ABDOMEN. 2. The highest branch of the abdominal aorta is: (a) R suprarenal a (b) Coeliac trunk (c) L renal a (d) L gonadal a (e) SMA
|
|
|
- Shanna Wilcox
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABDOMEN 1. The duodenum: (a) is a retroperitoneal structure (b) is 25cm long (c) lies between the levels of L2-L4 (d) in its fourth part lies to the R of the aorta (e) all of the above 2. The highest branch of the abdominal aorta is: (a) R suprarenal a (b) Coeliac trunk (c) L renal a (d) L gonadal a (e) SMA 3. Which lymph nodes drain the lower anal canal (a) Superficial inguinal (b) External iliac (c) Deep inguinal (d) Para-aortic (e) Internal iliac 4. Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein drains into (a) L gastric vein (b) Portal vein (c) Splenic vein (d) Superior mesenteric vein (e) IVC 5. Which is not true of the stomach (a) Completely invested by peritoneum (b) Cardia at T12 (c) Pyloric opening at L1 (d) Aorta to the left of the lesser curve (e) Supplied by the branches of the coeliac trunk 6. Appendix (a) Usually lies retrocaecal in health (b) Drains to inguinal nodes (c) Has no mesentery (d) Has a tip constant in relation to the caecum (e) Opens into the caecum 2 cm below the ileocaecal valve
2 7. Which does not pass through the transpyloric plane? (a) Splenic vein (b) Tips of the 9 th costal cartilage (c) Lower border of L1 (d) Spleen (e) SMA 8. All of the following are veins which drain the stomach except (a) Gastroepiploic (b) Gastroduodenal (c) Right gastric (d) Left gastric (e) Short gastric 9. The main vessel supplying the body of the pancreas is the (a) Superior pancreaticoduodenal a (b) Splenic a (c) Left gastric a (d) Left gastroepiploic (e) Inferior pancreaticoduodenal 10. Regarding the abdominal aorta (2 CORRECT) (a) Renal arteries originate at T12 (b) Splenic vein crosses the aorta just below the SMA origin (c) Surface marking from a point just above the transpyloric plane to a point to the left of the umbilicus (d) Lies to the right of the IVC (e) Enters the abdomen at the level of T10 (f) Gives off renal arteries at L2 (g) Is crosses anteriorly by the tail of the pancreas (h) Divides over the sacrum into 2 common iliac aa 11. Regarding the testicular blood supply (a) Division of the testicular a results in testicular infarction (b) Testicular artery has numerous anastomoses with the cremasteric a (c) Pampiniform plexus is a superficial plexus surrounding the testicular a 12. Which of the following is untrue about the appendix (a) It has a base constant in relation to the caecum (b) It has its own mesentery (c) It is formed by teneae coli convergence (d) Varies in length from 2 to 25cm (e) It always lies in retro-ileal position with disease
3 13. The ureters (a) Widest in diameter at the PUJ (b) Innervated by sympathetic n T12-L1 (c) Lie lateral to the tips of the lumbar transverse processes (d) Depend on innervation from the pelvis for peristalsis (e) None of the above are true 14. The ureters (a) Cross the gonadal vessels (b) Cross over the vas deferens (c) Are crossed by the genitofemoral n (d) Pass under the cover of the psoas (e) Lie lateral to the lumbar transverse processes (f) Do not cross the SI joint 15. The internal anal sphincter (a) Is skeletal muscle (b) Has longitudinal fibres (c) Has no bony attachments 16. Referred pain from pancreatitis is at what level (a) T7,8 (b) L1,2 (c) T3,4 (d) T12,L1 17. Superficial inguinal lymph nodes drain all of the following except (a) Anterior thigh (b) Base of penis (c) Testis 18. Which is true of colon (a) Ascending is longer than descending (b) Only part suspended on mesentery is transverse (c) Marginal artery is weakest at hepatic flexure (d) Lymphatic drainage is via superior and inferior mesenteric LN 19. Where does the appendix mostly lie in health (a) Retro-ilial (b) Retrocaecal
4 20. With regard to the blood supply of the rectum and anus: (a) It is principally the inferior rectal artery (b) The anal canal is a site of porto-systemic anastomoses (c) The veins do not correspond with the arteries (d) The IMA changes to the superior rectal artery at L3 (e) The vessels do not supply the full thickness of the anal wall 21. Lymph drainage of testes (a) The deep inguinal nodes (b) The mediastinal nodes (c) The para-aortic nodes (d) The pectoral group of axillary nodes (e) The external iliac nodes 22. Lymph drainage of scrotum (a) The superficial inguinal nodes (b) The internal iliac nodes (c) The deep inguinal nodes (d) The external iliac nodes (e) Non of the above 23. Regarding radiology of GIT (a) The terminal ileum can be identified by haustrations (b) Haustrations represent teniae coli (c) Air fluid levels are diagnostic of large bowel obstruction (d) Gas should always be visible in the rectum (e) Small bowel is always visible on a normal AXR 24. Regarding the kidneys (a) Each weigh around 340g (b) The left kidney lies below the transpyloric plane (c) The iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves lie in front of the posterior surface of the kidney (d) Each kidney has 6 segments (e) The hilum is separated from the peritoneum on the right side by the 3 rd part of duodenum 25. The lumbar plexus (a) Is immediately medial to IVC (b) Is formed from the posterior rami (c) Is derive from the last 3 lumbar nn (d) The femoral nerve is formed from L2,3 and 4 (e) The pudendal nerve is a branch of the lumbar plexus
5 26. Regarding the ureters (a) They exit the hilum behind the renal artery (b) They are a continuation of the renal pelvis which is formed by the union of 10 major calyces (c) They are each 40cm long (d) On an XR KUB they run just lateral to the transverse process of the lumbar vertebrae (e) The lower ends are supplied by the ureteric branch of the renal artery (f) Derives its sole supply from the ureteric branch of the renal artery (g) Begins at the level of the tip of the 9 th costal cartilage (h) Run posteriorly to the internal iliac artery (i) Is more superficial than the ductus deferens in males 27. Regarding the innervation of the bladder (a) Parasympathetics are via pelvic splanchnic nn (b) Sympathetic innervation comes from L3 and L4 segments of the cord (c) Sympathetic fibres are excitatory to the bladder (d) Bladder distension sensation travels with the sympathetics (e) Bladder pain only travels with the superior ypogastric plexus 28. All of the following are relations to the body of the pancreas except (a) L crus of diaphragm (b) L psoas (c) L kidney hilum (d) Bile duct (e) Lesser sac 29. With regard to the spinal cord blood supply (a) There are 2 anterior spinal arteries (b) The anterior spinal artery arises from the vertebral a (c) The posterior spinal artery is singular (d) The posterior spinal artery arises from the posterior superior cerebellar (e) The anterior spinal artery retains a uniform size throughout its length 30. Which is incorrect (a) The inguinal canal of the female contains the round ligament of the uterus (b) The deep inguinal ring is an opening in transversus muscle (c) The spermatic cord in the male emerges from the deep ring (d) The inguinal canal lies above the medial half of the inguinal lig (e) The roof of the inguinal canal is formed by the lower edges of internal oblique and transversus muscles
