Simplified Overview of Urine Formation. Urinary System II Lecture Notes Pages Reproductive System I Lecture Notes Pages
|
|
|
- Amie Heath
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Urinary System II Lecture Notes Pages Reproductive System I Lecture Notes Pages Lecture Overview Urinary System Review/QuestionsUrine formation Reabsorption/Secretion Countercurrent multiplier and water conservation Renin-angiotensin pathway Reproductive System Introduction and Overview Male External anatomy (scrotum/penis) Erection Internal structures Testes Accessory organs (epididymis, vas (ductus) deferens, seminal vesicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral (Cowper s) gland Semen 2 Simplified Overview of Urine Formation Renal corpuscle provides the raw materials to the nephron for processing PCT reclaims those substances the body can use; gets rid of some things DCT gets rid of those substances the body doesn t want or need; reabsorbs some more Na +, Ca 2+ Collecting tubule (duct) provides the OPTION of reclaiming H 2 O or letting it pass out of the body [p ] 3 1
2 Reabsorption/Secretion in Kidney * * * Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill, 2007 * Keep in mind: Where Na + (or solute, in general) goes, H 2 O and Cl - usually follow. [p. 135] 4 Tubular Reabsorption [p ] Reabsorption by tubular cells is a selective process Diffusion Osmosis Carrier-mediated transport Facilitated diffusion Active transport Co- and counter-transport Occurs mainly in the proximal convoluted tubules (PCT) Has a transport maximum, T m, for most substances besides Na + T m is the rate at which solutes can be transported, e.g., 375 mg/min Renal threshold is the plasma level (concentration) above which a particular solute will appear in urine, e.g., 180 mg/dl Peritubular capillaries are well-suited for reabsorption Low hydrostatic pressure High degree of permeability Higher colloid osmotic pressure due to filtration 5 Reabsorption in PCT [p ] 65% of filtrate volume is reabsorbed in the PCT 8 mm Hg COP Tubular fluid All uric acid, about 50% of urea, and no creatinine is reabsorbed Figure from: Saladin, Anatomy & Physiology, McGraw Hill,
3 Substance Reabsorption in the PCT. Mechanism of Reabsorption Notes Na + (Cl - ) Primary Active Transport Na + reabsorption is the driving force for most other reabsorption H 2 O Osmosis Closely associated with movement of Na + (Obligatory water reabsorption) Glucose Secondary Active transport Limited # of molecules can be handled (T m = 375 mg/min); attracts H 2 0 Amino Acids Secondary Active transport Three different active transport modalities; difficult to overwhelm Other electrolytes Secondary Active transport [p ] 7 Overview of Facultative H 2 O Reabsorption Note that outflow of water from collecting duct is dependent upon the osmotic gradient in the medulla Increasing concentration Urea Under influence of ADH (Facultative water reabsorption) 8 The Loop of Henle (Nephron Loop) [p. 138] Crucial renal function is to keep the body fluids at about 300 mosm (osmolarity of blood plasma) by varying the concentration of urine The mechanism shown is called the countercurrent multiplier SO HOW DOES THIS HELP? Increasing concentration Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
4 The Countercurrent Multiplier Recall that all movement of H 2 O occurs passively by osmosis We would like some mechanism to concentrate urine Excrete more H 2 O when body fluids are tending to become hypotonic (more dilute) Excrete less H 2 O when body fluids are tending to become hypertonic (more concentrated) Utilizes two factors Hypertonicity of the peritubular fluid, established by the countercurrent multiplier Variable permeability of the collecting tubules to H 2 O depending upon levels of ADH We will use the phrase, Water follows salt (solute) when it can 10 Vasa Recta of Juxtamedullary Nephrons Recall that the vasa recta is present in juxtamedullary nephron loops (which give the kidneys the ability to produce a concentrated urine) The vasa recta functions to 1. Deliver blood to medullary cells 2. Return reabsorbed solutes and water in the medulla to the general circulation without disrupting the medullary concentration gradient [p. 138] 11 Influence of ADH on H 2 O Reabsorption [p ] Note that amount of water pulled out of collecting duct is dependent upon the osmotic gradient in the medulla that was established by the countercurrent multiplier. Figure from: Hole s Human A&P, 12 th edition, 2010 Urea Under influence of ADH (Facultative water reabsorption) 12 4
