Urogenital System Objectives - see handout or website
|
|
|
- Harvey Black
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urogenital System Objectives - see handout or website
2 Urogenital System shared ducts due to evolutionary legacy and development Urinary or Excretory System blood filtration and excretion of salts and nitrogenous wastes osmoregulation hormonally mediated influence on blood pressure Reproductive System procreation (and recreation) hormonally mediated influence on other organ systems and behavior
3 Organs of the Excretory or Urinary System Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra External Genitalia
4 Kidneys Perirenal Fascia contains kidney and adrenal gland Perirenal Fat cushions kidney within location retroperitoneal on superior posterior abdominal wall both kidneys capped superiorly by suprarenal (= adrenal) gland anterior to quadratus lumborum muscle and lowermost ribs Right Kidney Superior margin 11 th intercostal space Superior and anterior suprarenal gland and liver Anterior inferiorly colon Medial duodenum Left Kidney Superior margin 11 th rib Superior suprarenal gland and respiratory diaphragm Anterior stomach (superior to hilum), pancreas (at hilum), jejunum (inferior to hilum) Anterior/left spleen
5
6 Kidneys Renal Capsule Hilum medial surface entrance of renal artery, exit of renal vein and ureter, from which the kidney is more or less suspended Cortex granular appearance Medulla striped appearance Renal Pyramids Renal Pelvis
7 Nephron microscopic functional unit of the kidney Cardiovascular component ultrafiltration Afferent Arteriole (most in cortex) Glomerulus (most in cortex) Efferent Arteriole (most in cortex) Peritubular Capillaries or Vasa Rectae (in medulla) Collecting duct component countercurrent multiplier (continued)
8 Collecting Duct Components of the Nephron Glomerular or Bowman s Capsule (cortex) envelops glomerulus Proximal Convoluted Tubule (most in cortex) Loop of Henle (in medulla) Distal Convoluted Tubule (most in cortex) Collecting system uniting multiple Nephrons Collecting Tubule Renal Papilla Minor Calyx (pl. calyces) Major Calyx (pl. calyces) Renal Pelvis most proximal part of ureter
9 Juxtaglomerular Apparatus self-regulation of kidney compares blood pressure in Afferent and Efferent Arterioles measures osmolarity of Distal Convoluted Tubules Renin stimulates conversion of angiotensinogen Angiotensin I (angiotensinogen secreted by liver into blood) Angiotensin I Angiotensin II (= Vasopressin or Antidiuretic Hormone) in lungs increases blood pressure by vasoconstriction increases water and salt resorption by kidney antidiuretic
10 Ureters conduct urine from kidneys to urinary bladder thin walled smooth muscle retroperitoneal on posterior abdominal wall enter urinary bladder posterolaterally open within trigone of urinary bladder on posterior wall
11 Urinary Bladder storage organ Diuresis = Micturition = Urination = Voiding location posterior to pubic symphysis in pelvic cavity Females anterior to vagina, inferior to uterus (posteriorly) Males anterior to rectum, superior to prostate gland Rectovesical pouch - males Vesicouterine pouch - females
12 Urinary Bladder layers transitional epithelium smooth muscle detrussor muscle adventitia and peritoneum parts and surfaces: Roof Inferolateral walls Base Apex Urachus extends from apex within median umbilical ligament occluded vestige of allantois ending at umbilicus Urachal Fistula (pathology) Trigone triangular area of smooth epithelium of inferior base located between openings of ureters and urethra
13 Urethra expels urine passes through urogenital diaphragm Divisions: Female Male - Prostatic within Prostate Gland Membranous Membranous passes through Urogenital Diaphragm - Spongy or Penile within Corpus Spongiosum of penis
14 External Genitalia Male Penis Glans Prepuce Body Scrotum Female Labia Majora (s. Labium Majus) Labia Minora (s. Labium Minus) Clitoris Vestibule of the Vagina
15 Fetal Differentiation of the External Genitalia Undifferentiated Male Female Genital Tubercle Glans Penis of the Clitoris Corpus Spongiosum Urogenital Sinus lumen of the Spongy Vestibule Urethra Urogenital Folds Spongy Urethra Labia Minora Labioscrotal Folds Scrotum Labia Majora
16
17
18 Male Reproductive System Testes sexual ducts glands erectile tissues Penis Scrotum contents: receives Spermatic Cord Tunica Vaginalis Testes Epididymis Gubernaculum
19 Testes internal architecture: Capsule or Tunica Albigunea Septa Seminiferous tubules Interstitial cells Sertoli cells supportive Leydig cells secrete testosterone Spermatogonia reproduce by mitosis throughout life Rete Testis Efferent Ductules or Vasa Efferentia Spermatogenesis two meiotic cell divisions producing gametes Primary Spermatocytes Secondary Spermatocytes Spermatids Spermiogenesis morphological maturation of gametes Spermatids Spermatozoans