6 31. Regarding the kidneys (a) The hilum of the left is just below that of the right (b) The hilum faces medially and somewhat posteriorly (c) The long axis is parallel with the lateral border of the psoas (d) The perinephric fat is surrounded by renal fascia (e) The renal artery lies in front of the renal vein 32. Concerning the colon (a) Appendices epiploicae are most frequent on the ascending colon (b) The transverse colon is normally shorter than the descending colon (c) The blood supply includes the SMA (d) Parasympathetic supply does not include the X (e) None of the above 33. Regarding the left kidney (a) Anterior relations include the spleen (b) Posteriorly lies the costodiaphragmatic recess (c) The suprarenal gland lie within the renal fascia (d) The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve lies posteriorly (e) The median arcuate ligament lies posteriorly 34. The pelvic floor (a) Consists of ischiococcygeus, iliococcygeus ad pubococcygeus (b) Muscles have significant insertion into the sacrum (c) Creates a gutter that slopes down and back (d) Has the anococcygeal raphe a superficial part (e) None of the above 35. The bladder (a) Main motor innervation via parasympathetic fibres (b) In its non-distended state has 1/5 of it volume in the abdominal cavity (c) Is connected via the pubovesical ligaments to the superior aspect of the pubic bone (d) Has the openings of the urethral orifice 5cm apart in its non-distended state (e) Receives its major blood supply from the obturator artery 36. With regards to the spleen (a) Innervated by the coeliac plexus with the sympathetic and parasympathetic fibres (b) Lymphatic drainage is through retropancreatic and coeliac nodes (c) There is a colonic resonance found on percussion over the organ (d) It is developed from the ventral mesogastrium (e) Its hilum lies in the angle between the stomach and the right kidney
7 37. With regard to the blood supply of the liver (a) The right branch of the hepatic artery normally passes in front of the common hepatic duct (b) The hepatic artery sometimes arises from the SMA of aorta (c) The hepatic artery, portal vein and accompanying tributaries of the hepatic ducts lie together in the sinusoids (d) There are 2 main hepatic veins (e) Arterial and portal venous blood becomes mixed in the canals 38. The ilioinguinal nerve (a) Enters the inguinal canal though the deep ring (b) Supplies motor fibres to internal oblique and transversus (c) Has roots from L1 and L2 (d) Supplies sensory fibres to the anterior 2/3 of the scrotum (e) Has a collateral branch the iliohypogastric 39. The ureters (a) The lower 1/3 are supplied by gonadal arteries (b) They are supplied by somatic fibres T11 L2 (c) They are superficial to uterine arteries in females (d) The apex of the sigmoid mesocolon is a guide to position of left ureter (e) The pelvic part accounts for a quarter of its length 40. The porta hepatis is on the posterior surface (a) at the porta hepatis, the vessels lie in order: vein, duct, artery (posterior to anterior) (b) there is no arterial connection between the left and right halves of the liver (c) parasympathetic nerves synapse in the coeliac ganglia (d) the portal triad contains the hepatic artery, central vein and bile ductules 41. Regarding the spleen, which is false (a) It weighs 7 oz (b) Lymph drains to pancreaticosplenic nodes (c) It lies between the 9 th and 11 th ribs (d) Its lower pole often extends beyond the MAL (e) It is supplied by sympathetic fibres only 42. The anterior abdominal wall (a) Is supplied by lower and subcostal nerves T5-L1 (b) Is divided for clinical purposes into 6 regions (c) Contains rectus abdominis which is formed by fusion of external oblique, internal oblique and transversus abdominis (d) Contains transversus abdominis which arises from the medial 1/3 of the inguinal ligament (e) Contains the rectus sheath which is derived from the aponeurosis of external oblique
8 43. Regarding CBD all are true except (a) Opens into the posteromedial wall of the 3 rd part duodenum (b) Is approximately 8cm long (c) Upper 1/3 lies in the free edge of the lesser omentum (d) The middle 1/3 runs behind the 1 st part of the duodenum (e) Lower 1/3 grooves the back of the head of the pancreas 44. The ureter (a) On Xray lies lateral to tips of transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae (b) Runs down on quadratus lumborum (c) Is intraabdominal (d) Passes over the SIJ to enter pelvis (e) On the right is in front of the duodenum 45. the abdominal aorta (a) left renal vein lies between the origins of coeliac trunk and SMA (b) renal arteries arise at L1 (c) body of the pancreas lies in front of the coeliac trunk (d) gives off 5 lumbar aa (e) gives off the CIA at L3 46. Lymph from the perineal region drains initially to the (a) Paraaortic nodes (b) Rectal nodes (c) Deep inguinal nodes (d) Medial group of superficial inguinal nodes (e) Lateral group of superficial inguinal nodes 47. The rectum (a) Is continuous with sigmoid colon at the level S3 (b) Has an incomplete outer later of longitudinal muscle (c) Is attached to mesentery (d) Has a small amount of lymphatic drainage to inguinal LN (e) Is principally supplied by branches of IIA 48. The duodenum (a) Is retroperitoneal except for the 4 th part (b) IVC is behind 2 nd part (c) 2 nd part lies alongside the head of the pancreas (d) inferior border of the 4 th part lie at the origin of the IMA (e) ligament of Trietz marks the opening of the bile duct into the duodenum