5 Summary of Events in the Nephron/Collecting Duct (Aldosterone) (Aldosterone) 1. Filtrate produced 2. Reabsorption of 65% of filtrate 3. Obligatory water reabsorption 4. Reabsorption of Na + and Cl - by active transport 5,6. Facultative reabsorption of water 7. Absorption of solutes and water by vasa recta 13 Some Factors Influencing Salt/H 2 O... Diuretics Increase water loss in urine - Caffeine (coffee, cola, tea); causes dilation of afferent arteriole (effect on GFR?) -Alcohol/narcotics; inhibit ADH (result?) - Antihypertensive drugs, CHF meds; decrease retention of Na+ (result?) - Diabetes mellitus; increased glucose in tubular fluid (result?) -Diabetes inspidus; decrease secretion of ADH [p ] - Addison s Disease; decreased aldosterone secretion (result?) [Mnemonic: Addison ADD SALT] 14 [p. 141] Juxtaglomerular Apparatus Juxtaglomerular cells (JG) - modified smooth muscle cells in the wall of the afferent arteriole that contract (and secrete renin) Cells of the macula densa (MD) are osmoreceptors responding to solute concentration of filtrate MD + JG cells = juxtaglomerular apparatus Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
6 Renin-Angiotensin System [p. 141] (ACE) Figure from: Hole s Human A&P, 12 th edition, 2010 Renin is released by the juxtaglomerular apparatus due to: 1) Decline of BP (Renin 1/Pressure) 2) Juxtaglomerular stimulation by sympathethic NS 3) Decline in osmotic concentration of tubular fluid at macula densa ( Renin 1/[NaCl] ) Stabilizes systemic blood pressure and extracellular fluid volume 16 Reproductive System I Lecture Notes Pages Overview of the Reproductive System Produce and maintain sex cells, or gametes ( sperm, ova) Transport gametes and supplemental fluids to appropriate location so that fertilization can occur Development and Birth (Females, in humans) [p. 147] 18 6
7 Male Reproductive System [p. 147] Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, 2001 Testis Epididymis Vas (ductus) deferens Ejaculatory duct Urethra 19 Male External Reproductive Organs [p. 147] Temperature control Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, Descent of Testes [p. 147] Descent begins around 7 th month of pregnancy under the influence of testosterone Descent is necessary for sperm production (temp about 3 o C lower than body temp) Failure of testes to descend = cryptorchidism 21 7
8 Scrotum [p. 147] Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, 2001 pouch of skin and subcutaneous tissue dartos muscle smooth muscle in dermis; contracts to cause wrinkling of the scrotum (traps heat) medial septum divides scrotum into two chambers each chamber lined with a serous membrane each chamber houses a testis and epididymis Cremaster muscle can retract testes 22 Penis [p. 148] Connection of penis to body wall (root) Parasympthetic stimulation (S4) causes vasodilation and filling of erectile tissues with blood, resulting in erection and compression of veins draining penis 23 Penis [p. 148] Preputial glands in the prepuce (foreskin) produce a waxy material called smegma. This can be a source of bacterial growth if hygiene is poor. Circumcision is the surgical removal of the prepuce. 24 8
9 Structure of the Testis [p ] Rete Testis Epididymis is about 16 FEET in length! Surrounded by the tunica vaginalis and tunica albuginea a tough, white, fibrous capsule that encloses each testicle Septa of albuginea divide each testicle into about 250 lobules Each lobule contains 1-4 highly coiled seminiferous tubules that give rise to sperm Interstitial cells (of Leydig) lie in between seminiferous tubules and secrete male sex hormones 25 Epididymis Figures from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, 2001 Takes about 2 weeks for sperm to travel through the epididymis - Maintains fluid produced in the seminiferous tubules - Recycles damaged sperm and cellular debris - Store and protects sperm, and aids in their maturation 26 Ductus (Vas) Deferens muscular tube about 45 cm long; transports sperm ( can store sperm for several months) extends from epididymis to ejaculatory duct Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
10 Male Internal Accessory Organs - Glands X 2 [p. 150] (1) 28 Seminal Vesicles [p. 151] attached to ductus deferens near base of bladder secretes alkaline fluid (60% of the volume of semen) secretes fructose, prostaglandins, and proseminogelin begins capacitation of sperm contents empty into ejaculatory duct Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, Prostate Gland [p. 151] surrounds beginning of urethra ducts of gland open into urethra secretes a thin, milky, slightly alkaline fluid (20-35% of semen volume) secretion enhances fluid mobility (PSA) contains seminalplasmin secretes Prostate-specific Antigen (PSA) composed of tubular glands in connective tissue also contains smooth muscle Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall,
