tomography (CT) diagnosis of a left paraduodenal hernia with bowel obstruction was made. The sac connected with the duodenum through a narrow neck. The afferent loop (proximal jejunum) was on the right of the efferent loop but both loops had no direct connection to the sac. The distal afferent, proximal efferent, and both sides of the C-shaped loop were concentrated to a point and showed irregular blind ends (Figure 2). On the arterial phase of the dynamic contrast-enhanced CT scan, the coexisting variant of the hepatic arteries (superior mesenteric artery) was clearly demonstrated and the superior mesenteric artery was shown to be orthotopically left to the superior mesenteric vein. The proximal jejunal venous tributaries of the superior mesenteric vein, as well as the first jejunal arterial branch of the superior mesenteric artery, were visualized to be extending left and posterior to the abnormally positioned bowel in the sac. The first jejunal arterial branch from the superior mesenteric artery was in drumstick congestion with twisted termi Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):
3 Figure 4. Oblique-coronal MPR image shows the first jejunal arterial branch with a drumstick appearing, congested trunk (arrowhead) and twisting shape of the terminal branches (arrow). Figure 6. Axial contrast-enhanced CT shows the left branch of the middle colic artery, ascending left colic artery (arrow), and inferior mesenteric vein (arrowhead) to be located in the posterior wall of the hernia. Figure 5. CTA shows the congested trunk (arrowhead) of first jejunal arterial branch from the superior mesenteric artery. nal branches on MPR (Figures 3, 4) and CT angiography (CTA) images (Figure 5), the second and third arterial branches extending lateral and inferior to the displaced jejunum, around the anterior wall of the sac. All of the above signs indicated the possibility of a volvulus with a rotation of greater than 180. Although there was exudation in the sac, the densities of the loops in the sac on plain and contrast-enhanced CT scan were uniform with those outside of the sac, indicating that no intestinal necrosis had occurred but the ischemic changes was possible. The transverse and descending colon were located in the lower abdomen and the splenic flexure was located Figure 7. Oblique-sagittal MPR shows the inferior mesenteric vein (arrowhead) was medially and posteriorly displaced by the sac. under the left kidney, posterior to the hernia sac. The left branch of the middle colic artery, ascending left colic artery, and inferior mesenteric vein were located in the posterior hernia wall (Figure 6), with slight medial and posterior displacement by the sac (Figure 7). Emergency laparotomy was performed and the diagnosis left paraduodenal hernia and volvulus with obstruction was confirmed. Approximately 30 cm of proximal jejunum, with 360 rotation and extensive adhesions, was found to be entrapped by the hernia. The herniated bowel was dilated with vascular congestion of the bowel wall due to venous compression caused by the volvulus. The first jejunal arterial branch from the superior mesenteric artery Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):
4 demonstrated drumstick congestion with stranding; the second and third arterial branches showed the same appearance as on the CT. The inferior mesenteric vein was located at the superior edge of the hernia orifice without dilation and the inferior mesenteric artery was closed to the posterior wall of the sac. The small bowel was released and its blood supply was restored after hernia reduction; the orifice was closed. The postoperative recovery was uneventful and there was no relapse during the 12 month follow-up period. Discussion Internal hernia, an uncommon cause of intestinal obstruction (5.8%) [3], refers to an abdominal organ protruding through a normal or abnormal aperture in the mesentery or peritoneum, located within the scope of the peritoneal cavity [6]. The hernial orifice can be congenital or acquired (due to prior abdominal surgery, trauma, or peritoneal inflammation). Meyers described the following types of internal hernia based on location: paraduodenal, primeval, foramen of Winslow, transmesenteric and transmesocolic, intersigmoid, retroanastomotic, and paravesical hernia [7]. Paraduodenal hernias are the most common type of internal hernias and account for approximately 53% of all internal hernia cases [1, 2]. Nearly 75% of paraduodenal hernias occur on the left and the majority involve the paraduodenal fossa of Landzert [3, 4]. Landzert s fossa is located lateral to the fourth portion of the duodenum, posterior to a fold of peritoneum, and associated with the left colic artery and inferior mesenteric vein, and is present in approximately 2% of autopsies [3]. Other associated causes may be other fossa (superior duodenal fossa, fossa of Waldeyer, fossa of Brosike, etc.) abnormalities of bowel fixation, an unusual separated peritoneal