Academic Review 3. Muscle OIA s Hydrotherapy Cardiovascular System Lymphatic System Boundaries
|
|
|
- Willis Jefferson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Academic Review 3 Muscle OIA s Hydrotherapy Cardiovascular System Lymphatic System Boundaries
2 Lesson Plan: Academic Review #3 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival and Attendance 50 minutes: OIA s Hydrotherapy Cardiovascular Lymphatic Boundaries
3 Classroom Rules Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: Be ready to learn by 9:00, we'll have you out of here by 1:30 Tardiness: arriving late, late return after breaks, leaving early The following are not allowed: Bare feet Side talking Lying down Inappropriate clothing Food or drink except water Phones in classrooms, clinic or bathrooms You will receive one verbal warning, then you'll have to leave the room.
4 Deltoid Origin: Anterior: lateral third of clavicle Middle: acromion process of scapula Posterior: spine of scapula Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Actions: All fibers: Shoulder abduction Anterior: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Shoulder medial rotation Posterior: Shoulder horizontal abduction Shoulder extension Shoulder lateral rotation
5 Deltoid Origin: Anterior: lateral third of clavicle Middle: acromion process of scapula Posterior: spine of scapula Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Abduction Actions: All fibers: Shoulder abduction Anterior: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Shoulder medial rotation Posterior: Shoulder horizontal abduction Shoulder extension Shoulder lateral rotation
6 Deltoid Origin: Anterior: lateral third of clavicle Middle: acromion process of scapula Posterior: spine of scapula Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Horizontal adduction Flexion Actions: All fibers: Shoulder abduction Anterior: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Shoulder medial rotation Posterior: Shoulder horizontal abduction Shoulder extension Shoulder lateral rotation Medial rotation
7 Deltoid Origin: Anterior: lateral third of clavicle Middle: acromion process of scapula Posterior: spine of scapula Horizontal abduction Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of humerus Extension Actions: All fibers: Shoulder abduction Anterior: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Shoulder medial rotation Posterior: Shoulder horizontal abduction Shoulder extension Shoulder lateral rotation Lateral rotation
8 Pectoralis Major Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of clavicle Sternocostal head: Sternum and cartilages of 1-6 ribs Insertion: Crest of the greater tubercle of humerus Actions: All fibers: Shoulder adduction Shoulder medial rotation Upper fibers: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Lower fibers: Shoulder extension
9 Pectoralis Major Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of clavicle Sternocostal head: Sternum and cartilages of 1-6 ribs Adduction Insertion: Crest of the greater tubercle of humerus Actions: All fibers: Shoulder adduction Shoulder medial rotation Upper fibers: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Lower fibers: Shoulder extension Medial rotation
10 Pectoralis Major Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of clavicle Sternocostal head: Sternum and cartilages of 1-6 ribs Horizontal adduction Insertion: Crest of the greater tubercle of humerus Actions: All fibers: Shoulder adduction Shoulder medial rotation Upper fibers: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Lower fibers: Shoulder extension Flexion
11 Pectoralis Major Origin: Clavicular head: Medial half of clavicle Sternocostal head: Sternum and cartilages of 1-6 ribs Insertion: Crest of the greater tubercle of humerus Actions: All fibers: Shoulder adduction Shoulder medial rotation Upper fibers: Shoulder horizontal adduction Shoulder flexion Lower fibers: Shoulder extension Extension
12 Biceps Brachii Origin: Short head: coracoid process of the scapula Long head: supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Insertion: Tuberosity of the radius Aponeurosis of the biceps brachii Actions: Elbow flexion Forearm supination Shoulder flexion
13 Biceps Brachii Origin: Short head: coracoid process of the scapula Long head: supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Flexion Insertion: Tuberosity of the radius Aponeurosis of the biceps brachii Actions: Elbow flexion Forearm supination Shoulder flexion Supination Flexion
14 Triceps Brachii Origin: Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Lateral head: upper posterior humerus Medial head: lower posterior humerus Insertion: Olecranon process of the scapula Actions: Elbow extension Shoulder extension Shoulder adduction
15 Triceps Brachii Origin: Long head: infraglenoid tubercle of the scapula Lateral head: upper posterior humerus Medial head: lower posterior humerus Extension Insertion: Olecranon process of the scapula Extension Actions: Elbow extension Shoulder extension Shoulder adduction Adduction
16 Hydrotherapy Hydrotherapy Internal and external therapeutic use of water and complementary agents. Thermotherapy External therapeutic application of heat. Cryotherapy External therapeutic application of cold.
17 Chemical Factors of Hydrotherapy Minerals
18 Physical Factors of Hydrotherapy Hydrostatic Pressure and Relative Density
19 Thermal Factors of Hydrotherapy Vasodilation, Vasoconstriction, and Vasostasis Sweating The greater the difference between the body temperature and water temperature, the greater the effect will be.
