THE HOLOCRINE CELLS of the epithelium of the rat epididymis and vas
|
|
|
- Willa Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Holocrine Cells of the Human Epididymis JAN MARTAN, Ph.D.,"' PAULL. RISLEY, Ph.D., and ZDENEK HRUBAN, M.D., Ph.D. t THE HOLOCRINE CELLS of the epithelium of the rat epididymis and vas deferens undergo a secretory cycle described recently by Martan and Risley.6 This cellular cycle begins with an activation of basal cells; a second step is their development into "apical cells" and "clear cells." These cells eventually disintegrate within the epithelium or are released intact into the lumen, where they disintegrate. Epididymal holocrine cells are characterized by their staining properties with the periodic acid-schiff technic and Aoyama silver-impregnation method (Figs. 1 and 13); they can be identified easily among the principal cells. they are also present in epididymides of guinea pigs and hamsters. 6 The secretory cycle was shown to be influenced by male testicular hormone an9. by frequency of mating. Although the function of the holocrine cells of the epididymis is not definitely known, it seems that the epididymal secretions, to which the holocrine cells contribute, might facilitate and hasten the maturation of spermatozoa. 5 6 Since the epididymal holocrine cells could thus be important in the understanding of human sterility, the purpose of the present study is to examine and identify the characteristics of holocrine cells in the human epididymis. MATERIALS AND METHODS Testes and epididymides were obtained at autopsy from 25 male patients. The respective ages and diagnoses of these patients had been: 4 weeks, bacterial meningitis; 6 weeks, congenital heart disease and cryptorchism; 1 year, meningitis; H~ years, burns; 4 years ( 2 patients) and 7 years, acute leukemia; 11 years, Hodgkins disease; 15 years, tetralogy of Fallot; 18 years, rheumatic From the Department of Biology, University of Oregon, Eugene, Ore., and the Department of Pathology, University of Chicago, Chicago, Ill. This work was supported by U.S. Public Health Service Grants NB and CA The authors wish to thank Miss Ute Paetsch for the preparation of the histological material described. *Present address: Department of Zoology, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Mich. tadvanced Clinical Fellow of the American Cancer Society. 180
2 VoL. 15, No.2, 1964 HoLOCRINE CELLS of EPIDIDYMIS heart disease; 21 y~rs, sarcoma of chest wall; 28 years, astrocytoma; 32 years, pulmonary emboli; 39 years, carcinoma of lung; 45 years, rheumatic heart disease; 47 years, viral hepatitis; 49 years, diffuse myocardial scarring, 50 years, fibrosarcoma; 52 years, carcinoma of lung; 54 years, myocardial in farction; 58 years, diabetes mellitus; 65 years, carcinoma of lung; 67 years, myocardial infarction; 68 years, carcinoma of stomach; and 70 years, myocardial infarction. Tissues were fixed in 10% neutral formalin containing 1% cadmium chloride. Tissues from one side were impregnated with silver nitrate by the Aoyama method,! embedded in paraffin, and 4- or 6-p. sections were cut. Some of the silver-impregnated sections were toned in 0.1% gold chloride, and nuclei were counterstained by the Feulgen method. Tissues from the opposite side were embedded in paraffin, and 4- or 6-p. sections were made. These were stained with hematoxylin eosin, Alcian blue-periodic acid-schiff method, 8 Azure B for ribonucleic acid localization,9 and Azure A-eosin B technic for demonstration of lipofuscins. 4 Control sections for demonstration of ribonucleic acid were incubated for 1 hr. at 50 C in 0.01% solution of ribonuclease in 0.8% saline solution buffered with phosphate to ph 6.4 Three controls were used for PAS reactive materials, namely: (I) sections digested in 0.1% malt diastase in 0.02 M phosphate buffer at ph 6 for one hour at 38 o C to remove gylcogen; ( 2) other sections extracted in equal parts of methanol and chloroform at 58 o C for 16 hr. to remove glycolipids;3 and ( 3) some sections immersed in Schiff reagent without pretreatment with periodic acid. RESULTS., ; t - l In Alcian blue-pas-stained sections, the epithelium of the human epididymis contained basal, holocrine, and principal cells. The holocrine and principal cells were exceptionally tall and narrow as compared with those of the rat and hamster, and these two types of cells were less well-defined (Fig. 1-3). Most of the epithelial cells showed a weak-to-mild periodic acid-schiff reaction throughout their cytoplasm, and strongly positive granules were present in their apical regions. Purple coloration of some granules and the stereocilia in some regions indicated that both PAS and Alcian-blue stains were positive. This apparently was indicative of the presence of a mucopolysaccharide complex. Nonstereociliated cells with pronounced PAS cytoplasmic staining and numerous PAS-positive granules were frequently seen in the ductus epididymidis (Fig. 2-4). The cytoplasm of some basal cells was also strongly PAS positive. The nuclei of strongly PAS-positive epididymal columnar