9 49. With respect to the blood supply of the gut (a) Coeliac trunk supplies the 3 rd part of duodenum (b) The SMA arises at L2 (c) SMA supplies the hepatic flexure (d) IMA supplies the hind gut to anus (e) IMV drains directly into IVC 50. The first part of the duodenum (a) Lies at the level of L2 in the supine body (b) Is approximately 10cm long in adults (c) Partially overlies the right crus of the diaphragm and psoas muscle (d) Is entirely retroperitoneal (e) Receives the common opening of the bile duct on its posteromedial wall 51. The pancreas (a) Has no anatomical relationship with the spleen (b) Lies over the IVC at L2 (c) Receives its blood supply from the SMA (d) Receives no sympathetic nerve supply (e) Passes anterior to the duodenum 52. All of the following structures pass though the deep inguinal ring except (a) Pampiniform plexus (b) Ilioinguinal nerve (c) Genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve (d) Processus vaginalis (e) External spermatic fascia 53. Directly in front of the right kidney lies (a) 2 nd part of duodenum (b) portal vein (c) bile duct (d) splenic flexure of colon (e) IVC 54. All are true of the spleen except (a) It is related to the 9, 10, 11 th ribs (b) its blood supply is from a branch of the coeliac trunk (c) the splenic vessels are contained in the lienorenal ligament (d) its anterior relation include the head of the pancreas (e) it has a notched anterior border
10 55. The spleen (a) Has a lower pole which normally projects forward to the anterior axillary line (b) Lies between the 8 th and 10 th rib (c) Has a long axis lying in the line of the 9 th rib (d) As it enlarges, glides in contact with the anterior abdominal wall in front of the splenic flexure (e) When palpable on abdominal examination is identified by being resonant to percussion 56. Which is false regarding the duodenum (a) The duodenal cap has plicae circulares which are often evident on Xray (b) The 3 rd part may be compressed by the SMA (c) The 2 nd part lies at the level of L2 in cadavers (d) The duodenal cap lies upon the bile duct, hepatic artery and portal vein (e) The accessory pancreatic duct opens into it proximal to the ampulla of Vater 57. With regard to the cutaneous innervation of the thorax and abdomen (a) Above the 2 nd rib, the skin is supplied by the cervical plexus (C4) (b) Loss of a single spinal segment will produce a sensory deficit (c) It is supplied segmentally by the anterior primary rami of T1 to L1 (d) T8 supplies the skin at the level of the umbilicus (e) The lower 8 thoracic nerves pass beyond the costal margin to supply the skin of the abdominal wall 58. The anterior relations of the abdominal aorta include (a) The lateral arcuate ligament (b) The splenic vein inferior to the SMA (c) The left renal vein inferior to the IMA (d) The parietal peritoneum inferior to the duodenum (e) The sympathetic trunk 59. The ureter (a) Passes anterior to the genitofemoral nerve (b) Develops from the metanephric cap (c) Is represented by the dermatome L2 (d) In the male is crossed anteriorly by the ductus deferens (e) Passes anterior to the uterine artery in females 60. The abdominal aorta is crosses anteriorly by (a) Left renal artery (b) IMA (c) Left renal vein (d) Right gonadal artery (e) Right renal vein
11 61. Which is not a branch of the IIA (a) Internal pudendal (b) Superior gluteal (c) Uterine (d) Obturator (e) Superior vesicle 62. Which is not true of the abdominal aorta (a) Begins at T12 (b) Ends at L5 (c) Inclines to the left (d) Direct continuation is median sacral artery (e) Gives off 4 pairs of lumbar arteries 63. Which structure in the inguinal canal is not part of the spermatic cord (a) Testicular artery (b) Genital branch of the genitofemoral n (c) Ilioinguinal n (d) Ductus deferens (e) Cremasteric artery 64. Pick the boundary of the inguinal canal (a) Floor lacunar ligament (b) Posterior wall inguinal ligament (c) Superficial ring opening in internal oblique (d) Anterior wall conjoint tendon (e) Roof external oblique 65. Which is true of the coeliac trunk and its branches (a) Inferior pancreaticoduodenal artery encircles the head of the pancreas (b) Left gastric artery supplies the stomach only (c) Gastroduodenal artery runs in front of the 1 st part of the duodenum (d) Hepatic artery runs in front of the portal vein (e) Right gastroepiploic artery runs along the lesser curvature of the stomach 66. Which is true of the SMA and its branches (a) Right colic artery is the main supply of the caecum (b) SMA runs anterior to the 1 st part of the duodenum (c) Right colic artery passes behind the right ureter (d) SMA arises from the aorta at L2 (e) Main trunk of the SMA ends at the level of Meckel s diverticulum
12 67. Which is true of the IMA and its branches (a) IMA ends as the superior rectal artery (b) The main trunk crosses the left ureter, but its branches pass behind it (c) It arises from the aorta at the level of L2 (d) The descending branch of the left colic supplies the sigmoid only (e) There is very little anastomosis between the branches 68. Direct tributaries of the portal vein include all except (a) Right gastric vein (b) Short gastric vein (c) Splenic vein (d) Superior pancreaticoduodenal vein (e) Left gastric vein 69. Which is the correct porto-systemic anastomosis (a) Portal tributary of inferior mesenteric vein, systemic tributary of the internal iliac vein (b) Portal periumbilical vein, systemic phrenic vein (c) Portal intrahepatic portal branches, systemic azygous vein (d) Portal left gastric vein, systemic IVC via oesophageal veins (e) Portal middle rectal vein, systemic inferior rectal vein 70. Which is not true of the surface markings of the liver (a) Lies below the 7-11 th ribs in the right MAL (b) Highest point on the right is the 5 th rib (c) Superior surface crosses the xiphisternal joint (d) Inferior margin lies level with the right costal margin in most cases (e) Highest point on left is the 6 th IC space 71. Which is the correct order of the structures in the porta hepatis (ant post) (a) Right and left hepatic arteries right and left portal veins right and left hepatic ducts (b) R/L portal veins, R/L hepatic ducts, R/L hepatic arteries (c) R/L hepatic ducts, cystic duct, R/L hepatic arteries, R/L portal veins (d) R/L hepatic ducts, R/L hepatic arteries, cystic duct, R/L portal veins (e) R/L hepatic ducts, R/L hepatic arteries, R/L portal veins 72. Which is true of the liver (a) Protected from ischaemia by good anastomosis between R & L lobes (b) Divided functionally into right and left lobes along the falciform ligament (c) Drains into 3 hepatic veins which have a long extrahepatic course (d) Left lobe may be supplied by a branch of the left gastric artery (e) Caudate lobe has no connections with the right lobe