11 Clinical Application - Prostate Enlargement benign prostatic hyperplasia occurs in most men over 50 BPH causes frequent urination risk factors include a fatty diet, having had a vasectomy(?), or exposure to certain environmental factors treatments include surgical removal drugs insertion of balloon into urethra freezing of tumor insertion of stent between lobes of prostate to relieve pressure on urethra 31 Bulbourethral (Cowper s) Gland inferior to the prostate gland secretes thick, alkaline mucus - helps lubricate the tip of the penis (glans) and neutralize any urinary acids in urethra fluid released in response to sexual stimulation [p. 150] Figure from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, sperm cells (spermatozoa) Semen [p ] secretions of seminal vesicles, prostate gland, and bulbourethral glands (seminal fluid) slightly alkaline (offsets acidity of reproductive tract) prostaglandins (stimulates contraction in reproductive tract) nutrients enzymes (protease, seminalplasmin, fibrinolysin) million sperm cells per milliliter (< 20 mil/ml = sterile) usually about 2-5 ml of fluid per ejaculate 33 11
12 Seminiferous Tubules and Sperm Maturation [p. 152] Figures from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, 2001 Spermatogonium = stem cell 34 Structure of a Sperm Cell [p. 152] Mitochondria Only flagellum in human body Approx 0.06 mm long Enzymes used to penetrate the egg during fertilization 35 Spermatogenesis [p. 152] Spermatogonium (2n) Primary spermatocyte (2n) Meiosis I Secondary spermatocyte (n) Meiosis II Spermatid (n) Spermiogenesis Spermatozoan (n) 36 12
13 Review of Mitosis and Meiosis Figures from: Martini, Anatomy & Physiology, Prentice Hall, 2001 [p. 152] Mitosis production of two identical diploid daughter cells *Meiosis production of four genetically varied, haploid gametes 37 Mechanism of Emission and Ejaculation Figure from: Hole s Human A&P, 12 th edition, 2010 [p. 153] Loss of arterial vasodilation -> detumesence - > refractory period 38 Hormonal Control of Male Reproductive Functions hypothalamus controls maturation of sperm cells and development of male secondary sex characteristics negative feedback controls concentration of testosterone 39 13
The Reproductive System
 PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Patty Bostwick-Taylor, Florence-Darlington Technical College The Reproductive System 16PART A The Reproductive System Gonads primary sex organs Testes in males
The Reproductive System
 16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
16 PART A The Reproductive System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB The Reproductive
The Reproductive System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 16 The Reproductive System Slides 16.1 16.20 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook The Reproductive System Gonads
Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries. Accessory reproductive organs: ducts, glands, and external genitalia
 Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System Primary sex organs (gonads): testes and ovaries Produce sex cells (gametes) Secrete steroid sex hormones Androgens (males) Estrogens and progesterone (females) Accessory reproductive
Male Reproductive System. Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD
 Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Male Reproductive System Dr Maan Al-Abbasi PhD, MSc, MBChB, MD Learning Objectives 1. Describe the General Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System 2. Identify the structures that are related to the prostate.
Urinary System Organization. Urinary System Organization. The Kidneys. The Components of the Urinary System
 Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Urinary System Organization The Golden Rule: The Job of The Urinary System is to Maintain the Composition and Volume of ECF remember this & all else will fall in place! Functions of the Urinary System
Male Reproductive System
 21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
21-1 21-2 Reproductive System Male Reproductive System Genital Tract In males the testes, held outside the body in the scrotum (optimum temp of about 35 0 C), produce sperm. Sperm mature in coiled tubes
- production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote
 Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Male reproductive system I. Sexual reproduction -- overview - production of two types of gametes -- fused at fertilization to form zygote - promotes genetic variety among members of a species -- each offspring
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System. Chapter 50
 Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmotic Regulation and the Urinary System Chapter 50 Challenge Questions Indicate the areas of the nephron that the following hormones target, and describe when and how the hormones elicit their actions.
