Department of Medical Imaging, National Taiwan University Hospital Yun Lin Branch, Yun-Lin 640, Taiwan
|
|
|
- Jerome Bridges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Thoracic Imaging pissn eissn Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6): Quantitative Computed Tomography of Pulmonary Emphysema and Ventricular Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Yu-Sen Huang, MD 1, 2, 3, Hsao-Hsun Hsu, MD 4, Jo-Yu Chen, MD 2, 3, Mei-Hwa Tai, MS 2, Fu-Shan Jaw, PhD 1, Yeun-Chung Chang, MD, PhD 2 1 Institute of Biomedical Engineering, College of Medicine and College of Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei 100, Taiwan; Departments of 2 Medical Imaging and 4 Surgery, National Taiwan University Hospital and National Taiwan University College of Medicine, Taipei 100, Taiwan; 3 Department of Medical Imaging, National Taiwan University Hospital Yun Lin Branch, Yun-Lin 640, Taiwan Objective: This study strived to evaluate the relationship between degree of pulmonary emphysema and cardiac ventricular function in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) using electrocardiographic-gated multidetector computed tomography (CT). Materials and Methods: Lung transplantation candidates with the diagnosis of COPD and PH were chosen for the study population, and a total of 15 patients were included. The extent of emphysema is defined as the percentage of voxels below -910 Hounsfield units in the lung windows in whole lung CT without intravenous contrast. Heart function parameters were measured by electrocardiographic-gated CT angiography. Linear regression analysis was conducted to examine the associations between percent emphysema and heart function indicators. Results: Significant correlations were found between percent emphysema and right ventricular (RV) measurements, including RV end-diastolic volume (R 2 = 0.340, p = 0.023), RV stroke volume (R 2 = 0.406, p = 0.011), and RV cardiac output (R 2 = 0.382, p = 0.014); the correlations between percent emphysema and left ventricular function indicators were not observed. Conclusion: The study revealed that percent emphysema is correlated with RV dysfunction among COPD patients with PH. Based on our findings, percent emphysema can be considered for use as an indicator to predict the severity of right ventricular dysfunction among COPD patients. Index terms: Pulmonary hypertension; Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Emphysema; Right ventricular function Received February 6, 2014; accepted after revision July 18, This study was presented in part at the 3rd World Congress of Thoracic Imaging (WCTI), June 8-11, 2013, Seoul, Korea. Corresponding author: Yeun-Chung Chang, MD, PhD, Department of Medical Imaging, National Taiwan University Hospital and National Taiwan University College of Medicine, No. 7, Chung-Shan S. Rd., Taipei 100, Taiwan. Tel: (8862) ext Fax: (8862) ycc5566@ntu.edu.tw This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License ( which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. INTRODUCTION In patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), cor pulmonale could occur, which is characterized by elevated pulmonary vascular resistance and right heart failure with an associated reduction of the left ventricular diastolic function (1). This disorder might occur as a result of various mechanisms including loss of pulmonary vascular capacity due to lung parenchymal destruction or hypoxic pulmonary arterial vasoconstriction (2). Prior studies revealed that decreased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor causes endothelial apoptosis, epithelial 871
2 Huang et al. apoptosis, and emphysema (3), which implied the existence of a complicated pathogenesis between emphysema and impaired pulmonary vascular capacity. Hyperinflation could cause intrathoracic pressure to exceed venous pressure, with the reduction of the blood volume returning to both ventricles (4). The elevated intrinsic positive end-expiratory pressure redistributes intrapulmonary and intracardiac blood volumes in emphysema patients (5). However, the detailed pathophysiology of emphysema on hemodynamics and cardiac function remains debatable. Computed tomography (CT) emphysema quantification has already demonstrated a good correlation between histopathology and pulmonary function (6). In addition, multidetector CT (MDCT) not only accurately quantify ventricular function, as compared with cardiac magnetic resonance (MR) (7), but also evaluate right ventricle (RV) function in patients with COPD and cor pulmonale (8). Recent population-based cohort studies revealed that a greater extent of emphysema on CT was linearly related to impaired left ventricular (LV) filling, reduced stroke volume, and lower cardiac output. These were measured by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) across a spectrum of normal lung structure and function to severe emphysema and airflow obstruction (9). Further population-based study also showed that percent emphysema was inversely associated with RV end-diastolic volume, stroke volume, cardiac output, and mass using cardiac MRI (10). The measurements of RV dysfunction can predict future right-sided heart failure, clinical deterioration, and mortality in patients with pulmonary hypertension (PH) (11). However, use of echocardiogram to measure RV dysfunction is technically problematic particularly in patients with severe emphysema (12). The relationship of the ventricular heart function of COPD patients to PH and pulmonary emphysema obtained in one single CT study is lacking. Our study aimed to evaluate the relationship between degree of pulmonary emphysema and cardiac ventricular function in COPD patients with PH using electrocardiographic (ECG)- gated MDCT. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subjects The study protocol was approved by the Research Ethics Committee of our hospital ( RIC). Lung transplantation candidates with the diagnosis of COPD and PH were included retrospectively. Between 2006 and 2012, a total of 15 patients received ECG-gated MDCT of the chest to evaluate the possibility of lung transplantation at our institution. These 15 patients met the international guidelines for the selection of lung transplant candidates (13). All patients had COPD as the cause of their primary disease. None of the patients had a history of coronary artery disease. All 15 patients had evidence of secondary pulmonary hypertension, based on the findings of conventional right heart catheterization (n = 7) with mean pulmonary arterial pressure of greater than 25 mm Hg and doppler echocardiography (n = 8) with an estimation of systolic pulmonary arterial pressure of greater than 50 mm Hg. CT Acquisition Whole lung CT without intravenous contrast was performed with a 64-section CT scanner (LightSpeed VCT; GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). All patients were imaged in the supine position while holding their breath at full inspiration. The following standard acquisition parameters were used: 120 ma, 120 kvp, 1.3 pitch, and 0.7-second rotation time. CT scans were reconstructed at section widths of mm. ECG-gated CT angiography was performed afterward, with 90 ml of intravenous non-ionic contrast agent (Iopromide, Ultravist 300; Bayer Healthcare, Berlin, Germany) injected biphasically at 4 5 ml/sec (Stellant D injector; Medrad Inc., Warrendale, PA, USA); timing bolus was used to trigger CT acquisition. The average estimated radiation dose ranged from 6 to 16 msv. Measurements of Bilateral Ventricular Structure and Function CT angiography has been proven to accurately quantify RV function (14). We measured left and right ventricular structures and functions by utilizing the techniques of multiphase reconstruction and cardiac segmentation from CT angiography, using a dedicated commercially available workstation (CT Comprehensive Cardiac Analysis IntelliSpace Portal, Philips Extended Brilliance TM Workspace V ; Philips Healthcare, Eindhoven, the Netherlands). Endocardial contours were traced on the diastolic and systolic images. The ventricular volume (diastolic or systolic) equaled to the sum of all the endocardial areas (of the diastolic or systolic images, respectively) multiplied by the slice thickness. The CT imaging was reviewed by two radiologists who had more than 5 years of related cardiac CT experience, in order to 872 Korean J Radiol 15(6), Nov/Dec 2014 kjronline.org