20 Male Sexual ducts Epididymis head, body, tail within Tunica Vaginalis of Scrotum Vas (or Ductus) Deferens path: 1) begins within Tunica Vaginalis of Scrotum 2) Spermatic Cord parts and contents: Dartos muscle Cremaster muscle Pampiniform Plexus of Testicular vein Testicular Artery and Vas Deferens 3) Inguinal Canal 4) crosses roof and base of urinary bladder medial to ureters and Seminal Vesicles (continued)
21 Male Sexual ducts Ejaculatory Ducts union of Vas Deferens and Seminal Vesicles Prostatic Urethra Prostatic Utricle openings of Ejaculatory Ducts Spongy or Penile Urethra Intrabulbar Fossa (more on this later) Navicular Fossa
22 Semen vs sperm Male Sexual Glands 1) Seminal Vesicles paired on base of Urinary Bladder lateral to Vas Deferens join Vas Deferens to form Ejaculatory Ducts 2) Prostate unpaired surrounds Prostatic Urethra inferior to Urinary Bladder anterior to Rectum superior to Urogenital Diaphragm (continued)
23 Male Sexual Glands (continued) 3) Bulbourethral or Cowper s Glands paired within Bulb of Penis open to Intrabulbar Fossa homologous to Greater Vestibular glands of female 4) Intrinsic Glands of the Spongy Urethra pre-ejaculatory secretions
24 Male Erectile tissues 1) Corpus Spongiosum unpaired parts: Bulb of Penis, including: Intrabulbar Fossa widening of urethra Bulbospongiosus muscle responsible for ejaculation Bulbourethral Glands Spongy Urethra Glans Penis 2) Corpora Cavernosa (sing. Corpus Cavernosum) paired forms Body of Penis Crura buttressed by Inferior Rami of Pubes
25
26
27 Female Reproductive System Ovaries sexual ducts Oviducts or Fallopian Tubes Uterus Vagina mesenteries external genitalia erectile tissues glands
28 Ovaries paired intraperitoneal suspended from posterolateral abdominal wall walnut-size internal architecture: Stroma Follicles Follicular or Granulosa cells Oocytes at birth non-replicating Oogenesis Oogonia reproduce mitotically before birth Primary Oocytes: Oogenesis arrested in Prophase of first meiotic division until puberty or even much later in life Secondary Oocytes: develop within maturing follicle prior to ovulation; second meiotic division arrested in Metaphase completion of meiosis II stimulated by fertilization
29 Female Sexual ducts 1) Oviducts or Fallopian Tubes paired intraperitoneal divisions, listed from proximal to distal: a) Ostium opening to peritoneal cavity, facing medially toward ovary b) Fimbria finger like margins of Ostium c) Infundibulum normal site of fertilization ~ 10 days for embryo to move to and implant in Uterus Ectopic Pregnancy d) Ampulla widening e) Isthmus narrowing proximal to Uterus 2) Uterus 3) Vagina
30
31
32 Uterus unpaired (normally) located in Pelvic Cavity superior to Vagina and posterior of Urinary Bladder anterior to Rectum intraperitoneal
33 Layers of Uterus listed from luminal to superficial: 1) Endometrium - mucosa epithelium connective tissue, supporting: arteries Spiral Glands 2) Myometrium - smooth muscle stimulated by oxytocin (secreted by Neurohypophysis or Posterior Pituitary) 3) Peritoneum
34 Parts of Uterus Fundus Body Cervix Ostium External Os Internal Os Cervical Plug
35 Vagina unpaired located in Pelvic Cavity posterior to Urinary Bladder anterior to Rectum inferior to Uterus superior to Urogenital Diaphragm opening to Vestibule posterior to Urethra
36 Layers of Vagina from luminal to superficial: 1) Mucosa stratified squamous epithelium, lightly keratinized or cornified intrinsic glands? 2) Muscularis smooth muscle voluntary Bulbospongiosus muscle inferiorly 3) Adventitia
37 Mesenteries of the Female Reproductive system Suspensory ligament of Ovaries Broad ligament of Uterus Mesovarium between Epöophoron and Ovary Mesosalpinx between Epöophoron and Oviduct female homologs of the Gubernaculum (continued)
38 Female homologs of the Gubernaculum Ovarian Ligament homolog of proximal Gubernaculum location from Ovary to Uterus within Broad Ligament Round ligament or Ligamentum Teres homolog of distal Gubernaculum, i.e., distal to Uterus Location: within Broad Ligament in peritoneal cavity passes through Inguinal Canal terminates in Labium Majus
39 Erectile tissues and glands of the Female Reproductive System Lesser Vestibular (= Skene s or Paraurethral) Glands located in anterior Vestibule lateral to urethtral orifice Greater Vestibular or Bartholin s glands located in posterior Vestibule posterolateral to vagina Clitoris Glans Clitoris anterior to Vestibule Crura paired, buttressed by Inferior Ramus of Pubes lateral to Vestibule
40 Menstrual Cycle Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) gonadotropin secreted by Adenohypophysis stimulates maturation of follicle Primordial Follicle Secondary Follicle Mature (= Graafian) Follicle Secondary Follicle, includes: Antrum Cumulus Oophorus vs Parietal Follicular cells Estrogen Follicular Fluid of Antrum produced by Follicular cells stimulates Proliferative Phase hypertrophy of Endometrium, its arteries and spiral glands (continued)
