Localization of talin in skeletal and cardiac muscles
|
|
|
- Beatrice Carr
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Volume 200, number 1 FEBS 3591 May 1986 Localization of talin in skeletal and cardiac muscles A.M. Belkin, N.I. Zhidkova and V.E. Koteliansky* Laboratory of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, Institute of Experimental Cardiology, USSR Cardiology Research Center, Academy of Medical Sciences, 3rd Cherepkovskaya Str. ISA, Moscow , USSR Received 3 January 1986; revised version received 24 February 1986 Antibodies to talin and vinculin were used for localization of these proteins in skeletal and cardiac muscles by the indirect immunofluorescence method. We have found that talin is localized in intercalated discs of cardiac muscle and in costameres of skeletal and cardiac muscles. It is suggested that in striated muscles talin and vinculin play an important role in interactions between actin filaments and membranes. (Cardiac muscle, Skeletal muscle) Talin Vinculin ImmunoJ7uorescence Microjilament Membrane-protein interaction 1. INTRODUCTION Studies on membrane-microfilament interactions have focused a lot of interest on the protein vinculin. Vinculin was localized to the termini of actin filaments in focal contacts of cultured cells, zonula adherens of intestinal epithelium, intercalated discs of cardiac muscle and dense plaques of chicken gizzard smooth muscle [l-5]. Vinculin has also been identified in specific regions of attachment between striated muscle myofibrils and the surrounding membrane of sarcolemma [6-81. In skeletal and cardiac muscles vinculin was found in a two-dimensional orthogonal membrane lattice - the transverse elements of the vinculin lattice being called costameres [6-81. The membraneassociated costameres are highly organized and periodic with the underlying sarcomeres which overlie the I band of the sarcomere [6-81. The costameres appear to be physically coupled to the actin filaments of sarcomeres [6-81. Recently a new protein in adhesion plaques of cultured cells was discovered which was referred to as talin [9]. Talin was found to have an M, of [9]. Talin forms a complex with vinculin with a dissociation * To whom correspondence should be addressed constant of about lo- M [lo]. Talin, however, does not bind to actin [9,10]. Here we present the results of immunofluorescence localization of talin in avian skeletal and cardiac muscles. We report that talin is localized in intercalated discs of cardiac muscle and in costameres of skeletal and cardiac muscles. 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS The preparation and characterization of rabbit affinity-purified antibody to chicken gizzard vinculin have been described [7]. The rabbit antiserum to chicken gizzard talin used in this study was a gift from Dr K. Burridge (University of North Carolina, USA). The preparation and characterization of antitalin antiserum have been described [9]. The affinity-purified antibody to vinculin and antiserum to talin were characterized by standard immunological techniques and in all tests interacted only with vinculin (antivinculin antibody) or with talin (antitalin antiserum) [7,9]. The antitalin antiserum and affinity-purified antibody against vinculin were found to interact only with talin and vinculin, respectively, in immunoblots of SDS-soluble proteins from chicken cardiac and skeletal muscles (not shown). 32 Published by Elsevier Science Publishers B. V. (Biomedical Division) /86/$ Federation of European Biochemical Societies
2 For immunofluorescence staining 3-4 /cm longitudinal and transverse sections from frozen chicken cardiac and skeletal muscles were cut on a cryostat at -20 C and mounted on glass slides. After incubation with 0.04 mg/ml affinitypurified antivinculin IgG or antitalin antiserum (dilution 1:400) for 60 min, sections were washed and then fluorescein-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG added. After incubation for 45 min sections were washed and viewed in a Zeiss epifluorescence photomicroscope III with 40 x and 60 x objectives. To intensify the fluorescence, sections were incubated for 45 min with fluorescein-conjugated rabbit anti-goat IgG. 3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION To localize talin in striated muscles, cryostat sections of chicken skeletal and cardiac muscles were studied by indirect immunofluorescence using antiserum to chicken smooth muscle talin. When transverse sections were examined (fig. la,c) we observed that fluorescence was confined to the cell margins. No staining is observed intracellularly in the fibers. Occasional bright patches of stain (cardiac muscle, fig.la) correspond to vessels. The localization pattern of talin is similar to that of vinculin (fig.lb,d). Staining for talin was significantly less intense compared to vinculin. In F&l. Immunofluorescence localization of talin and vinculin in chicken striated muscles. Transverse section of: (A) cardiac muscle stained for talin, x 810; (B) cardiac muscle stained for vinculin, x 810; (C) skeletal muscle stained for talin, x 910; (D) skeletal muscle stained for vinculin, x
