EKG Sensor (Order Code EKG-BTA)
|
|
|
- Maud Stevenson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 EKG Sensor (Order Code EKGBTA) The Vernier EKG (Electrocardiogram or ECG) Sensor measures electrical potential waveforms (voltages produced during the contraction of the muscle). The following is a partial list of activities and experiments that can be performed using this sensor: Monitor resting EKG. Study the meaning of P, Q, R, S, and T waveforms. Monitor EKG after mild exercise. Determine the axis of the heart. Investigate the effect of the central nervous system influence on reflex amplitude. Associate the electrical activity of a muscle with movement of joints. Collecting Data with the EKG Sensor This sensor can be used with the following interfaces to collect data: Vernier LabQuest 2 or original LabQuest as a standalone device or with a computer Vernier LabQuest Mini with a computer Vernier LabPro with a computer or TI graphing calculator Vernier Go! Link 1 Vernier EasyLink Vernier SensorDAQ CBL 2 TINspire Lab Cradle Here is the general procedure to follow when using the EKG Sensor: 1. Connect the EKG Sensor to the interface. 2. Start the datacollection software The software will identify the EKG Sensor and load a default datacollection setup. You are now ready to collect data. DataCollection Software This sensor can be used with an interface and the following datacollection software. Logger Pro 3 This computer program is used with LabQuest 2, LabQuest, LabQuest Mini, LabPro, or Go!Link. Logger Lite This computer program is used with LabQuest 2, LabQuest, LabQuest Mini, LabPro, or Go!Link. 1 EKGDIN sensors will not work with Go! Link. 2 If you are using Logger Pro 2 with either a ULI or SBI, the sensor will not autoid. Open an experiment file for the EKG Sensor in the Probes & Sensors folder.
2 LabQuest App This program is used when LabQuest 2 or LabQuest is used as a standalone device. DataQuest Software for TINspire This calculator application for the TINspire can be used with the EasyLink or TINspire Lab Cradle. EasyData App This calculator application for the TI83 Plus and TI84 Plus can be used with CBL 2, LabPro, and Vernier EasyLink. We recommend version 2.0 or newer, which can be downloaded from the Vernier web site, and then transferred to the calculator. See the Vernier web site, for more information on the App and Program Transfer Guidebook. DataMate program Use DataMate with LabPro or CBL 2 and TI73, TI83, TI84, TI86, TI89, and Voyage 200 calculators. See the LabPro and CBL 2 Guidebooks for instructions on transferring DataMate to the calculator. LabVIEW National Instruments LabVIEW software is a graphical programming language sold by National Instruments. It is used with SensorDAQ and can be used with a number of other Vernier interfaces. See for more information. This sensor is equipped with circuitry that supports autoid. When used with LabQuest 2, LabQuest, LabQuest Mini, LabPro, Go! Link, SensorDAQ, TINspire Lab Cradle, EasyLink, or CBL 2, the datacollection software identifies the sensor and uses predefined parameters to configure an experiment appropriate to the recognized sensor. Specifications Offset: ~1.00 V (±0.3 V) Gain: 1 mv body potential / 1 V sensor output NOTE: Vernier products are designed for educational use. Our products are not designed nor recommended for any industrial, medical, or commercial process such as life support, patient diagnosis, control of a manufacturing process, or industrial testing of any kind. How the EKG Sensor Works Muscle cells are polarized at rest. This means the cells have slightly unequal concentrations of ions across their cell membranes. An excess of positive sodium ions on the outside of the membrane causes the outside of the membrane to have a positive charge relative to the inside of the membrane. The inside of the cell is at a potential of about 90 millivolts (mv) less than the outside of the cell membrane. The 90 mv difference is called the resting potential. The typical cell membrane is relatively impermeable to the entry of sodium. However, stimulation of a muscle cell causes an increase in its permeability to sodium. Sodium ions migrate into the cell through the opening of voltagegated sodium channels. This causes a change (depolarization) in the electrical field around the cell. This change in cell potential from negative to positive and back is a voltage pulse called an action potential. In muscle cells, action potential trigger muscle contractions. 2
3 Other ions and charged molecules are involved in the depolarization and repolarization of cardiac muscle. These include potassium, calcium, chlorine, and charged protein molecules. The sum action potential generated during the depolarization and repolarization of the cardiac muscle can be recorded by electrodes at the surface of the skin. A recording of the heart s electrical activity is called an electrocardiogram (EKG). The cells of the heart s conducting system will depolarize spontaneously. This spontaneous depolarization is most apparent in a cluster of cardiacmuscle cells embedded in the upper wall of the right atrium. This group of cells is called the pacemaker (also known as the sinoatrial or SA node). Depolarization of the pacemaker generates a current that leads to the 3 Outside the cell Lipid bilayer Inside the cell Layers of protein molecules Animal cell membrane (section view) depolarization of all other cardiacmuscle cells. The wave of depolarization travels from the right atrium to the left atrium quickly enough that both atria contract at essentially the same time. The atria and the ventricles are isolated from each other electrically by connective tissue that acts like the insulation on an electric wire. The depolarization of the atria does not directly affect the ventricles. There is another group of cells in the right atria, called the atrioventricular or AV node, that will conduct the depolarization of the atria down a special bundle of conducting fibers (called the Bundle of His) to the ventricles. In the muscle wall of the ventricles are Purkinje fibers, which are a special system of muscle fibers that bring depolarization to all parts of the ventricles almost simultaneously. This process causes a small time delay, so there is a short pause after the atria contract and before the ventricles contract. Because the cells of the heart muscle are interconnected, this wave of depolarization, contraction, and repolarization spreads across all of the connected muscle of the heart. Sinoatrial (SA) Node Atrioventricular (AV) Node Right Atrium Right Ventricle When a portion of the heart is polarized and the adjacent portion is depolarized, an electrical current is created that moves through the body. This current is greatest when one half of the connected portion of the heart is polarized and the adjacent half is not polarized. The current decreases when the ratio of polarized tissue to nonpolarized tissue is less than one to one. The changes in these currents can be measured, amplified, and plotted over time. The EKG represents the summation of all the action potentials from the heart, as detected on the surface of the body. It does not measure the mechanical contractions of the heart directly. The impulse originating at the SA node causes the atria to contract, forcing blood Bundle of His (Atricoventricular Bundle) Purkinje Fibers (Conduction Myofibe