membrane or mesocolic fossa [8-10]. The current hernia case involved the fossa of Landzert. Paraduodenal hernias usually occur in adulthood at an average age of 38.5 years, and are three times more common in males [11, 12]. The clinical signs and symptoms lack specific characteristics, and vary from asymptomatic to intermittent or severe abdominal pain lasting a few hours to several years. In the elderly, the small intestine may be herniated and reduce spontaneously and repeated onset may lead to progressive thinning and enlarging of the hernia orifice, which possibly results from an ischemic insult or mechanical expansion. The enlargement of the orifice may result in more intestinal loops entrapped into the sac that are difficult to reduce spontaneously, leading to persistent abdominal discomfort even for small bowel obstruction, strangulation, and volvulus. With regards to new emergency cases without similar histories, a strictured hernia orifice may suppress the loops and lead to the intestinal obstruction; symptoms appear gradually and worsen, as in the present case. The high mortality rate (approximately 20%) is primarily due to complete obstruction, strangulation, bowel ischemia, and volvulus; mortality can be as high as 50% in untreated strangulation [5]. Therefore, accurate and prompt preoperative diagnosis is vital. The diagnosis of asymptomatic left paraduodenal hernia is difficult, and often occurs incidentally at laparotomy, autopsy, or during radiological investigation for unrelated diseases [11, 12]. Symptomatic patients are more likely to be diagnosed preoperatively [3, 6]. Abdominal plain radiographs, small bowel follow-through barium examination, ultrasound, celiac arteriography, CT, and magnetic resonance imaging have been used to diagnose paraduodenal hernias. CT, especially MSCT with oral or intravenous contrast plays an important role in the diagnosis and evaluation of suspected paraduodenal hernias [2, 6, 13]. On CT, the specific findings include a well-circumscribed clustering of small bowel loops lateral to the fourth portion of the duodenum, within the fossa of Landzert, with or without bowel obstruction. Mesenteric vessel abnormalities, such as engorgement, crowding, stretching and displacement of the trunk [3, 14, 15], and the evidence of bowel ischemia (mural thickening and low enhancement) can be seen on CT [14-16]. These findings are helpful in establishing the preoperative diagnosis of paraduodenal hernia, as in the present case. In paraduodenal hernia, the jejunal branches of the superior mesenteric vessels supplied the herniated loops, converging to a point in the hernial orifice and stretched within the sac. In Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):
5 addition, the afferent and efferent bowel loop may be visualized at the hernial orifice in continuity with the hernia bowel loops, which may appear as a beaked appearance on barium study. In our case, the proximal jejunal arterial branch of the superior mesenteric artery was of drumstick congestion, with twisting terminal branches on CTA and MPR. The afferent and efferent loops were detected at the hernial orifice on MPR, but the afferent and efferent loops showed no direct connection with the sac loops. These findings indicate a suspected volvulus, which was confirmed intraoperatively. These signs should be clearly identified in a patient presenting with bowel obstruction. Normally, the inferior mesenteric vein runs along and above the lateral side of Landzert s fossa, and is associated with the peritoneal fold; in left paraduodenal hernia, the inferior mesenteric vein can be located in the hernia neck and lateral-posterior wall of the hernia sac, spread outwards, or upwards, or both [6, 11]. Schaffler et al. [17] reported a left paraduodenal hernia with anterior and upward displacement of the inferior mesenteric vein, and postulated that its presence may be a new diagnostic clue to left paraduodenal hernia. In Nishida s study [18], the inferior mesenteric vein showed no anterior and upward displacement; in our case, slight medial and posterior displacement occurred and both cases differed from that of Schaffler et al. [17]. By comparing CT images, we regard sac size as the possible reason. Seya et al. [12] reported an incidentally diagnosed left paraduodenal hernia, described the hernia sac located between the shifted left branch of the middle colic artery and ascending left colic artery, and considered finding the ascending left colic artery at the lateral edge of the sac as diagnostic of left paraduodenal hernia. In the present case, the transverse and descending colon were located in the lower abdomen and the ascending left colic artery was located behind the hernia sac, which did not aid in the diagnosis. Therefore, the absence of an ascending left colic artery at the lateral edge of the sac cannot exclude the diagnosis of a left paraduodenal hernia, which may be caused by low lying transverse and descending colon. In summary, the preoperative diagnosis of left paraduodenal hernia by specific CT findings is not difficult. We reported a case of left paraduodenal hernia accompanied by bowel obstruction due to volvulus, and aimed to remind the readers of how to further recognize this entity. With regards to the patients presenting with intestinal obstruction, focus should be made on the changes around the herniation, including supplying vessels, as well as afferent loop and efferent loop anatomy using the multi postprocessing technique, to determine the etiology of the obstruction and to plan the surgical approach. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Dr. Peiyuan Wang, Department of Radiology, Yantai Affiliated Hospital of Binzhou Medical University, 717 Jinbu Road, Yantai , Shandong, PR China. Tel: ; Fax: ; wangpeiyuan1640@163.com References [1] Zizzo M, Smerieri N, Barbieri I, Lanaia A, Bonilauri S. Laparoscopic treatment of acute small bowel obstruction due to left paraduodenal hernia: A case report and literature review. Int J Surg Case Rep 2016; 20: [2] Licciardello A, Rapisarda C, Conti P, Trombatore G. Small bowel obstruction caused by an unusual variant of paraduodenal hernia. The middle congenital mesocolic hernia : case report. J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 18: [3] Martin LC, Merkle EM, Thompson WM. Review of internal hernias: radiographic and clinical findings. Am J Roentgenol 2006; 186: [4] Suwanthanma W, Euanorasetr C, Soom-im S, Lertbannaphong S. Left Paraduodenal Hernia As a Rare Cause of Small Bowel Obstruction in Elderly: A Case Report and Review of Literature. J Med Assoc Thai 2015; 98: [5] Cho EY, Choi CS, Yoo NJ, Hwang ET, Lee JY, Kang DB, Choi SC. A case of left paraduodenal hernia combined with acute small bowel obstruction. Korean J Gastroenterol 2009; 53: [6] Kandpal H, Sharma R, Saluja S, Sahni P, Vashisht S. Combined transmesocolic and left paraduodenal hernia: barium, CT and MRI features. Abdom Imaging 2007; 32: [7] Meyers MA. Dynamic radiology of the abdomen: normal and pathologic anatomy. Chapter Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):
6 16, 5th edition. Berlin Heidelberg New York: Springer; pp [8] Poh BR, Sundaramurthy SR, Mirbagheri N. Left paraduodenal hernia causing small bowel obstruction. J Gastrointest Surg 2014; 18: [9] Kumar S, Dikshit P, Bhaduri S, Sattavan S. Gangrenous Appendicitis: A Rare Presentation of Pericecal Hernia; Case Report and Review of the Literature. Bull Emerg Trauma 2015; 3: [10] Kannan NS, Usha K, Arun T, Naseeruddin MP, Ganesh Babu PC, Karthikesh S. Congenital middle mesocolic hernia: A case report. Australas Med J 2014; 7: [11] Kurachi K, Nakamura T, Hayashi T, Asai Y, Kashiwabara T, Nakajima A, Suzuki S, Konno H. Left paraduodenal hernia in an adult complicated by ascending colon cancer: a case report. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12: [12] Seya T, Tanaka N, Yokoi K, Okada S, Oaki Y, Uchida E. Left paraduodenal hernia incidentally diagnosed during operation for transverse colon cancer. J Nippon Med Sch 2010; 77: [13] Kandpal H, Sharma R, Saluja S, Sahni P, Vashisht S. Combined transmesocolic and left paraduodenal hernia: barium, CT and MRI features. Abdom Imaging 2007; 32: [14] Doishita S, Takeshita T, Uchima Y, Kawasaki M, Shimono T, Yamashita A, Sugimoto M, Ninoi T, Shima H, Miki Y. Internal Hernias in the Era of Multidetector CT: Correlation of Imaging and Surgical Findings. Radiographics 2016; 36: [15] Hong SS, Kim AY, Kim PN, Lee MG, Ha HK. Current diagnostic role of CT in evaluating internal hernia. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2005; 29: [16] Geffroy Y, Boulay-Coletta I, Jullès MC, Nakache S, Taourel P, Zins M. Increased unenhanced bowel-wall attenuation at multidetector CT is highly specific of ischemia complicating smallbowel obstruction. Radiology 2014; 270: [17] Schaffler GJ, Groell R, Kammerhuber F, Stacher R, Hammerl R, Rabl H, Hoess G, Szolar DH. Anterior and upward displacement of the inferior mesenteric vein: a new diagnostic clue to left paraduodenal hernias? Abdom Imaging 1999; 24: [18] Nishida T, Mizushima T, Kitagawa T, Ito T, Sugiura T, Matsuda H. Unusual type of left paraduodenal hernia caused by a separated peritoneal membrane. J Gastroenterol 2002; 37: Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(11):
A rare case of intestinal obstruction due to internal hernia. Dr. Jayanth 3 rd year PG Dept. Of General Surgery
 A rare case of intestinal obstruction due to internal hernia Dr. Jayanth 3 rd year PG Dept. Of General Surgery One of the common cause of acute abdomen May lead to high morbidity and mortality if not treated
A rare case of intestinal obstruction due to internal hernia Dr. Jayanth 3 rd year PG Dept. Of General Surgery One of the common cause of acute abdomen May lead to high morbidity and mortality if not treated
Case Internal herniation with bowel ischemia after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery.