3 CT of Ventricular Function and Pulmonary Emphysema in COPD Patients with PH establish a consensus. All axial, coronal, and sagittal slices were reviewed after being processed and adjusted manually for the precise segmented area of each cardiac structure (Fig. 1). Assessment of Emphysema Computed tomography scans were reconstructed at section widths of mm with standard filter algorithm (GE Healthcare, Milwaukee, WI, USA). Densitometric measures of emphysema of the whole lung were performed by using a dedicated commercially available workstation (CT lung density software program, IntelliSpace Portal, Philips Extended Brilliance TM Workspace V ). The extent of emphysema, expressed as percent emphysema, was defined as the percentage of voxels below -910 Hounsfield units in the lung on non-contrast CT scans using 1 mm collimation at full inspiration (Fig. 2). This threshold was chosen on the basis of quantitative histological comparison (15). Statistical Analysis Statistical analysis was performed using the R software (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) and the Statistical Package for Social Sciences for Windows, version 17.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Regarding statistical testing, a two-sided p value of 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. A simple linear regression model was used to assess the association between percent emphysema derived from CT scan and each of the heart function indicators. The goal of regression analysis was to find one or a few parsimonious regression models that fit the observed data well for an effective estimation. To ensure the quality of analysis results, the basic model-fitting techniques for variable selection, goodness-of-fit (GOF) assessment, or regression diagnostics were used in our regression analyses. Specifically, a stepwise variable selection procedure (with iterations between the forward and backward steps) was applied to obtain the candidate s final linear regression model. The coefficient of determination (R 2 ) was examined to assess the GOF of the linear regression model. lung disease stage IV patients. The mean value for percent predicted forced vital capacity and percent predicted forced expiratory volume in one second was 44.8% (range, %) and 29.3% (range, %), respectively. The mean value for percent emphysema was 36.1% (range, %). Two patients eventually received lung Fig. 1. Snap shot of successful segmentation of each of cardiac chambers after semiautomatic processing and manual adjustment during different cardiac phases. Ventricular volume equals sum of all endocardial areas multiplied by slice thickness. RESULTS The demographic and clinical characteristics of the 15 patients are shown in Table 1. The median age of the study patients was 55 years (range, years); 60% were men, and 80% were global initiative for chronic obstructive Fig. 2. Coronal reformatted lung window image in 57-yearold man with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease amenable to lung transplantation. Red areas indicate voxels below -910 Hounsfield units in lung parenchyma, which represent emphysematous change. 873
4 Huang et al. Table 1. Pulmonary Function in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Clinical Parameter Value Range Percent predicted forced vital capacity (%)* 44.8 ± Percent predicted forced expiratory volume in one second (%)* 29.3 ± Percent emphysema (%)* 36.1 ± GOLD grading system III:IV 3:12 Note. *Mean ± standard deviation. GOLD = global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease transplantation surgery. The image assessment is demonstrated in Figure 3 and 4. According to the protocol, whole lung CT without intravenous contrast demonstrated severe emphysema in the lung window (Fig. 3), and contrast-enhanced CT short-axis image in end-systole phase demonstrated RV dysfunction by straightening of interventricular septum to LV (Fig. 4). The ventricular function parameters of the 15 patients are shown in Table 2. The mean values for RV end-diastolic volume (RVEDV), RV end-systolic volume, and RV stroke volume (RVSV) were ml (range, ml), 87.7 ml (range, ml), and 57.3 ml (range, ml), respectively. The mean value for RV ejection fraction was 39.9% (range, %). The mean value for RV cardiac output (RVCO) was 5.07 L/min (range, L/ min). The associations between percent emphysema and heart function indicators in the linear regression analysis are shown in Table 3. In COPD patients with PH, significant correlations were found between percent emphysema and three RV measures (Fig. 5). A 1% increase of percent emphysema would lead to a 1.8 ml decrement in the mean value of RVEDV (R 2 = 0.340, p = 0.023), a 0.8 ml decrement in RVSV (R 2 = 0.406, p = 0.011), and a 0.07 L decrement in RVCO (R 2 = 0.382, p = 0.014); the correlations between percent emphysema and LV function indicators were not observed. DISCUSSION The current study is presently the first study that uses MDCT to evaluate the association between percent emphysema and parameters of the heart function. This study demonstrated the significant correlations between percent emphysema and RVEDV, RVSV, and RVCO in COPD patients with PH. Catheterization of the right heart for functional assessment is invasive and increases the risk for patients. Measurement of the transverse/radial function by cardiac ultrasound does not directly reflect the major component of Fig. 3. Axial image of whole lung CT without intravenous contrast, in 60-year-old man with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, demonstrates severe emphysema in lung window. RV function (12). Compared to cardiac MRI, MDCT provide information on the extent of pulmonary emphysema and bilateral ventricular function simultaneously, indicating the advantages of time saving and insensitivity to movements in patients with critical illness. CT is more suitable for dyspneic patients who cannot tolerate breath hold in the time-consuming MR study. In this study, we used an ECG-gated MDCT protocol to evaluate both cardiac ventricular function and pulmonary parenchyma for lung transplantation candidates with PH. A greater extent of emphysematous change on CT scanning was linearly related to impaired RV diastolic function in COPD patients with PH. These results suggest that greater percent emphysema may lead to reduced filling of the right ventricle and reduced pulmonary blood flow. Right heart has been known to be a lower pressure system. The pulmonary temponade effect compromises the right heart and systemic venous return more apparently 874 Korean J Radiol 15(6), Nov/Dec 2014 kjronline.org
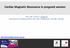