4 into the ventricles. Shortly after this contraction, the ventricles contract due to the signal conducted to them from the atria. The blood leaves the ventricles through the aorta and pulmonary artery. The polarity of the cardiacmuscle cells returns to normal and the heart cycle starts again. The Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (EKG) is a graphic tracing of the heart s electrical activity. A typical tracing consists of a series of waveforms occurring in a repetitive order. These waveforms arise from a flat baseline called the isoelectric line. Any deflection from the isoelectric line denotes electrical activity. The five major deflections on a normal EKG are designated by the letters P, Q, R, S, and T. One heart cycle is represented by a group of waveforms beginning with the P wave, followed by the QRS wave complex, and ending with the T wave. The P wave represents the depolarization of the atria and is associated with their contraction. The QRS wave complex consists of three waves. The first negative deflection is the Q wave and is followed by a positive deflection called the R wave. The complex ends with a negative deflection known as the S wave. The QRS wave complex denotes depolarization of the ventricles and is associated with their contraction. Atrial repolarization occurs during the depolarization of the ventricles. For this reason, the waveform associated with atrial repolarization is undetectable on an EKG. The last wave is called the T wave, and is usually represented by a positive deflection. The T wave indicates ventricular repolarization. Electrical energy is also generated by skeletal muscle, and can be seen as muscle artifacts if your arm is moved while the EKG is attached. The sequence from P wave to P wave represents one heart cycle. The number of cycles in a minute is called the heart rate and is typically 7080 beats per minute at rest. Some typical times for portions of the EKG are: PR interval 0.12 to 0.20 seconds QRS interval less than 0.1 seconds QT interval less than 0.38 seconds If your EKG does not correspond to the above numbers, DO NOT BE ALARMED! These numbers represent typical averages and many healthy hearts have data that fall outside of these parameters. To read an EKG effectively takes considerable training and skill. This sensor is NOT intended for medical diagnoses. 4
5 Connecting the EKG Sensor to a Person Use three electrode patches per subject. The electrodes can be reused, but they tend to absorb moisture (they are very hygroscopic) and, therefore, reuse is not recommended. Note: Once opened, the electrodes should be kept refrigerated in a clean, dry, airtight container for storage. Even with airtight storage, opened electrode packages cannot be stored from one year to the next. Because the electrical signal produced by the heart and detected at the body s surface is so small, it is very important that the electrode patch makes good contact with the skin. Scrub the areas of skin where the patches will be attached with a paper towel to remove dead skin and oil. Peel three electrode patches from the backing paper. Firmly place the first electrode on the right wrist. Place a second electrode on the inside of the right elbow. Place a third electrode on the inside of the left elbow. Place each electrode so it is on the inside part of the arm (closer to the body) and the tab on the edge of the electrode patch points down. This way, the wire of the sensor can hang freely without twisting the edge of the electrode patch. negative green reference black positive red EKG Sensor to interface Connect the micro alligator clips from the sensor to the tabs on the edges of the electrode patches. Connect the black (or reference ) alligator clip to the right wrist electrode patch. This is the reference point for the isoelectric line (baseline). Connect the green (or negative) alligator clip to the right elbow electrode patch. Connect the red (or positive) alligator clip to the left elbow electrode patch. There are several different ways to connect the EKG sensor. This simple arrangement is appropriate for the classroom. For best results, disconnect the computer or LabQuest from A/C power, keep the sensor away from the computer monitor, and hold the senor box in the palm of your hand. Calibration You should never have to calibrate the EKG Sensor. Because you are primarily interested in the shape and periodicity of the signal, the EKG sensor does not need to be calibrated. You can simply load the appropriate calibration file and experiment file. Any experiments we describe in this booklet can be done using a stored Vernier calibration in volts, as described in the previous section. The sensor is designed to produce a signal between 0 and 5 volts, with 1 volt being the isoelectric line. Deviation from the isoelectric line indicates electrical activity. 5