13 73. Which is true of the relations of the kidneys (a) Left hilum lies just below the transpyloric plane (b) Middle colic artery crosses the lower pole of the right kidney (c) The structures in the hilum from front to back are vein, artery, ureter (d) Vertical axis lies in the same axis at the vertebral column (e) Right adrenal gland lies medial to the upper pole 74. Which does not cross the ureter (a) Right colic artery (b) Gonadal vessels (c) Apex of the sigmoid mesocolon (d) Ileocolic artery (e) IMA 75. Which is true of the ureter s blood supply (a) Poor anastomosis makes blood supply easily endangered (b) Receives supply from the gonadal vessels (c) CIA supplies only the most distal portion (d) Distal portion receives its supply from the posterior division of the IIA (e) Renal artery provides no blood supply 76. Right adrenal gland (a) Lies on the medial surface of the upper pole of right kidney (b) Lies on the quadrate lobe of liver (c) Adrenal vein drains into right renal vein (d) Is supplied by a branch of the renal artery only (e) Is separated from the kidney by renal fascia 77. Which is true of the spleen (a) Lower pole extends forwards to the anterior axillary line (b) Long axis lies in the line of the 10 th rib (c) Medial border is notched (d) Kidney lies anterior to the hilum (e) Gastrosplenic ligament runs from the lower pole to the lesser curvature of stomach 78. Which is the correct relation of the duodenum (a) 1 st part behind IVC (b) 2 nd part anterior to the hilum of right kidney (c) 3 rd part crossed by the IMA (d) 3 rd part level of L2 (e) all but last 2cm is retroperitoneal
14 79. Which of the structures is not retroperitoneal (a) Kidney (b) Adrenal gland (c) Cisterna chyli (d) Spleen (e) Pancreas 80. Which is not a structure in the transpyloric plane (a) Pancreas (b) SMA origin (c) Fundus of gallbladder (d) Tip of 9 th costal cartilage (e) Lower pole of right kidney
15 ANSWERS 1. B 2. B 3. A 4. B 5.?B/D 6. E 7. D 8. B 9. B 10. C & F 11. C 12. E 13. E 14.? 15. C 16. A 17. C 18. D 19. A 20. B C 22. A 23. B 24. A 25. D 26. A & G 27. A 28. D 29. B 30. B 31. C 32. C 33. A 34. A 35. A 36. B 37. B 38. B 39. D 40. C 41. D 42. C 43. A 44. D 45. C 46. D 47. A 48. C 49. C 50. C 51. B 52. B 53. A 54. D 55. D 56. A 57. A 58. D 59. A 60. C 61. B 62. B 63. C 64. A 65. D 66. E 67. A 68. B 69. A 70. E 71. E 72. D 73. C 74. E 75. B 76. E 77. B 78. B 79. D 80. E
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The abdominal Esophagus, Stomach and the Duodenum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Viscera of the abdomen Abdominal esophagus: Terminal part of the esophagus The stomach Intestines: Small and Large
The posterior abdominal wall. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
The posterior abdominal wall Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar vertebrae and discs. Muscles opsoas, quadratus lumborum, iliacus, transverse, abdominal wall
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS
 BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
BLOCK IV: OFFICIAL BODY PARTS LIST FOR ANTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL AND ABDOMINAL CONTENTS External oblique muscle Muscular portion Aponeurotic portion Superficial inguinal ring Lateral (inferior) crus Medial
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
GI module Lecture: 9 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To list structures forming posterior abdominal wall. To follow aorta & its main branches. To describe IVC & its main tributaries. To list nerves of posterior
د. عصام طارق. Objectives:
 GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 5 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe anatomy of stomach, duodenum & pancreas. To list their main relations. To define their blood & nerve supply. To list their lymph drainage. To
Pancreas & Biliary System. Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila
 Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Pancreas & Biliary System Dr. Vohra & Dr. Jamila 1 Objectives At the end of the lecture, the student should be able to describe the: Location, surface anatomy, parts, relations & peritoneal reflection
Anatomy of the Large Intestine
 Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Large intestine Anatomy of the Large Intestine 2 Large Intestine Extends from ileocecal valve to anus Length = 1.5-2.5m = 5 feet Regions Cecum = 2.5-3 inch Appendix= 3-5 inch Colon Ascending= 5 inch Transverse=
Duodenum retroperitoneal
 Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Duodenum retroperitoneal C shaped Initial region out of stomach into small intestine RETROperitoneal viscus Superior 1 st part duodenal cap ; moves upwards and backwards to lie on the R crura medial to
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 4 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577335/ Section 4 Abdomen (31 cards) Plate 4-1 Bony Framework of Abdomen 1.1 Costal cartilages 1.2 Iliac crest 1.3
Accessory Glands of Digestive System
 Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Accessory Glands of Digestive System The liver The liver is soft and pliable and occupies the upper part of the abdominal cavity just beneath the diaphragm. The greater part of the liver is situated under
Anatomy of the renal system. Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi
 Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy of the renal system Professor Nawfal K. Al-Hadithi Objectives To describe the posterior abdominal wall To identify the main anatomical landmarks of the kidneys & ureters To describe the suprarenal
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen
 Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
Anatomy: Know Your Abdomen Glossary Abdomen - part of the body below the thorax (chest cavity); separated by the diaphragm. Anterior - towards the front of the body. For example, the umbilicus is anterior
To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis.
 GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
GI anatomy Lecture: 6 د. عصام طارق Objectives: To describe the liver. To list main structures in porta hepatis. To define portal system & portosystemic anastomosis. To list parts of biliary system. To
Posterior Abdominal wall-
 Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Structures of posterior abdominal wall: o Bony boundaries: 5 lumber vertebra and their intervertebral disc, iliac fossa and iliac crest. o Muscles: psoas major, quadrates lumborum, transversus abdominis,
Dr. Zahiri. In the name of God
 Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
Dr. Zahiri In the name of God small intestine = small bowel is the part of the gastrointestinal tract Boundaries: Pylorus Ileosecal junction Function: digestion and absorption of food It receives bile
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES. Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga
 ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
ANATOMY OF THE SMALL & LARGE INTESTINES Semester 1, 2011 A. Mwakikunga LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. List the parts and anatomical regions of the small and large intestines 2. State anatomical relations of the
Benha University. Faculty of Medicine. Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination. (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax)
 1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
1 Benha University Faculty of Medicine Anatomy Department Course code (MED 0701) Model answer of Anatomy examination (Abdomen,Pelvis and Thorax) 1 st year 2 nd term Date :18 /5 /2013 2 I-Short account
Small Plicae Circularis. Short Closely packed together. Sparse, completely absent at distal part Lymphoid Nodule
 Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
Intestines Differences Between Jejunum and Ileum Types Jejunum Ileum Color Deeper red Paler pink Calibre Bigger Smaller Thickness of wall Thick and Heavy Thin and Lighter Vascularity Highly vascularised
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER
 THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
THE ABDOMEN SUPRARENAL GLANDS KIDNEY URETERS URINARY BLADDER THE SUPRARENAL GLANDS The suprarenal (adrenal) glands lie immediately superior and slightly anterior to the upper pole of either kidney. Golden
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System
 Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
Lab Monitor Images Dissection of the Abdominal Vasculature + Lower Digestive System Stomach & Duodenum Frontal (AP) View Nasogastric tube 2 1 3 4 Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR
 BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
BY DR NOMAN ULLAH WAZIR The stomach (from ancient Greek word stomachos, stoma means mouth) is a muscular, hollow and the most dilated part of the GIT. It starts from the point where esophagus ends. It
1 Right & left Hepatic ducts Gastric Impression of spleen
 Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Pancreatic Model 1 Right & left Hepatic ducts 14 Gastric Impression of spleen 2 Common hepatic duct 15 Renal Impression of spleen 3 Cystic Duct 16 Colic Impression of spleen 4 Common Bile Duct 17 Splenic
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space
 Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Abdomen. Retroperitoneal space Abdominal cavity The space bounded by: Anterolateral abdominal wall Posterior abdominal wall Diaphragm Pelvic walls and pelvic floor. Subdivided into: True abdominal cavity
Preview from Notesale.co.uk Page 1 of 34
 Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Abdominal viscera and digestive tract Digestive tract Abdominal viscera comprise majority of the alimentary system o Terminal oesophagus, stomach, pancreas, spleen, liver, gallbladder, kidneys, suprarenal
Pancreas and Biliary System
 Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
Pancreas and Biliary System Please view our Editing File before studying this lecture to check for any changes. Color Code Important Doctors Notes Notes/Extra explanation Objectives At the end of the lecture,
The peritoneum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website:
 The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
The peritoneum Prof. Oluwadiya KS, MBBS, FMCS(Orthop) Website: http://oluwadiya.com The peritoneum Serous membrane that lines the abdominopelvic cavity and invests the viscera The largest serous membrane
Omran Saeed. Mohammad Al-muhtaseb. 1 P a g e
 13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
13 Omran Saeed Mohammad Al-muhtaseb 1 P a g e Posterior abdominal wall - The diaphragm separates between thoracic cavity and abdominal cavity. Structures of posterior abdominal wall: (below diaphragm)
Dana Alrafaiah. - Amani Nofal. - Ahmad Alsalman. 1 P a g e
 - 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
- 2 - Dana Alrafaiah - Amani Nofal - Ahmad Alsalman 1 P a g e This lecture will discuss five topics as follows: 1- Arrangement of pelvic viscera. 2- Muscles of Pelvis. 3- Blood Supply of pelvis. 4- Nerve
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm. Prof Oluwadiya KS
 The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
The Thoracic wall including the diaphragm Prof Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Components of the thoracic wall Skin Superficial fascia Chest wall muscles (see upper limb slides) Skeletal framework Intercostal
Inferior Pelvic Border
 Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
Pelvis + Perineum Pelvic Cavity Enclosed by bony, ligamentous and muscular wall Contains the urinary bladder, ureters, pelvic genital organs, rectum, blood vessels, lymphatics and nerves Pelvic inlet (superior
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution,
 SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
SUBJECTS 2nd year, 1st semester I. 1. Primitive gut - limits, derivatives 2. Foregut -limits, evolution, derivatives 3. Midgut -limits, evolution, derivatives 4. Hindgut- limits, evolution, derivatives
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE. Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC
 Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Anatomy of the SMALL INTESTINE Dr. Noman Ullah Wazir PMC SMALL INTESTINE The small intestine, consists of the duodenum, jejunum, and illium. It extends from the pylorus to the ileocecal junction were the
Group of students. - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e
 - 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
- 14 - Group of students - Rawan almujabili د. محمد المحتسب - 1 P a g e Nerves of the posterior abdominal wall The spinal cord gives off spinal nerves between the vertebrae. In the abdomen, through the
It passes through the diaphragm at the level of the 10th thoracic vertebra to join the stomach
 The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
The esophagus is a tubular structure (muscular, collapsible tube ) about 10 in. (25 cm) long that is continuous above with the laryngeal part of the pharynx opposite the sixth cervical vertebra The esophagus
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera.
 Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Peritoneum: Def. : It is a thin serous membrane that lines the walls of the abdominal and pelvic cavities and clothes the viscera. Layers of the peritoneum: 1. Outer Layer ( Parietal Peritoneum) : lines
Surface Anatomy. Location Shape Weight Role of Five Surfaces Borders Fissures Lobes Peritoneal Lig
 The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
The Liver Functions Bile production and secretion Detoxification Storage of glycogen Protein synthesis Production of heparin and bile pigments Erythropoiesis (in fetus) Surface Anatomy Location Shape Weight
Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER
 1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
1 Block 3: DISSECTION 2 CELIAC TRUNK, JEJUNUM/ILEUM, LARGE INTESTINE, DUODENUM, PANCREAS, PORTAL VEIN; MOBILIZATION OF THE LIVER Attempt to complete as much as you can of the dissection explained in the
-the stones will obstruct the common bile duct and it might also be precancerous. -so the best treatment is chlolycyctoctomy.
 At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
At the beginning this sheet includes the rest of last lecture s slides liver +gallbladder and the new lecture posterior abdominal wall and its vessels. We will start talking about Cholelithiasis -it means
Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal. - Dana AF
 - 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
- 10 - Bushra Arafa Zayed & Hanan Jamal - Dana AF - Mohammad Al Muhtaseb Notes: This sheet was written in the same order as the slides, and everything in the slides is mentioned in this sheet. Pictures
Abdomen: Introduction. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
Abdomen: Introduction Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Abdominopelvic Cavity Abdominal Cavity Pelvic Cavity Extends from the inferior margin of the thorax to the superior margin of the pelvis and the
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 17, 2014
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 17, 2014 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH
 ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
ABDOMINAL WALL & RECTUS SHEATH Learning Objectives Describe the anatomy, innervation and functions of the muscles of the anterior, lateral and posterior abdominal walls. Discuss their functional relations
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION. The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants:
 LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
LECTURE 11 & 12: ABDOMINAL VISCERA ABDOMINAL CONTENTS DIVISION The location of abdominal viscera is divided into 4 quadrants: - horizontal line across the umbilicus divides the upper quadrants from the
-Ensherah Mokheemer. -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e
 9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
9-9 -Ensherah Mokheemer -Shatha Al-Jaberi محمد المحتسب- 1 P a g e Small intestine has three regions: ( االثني عشر( The duodenum The jejunum The ileum Small intestine Duodenum: -c-shaped -The concavity
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities Please place your name and I.D. number on the back of the last page of this exam. You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics
ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA
 1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
1 ANATOMY OF PELVICAYCEAL SYSTEM -DR. RAHUL BEVARA 2 KIDNEY:ANATOMY OVERVIEW Kidneys are retroperitoneal, in posterior abdominal region, extending from T12 L3 Bean-shaped Right kidney is lower than left
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. October 16, 2015
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3 October 16, 2015 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) A. B. A B C. D. C D 2. Identify the structures. (2
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES
 Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
Lab 9 Abdomen MUSCLES External abdominal oblique continuous with the external intercostal muscle; its fibers point in a caudal direction as it moves anteriorly until it inserts on the linea alba via its
1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures would have been cut EXCEPT the:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 07, 1997. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTION 1-42. 1. A stab wound into the abdomen transected the hepatoduodenal ligament. Each of the following structures
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System
 Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
Gross Anatomy of the Urinary System Lecture Objectives Overview of the urinary system. Describe the external and internal anatomical structure of the kidney. Describe the anatomical structure of the ureter
[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013
![[ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013 [ANATOMY #12] April 28, 2013](/thumbs/86/93473883.jpg) Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Sympathetic chain : Sympathetic chain is each of the pair of ganglionated longitudinal cords of the sympathetic nervous system; extend from level of atlas (base of skull) till coccyx. It is paravertebral
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment. Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD
 Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
Peritoneal cavity. Infracolic compartment Assoc. prof. dr. S. Delchev, MD, PhD Infracolic compartment The infracolic compartment lies inferior to the transverse mesocolon and posterior to the greater omentum
The jejunum and the Ileum. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
The jejunum and the Ileum Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.siteled.com Introduction Introduction The small intestine (SI) comprises of the duodenum, jejunum and the ileum The jejunum is the second part
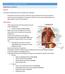
In the name ofgod. Abdomen 3. Dr. Zahiri
 In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
In the name ofgod Abdomen 3 Dr. Zahiri Peritoneum Peritoneum It is the serous membrane(a type of loose connective tissue and is covered by mesothelium) that lines the abdominal cavity. Extensions of the
Anatomy of the Thorax
 Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
Anatomy of the Thorax A) THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD
 CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
CARDIOVASCULAR DANIL HAMMOUDI.MD 18 Systemic Circulation Figure 19.19 Pulmonary Circulation Figure 19.18b 1. Thyroid gland 2. Trachea 3. Brachiocephalic 4. Common carotid 5. Internal jugular 6. Superior
-12. -Renad Habahbeh. -Dr Mohammad mohtasib
 -12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
-12 -Renad Habahbeh - -Dr Mohammad mohtasib The Gallbladder -The gallbladder has a body, a fundus (a rounded end), a neck, Hartmann s pouch before the neck and a cystic duct that meets the common hepatic
The Spleen. Dr Fahad Ullah
 The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