 Case 14127 Internal herniation with bowel ischemia after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Peters B 1, 2, Waked K 3, Vanhoenacker FM 1, 2, 4, Ceulemans J 5, Mespreuve M 2, 4 University Hospital Antwerp,
Case 14127 Internal herniation with bowel ischemia after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. Peters B 1, 2, Waked K 3, Vanhoenacker FM 1, 2, 4, Ceulemans J 5, Mespreuve M 2, 4 University Hospital Antwerp,
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update
 Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Nordic Forum - Trauma & Emergency Radiology Bowel Obstruction: Imaging Update Borut Marincek Institute of Diagnostic Radiology University Hospital Zurich, Switzerland Acute Abdomen Bowel Obstruction Bowel
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Left Paraduodenal Hernia Successfully Treated with Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report
 71 Left Paraduodenal Hernia Successfully Treated with Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report Tuyoshi Shoji Raisuke Nishiyama Koji Oba Masaki Azuma Department of Surgery, Haibara General Hospital, Makinohara
71 Left Paraduodenal Hernia Successfully Treated with Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report Tuyoshi Shoji Raisuke Nishiyama Koji Oba Masaki Azuma Department of Surgery, Haibara General Hospital, Makinohara
Para-duodenal hernia: a report of five cases and review of literature
 Shadhu et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:32 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0365-8 CASE REPORT Para-duodenal hernia: a report of five cases and review of literature Kamleshsingh Shadhu 1,2, Dadhija Ramlagun
Shadhu et al. BMC Surgery (2018) 18:32 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12893-018-0365-8 CASE REPORT Para-duodenal hernia: a report of five cases and review of literature Kamleshsingh Shadhu 1,2, Dadhija Ramlagun
Review of Internal Hernias: Radiographic and Clinical Findings
 Radiographic and Clinical Findings of Hernias Gastrointestinal Imaging Review C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Lucie C. Martin 1 Elmar M. Merkle William M. Thompson Martin LC, Merkle EM, Thompson
Radiographic and Clinical Findings of Hernias Gastrointestinal Imaging Review C D E M N E U T R Y L I M C I G O F I N G Lucie C. Martin 1 Elmar M. Merkle William M. Thompson Martin LC, Merkle EM, Thompson
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine. ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama
 Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
Development of pancreas and Small Intestine ANATOMY DEPARTMENT DR.SANAA AL-AlSHAARAWY DR.ESSAM Eldin Salama OBJECTIVES At the end of the lecture, the students should be able to : Describe the development
TRANSOMENTAL HERNIATION CAUSING ACUTE INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION N. Suresh Kumar 1, Rahul Rai 2, P. Kulandai Velu 3
 TRANSOMENTAL HERNIATION CAUSING ACUTE INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION N. Suresh Kumar 1, Rahul Rai 2, P. Kulandai Velu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: N. Suresh Kumar, Rahul Rai, P. Kulandai Velu. Transomental Herniation
TRANSOMENTAL HERNIATION CAUSING ACUTE INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION N. Suresh Kumar 1, Rahul Rai 2, P. Kulandai Velu 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: N. Suresh Kumar, Rahul Rai, P. Kulandai Velu. Transomental Herniation
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
An Interesting case of Retrocaecal internal herniation causing Small bowel Obstruction
 Accepted Manuscript An Interesting case of Retrocaecal internal herniation causing Small bowel Obstruction A.O. Rae, Core trainee,year 2 General Surgery, A. Kalyanaraman, SpR in General Surgery, A.E. Ward,
Accepted Manuscript An Interesting case of Retrocaecal internal herniation causing Small bowel Obstruction A.O. Rae, Core trainee,year 2 General Surgery, A. Kalyanaraman, SpR in General Surgery, A.E. Ward,
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum. Elective Student S. C.
 Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Perforation of a Duodenal Diverticulum 2008 4 Elective Student S. C. Case History An elderly male presented to the Emergency Department with abdominal pain. Chief Complaint: Worsening, diffuse abdominal
Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know.
 Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know. Ken F Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology UW Medicine Harborview Medical Center klinnau@uw.edu Nordic Forum 2017 Helsinki,
Emergency presentation of hernias of the torso: What your surgeon wants to know. Ken F Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology UW Medicine Harborview Medical Center klinnau@uw.edu Nordic Forum 2017 Helsinki,
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN
 UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
UNDERSTANDING X-RAYS: ABDOMINAL IMAGING THE ABDOMEN Radiology Enterprises radiologyenterprises@gmail.com www.radiologyenterprises.com STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL STOMACH AND SMALL BOWEL Swallowed air is a
U Lecture Objectives. U Nordic Forum Trauma & Emergency Radiology. Bowel obstruction. U Bowel Obstruction: Etiologies
 Nordic Forum Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives Bowel Obstruction To illustrate the spectrum of acute obstruction of the small and the large bowel To explain how these bowel obstructions may
Nordic Forum Trauma & Emergency Radiology Lecture Objectives Bowel Obstruction To illustrate the spectrum of acute obstruction of the small and the large bowel To explain how these bowel obstructions may
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction
 Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
Imaging in gastric cancer
 Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Imaging in gastric cancer Gastric cancer remains a deadly disease because of late diagnosis. Adenocarcinoma represents 90% of malignant tumors. Diagnosis is based on endoscopic examination with biopsies.