6 Suggested Experiments RESTING EKG Record the EKG of a person who is at rest. The person whose EKG is being recorded should remain calm and relaxed. Encourage the person to breath normally. Using the displayed graph, record the following information: Interval Analysis Interval Time (milliseconds) PQ QRS QT Heart Rate Analysis Item Rate (per minute) Minimum Maximum Average EKG AFTER MILD EXERCISE Using the EKG Sensor, record an EKG of a person who is initially at rest. Disconnect the sensor wires from the electrode patches, but leave the patches on the person being monitored. Have the person exercise for three minutes by jogging in place or by stepping in time. Reattach the sensor wires to the electrodes on the person when they have finished exercising and record a new EKG. Compare the resting EKG to the EKG after mild exercise. EKG AND DIFFERENT BODY POSITIONS Use body position as your independent variable. Record the resting EKG as before. Then have the person sit, stand, or lie down. Make no other changes. Compare your results with your resting EKG. Note any changes in heart rate, interval times, height of R wave, etc. EKG AND MILD STIMULANTS Drink a couple of cups of caffeinated coffee or cola. Record an EKG. Compare your results with those at rest and following mild exercise. Note: This might show less effect on people who are accustomed to large amounts of caffeine. EKG AND ELECTRODE POSITION: The Axis of the Heart Different arrangements of electrode patches will change the shape and intensity of the measured signal. Each arrangement is called a lead. Each lead reveals unique information based on the lead s orientation relative to the axis of the heart. Remember to scrub the areas of the skin where the electrode patches are placed with a paper towel to remove skin oil and moisture. Lead I: Put an electrode patch on the right upper arm. Connect the green (or negative) alligator clip to the right upper arm electrode patch. Put an electrode patch on the left upper arm. Connect the red (or positive) alligator clip to the left upper arm electrode patch. 6
7 Put an electrode patch on the inside surface of the area behind the right ankle bone. Connect the black (or reference ) alligator clip to the ankle electrode patch. This is the reference point for the isoelectric line. Drawing an imaginary line between the red and green electrodes shows that this lead is measuring polarity changes across the chest, above the heart, and parallel to the shoulders. Lead II: Put an electrode patch on the right upper arm. Connect the green (or negative) alligator clip to the right upper arm electrode patch. Put an electrode patch on the inner surface of the left thigh. Connect the red (or positive) alligator clip to the left inner thigh electrode patch. Note: Instead of the left thigh, you can use the inner surface of the left ankle just behind the left ankle bone. Put an electrode patch on the inside surface of the area behind the right ankle bone. Connect the black (or reference ) alligator clip to the ankle electrode patch. Drawing an imaginary line between the red and green electrodes yields an oblique line from the right shoulder towards the left leg. Lead II generally gives the greatest variation of impulse and is the EKG usually shown in movies, text books, etc. Lead III: The lead III arrangement has the green (or negative) electrode connected to the left arm and the red (or positive) electrode connected to the left inner thigh with the black (reference) electrode connected to the inside of the right ankle as before. Note: Instead of the left thigh, you can use the inner surface of the left ankle just behind the left ankle bone. This arrangement of the red and green electrodes yields an imaginary line from the left shoulder to the left leg. If the three imaginary lines were connected, they would make a triangle. This triangle is called the Einthoven triangle. The measured intensity of voltage on its three sides can be used to study heart functions and anatomy. You can make an approximation of the axis of your heart; that is, the orientation of the centerline of the mass of your heart. Conduct a Lead I EKG. Conduct a Lead II EKG. Finally, conduct a Lead III EKG. Compare the results. Determine which lead yields the maximum Rwave amplitude. If the maximum R wave is with Lead I, then the axis of your heart is approximately at 0 degrees as measured from the horizontal and your left. If the maximum R wave is with Lead II, then the axis of the heart is approximately 60 degrees down from the horizontal and to the left. If the maximum R wave is with Lead III, then the axis is approximately 120 degrees from the horizontal and your left. You can make a further refinement in your estimate by noting the relative proportion of R wave strength between the two leads with the largest R wave. 7
8 If the Lead II and the Lead III R waves are about equal, then the axis is about halfway between the 60 degree angle and the 120 degree angle. You could therefore estimate the axis of the heart to be nearly vertical. The heart s axis tends to vary with general body shape. Very slender and elongated people tend to have a more vertical heart. Short and stocky people tend to have a more horizontal axis for their heart. Warranty Vernier warrants this product to be free from defects in materials and workmanship for a period of five years from the date of shipment to the customer. This warranty does not cover damage to the product caused by abuse or improper use. Vernier Software & Technology S.W. Millikan Way Beaverton, OR Toll Free (888) (503) FAX (503) info@vernier.com Rev. 5/16/2012 Logger Pro, Logger Lite, Vernier LabQuest 2, Vernier LabQuest, Vernier LabQuest Mini, Vernier LabPro, Go! Link, Vernier EasyLink and other marks shown are our trademarks or registered trademarks in the United States. TINspire, CBL 2 and CBL, TIGRAPH LINK, and TI Connect are trademarks of Texas Instruments. All other marks not owned by us that appear herein are the property of their respective owners, who may or may not be affiliated with, connected to, or sponsored by us. Sole Australian distributor: Scientrific Pty Ltd Ph: Fax:
EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189
 imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
imagine explore learn EKG Sensor Product Number: ENEKG189 Overview An electrocardiogram abbreviated as EKG or ECG is a test that measures the electrical activity of the heartbeat. With each beat, an electrical
Science in Sport. 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read. The Electrocardiogram. ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE. Sensors: Loggers: Logging time: 10 seconds
 Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Sensors: Loggers: ECG Any 12 bit EASYSENSE Science in Sport Logging time: 10 seconds 204a ECG demonstration (Graph) Read Regular medical check ups are essential part of the life of a professional sports
Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor)
 [KDS-1040] Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor) User's Manual Note This product is designed for educational use only. Not recommended for industrial, medical, commercial use. What is Electrocardiogram?