3 transverse sections of striated muscles vinculin is culin. For both vinculin and talin the imdetectable only at the sarcolemma (fig.lb,d) munofluorescence staining was very similar (not [f&8]. Because there was no difference in the shown), the only difference was the intensity of the distribution of talin and vinculin in serial staining. Staining for vinculin in muscles was obtransverse sections of striated muscles we conclude viously greater compared to talin. Based on these that talin is also concentrated very close to the sar- co-localization studies, we conclude that in striated colemmal membrane. Immunofluorescence analy- muscles talin could be a structural component of sis of longitudinal sections of chicken skeletal and myofibril-membrane attachment sites defined cardiac muscles demonstrates different types of earlier by the localization of vinculin ]4-g]. One of talin localization in striated muscles. Talin is those sites is inter~ated discs in cardiac muscle, located in specific cardiomyocyte contact regions - another being the transverse components of the in intercalated discs (figs 2B,3C). The periphery of lattice of myofibril-to-sarcolemmal membrane atthe myocytes along the cell margins was stained by tachment sites (costameres) in skeletal and cardiac the antibody to talin (fig.za). The membrane- muscles. Recently a number of new proteins were associated talin in a twodimension~ lattice with identified in intercalated discs of cardiac muscle longitudinal and transverse periodicity was found and in co&meres of striated muscle, including in sections that provide a surface view of the cell filamin, cr-actinin, desmin, vinculin, 200 kda pro- (figs 2A,B,3D). The longitudinal sections selected tein - for intercalated discs and vinculin, y-actin, to contain the surface of the fibers demonstrate spectrin, intermediate filament antigens - for that antitalin staining near the sarcolemmal mem- costameres [3,5-&l l-13]. It was shown that in inbrane is periodic and corresponds to the I bands of tercalated discs vinculin is more closely associated sarcomeres around the Z-line region (fig3a,c) with the membrane than other proteins and is [the phase-contrast micrograph (fig.3b) illustrates located at the fascia adherens of the intercalated that fluorescent bands in fig.3a overlie I bands of disc membrane [3,5]. On the other hand, vinculin subjacent myofibrils]. Talin was not found on in- and talin are two proteins that interact with each ternal or glycerinated myofibrils (figs 2,3&F). it other [lo]. Based on these data and results obshould be mentioned that in parallel to antitalin tained here we suggest that in striated muscles a staining of striated muscle sections the same serial complex of vinculin and talin may form a longitudinal sections were stained with antivin- peripheral domain playing an important role in the Fig.2. Immunofluorescence localization of talin in chicken skeletal (A) and cardiac (EN muscles (longitudinal sections). In (A) talin is associated with cell margins; arrows, presence of talin in sarcolemma; x 770. In (B) tab is associated with intercalated discs (small arrow) and with costameres (Iarge arrow), x I
4 Fig.3. are periodic and overlie the I band, immunofluorescence. (B) Phase-contrast micrograph of (A), x (C) Cardiac muscle discontinuous costameres, x (D) Skeletal muscle; talin is organized at the sarcolemma in a twodimensional lattice, x (E,F) Glycerinated chicken skeletal muscle myofibrils, (E) immunofluorescence, (F) phase contrast, x 390. (G) Chicken skeletal muscle incubated with non-immune IgG, x No staining was observed when antitalin antiserum was pre-adsorbed with talin. attachment of microfilaments to membrane in two specialized structures of skeletal and cardiac muscles. ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS The authors thank Dr K. Burridge (The University of North Carolina, USA) for generously providing the rabbit antiserum to chicken gizzard talin used in this study. REFERENCES [I] Geiger, B. (1979) Cell 18, Burridge, K. and Feramisco, V.R. (1980) Cell 19, ]3] Geiger, B., Tokuyasu, K.T., Dutton, A.H. and Singer, S.J. (1980) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, [4] Geiger, B., Dutton, A.H., Tokuyasu, K.T. and Singer, S.J. (1981) J. Cell Biol. 91,
5 [Sl Tokuyasu, K.T., Dutton, A.H., Geiger, B. and Singer, S.J. (1981) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 78, Pardo, J.V., Siliciano, J.D. and Craig, S. W. (I 983) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, Koteliansky, V.E. and Gneushev, G.N. (1983) FEBS Lett. 159, [81 Pardo, J.V., Siliciano, J.D. and Craig, S. W. (1983) J. Cell. Biol. 97, f91 Burridge, K. and Conneil, L. (1983) J. Cell Biol. 97, [lo] Burridge, K. and Mangeat, P. (1984) Nature 308, [ll] Koteliansky, V.E., Glukhova, M.A., Gneushev, G.N., Samuel, J.L. and Rappaport, L. (1985) Eur. J. Biochem., in press. 114 Maher, P. and Singer, S.J. (1983) Cell Motility 3, [13] Craig, S.W. and Pardo, J.V. (1983) Cell Motility 3,
How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? Muscles are excitable & contractile, extensible and elastic to some extent.
 Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscles How many skeletal muscles are present in our body? -646 muscles The functions of the muscles are: Movement Maintenance of posture Generation of heat Stabilization of joints : amount of muscle surrounding
Muscle tissue. 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue.
 Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Muscle tissue 1) Striated skeletal muscle tissue. 2) Striated cardiac muscle tissue. 3) Smooth muscle tissue. General characteristic of muscle tissue Origin: mesoderm and mesenchyme Excitability Contraction
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE
 Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Connective tissue MUSCLE TISSUE Part 1 General features of MT Develop from mesoderm Many cells, less intercellular matrix Function contraction (shortening) Skeletal (striated, voluntary) Types of MT Cardiac
Muscle tissues. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle tissues Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Muscle tissue is a soft tissue that composes muscles in animal bodies, and gives rise to muscles' ability to contract. Muscle tissue
Muscle Tissue. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Tendon Belly Tendon Types of
Muscle Tissue. General concepts. Classification of muscle. I. Functional classification is based on the type of neural control.
 Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Muscle Tissue LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Identify the three types of muscle tissue at the light microscopic level. 2. List and compare the structural and functional features of each of the three muscle fiber
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden
 Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
Contraction, Locomotion (Ch 16), Shelden 1 Molec Biol Cell 5 th ed. Supplemental Videos Actin-dependent ATP hydrolysis by myosin generates motile force The Myosin ATPase activity cycle 2 ATP binding releases
Skeletal muscle. General features :
 Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscular tissues In the first embryonic life the muscular tissues arise from mesoderm, The function of movement in multicellular organisms is usually assumed by specialized cells called muscle fibers which
Muscle Histology. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Histology Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Assistant Professor of Anatomy and Histology Functions of muscle tissue Movement Maintenance of posture Joint stabilization Heat generation Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal
Muscle Tissue. Muscle Development and Repair. Development: fusion of myoblasts. Repair: Satellite cells (S) 3 Types of Muscle
 ANNOUNCEMENTS Review Session Every Friday at 12:20 Muscle Tissue 3 Types of Muscle Function: Force generation Lab Practical Coming up! October 26 th, 27 th Muscle Tissue Striated Nonstriated Skeletal Smooth
ANNOUNCEMENTS Review Session Every Friday at 12:20 Muscle Tissue 3 Types of Muscle Function: Force generation Lab Practical Coming up! October 26 th, 27 th Muscle Tissue Striated Nonstriated Skeletal Smooth
Integrated Muscle. Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File
 Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Integrated Muscle Red: important. Black: in male female slides. Gray: notes extra. Editing File OBJECTIVES Identify and describe the histological structure of the three types of muscle cells and list the
Medical Biology. Dr. Khalida Ibrahim
 Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
Dr. Khalida Ibrahim Medical Biology MUSCLE TISSUE 1. Muscle tissue is characterized by its well-developed properties of contraction. 2. Muscle is responsible for the movements of the body and the various
U 'NIDIRECTIONAL blood flow through the embryonic
 Immunocytochemical Studies of Cardiac MyofibriUogenesis in Early Chick Embryos. III. Generation of Fasciae Adherentes and Costameres K. T. Tokuyasu Department of Biology, University of California at San
Immunocytochemical Studies of Cardiac MyofibriUogenesis in Early Chick Embryos. III. Generation of Fasciae Adherentes and Costameres K. T. Tokuyasu Department of Biology, University of California at San
GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue
 Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Biology-232 GENERAL HISTOLOGY 4. Muscular Tissue Dr. Manal Othman Anatomy Department CMMS, AGU Responsible for MOST types of BODY MOVEMENT Made up of groups of elongated MUSCLE cells with contractile filaments
Muscular System. Human A & P
 Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Muscular System Human A & P There are 3 types of muscle tissue: A. Skeletal B. Smooth C. Cardiac The essential function of a muscle is contraction, or shortening, and are responsible for essentially all
Chapter 7 The Muscular System. Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1
 Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
Chapter 7 The Muscular System Mosby items and derived items 2012 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. 1 INTRODUCTION A. Muscular tissue enables the body and its parts to move 1. Three types of
******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY
 BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
BIOLOGY 211: HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY ******************************************************************************************************* MUSCLE CYTOLOGY AND HISTOLOGY *******************************************************************************************************
The Muscular System PART A
 6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
6 The Muscular System PART A PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Muscular System
Microanatomy of Muscles. Anatomy & Physiology Class
 Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Microanatomy of Muscles Anatomy & Physiology Class Three Main Muscle Types Objectives: By the end of this presentation you will have the information to: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Describe the 3 main types of muscles.