Osmoregulation and Renal Function
 1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
1 Bio 236 Lab: Osmoregulation and Renal Function Fig. 1: Kidney Anatomy Fig. 2: Renal Nephron The kidneys are paired structures that lie within the posterior abdominal cavity close to the spine. Each kidney
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization
 Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Male Reproductive Structures I. Overview A. Main functions: 1. Produce a haploid male gamete (sperm) 2. Deposit sperm in the female so fertilization may occur! A. Scrotum 1. Muscular pouch that holds the
Questions? Homework due in lab 6. PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!)
 Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Questions? Homework due in lab 6 PreLab #6 HW 15 & 16 (follow directions, 6 points!) Part 3 Variations in Urine Formation Composition varies Fluid volume Solute concentration Variations in Urine Formation
Reproductive System Purpose General Structures Male Structures Functions Female Anatomy Structures Functions Clinical Applications
 The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
The Reproductive System: Male, Ch 23 Outline of class lecture After studying the male reproductive system you should be able to: 1. Define the purpose of reproduction and identify the general organs of
Outline Urinary System. Urinary System and Excretion. Urine. Urinary System. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system
 Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Outline Urinary System Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Chapter 16 Renal will be on the Final only. I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of
Chapter 25: Urinary System
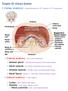 Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
Chapter 25: Urinary System I. Kidney anatomy: retroperitoneal from 12 th thoracic to 3 rd lumbar area A. External anatomy: hilus is the indentation 1. Adrenal gland: in the fat at the superior end of each
describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it
 You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
You need to be able to: describe spermatogenesis (How is sperm made?) describe the anatomy of a sperm describe the parts and function of semen and the glands that contribute to it How is sperm made? Spermatogenesis
Urinary System Chapter 16
 Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
Urinary System Chapter 16 1 Urology- the branch of medicine that treats male and female urinary systems as well as the male reproductive system. Nephrology- the scientific study of the anatomy, physiology,
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues
 BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
BCH 450 Biochemistry of Specialized Tissues VII. Renal Structure, Function & Regulation Kidney Function 1. Regulate Extracellular fluid (ECF) (plasma and interstitial fluid) through formation of urine.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
BIO 210 Anatomy and Physiology Homework #10: Chs. 26-28 DUE: (see course schedule) Assignments not turned in at the beginning of class will be accepted. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that
Urinary System. consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra
 Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Urinary System 1 Urinary System consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra 2 Location of Kidneys The kidneys which are positioned retroperitoneally lie on either side of the vertebral
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Male Reproductive System Dr. Gary Mumaugh Reproductive System Basics Primary sex organs (gonads) testes in males, ovaries in females Gonads produce sex cells called gametes (gametes means spouses) and
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems. Male Reproductive Organs. Male Reproductive Organs. Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm)
 Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
Chapter 22 Reproductive Systems Male reproductive organs 1 Male Reproductive Organs posterior view 2 Male Reproductive Organs Specialized to produce, maintain the male sex cells (sperm) Transport these
2) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure.
 Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
Class: A&P2-1 Description: Test: Excretory Test Points: 144 Test Number: 28379 Printed: 31-March-10 12:03 1) This is a Point and Click question. You must click on the required structure. Click on the Bowman's
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M
 A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
A&P 2 CANALE T H E U R I N A R Y S Y S T E M URINARY SYSTEM CONTRIBUTION TO HOMEOSTASIS Regulates body water levels Excess water taken in is excreted Output varies from 2-1/2 liter/day to 1 liter/hour
1. a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z
 Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Excretory System 1 1. Excretory System a)label the parts indicated above and give one function for structures Y and Z W- renal cortex - X- renal medulla Y- renal pelvis collecting center of urine and then
Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion.