[KDS-1040] Electrocardiogram sensor (ECG/EKG sensor) User's Manual Note This product is designed for educational use only. Not recommended for industrial, medical, commercial use. What is Electrocardiogram?
2The Concept of Periodic Functions
 The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
The Concept of Periodic Functions EKG INTRODUCTION The heart is a fist-sized muscle that acts as an electrical generator lying in a conducting medium made of body tissue and fluids. The heart pumps oxygen-rich
Sample. Analyzing the Heart with EKG. Computer
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG Computer An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab 11: Performing and analyzing an EKG Lab report due April 17 th
 BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
BIO 60: Vertebrate Physiology Lab : Lab report due April 7 th All muscles produce an electrical current when they contract. The heart is no exception. An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body
 How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
How Do We Sense, Think, and Move? -- Lab #11 Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION
 LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
LABORATORY INVESTIGATION Recording Electrocardiograms The taking of an electrocardiogram is an almost universal part of any complete physical examination. From the ECG record of the electrical activity
Analyzing the Heart with EKG
 Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Analyzing the Heart with EKG LabQuest An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring within the heart. In a healthy heart there is a natural pacemaker in
Figure 1 muscle tissue to its resting state. By looking at several beats you can also calculate the rate for each component.
 ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
ANALYZING THE HEART WITH EKG WITH LABQUEST LAB From Human Physiology with Vernier Westminster College INTRODUCTION An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a graphical recording of the electrical events occurring
L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body
 L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment Warnings for Today's Lesson In general
L63 - Bioelectronics Measuring Electrical Properties of the Body Experiment #1 Your Body's Resistance Equipment: Digital multimeter, Banana leads Important Equipment Warnings for Today's Lesson In general
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE. CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS
 ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
ECG SENSOR ML84M USER S GUIDE CENTRE FOR MICROCOMPUTER APPLICATIONS http://www.cma-science.nl Short description The ECG sensor measures electrical potentials produced by the heart (Electro- cardiogram).
3/26/15 HTEC 91. EKG Sign-in Book. The Cardiac Cycle. Parts of the ECG. Waves. Waves. Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2)
 EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
EKG Sign-in Book HTEC 91 Review of protocol Review of placement of chest leads (V1, V2) Medical Office Diagnostic Tests Week 2 http://www.cvphysiology.com/arrhythmias/a013c.htm The Cardiac Cycle Represents
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular
 Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Lab 4: Introduction to Physiological Measurements - Cardiovascular INTRODUCTION: This lab will demonstrate cardiovascular measurements by creating an ECG with instruments used in previous labs. Students
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II. Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #5: Physiology of the Cardiovascular System For Labs Associated With Dr. Thompson s Lectures References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY NAME Detection of heart sounds. Clean the ear pieces of the stethoscope before using. The ear pieces should be pointing slightly forward when inserted into the ears because
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II
 PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet EKG Lab (IBEAM) 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to study the electrical activity of human heart b. to observe
PHYS 1112L - Introductory Physics Laboratory II Laboratory Advanced Sheet EKG Lab (IBEAM) 1. Objectives. The objectives of this laboratory are a. to study the electrical activity of human heart b. to observe
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
INTRODUCTION TO ECG. Dr. Tamara Alqudah
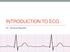 INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
INTRODUCTION TO ECG Dr. Tamara Alqudah Excitatory & conductive system of the heart + - The ECG The electrocardiogram, or ECG, is a simple & noninvasive diagnostic test which records the electrical
Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography
 7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
7.1 Lab 7. Physiology of Electrocardiography The heart is a muscular pump that circulates blood throughout the body. To efficiently pump the blood, cardiac contractions must be coordinated and are regulated
Electrocardiography I Laboratory
 Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Introduction The body relies on the heart to circulate blood throughout the body. The heart is responsible for pumping oxygenated blood from the lungs out to the body through the arteries and also circulating
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System
 Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
Birmingham Regional Emergency Medical Services System 2018 ALCTE Summer Conference EKG Basics Brian Gober, MAT, ATC, NRP, CSCS Education Services Manager ECC Training Center Coordinator Birmingham Regional
Full file at