Muscle Tissue. Xie Fenfen. Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Anhui Medical University
 Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Muscle Tissue Xie Fenfen Email:xff2005024@126.com Department of Histology and Embryology School of Basic Medicine Key points The structural differences (LM) of 3 types of muscle fibers Molecular structure
Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours
 J Clin Pathol 1983;36:57-61 Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours DJ EVANS, IA LAMPERT, M JACOBS* From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
J Clin Pathol 1983;36:57-61 Intermediate filaments in smooth muscle tumours DJ EVANS, IA LAMPERT, M JACOBS* From the Department of Histopathology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School, Hammersmith Hospital,
Rearrangement of mrnas for costamere proteins during costamere development in cultured skeletal muscle from chicken
 Journal of Cell Science 107, 377-386 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 377 Rearrangement of mrnas for costamere proteins during costamere development in cultured skeletal
Journal of Cell Science 107, 377-386 (1994) Printed in Great Britain The Company of Biologists Limited 1994 377 Rearrangement of mrnas for costamere proteins during costamere development in cultured skeletal
Microfilament-membrane interaction
 456 TIBS - November 1985 Microfilament-membrane interaction Benjamin Geiger One of the major topics of research in modern cell biology involves the structure and organization of the cytoskeleton and, in
456 TIBS - November 1985 Microfilament-membrane interaction Benjamin Geiger One of the major topics of research in modern cell biology involves the structure and organization of the cytoskeleton and, in
Muscle tissue- part 2
 Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
Muscle tissue- part 2 Motor unit: The muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, its size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle is a large muscle and its contraction
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory
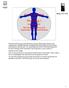 Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
Human Anatomy and Physiology I Laboratory Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle This lab involves study of the laboratory exercise Microscopic Anatomy and Organization of Skeletal Muscle,
Muscle Tissue.
 Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
Muscle Tissue Email:lizhongjie@zju.edu.cn General description 1) components: ---cell: muscle cell - myofiber ---extracellular ground substance: CT with BV, LV and nerve Nomenclature in muscular cell Muscular
Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle)
 Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle) What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal: morphology and functionality? Cardiac: morphology and functionality? Smooth: morphology and functionality? Skeletal
Histology Exam 2: Smith Lecture 5 (Muscle) What are the three types of muscle? Skeletal: morphology and functionality? Cardiac: morphology and functionality? Smooth: morphology and functionality? Skeletal
The Muscular System. Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle
 The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle The Muscular System Muscle tissue is one of the 4 tissue types in vertebrates Muscle Nervous The
Skeletal Muscle : Structure
 1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
1 Skeletal Muscle : Structure Dr.Viral I. Champaneri, MD Assistant Professor Department of Physiology 2 Learning objectives 1. Gross anatomy of the skeletal muscle 2. Myofilaments & their molecular structure
8 - Muscular System. Introduction Taft College Human Physiology
 8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
8 - Muscular System Introduction Taft College Human Physiology Muscular System - Introduction The bones provide the levers and structure of the skeleton but it is the muscles that cause movement. Motion
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. 1 Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5.
1. Locomotion. 2. Repositioning. 3. Internal movement
 MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
MUSCLE and MOVEMENT Chapters 20, 8, 21 1. Locomotion A. Movement B. 2. Repositioning A. 3. Internal movement A. Muscle Cells 1. Contractile 2. Myocytes 3. Striated A. Skeletal B. Cardiac 4. Smooth 5. Striated
Outline. Bio 105: Muscular System. Muscular System. Types of Muscles. Smooth Muscle. Cardiac Muscle 4/6/2016
 Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Outline Bio 105: Muscular System Lecture 11 Chapter 6 Characteristics of muscles 3 types of muscles Functions of muscles Structure of skeletal muscles Mechanics of muscle contraction Energy sources for
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Ragad Alhawi. Heba Kalbouneh
 13 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Heba Kalbouneh Motor unit: it s the muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, it s size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle
13 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Ragad Alhawi Heba Kalbouneh Motor unit: it s the muscle cells that are supplied by a single neuron/axon, it s size is variable according to the muscle action. EX: quadriceps muscle
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: 2. A. Skeletal muscle tissue ("striated muscle tissue")
 1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
1. General characteristics of muscle tissues: Muscle fibers, AKA, muscle cells Vascularized. Other tissues dense and loose C.T. nerves and nerve fibers Muscle fibers (muscle cells) close together. From
Muscular System- Part 1. Unit 5 Miss Wheeler
 Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