 The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
The Kidney Vertebrates possess kidneys: internal organs which are vital to ion and water balance and excretion. The kidney has 6 roles in the maintenance of homeostasis. 6 Main Functions 1. Ion Balance
Urinary System and Excretion. Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture 20 Chapter 16 1 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure III. Disorders of the urinary system
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX
 One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
One Minute Movies: Molecular Action at the Nephron Joy Killough / Westwood High School / Austin,TX To prepare your nephron model: ( A nephron is a tubule and the glomerulus. There are about a million of
Urinary Physiology. Chapter 17 Outline. Kidney Function. Chapter 17
 Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Urinary Physiology Chapter 17 Chapter 17 Outline Structure and Function of the Kidney Glomerular Filtration Reabsorption of Salt and Water Renal Plasma Clearance Renal Control of Electrolyte and Acid-Base
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems. Male 11/29/2015. Male reproductive system is composed of... BIO 218 Fall Gonads (testes)
 Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
Chapter 26: Reproductive Systems BIO 218 Fall 2015 Male Male reproductive system is composed of... Gonads (testes) Duct system (epididymis, ductus deferens, ejaculatory ducts, urethra) Accessory sex glands
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System)
 NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
NOTES: CH 44 Regulating the Internal Environment (Homeostasis & The Urinary System) HOMEOSTASIS **Recall HOMEOSTASIS is the steady-state physiological condition of the body. It includes: 1) Thermoregulation:
Lab Activity 31. Anatomy of the Urinary System. Portland Community College BI 233
 Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Lab Activity 31 Anatomy of the Urinary System Portland Community College BI 233 Urinary System Organs Kidneys Urinary bladder: provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters: transport
Male Reproduction Organs. 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Vas deferens 4. Urethra 5. Penis 6. Prostate 7. Seminal vesicles 8. Bulbourethral glands
 Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Outline Terminology Human Reproduction Biol 105 Lecture Packet 21 Chapter 17 I. Male Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Sperm development II. Female Reproduction A. Reproductive organs B. Egg development
Male Reproductive Physiology
 Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
Male Reproductive Physiology Overview Anatomy Function Endocrine and spermatogenesis Testis epididymus,vas deferens,seminal vesicles and prostate Hypothalamic pituitary testicular axis Hormones of the
STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Unit 7A STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OF THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Learn the structures of the male reproductive system. 2. Learn the functions of the male reproductive system. 3. Learn
Renal System and Excretion
 Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
Renal System and Excretion Biology 105 Lecture 19 Chapter 16 Outline Renal System I. Functions II. Organs of the renal system III. Kidneys 1. Structure 2. Function IV. Nephron 1. Structure 2. Function
5.Which part of the nephron removes water, ions and nutrients from the blood?
 Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
Uro question 1.While reading a blood test I notice a high level of creatinine, I could assume from this that A) There is a possibility of a UTI B) There is a possibility of diabetes C) There is a possibility
28/04/2013 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS URINARY SYSTEM & EXCRETION
 LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
LEARNING OUTCOME C13 Analyse the functional interrelationships of the structures of the urinary system Learning Outcome C13 URINARY SYSTEM STUDENT ACHIEVEMENT INDICATORS Students who have fully met this
1.&Glomerular/Pressure&Filtration&
 Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urine&Formation& Overall&Process&! Urine gets rid of wastes (NH 3, urea, uric acid, creatinine) and other substances (vitamins, penicillin, histamines) found in excess in the blood!! blood is filtered
Urinary System BIO 250. Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat. Routes of Waste Elimination
 Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Urinary System BIO 250 Waste Products of Metabolism Urea Carbon dioxide Inorganic salts Water Heat Routes of Waste Elimination Skin: Variable amounts of heat, salts, and water; small amounts of urea and
Human Urogenital System 26-1
 Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Human Urogenital System 26-1 Urogenital System Functions Filtering of blood, Removal of wastes and metabolites Regulation of blood volume and composition concentration of blood solutes ph of extracellular
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure
 Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Glomerular Capillary Blood Pressure Fluid pressure exerted by blood within glomerular capillaries Depends on Contraction of the heart Resistance to blood flow offered by afferent and efferent arterioles
Renal Functions: Renal Functions: Renal Function: Produce Urine
 Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