20 Moisture Factors of Hydrotherapy Percentage of moisture contributes pros and cons to hydrotherapy treatments. Steam bath Moisture content: 100%. Moistens nasal passages and throat. Keeps skin supple. Breathing difficulties due to heaviness of the air. Sauna Moisture content: 10-20%. Easier to breath. Drying and irritating to skin and mucous membranes.
21 Variables of Hydrotherapy Character of Effect Intrinsic or extrinsic Type of Effect on Metabolism and Circulation Stimulative or Depressive Temperature Hot or Cold
22 Character of Effects Intrinsic Direct result of the temperature on the tissue it is applied to. Reactive Result of the body's protective reaction to the temperature.
23 Type of Effect Stimulative Circulation: vasodilation Metabolism: increased oxygen absorption, carbon dioxide excretion, and increasing demand for fuel (energy sources)
24 Type of Effect Depressive Circulation: vasoconstriction or vasostasis. Metabolism: decreased oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide excretion.
25 Temperatures For Hydrotherapy purposes: Hot: 105º F to110º F Cold: 55º F to 65º F
26 Thermotherapy Treatments Short hot Temperature: º F Time: < 5 minutes Circulation: stimulated (intrinsic vasodilation) Metabolism: stimulated Tissue tone: decreased Flexibility: increased Long hot Temperature: º F Time: > 5 minutes Circulation: depressed (reactive vasostasis) Metabolism: stimulated Tissue tone: decreased Flexibility: increased
27 1. Vasodilation 2. Vasostasis Circulation Metabolism Short Hot Long Hot (minutes)
28 Cryotherapy Treatments Short cold Temperature: 55-65º F Time: < 1 minute Circulation: stimulated (reactive vasodilation) Metabolism: stimulated Tissue tone: increased Inflammation: decreased Long cold Temperature: 55-65º F Time: > 1 minute Circulation: depressed (intrinsic vasoconstriction) Metabolism: depressed Tissue tone: increased Inflammation: decreased
29 1. Vasoconstriction 2. Vasodilation 3. Vasoconstriction Circulation Metabolism Short Cold Long Cold (minutes)
30 Contrast Bath Short Hot, Short Cold, Repeat up to Three Times Short hot Temperature: º F Time: 1 minute OR Time: 3 minutes Short cold Temperature: 55-65º F Time: 30 seconds OR Time: 1 minute This is the most effective means of flushing the area with fresh blood.
31 1. Vasodilation 2. Vasodilation Hot Cold No application Circulation Metabolism (minutes)
32 Dangers of long hot treatments Circulation depressed Metabolism increased Lack of nutrient delivery and waste removal at the same time as increased consumption of nutrients by cells can result in toxic tissues.
33 Avoiding the dangers of Long Hot Treatments by stimulating circulation Exercise Massage Cold application
34 Long cold treatment effect on an acute inflammation or nerve root compression Local metabolism is slowed which kills pain by causing the neurons to fire more slowly. Reduces the likelihood of secondary cell death. Minimizes swelling.
35 Hydrotherapy Precautions Q. Why should there always be time for the client to rest after a hydrotherapy treatment? A. To allow the body time to recover from the reactive effects.
36 Hydrotherapy Precautions Q. Why should hot always be followed by cold in hydrotherapy? A. To prevent vasostasis caused by hot treatment. Always start with HOT, always end with COLD
37 Hydrotherapy Precautions Q. Why treat the young, old, feeble, and obese with care especially while doing cold hydrotherapy applications? A. Poor capacity to respond to intense treatments.
38 Hydrotherapy Precautions Q. What should you do if your client is chilled by a hydrotherapy treatment? A. Stop the treatment and warm the client with heat, friction, blankets and warm drinks.
39 Hydrotherapy Precautions Q. Why should hydrotherapy be administered before meals? A. To avoid interference with food digestion.
40 Cardiovascular System
41 Anatomy Blood Blood vessels such as arteries, Heart veins, and capillaries
42 Physiology Transportation Protection Combat Hemorrhage
43 Plasma Liquid portion of blood. Blood
44 Blood Erythrocyte Red blood cell. Transports oxygen and carbon dioxide using hemoglobin. Leukocyte White blood cell. Serves as a part of the body's immune system. Thrombocyte Platelet. Prevents blood loss through clotting mechanisms.
45 Blood Thrombus Blood clot. Embolus Floating mass of broken thrombus flowing through the blood stream. Embolism Blockage of a blood vessel with an embolus. Embolism Embolus
46 Heart Wall Pericardium Tissue that surrounds the heart. Epicardium Thin outer connective tissue layer. Myocardium Thick muscular layer that makes up the bulk of the heart wall. Endocardium Thin, inner lining of the heart.