Muscular System- Part 1 Unit 5 Miss Wheeler Fun Facts! The tongue is the strongest muscle in your body The smallest muscles in the body are in the middle ear The largest muscle in the body is the gluteus
MUSCLE TISSUE (MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY) PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE
 PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
PART I: MUSCLE STRUCTURE Muscle Tissue A primary tissue type, divided into: skeletal muscle cardiac muscle smooth muscle Functions of Skeletal Muscles Produce skeletal movement Maintain body position Support
Muscle Tissue and Motion
 Muscle Tissue and Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they
Muscle Tissue and Motion Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Muscle tissue is characterized by properties that allow movement. Muscle cells are excitable; they respond to a stimulus. They are contractile, meaning they
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
Chapter 10 -Muscle Tissue Muscles: 1. Overview of Muscle Tissue A. Review 5 functions of muscle tissue. B. Review the 5 properties of muscle tissue. WHICH do they share with nervous tissue? (2, plus the
SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS
 THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
THE MUSCULAR SYSTEM SKELETAL MUSCLE CHARACTERISTICS Most are attached by tendons to bones Cells are multinucleate Striated have visible banding Voluntary subject to conscious control Cells are surrounded
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Chapter 10 Muscle Tissue Lecture Outline Muscle tissue types 1. Skeletal muscle = voluntary striated 2. Cardiac muscle = involuntary striated 3. Smooth muscle = involuntary nonstriated Characteristics
Lecture Overview. CT Framework of the Body. Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11. Connective tissue framework of the body
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Muscle & Nervous Tissues Lecture 11 Lecture Overview Connective tissue framework of the body Introduction to muscle tissue Classification/characteristics
Lecture 9A. Muscle structure. Outline
 Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Lecture 9A Muscle structure Outline Smooth, skeletal, and cardiac muscle tissues Structure and function of skeletal muscle cells. Sarcomeres structure and contraction Actin-myosin interaction and sliding
Muscles and Animal Movement
 Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Muscles and Animal Movement Evolution of Muscle and Movement Animals are the only multicellular organisms that actively move. Movement is due to muscle cells (motor proteins) Muscle proteins have homologues
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology)
 Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
Ch 10: Skeletal Muscle Tissue (Myology) main objectives: Describe the distinguishing characteristics of the different muscle tissues Discuss the organization of skeletal muscle Explain the micro-anatomy
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.49 - MUSCLE SYSTEMS.
 !! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
!! www.clutchprep.com BIOLOGY - CLUTCH Muscle system organ system that includes skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle Muscle tissue capable of contracting through the interaction of actin and myosin proteins
Muscle. Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series
 Muscle Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 Muscle Introduction Contractivity is one
Muscle Undergraduate Graduate Histology Lecture Series Larry Johnson, Professor Veterinary Integrative Biosciences Texas A&M University College Station, TX 77843 Muscle Introduction Contractivity is one
CVS HISTOLOGY. Dr. Nabil Khouri.
 CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
CVS HISTOLOGY Dr. Nabil Khouri http://anatomy.kmu.edu.tw/blockhis/block3/slides/block4_24.html The Heart Wall Contract as a single unit Cardiac Muscle Simultaneous contraction due to depolarizing at the
Structure of the striated muscle general properties
 Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Structure of the striated muscle general properties Structure of the striated muscle membrane systems 1. Myofibrillum (contractile proteins) 2. Sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) longitudinal tubule 3. SR terminal
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions. Packet #8
 Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Muscle Cells & Muscle Fiber Contractions Packet #8 Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for movement. Introduction Introduction II Skeletal muscle is composed of bundles of muscle fibers
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 5/11/2017 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle
 Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Skeletal Muscle Skeletal Muscle Types of muscle Skeletal muscle-moves the skeleton by pulling on the tendons that are connected to the bones Cardiac muscle-pumps blood through the heart and blood vessels
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle Physiological Anatomy of Skeletal Muscle
 Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Ch. 6: Contraction of Skeletal Muscle 40% skeletal muscle + 10% smooth and cardiac muscle Ch. 7: Excitation of Skeletal Muscle Ch. 9: Contraction and Excitation of Smooth Muscle Physiological Anatomy of
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue. Copyright 2009, John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
 Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch.10 Muscle Tissue Preview Chapter 10 In groups we will define the following terms 1. Skeletal muscle 2. Smooth muscle 3. Cardiac muscle 4. Sarcomere 5. Myofibril 6. Myofilament 7. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle cells have unique characteristics which allow for body movement.
 Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Anatomy Review: Skeletal Muscle Tissue Graphics are used with permission of: adam.com (http://www.adam.com/) Benjamin Cummings Publishing Co (http://www.awl.com/bc) Page 1. Introduction Skeletal muscle
Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue
 Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue Muscle is one of the 4 primary types of tissue. It is subdivided into skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. I. Skeletal Muscle Tissue and the Muscular System, p. 284 Objective
Chapter 10: Muscle Tissue Muscle is one of the 4 primary types of tissue. It is subdivided into skeletal, cardiac and smooth muscle. I. Skeletal Muscle Tissue and the Muscular System, p. 284 Objective
PRACTICAL ROADMAP. MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy
 PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
PRACTICAL ROADMAP MUSCLE WJ van der Spuy MUSCLE Skeletal (striated) Cardiac (striated) Smooth Identification based on Fiber size, shape and presence/absence of branching Number, shape and position of nuclei
Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1)
 Cytoskeleton Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1) Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 4) 5.3 Eukaryotic Cells Contain Organelles Cytoskeleton: Supports and maintains cell shape Holds organelles in position
Cytoskeleton Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 1) Figure 5.7 Eukaryotic Cells (Part 4) 5.3 Eukaryotic Cells Contain Organelles Cytoskeleton: Supports and maintains cell shape Holds organelles in position
Muscle. Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College
 Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
Muscle Dr. Carmen E. Rexach Anatomy 35 Mt San Antonio College Functions Movements of bones and soft body parts Movements of fluids through a tube (blood, digestive) Functions Maintain posture Support soft
#1 20. physiology. Muscle tissue 30/9/2015. Ahmad Adel Sallal. Mohammad Qudah
 # 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
# 20 physiology Muscle tissue Ahmad Adel Sallal 30/9/205 Mohammad Qudah MUSCLES PHYSIOLOGY Awn, welcome to the first physiology lecture in the MSS, I wish you a perfect exams with high grades, and never
Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure
 Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
Mechanism of contraction of Skeletal muscle in the light of its structure By Dr. Mudassar Ali Roomi (MBBS, M. Phil) Muscle Tissue Skeletal Muscle Cardiac Muscle Smooth Muscle Skeletal Muscle Long cylindrical
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP
 The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
The Nervous and Muscular Systems and the role of ATP Overview of the Nervous System General parts: The brain The spinal cord The nerves and sense organs General functions: controls and coordinates body
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh
 Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Histology Final Exam Done by:maha AbuAjamieh 1) Which of the following is the least valuable when distinguishing between bone and hyaline cartilage?? A- lacunae B-canaliculi C-lamella D-cell nest E- harversian
Lab Animal Tissue. LEARNING OBJECTIVES: To understand the relationship between the structure and function of different animal tissues
 Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
Name: Bio A.P. PURPOSE: HYPOTHESIS: NONE Lab Animal Tissue BACKGROUND: In animals, groups of closely related cells specialized to perform the same function are called tissues. There are four general classes
BIOH111. o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system
 BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
BIOH111 o Cell Module o Tissue Module o Integumentary system o Skeletal system o Muscle system o Nervous system o Endocrine system Endeavour College of Natural Health endeavour.edu.au 1 TEXTBOOK AND REQUIRED/RECOMMENDED
Muscle Tissue. C h a p t e r. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris
 C h a p t e r 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An Introduction
C h a p t e r 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College - North Harris Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings An Introduction
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology. The Muscular System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology The Muscular System The Muscular System Muscles are responsible for all types of body movement they contract or shorten and are the machine of the body Three basic
Chapter Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function
 Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Chapter 10.2 Skeletal Muscle Structure and Function Introduction to Muscle Physiology Movement is a fundamental characteristic of all living things All muscle cells (skeletal, cardiac, and smooth) are
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Skeletal Muscle Contraction 4/11/2018 Dr. Hiwa Shafiq Skeletal Muscle Fiber About 40 per cent of the body is skeletal muscle, and 10 per cent is smooth and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscles are composed
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function
 Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Chapter 8: Skeletal Muscle: Structure and Function Objectives Draw & label the microstructure of skeletal muscle Outline the steps leading to muscle shortening Define the concentric and isometric Discuss:
Muscle Tissue. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres. Lone Star College North Harris Pearson Education, Inc.
 10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 10-1 An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Learning Outcomes 10-1 Specify the functions of skeletal
10 Muscle Tissue PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 10-1 An Introduction to Muscle Tissue Learning Outcomes 10-1 Specify the functions of skeletal
Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types.
