Dissection of the Rat
|
|
|
- Loraine Bates
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Dissection of the Rat The classification of the Rat ( Rattus norvegicus ) Kingdom Animalia Phylum Chordata Subphylum Vertebrata Class Mammalia Order Rodentia Family Muridae Genus Rattus Species norvegicus The lab information and diagrams available to you are supplemental. You are expected to follow the directions in this lab. You will be held responsible for being able to locate all the structures. Using the available material, instructions and diagrams, most students will be able to locate many structures for themselves. If after an earnest effort, you cannot find a structure, ask for assistance. Remember, this is a learning experience, it is quite permissible to discuss and observe other students' specimens. Compare you dissection with others, for animals often differ. The specimen you will receive is a preserved double-injected specimen. Double injected refers to the arteries being filled with a red latex, and the veins being filled with blue latex. You will notice various incisions on the external surface of the rat where the latex was injected. The rat is a vertebrate, which means that many aspects of its structural organization are common with all other vertebrates, including man. The similarity of structures among related organisms shows evidence of common ancestry. In a way, studying the rat is like studying a human. As the leading theme of this lab, ask yourself: for every structure observed in the rat, there is an equivalent structure in your own body - what is the structure and where is it located. As the second leading theme, pay particular attention to the relationships among organs and groups of organs. Structural parts are not "just there" in random locations. Their specific layout within the body contributes to making certain functions possible. Therefore, for every structure seen, you should determine the following: What organ system it belongs to How it is connected with other components Its general function Its specific function (if applicable) Dissection Dissecting tools will be used to open the body cavity of the rat and observe the structures. Keep in mind that dissecting does not mean "to cut up"; in fact, it means "to expose to view". Careful dissecting techniques will be needed to observe all the structures and their connections to other structures. You will not need to use a scalpel. Contrary to popular belief, a scalpel is not the best tool for dissection. Scissors serve better because the point of the scissors can be pointed upwards to prevent damaging organs underneath. Always raise structures to be cut with your forceps before cutting, so that you can see exactly what is underneath and where the incision should be made. Never cut more than is necessary to expose a part.
2 Grading Your grade on this laboratory will be assessed according to the following criteria Class Participation (serious approach, proper cleanup and lab safety) Lab Checklist Quizzes throughout Lab Practical Exam (at the end of lab) Glossary of Terms Dorsal : toward the back Ventral : toward the belly Lateral : toward the sides Median : near the middle Anterior : toward the head Posterior : toward the hind end (tail) Deep : some distance below the surface Caudal : toward the tail end Pectoral : relating to the chest and shoulder region Pelvic : relating to the hip region Dermal : relating to the skin Longitudinal : lengthwise Right & Left : refers to the specimen's right and left, not yours Abdominal Cavity : related to the area below (posterior) the ribcage Thoracic Cavity : related to the area above (anterior) the ribcage Rat External Anatomy Procedure: Obtained your rat. Rinse it off with water and place it in your dissecting pan to observe the general characteristics. Make sure you know each of the highlighted words. The rat's body is divided into six anatomical regions: cranial region - head cervical region - neck pectoral region - area where front legs attach thoracic region - chest area abdomen - belly pelvic region - area where the back legs attach 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face, called vibrissae. 2. The mouth has a large cleft in the upper lip which exposes large front incisors. Rats are gnawing mammals, and these incisors will continue to grow for as long as the rat lives. 3. Note the eyes with the large pupil and the nictitating membrane found at the inside corner of the eye. This membrane can be drawn across the eye for protection. The eyelids are similar to those found in humans.