47 Heart Chambers Atrium Superior heart chamber. Ventricle Inferior heart chamber.
48 Coronary Vessels Coronary vessels Arteries and veins that circulate blood to and from the myocardium.
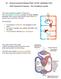
49 Stage 1: End of Systemic Circuit, Blood fills the right side of the heart
50 Stage 2: Pulmonary Circuit, Heart pumps blood to lungs and back to the heart
51 Stage 3: Beginning of Systemic Circuit, Heart pumps blood out to the entire body
52 1 1
53 2
54 3
55 4
56 5
57 6
58 7 7
59 8 Lungs 8 Lungs
60 9 9
61 10
62 11
63 12
64 13
65 14
66 Walls of Arteries and Veins Tunica interna Innermost layer of a blood vessel. Tunica media Middle layer. Connective tissue and smooth muscle. Tunica externa Outer layer of a blood vessel.
67 Walls of Arteries and Veins Vasodilation Enlargement of the vascular lumen s diameter. Vasoconstriction Narrowing of the vascular lumen s diameter. Vasodilation Normal Vasoconstriction
68 Walls of Arteries and Veins Hyperemia Increased local blood flow causing the skin to become reddened and warm. Ischemia Local abnormal decrease in blood flow. Often marked by pain and tissue dysfunction.
69 Blood Vessels Artery Vessel that carries blood away from the heart to the tissues of the body. Vein Vessel that carries blood toward the heart. Avascular Lacking blood vessels.
70 Arteries Pulse Expansion effect of arteries that occurs when the left ventricle contracts and produces a wave of blood that surges through and expands arterial walls.
71 Capillaries Capillary Vessel between an arteriole and a venule. Possesses a thin, permeable membrane for efficient gas exchange with tissues.
72 Venous Return Venomotor tone Changes in smooth muscle tone in the walls of veins can increase or decrease venous circulation.
73 Venous Return Skeletal muscle pump Skeletal muscle contract and squeeze walls which moves blood toward the heart. venous
74 Venous Return Respiratory pump Pressure changes in the thorax and abdomen caused by skeletal muscular contractions of breathing muscles that act as a mechanism to assist venous return.
75 Blood Pressure Blood pressure Pressure exerted by blood on the blood vessel walls. Systolic pressure Maximal pressure in blood pressure measurement. Occurs when the left ventricle contracts. Diastolic pressure Lowest pressure in blood pressure measurement. Occurs when the left ventricle relaxes. High blood pressure Persistently more than 140/90 mm Hg. AKA: hypertension. Average blood pressure 120/80 mm Hg. Low blood pressure Persistently less than 90/60 mm Hg. AKA: hypotension
76 Paths of Circulation Pulmonary circuit Circuit that brings de-oxygenated blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs to release carbon dioxide and regain oxygen, then transports the oxygenated blood to the left atrium. Systemic circuit Circuit that brings oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart through numerous arteries into the capillaries, then moves it through the veins and returns the now de-oxygenated blood to the right atrium of the heart. Microcirculation Flow of blood through a capillary bed.
77 Paths of Circulation Systemic Circuit 1. Left ventricle 2. Aortic semilunar valve 3. Aorta 4. Ascending and descending aortae 5. Arteries 6. Arterioles 7. Capillaries 8. Venules 9. Veins 10. Inferior and superior venae cavae 11. Right atrium
78 Lymphatic System
79 Physiology Transportation The process of transporting dietary proteins, lipids, and lipidsoluble vitamins such as A, D, E, and K from the digestive tract to the blood.
80 Physiology Immune response The process of active immune defense.
81 Physiology Maintains homeostasis The process of collecting accumulated tissue fluid and returning it to blood circulation. This maintains blood volume, blood pressure, and prevents edema (swelling).
82 Lymph Lymph Liquid connective tissue that is part of the lymphatic system. Nearly colorless fluid. Chemically it is very similar to blood plasma. contains white blood cells, proteins, and fats.
83 Lymph Vessels Lymph capillary Tiny, open -ended channel located in tissue space throughout most of the body. Lymph vessel Larger vessels than a lymph capillary. Has thinner walls and more valves than veins. Has lymph nodes situated along them. Lymphatic trunk Made up of large vessels into which lymph is drained from the lymph vessels.
84 Lymph Vessels
85 Lymph Vessels Lymphatic duct The joining of lymphatic trunks. Examples: Right lymphatic duct drains the right side of the head, right arm, and right torso (in green) Thoracic duct drains the rest of the body.
86 Lymph Vessels Lymphatic duct The joining of lymphatic trunks. Examples: Right lymphatic duct drains the right side of the head, right arm, and right torso (in green) Thoracic duct drains the rest of the body.