 1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
1 Since we ll be studying muscular and nervous tissue extensively later on in the year, this is just a brief overview of these two tissue types. Muscular tissue is unique because it is the only tissue
FROM MOVEMENT to meat production, the muscular
 Structures and Functions of the Muscular System FROM MOVEMENT to meat production, the muscular system provides benefits to animals and producers. Like other body systems, the muscular system is a fantastic
Structures and Functions of the Muscular System FROM MOVEMENT to meat production, the muscular system provides benefits to animals and producers. Like other body systems, the muscular system is a fantastic
Muscle Tissue- 3 Types
 AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
AN INTRODUCTION TO MUSCLE TISSUE Muscle Tissue- 3 Types Skeletal muscle (focus on these) Cardiac muscle Smooth muscle FUNCTIONS OF SKELETAL MUSCLES Produce movement of the skeleton Maintain posture and
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function
 Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
Concept 50.5: The physical interaction of protein filaments is required for muscle function Muscle activity is a response to input from the nervous system The action of a muscle is always to contract Vertebrate
MUSCULAR TISSUE. Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
MUSCULAR TISSUE Dr. Gary Mumaugh MUSCLE OVERVIEW The three types of muscle tissue are skeletal, cardiac, and smooth These types differ in structure, location, function, and means of activation FUNCTIONAL
Muscle Tissue. Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells. Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy
 Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Know these muscles Muscle Tissue Alternating contraction and relaxation of cells Chemical energy changed into mechanical energy 3 Types of Muscle Tissue Skeletal muscle attaches to bone, skin or fascia
Myology. Types of muscle: There are 3 types of muscle in the body 1-Skeletal muscle:the skeletal muscle characterized by
 Myology Myology: Is the science deal with study of the description of muscles in the body including tendon, apenurosis, and accessory structures like fascia, s y n o v i a l b u r s a, a n d s y n o v
Myology Myology: Is the science deal with study of the description of muscles in the body including tendon, apenurosis, and accessory structures like fascia, s y n o v i a l b u r s a, a n d s y n o v
Muscle Physiology. Introduction. Four Characteristics of Muscle tissue. Skeletal Muscle
 Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscle Physiology Introduction Muscle = tissue capable of forceful shortening or contraction Converts chemical energy (ATP) into mechanical energy Important in: Respiration Urine collection & flow Gastrointestinal
Muscular system MOVE ME!
 Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
Muscular system MOVE ME! MUSCLES Day 1 Nov 13 and 16 TYPES OF MUSCLES, STRUCTURE AND FUNCTIONS. FUNCTIONS of MUSCLE Movement Maintains posture Stabilize joints Generates heat Byproduct of muscular contraction
1/4/2017. Introduction. Connective Tissue Coverings. 9.1: Structure of a Skeletal Muscle. Skeletal Muscle Fibers. Connective Tissue Coverings
 Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Introduction Chapter 09 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Cardiac Muscle Tissue. Cardiac Muscle Tissue
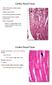 Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Walls of the heart (cardia: heart); myocardium. Cardiac muscle fibers not as densely packed as skeletal cardiac muscle tissue is highly vascularized Other components; dense C.T. septa, larger blood vessels,
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand
 Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and ATP Demand Anatomy & Structure Contraction Cycling Calcium Regulation Types of Contractions Force, Power, and Contraction Velocity Epimysium - separates fascia and muscle
THE CHROMAFFIN GRANULE SURFACE: THE PRESENCE OF ACTIN AND THE NATURE OF ITS INTERACTION WITH THE MEMBRANE Isolation and granule
 Volume 101. number I FEBS LETTERS May 1979 THE CHROMAFFIN GRANULE SURFACE: THE PRESENCE OF ACTIN AND THE NATURE OF ITS INTERACTION WITH THE MEMBRANE David I. MEYER* and Max M. BURGER Department of Biochemistry,
Volume 101. number I FEBS LETTERS May 1979 THE CHROMAFFIN GRANULE SURFACE: THE PRESENCE OF ACTIN AND THE NATURE OF ITS INTERACTION WITH THE MEMBRANE David I. MEYER* and Max M. BURGER Department of Biochemistry,
Chapter 50. You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium. Chemoreception taste and smell
 1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
1 Sensory and Motor Mechanisms 2 Chapter 50 You re on your own for: Sensory Reception Mechanoreceptors Gravity, Hearing and Equilibrium Chemoreception taste and smell Photoreceptors vision It s interesting.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues. V. Muscle Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues V. Muscle Tissues Nomenclature Sarcolemma = plasma membrane Sarcoplasmic reticulum = endoplasmic reticulum Muscle fiber = cell Myofibril = subcellular fibers
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues V. Muscle Tissues Nomenclature Sarcolemma = plasma membrane Sarcoplasmic reticulum = endoplasmic reticulum Muscle fiber = cell Myofibril = subcellular fibers