3 182 MARTAN ET AL. FERTILITY & STERILITY cells were located either in basal positions or in the upper halves of the cells. The cells with basal nuclei were slender and rectangular (Fig. 2 and 3). They assumed a club-like form when the nuclei moved into the upper cytoplasm (Fig. 4). Some club-shaped strongly PAS-positive cells were becoming detached from the epididymal epithelium, and numerous rounded cells Fig. 1. PAS-positive holocrine cells in cauda epididymidis of a normal mated rat. (PAS Alcian blue, X 900) Fig. 2. Arrow indicates a PAS-positive holocrine cell in cauda epididymidis of 52-year-old man. Compare with Fig. 1. (PAS-Alcian blue, X 900) Fig. 3. Same as in Fig. 2. (X 900) Fig. 4. Arrow indicates PAS-positive holocrine cell escaping into lumen of caput epididymidis of 50-year-old man. (PAS-Alcian blue, X 2200) Fig. 5. Arrows point to exhausted holocrine cell which lost its contents in situ and to mass of PAS-positive lipofuscin in caput epididymidis of 70-year-old man. (PAS Alcian blue & hematoxylin, X 900) Fig. 6. Arrow points to basophilia concentrated in stalk of holocrine cell in epididymis of 50-year-old man. Compare nucleus of this cell with principal cell below. (Azure B, X 2200)
4 VoL. 15, No.2, 1964 HoLOCRINE CELLS of EPIDIDYMIS 183 of a similar type were present in the lumen in all stages of disintegration. Similarly stained cells also occurred in the epithelium and lumen of the vas deferens and in the lower folded or festooned epithelium of the ductuli efferentes (Fig. 8). These cells were present in the epididymides and efferent ductuli of all male patients between the ages of 7 and 70 years. Though the strong PAS reaction was absent in the epididymides of 4-year-old patients, the presence of holocrine cells was indicated by the position of their nuclei within the epi- Fig. 7. Silver-positive cells in ductus efferens of 60-day-old normal unmated rat. (Aoyama-Feulgen reaction, X 900) Fig. 8. PAS-positive-cell in ductus efferens of 50- year-old man. (PAS-Alcian blue, X 2200) Fig. 9. Silver-positive cells in ductus efferens of 49-year-old man. Compare with Fig. 7. (Aoyama reaction, X 900) Fig. 10. Same as Fig. 9. (X 2200). Fig. 11. Mitosis of holocrine cell in basal region of epididymal epithelium of 15-year-old boy. (Azure B, X 2200) Fig. 12. Apical mitosis of a principal cell in epididymis of 7-year-boy. (PAS-Alcian blue & hematoxylin, X 2200)
5 184 MARTAN ET AL. FERTILITY & STERILITY theliallayer. The PAS reaction was somewhat weaker in the 7 and 11-yearold boys than it was in patients between 15 and 70 years old. The relative numbers of club-shaped cells were reduced in patients less than 15 or more than 50 years old. Large granular masses of strongly PAS-positive material were found fre- Fig. 13. Holocrine cells, with cytoplasm blackened with silver, about to leave epididymal epithelium in lower cauda on operated side of mated hemicastrated rat. (Aoyama-Feulgen reaction, X 2200) Fig. 14. Holocrine cell escaping from epithelium in cauda epididymidis of 15-year-old boy. Compare with Fig. 13. (Aoyama-Feulgen reaction, X 2200) Fig, 15. Holocrine cell in cauda epididymidis of 15-year-old boy. Compare with Fig. 13. (Aoyama-Feulgen reaction, X 2200) Fig. 16. Holocrine cell in corpus epididymidis of 47-year-old man. (Aoyama reaction, X 900) Fig. 17. Holocrine cells in vas deferens of 15-year-old boy. (Aoyama reaction, X 900) Fig. 18. Holocrine cell disintegrating in lumen of cauda epididymidis of 15-year-old boy. (Aoyama-Feulgen reaction, X 2200)
6 VoL. 15, No.2, 1964 HoLOCRINE CELLS of EPIDIDYMIS 185 quently in the basal and less often in the apical regions of the epithelium lining the middle and lower ductus epididymidis (Fig. 5). Smaller PASpositive granules occurred in the ductuli efferentes. Both types of these granules were present in patients older than 15 years and became more abundant with age. The PAS reactions of cells and granules mentioned above were not abolished by malt diastase and hot methanol chloroform extractions. Control sections in which periodic acid oxidation was omitted were negative in epididymides, while certain granules in the ductuli efferentes were "Schiffpositive" after 15-min. incubation in Schiff's reagent without prior oxidation. These granules and the granular PAS-positive masses in the basal epithelium of the epididymis stained greenish in Azure A-eosin B stain. The PAS-positive, nonstereociliated, club-shaped cells of the epididymis and vas deferens were differentiated readily from the principal cells in sections stained by the Aoyama silver method. The principal cells contained numerous silver granules in the apical portions of their cytoplasm, but the club-shaped cells were black throughout their cytoplasm (Fig. 15 and 16). Some of these dark cells bulged with rounded apical ends beyond the epithelial surface, or appeared to be detaching from the epithelial layer, and some were present in the lumen (Fig. 14 and 18). Many similar dark cells were present in the ductuli efferentes (Fig. 9 and 10). The dark cells were found in the