41 Menstrual Cycle Luteinizing Hormone (LH) gonadotropin secreted by Adenohyphysis pulse together with FSH stimulates Ovulation rupture of oocyte with Corona Radiata (Cumulus Oophorus) from ovary into Peritoneal cavity Parietal Follicular cells Corpus Luteum secrete Progesterone stimulates Secretory Phase maintenance of hypertrophied endometrium for implantation cessation of progesterone production results in: Ischemic Phase atrophy of endometrium, followed by: Menstrual Phase sloughing of endometrium Corpus Luteum Corpus Albicans scar tissue Chorionic Gonadotropin produced by embryo, if present maintains Corpus Luteum (hence, Progesterone and Secretory Phase)
42 Embryonic and Fetal Development Key Terms Extraembryonic Membranes membranes that are derived from the zygote and surround and support the developing embryo but are not part of the embryo 1) Amnion membrane that encloses developing embryo in amniotic cavity and fluid 2) Chorion membrane that encloses extraembryonic coelom; interacts with endometrium of uterus to form embryonic contribution of placenta 3) Chorioamniotic membrane fusion of the two above in later development Connecting Stalk tissue uniting developing embryo with extraembryonic membranes and maternal tissue; as embryo enlarges as fetus the connecting stalk will be recognized as the umbilical cord Yolk Sac a cavity, continuous with primitive gut; contained within connecting stalk Allantois a cavity, outgrowth of primitive gut; grows into connecting stalk carrying with it umbilical arteries and vein; unites with chorion to form embryonic contribution of placenta
43
44
45
46 Fetal Development More Key Terms Decidua Basalis portion of endometrium that lines the uterine wall and that interacts with chorion basalis to form maternal contribution of placenta Decidua Parietalis portion of endometrium that lines the uterine wall and does not contribute to the placenta Decidua Capsularis portion of endometrium that overlies the chorion but does not contribute to the placenta Chorion Frondrosum portion of the chorion that interacts with the decidua basalis to form the embryonic contribution of the placenta Chorion Laeve portion of the chorion that does not contribute to the placenta
47
48
49
50 Early Embryonic Circulation
51 Abdominal Hernias Inguinal Direct most common form in men Indirect congenital birth defect Femoral most common form in women
52
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology
 Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Name Date Lab #9: Kidney: Gross Anatomy & Histology Lab #10: Male Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Lab #11: Female Reproductive System: Human Models & Histology Stuff to Know Dr. L. Bacha
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
The Reproductive System
 The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
The Reproductive System The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males Ovaries in females Gonads produce gametes (sex cells) and secrete hormones Sperm male gametes Ova (eggs) female
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception
 PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
PELVIS II: FUNCTION TABOOS (THE VISCERA) Defecation Urination Ejaculation Conception REVIEW OF PELVIS I Pelvic brim, inlet Pelvic outlet True pelvis-- --viscera Tilt forward Mid-sagital views-- --how the
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM 1. The male reproductive system is made up of the following structures, EXCEPT: a. prostate; b. testicle; c. spermatic ducts; d. vestibular bulbs; e. seminal vesicles. 2.The testicle:
Outline. Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation
 Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
Outline Male Reproductive System Testes and Sperm Hormonal Regulation Female Reproductive System Genital Tract Hormonal Levels Uterine Cycle Fertilization and Pregnancy Control of Reproduction Infertility
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY HOMEWORK CHAPTER 15 AND 16 Name Identify the following: 1) The ureter is indicated by letter 2) The renal pyramid is indicated by letter 3) The fibrous capsule is indicated by letter
Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature
 REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
REPRODUCTION Testes (male gonads) -Produce sperm -Produce sex hormones -Found in a sac called the scrotum -Suspended outside of the body cavity for temperature reduction -Testes wall made of fibrous connective
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Aniko Szabo Hill 1 of 12
 Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
Common Function: produce offsprings endocrine glands: sex hormone production Primary organs or gonads: sex cell or gametes production Secondary or accessory organs: glands nourish gametes ducts transport
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia. Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde
 The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
The Male and Female Internal Genitalia Dr Oluwadiya Kehinde www.oluwadiya.com Overview The reproductive role of the male is to produce sperm, deliver them to the female Primary sex organs are the gonads