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction. Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College
 Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Dr. M. Madhavan, MBBS., MD., MIAC, Professor of Pathology Saveetha Medical College Pathology of Intestinal Obstruction Objectives list the causes of intestinal obstruction
ABDOMEN - GI. Duodenum
 TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
TALA SALEH ABDOMEN - GI Duodenum - Notice the shape of the duodenum, it looks like capital G shape tube which extends from the pyloroduodenal junction to the duodenojejunal junction. - It is 10 inches
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings
 August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
August 2011 Cecal Volvulus: Case Presentation and Review of CT Findings Omar Pardesi, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient LD: History & Physical HPI: 28 y.o. female presents with diffuse abdominal
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Case Report Transmesenteric Internal Herniation Leading to Small Bowel Obstruction Postlaparoscopic Radical Nephrectomy
 Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 5128246, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5128246 Case Report Transmesenteric Internal Herniation Leading to Small Bowel Obstruction Postlaparoscopic
Hindawi Case Reports in Surgery Volume 2017, Article ID 5128246, 4 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5128246 Case Report Transmesenteric Internal Herniation Leading to Small Bowel Obstruction Postlaparoscopic
Christopher Lau Kings County Hospital SUNY Downstate Medical Center February 24, 2011
 Christopher Lau Kings County Hospital SUNY Downstate Medical Center February 24, 2011 37 year old male presented with 1 day history of abdominal pain Pain was diffuse but worst in the epigastric area No
Christopher Lau Kings County Hospital SUNY Downstate Medical Center February 24, 2011 37 year old male presented with 1 day history of abdominal pain Pain was diffuse but worst in the epigastric area No
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus
 A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
A novel plain abdominal radiograph sign to diagnose malrotation with volvulus Nataraja RM 1, Mahomed AA 1* 1. Department of Paediatric Surgery, Royal Alexandra Hospital for Sick Children, Brighton,UK *
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 6/23/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 78 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Diagnosis of incarcerated intramesosigmoid hernia aided by multiplanar reconstruction images of multidetector computed tomography: a case report
 Nagano et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:128 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0535-z CASE REPORT Open Access Diagnosis of incarcerated intramesosigmoid hernia aided by multiplanar reconstruction
Nagano et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:128 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0535-z CASE REPORT Open Access Diagnosis of incarcerated intramesosigmoid hernia aided by multiplanar reconstruction
International Surgery Strangulated lesser omentum hiatus hernia: a rare case report and a literature review
 International Surgery Strangulated lesser omentum hiatus hernia: a rare case report and a literature review --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords: Corresponding Author:
International Surgery Strangulated lesser omentum hiatus hernia: a rare case report and a literature review --Manuscript Draft-- Manuscript Number: Full Title: Article Type: Keywords: Corresponding Author:
A Rare but Serious Complication of Ladd s Procedure: Recurrent Midgut Volvulus
 130 A Rare but Serious Complication of Ladd s Procedure: Recurrent Midgut Volvulus Murat Alkan a Pelin Oğuzkurt a Ozlem Alkan b Semire Serin Ezer a Akgün Hiçsönmez a Departments of a Pediatric Surgery
130 A Rare but Serious Complication of Ladd s Procedure: Recurrent Midgut Volvulus Murat Alkan a Pelin Oğuzkurt a Ozlem Alkan b Semire Serin Ezer a Akgün Hiçsönmez a Departments of a Pediatric Surgery
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help. Print this Page Add to my Bookmarks Page 3 of 10
 Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
Welcome Kristin Ingstrup [ Logout ] SEARCH Home FAQ Archives ABP Topics NeoReviews.org My Bookmarks CME Information Help Overview Editorial Board My Learning Plan January February March May June July August
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
Congenital Internal Hernia Presented with Life Threatening Extensive Small Bowel Strangulation
 pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2013.16.3.190 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2013 September 16(3):190-194 Case Report PGHN Congenital Internal Hernia
pissn: 2234-8646 eissn: 2234-8840 http://dx.doi.org/10.5223/pghn.2013.16.3.190 Pediatric Gastroenterology, Hepatology & Nutrition 2013 September 16(3):190-194 Case Report PGHN Congenital Internal Hernia
Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen
 CASE SERIES Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen Gupta MK 1, Ahmad K 1, Kumar A 1, Santhalia PK 1, Joshi BR 2, Rauniyar RK 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, 2 Department
CASE SERIES Isolated Gallbladder Perforation in Cases of Blunt Trauma Abdomen Gupta MK 1, Ahmad K 1, Kumar A 1, Santhalia PK 1, Joshi BR 2, Rauniyar RK 1 1 Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, 2 Department
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls
 MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
MDCT signs differentiating retroperitoneal and intraperitoneal lesions- diagnostic pearls Poster No.: C-0987 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: D. V. Bhargavi, R. Avantsa, P. Kala; Bangalore/IN
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes
 Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes Poster No.: C-0027 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, R. Moschona, S. Paschalidou ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3 GR, Rethymno/GR,
Lesser sac: Anatomy and non-neoplastic processes Poster No.: C-0027 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, R. Moschona, S. Paschalidou ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3 GR, Rethymno/GR,
The Whipple Operation Illustrations
 The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
The Whipple Operation Illustrations Fig. 1. Illustration of the sixstep pancreaticoduodenectomy (Whipple operation) as described in a number of recent text books by Dr. Evans. The operation is divided
Article begins on next page
 Sudden Death Associated with Incarcerated Small Bowel due to Mesodiverticular Band Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Sudden Death Associated with Incarcerated Small Bowel due to Mesodiverticular Band Rutgers University has made this article freely available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters.