3 4. The ears are composed of the external part, called the pinna, and the auditory meatus, the ear canal. 5. Locate the teats on the ventral surface of the rat. Check a rat of another sex and determine whether both sexes have teats. 6. Examine the tail, the tails of rats do not have hair. Though some rodents, like gerbils, have hair on their tails. 7. Locate the anus, which is ventral to the base of the tale. 8. On female rats, just posterior to the last pair of teats, you will find the urinary aperture and behind that the vaginal orifice which is in a small depression called the vulva. 9. On males, you will find a large pair of of scrotal sacs which contain testes. Just anterior to the scrotal sacs is the prepuce, which is a bulge of skin surrounding the penis. The end of the penis has a urogenital orifice, where both urine and sperm exit. The Muscular and Skeletal System of the Rat Procedure: Skinning the Rat Identify the following muscles: You will carefully remove the skin of the rat to expose the muscles below. This task is best accomplished with scissors and forceps where the skin is gently lifted and snipped away from the muscles. You can start at the incision point where the latex was injected and continue toward the tail. Use the lines on the diagram to cut a similar pattern, avoiding the genital area. Gently peel the skin from the muscles, using scissors and a probe to tease away muscles that stick to the skin. Muscles are attached to bones by connective tissue called tendons that adhere to spines, knobs, and ridges on bones. You will need to refer to the rat skeleton to determine where the muscles are attached to bones. The end attached to the bone that does not move during contraction is called the origin. The end of the muscle that attaches to the bone that does move is called the insertion. The movement caused by the contraction of the muscle is called the action. Muscles can be easily identified from one another by their shape and overlap. 1. Biceps brachii - located on the anterior surface of the humerus. Action: flexes lower arm 2. Triceps brachii - located on the sides and back of the upper arm. Action: extends lower arm 3. Spinotrapezius - located across the dorsal thoracic region of the rat. Action: moves scapula up and backward 4. Latissimus dorsi - located posterior (and partially covered) by the spinotrapezius. Action: moves the humerus 5. Biceps femoris - located on the side of the thigh, in two bundles. Action: flexes the lower leg
4 6. Tibialis Anterior - located on the front of the leg. Action: flexes foot 7. Gastrocnemius - located on lower leg, bulk of the calf muscle. Attaches to heel by the Achilles Tendon. Action: extends the foot 8. External Oblique - located on the sides of the abdomen.action: flexes body wall. 9. Gluteus Maximus - located on the lower back and rear. Action: extends the thigh at the hip 10. Pectoralis Major/Minor - located in chest area. Action: adducts arm (draws it forward) Procedure: Identify each of the above mentioned organs. Procedure: The Skeletal structure Carefully tease away the biceps femoris and gastrocnemius to expose the 3 leg bones: Tibia, Fibula, and Femur and the small patella (kneecap). You can also see the ligaments around the knee that attach the bones of the lower leg to the femur and the achilles tendon which attaches the the gastrocnemius to the ankle. Note that the joint of the hip is called a ball and socket Procedure: Identify each of the above mentioned bones.
5 Rat Anatomy - Thoracic and Abdominal Organs The Thoracic Organs Procedure: Cut through the abdominal wall of the rat following the incision marks in the picture. Be careful not to cut to deeply and keep the tip of your scissors pointed upwards. Do not damage the underlying structures. Once you have opened the body cavity, you will need to rinse it in the sink. 1. Locate the diaphragm, which is a thin layer of muscle that separates the thoracic cavity from the abdominal cavity. 2. The heart is centrally located in the thoracic cavity. The two dark colored chambers at the top are the atria (single: atrium), and the bottom chambers are the ventricles. The heart is covered by a thin membrane called the pericardium. (We will come back to the heart later.) 3. Locate the thymus gland, which lies directly over the upper part of the heart. The thymus functions in the development of the immune system and is much larger in young rats than it is in older rats. 4. The lungs are spongy organs that lie on either side of the heart and should take up most of the thoracic cavity. Procedure: Identify each of the above mentioned organs. The Abdominal Organs 1. The coelom is the body cavity within which the viscera (internal organs) are located. The cavity is covered by a membrane called the peritoneum, which is very thin and web-like, you may need to use forceps to remove some of this membrane to see the organs clearly. 2. Locate the liver, which is a dark colored organ suspended just under the diaphragm. The liver has many functions, one of which is to produce bile, which aids in digesting fat. The liver also transforms wastes into less harmful substances. There are four parts to the liver.