87 Lymphatic Structures Red bone marrow Blood forming cells found in flat and long bones. Produce red blood cells, platelets, and white blood cells (specifically lymphocytes called B cells).
88 Lymphatic Structures Lymphocyte Type of white blood cell. Examples: B cell, T cell, macrophage
89 Lymphatic Structures Thymus Bi-lobed gland posterior to the sternum. Secretes thymosin and thymopoietin, which stimulate the production and activation of T cells. Spleen Largest lymphatic organ. Located within the left lateral rib cage just posterior to the stomach. Stores lymphocytes, releasing them during immune responses. Lymph node Bean-shaped structures located along lymph vessels. Filters lymph. Houses phagocytes and lymphocytes that destroy pathogens and other foreign substances in the lymph before it returns to the blood. Lymphatic drainage The movement of lymph.
90 Lymph Flow Lymphatic pump The mechanism of lymphatic drainage that uses pressure gradients from external sources exerted on its vessel walls to move lymph. Examples: Skeletal muscle contractions against vessel walls Pressure changes in the thorax and abdomen during breathing. Pulling of the skin and fascia during movement. Contraction of smooth muscle in the walls of lymphatic vessels Rhythmic pumping of walking and grasping.
91 Lymph Flow
92 Immunity Immunity Reaction that involves all body systems as they join together to destroy and eliminate pathogens, foreign substances, or toxic materials. Non-specific immunity Non-specific response to invading pathogens. Includes intact skin and mucous membranes, saliva, gastric juices, vomiting, urine flow, certain white blood cells, fever, and inflammation. AKA: innate immunity. Specific immunity Body's response to invaders. T cells and B cells become activated for a specific pathogen after they come into contact with it and then destroy it. AKA: adaptive immunity.
93 Immunity T cells Lymphocytes that begin as B cells that migrate from bone marrow to the thymus where they fully mature. They recognize pathogens and respond by releasing inflammatory and toxic substances. B cells Lymphocytes that grow and mature in the bone marrow. Produce antibodies which circulate in body fluids such as blood and lymph. Their antibodies inactivate pathogens as they come across them.
94 Transference and Countertransference Transference is when a client feels consciously or unconsciously that the therapist is someone other than a health care provider. For instance, they want the therapist to be their friend, not only a health care provider. Countertransference is when a therapist feels the client is something more than just a client. Either of these can be positive or negative (e.g. strong attraction or disappointment).
95 Dual Relationships Dual relationships occur when we have more than one type of relationship with a client; more than just a therapeutic, relationship. Dual relationships may thwart professionalism and ability to focus on client s needs. It changes roles and expectations. Boundaries may be harder to manage.
96 Sexual Misconduct Sexual misconduct Any sexual contact between the therapist and client or sexualizing of the therapeutic relationship. Includes: Innocent comments about client s body, Dating a client Sexual harassment Offering clients sexual services.
97 Sexual Misconduct Examples of Sexual Misconduct: Flirting or seductive gestures Telling sexual jokes Failure to ensure privacy through proper draping practices Entering room before client is completely draped or dressed Masturbation, intercourse, and rape.
98 Academic Review 3 Muscle OIA s Hydrotherapy Cardiovascular System Lymphatic System Boundaries
99 Academic Review 4 Respiratory System Reproductive System Pregnancy Pathology History of Massage
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying.
 When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
When an ordinary man attains knowledge, he becomes a sage. When a sage attains knowledge, he becomes an ordinary man. -Zen saying Lymphatic System Lesson Plan: Lymphatic System 5 minutes: Breath of Arrival
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Vessels Arteries Arteries Arteries
 CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
CH 12 The Cardiovascular and s The Cardiovascular and s OUTLINE: Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Blood Pressure Cardiovascular System The cardiovascular system is composed of Blood vessels This system
The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 12 The Cardiovascular and Lymphatic Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and
2/28/18. Cardiovascular System. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 26. Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are:
 Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Cardiovascular System Chapter 26 1 Introduction Body is 60% to 80% fluid (by volume) Systems responsible for fluid movement are: - Cardiovascular helps move fluid - Lymphatic Both called pick-up and delivery
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System
 Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Introduction to Lesson 4 - The Lymphatic System Your circulatory system is not your body s only vascular transport system. Closely associated with the blood vessels of the circulatory system is the lymphatic
Cardiovascular System. I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart
 Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
Cardiovascular System I. Structures of the heart A. : Pericardium sack that surrounds the heart 1. : Pericardial Cavity serous fluid filled space between the heart and the pericardium B. Heart Wall 1.