Emergency radiology of the large-bowel: What radiologists should know
 Emergency radiology of the large-bowel: What radiologists should know Poster No.: C-1659 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Falkowski, D. Boll; Basle/CH Keywords: Colon, Emergency,
Emergency radiology of the large-bowel: What radiologists should know Poster No.: C-1659 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Falkowski, D. Boll; Basle/CH Keywords: Colon, Emergency,
Gastrointestinal Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. Anatomy of GI Tract. (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%)
 Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Gastrointestinal Tract (Effective February 2007) (1%-5%) Anatomy of GI Tract Esophagus bulls-eye or target EG junction seen on sagittal scan posterior to left lobe of liver and anterior to aorta Anatomy
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency
 Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Pneumatosis intestinalis, not always a surgical emergency Poster No.: C-2233 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Vanhoutte, M. Lefere, R. Vanslembrouck, D. Bielen, G. De 1 1 2 1 1
Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction
 Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 453128, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/453128 Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction Mesut Sipahi, 1 Kasim Caglayan,
Case Reports in Surgery, Article ID 453128, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/453128 Case Report Intestinal Malrotation: A Rare Cause of Small Intestinal Obstruction Mesut Sipahi, 1 Kasim Caglayan,
Case Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus
 Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
Case 11454 Whirlpool sign in midgut volvulus Emad El-din Althamer 1, Shagufta Jabeen 2, Nada Al-Assaf 1, Akram Jawad 1, Muhammad Hassan 1, Muhammad Fatani 1, Rumayan Al-Rumyan 1, A Aziz Mosabihi 1, Ahmeduddin
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL
 SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
SIGNIFICANCE OF EXTRALUMINAL ABDOMINAL GAS: LOOKING FOR AIR IN ALL THE WRONG PLACES Richard M. Gore, MD North Shore University Health System University of Chicago Evanston, IL SCBT/MR 2012 October 26,
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings
 Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Case 9799 Stanford type A aortic dissection: US and CT findings Accogli S, Aringhieri G, Scalise P, Angelini G, Pancrazi F, Bemi P, Bartolozzi C Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology, University
Hirschprung s. Meconium plug R/S >1 R/S <1
 NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
NEONATAL ABDOMINAL EMERGENCIES LOW OBSTRUCTION HIGH OBSTRUCTION INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION High obstruction - proximal to mid-ileumileum Few dilated, air filled bowel loops Complete obstruction diagnosed by
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome
 October, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue9 http://iamresearcher.online The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome Yanik Fazli 1, Karamustafaoglu Yekta Altemur 1, Tarladacalisir Taner 2, Yoruk Y. 1 1 Trakya University,
October, 2017 2017; Vol1; Issue9 http://iamresearcher.online The Importance of Chiliaditi s Sign- Syndrome Yanik Fazli 1, Karamustafaoglu Yekta Altemur 1, Tarladacalisir Taner 2, Yoruk Y. 1 1 Trakya University,
Introduction and Definitions
 Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Bowel obstruction Introduction and Definitions Accounts for 5% of all acute surgical admissions Patients are often extremely ill requiring prompt assessment, resuscitation and intensive monitoring Obstruction
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently
 Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Abdominal Pain in Pediatric Patients Image Gently Susan D. John, M.D. Baptist Health Emergency Radiology 2017 Disclosure I have no financial relationships with a commercial entity producing healthcarerelated
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Midgut. Over its entire length the midgut is supplied by the superior mesenteric artery
 Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Gi Embryology 3 Midgut the midgut is suspended from the dorsal abdominal wall by a short mesentery and communicates with the yolk sac by way of the vitelline duct or yolk stalk Over its entire length the
Case MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve
 Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Case 12688 MDCT 3D reconstructed features of posterior urethral valve Hidayatullah Hamidi Third year Resident of Radiology French medical institute for children Radiology Department; Kabul, Afghanistan;
Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review Yashpal, M Bansal, A Kudva
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 25 Number 1 Small Bowel Intussusception in an Adult due to Lipoma: a Rare Cause of Obstruction. Case report and Literature Review Yashpal, M Bansal, A Kudva
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings
 Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
Adult bowel obstruction with acute abdomen: spectrum of CT findings Poster No.: C-1571 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. Turturici, G. Gherarducci, F. Bianchi, R. Pascale, M. Tonerini,
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O The University of Hong Kong
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O The University of Hong Kong Plan for the GI system Then GI system in the abdomen first develops as a tube suspended by dorsal and ventral mesenteries. Blood
Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy?