6 3. The esophagus pierces the diaphragm and moves food from the mouth to the stomach. It is easiest to locate where it enters the stomach. 4. Locate the stomach on the left side just under the diaphragm. The functions of the stomach include food storage, physical breakdown of food, and the digestion of protein. 5. The outer margin of the curved stomach is called the greater curvature, the inner margin is called the lesser curvature. 6. You can make a slit in the stomach and see what is inside it. Most of the contents should be partly digested rat food. 7. At each end of the stomach (on the inside) is muscular valve. The opening between the esophagus and the stomach is called the cardiac sphincter. The opening between the stomach and the intestine is called the pyloric sphincter. 8. The spleen is about the same color as the liver and is attached to the greater curvature of the stomach. It is associated with the circulatory system and functions in the destruction of blood cells and blood storage. A person can live without a spleen, but they're more likely to get sick as it helps the immune system function. 9. The pancreas is a brownish, flattened gland found in the tissue between the stomach and small intestine. The pancreas produces digestive enzymes that are sent to the intestine via small ducts (the pancreatic duct). The pancreas also secretes insulin, which is important in the regulation of glucose metabolism. 10. The small intestine is a slender coiled tube that receives partially digested food from the stomach (via the pyloric sphincter). It consists of three sections: duodenum, jejunum and ileum, (Listed in order from the stomach to the large intestine.) The duodenum is recognizable as the first stretch of the intestine leading from the stomach, it is mostly straight. The jejunum and ileum are both curly parts of the intestine, with the ileum being the last section before the small intestine becomes the large intestine. 11. Locate the colon, which is the large greenish tube that extends from the small intestine and leads to the anus. The colon is also known as the large intestine. Food entering the colon from the small intestine is controlled by the ileocecal valve. The colon is where the finals stages of digestion and water absorption occurs and it contains a variety of bacteria to aid in digestion. Procedure: Identify each of the above mentioned organs. Rat - Circulatory System The general structure of the circulatory system of the rat is almost identical to that of humans. Pulmonary circulation carries blood through the lungs for oxygenation and then back to the heart. Systemic circulation moves blood through the body after it has left the heart. You will begin your dissection at the heart. It is important that you do not cut the vessels as you carefully remove any
7 muscles and surrounding tissue to expose them. Trace the Flow of Blood Inside the Heart 1. Blood from the posterior portion of the body enters the right atrium of the heart through the inferior vena cava. The inferior vena cava is also referred to as the caudal vena cava. 2. Blood from the anterior parts of the rat enter the heart from the right and left superior vena cava, also known as the cranial vena cava. 3. Blood flows from the right atrium to the right ventricle via the tricuspid valve. 4. Blood is then pumped through the pulmonary semilunar valve and into the pulmonary trunk, which divides into the left and right pulmonary arteries - these are the only arteries in the body that carry deoxygenated blood. 5. Blood then flows through the pulmonary arteries to the lungs where it is oxygenated and then returns from the lungs to enter the left atrium via four pulmonary veins. 6. Blood goes from the left atrium to the left ventricle via the biscupid (or mitral) valve. blood Procedure: Identify the main parts of the heart and describe the flow of
8
Dissection of the Rat
 Dissection of the Rat Introduction In this laboratory exercise, the anatomy of the rat will be examined in some detail. You may recall that in your first year biology course you dissected a grass frog
Dissection of the Rat Introduction In this laboratory exercise, the anatomy of the rat will be examined in some detail. You may recall that in your first year biology course you dissected a grass frog
Rat Dissection Lab Partner 1.
 Rat Dissection Lab Partner 1. 2. In Anatomy this year we have looked at several systems of the human body. This final laboratory exercise will allow you to examine how these systems are interrelated. We
Rat Dissection Lab Partner 1. 2. In Anatomy this year we have looked at several systems of the human body. This final laboratory exercise will allow you to examine how these systems are interrelated. We
Biology Overview Dissection Assignment
 Biology Overview Dissection Assignment What is this assignment about? After learning several major systems of the human body, this overview dissection assignment is for you to review all of those major
Biology Overview Dissection Assignment What is this assignment about? After learning several major systems of the human body, this overview dissection assignment is for you to review all of those major
Dissection: The Fetal Pig
 Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Lab Exercise Dissection: The Fetal Pig Objectives - To learn some of anatomical structures of the fetal pig. - To be able to make contrasts and comparisons of structures between different animal phyla
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection
 Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
Student Guide to the Frog Dissection Dissection Instructions 1. Place the frog in the dissecting pan ventral side up. 2. Use scissors to life the abdominal muscles away from the body cavity. Cut along
Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT
 Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Name: Honors Biology: Rat Dissection ONLINE ASSIGNMENT You and your group members will use the Honors Biology WIKI to create an online dissection manual. The point of this assignment is to illustrate what
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content
 Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Dissection Lab Manuals: Required Content 1. Introduction a. Basic terminology (directions) b. External features of the cat c. Adaptations to predatory niche d. How to skin a cat e. How to make the incisions
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet (2019)
 Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
Name Period [Each person will turn in his/her own packet] [ Final Score out of 166 points: ] You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages
Name: Fetal Pig Dissection Internal Anatomy
 In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
In this lab exercise you will open the thoracic cavities and abdominal pelvic of a fetal pig and identify its major organs. Remember you are dissecting not butchering. The goal is for you to identify all
Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy
 Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Name Fetal Pig Dissection: External Anatomy External Anatomy 1. Determine the sex of your pig by looking for the urogenital opening. On females, this opening is located near the anus. On males, the opening
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet
 Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
Fetal Pig Dissection Packet Name Period * Each person will turn in his/her own packet You may use the Virtual Fetal Pig Dissection website from Whitman College as a visual reference for all stages of dissection.