Renal Functions: Excrete metabolic waste products Reabsorb vital nutrients Regulate osmolarity: Maintain ion balance Regulate extracellular fluid volume (and thus blood pressure) Renal Functions: Regulate
URINARY SYSTEM. Primary functions. Major organs & structures
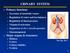 URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
URINARY SYSTEM Primary functions Excretion of metabolic wastes Regulation of water and ion balances Regulation of blood pressure Vitamin D activation Regulation of rbc s (erythropoietin) Gluconeogenesis
PARTS OF THE URINARY SYSTEM
 EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
EXCRETORY SYSTEM Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid-base concentrations and metabolite concentrations 1 ORGANS OF EXCRETION Skin and
November 30, 2016 & URINE FORMATION
 & URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
& URINE FORMATION REVIEW! Urinary/Renal System 200 litres of blood are filtered daily by the kidneys Usable material: reabsorbed back into blood Waste: drained into the bladder away from the heart to the
Outline Urinary System
 Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Urinary System and Excretion Bio105 Lecture Packet 20 Chapter 16 Outline Urinary System I. Function II. Organs of the urinary system A. Kidneys 1. Function 2. Structure B. Urine formation 1. Hormonal regulation
Chapter 25 The Urinary System
 Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
Chapter 25 The Urinary System 10/30/2013 MDufilho 1 Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph Gluconeogenesis
describe the location of the kidneys relative to the vertebral column:
 Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
Basic A & P II Dr. L. Bacha Chapter Outline (Martini & Nath 2010) list the three major functions of the urinary system: by examining Fig. 24-1, list the organs of the urinary system: describe the location
BIOLOGY - CLUTCH CH.44 - OSMOREGULATION AND EXCRETION.
 !! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
!! www.clutchprep.com Osmoregulation regulation of solute balance and water loss to maintain homeostasis of water content Excretion process of eliminating waste from the body, like nitrogenous waste Kidney
Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine
 Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Urinary System Organs Kidney Filters blood, allowing toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions to leave the body in urine Urinary bladder provides a temporary storage reservoir for urine Paired ureters
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Figure 19-1c. Efferent arteriole. Juxtaglomerular apparatus
 /6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
/6/0 About this Chapter Functions of the Kidneys Anatomy of the urinary system Overview of kidney function Secretion Micturition Regulation of extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure Regulation of
CHAPTER 25 URINARY. Urinary system. Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1. functions
 CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
CHAPTER 25 URINARY Kidneys 2 Ureters 2 Urinary Bladder 1 Urethra 1 fluid waste elimination secretion of wastes control blood volume and BP control blood ph electrolyte levels RBC levels hormone production
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY. Physiology Unit 4
 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Physiology Unit 4 Renal Functions Primary Function is to regulate the chemistry of plasma through urine formation Additional Functions Regulate concentration of waste products Regulate
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Human Anatomy Unit 3 REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM In Anatomy Today Male Reproductive System Gonads = testes primary organ responsible for sperm production development/maintenan ce of secondary sex characteristics
Kidney and urine formation
 Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
Kidney and urine formation Renal structure & function Urine formation Urinary y concentration and dilution Regulation of urine formation 1 Kidney and urine formation 1.Renal structure & function 1)General
The Repr duct ve System. Function: producing offspring
 The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
The Repr duct ve System Function: producing offspring Anatomy of male reproductive system Location: The reproductive organs are classified as external and internal genitalia. The external genitalia are
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 16 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction
Sunday, July 17, 2011 URINARY SYSTEM
 URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
URINARY SYSTEM URINARY SYSTEM Let s take a look at the anatomy first! KIDNEYS: are complex reprocessing centers where blood is filtered through and waste products are removed. Wastes and extra water become
Chapter 23. The Nephron. (functional unit of the kidney
 Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 23 The Nephron (functional unit of the kidney Renal capsule The Nephron Renal cortex Nephron Collecting duct Efferent arteriole Afferent arteriole (a) Renal corpuscle: Glomerular capsule Glomerulus
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE
 Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Chapter 28: REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM: MALE I. FUNCTIONAL ANATOMY (Fig. 28.1) A. Testes: glands which produce male gametes, as well as glands producing testosterone 2. Seminiferous tubules (Fig.28.3; 28.5) a.