 January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
January 2013 Adult Intussusception: A Complication of Metastatic Melanoma or Primary Malignancy? Johanna Sheu, Harvard Medical School Year III 1 Agenda Menu of tests Definition/anatomy/classification Pediatrics
Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to:
 RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
RAD 451 Abdomen and Pelvis CT (1) By the end of the lecture students should be able to: State the common indications for Abdomen and pelvis CT exams Identify possible contra indications for Abdomen and
A case of cecal volvulus in a cerebral palsy patient: Usefulness of multidetector computed tomography for preoperative diagnosis
 Kawasaki Medical Journal 38(4):205-209,2012 205 A case of cecal volvulus in a cerebral palsy patient: Usefulness of multidetector computed tomography for preoperative diagnosis Yusuke MATSUI 1), Munenori
Kawasaki Medical Journal 38(4):205-209,2012 205 A case of cecal volvulus in a cerebral palsy patient: Usefulness of multidetector computed tomography for preoperative diagnosis Yusuke MATSUI 1), Munenori
The front of the thigh. Dr.Amjad shatarat
 The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
The front of the thigh Femoral triangle (Scarpa s triangle) Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper part of the medial aspect of the thigh immediately below the inguinal ligament. Superiorly:
Complications after laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Background LGBP. Eirik Hornes Halvorsen, MD, PhD Oslo
 Complications after laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity Eirik Hornes Halvorsen, MD, PhD Oslo 20.05.2015 Background Ca 3000 patients are surgically treated for morbid obesity in Norway each year.
Complications after laparoscopic gastric bypass for morbid obesity Eirik Hornes Halvorsen, MD, PhD Oslo 20.05.2015 Background Ca 3000 patients are surgically treated for morbid obesity in Norway each year.
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form.
 Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title:
Early View Article: Online published version of an accepted article before publication in the final form. Journal Name: Journal of Case Reports and Images in Surgery Type of Article: Case Report Title:
Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT
 Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT Obturator hernia (OH) is a rare pelvic hernia. It is diffucult to make an early diagnosis
Consecutive, Bilateral Obturator Hernia in a Single Case HO Aydın¹, EHA Soy¹, T Avcı¹, T Tezcaner¹, S Yıldırım ABSTRACT Obturator hernia (OH) is a rare pelvic hernia. It is diffucult to make an early diagnosis
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
A rare case of secondary small bowel volvulus laparoscopically repositioned: literature review and classification
 Inukai et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0470-z CASE REPORT A rare case of secondary small bowel volvulus laparoscopically repositioned: literature review and
Inukai et al. Surgical Case Reports (2018) 4:65 https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-018-0470-z CASE REPORT A rare case of secondary small bowel volvulus laparoscopically repositioned: literature review and
CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION
 CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION *Sagar H S, Basanta Manjari Swain, Jayashree Mohanty and Sasmita Parida Department of Radio diagnosis, S.C.B. Medical College, Cuttack
CASE OF HETEROTAXY SYNDROME WITH POLYSPLENIA AND INTESTINAL MALROTATION *Sagar H S, Basanta Manjari Swain, Jayashree Mohanty and Sasmita Parida Department of Radio diagnosis, S.C.B. Medical College, Cuttack
Radiologists' Guide to the Whirl Sign
 Radiologists' Guide to the Whirl Sign Poster No.: C-1478 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. layton, R. magennis, V. Rudralingam, S. Sukumar; Manchester/ UK Keywords: Ischemia / Infarction,
Radiologists' Guide to the Whirl Sign Poster No.: C-1478 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: B. layton, R. magennis, V. Rudralingam, S. Sukumar; Manchester/ UK Keywords: Ischemia / Infarction,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O
 ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
ASSESSING THE PLAIN ABDOMINAL RADIOGRAPH M A A M E F O S U A A M P O F O Introduction The abdomen (less formally called the belly, stomach, is that part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis,
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Internal hernias after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass
 The American Journal of Surgery 188 (2004) 796 800 Scientific paper Internal hernias after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Ernesto Garza, Jr., M.D., Joseph Kuhn, M.D., David Arnold, M.D., William
The American Journal of Surgery 188 (2004) 796 800 Scientific paper Internal hernias after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass Ernesto Garza, Jr., M.D., Joseph Kuhn, M.D., David Arnold, M.D., William
General Data. 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性
 General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
General Data 王 X 村 78 y/o 男性 Chief Complaint Vomiting twice this early morning Fever up to 38.9ºC was noted Present Illness (1) Old CVA with left side weakness for more than 10 years and with bed ridden
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE. T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar
 ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
ACUTE PANCREATITIS: NEW CLASSIFICATION OF AN OLD FOE T Barrow, A Nasrullah, S Liong, V Rudralingam, S A Sukumar LEARNING OBJECTIVES q Through a series of cases illustrate the updated Atlanta symposium
Development of the Digestive System. W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong.
 Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Development of the Digestive System W.S. O School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Hong Kong. Organization of the GI tract: Foregut (abdominal part) supplied by coeliac trunk; derivatives include
Which Blunt Trauma Patients Should Be Studied by Abdominal CT?
 MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
MDCT of Bowel and Mesenteric Injury: How Findings Influence Management 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 4 th Nordic Trauma Radiology Course 2006 Stuart E. Mirvis, M.D., FACR Department of Radiology
The Physician as Medical Illustrator
 The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
The Physician as Medical Illustrator Francois Luks Arlet Kurkchubasche Division of Pediatric Surgery Wednesday, December 9, 2015 Week 5 A good picture is worth a 1,000 bad ones How to illustrate an operation
Always keep it in the differential
 Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Acute Appendicitis Lissa C. Sakata and Lindsey Perea 2 Always keep it in the differential Learning Objectives 1. The learner should be able to describe the etiology of acute appendicitis. 2. The learner
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
Patient data. Present illness. Past history. Initial Impression
 GS-ER combine meeting 報告者 :R1 王帝皓指導者 :VS 連楚明 100.12.14 Patient data 25 y/o man Visited at 23:22 Chief complain: abd pain since 5:00 pm Triage: III Vital signs: BT: 35.7, PR: 75, RR: 18, BP: 121/70 SpO2:
GS-ER combine meeting 報告者 :R1 王帝皓指導者 :VS 連楚明 100.12.14 Patient data 25 y/o man Visited at 23:22 Chief complain: abd pain since 5:00 pm Triage: III Vital signs: BT: 35.7, PR: 75, RR: 18, BP: 121/70 SpO2:
Primary epiploic appendagitis versus omental infarction : The role of MDCT
 Primary epiploic appendagitis versus omental infarction : The role of MDCT e-poster: EE-125 Congress: ESGAR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Diagnostic / Mesentery and Peritoneum Authors: P. Kraniotis,
Primary epiploic appendagitis versus omental infarction : The role of MDCT e-poster: EE-125 Congress: ESGAR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Diagnostic / Mesentery and Peritoneum Authors: P. Kraniotis,
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors
 CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
CT evaluation of small bowel carcinoid tumors Poster No.: C-0060 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. V. V. P. Costa, L. Nascimento, T. Bilhim ; Estoril/PT, PT, 1 2 3 1 2 3 Lisbon/PT
Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging
 Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging Poster No.: C-0076 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, S. Paschalidou, S. GIANNOU ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3
Volvulus of the Gastrointestinal Tract: x-ray and CT imaging Poster No.: C-0076 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Papadaki, S. Paschalidou, S. GIANNOU ; Rethymno, CR/ 1 2 2 3 1 3
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study. Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School
 A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
A Frame of Reference for Anatomical Study Anatomy and Physiology Mr. Knowles Chapter 1 Liberty Senior High School Anatomical Terms of Direction and Position Created for communicating the direction and
Key words: anomaly of intestine, reversed rotation, adult
 Key words: anomaly of intestine, reversed rotation, adult n92+ 4 n Fig. 1 Barium enema obstruction of the arrows) and mobile seen. (prone position, : Extrinsic transvers colon (between cecum (round arrow)
Key words: anomaly of intestine, reversed rotation, adult n92+ 4 n Fig. 1 Barium enema obstruction of the arrows) and mobile seen. (prone position, : Extrinsic transvers colon (between cecum (round arrow)
Internal supravesical hernia - a rare cause of intestinal obstruction: report of two cases
 Case report Open Access Internal supravesical hernia - a rare cause of intestinal obstruction: report of two cases Mahdi Bouassida 1,&, Selim Sassi 1, Hassen Touinsi 1, Helmi Kallel 1, Mohamed Mongi Mighri
Case report Open Access Internal supravesical hernia - a rare cause of intestinal obstruction: report of two cases Mahdi Bouassida 1,&, Selim Sassi 1, Hassen Touinsi 1, Helmi Kallel 1, Mohamed Mongi Mighri
Abdominal Assessment
 Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
Abdominal Assessment Mary Marian, MS,RD,CSO University of AZ, Tucson, AZ Neha Parekh, MS,RD,LD,CNSC Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH Objectives: 1. Outline the steps in performing an abdominal examination.