7 weeks: 28 mm 8 weeks: 40 mm 15 weeks: 220 mm 17 weeks: 300 mm
 Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection Background Pigs are placental mammals and show the distinguishing characteristics of that group. In studying the anatomy of the fetal, or unborn, pig, you will see that its various
Fetal Pig Dissection:
 Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
Fetal Pig Dissection: REMEMBER: Dissection involves disassembling and observing something to determine its internal structure and develop an understanding of the relationship of those structures to function.
LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection
 Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Biology 12 Name: Circulatory System Per: Date: Observation: External Anatomy LAB: Sheep or Pig Heart Dissection 1. Line a dissecting tray with paper towel for easy clean up as the heart is fatty and will
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Introduction A. Preparing the Fetal Pig Anterior Posterior Dorsal Ventral length gender mammary papillae
 Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Fetal Pig Dissection Materials Preserved Fetal Pig Cotton String Dissection tray Dissection pins Disposable Gloves Paper towels Dissection scissors Label pins Lab apron Re-sealable bag Dissection probe
Name Date Per. HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab
 Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Name Date Per UNIT 6 HANDOUT Frog Dissection Lab Purpose: To observe the anatomy of an amphibian To discover characteristics of complex vertebrates To compare anatomy of the frog to that of other organisms
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART
 LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
LAB 12-1 HEART DISSECTION GROSS ANATOMY OF THE HEART Because mammals are warm-blooded and generally very active animals, they require high metabolic rates. One major requirement of a high metabolism is
Name Partner(s) Name. Name your rat. Rat Dissection Lab
 Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Name Partner(s) Name Name your rat Rat Dissection Lab!!CAUTION!! You must follow all safety instructions as outlined in this lab manual and by your teacher. There are several sharp objects being used during
Heart Dissection. 5. Locate the tip of the heart or the apex. Only the left ventricle extends all the way to the apex.
 Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Heart Dissection Page 1 of 6 Background: The heart is a four-chambered, hollow organ composed primarily of cardiac muscle tissue. It is located in the center of the chest in between the lungs. It is the
Human Body Systems. Human Body Project Notes
 Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
Human Body Systems Human Body Project Notes Human Body Organ Systems for the Project Big Idea: Organ systems are composed of organs that are made of more than one type of tissue. Tissues are made of one
STREAM. Human Body Project Pages Website QR Code body project/
 STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
STREAM Human Body Project Pages 1 16 Website QR Code https://sites.google.com/a/wyckoffschools.org/human body project/ Project Checklist Did you include Head a brain that can open to show the inside as
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science. Mr. Diaz
 Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
Frog Dissection-Skin Vista Murrieta High School-- Biomedical Science Mr. Diaz Background: Please read entire lab As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but
The Human Body. Lesson Goal. Lesson Objectives 9/10/2012. Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy
 The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
The Human Body Lesson Goal Provide a brief overview of body systems, anatomy, physiology, and topographic anatomy Medial Lateral Proximal Distal Superior Inferior Anterior Lesson Objectives Explain the
Frog Dissection. Name: Block:
 Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
Name: Block: Frog Dissection Background: As members of the class Amphibia, frogs may live some of their adult lives on land, but they must return to water to reproduce. Eggs are laid and fertilized in
Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10
 Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10 The Domestic Pig: Sus scrofa Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia - Skin covered in hair or fur; Milk-producing glands (mammary glands) in the female to
Fetal Pigs and You BIO 171 WEEK 10 The Domestic Pig: Sus scrofa Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia - Skin covered in hair or fur; Milk-producing glands (mammary glands) in the female to
Fetal Pig Dissection. preserved fetal pig dissecting tray and paper towels length of string plastic storage bag and twist tie
 Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
Name Date Class LAB PROGRAM INQUIRY SKILLS B29 Fetal Pig Dissection Skills Objectives using dissection instruments and techniques Describe the appearance of various organs found in a fetal pig. Name the
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2013 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE
 FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
FROG DISSECTION GUIDE I. Introduction Frogs belong to the class amphibian. Although many differences exist between humans and frogs, the basic body plans are similar. Humans and frogs both belong to the
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection and a human model Dissect and identify a list of arteries and veins in the cat
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet
 BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
BIOLOGY 30S: Fetal Pig Dissection Worksheet Name: Part A: External Anatomy & Oral Cavity 1. How long (metric) is your fetal pig? 2. What is the age of your fetal pig? 3. What sense organs are located on
The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it!)%! DIGENIS!CLASSES!!2016!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Name:!!!!! Block:!!