5 CT of Ventricular Function and Pulmonary Emphysema in COPD Patients with PH Table 2. Ventricular Functions in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Ventricular Functions Parameter Value* Range LVEDV (ml) ± LVESV (ml) 37.8 ± LVSV (ml) 66.0 ± LVEF (%) 63.4 ± LVCO (L/min) 5.87 ± LV mass (ml) ± RVEDV (ml) ± RVESV (ml) 87.7 ± RVSV (ml) 57.3 ± RVEF (%) 39.9 ± RVCO (L/min) 5.07 ± Note. *Mean ± standard deviation. CO = cardiac output, EDV = end-diastolic volume, EF = ejection fraction, ESV = end-systolic volume, LV = left ventricle, RV = right ventricle, SV = stroke volume Fig. 4. Coronal short-axis image of contrast-enhanced CT in end-systole phase, in 67-year-old woman with severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, demonstrates straightening of interventricular septum (arrow) to left ventricle (LV) which indicates right ventricle (RV) dysfunction. than the left heart (16). It is reasonable to hypothesize that emphysema primarily impair RV diastolic function and indirectly affect the LV function via the decreased RV stroke volume. More potential confounder affecting the LV end-diastolic volume has been recognized, including compensation of the impaired LV diastolic function by the left atrium contraction. Hence, our results showed that percent emphysema had no relation between percent emphysema and LV function in patients with COPD and PH. Barr et al. (9) demonstrated that percent emphysema was linearly related to impaired LV functions in patients with COPD. However, the study excluded patients with severe lung disease, clinical cardiovascular manifestations, or lung disease with restrictive patterns. In contrast, our study included lung transplant candidates who had more severe clinical conditions. Our results did not demonstrate any association between percent emphysema and LV diastolic function in COPD patients with PH, while percent emphysema was correlated with RVEDV, RVSV, and RVCO. Several possibilities might be relevant to the different results from our study, including small sample size and different study cohort in clinical manifestations of both pulmonary emphysema and PH in our patients. Therefore, a prospective study with larger cohort and different degrees of pulmonary emphysema and PH might be needed. Table 3. Linear Regression Analysis of Associations between Percent Emphysema and Heart Function Indicators in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Patients with Pulmonary Hypertension Covariate R 2 Estimate P* LVEDV (ml) LVESV (ml) LVSV (ml) LVEF (%) LVCO (L/min) LV mass (ml) RVEDV (ml) RVESV (ml) RVSV (ml) RVEF (%) RVCO (L/min) Note. *Correlations were examined using linear regression correlation coefficient, p < CO = cardiac output, EDV = enddiastolic volume, EF = ejection fraction, ESV = end-systolic volume, LV = left ventricle, RV = right ventricle, SV = stroke volume Right ventricular function was significantly decreased in patients with severe COPD than in mild or moderate COPD (8, 17). The correlation was observed between RV ejection fraction and pulmonary function tests including forced expiratory volume in one second and forced vital capacity (17). Moreover, population-based study showed that percent emphysema was inversely associated with RV parameters using cardiac MRI (10). Hyperinflation and gas trapping might impair right heart function by reducing venous return to the thorax, increasing end-diastolic stiffness of the right ventricle, or increasing pulmonary arteriovenous pressure gradients (4, 18). To summarize recent studies and our result, deteriorating RV function is correlated with percent 875
6 Huang et al. 300 p = p = RV end-diastolic volume (ml) RV stroke volume (ml) Percent emphysema (%) Percent emphysema (%) A B RV cardiac output (L/min) p-value p = = Percent emphysema (%) C Fig. 5. Relationship of pulmonary percent emphysema and right ventricle parameters in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients with pulmonary hypertension. A. Right ventricular end-diastolic volume (R 2 = 0.340, p = 0.023). B. Right ventricular stroke volume (R 2 = 0.406, p = 0.011). C. Right ventricular cardiac output (R 2 = 0.382, p = 0.014). emphysema or functional pulmonary parameters in COPD patients. Except for the drawback of radiation exposure, CT is a convenient modality to evaluate the structures of lung, vasculature, and heart, as well as providing a noninvasive evaluation of cardiac function. Compared with echocardiography, CT has less inter-observer bias and is more objective and precise in evaluating the right heart function (19). The current state-of-the-art CT technology with the use of adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction further decreases the radiation exposure dose (20). Therefore, more reasonable CT radiation exposure can be expected in the near future. Our study has several limitations. The sample size was relatively small. Our findings should be interpreted with caution given the possible uncertainty introduced by CT-measured heart and lung functions. CT-measured pulmonary or cardiac parameters were not correlated with pulmonary function tests, cardiac catheterization, or cardiac echocardiography. More detailed validation strategies are still required between CT-measured values and real-time clinical condition. In conclusion, the present study revealed that CTmeasured percent emphysema had a significant correlation with RVEDV, RVSV, and RVCO in COPD patients with PH. The pathophysiologic mechanism of emphysematous change to 876 Korean J Radiol 15(6), Nov/Dec 2014 kjronline.org
7 CT of Ventricular Function and Pulmonary Emphysema in COPD Patients with PH deteriorate cardiac function was complicated, but impaired RV function was an important contributor. Once COPD is observed as the primary etiology, CT-measured percent emphysema can be utilized as a convenient predictor for the severity of RV dysfunction, which might help to indicate prognosis of future right-sided heart failure and mortality. REFERENCES 1. MacNee W. Pathophysiology of cor pulmonale in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Part One. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1994;150: Barberà JA, Peinado VI, Santos S. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Eur Respir J 2003;21: Kasahara Y, Tuder RM, Cool CD, Lynch DA, Flores SC, Voelkel NF. Endothelial cell death and decreased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 in emphysema. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001;163(3 Pt 1): Jörgensen K, Müller MF, Nel J, Upton RN, Houltz E, Ricksten SE. Reduced intrathoracic blood volume and left and right ventricular dimensions in patients with severe emphysema: an MRI study. Chest 2007;131: Jörgensen K, Houltz E, Westfelt U, Nilsson F, Scherstén H, Ricksten SE. Effects of lung volume reduction surgery on left ventricular diastolic filling and dimensions in patients with severe emphysema. Chest 2003;124: Shin KE, Chung MJ, Jung MP, Choe BK, Lee KS. Quantitative computed tomographic indexes in diffuse interstitial lung disease: correlation with physiologic tests and computed tomography visual scores. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2011;35: Raman SV, Shah M, McCarthy B, Garcia A, Ferketich AK. Multi-detector row cardiac computed tomography accurately quantifies right and left ventricular size and function compared with cardiac magnetic resonance. Am Heart J 2006;151: Gao Y, Du X, Liang L, Cao L, Yang Q, Li K. Evaluation of right ventricular function by 64-row CT in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and cor pulmonale. Eur J Radiol 2012;81: Barr RG, Bluemke DA, Ahmed FS, Carr JJ, Enright PL, Hoffman EA, et al. Percent emphysema, airflow obstruction, and impaired left ventricular filling. N Engl J Med 2010;362: Grau M, Barr RG, Lima JA, Hoffman EA, Bluemke DA, Carr JJ, et al. Percent emphysema and right ventricular structure and function: the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis-Lung and Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis-Right Ventricle Studies. Chest 2013;144: Sachdev A, Villarraga HR, Frantz RP, McGoon MD, Hsiao JF, Maalouf JF, et al. Right ventricular strain for prediction of survival in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest 2011;139: Fisher MR, Criner GJ, Fishman AP, Hassoun PM, Minai OA, Scharf SM, et al. Estimating pulmonary artery pressures by echocardiography in patients with emphysema. Eur Respir J 2007;30: Orens JB, Estenne M, Arcasoy S, Conte JV, Corris P, Egan JJ, et al. International guidelines for the selection of lung transplant candidates: 2006 update--a consensus report from the Pulmonary Scientific Council of the International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2006;25: Remy-Jardin M, Delhaye D, Teisseire A, Hossein-Foucher C, Duhamel A, Remy J. MDCT of right ventricular function: impact of methodologic approach in estimation of right ventricular ejection fraction, part 2. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006;187: Coxson HO, Mayo JR, Behzad H, Moore BJ, Verburgt LM, Staples CA, et al. Measurement of lung expansion with computed tomography and comparison with quantitative histology. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1995;79: Boussuges A, Pinet C, Molenat F, Burnet H, Ambrosi P, Badier M, et al. Left atrial and ventricular filling in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. An echocardiographic and Doppler study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162(2 Pt 1): Hur J, Kim TH, Kim SJ, Ryu YH, Kim HJ. Assessment of the right ventricular function and mass using cardiac multidetector computed tomography in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Korean J Radiol 2007;8: Watz H, Waschki B, Meyer T, Kretschmar G, Kirsten A, Claussen M, et al. Decreasing cardiac chamber sizes and associated heart dysfunction in COPD: role of hyperinflation. Chest 2010;138: Berger HJ, Matthay RA. Noninvasive radiographic assessment of cardiovascular function in acute and chronic respiratory failure. Am J Cardiol 1981;47: Hara AK, Paden RG, Silva AC, Kujak JL, Lawder HJ, Pavlicek W. Iterative reconstruction technique for reducing body radiation dose at CT: feasibility study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2009;193:
Aims and objectives. Page 2 of 13
 Evaluation of right heart function with use of retrospectively ECG- gated 64-slice low dose computed tomography in subjects with and without pulmonary hypertension Poster No.: C-2562 Congress: ECR 2015
Evaluation of right heart function with use of retrospectively ECG- gated 64-slice low dose computed tomography in subjects with and without pulmonary hypertension Poster No.: C-2562 Congress: ECR 2015
Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular Volumetry in Late Postoperative Patients with Tetralogy of Fallot
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:71-77 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.71 Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2017;50:71-77 ISSN: 2233-601X (Print) ISSN: 2093-6516 (Online) CLINICAL RESEARCH https://doi.org/10.5090/kjtcs.2017.50.2.71 Use of Cardiac Computed Tomography for Ventricular
Cor pulmonale. Dr hamid reza javadi
 1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
1 Cor pulmonale Dr hamid reza javadi 2 Definition Cor pulmonale ;pulmonary heart disease; is defined as dilation and hypertrophy of the right ventricle (RV) in response to diseases of the pulmonary vasculature
Min Hur, Eun-Hee Kim, In-Kyung Song, Ji-Hyun Lee, Hee-Soo Kim, and Jin Tae Kim INTRODUCTION. Clinical Research
 Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Anesth Pain Med 2016; 11: 375-379 https://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375 Clinical Research http://crossmark.crossref.org/dialog/?doi=10.17085/apm.2016.11.4.375&domain=pdf&date_stamp=2016-10-25 pissn
Automatic cardiac contour propagation in short axis cardiac MR images
 International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 351 356 www.ics-elsevier.com Automatic cardiac contour propagation in short axis cardiac MR images G.L.T.F. Hautvast a,b, T, M. Breeuwer a, S. Lobregt a, A. Vilanova
International Congress Series 1281 (2005) 351 356 www.ics-elsevier.com Automatic cardiac contour propagation in short axis cardiac MR images G.L.T.F. Hautvast a,b, T, M. Breeuwer a, S. Lobregt a, A. Vilanova
LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze
 LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction page 3 2. Segmentation page 4 3. Measurement Instructions page 11 4. Calculation Instructions page 14 5. References
LEFT VENTRICLE SEGMENTATION AND MEASUREMENT Using Analyze 2 Table of Contents 1. Introduction page 3 2. Segmentation page 4 3. Measurement Instructions page 11 4. Calculation Instructions page 14 5. References
PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT OF VASCULAR OCCLUSION EXTENT AND LOCALIZATION OF EMBOLI 1. BACKGROUND
 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
JOURNAL OF MEDICAL INFORMATICS & TECHNOLOGIES Vol. 11/2007, ISSN 1642-6037 Damian PTAK * pulmonary embolism, AngioCT, postprocessing techniques, Mastora score PULMONARY EMBOLISM ANGIOCT (CTA) ASSESSMENT
Left atrial function. Aliakbar Arvandi MD
 In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
In the clinic Left atrial function Abstract The left atrium (LA) is a left posterior cardiac chamber which is located adjacent to the esophagus. It is separated from the right atrium by the inter-atrial
Improvement of Image Quality with ß-Blocker Premedication on ECG-Gated 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography
 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Shim et al. 16-MDCT Coronary Angiography Sung Shine Shim 1 Yookyung Kim Soo Mee Lim Received December 1, 2003; accepted after revision June 1, 2004. 1 All authors: Department
Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function
 Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Kara, Y. Paksoy, C. Erol,
Comparison of Cardiac MDCT with MRI and Echocardiography in the Assessement of Left Ventricular Function Poster No.: C-0969 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: B. Kara, Y. Paksoy, C. Erol,
Noncoronary Cardiac MDCT
 Noncoronary Cardiac MDCT David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, of Radiology and Medicine Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland Toshiba Disclosures Grant support Noncoronary
Noncoronary Cardiac MDCT David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D. Professor, of Radiology and Medicine Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine Baltimore, Maryland Toshiba Disclosures Grant support Noncoronary
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008:
 Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Copyright 2008 Society of Photo Optical Instrumentation Engineers. This paper was published in Proceedings of SPIE, vol. 6915, Medical Imaging 2008: Computer Aided Diagnosis and is made available as an
Imaging heart. UK Biobank Annual Meeting 13 th June 2016
 NIHR Barts and The London Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit National Institute for Health Research Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit at Barts Imaging heart UK Biobank Annual Meeting 13 th June
NIHR Barts and The London Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit National Institute for Health Research Cardiovascular Biomedical Research Unit at Barts Imaging heart UK Biobank Annual Meeting 13 th June
General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 2 General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 Peter G. Danias, Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions and Answers Humana Press 2008 20 Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions
2 General Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Imaging 19 Peter G. Danias, Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions and Answers Humana Press 2008 20 Cardiovascular MRI: 150 Multiple-Choice Questions
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous?
 High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
High density thrombi of pulmonary embolism on precontrast CT scan: Is it dangerous? Poster No.: C-1753 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit B. Y. Lee, H. R. KIM, J. I. Jung,
Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose?
 Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Journal of Physics: Conference Series PAPER OPEN ACCESS Pediatric chest HRCT using the idose 4 Hybrid Iterative Reconstruction Algorithm: Which idose level to choose? To cite this article: M Smarda et
Scientific Exhibit. Authors: D. Takenaka, Y. Ohno, Y. Onishi, K. Matsumoto, T.