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) What electrical event must occur for atrial kick to occur? 1) A) Atrial repolarization B) Ventricular
ECG. Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13
 ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
ECG Prepared by: Dr.Fatima Daoud Reference: Guyton and Hall Textbook of Medical Physiology,12 th edition Chapters: 11,12,13 The Concept When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current
11/18/13 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN. Origin of Bioelectric Signals
 ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
ECG SIGNAL ACQUISITION HARDWARE DESIGN Origin of Bioelectric Signals 1 Cell membrane, channel proteins Electrical and chemical gradients at the semi-permeable cell membrane As a result, we get a membrane
Cardiovascular Physiology
 Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
Cardiovascular Physiology The mammalian heart is a pump that pushes blood around the body and is made of four chambers: right and left atria and right and left ventricles. The two atria act as collecting
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG)
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY (ECG) The heart is a muscular organ, which pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. Blood provides the body with oxygen and nutrients, as well as assists in
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG)
 Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Lab #3: Electrocardiogram (ECG / EKG) An introduction to the recording and analysis of cardiac activity Introduction The beating of the heart is triggered by an electrical signal from the pacemaker. The
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per:
 Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
Interpreting Electrocardiograms (ECG) Physiology Name: Per: Introduction The heart has its own system in place to create nerve impulses and does not actually require the brain to make it beat. This electrical
CARDIOCOMP Electrocardiography Primer
 TM CARDIOCOMP Electrocardiography Primer Richmond, VA, USA 23230 CARDIOCOMP 1 Version 8 Electrocardiography Primer Revised: June 2015 Copyright 2015. Phipps & Bird, Inc. All Rights Reserved. This is a
TM CARDIOCOMP Electrocardiography Primer Richmond, VA, USA 23230 CARDIOCOMP 1 Version 8 Electrocardiography Primer Revised: June 2015 Copyright 2015. Phipps & Bird, Inc. All Rights Reserved. This is a
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Overview Heart and Vessels 2 Major Divisions Pulmonary Circuit Systemic Circuit Closed and Continuous Loop Location Aorta Superior vena cava Right lung Pulmonary trunk Base of heart
BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG
 BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of cardiac electrical activity. The electrical activity is readily detected by electrodes attached to the skin. After the
BASIC CONCEPT OF ECG Electrocardiogram The electrocardiogram (ECG) is a recording of cardiac electrical activity. The electrical activity is readily detected by electrodes attached to the skin. After the
Outline. Electrical Activity of the Human Heart. What is the Heart? The Heart as a Pump. Anatomy of the Heart. The Hard Work
 Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Electrical Activity of the Human Heart Oguz Poroy, PhD Assistant Professor Department of Biomedical Engineering The University of Iowa Outline Basic Facts about the Heart Heart Chambers and Heart s The
Lab Activity 24 EKG. Portland Community College BI 232
 Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
Lab Activity 24 EKG Reference: Dubin, Dale. Rapid Interpretation of EKG s. 6 th edition. Tampa: Cover Publishing Company, 2000. Portland Community College BI 232 Graph Paper 1 second equals 25 little boxes
Objectives of the Heart
 Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
Objectives of the Heart Electrical activity of the heart Action potential EKG Cardiac cycle Heart sounds Heart Rate The heart s beat separated into 2 phases Relaxed phase diastole (filling of the chambers)
PART I. Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles
 PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
PART I Disorders of the Heart Rhythm: Basic Principles FET01.indd 1 1/11/06 9:53:05 AM FET01.indd 2 1/11/06 9:53:06 AM CHAPTER 1 The Cardiac Electrical System The heart spontaneously generates electrical
5- The normal electrocardiogram (ECG)
 5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
5- The (ECG) Introduction Electrocardiography is a process of recording electrical activities of heart muscle at skin surface. The electrical current spreads into the tissues surrounding the heart, a small
Cardiac Cycle. Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time.
 The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
The Heartbeat Cardiac Cycle Each heartbeat is called a cardiac cycle. First the two atria contract at the same time. Next the two ventricles contract at the same time. Then all the chambers relax. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=frd3k6lkhws
37 1 The Circulatory System
 H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
H T H E E A R T 37 1 The Circulatory System The circulatory system and respiratory system work together to supply cells with the nutrients and oxygen they need to stay alive. a) The respiratory system:
Evaluation copy. EMG and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
EMG and Muscle Fatigue Computer 18 Voluntary muscle contraction is the result of communication between the brain and individual muscle fibers of the musculoskeletal system. A thought is transformed into
CASE 10. What would the ST segment of this ECG look like? On which leads would you see this ST segment change? What does the T wave represent?
 CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CASE 10 A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency center with complaints of chest pain with radiation to the left arm and jaw. He reports feeling anxious, diaphoretic, and short of breath. His past history
CAMOSUN COLLEGE BIOLOGY 144 (2010) LABS
 LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
LAB 8: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY PART 1. HEART SOUNDS AND PULSE DETERMINATIONS Introduction Two distinct sounds can be heard during each cardiac cycle. These sounds are commonly described as lub and dup
Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week
 Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week Semester: winter Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology Faculty of Medicine PJŠU Cardiovascular
Department of medical physiology 7 th week and 8 th week Semester: winter Study program: Dental medicine Lecture: RNDr. Soňa Grešová, PhD. Department of medical physiology Faculty of Medicine PJŠU Cardiovascular
The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions. A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG
 The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG Written by Erhan Selvi July 28, 2014 Audience and Scope
The Function of an ECG in Diagnosing Heart Conditions A useful guide to the function of the heart s electrical system for patients receiving an ECG Written by Erhan Selvi July 28, 2014 Audience and Scope
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease
 Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Biology 13A Lab #10: Cardiovascular System II ECG & Heart Disease Lab #10 Table of Contents: Expected Learning Outcomes...... 83 Introduction....... 84 Activity 1: Collecting ECG Data..... 85 Activity
Cardiac Telemetry Self Study: Part One Cardiovascular Review 2017 THINGS TO REMEMBER
 Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Please review the above anatomy of the heart. THINGS TO REMEMBER There are 3 electrolytes that affect cardiac function o Sodium, Potassium, and Calcium When any of these electrolytes are out of the normal
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #4: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY AND THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #4: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY AND THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 7 th (2015). Be sure you
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Lab #4: CARDIOVASCULAR PHYSIOLOGY AND THE ELECTROCARDIOGRAM References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 7 th (2015). Be sure you
Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography-
 *questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
*questions asked by some students Sheet 5 physiology Electrocardiography- -why the ventricles lacking parasympathetic supply? if you cut both sympathetic and parasympathetic supply of the heart the heart
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
Cardiovascular System Notes: Physiology of the Heart Interesting Heart Fact Capillaries are so small it takes ten of them to equal the thickness of a human hair. Review What are the 3 parts of the cardiovascular
- why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave?
 Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
Cardiac Electrograph: - why the T wave is deflected upwards although it's a repolarization wave? After depolarization the ventricle contracts but since the heart is a volume conductor (3D not 2D), when
The Electrocardiogram
 The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
The Electrocardiogram Chapters 11 and 13 AUTUMN WEDAN AND NATASHA MCDOUGAL The Normal Electrocardiogram P-wave Generated when the atria depolarizes QRS-Complex Ventricles depolarizing before a contraction
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart
 Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
Chapter 20 (2) The Heart ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Describe the component and function of
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG
 By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
By the end of this lecture, you will be able to: Understand the 12 lead ECG in relation to the coronary circulation and myocardium Perform an ECG recording Identify the ECG changes that occur in the presence
The Normal Electrocardiogram
 C H A P T E R 1 1 The Normal Electrocardiogram When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current also spreads from the heart into the adjacent tissues surrounding the heart. A small
C H A P T E R 1 1 The Normal Electrocardiogram When the cardiac impulse passes through the heart, electrical current also spreads from the heart into the adjacent tissues surrounding the heart. A small
Introduction to Electrocardiography
 Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
Introduction to Electrocardiography Class Objectives: Introduction to ECG monitoring Discuss principles of interpretation Identify the components and measurements of the ECG ECG analysis ECG Monitoring
Each student should record the ECG of one of the members of the lab group and have their own ECG recorded.
 EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
EXPERIMENT 1 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY The purpose of this experiment is to introduce you to the techniques of electrocardiography and the interpretation of electrocardiograms. In Part A of the experiment, you
Lab 2. The Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System. 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1
 Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Lab 2 he Intrinsic Cardiac Conduction System 1/23/2016 MDufilho 1 Figure 18.13 Intrinsic cardiac conduction system and action potential succession during one heartbeat. Superior vena cava ight atrium 1
Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction
 Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction Learning objectives: What is in a nerve fibre? How does a nerve fibre transmit an electrical impulse? What do we mean by action potential? Nerve cells
Chapter 3 Biological measurement 3.1 Nerve conduction Learning objectives: What is in a nerve fibre? How does a nerve fibre transmit an electrical impulse? What do we mean by action potential? Nerve cells
Electrocardiography Normal 5. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Normal 5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives 2 1. Describe the different waves in a normal electrocardiogram. 2. Recall the normal P-R and Q-T interval time of the QRS wave. 3.
Electrocardiography Normal 5 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Objectives 2 1. Describe the different waves in a normal electrocardiogram. 2. Recall the normal P-R and Q-T interval time of the QRS wave. 3.
Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography
 Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Physiology Lessons for use with the Biopac Science Lab MP40 Lesson 4 ECG 2 Electrocardiography PC running Windows XP or Mac OS X 10.3-10.4 Lesson Revision 1.20.2006 BIOPAC Systems, Inc. 42 Aero Camino,
Evaluation copy. Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue. Computer
 Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Computer 17 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting.
Grip Strength and Muscle Fatigue Computer 17 Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of individual muscle fibers (see Figure 1) and has unique properties which allow it to respond to stimuli by contracting.