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Cardiovascular System. Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12
 Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System Biology 105 Lecture 15 Chapter 12 Outline I. Functions of cardiovascular system II. Components of the cardiovascular system: I. Blood vessels II. Heart III. Regulation of the heartbeat
Cardiovascular System. Supplementary Information
 Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
Cardiovascular System Supplementary Information THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM - 1 - THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM FUNCTION Transport system carrying nutrient, gases, hormones and waste products to and from the
The Cardiovascular System home study course
 The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
The Cardiovascular System home study course harmony house holistic therapy treatment centre and training academy www.harmony-house.org 1 Copyright 2010 by Mark and Katy Rogers All rights reserved. No part
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ONLINE COURSE - SESSION 11 THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM AND IMMUNITY Functions of the Lymphatic System The lymphatic system has three primary functions. First of all, it returns excess interstitial
Major Function of the Cardiovascular System. Transportation. Structures of the Cardiovascular System. Heart - muscular pump
 Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Structures of the Cardiovascular System Heart - muscular pump Blood vessels - network of tubes Blood - liquid transport vehicle brachiocephalic trunk superior vena cava right pulmonary arteries right pulmonary
Cardiovascular. Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Nutrients Waste Hormones Immune cells Oxygen
 Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Cardiovascular The Cardiovascular System - Arteries Arteries Cardiovascular System Function of the cardiovascular system is to transport blood containing: Carry blood away from heart Carotid arteries Deliver
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 11 AND 12 Name Identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label. 2) The sinoatrial (SA) node is indicated by letter. 3) The specific chamber
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Practical Histology. Cardiovascular System. Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad
 Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Practical Histology Cardiovascular System Dr Narmeen S. Ahmad The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels Functions of cardiovascular system: Transport nutrients, hormones
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System
 Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
Unit 10 Cardiovascular System I. Functions Deliver nutrients to cells > O 2, sugars, amino acids, lipids, ions, H 2 O... Remove waste from cells > CO 2, pathogens, toxins, lactic acid... Fight off infection
1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary.
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM 1. Which of the following blood vessels has a thin elastic layer? A. Aorta. B. Pulmonary artery. C. Posterior vena cava. D. Mesenteric capillary. 2. Capillary beds are equipped with
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet
 CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM TASK CARDS Worksheet Name: Date: Instructions: Put the answers to each task card in the numbered boxes on the chart. 1 a) left semilunar valve / aortic valve b) blood would backflow
Hydrotherapy 1. Liquid. Ice. Steam
 Hydrotherapy 1 Liquid Ice Steam Hydrotherapy Hydrotherapy Internal and external therapeutic use of water and complementary agents. Complementary agents Soaps, essences, aromatics, minerals, seaweed, salt,
Hydrotherapy 1 Liquid Ice Steam Hydrotherapy Hydrotherapy Internal and external therapeutic use of water and complementary agents. Complementary agents Soaps, essences, aromatics, minerals, seaweed, salt,
Circulatory System Review
 Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
Circulatory System Review 1. Know the diagrams of the heart, internal and external. a) What is the pericardium? What is myocardium? What is the septum? b) Explain the 4 valves of the heart. What is their
The cardiovascular system
 The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
The cardiovascular system Components of the Cardiovascular system Heart Vessels: Arteries Capillaries Veins Functions of CVS: Transportation system where blood is the transporting vehicle Carries oxygen,
Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation
 1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
1 Chapter 9 Homeostasis and Circulation Section 9.1 Homeostasis: Life in the Balance Outcomes: I can explain homeostasis I can describe the importance of homeostasis to living things I can explain the
Chapter 16: Circulation
 Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Chapter 16: Circulation Section 1: The Body s Transport System Beating Heart Cardiac muscle is Striated and branched Under involuntary control by the brain stem Functions of the Cardiovascular System 1.
Circulation.notebook March 07, Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Circulatory System p
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Circulatory system The heart Blood Blood Pressure Circulatory Disorders Oct 11 3:27 PM Circulatory System p.304 307 If an organism is small and flat it can transport
Chapter 14. The Cardiovascular System
 Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Chapter 14 The Cardiovascular System Introduction Cardiovascular system - heart, blood and blood vessels Cardiac muscle makes up bulk of heart provides force to pump blood Function - transports blood 2
Figure ) The specific chamber of the heart that is indicated by letter A is called the. Diff: 1 Page Ref: 364
 Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Essentials of Anatomy and Physiology, 9e (Marieb) Chapter 11 The Cardiovascular System Short Answer Figure 11.1 Using Figure 11.1, identify the following: 1) The Purkinje fibers are indicated by label.