 The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
The feasibility of biphasic contrast-media-injection-protocol for chest imaging on 320-slice volume MDCT: Direct comparison of biphasic and bolus contrast-media injection protocols on 320-slice volume
Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration SINE Wave Curve On Magnetic Resonance Imaging
 Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Original Article Impaired Regional Myocardial Function Detection Using the Standard Inter-Segmental Integration Ngam-Maung B, RT email : chaothawee@yahoo.com Busakol Ngam-Maung, RT 1 Lertlak Chaothawee,
Isolated congenital coronary anomalies: Evaluation by multislice-ct or MRI
 Isolated congenital coronary anomalies: Evaluation by multislice-ct or MRI B.K. Velthuis, Dept. of Radiology UMC Utrecht, the Netherlands ESC 2010 Coronary artery anomalies CAA Uncommon 0.3-5% normal population
Isolated congenital coronary anomalies: Evaluation by multislice-ct or MRI B.K. Velthuis, Dept. of Radiology UMC Utrecht, the Netherlands ESC 2010 Coronary artery anomalies CAA Uncommon 0.3-5% normal population
Jin Hur, MD 1 Tae Hoon Kim, MD 1 Sang Jin Kim, MD 1 Young Hoon Ryu, MD 1 Hyung Jung Kim, MD 2
 ssessment of the Right Ventricular Function and Mass Using Cardiac Multi-Detector Computed Tomography in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Jin Hur, MD 1 Tae Hoon Kim, MD 1 Sang Jin Kim,
ssessment of the Right Ventricular Function and Mass Using Cardiac Multi-Detector Computed Tomography in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Jin Hur, MD 1 Tae Hoon Kim, MD 1 Sang Jin Kim,
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement
 Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
Fundamentals, Techniques, Pitfalls, and Limitations of MDCT Interpretation and Measurement 3 rd Annual Imaging & Physiology Summit November 20-21, 21, 2009 Seoul, Korea Wm. Guy Weigold, MD, FACC Cardiovascular
MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
 MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT Linda B Haramati MD, MS Departments of Radiology and Medicine Bronx, New York OUTLINE Pathogenesis Variants Initial surgical treatments Basic MR protocols
MRI (AND CT) FOR REPAIRED TETRALOGY OF FALLOT Linda B Haramati MD, MS Departments of Radiology and Medicine Bronx, New York OUTLINE Pathogenesis Variants Initial surgical treatments Basic MR protocols
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Right Heart Catheterization. Franz R. Eberli MD Chief of Cardiology Stadtspital Triemli, Zurich
 Right Heart Catheterization Franz R. Eberli MD Chief of Cardiology Stadtspital Triemli, Zurich Right Heart Catheterization Pressure measurements Oxygen saturation measurements Cardiac output, Vascular
Right Heart Catheterization Franz R. Eberli MD Chief of Cardiology Stadtspital Triemli, Zurich Right Heart Catheterization Pressure measurements Oxygen saturation measurements Cardiac output, Vascular
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients
 128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
128-slice dual-source CT coronary angiography using highpitch scan protocols in 102 patients Poster No.: C-0634 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit Topic: Cardiac Authors: Y. H. Choe, J. W. Lee,
Case Report. Heon Lee, MD, PhD 1, Seok-Yeon Kim, MD 2, U. Joseph Schoepf, MD 3 CASE REPORT INTRODUCTION
 Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.2.244 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(2):244-248 Isolated Non-Compaction of the Left Ventricle in a Patient with New-Onset Heart
Case Report http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2012.13.2.244 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2012;13(2):244-248 Isolated Non-Compaction of the Left Ventricle in a Patient with New-Onset Heart
Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB
 Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB Poster No.: C-0757 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Yoon, H. Soohee; Changwon-si/KR Thorax, Lung, Respiratory system,
Comparison of CT findings between MDR-TB and XDR-TB Poster No.: C-0757 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit K. Yoon, H. Soohee; Changwon-si/KR Thorax, Lung, Respiratory system,
Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors
 Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Background Coronary artery disease (CAD) risk factors CAD Risk factors Hypertension Insulin resistance /diabetes Dyslipidemia Smoking /Obesity Male gender/ Old age Atherosclerosis Arterial stiffness precedes
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women
 Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Cardiac Magnetic Resonance in pregnant women Chen SSM, Leeton L, Dennis AT Royal Women s Hospital and The University of Melbourne, Parkville, Australia alicia.dennis@thewomens.org.au Quantification of
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We. ACHD Patients
 Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
Cardiac MRI in ACHD What We Have Learned to Apply to ACHD Patients Faris Al Mousily, MBChB, FAAC, FACC Consultant, Pediatric Cardiology, KFSH&RC/Jeddah Adjunct Faculty, Division of Pediatric Cardiology
A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis
 Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550038 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis Catalina Sanchez-Alvarez
Archives of Clinical and Medical Case Reports doi: 10.26502/acmcr.96550038 Volume 2, Issue 5 Case Report A Case of Impending Cardiac Tamponade Caused by Effusive Constrictive Pericarditis Catalina Sanchez-Alvarez
Heart Failure. Cardiac Anatomy. Functions of the Heart. Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics. Determinants of Cardiac Output. Cardiac Output
 Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
Cardiac Anatomy Heart Failure Professor Qing ZHANG Department of Cardiology, West China Hospital www.blaufuss.org Cardiac Cycle/Hemodynamics Functions of the Heart Essential functions of the heart to cover
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital
 LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
LV geometric and functional changes in VHD: How to assess? Mi-Seung Shin M.D., Ph.D. Gachon University Gil Hospital LV inflow across MV LV LV outflow across AV LV LV geometric changes Pressure overload
PMP. Original Article. Introduction. Hee Jung Kim, Sung Yong Park, Young Hee Park, Ah Ram Chang
 Original Article PMP Progress in Medical Physics 28(1), March 217 https://doi.org/1.14316/pmp.217.28.1.27 pissn 258-4445, eissn 258-4453 Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative
Original Article PMP Progress in Medical Physics 28(1), March 217 https://doi.org/1.14316/pmp.217.28.1.27 pissn 258-4445, eissn 258-4453 Dosimetric Effects of Low Dose 4D CT Using a Commercial Iterative
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies
 Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Echocardiography as a diagnostic and management tool in medical emergencies Frank van der Heusen MD Department of Anesthesia and perioperative Care UCSF Medical Center Objective of this presentation Indications
Introduction. Cardiac Imaging Modalities MRI. Overview. MRI (Continued) MRI (Continued) Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03
 Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Introduction Cardiac Imaging Modalities Arnaud Bistoquet 12/19/03 Coronary heart disease: the vessels that supply oxygen-carrying blood to the heart, become narrowed and unable to carry a normal amount
Cardiac Imaging Tests
 Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Cardiac Imaging Tests http://www.medpagetoday.com/upload/2010/11/15/23347.jpg Standard imaging tests include echocardiography, chest x-ray, CT, MRI, and various radionuclide techniques. Standard CT and