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise. Evaluation copy
 Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
Heart Rate, Blood Pressure, and Exercise Computer 11 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of skeletal muscles increases. The cardiovascular system,
12 Lead EKG. Brigham and Women's Hospital
 12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
12 Lead EKG What is the heart? The heart is the organ that is responsible for pumping blood rich in oxygen to all parts of the body It is located in the center of the chest and is approximately the size
Electrocardiogram ECG. Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University
 Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
Electrocardiogram ECG Hilal Al Saffar FRCP FACC College of medicine,baghdad University Tuesday 29 October 2013 ECG introduction Wednesday 30 October 2013 Abnormal ECG ( ischemia, chamber hypertrophy, heart
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control. Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics
 BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
BME 5742 Bio-Systems Modeling and Control Lecture 41 Heart & Blood Circulation Heart Function Basics Dr. Zvi Roth (FAU) 1 Pumps A pump is a device that accepts fluid at a low pressure P 1 and outputs the
Ask Mish. EKG INTERPRETATION part i
 EKG INTERPRETATION part i What is EKG? EKG or ECG= electrocardiogram(~graphy) means the recording of the heart electrical activity from Greek kardio= heart, graphein= to write cardiac cell physiology Cardiac
EKG INTERPRETATION part i What is EKG? EKG or ECG= electrocardiogram(~graphy) means the recording of the heart electrical activity from Greek kardio= heart, graphein= to write cardiac cell physiology Cardiac
iworx Sample Lab Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram
 Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Experiment HH-4: The Six-Lead Electrocardiogram Background The cardiac cycle involves a sequential contraction of the atria and the ventricles. These contractions are triggered by the coordinated electrical
Cardiac physiology. b. myocardium -- cardiac muscle and fibrous skeleton of heart
 I. Heart anatomy -- general gross. A. Size/orientation - base/apex B. Coverings D. Chambers 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral pericardium 3. Layers of heart wall a. epicardium Cardiac physiology b. myocardium
I. Heart anatomy -- general gross. A. Size/orientation - base/apex B. Coverings D. Chambers 1. parietal pericardium 2. visceral pericardium 3. Layers of heart wall a. epicardium Cardiac physiology b. myocardium
EKG Abnormalities. Adapted from:
 EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
EKG Abnormalities Adapted from: http://www.bem.fi/book/19/19.htm Some key terms: Arrhythmia-an abnormal rhythm or sequence of events in the EKG Flutter-rapid depolarizations (and therefore contractions)
4. The two inferior chambers of the heart are known as the atria. the superior and inferior vena cava, which empty into the left atrium.
 Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
Answer each statement true or false. If the statement is false, change the underlined word to make it true. 1. The heart is located approximately between the second and fifth ribs and posterior to the
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System
 12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
12.2 Monitoring the Human Circulatory System Video 1: 3D Animation of Heart Pumping Blood blood flow through the heart... Video 2: Hank Reviews Everything on the Heart https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=x9zz6tcxari
Atlantic Health System
 Atlantic Health System Morristown Medical Center Newton Medical Center Overlook Medical Center Basic Dysrhythmia Course Day 1 1 2 Chapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology Learning Objectives 1) Identify electrophysiology
Atlantic Health System Morristown Medical Center Newton Medical Center Overlook Medical Center Basic Dysrhythmia Course Day 1 1 2 Chapter 1 Anatomy and Physiology Learning Objectives 1) Identify electrophysiology
Cardiac Conduction System
 Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Cardiac Conduction System What causes the Heart to Beat? Heart contracts by electrical signals! Cardiac muscle tissue contracts on its own an electrical signal is sent out by the heart so that all cells
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function
 Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Chapter 13 The Cardiovascular System: Cardiac Function Overview of the Cardiovascular System The Path of Blood Flow through the Heart and Vasculature Anatomy of the Heart Electrical Activity of the Heart
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7. Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD
 Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
Electrocardiography Abnormalities (Arrhythmias) 7 Faisal I. Mohammed, MD, PhD 1 Causes of Cardiac Arrythmias Abnormal rhythmicity of the pacemaker Shift of pacemaker from sinus node Blocks at different
What the ECG is about
 What to expect from the ECG 00 The electricity of the heart 00 The shape of the ECG 00 The ECG electrical pictures 00 The shape of the QRS complex 00 Making a recording practical points 00 How to report
What to expect from the ECG 00 The electricity of the heart 00 The shape of the ECG 00 The ECG electrical pictures 00 The shape of the QRS complex 00 Making a recording practical points 00 How to report
The Heart. Size, Form, and Location of the Heart. 1. Blunt, rounded point; most inferior part of the heart.
 12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
12 The Heart FOCUS: The heart is composed of cardiac muscle cells, which are elongated, branching cells that appear striated. Cardiac muscle cells behave as a single electrical unit, and the highly coordinated
Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D.
 Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Brief review of basic concepts Introduction to ECG Gary Martin, M.D. The electrical activity of the heart is caused by a sequence of rapid ionic movements across cell membranes resulting first in depolarization
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart
 Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Chapter 20: Cardiovascular System: The Heart I. Functions of the Heart A. List and describe the four functions of the heart: 1. 2. 3. 4. II. Size, Shape, and Location of the Heart A. Size and Shape 1.
Topic 6: Human Physiology
 Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
Topic 6: Human Physiology 6.2 The Blood System D.4 The Heart Essential Questions: 6.2 The blood system continuously transports substances to cells and simultaneously collects waste products. D.3 The chemical
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES
 WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
WHAT S THAT RHYTHM I AM HEARING? GUIDE TO AUSCULTATION OF ARRHYTHMIAS IN HORSES Michelle Henry Barton DVM, PhD, DACVIM University of Georgia, Athens, GA INTRODUCTION The purpose of this talk is to review
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview
 Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
Chapter 12: Cardiovascular Physiology System Overview Components of the cardiovascular system: Heart Vascular system Blood Figure 12-1 Plasma includes water, ions, proteins, nutrients, hormones, wastes,
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY, ECG
 ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY, ECG Introduction: Electrocardiography is a method to register the heart electric activity, e.g. electric potentials from outside of body. It is possible to record the changes of these
ELECTROCARDIOGRAPHY, ECG Introduction: Electrocardiography is a method to register the heart electric activity, e.g. electric potentials from outside of body. It is possible to record the changes of these
Muscle Function Analysis
 Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
Muscle Function Analysis LabQuest 15 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes.