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3
 Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Circulatory System Objective sheet 3 10. Functions of blood 1) Transport oxygen and nutrients 2) Transport of carbon dioxide and waste 3) Protection against disease causing micro-organisms 4) Clotting
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone The Function and Interdependence of Organs and Tissues Main Idea 1. We are made of cells. Supporting Information 1. A group of specialized cells form
Human Body Systems Study Guide
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
Human Body Systems Study Guide Nervous System 1. Brain stem part of nervous system and controls the heartbeat and breathing by controlling the cardiac muscle and diaphragm. Also receives information from
This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia)
 Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
Biology 20 Unit D This is a TRANSPORT system that allows every cell: i) uptake of nutrients ( ex. oxygen, glucose) ii) excretes wastes (ex C02, ammonia) requires action of: heart: muscular force to move
The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide.
 Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
Section 1: The circulatory system transports blood to deliver important substances, such as oxygen, to cells and to remove wastes, such as carbon dioxide. K What I Know W What I Want to Find Out L What
10. Thick deposits of lipids on the walls of blood vessels, called, can lead to serious circulatory issues. A. aneurysm B. atherosclerosis C.
 Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
Heart Student: 1. carry blood away from the heart. A. Arteries B. Veins C. Capillaries 2. What is the leading cause of heart attack and stroke in North America? A. alcohol B. smoking C. arteriosclerosis
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System A closed system of the heart and blood vessels The heart pumps blood Blood vessels allow blood to circulate to all parts of the body The function of
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes
 Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Lower Secondary Science Blood Circulatory System Notes / Advanced Notes Double Circulation in Mammals In mammals, there is a double circulation (i.e. blood passes through the heart twice in one complete
Equine biological systems
 Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Equine biological systems Pack 3 Circulation Pack Code: EBS3 This pack you will help you to: describe how blood circulates round the horse's body. www.lbcnc.org.uk About this pack Objectives When you have
Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system. What are the function of the cardiovascular system? Arteries and arterioles:
 5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
5.1 Overview of the cardiovascular system Chp. 5 The cardiovascular system Includes the heart and blood vessels Brings nutrients to cells and helps get rid of wastes Blood is refreshed in the lung, kidneys,
Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Circulation And Blood. Blood 10/22/2012
 Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cells in our body build their own membranes and organelles Make their own ATP Assemble their own enzymes and other proteins And may manufacture substances used elsewhere in the body To do these things,
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System. The heart. The heart is a double pump. A quick note on arteries vs. veins. = the muscular pump of the CV system
 Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Ch. 12 The Circulatory System The heart A.k.a. the cardiovascular system Blood was discussed in Ch. 11 Focus of Ch. 12: heart and blood vessels = the muscular pump of the CV system ~ 100,000 heartbeats/day!
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 27 The Heart and Blood Vessels Most animals have a closed blood system. The blood flows continuously in vessels back to the heart. In an open system the blood is pumped into open ended tubes and
Chapter 17. The Lymphatic System and Immunity. Copyright 2010, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
Chapter 17 The Lymphatic System and Immunity Immunity Innate Immunity Fast, non-specific and no memory Barriers, ph extremes, Phagocytes & NK cells, fever, inflammation, complement, interferon Adaptive
- Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body. - Has disease-fighting functions - Helps maintain homeostasis
 Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Introduction Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
The Cardiovascular System
 The Cardiovascular System Heart Vena Cava Aorta Veins Arteries Venules Arterioles Capillaries Structures of the Cardiovascular system Veins have valves to prevent back flow of blood and carry blood back
The Cardiovascular System Heart Vena Cava Aorta Veins Arteries Venules Arterioles Capillaries Structures of the Cardiovascular system Veins have valves to prevent back flow of blood and carry blood back
2/28/18. Lymphatic System and Immunity. Introduction. Anatomy. Chapter 27. Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system
 Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Lymphatic System and Immunity Chapter 27 1 Introduction Component of the circulatory system Lymphatic system - Helps maintain fluid balance - Supports transport of nutrients within the body - Has disease-fighting
Organ Systems (ch21-26) Practice Questions. Name:
 1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
1. Which one of the following types of tissue stores fat in the body? A) blood B) cartilage C) bone D) adipose tissue E) fibrous connective tissue 2. Which of the following tissues does not match its function?
Lymphatic System. The most important functions of the lymphatic system are: Maintenance of fluid balance in the internal environment
 Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
Lymphatic System Lymphatic System The lymphatic system is a complex network of connective tissue that is composed of: Lymphoid organs Lymph nodes Lymph ducts Lymph vessels Lymph capillaries Lymphatic System
The Circulatory System. The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types
 The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Circulatory System The Heart, Blood Vessels, Blood Types The Closed Circulatory System Humans have a closed circulatory system, typical of all vertebrates, in which blood is confined to vessels and
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
Human Organ Systems. Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive
 Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
Human Organ Systems Circulatory, Respiratory, Digestive The Circulatory System The circulatory system picks up and transports nutrients and oxygen to all the cells in the body, and carries wastes to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL
 1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
1 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY CAPTAINS TRYOUT TEST- WAUBONSIE VALLEY HIGH SCHOOL NAMES: Multiple choice (1 pt per question) 1. What percentage of blood plasma is not reabsorbed by the blood capillaries? a.