Anatomy Lecture Notes Chapter 24
 primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
primary sex organs = gonads produce gametes secrete hormones that control reproduction secondary sex organs = accessory structures Development and Differentiation A. gonads develop from mesoderm starting
The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska
 27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
27 The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Lincoln, Nebraska Introduction The reproductive system is designed to perpetuate the species
The Urinary System Pearson Education, Inc.
 26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
26 The Urinary System Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion concentrations Regulates blood volume and blood pressure Stabilizes blood
Reproductive System. Where it all begins
 Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Reproductive System Where it all begins When it comes the reproductive anatomy of my gender, I would rate my knowledge (1 very poor, 10 excellent) When it comes the reproductive anatomy of the opposite
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
The Reproductive System
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II The Reproductive System References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapters
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide
 Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Unit 15 ~ Learning Guide Name: INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit
Lab Activity 33. Anatomy of the Reproductive System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 33 Anatomy of the Reproductive System Portland Community College BI 233 Scrotum Sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis Contains
Lab Activity 33 Anatomy of the Reproductive System Portland Community College BI 233 Scrotum Sac of skin and superficial fascia that hangs outside the abdominopelvic cavity at the root of the penis Contains
Lecture 28, The Reproductive System
 Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Fundamentals of Anatomy & Physiology Lecture 28, The Reproductive System SIXTH EDITION Frederic H. Martini Lecturer: Dr. Barjis Room: P313 Phone: (718) 260-5285 E-Mail: ibarjis@citytech.cuny.edu Copyright
Bio 104 Reproductive System
 63 Lecture Outline: Reproductive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 22, 23] I. Introduction A. Primary sex characteristics Male Female B. Secondary sex characteristics Male: 9 14 yrs. Reproductive development
63 Lecture Outline: Reproductive System Hole s HAP [Chapters 22, 23] I. Introduction A. Primary sex characteristics Male Female B. Secondary sex characteristics Male: 9 14 yrs. Reproductive development
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
SISTEMA REPRODUCTOR (LA IDEA FIJA) How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development,
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES
 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM OBJECTIVES OBJECTIVES: 1. List the organs and functions of the reproductive system. Female Organs Male Organs Functions 1 OVARIES 1 TESTES 1 Produce gametes 2 fallopian tubes 2 scrotum
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
REPRODUCCIÓN. La idea fija. Copyright 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
REPRODUCCIÓN La idea fija How male and female reproductive systems differentiate The reproductive organs and how they work How gametes are produced and fertilized Pregnancy, stages of development, birth
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 27.3 Using Figure 27.3, match the following: 1) The stage called ovulation. 2) Corpus
Cardiovascular Digestive. Endocrine Integumentary
 General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
General Anatomy Match the Components and Functions with their respective primary Anatomical System COMPONENTS / DESCRIPTION CODE Anatomical System Primary Function 1. Fallopian tubes and seminal vesicles
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction
 Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Chapter 46 ~ Animal Reproduction Overview Asexual (one parent) fission (parent separation) budding (corals) fragmentation & regeneration (inverts) parthenogenesis Sexual (fusion of haploid gametes) gametes
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida. Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System
 Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Biology 224 Human Anatomy and Physiology II Week 9; Lecture 2; Wednesday Stuart Sumida Development and Structure, of the Reproductive System Don t forget the relationships of the structures of the layers
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems 3. Male Reproductive anatomy and physiology. Testes = paired
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System
 Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