BIO 360: Vertebrate Physiology Lab 8b: Electrical activity of muscular contractions
 Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
Lab report DUE 3/19 Muscle tissues maintain electrical imbalances, or potentials, across cell membranes by concentrating positive or negative charges on opposite sides of those membranes. These potentials
Cardiovascular system
 BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
BIO 301 Human Physiology Cardiovascular system The Cardiovascular System: consists of the heart plus all the blood vessels transports blood to all parts of the body in two 'circulations': pulmonary (lungs)
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders
 Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Cardiovascular System Notes: Heart Disease & Disorders Interesting Heart Facts The Electrocardiograph (ECG) was invented in 1902 by Willem Einthoven Dutch Physiologist. This test is still used to evaluate
Heart Rate and Exercise. Evaluation copy. Figure 1
 Heart Rate and Exercise Computer 4 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of muscle tissue increases. The cardiovascular system, consisting of the heart
Heart Rate and Exercise Computer 4 The adaptability of the heart can be observed during exercise, when the metabolic activity of muscle tissue increases. The cardiovascular system, consisting of the heart
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM. Heart 2
 THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM Heart 2 PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Cardiac muscle Striated Short Wide Branched Interconnected Skeletal muscle Striated Long Narrow Cylindrical PROPERTIES OF CARDIAC MUSCLE Intercalated
Collin County Community College. ! BIOL Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5. The Heart
 Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
Collin County Community College! BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology! WEEK 5 The Heart 1 (1578-1657) A groundbreaking work in the history of medicine, English physician William Harvey s Anatomical Essay on
ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology
 ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology Simon Some very basic electrophysiology Intracellular fluid: 10 mm Na, 140 mm K, etc. K Na-K ATPase Extracellular fluid: 140mM Na, 4mM K, etc. Na Ion gradient plus selective
ECG and Cardiac Electrophysiology Simon Some very basic electrophysiology Intracellular fluid: 10 mm Na, 140 mm K, etc. K Na-K ATPase Extracellular fluid: 140mM Na, 4mM K, etc. Na Ion gradient plus selective
SAMPLE CHAPTER CHAPTER
 2.1 Introduction CHAPTER 2 Cardiovascular Structure and Function One may question why it is important for a biomedical engineer to study physiology. To answer this question, we can begin by recognizing
2.1 Introduction CHAPTER 2 Cardiovascular Structure and Function One may question why it is important for a biomedical engineer to study physiology. To answer this question, we can begin by recognizing
This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of
 Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
Snímka 1 Electrocardiography basics This presentation will deal with the basics of ECG description as well as the physiological basics of Snímka 2 Lecture overview 1. Cardiac conduction system functional
BME 365 Website. Project Directions
 Lecture 17 EKG BME 365 Website Project Directions Heart rate Factors Affecting CO Parasympathetic activity decreases HR Sympathetic activity increases HR Stroke volume Depends on force generated by cardiac
Lecture 17 EKG BME 365 Website Project Directions Heart rate Factors Affecting CO Parasympathetic activity decreases HR Sympathetic activity increases HR Stroke volume Depends on force generated by cardiac
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise. Background Cardiac function
 Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Cardiovascular Effects of Exercise In this experiment, you will record an electrocardiogram, or ECG, and finger pulse from a healthy volunteer. You will then compare the ECG and pulse recordings when the
Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat
 Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat Activity: Locate your pulse at rest. Count how many times it beats in 15 seconds (look at a clock), then multiply this number by 4. This is your pulse rate Approximately
Introduction to Lesson 2 - Heartbeat Activity: Locate your pulse at rest. Count how many times it beats in 15 seconds (look at a clock), then multiply this number by 4. This is your pulse rate Approximately
Cardiovascular System
 Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
Cardiovascular System Purpose Transport oxygen and nutrients Take waste products away from tissues & organs Things we learned Blood pressure: the force of blood pushing against the walls of blood vessels
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION INTRODUCTION
 ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
ELECTROMYOGRAM ANALYSIS OF MUSCLE FUNCTION STANDARDS: 3.3.10.B - Explain cell functions and processes in terms of chemical reactions and energy changes. 3.3.12.B - Evaluate relationships between structure
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG. Jakub Dorożyński
 Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
Family Medicine for English language students of Medical University of Lodz ECG Jakub Dorożyński Parts of an ECG The standard ECG has 12 leads: six of them are considered limb leads because they are placed
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology)
 ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
ECG Interpretation Cat Williams, DVM DACVIM (Cardiology) Providing the best quality care and service for the patient, the client, and the referring veterinarian. GOAL: Reduce Anxiety about ECGs Back to