Function: Transportation of. Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases
 Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Function: Transportation of Oxygen Nutrients Waste Hormones gases Pericardium: double sac of serous membrane filled with fluid (pericardial fluid to be exact) that surrounds the heart. Parietal pericardium:
Name Score. The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone
 Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Name Score The Neck Bone s Connected to the Head Bone You have pictures of either organs or organ system. Each part has been identified. Color each part a different color. Digestive System - 1 - Nerve
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS
 Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Mr. Epithelium s Anatomy and Physiology Test SSSS You have 50 minutes to complete this test packet. One 8.5 x 11 cheat sheet is allowed, along with 1 non-programmable calculator dedicated to computation.
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
Chapter 23. Circulation
 Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Chapter 23 Circulation Standards CORE: I can describe the components and function of blood. I can describe structure and function of blood vessels. I can compare and contrast systemic and pulmonary systems.
Levels of Organization. Chapter 19 6/11/2012. Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body. 4 Primary Tissues
 Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
Levels of Organization Chapter 19 Homeostasis & Organization of the animal body Chemical Cellular Tissue Organs System Level Organismic 1-2 4 Primary Tissues 1. Epithelial Tissue: covers surfaces lines
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System (p )
 The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
The Circulatory System (p. 268-281) How Does Gravity Affect Blood Circulation? As with all land animals, the giraffe and the corn snake are constantly subject to the force of gravity The circulatory system
1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated)
 Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Carl Christennsen, PhD Chap. 19, 20, & 21 - Circulatory System Bio. 2304 Human Anatomy HEART 1. What kind of blood is found in the rt. atrium? (oxygenated or deoxygenated) Where does this blood come from?
Main Menu. Circulatory System. click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Circulatory System click here Main Menu http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/ap6/ap6entry.htm[3/20/18, 12:56:19 PM] Circulatory System The vascular or circulatory system controls the circulation
Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems
 34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
34 Circulatory, Respiratory, and Excretory Systems section 1 Circulatory System Before You Read Press the tips of two fingers to the inside of your wrist, at a point just below your thumb. Can you feel
: thick middle layer; cardiac muscles : thin inner layer; endothelial lining
 1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
1 2 3 4 Bio 1102 Lecture 5 (guided) Chapter 8: Heart & Blood Vessels Functions of Circulatory System: To carry from lungs to all cells, tissues, and organs of body To carry from digestive system to all
Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems
 Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
Biology 12 Name: Human Biology Per: Date: Chapter 10 The Circulatory & Lymphatic Systems Complete using BC Biology 12, pages 298 325 10.1 The Blood Vessels pages 298-299 1. Label the blood vessels in this
7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes. Circulation
 1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
1 7.L.1.4 Circulatory System Guided Study Notes Circulation Sect. 1: The Body s Transport System Sect. 2: A Closer Look at Blood Vessels Sect. 3: Blood and Lymph Sect. 4: Cardiovascular Health Sect. 1:
Glossary: The Cardiovascular System
 This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
This glossary includes terms that have been introduced in Lesson 14. Student Resource 14.14 Glossary: The Cardiovascular System Anatomy Terms aorta Large artery that transports blood from the left ventricle
Structure and organization of blood vessels
 The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
The cardiovascular system Structure of the heart The cardiac cycle Structure and organization of blood vessels What is the cardiovascular system? The heart is a double pump heart arteries arterioles veins
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels
 Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
Chapter 27 -The Heart & Blood Vessels 3.2 Learning Objectives 3.2.2 Organisational Complexity of the human 1. Describe the structures and organisation of tissues in the closed circulatory system. 2. Discuss
THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
 Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Biology 30S THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM Name: This module adapted from bblearn.merlin.mb.ca 1 Introduction to Circulation The first organ to form, and the last organ to die. The heart is the pump of life. The
Human Anatomy and Body Systems
 Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Anatomy and Body Systems Levels of Organization The human body is organized in several levels, from the simplest to the most complex... Cells the basic unit of life Tissues clusters of cells performing
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm
 Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Done By : Saleh Salahat Upper Limb Muscles Muscles of Axilla & Arm 1) Muscles around the axilla A- Muscles connecting the upper to thoracic wall (4) 1- pectoralis major Origin:- from the medial half of
Cardiovascular System. Heart Anatomy
 Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
Cardiovascular System Heart Anatomy 1 The Heart Location & general description: Atria vs. ventricles Pulmonary vs. systemic circulation Coverings Walls The heart is found in the mediastinum, the medial
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet
 Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Biology 105 Midterm Exam 4 Review Sheet The fourth midterm exam will cover the following lecture material (lectures 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, and 19): Blood (from chapter 11 in the textbook), Cardiovascular