Bio 322 Human Anatomy Objectives for the laboratory exercise Female Reproductive System Required reading before beginning this lab: Saladin, KS: Human Anatomy 5 th ed (2017) Chapter 26 For this lab you
LESSON ASSIGNMENT. After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 8 The Human Urogenital Systems. TEXT ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 8-1 through 8-16. LESSON OBJECTIVES After completing this lesson, you should be able to: 8-1. Define urogenital systems.
Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems
 CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
CH. 15 - REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Objectives: 1. Review male & female reproductive anatomy 2. Gametogenesis & steroidogenesis 3. Reproductive problems Review of Male Reproductive Anatomy Fig 15.9 Vas deferens
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
Essentials of Anatomy & Physiology, 4th Edition Martini / Bartholomew The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Outlines prepared by Alan Magid, Duke University Slides 1 to 84 Overview of Reproduction
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Essential question What are the structures of the reproductive system? 2 Structures of the
Sperm production. Sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production Ductus deferens Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Sperm production. Sperm production. Controlling sperm production. Meiosis. Mitosis. The cells of Leydig in testes secrete
 Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Ductus deferens Sperm production Epididymis The cells of Leydig in testes secrete Seminiferous testosterone (T) tubules T secreted at puberty produces 2 o sex characteristics, spermatogenesis, & maintain
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O.
 UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES, ONDO DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY REPRODUCTION LECTURER: MR. AKINOLA A.O. OBJECTIVES Introduction Functional anatomy of male sex organ Functional anatomy of female sex organ
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
a. the tail disappears b. they become spermatids c. they undergo capacitation d. they have been stored in the uterus for several days
 (2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
(2 points each) Multiple Choice. Read each question thoroughly before answering. From the choices available, choose the answer that is the most correct. Place all answers on the accompanying answer sheet.
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male=s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Indifferent ducts of embryo Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Phenotypic sex is depends on development of external
Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor)
 Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
Indifferent ducts of embryo Y chromosome present Y chromosome absent Male Female penis ovary uterus vagina testis Biology of gender Sex chromosomes determine gonadal sex (testis-determining factor) Phenotypic
cord: a) Ductus deferens b) Dartos muscle c) Testicle d) Epididymis e) Bulbourethreal gland
 Which of the following is found in the spermatic cord: a) Ductus deferens b) Dartos muscle c) Testicle d) Epididymis e) Bulbourethreal gland a) ductus deferns What structure is superior to the urogenital
Which of the following is found in the spermatic cord: a) Ductus deferens b) Dartos muscle c) Testicle d) Epididymis e) Bulbourethreal gland a) ductus deferns What structure is superior to the urogenital
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system
 4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
4.05 Remember the structures of the reproductive system Scrub In The external area between the vulva and the anus is the : a. Cervix b. Endometrium c. Perineum d. Vagina What structure connects the testes
Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
Biology 12 Human Biology Textbook: BC Biology 12 Study Guide Answer Key Reproductive System 1. Distinguish between a gamete and a gonad using specific examples from the male and female systems. Gonads
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
Chapter 14 The Reproductive System
 Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
Biology 12 Name: Reproductive System Per: Date: Chapter 14 The Reproductive System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 436-467 14. 1 Male Reproductive System pages 440-443 1. Distinguish between gametes
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins? A) LH
Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport
 Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport (epididymis, ductus deferens(vas deferens), ejaculatory
Male Reproductive System I. Overview A. gonads organs producing sex cells (gametes) = B. support for gonads = C. ducts for storage and transport (epididymis, ductus deferens(vas deferens), ejaculatory
AP Biology Ch ANIMAL REPRODUCTION. Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below.
 AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
AP Biology Ch. 46 - ANIMAL REPRODUCTION Using only what you already know (you cannot look up anything) complete the chart below. I. Overview of Animal Reproduction A. Both asexual and sexual reproduction
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I)
 Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Chapter 22 The Reproductive System (I) An Overview of Reproductive Physiology o The Male Reproductive System o The Female Reproductive System 22.1 Reproductive System Overview Reproductive system = all
Female Reproductive System
 21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
21 Female Reproductive System I. Introduction to the Female Reproductive System Concept: The female reproductive system produces ova, secretes sex hormones, receives spermatozoa from the male, and provides
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
Human Anatomy Unit 3 URINARY SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Components Kidneys Ureters Urinary bladder Urethra Functions Storage of urine Bladder stores up to 1 L of urine Excretion of urine Transport of urine
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
Chapter 2. Reproductive system matures and becomes capable of reproduction
 Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 2 Human Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology Key Terms Embryo Menarche Menopause Oxytocin Ovum Prostate gland Puberty Smegma zygote Puberty Involves changes in the whole body and psyche Reproductive
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
 MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
MOCK TEST I (HUMAN REPRODUCTION) 1. In human transfer of sperms into female genital tract is called as 1) Fertilization 2) Implantation 3) Insemination 4) Gestation 2. In male human scrotum maintains the
2. Which of the following factors does not contribute to ion selectivity?
 General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
General Biology Summer 2014 Exam II Sample Answers 1. Which of the following is TRUE about a neuron at rest? A. The cytosol is positive relative to the outside B. Na+ concentrations are higher inside C.
Urinary System VASTACCESS, INC.
 Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
Urinary System www.vastaccess.com 2 Urinary Tract Kidney Ureter Urinary Bladder Urethra Prostate (male) Membranous (male) Spongy (male) 3 Kidney Relations Suprarenal (Adrenal) Glands Liver Duodenum Transverse
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
The Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system Testes Genital ducts Accessory sex glands: seminal vesicles prostate bulbourethral glands External genitalia: penis Structure of the Testis Tunica
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment
 Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
Date: Mark: _/45 Chapter 14 Reproduction Review Assignment Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Use the diagram above to answer the next question.
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive system
 Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Health Science: the structures & functions of the reproductive BELLWORK 1. List (4) careers that are r/t the Reproductive, Urinary, and Endocrine Systems 2. Copy down the following terms: -ologist = one
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY
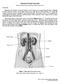 URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
URINARY SYSTEM ANATOMY Adapted from Human Anatomy & Physiology Marieb and Hoehn (9 th ed.) OVERVIEW Metabolism of nutrients by the body produces wastes that must be removed from the body. Although excretory
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2
 Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Biology of Reproduction- Zool 346 Exam 2 ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER. Some critical words are boldfaced. This exam is 7 pages long.
Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester
 Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
Laboratory 9 Cat Dissection II Respiratory Urinary/Reproductive Systems Lab Schedule for Rest of Semester Cat dissection labs Dissection II (today) Respiratory (Ex. 57 in Hole) Human Reproductive Systems
under its influence, male development occurs; in its absence, female development is established.
 Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Sex differentiation is a complex process that involves many genes, including some that are autosomal. The key to sexual dimorphism is the Y chromosome, which contains the testis determining gene called
Refer to the figure below, a diagram of a renal tubule, to answer the following questions.
 1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
1. The digestion and utilization of which nutrient creates the greatest need for osmoregulation by the kidneys? a. protein b. starch c. fat d. oil e. cellulose 2. Which of the following is true of urea?