 The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it)% DIGENISCLASSES2016 Name: Block: Fetal Pig Lab Check off each organ/structure as you locate it on your pig. Answer questions where indicated.
The$Pig$ $ Dissection$Manual$ (you%only%get%one,%don t%lose%it)% DIGENISCLASSES2016 Name: Block: Fetal Pig Lab Check off each organ/structure as you locate it on your pig. Answer questions where indicated.
This booklet belongs to: Spring Page 1 of 10
 This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
This booklet belongs to: Spring 2017 Page 1 of 10 Frog Dissection Background Amphibians are studied in science for a variety of reasons. Amphibians are unique in many ways because their anatomy allows
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART
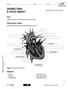 DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
DISSECTING A PIG S HEART LAB 59 OBSERVATION STUDENT BOOK Chapter 6, page 185 Goal Locate and observe structures of a mammal s heart. Observation criteria Identify the structures of the heart indicated
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body
 1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
1 Chapter 5 The Human Body 2 The Planes of the Body : Front side (Ventral) Posterior: Back side (Dorsal) : Imaginary line that divides body Midclavicular line: Imaginary line at center of clavicle (collar
Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide
 Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide 1. Anatomical terms: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior 2. Body sections: head, neck, thorax, abdomen, tail 3. Body Cavities: oral, thoracic, abdominal, cranial 4. Know
Vertebrate Anatomy Study Guide 1. Anatomical terms: dorsal, ventral, anterior, posterior 2. Body sections: head, neck, thorax, abdomen, tail 3. Body Cavities: oral, thoracic, abdominal, cranial 4. Know
OVARIES URETER FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS
 URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
URETER OVARIES FALLOPIAN TUBES BLADDER UROGENITAL OPENINGS (BOTH SEXES) PENIS VAGINA UTERUS REPRODUCTIVE PRODUCE FEMALE HORMONES EXCRETORY FROM KIDNEY TO BLADDER EXCRETORY STORES URINE REPRODUCTIVE TRANSPORTS
An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian. rr= Heart. Right ventricle+---, by David H. Hall
 An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian rr= Heart ventricle+---, by David H. Hall The Mam.malian Heart Because mammals are warm blooded (endothermic) and generally very active animals,
An Illustrated 1. Dissection Guide. To The... Mammalian rr= Heart ventricle+---, by David H. Hall The Mam.malian Heart Because mammals are warm blooded (endothermic) and generally very active animals,
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
 CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
CHAPTER 3 BASIC ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SURFACE ANATOMY Surface anatomy is the identification of landmarks on the surface of the skin which allows us to compare our knowledge of our own surface anatomy
Rat Dissection External Anatomy
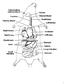 1 Rat Dissection External Anatomy 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face, called vibrissae. 2. The mouth has a large cleft in the upper lip
1 Rat Dissection External Anatomy 1. Note the hairy coat that covers the rat and the sensory hairs (whiskers) located on the rat's face, called vibrissae. 2. The mouth has a large cleft in the upper lip
Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Name: Date: Period: Fetal Pig Dissection Day 2 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Dissection Roles (choose a different role from Day 1): Recorder reads directions out loud to group and records answers
Cat Dissection. Muscular Labs
 Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
Cat Dissection Muscular Labs Tibialis anterior External oblique Pectroalis minor Gastrocnemius Sartorius Pectoralis major Gastrocnemius Semitendinosis Sartorius External oblique Trapezius Latissimus dorsi
MATERIALS: preserved fetal pig, dissecting pan, dissecting kit, dissecting pins, string, plastic bag, metric ruler, paper towels
 ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 12 ROCKRIDGE Fetal Pig Dissection NAME: BLOCK: DATE: Partner: BACKGROUND: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority
ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY 12 ROCKRIDGE Fetal Pig Dissection NAME: BLOCK: DATE: Partner: BACKGROUND: Mammals are vertebrates having hair on their body and mammary glands to nourish their young. The majority
THE HEART OBJECTIVES: LOCATION OF THE HEART IN THE THORACIC CAVITY CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM
 BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
BIOLOGY II CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEM ACTIVITY #3 NAME DATE HOUR THE HEART OBJECTIVES: Describe the anatomy of the heart and identify and give the functions of all parts. (pp. 356 363) Trace the flow of blood
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig Integrated Science 4 Honors Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06
 Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Mammalian Dissection: Fetal Pig 11/06 Integrated Science 4 Name Per. Introduction Organisms are classified based on similarities and differences to: 1) make sense of the millions of organisms on record,
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things
 Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
Frog Dissection SNC2P Grade 10 Science Applied Biology Tissues, Organs and Systems of Living Things Purpose To identify and examine the external and internal structures of the frog and compare them with
This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors
 1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
1 This lab activity is aligned with Visible Body s Human Anatomy Atlas app. Learn more at visiblebody.com/professors 2 A. Digestive System Overview To Start: Go to the Views menu and scroll down to the
Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology
 Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology Introduction In this lab, you will study the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig, relate its structures to those of other mammals, and determine differences
Fetal Pig Dissection Honors Biology Introduction In this lab, you will study the external and internal anatomy of a fetal pig, relate its structures to those of other mammals, and determine differences
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions?
 Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
Name Date: Block: Honors Marine Biology Mr. Conlan - Squid Dissection Lab Objective: Can you identify a squid s structures and their functions? Helpful Hints Everyone must wear safety goggles during the
 Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
Name: Date: Period: The Dissection 1. Place your specimen dorsal side down. Make your incisions following the diagram below. Make sure to make shallow cuts with the scissors. DO NOT CUT TOO DEEP! You will
S.A.F.E. Elements of Technique. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and STRENGTH ALIGNMENT FLEXIBILITY ENDURANCE
 Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Elements of Technique S.A.F.E. S.A.F.E. is an acronym for strength, alignment, flexibility, and endurance. These are all elements that are innate in the study of dance. STRENGTH The amount of control and
Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems
 Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
Name Date Vocabulary Crossword - Ch22 Body Systems 1 2 Per. 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 13 14 12 16 17 18 15 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART BLOOD
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 4e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N
 Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Module: Foundation Principles of Life Science for Midwifery Practice. WHH1008-N 2015 Welcome to the Anatomy Workbook. This directed learning has been developed to prepare you for lectures designed to study
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet
 Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 1 Review Sheet Chapter 1 Name Date Hour 1. investigates the body's structure, whereas investigates the processes or functions of living things. A. Physiology, cytology B. Physiology,
EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT
 EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT Exercise 13: Respiratory, Circulatory and Digestive Systems of the Rat Workbook Contents Corresponding Section
EXPLORING LIFE EXERCISE 13: THE RESPIRATORY, CIRCULATORY AND DIGESTIVE SYSTEMS OF THE RAT Exercise 13: Respiratory, Circulatory and Digestive Systems of the Rat Workbook Contents Corresponding Section
The Digestive System
 The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
The Digestive System Identify the Structure and Function. Mesentery of the Large Intestine The mesentery functions to connect the visceral organs to the abdominal wall. Identify the Structure. Nasal Cavity
Heart and Lung Dissection
 Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Heart and Lung Dissection Name(s) Before you begin any work or dissection of your specimen, please try to identify the following. You will need to illustrate what you see, so make sure to note size, texture
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al
 ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
ACTIVITY 9: BLOOD AND HEART OBJECTIVES: 1) How to get ready: Read Chapters 21 & 22, McKinley et al., Human Anatomy, 5e. All text references are for this textbook. Read dissection instructions BEFORE YOU
Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim
 Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim Objective: In this exercise you will examine the organization of the many body systems studied this semester in the context of a single specimen, the fetal pig. Be
Fetal Pig Dissection Labs Dr. J. Lim Objective: In this exercise you will examine the organization of the many body systems studied this semester in the context of a single specimen, the fetal pig. Be
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Day 1 - External Anatomy 1. Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate
Fetal Pig Dissection Guide Day 1 - External Anatomy 1. Obtain a fetal pig and rinse off the excess preservative by holding it under running water. Lay the pig on its side in the dissecting pan and locate
Course: Human Body Systems Year: Teacher: Meghann Redman
 Course: Human Body Systems Year: 2015 2016 Teacher: Meghann Redman Unit 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Approximate Time Frame: 2 Weeks The human body has its own set of medical terminology. What terms
Course: Human Body Systems Year: 2015 2016 Teacher: Meghann Redman Unit 1: The Human Body: An Orientation Approximate Time Frame: 2 Weeks The human body has its own set of medical terminology. What terms
DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS
 8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
8546d_c01_1-42 6/25/02 4:32 PM Page 38 mac48 Mac 48: 420_kec: 38 Cat Dissection DISSECTION 8: URINARY AND REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEMS Typically, the urinary and reproductive systems are studied together, because
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1. Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book)
 CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
CJ Shuster A&P2 Lab Addenum Beef Heart Dissection 1 Heart Dissection. (taken from Johnson, Weipz and Savage Lab Book) Introduction When you have finished examining the model, you are ready to begin your
Anatomy of the Heart
 Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Biology 212: Anatomy and Physiology II Anatomy of the Heart References: Saladin, KS: Anatomy and Physiology, The Unity of Form and Function 8 th (2018). Required reading before beginning this lab: Chapter
Introduction to The Human Body
 1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
1 Introduction to The Human Body FOCUS: The human organism is often examined at seven structural levels: chemical, organelle, cell, tissue, organ, organ system, and the organism. Anatomy examines the structure
Pig Dissection for Dummies
 Pig Dissection for Dummies External Anatomy 1. Say hello to your pig. To determine the sex of your pig so that you can give him/her an appropriate name, look for a little hole DIRECTLY posterior (toward
Pig Dissection for Dummies External Anatomy 1. Say hello to your pig. To determine the sex of your pig so that you can give him/her an appropriate name, look for a little hole DIRECTLY posterior (toward
#5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels
 Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Page1 #5 Cardiovascular II Blood Vessels Objectives: Observe slide of artery and vein cross-section Identify a list of human arteries and veins using a virtual human dissection Dissect and identify a list
Chapter 1. Introduction to Human. Anatomy and Physiology 8/16/2012. believe are the major requirements
 Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 1 Introduction to Human Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy deals with the structure (morphology) of the body and its parts, in other words, what things are called. Physiology
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide
 Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
Human Anatomy Key Points Unit 1/ Study Guide I. Anatomy and Physiology a. Anatomy 1. Means cutting apart (dissection) 2. Study of the body and the relationships of its parts to each other. 3. Dissection
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p.
 General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
General Anatomy p. 1 Organization of the Human Body p. 1 Skeleton of the Human Body p. 4 Ossification of the Bones p. 6 Bone Structure p. 8 Joints p. 10 Principal Joints (Immovable) p. 12 Synovial Joints
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL Phone: (630) Fax: (630)
 319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
319 S. Naperville Road Wheaton, IL 60187 www.questionsgalore.net Phone: (630) 580-5735 E-Mail: info@questionsgalore.net Fax: (630) 580-5765 STUDY GUIDE: HUMAN ANATOMY I The smallest unit part of any living
Homework Packet. The branch of biological science that studies and describes how body parts. The study of the shape and structure of body parts
 Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Anatomy & Physiology Chap. 1: The Human Body Name Block: P/W Homework Packet ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY DISTINCTIONS 1. Match the term on the right to the appropriate description on the left. Enter the correct
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Rat Dissection Lab. Background
 Anatomy & Physiology Corvallis High School Rat Dissection Lab Name: Class Period: Background Dissection of any organism or organ allows a 3-dimensional look at structural connections within the body. It
Anatomy & Physiology Corvallis High School Rat Dissection Lab Name: Class Period: Background Dissection of any organism or organ allows a 3-dimensional look at structural connections within the body. It
THE HEART. Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration
 THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
THE HEART Unit 3: Transportation and Respiration The Circulatory System Also called the Cardiovascular System Circulates blood in the body Transports nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide, hormones, and blood
"...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..."
 London and District Science Olympics Annual Competition "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." Senior Biology "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." RULES Biology Grades 9-12 Changes to the rules are marked by a vertical line
London and District Science Olympics Annual Competition "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." Senior Biology "...AND THIS LITTLE PIG..." RULES Biology Grades 9-12 Changes to the rules are marked by a vertical line
Grasshopper Dissection
 Grasshopper Dissection Introduction: Insects are arthropods with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and an exoskeleton composed of chitin. Insects are in the class Insecta, & are the largest and most
Grasshopper Dissection Introduction: Insects are arthropods with jointed appendages, segmented bodies, and an exoskeleton composed of chitin. Insects are in the class Insecta, & are the largest and most
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Urinary 1 Checklist Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Urinary system Kidneys Parietal peritoneum Retroperitoneal Renal fascia The urinary system consists of two kidneys, two ureters, the urinary bladder,
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
PHYSICAL EDUCATION. 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems.
 PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
PHYSICAL EDUCATION 4º E.S.O. 2nd TERM. The skeletal and muscular systems. PARTS OF THE BODY Head Torso / Trunk Dorsal: Back Ventral: Thorax y Abdomen Extremities Superior: Arm Forearm Hand Joint: Shoulder
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook
 Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe strowe@crec.org www.gomlc.com IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook Topic Table of Contents Page Number Intro and Note to Students 3 Anatomical Position - Diagram 4 Anatomical
Name: Class: IB SEHS (SL) Teacher: Mrs. Rowe strowe@crec.org www.gomlc.com IB SEHS Anatomy Handbook Topic Table of Contents Page Number Intro and Note to Students 3 Anatomical Position - Diagram 4 Anatomical
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX
 SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
SESSION 2: THE MOUTH AND PHARYNX 9 In the pig s digestive tract, food flows in only one direction from mouth to anus.this allows for greatly specialized sections that can act independently of each other.
Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete)
 Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
Activity #12 What s happening inside? Challenge Question: Prediction: (Wait for directions) Evidence: (Draw, color and label how your Clay model looked when it was complete) Act #12 pg 1 of 3 Analysis
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin. KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body.
 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin KEY CONCEPT The integumentary system has many tissues that protect the body. 36.3 The Integumentary System The Skin The integument is the body system that surrounds
Danil Hammoudi.MD 1/12/2009
 Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
Danil Hammoudi.MD Aorta the biggest and longest artery (a blood vessel carrying blood away from the heart) in the body. It carries oxygen rich blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the body.inferior
OBJECTIVES. Unit 7:5 PROPERTIES OR CHARACTERISTICS OF MUSCLES. Introduction. 3 Kinds of Muscles. 3 Kinds of Muscles 4/17/2018 MUSCULAR SYSTEM
 OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
OBJECTIVES Unit 7:5 MUSCULAR SYSTEM Compare the three main kinds of muscles by describing the action of each Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles List at least three functions of muscles
The Musculoskeletal System
 The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
The Musculoskeletal System Introduction The skeletal system and muscular system are often considered together because they are close in terms of structure and function. The two systems are referred to
Carolina Biological Supply Company. Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens
 Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Carolina Biological Supply Company Rats! Inquiry-Based Dissection with Carolina s Perfect Solution Specimens Objectives Introduce basic mammalian anatomy using the rat Perform a rat dissection focusing
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION. The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include:
 Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Anatomy Review-INTRODUCTION The study of the organs and parts of the body is called Examples include: The study of the function of the body parts is called. Examples include: Use the numbers from the diagram
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV
 Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Unit 1: Human body: combination I - IV Study online at quizlet.com/_1kzmm2 1. alveoli 6. bronchioles microscopic air sacs in the lung where diffusion of the respiratory gases, oxygen and carbon dioxide
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide
 Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
Fetal Pig Visual Dissection Guide WARD470156-776 Orientation Cranial Anterior Sagittal plane Frontal plane Ventral Dorsal Transverse plane Caudal Posterior 1 Incisions 1 Gender Key Male Female Both 4 3
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM:
 ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM: OBJECTIVE: This dissection activity is designed to help you learn anatomical terms, and also to help you practice doing a dissection without the gross-out
ANATOMY PHYSIOLOGY LAB 1-1 AUTOPSY OF A BANANA TEAM: OBJECTIVE: This dissection activity is designed to help you learn anatomical terms, and also to help you practice doing a dissection without the gross-out
Anatomy & Physiology. Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout
 Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Anatomy & Physiology Advanced Biology Mrs. Layton-Krout A & P Anatomy - study of structure Physiology - study of function Structure is always related to function Levels of Organization Atom Chemical Molecule
Fig. A.1. Frontal. plane. Transverse. plane. Sagittal plane. Copyright McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction or display.
 Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
Fig. A.1 Frontal plane Transverse plane Sagittal plane McGraw-Hill Education/Joe DeGrandis Fig. A.2 (a) Sagittal section (b) Frontal section (c) Transverse section Table A.1 Fig. A.3 Cephalic r. (head)
REVISION BOOKLET. The Body Systems
 REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
REVISION BOOKLET The Body Systems GCSE PE 2016 Skeletal System Functions of the skeleton Joints for movement Muscle attachment Protection of vital organs Red and white blood cell production platelets Storage