Cardiovascular system:
 Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Cardiovascular system: Mediastinum: The mediastinum: lies between the right and left pleura and lungs. It extends from the sternum in front to the vertebral column behind, and from the root of the neck
Summary table: artery capillary vein Blood pressure Hi Low lowest Valves present or Absent Absent Present
 Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
Bi 067: Review of sectn 7-9 - cardiovascular and lymphatic Heart and Blood vessels: 3 Types of blood vessels: 1. Arteries, arterioles -away from heart, O2 rich 2. Capillaries gas and nutrient/waste exchange
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Blood Vessels. Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels. Veins carry blood toward the heart
 C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
C H A P T E R Blood Vessels 20 Types of Blood Vessels Arteries carry blood away from the heart Capillaries smallest blood vessels The site of exchange of molecules between blood and tissue fluid Veins
Chapter 12. Capillaries. Circulation. The circulatory system connects with all body tissues
 Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Chapter 12 Circulation The circulatory system connects with all body s In many animals, microscopic blood vessels called capillaries Form an intricate network among the Red blood cell song Figure 23.1A
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process:
 Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
Scrub In: Red blood cells are called: a. erythrocytes b. leukocytes c. melanocytes d. thrombocytes Which component of blood is necessary for the initiation of the blood clotting process: a. erythrocytes
The Circulatory System. The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels.
 The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
The Circulatory System The circulatory system includes the Heart, Blood Tissue and the Blood Vessels. The Circulatory System-Transport The absorption and circulation of materials throughout an organism
Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93)
 Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Name: Date: Lesson 10 Circulatory System (Nelson p.88-93) Learning Goals: A. I can explain the primary functions of the circulatory system in animals. B. I can identify and explain all the parts of the
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes
 Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Health Science 20 Circulatory System Notes Functions of the Circulatory System The circulatory system functions mainly as the body s transport system. It transports: o Oxygen o Nutrients o Cell waste o
Blood and Heart. Student Learning Objectives:
 Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
Blood and Heart Student Learning Objectives: Identify the major components of the blood. Identify the primary structures associated with the heart Follow the blood through the path of the circulation.
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The circulatory system brings many different materials to all the cells of the body and picks up waste from the same cells.
 CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
CIRCULATION AND IMMUNITY The Circulatory System The circulatory system, otherwise known as the cardiovascular system, consists of the heart, blood vessels, and blood. This important system is a large network
Types of circulatory systems
 Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Types of circulatory systems Open system Mostly invertebrates Low pressure Haemocoel Suitable for small organisms Closed system Vertebrates High pressure Blood remains in blood vessels Separate tissue
Cardiovascular & lymphatic system both are supply fluid flow in to the body. but bothe are deferent type of fluid..
 Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
Hap unit 6th Introduction:- All body tissues are bathed in tissue fluid, consisting of the diffusible constituent of blood & waste material from cell. Some tissue fluid returnes to capillaries at their
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system
 2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
2.01 Remember the structures of the circulatory system Essential questions What are the structures of blood? What are the structures of the circulatory system? circulatory system 2 Structures of the circulatory
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, Name Student Number
 Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
Anatomy and Physiology, Spring 2015 Exam II: Form A April 9, 2015 Name Student Number For Questions 1 2 refer to the following table. 1 Ventricular pressure is greater than aortic 6 AV valve is open 2
The Cardiovascular System. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Structure of Blood Vessels. The Blood Vessels. Blood Vessel Review
 The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
The Cardiovascular System The Blood Vessels The Structure of Blood Vessels Blood Vessel Review Arteries carry blood away from the heart Pulmonary trunk to lungs Aorta to everything else Microcirculation
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System. Chapters 11, 12
 Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
Cardiovascular System Chapters 11, 12 Oxygen enters the cardiovascular system by diffusing from alveoli into blood cells in the capillaries, then binding to hemoglobin in red blood cells. Blood Hematology-
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle.
 The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
The blood returns from the body and enters right atrium using the vena cava. It passes through the tricuspid valve to the right ventricle. From this camber, it passes through the pulmonary semilunar valve
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels
 Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Cardiovascular System Blood Vessels Structure of Blood Vessels The three layers (tunics) Tunica intima composed of simple squamous epithelium Tunica media sheets of smooth muscle Contraction vasoconstriction
Heart Facts. The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime.
 Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
Circulatory System Heart Facts The average adult heart beats 72 times a min 100,000 times a day 3,600,000 times a year 2.5 billion times during a lifetime. Heart Facts Weighs 11 oz A healthy heart pumps