The Spleen BY Dr Fahad Ullah Spleen The spleen is an largest lymphoid organ shaped like a shoe that lies relative to the 9th and 11th ribs and is located in the left hypochondrium. Thus, the spleen is
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
musculoskeletal system anatomy nerves of the lower limb 1 done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer What is the importance of plexuses? plexuses provides us the advantage of a phenomenon called convergence
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall
 Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Nerves on the Posterior Abdominal Wall Lumbar Plexus The lumbar plexus, which is one of the main nervous pathways supplying the lower limb, is formed in the psoasmuscle from the anterior ramiof the upper
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER
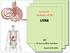 Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Lecture 02 Anatomy of the LIVER BY Dr Farooq Khan Aurakzai Dated: 02.01.2018 Introduction to Liver Largest gland in the body. 2 nd largest organ of the body. Weight approximately 1500 gm, and is roughly
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
Diaphragm and intercostal muscles Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skeletal System Adult Human contains 206 Bones 2 parts: Axial skeleton (axis): Skull, Vertebral column,
THE THORACIC WALL. Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column. Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages
 THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
THE THORACIC WALL Boundaries Posteriorly by the thoracic part of the vertebral column Anteriorly by the sternum and costal cartilages Laterally by the ribs and intercostal spaces Superiorly by the suprapleural
3 Circulatory Pathways
 40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
40 Chapter 3 Circulatory Pathways Systemic Arteries -Arteries carry blood away from the heart to the various organs of the body. -The aorta is the longest artery in the body; it branches to give rise to
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II
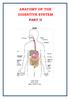 ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
ANATOMY OF THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM PART II 9.12.2014 Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs121.org Dr.Kaan Yücel http://fhs121.org Digestive system Part II 1. LIVER The liver is the largest gland in the body and,
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013
 Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Lecturer: Ms DS Pillay ROOM 2P24 25 February 2013 Thoracic Wall Consists of thoracic cage Muscle Fascia Thoracic Cavity 3 Compartments of the Thorax (Great Vessels) (Heart) Superior thoracic aperture
Al-Mohtaseb. Saba Alfayoumi. Mo Alfarra
 8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
8 Al-Mohtaseb Saba Alfayoumi Mo Alfarra For the comparison purposes refer to the last page where you can find a table that summarizes them. Enjoy Jejunum and Ileum -They're intraperitoneal and freely mobile
Perineum. done by : zaid al-ghnaneem
 Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Perineum done by : zaid al-ghnaneem Hello everyone, this sheet will talk about 2 nd Lecture which is Perineum but there are some slides and info from 1 st Lecture. Everything included Slides + Pics Let
Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1. BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Jhia Anjela D. Rivera 1 1 BS Biology, Department of Biology, College of Science, Polytechnic University of the Philippines DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Consists of the digestive tract (gastrointestinal
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT:
 YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, 1996. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT: A. The fibrous
YR 1 GROSS ANATOMY/EMBRYOLOGY UNIT EXAM 3 -- November 13, 1996. CHOOSE THE SINGLE BEST ANSWER FOR QUESTIONS 1-42. 1. Which of the following statements regarding the pericardium is NOT CORRECT: A. The fibrous
OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function
 The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
The root of the neck Jeff Dupree, Ph.D. e mail: jldupree@vcu.edu OBJECTIVE: To obtain a fundamental knowledge of the root of the neck with respect to structure and function READING ASSIGNMENT: Moore and
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System
 Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
Lecture 56 Kidney and Urinary System The adrenal glands are located on the superomedial aspect of the kidney The right diagram shows a picture of the kidney with the abdominal walls and organs removed
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine Anatomy Department REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM By Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Professor of Anatomy &embryology Perineum It is the diamond-shaped lower end of the trunk
Nasogastric tube. Stomach. Pylorus. Duodenum 1. Duodenum 2. Duodenum 3. Duodenum 4
 Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
Esophagus Barium Swallow Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach and Duodenum 4 year old Upper GI Nasogastric tube Stomach Pylorus Duodenum 1 Duodenum 2 Duodenum 3 Duodenum 4
thoracic cage inlet and outlet landmarks of the anterior chest wall muscles of the thoracic wall sternum joints ribs intercostal spaces diaphragm
 Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Thoracic Wall Lecture Objectives Describe the shape and outline of the thoracic cage including inlet and outlet. Describe the anatomical landmarks of the anterior chest wall. List various structures making
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale. Category or Criterion. Rationale or Comments (1) (2) (3) (4)
 Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
Table 2. First Generated List of Expert Responses. Likert-Type Scale Category or Criterion Anatomical Structures and Features Skeletal Structures and Features (1) (2) (3) (4) Rationale or Comments 1. Bones
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 3. September 13, 2012 B C
 STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
STRUTURL SIS OF MEIL PRTIE EXMINTION 3 September 13, 2012 PRT l. nswer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts). Lumbocostal trigone. Lateral femoral cutaneous n.. Lumbosacral
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen
 Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Exploring Anatomy: the Human Abdomen PERITONEUM AND PERITONEAL CAVITY PERITONEUM The peritoneum is a thin serous membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers, in variable amounts, the viscera within
Mousa Salah. Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib. 1 P a g e
 8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
8 Mousa Salah Dr. Mohammad Al. Mohtasib 1 P a g e In the previous lecture we talked about the peritoneum, and we said that the peritonium is a serous sac, and it consists of two layers, visceral and parietal.