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy. John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
 Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
Radiation Exposure in Pregnancy John R. Mayo UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA Illustrative Clinical Scenario 32 year old female 34 weeks pregnant with recent onset shortness of breath and central chest pain
Pulmonary Hypertension: Echocardiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricular Function. Irmina Gradus-Pizlo, MD
 Pulmonary Hypertension: Echocardiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricular Function Irmina Gradus-Pizlo, MD Disclosures: Nothing to disclose Overview Is pulmonary hypertension
Pulmonary Hypertension: Echocardiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Hypertension and Right Ventricular Function Irmina Gradus-Pizlo, MD Disclosures: Nothing to disclose Overview Is pulmonary hypertension
Parametric response mapping
 Parametric response mapping Utility of a novel imaging biomarker in pulmonary disease Dharshan Vummidi MD, Lama VN MD, Yanik G MD, Kazerooni EA MD, Meilan Han MD, Galban C PhD Radiology, Pulmonary & Critical
Parametric response mapping Utility of a novel imaging biomarker in pulmonary disease Dharshan Vummidi MD, Lama VN MD, Yanik G MD, Kazerooni EA MD, Meilan Han MD, Galban C PhD Radiology, Pulmonary & Critical
Quantitative CT in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Inspiratory and Expiratory Assessment
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research kira et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Masanori kira 1 Kazushige Toyokawa 1 Yoshikazu Inoue 2 Toru rai
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research kira et al. CT of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Cardiopulmonary Imaging Original Research Masanori kira 1 Kazushige Toyokawa 1 Yoshikazu Inoue 2 Toru rai
Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning
 Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning Dmitry Beyder MPA, CNMT Nuclear Medicine, Radiology Barnes-Jewish Hospital / Washington University St. Louis, MO Disclaimers/Relationships Standard of care research
Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning Dmitry Beyder MPA, CNMT Nuclear Medicine, Radiology Barnes-Jewish Hospital / Washington University St. Louis, MO Disclaimers/Relationships Standard of care research
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary. Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging for the detection of coronary artery disease
 Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging for the detection of coronary artery disease April 2007 This technology summary is based
Horizon Scanning Technology Summary National Horizon Scanning Centre Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) imaging for the detection of coronary artery disease April 2007 This technology summary is based
Assessment of L.V. Function by Multislice Cardiac Ct As Compared to 2d_Echocardiography
 THE MULTISLICE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CARDIAC MEDICAL CT JOURNAL VOL. 14,NO.1, 2015 Assessment of L.V. Function by Multislice Cardiac Ct As Compared to 2d_Echocardiography Hayder Ryaid Abdul Satar*,Hasan Ali
THE MULTISLICE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE CARDIAC MEDICAL CT JOURNAL VOL. 14,NO.1, 2015 Assessment of L.V. Function by Multislice Cardiac Ct As Compared to 2d_Echocardiography Hayder Ryaid Abdul Satar*,Hasan Ali
Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases
 Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2011.12.3.395 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2011;12(3):395-399 Individual Pulmonary Vein Atresia in Adults: Report of Two Cases Hyoung Nam Lee, MD, Young
Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery Shunt Narrowing
 Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Case Reports in Cardiology Volume 2011, Article ID 802643, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2011/802643 Case Report Computed Tomography Angiography Successfully Used to Diagnose Postoperative Systemic-Pulmonary Artery
Michael Rose 1, Bernard Rubal 1, Edward Hulten 2, Jennifer N Slim 1, Kevin Steel 1, James L Furgerson 1, Todd C Villines 2 and Ahmad M Slim 1
 522789SMO0010.1177/2050312114522789SAGE Open MedicineRose et al. research-article2014 Original Article SAGE Open Medicine Chamber dimensions and functional assessment with coronary computed tomographic
522789SMO0010.1177/2050312114522789SAGE Open MedicineRose et al. research-article2014 Original Article SAGE Open Medicine Chamber dimensions and functional assessment with coronary computed tomographic
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography
 Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Velocity Vector Imaging as a new approach for cardiac magnetic resonance: Comparison with echocardiography Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman 1,
Pericardial Diseases. Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD. Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University
 Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Pericardial Diseases Smonporn Boonyaratavej, MD Division of Cardiology, Department of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Cardiac Center, King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital 21 AUGUST 2016 Pericardial
Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Adults
 Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Adults Linda B. Haramati, MD Disclosures Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Adults Linda B. Haramati MD, MS Jeffrey M. Levsky MD, PhD Meir Scheinfeld MD, PhD Department
Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Adults Linda B. Haramati, MD Disclosures Complex Congenital Heart Disease in Adults Linda B. Haramati MD, MS Jeffrey M. Levsky MD, PhD Meir Scheinfeld MD, PhD Department
Measurement of Ventricular Volumes and Function: A Comparison of Gated PET and Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance
 BRIEF COMMUNICATION Measurement of Ventricular Volumes and Function: A Comparison of Gated PET and Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Kim Rajappan, MBBS 1,2 ; Lefteris Livieratos, MSc 2 ; Paolo G. Camici,
BRIEF COMMUNICATION Measurement of Ventricular Volumes and Function: A Comparison of Gated PET and Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance Kim Rajappan, MBBS 1,2 ; Lefteris Livieratos, MSc 2 ; Paolo G. Camici,
UK Biobank. Imaging modality Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Version th Oct 2015
 Imaging modality Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Version 1.0 http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ 30 th Oct 2015 This document details the procedure for the CMR scan performed at an Imaging assessment centre
Imaging modality Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance (CMR) Version 1.0 http://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/ 30 th Oct 2015 This document details the procedure for the CMR scan performed at an Imaging assessment centre
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function
 Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
Global left ventricular circumferential strain is a marker for both systolic and diastolic myocardial function Toshinari Onishi 1, Samir K. Saha 2, Daniel Ludwig 1, Erik B. Schelbert 1, David Schwartzman
MR Advance Techniques. Cardiac Imaging. Class IV
 MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
MR Advance Techniques Cardiac Imaging Class IV Heart The heart is a muscular organ responsible for pumping blood through the blood vessels by repeated, rhythmic contractions. Layers of the heart Endocardium
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False?
 Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Mechanisms of False Positive Exercise Electrocardiography: Is False Positive Test Truly False? Masaki Izumo a, Kengo Suzuki b, Hidekazu Kikuchi b, Seisyo Kou b, Keisuke Kida b, Yu Eguchi b, Nobuyuki Azuma
Assessment of LV systolic function
 Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Tutorial 5 - Assessment of LV systolic function Assessment of LV systolic function A knowledge of the LV systolic function is crucial in the undertanding of and management of unstable hemodynamics or a
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
computed tomography Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Known
Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary
 1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
1 IMAGES IN CARDIOVASCULAR ULTRASOUND 2 3 4 Multimodality Imaging of Anomalous Left Coronary Artery from the Pulmonary Artery 5 6 7 Byung Gyu Kim, MD 1, Sung Woo Cho, MD 1, Dae Hyun Hwang, MD 2 and Jong
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT
 Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Low Dose Era in Cardiac CT DIANA E. LITMANOVICH, MD Department of Radiology Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Disclosures Neither I nor my immediate family members have a financial
Assignable revenue codes: Explanation of services:
 COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY Chest/Cardiac Assignable revenue codes: 0350 CT Scan General Classification 0351 CT Scan Head Scan 0352 CT Scan Body Scan 0359 CT Scan Other CT Scans Explanation of services: Known
The Location and Size of Pulmonary Embolism in Antineoplastic Chemotherapy Patients 1
 The Location and Size of Pulmonary Embolism in Antineoplastic Chemotherapy Patients 1 Yun Joo Park, M.D., Woocheol Kwon, M.D., Won-Yeon Lee, M.D. 2, Sang Baek Koh, M.D. 3, Seong Ah Kim, M.D., Myung Soon
The Location and Size of Pulmonary Embolism in Antineoplastic Chemotherapy Patients 1 Yun Joo Park, M.D., Woocheol Kwon, M.D., Won-Yeon Lee, M.D. 2, Sang Baek Koh, M.D. 3, Seong Ah Kim, M.D., Myung Soon
The 5th Congress of Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging
 The 5th Congress of Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging June 17 ~ June 19, 2011 HKEC, Hong Kong Number of Participants : 1,032 Country No. of Delegate Country No. of Delegate 1 Australia 15 18 Korea,
The 5th Congress of Asian Society of Cardiovascular Imaging June 17 ~ June 19, 2011 HKEC, Hong Kong Number of Participants : 1,032 Country No. of Delegate Country No. of Delegate 1 Australia 15 18 Korea,
Normal LV Ejection Fraction Limits Using 4D-MSPECT: Comparisons of Gated Perfusion and Gated Blood Pool SPECT Data with Planar Blood Pool
 Normal LV Ejection Fraction Limits Using 4D-MSPECT: Comparisons of Gated Perfusion and Gated Blood Pool SPECT Data with Planar Blood Pool EP Ficaro, JN Kritzman, JR Corbett University of Michigan Health
Normal LV Ejection Fraction Limits Using 4D-MSPECT: Comparisons of Gated Perfusion and Gated Blood Pool SPECT Data with Planar Blood Pool EP Ficaro, JN Kritzman, JR Corbett University of Michigan Health
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU
 THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
THE RIGHT VENTRICLE IN PULMONARY HYPERTENSION R. DRAGU Cardiology Dept. Rambam Health Care Campus Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Technion, Israel Why the Right Ventricle? Pulmonary hypertension (PH) Right
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy. Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea
 CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
CT for Myocardial Characterization of Cardiomyopathy Byoung Wook Choi, Yonsei University Severance Hospital, Seoul, Korea Cardiomyopathy Elliott P et al. Eur Heart J 2008;29:270-276 The European Society
Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult: A Diagnostic Imaging Challenge
 Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Case Reports in Medicine Volume 2015, Article ID 128462, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/128462 Case Report Sinus Venosus Atrial Septal Defect as a Cause of Palpitations and Dyspnea in an Adult:
Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling
 Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
Investigations and research Modifi ed CT perfusion contrast injection protocols for improved CBF quantifi cation with lower temporal sampling J. Wang Z. Ying V. Yao L. Ciancibello S. Premraj S. Pohlman
HISTORY. Question: What category of heart disease is suggested by the fact that a murmur was heard at birth?
 HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
HISTORY 23-year-old man. CHIEF COMPLAINT: Decreasing exercise tolerance of several years duration. PRESENT ILLNESS: The patient is the product of an uncomplicated term pregnancy. A heart murmur was discovered
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure
 The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
The right heart: the Cinderella of heart failure Piotr Ponikowski, MD, PhD, FESC Medical University, Centre for Heart Disease Clinical Military Hospital Wroclaw, Poland none Disclosure Look into the Heart
Pulmonary hypertension
 Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Pulmonary hypertension Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
Zurich Open Repository and Archive University of Zurich Main Library Strickhofstrasse 39 CH-8057 Zurich www.zora.uzh.ch Year: 2012 Pulmonary hypertension Glaus, T M Posted at the Zurich Open Repository
Institute of Cardiology Warsaw, Poland
 Mateusz Śpiewak, Elżbieta K. Biernacka, Łukasz A. Małek, Jolanta Miśko, Joanna Petryka, Mirosław Kowalski, Barbara Miłosz, Magdalena Żabicka, Piotr Hoffman, Witold Rużyłło Institute of Cardiology Warsaw,
Mateusz Śpiewak, Elżbieta K. Biernacka, Łukasz A. Małek, Jolanta Miśko, Joanna Petryka, Mirosław Kowalski, Barbara Miłosz, Magdalena Żabicka, Piotr Hoffman, Witold Rużyłło Institute of Cardiology Warsaw,
MRI protocol for post-repaired TOF
 2012 NASCI MRI protocol for post-repaired TOF Taylor Chung, M.D. Associate Director, Body and Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Oakland,
2012 NASCI MRI protocol for post-repaired TOF Taylor Chung, M.D. Associate Director, Body and Cardiovascular Imaging Department of Diagnostic Imaging Children s Hospital & Research Center Oakland Oakland,
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure
 The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
The new Guidelines: Focus on Chronic Heart Failure Petros Nihoyannopoulos MD, FRCP, FESC Professor of Cardiology Imperial College London and National & Kapodistrian University of Athens 2 3 4 The principal
Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle
 Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Advances in Tricuspid Regurgitation Congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Munich, August 25-29, 2012 Assessing the Impact on the Right Ventricle Stephan Rosenkranz, MD Clinic III for Internal
Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
 ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
ESC Congress 2011.No 85975 Evaluation of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction by Doppler and 2D Speckle-tracking Imaging in Patients with Primary Pulmonary Hypertension Second Department of Internal
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
 ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
ESC Congress 2011, Paris Imaging Unusual Causes of Cardiomyopathy Restrictive Cardiomyopathy Kazuaki Tanabe, MD, PhD Professor of Medicine Chair, Division of Cardiology Izumo, Japan I Have No Disclosures
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI -
 Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Advanced imaging of the left atrium - strain, CT, 3D, MRI - Monica Rosca, MD Carol Davila University of Medicine and Pharmacy, Bucharest, Romania Declaration of interest: I have nothing to declare Case
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle
 Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Echocardiographic Assessment of the Left Ventricle Theodora Zaglavara, MD, PhD, BSCI/BSCCT Department of Cardiovascular Imaging INTERBALKAN EUROPEAN MEDICAL CENTER 2015 The quantification of cardiac chamber
Cardiovascular Imaging Endpoints in Oncology Clinical Trials
 Cardiovascular Imaging Endpoints in Oncology Clinical Trials Bonnie Ky, MD, MSCE Assistant Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology Director, Penn Cardio-Oncology Center of Excellence Director, Penn Center
Cardiovascular Imaging Endpoints in Oncology Clinical Trials Bonnie Ky, MD, MSCE Assistant Professor of Medicine and Epidemiology Director, Penn Cardio-Oncology Center of Excellence Director, Penn Center
COMPLEX CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: WHEN IS IT TOO LATE TO INTERVENE?