Copyright 2003 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings. Dr. Nabil Khouri
 Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
Dr. Nabil Khouri Objectives: General objectives: - to identify the kidney s structures, function and location - to analyze the relationship between microscopic structure and function Specific objectives:
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 28 The Reproductive System Organs include: testes, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 28 The Reproductive System Organs include: testes, ductus deferens, epididymis, ejaculatory ducts, urethra, seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral
Reproductive Endocrinology. Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007
 Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
Reproductive Endocrinology Isabel Hwang Department of Physiology Faculty of Medicine University of Hong Kong Hong Kong May2007 isabelss@hkucc.hku.hk A 3-hormone chain of command controls reproduction with
BIOLOGY. Animal Reproduction CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 46 Animal Reproduction Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick 1. Asexual vs Sexual Reproduction Both
Female Reproductive System
 Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
Female Reproductive System (Part A-1) Module 10 -Chapter 12 Overview Female reproductive organs Ovaries Fallopian tubes Uterus and vagina Mammary glands Menstrual cycle Pregnancy Labor and childbirth Menopause
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5)
 IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
IB 140 Midterm #1 PRACTICE EXAM (lecture topics 1-5) For all the questions on this exam, the correct answer is the single best answer that is available in the answer key. 1) Which of the following is NOT
Chapter 26. The Urinary System. Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Chapter 26 The Urinary System Lecture Presentation by Steven Bassett Southeast Community College Introduction The urinary system does more than just get rid of liquid waste. It also: Regulates plasma ion
Development of the urogenital system
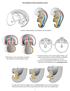 Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
Development of the urogenital system Location of the pronephros, mesonephros and metanephros Differentiation of the intermedierm mesoderm into nephrotome and mesonephric tubules Connection between aorta
The beginning of puberty is marked by the progressive increase in the production of sex hormones.
 Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Puberty is characterized by the changes that prepare the human body for the ability to reproduce. This stage generally occurs between the ages of 10 and 14 years old. The beginning of puberty is marked
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction
 Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Grade 9 Science - Human Reproduction The human reproductive system is a series of organs that work together for one purpose: reproduction (creating new humans). Each part has a specific role in the reproductive
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326
 Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Biology of Reproduction-Biol 326 READ ALL INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY. ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS ON THE ANSWER SHEET. THE ANSWER ON THE ANSWER SHEET IS YOUR OFFICIAL ANSWER REGARDLESS OF WHAT YOU MARK ON THE
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock)
 Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
Human Sexuality - Ch. 2 Sexual Anatomy (Hock) penis penile glans corona frenulum penile shaft erection foreskin circumcision corpora cavernosa corpus spongiosum urethra scrotum spermatic cords testicles
1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as:
 3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
3 rd Test Sp 09 3:30 1. When substances move from the nephron to the peritubular capillaries. This is known as: a. secretion b. excretion c. reabsorption d. filtration 2. The nephron is located in the:
6.7 IN. Continuity through Reproduction. What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes.
 6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
6.7 IN What are the differences between male and female gametes? Discuss their formation and physical attributes. Males - 4 sperm per parent cell; Females - 1 ovum per parent cell Sperm - motile (tail);
URINARY SYSTEM. These organs lie posterior or inferior to the. (membrane).
 URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
URINARY SYSTEM I. INTRODUCTION Each kidney is made up of about a million tiny tubules called nephrons. Each nephron individually filters the blood and makes urine and it does the job completely, from start
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
Reproductive Systems. BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues. Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 17 Reproductive Systems Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Unit 7B STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the female reproductive tract. 2. Learn the functions of the female reproductive tract. 3.
Fig Chapter 46. Animal Reproduction
 Fig. 46-1 Chapter 46 Animal Reproduction Overview: Pairing Up for Sexual Reproduction Each earthworm produces sperm and eggs; Aspects of animal form and function can be viewed broadly as adaptations contributing
Fig. 46-1 Chapter 46 Animal Reproduction Overview: Pairing Up for Sexual Reproduction Each earthworm produces sperm and eggs; Aspects of animal form and function can be viewed broadly as adaptations contributing