Basic Body Structure
 Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Basic Body Structure The Cell All life consists of microscopic living structures called cells. They perform various functions throughout the body. All cells are similar in structure, but not identical.
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Femoral Triangle and Adductor Canal Femoral triangle Is a triangular depressed area located in the upper
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina. Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3
 Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Dr. Weyrich G07: Superior and Posterior Mediastina Reading: 1. Gray s Anatomy for Students, chapter 3 Objectives: 1. Subdivisions of mediastinum 2. Structures in Superior mediastinum 3. Structures in Posterior
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System
 Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
Day 5 Respiratory & Cardiovascular: Respiratory System Be very careful not to damage the heart and lungs while separating the ribs! Analysis Questions-Respiratory & Cardiovascular Log into QUIA using your
أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان-
 -6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
-6 أحمد رواجبة- محمود الحربي- أحمد السالمان- 1 P a g e The Male Reproductive System The male genital system structures are divided into: Internal structures: 1- Prostate 3-Ejaculatory ducts External structures:
HBA 531 THE BODY. Trunk Examination September 30, What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5)
 HBA 531 THE BODY Trunk Examination September 30, 2013 Name: 1. What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5) a) Heart rate b) Male reproductive function c) Pylorus d) Internal anal
HBA 531 THE BODY Trunk Examination September 30, 2013 Name: 1. What is the effect of the parasympathetic nervous system on: (2.5) a) Heart rate b) Male reproductive function c) Pylorus d) Internal anal
NBME Anatomy Review. Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015
 NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
NBME Anatomy Review Sylvia Nelsen, Ph.D. March 19, 2015 UPPER & LOWER LIMBS 1. What is the most likely diagnosis in this case? A. Rotator cuff tendinitis: pain w/o weakness B. Adhesive capsulitis: absolute
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II
 Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Anatomical Considerations for Lab Practical II For each of the following please be prepared to provide: Identification System Organ(s) or ducts to Function(s) location which it is attached Use your lecture
Borders of the Abdomen
 Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
Abdominal wall Borders of the Abdomen Abdomen is the region of the trunk that lies between the diaphragm above and the inlet of the pelvis below Borders Superior: Costal cartilages 7-12. Xiphoid process:
Urinary Bladder. Prof. Imran Qureshi
 Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Urinary Bladder Prof. Imran Qureshi Urinary Bladder It develops from the upper end of the urogenital sinus, which is continuous with the allantois. The allantois degenerates and forms a fibrous cord in
Inguinal Canal. It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall. Present in both sexes
 Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
Inguinal canal Inguinal Canal It is an oblique passage through the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall Present in both sexes It allows structures to pass to and from the testis to the abdomen in
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics.
 NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
NOTES FROM GUTMAN LECTURE 10/26 Use this outline to study from. As you go through Gutman s lecture, fill in the topics. Anatomy above the arcuate line Skin Camper s fascia Scarpa s fascia External oblique
STERNUM. Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts:
 STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
STERNUM Lies in the midline of the anterior chest wall It is a flat bone Divides into three parts: 1-Manubrium sterni 2-Body of the sternum 3- Xiphoid process The body of the sternum articulates above
UNIVERSITY DEVELOPMENT CENTER. Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department 29/12/2015
 Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Course Specification 2015/2016 For the Anatomy (first year) Faculty : Department : Medicine Anatomy and Embryology Department Course Specification: Programme (s) on which the course is given : M.B.B.Ch
Misc Anatomy. Upper Limb! 2. Lower Limb! 5. Venous Drainage! Head & neck! 8
 Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Misc Anatomy Upper Limb! 2 Arteries!... 2 Veins!... 2 Spaces!... 4 Lower Limb! 5 Arteries!... 5 Venous Drainage!... 6 Spaces!... 7 Head & neck! 8 Artery!... 8 Ultrasound View for IJ CVL!... 8 Arteries
Anatomy of the spleen. Oluwadiya KS
 Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
Anatomy of the spleen Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.com Introduction The spleen is an ovoid, usually purplish, pulpy mass about the size and shape of one's fist. It is the largest lymphoid tissue in the body
بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم
 MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
MAY 3, 2012 [POSTERIOR ABDOMINAL WALL] LECTURE 26 ANATOMY Quick Revision: بسم االه الرحمن الرحيم Last time we started with the anterior abdominal wall and said that: 1. Diaphragm is the root of the abdomen.
Biology Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities
 Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Biology 351 - Human Anatomy Abdominal and Pelvic Cavities You must answer all questions on this exam. Because statistics demonstrate that, on average, between 2-5 questions on every 100-point exam are
Pelvis MCQs. Block 1. B. Reproductive organs. C. The liver. D. Urinary bladder. 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: E.
 Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
Pelvis MCQs Block 1 1. The pelvic diaphragm includes the following muscles: A. The obturator internus B. The levator ani C. The coccygeus D. The external urethral sphincter E. The internal urethral sphincter
2. List the 8 pelvic spaces: list one procedure or dissection which involves entering that space.
 Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Name: Anatomy Quiz: Pre / Post 1. In making a pfannensteil incision you would traverse through the following layers: a) Skin, Camper s fascia, Scarpa s fascia, external oblique aponeurosis, internal oblique
Lumbar Plexus. Ventral rami L1 L4 Supplies: Major nerves.. Abdominal wall External genitalia Anteromedial thigh
 Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
Lower Limb Nerves Lectures Objectives Describe the structure and relationships of the plexuses of the lower limb. Describe the course, relationships and structures supplied for the major nerves of the