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY
 MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
MODULE 6 MUSCLE PHYSIOLOGY III SEMESTER BOTANY Syllabi: Striated, Non striated and Cardiac muscle, Ultra structure of striated muscle fibre, Mechanism of muscle contraction, Threshold and spike potential,
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle
 Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Session 3-Part 2: Skeletal Muscle Course: Introduction to Exercise Science-Level 2 (Exercise Physiology) Presentation Created by Ken Baldwin, M.ED, ACSM-H/FI Copyright EFS Inc. All Rights Reserved. Skeletal
Ultrastructural Localization of Calsequestrin in Rat Skeletal Muscle by Immunoferritin Labeling of Ultrathin Frozen Sections
 Ultrastructural Localization of Calsequestrin in Rat Skeletal Muscle by Immunoferritin Labeling of Ultrathin Frozen Sections A. O. JORGENSEN, A. C.-Y. SHEN, K. P. CAMPBELL,* and D. H. MAcLENNAN* Department
Ultrastructural Localization of Calsequestrin in Rat Skeletal Muscle by Immunoferritin Labeling of Ultrathin Frozen Sections A. O. JORGENSEN, A. C.-Y. SHEN, K. P. CAMPBELL,* and D. H. MAcLENNAN* Department
OF LIGHT CHAINS OF CARDIAC MYOSIN ISOZYMES: ATRIAL AND VENTRICULAR MYOSINS
 CROSS-HYBRIDIZATION OF LIGHT CHAINS OF CARDIAC MYOSIN ISOZYMES: ATRIAL AND VENTRICULAR MYOSINS Gabor HOLLGSI*, Sudhir SRIVASTAVA** and Joan WIKMAN-COFFELT University of California, San Francisco Cardiovascular
CROSS-HYBRIDIZATION OF LIGHT CHAINS OF CARDIAC MYOSIN ISOZYMES: ATRIAL AND VENTRICULAR MYOSINS Gabor HOLLGSI*, Sudhir SRIVASTAVA** and Joan WIKMAN-COFFELT University of California, San Francisco Cardiovascular
Human Anatomy. Muscle Tissue and Organization. DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1
 Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
Human Anatomy Muscle Tissue and Organization DR.SADIQ ALI (K.E Medalist) 10-1 Tissue and Organization Over 700 skeletal muscles have been named. Form the muscular system. Muscle tissue is distributed almost
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit
 LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
LDL Uptake Cell-Based Assay Kit Catalog Number KA1327 100 assays Version: 07 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Background... 3 Principle of the Assay...
Sarcolemmal Organization in Skeletal Muscle Lacking Desmin: Evidence for Cytokeratins Associated with the Membrane Skeleton at Costameres
 Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 13, 2347 2359, July 2002 Sarcolemmal Organization in Skeletal Muscle Lacking Desmin: Evidence for Cytokeratins Associated with the Membrane Skeleton at Costameres Andrea
Molecular Biology of the Cell Vol. 13, 2347 2359, July 2002 Sarcolemmal Organization in Skeletal Muscle Lacking Desmin: Evidence for Cytokeratins Associated with the Membrane Skeleton at Costameres Andrea
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law).
 The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
The All-or-None Principle Motor units also comply to a rule known as the all-ornone principle (or law). This principle stipulates that, when a motor unit is stimulated to contract, it will do so to its
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition. Mrs. Hummer. Chapter 9 Muscular System
 Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
Hole s Human Anatomy and Physiology Eleventh Edition Mrs. Hummer Chapter 9 Muscular System 1 Chapter 9 Muscular System Skeletal Muscle usually attached to bones under conscious control striated Three Types
About This Chapter. Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Pearson Education, Inc.
 About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
About This Chapter Skeletal muscle Mechanics of body movement Smooth muscle Cardiac muscle Skeletal Muscle Usually attached to bones by tendons Origin: closest to the trunk or to more stationary bone Insertion:
Ch 12 can be done in one lecture
 Ch 12 can be done in one lecture Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Chapter 12: Muscles Review muscle anatomy (esp. microanatomy of skeletal muscle) Terminology: sarcolemma t-tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum
Ch 12 can be done in one lecture Developed by John Gallagher, MS, DVM Chapter 12: Muscles Review muscle anatomy (esp. microanatomy of skeletal muscle) Terminology: sarcolemma t-tubules sarcoplasmic reticulum
Muscular System. This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions:
 Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular System Slide 2 This chapter will focus on muscle cells and tissues. Muscle tissue has several functions: Movement: Muscles work as pulleys on bones to help create changes in body position. Muscles
Muscular Tissue. Functions of Muscular Tissue. Types of Muscular Tissue. Skeletal Muscular Tissue. Properties of Muscular Tissue
 Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
Muscular Tissue Functions of Muscular Tissue Muscle makes up a large percentage of the body s weight (40-50%) Their main functions are to: Create motion muscles work with nerves, bones, and joints to produce
The Sliding Filament Theory
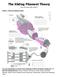 The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
The Sliding Filament Theory Model 1: Muscle Histology Review How do muscle cells contract? Use your knowledge of muscle tissue histology to fill in the blanks numbered 1-11 with the following terms: Fasicle,