Waste Products & Kidney Function
 Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Waste Products & Kidney Function urinary system principal means of metabolic waste removal urinary system is closely associated with reproductive system urogenital system share embryonic development share
Excretory System-Training Handout
 Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
Excretory System-Training Handout Karen L. Lancour National Rules Committee Chairman Life Science Excretion - Excretion is the removal of the metabolic wastes of an organism. Wastes that are removed include
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
Exam Name SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question. Figure 25.1 Using Figure 25.1, match the following: 1) Glomerulus. 2) Afferent arteriole. 3)
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19
![QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19](/thumbs/77/74887026.jpg) QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
QUIZ/TEST REVIEW NOTES SECTION 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY FILTRATION [THE KIDNEYS/URINARY SYSTEM] CHAPTER 19 CHAPTER 19 Learning Objectives: Differentiate the following processes: filtration, reabsorption, secretion,
Urinary system. Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal. Nephrons
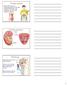 Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Urinary system Aids homeostasis by removing cellular wastes and foreign compounds, and maintains salt and water balance of plasma Kidney anatomy Renal cortex Renal pelvis Renal medulla Cortex Ureter Medulla
Collin County Community College RENAL PHYSIOLOGY
 Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
Collin County Community College BIOL. 2402 Anatomy & Physiology WEEK 12 Urinary System 1 RENAL PHYSIOLOGY Glomerular Filtration Filtration process that occurs in Bowman s Capsule Blood is filtered and
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST
 014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
014 Chapter 14 Created: 9:25:14 PM CST Student: 1. Functions of the kidneys include A. the regulation of body salt and water balance. B. hydrogen ion homeostasis. C. the regulation of blood glucose concentration.
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology)
 Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
Urinary System (Anatomy & Physiology) IACLD CME, Monday, February 20, 2012 Mohammad Reza Bakhtiari, DCLS, PhD Iranian Research Organization for Science & Technology (IROST) Tehran, Iran The Urinary System
General Anatomy of Urinary System
 General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
General Anatomy of Urinary System URINARY SYSTEM ORGANS Kidneys (2) Ureters (2) Urinary bladder Urethra KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Control blood volume and composition KIDNEY FUNCTIONS Filter blood plasma, eliminate
Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate
 Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
Renal physiology The kidneys Allow us to live on dry land. Body fluid volume is small (~5L (blood + serum)) Composition can change rapidly e.g. due to increase in metabolic rate Kidneys maintain composition
April 08, biology 2201 ch 11.3 excretion.notebook. Biology The Excretory System. Apr 13 9:14 PM EXCRETORY SYSTEM.
 Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Biology 2201 11.3 The Excretory System EXCRETORY SYSTEM 1 Excretory System How does the excretory system maintain homeostasis? It regulates heat, water, salt, acid base concentrations and metabolite concentrations
Nephron Anatomy Nephron Anatomy
 Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Kidney Functions: (Eckert 14-17) Mammalian Kidney -Paired -1% body mass -20% blood flow (Eckert 14-17) -Osmoregulation -Blood volume regulation -Maintain proper ion concentrations -Dispose of metabolic
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1
 Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Excretory Lecture Test Questions Set 1 1. The separation and ejection of metabolic wastes, usually in aqueous solution, is: a. reabsorption b. secretion c. filtration d. excretion e. endocrinology 2. Besides
Nephron Function and Urine Formation. Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S
 Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
Nephron Function and Urine Formation Ms. Kula December 1, 2014 Biology 30S The Role of the Nephron In order for the body to properly function and maintain homeostasis, the amount of dissolved substances
1. Urinary System, General
 S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
S T U D Y G U I D E 16 1. Urinary System, General a. Label the figure by placing the numbers of the structures in the spaces by the correct labels. 7 Aorta 6 Kidney 8 Ureter 2 Inferior vena cava 4 Renal
Urine Formation. Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages Urine Formation. Glomerular Filtration 4/24/2016
 Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urine Formation Urinary Physiology Urinary Section pages 9-17 Filtrate Blood plasma minus most proteins Urine
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Kidney Function Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Endocrine functions regulates
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015
 RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
RNPDC CCNP Anatomy and Physiology: Renal System Pre-Quiz 2015 1. In which abdominal cavity do the kidneys lie? a) Peritoneum. b) Anteperitoneal. c) Retroperitoneal. d) Parietal peritoneal 2. What is the
organs of the urinary system
 organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
organs of the urinary system Kidneys (2) bean-shaped, fist-sized organ where urine is formed. Lie on either sides of the vertebral column, in a depression beneath peritoneum and protected by lower ribs
URINARY SYSTEM CHAPTER 28 I ANATOMY OF THE URINARY SYSTEM. Student Name
 Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Student Name CHAPTER 28 URINARY SYSTEM L iving produces wastes. Wherever people live or work or play, wastes accumulate. To keep these areas healthy, there must be a method of disposing of these wastes
Human Reproductive System
 Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Human Reproductive System I. The male reproductive anatomy is a delivery system for sperm. A. The male s external reproductive organs consist of the scrotum and penis. 1. The penis is the external organ
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra
 Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System kidneys, ureters, bladder & urethra Filters blood removes waste products conserves salts, glucose, proteins, nutrients and water Produces urine Kidney Function Endocrine functions regulates
Urinary System. Chapter 17 7/19/11. Introduction
 7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
7/19/11 Chapter 17 Urinary System Introduction A. The urinary system consists of two kidneys that filter the blood, two ureters, a urinary bladder, and a urethra to convey waste substances to the outside.