 COMPLEX CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: WHEN IS IT TOO LATE TO INTERVENE? Aurora S. Gamponia, MD, FPPS, FPCC, FPSE OBJECTIVES Identify complex congenital heart disease at high risk or too late for intervention
COMPLEX CONGENITAL HEART DISEASE: WHEN IS IT TOO LATE TO INTERVENE? Aurora S. Gamponia, MD, FPPS, FPCC, FPSE OBJECTIVES Identify complex congenital heart disease at high risk or too late for intervention
How to Approach the Patient with CRT and Recurrent Heart Failure
 How to Approach the Patient with CRT and Recurrent Heart Failure Byron K. Lee MD Associate Professor of Medicine Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Section UCSF Update in Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias
How to Approach the Patient with CRT and Recurrent Heart Failure Byron K. Lee MD Associate Professor of Medicine Electrophysiology and Arrhythmia Section UCSF Update in Electrocardiography and Arrhythmias
ORIGINAL. Keywords : multidetector-row computed tomography, myocardial infarction, cardiac function
 ORIGINAL Department of Digestive and Cardiovascular Medicine, Institute of Health Biosciences, The University of Tokushima Graduate School, Tokushima, Japan, Faculty of Integrated Art and Sciences, Department
ORIGINAL Department of Digestive and Cardiovascular Medicine, Institute of Health Biosciences, The University of Tokushima Graduate School, Tokushima, Japan, Faculty of Integrated Art and Sciences, Department
Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009
 Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT
 Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
Impact of SSF on diagnostic performance of coronary CT angiography within one heart beat in patients with high heart rate using a 256-row detector CT Junfu Liang 1,2, Hui Wang 1, Lei Xu 1, Li Dong 1, Zhanming
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic)
 Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Cardiac CT - Coronary Calcium Basics Workshop II (Basic) J. Jeffrey Carr, MD, MSCE Dept. of Radiology & Public Health Sciences Wake Forest University School of Medicine Winston-Salem, NC USA No significant
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH
 Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Squeeze, Squeeze, Squeeze: The Importance of Right Ventricular Function and PH Javier Jimenez MD PhD FACC Director, Advanced Heart Failure and Pulmonary Hypertension Miami Cardiac & Vascular Institute
Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC CARDIOLOGY Review Article Brief View of Calculation and Measurement of Cardiac Hemodynamics Samah Alasrawi* Pediatric Cardiologist, Al Jalila Children Heart Center, Dubai, UAE *
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology
 Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
Cigna - Prior Authorization Procedure List Cardiology Category CPT Code CPT Code Description 33206 Insertion of new or replacement of permanent pacemaker with transvenous electrode(s); atrial 33207 Insertion
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1
 A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
A STUDY OF LEFT VENTRICULAR DIASTOLIC DYSFUNCTION IN HYPERTENSION Ravi Keerthy M 1 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Ravi Keerthy M. A Study of Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Hypertension. Journal of
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE)
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Rapid Cardiac Echo (RCE) Purpose: Rapid Cardiac Echocardiography (RCE) This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum
QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC. SPECT tomography has the advantage of quantifying biventricular volumes.
 QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC Thematic Units Arrhythmias and Electrophysiology Basic Research Bioengineering and Medical Informatics Cardiac Surgical Intensive
QCVC Committees Scientific Activities Central Hall General Information FAC Thematic Units Arrhythmias and Electrophysiology Basic Research Bioengineering and Medical Informatics Cardiac Surgical Intensive
MEDVISO WHITE PAPER ON STRAIN ANALYSIS IN TAGGED MR IMAGES
 Purpose of document The purpose of this document is to document validation of the Strain analysis module in Segment software packages. Intended audience The intended audiences of this document are: Engineering
Purpose of document The purpose of this document is to document validation of the Strain analysis module in Segment software packages. Intended audience The intended audiences of this document are: Engineering
The use of Cardiac CT and MRI in Clinical Practice
 The use of Cardiac CT and MRI in Clinical Practice Matthew W. Martinez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine LVPG - Lehigh Valley Heart Specialists Lehigh Valley Health Network Oct. 3, 2009 DISCLOSURE Relevant
The use of Cardiac CT and MRI in Clinical Practice Matthew W. Martinez, MD Assistant Professor of Medicine LVPG - Lehigh Valley Heart Specialists Lehigh Valley Health Network Oct. 3, 2009 DISCLOSURE Relevant
Imaging congestive heart failure: role of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA)
 Imaging congestive heart failure: role of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) Gianluca Pontone, MD, PhD, FESC, FSCCT Director of MR Unit Deputy Director of Cardiovascul CT Unit Clinical Cardiology
Imaging congestive heart failure: role of coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) Gianluca Pontone, MD, PhD, FESC, FSCCT Director of MR Unit Deputy Director of Cardiovascul CT Unit Clinical Cardiology
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new
 Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Myocardial viability testing. What we knew and what is new Dr B K S Sastry, MD, DM. CARE Hospitals, Hyderabad What is Viability Viability Dysfunctional myocardium subtended by diseased coronary arteries
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach
 Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Customizing Contrast Injection for Body MDCT: Algorithmic Approach Lincoln L. Berland, M.D., F.A.C.R. University of Alabama at Birmingham Before Contrast Prep and Hydration Hydration single most important
Chapter 11. Summary and general discussion
 Chapter 11 Summary and general discussion Low Dose Computed Tomography of the Chest: Applications and Limitations INTRODUCTION The introduction of spiral, multidetector-row computed tomography (CT) has
Chapter 11 Summary and general discussion Low Dose Computed Tomography of the Chest: Applications and Limitations INTRODUCTION The introduction of spiral, multidetector-row computed tomography (CT) has
B. CT protocols for the spine
 B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
B. CT protocols for the spine Poster No.: A-003 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Invited Speaker Topic: Neuro Authors: B. Tins; Oswestry/UK Keywords: CT, spine, diagnostic imaging protocol DOI: 10.1594/ecr2010/A-003
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging. Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes
 BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
BioMedical quantitative X-Ray Imaging Emmanuel Brun Researcher Inserm Université Grenoble Alpes 1 Outline Introduction K-Edge Imaging Patient imaging at the European synchrotron Medical Phase Contrast