Urinary System Review Questions:
 Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Urinary System Review Questions: 1. This system would be lined with what type of membrane? 2. What type of epithelial tissue would line the opening of the urethra (the exit of the tract)? 3. What type
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion. The Kidneys
 Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
Unit #4 Waste and Excretion The Kidneys Renal Hilus (Hilus) the doorway of the kidney Ureter leaves this region blood and lymphatic vessels enter and exit here Renal Capsule (Capsule) smooth fibrous tissue
A. Incorrect! The urinary system is involved in the regulation of blood ph. B. Correct! The urinary system is involved in the synthesis of vitamin D.
 Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Human Anatomy - Problem Drill 22: The Urinary System Question No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the functions of the urinary system is not correct? Question #01 (A) The urinary system
Other Factors Affecting GFR. Chapter 25. After Filtration. Reabsorption and Secretion. 5 Functions of the PCT
 Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Other Factors Affecting GFR Chapter 25 Part 2. Renal Physiology Nitric oxide vasodilator produced by the vascular endothelium Adenosine vasoconstrictor of renal vasculature Endothelin a powerful vasoconstrictor
Chapter 17: Urinary System
 Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
Introduction Chapter 17: Urinary System Organs of the Urinary System REFERENCE FIGURE 17.1 2 kidneys filters the blood 2 ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder Urinary bladder
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom
 1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
1. Both asexual and sexual reproduction occur in the animal kingdom Asexual reproduction involves the formation of individuals whose genes all come from one parent. There is no fusion of sperm and egg.
Kidney Structure. Renal Lobe = renal pyramid & overlying cortex. Renal Lobule = medullary ray & surrounding cortical labryinth.
 Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Structure Capsule Hilum ureter renal pelvis major and minor calyxes renal and vein segmental arteries interlobar arteries arcuate arteries interlobular arteries Medulla renal pyramids cortical/renal
Kidney Functions Removal of toxins, metabolic wastes, and excess ions from the blood Regulation of blood volume, chemical composition, and ph
 The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
The Urinary System Urinary System Organs Kidneys are major excretory organs Urinary bladder is the temporary storage reservoir for urine Ureters transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder Urethra
Nephron Structure inside Kidney:
 In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
In-Depth on Kidney Nephron Structure inside Kidney: - Each nephron has two capillary regions in close proximity to the nephron tubule, the first capillary bed for fluid exchange is called the glomerulus,
To General Embryology Dr: Azza Zaki
 Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
Introduction To General Embryology The Human Development is a continuous process that begins when an ovum from a female is fertilized by a sperm from a male. Cell division, growth and differentiation transform
The Urinary System. Jim Swan
 The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
The Urinary System Jim Swan These slides are from class presentations, reformatted for static viewing. The content contained in these pages is also in the Class Notes pages in a narrative format. Best
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Osmoregulation and Excretion
 Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
Animal Life and Excretion Harder for multicellular organisms Internal circulation Coordination, information transfer Structural maintenance Movement Maintenance of homeostatic internal environment 15 July
Kidney Physiology. Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed
 Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
Kidney Physiology Mechanisms of Urine Formation TUBULAR SECRETION Eunise A. Foster Shalonda Reed The purpose of tubular secrection To dispose of certain substances that are bound to plasma proteins. To