epididymides of patients between 7 and 70 years. Their numbers however were fewer in the very young and very old patients of this group. The narrow club-shaped cells in the epididymis were basophilic in Azure B-stained sections, and ribonuclease digestion demonstrated that ribonucleic acid was concentrated in their narrow stalks and around their nuclei (Fig. 6). Mitotic figures were located in positions similar to those described previously for the rat. 6 Larger mitoses occurred in the apical ends of the principal cells (Fig. 12), and smaller ones were seen in the basal epithelium (Fig. 11). The nuclei of club-shaped cells were smaller than those of the principal cells of the epididymis (Fig. 6), and their chromatin patterns were different. DISCUSSION Basal and principal cells of the human epididymis have been described by Montagna and Hamilton, 7 and were studied with the electron microscope by Horstman. 2 The present study shows that the human epididymis also contains periodic acid-schiff-positive and silver-positive holocrine cells similar to those identified earlier in the laboratory rat by Martan and Risley. 5 6 The renewal cycle of holocrine cells was demonstrated previously in the
7 186 MARTAN ET AL. FERTILITY & STERILITY epididymis of the rat 5 6 by comparative studies of mated, hemicastrated, and normal animals. Some stages of this cycle were observed in the present study suggesting that a similar renewal cycle of the holocrine cells of the epididymis is also present in the human male. This cycle in the rat and man appears to start with activation of basal cells that become PAS- and silverpositive. The growth of activated cells, observed in the rat epididymis, was not detected in the human material. Whether the scarcity of this stage is inherent in man or should be attributed to the effects of the disease and treatment of these patients cannot be decided at the present time. The fully developed, nonstereociliated, club-shaped cells within the epithelium, cells becoming separated from the epithelial layer, and intraluminar cells are however easily identified in the human epididymis. The characteristics of basophilia and mitoses in the holocrine cells of man and rat are also comparable. The basophilia of the club-shaped cells in the epididymis occurs predominantly in the stalks of the cells below the nucleus. Mitotic figures are in basal or apical positions. The holocrine cells are less numerous, but present, in the epididymides of the 7- and 11-year-old patients, and in men older than 50 years, which could be related to a lower production of androgens. PAS-positive and silverpositive cells occur also in other locations of the male genital tract. In the human vas deferens, they are comparable to the holocrine cells of the human epididymis (Fig. 17). The club-shaped PAS- and silver-positive cells of the ductuli efferentes are similar to those of the rat6 (Fig. 7). Their replacement and developmental stages are not obvious, suggesting either that the renewal of the cells is very slow in these ducts or that they are not holocrine cells. Peaked caps of glycogen granules over the nuclei of basal cells, described in human epididymides obtained surgically7 were not observed in our material, possibly due to the antemortem disease in our patients or a delay of a few hours between death and fixation. These factors may also be responsible for the somewhat less intensive PAS and silver reactions of the human materials compared with those of rats. The granules that stain greenish with the Azure A-eosin B method and red with Schiff's reagent, with and without periodic acid oxidation, and which become more numerous with age, represent probably lipofuscin pigments. SUMMARY Human epididymides, ductuli efferentes, and vasa deferentia obtained at autopsy were studied for presence of holocrine cells. The epithelia in all three regions contained club-shaped nonstereociliated cells with periodic acid-schiff and Aoyama silver-positive cytoplasm.
8 VoL. 15, No.2, 1964 HoLOCRINE CELLS of EPIDIDYMIS 187 The stages of the holocrine cell renewal cycle observed in the human epididymis and vas deferens corresponded to the stages described for the rat epididymis. The renewal cycle was found to start with a mitotic division of a basal cell. The fully developed club-shaped holocrine cells were observed to disintegrate in situ or to be released into the ductular lumina. Dept. of Zoology University of Michigan Ann Arbor, Mich. REFERENCES 1. AoYAMA, F. Eine Modifikation der Cajalschen Methode zur Darstellung der Golgischen Binnennetz Apparate. Ztschr. Wiss. Mikr. 46:489, HoRSTMAN, E. Elektronenmikroskopie des Menschlichen Nebenhodenepithels. Ztschr. Zellforsch. 57:692, LEBLOND, C. P. Distribution of periodic acid-reactive carbohydrates in the adult rat. Am. ]. Anat. 86:1, LILLIE, R. D. Histopathologic Technic and Practical Histochemistry. Blakiston, New York, MARTAN, J., and RisLEY, P. L. The epididymis of mated and unmated rats. ]. Morphol. 118:1, MARTAN, J., and RISLEY, P. L. Holocrine secretory cells of the rat epididymis. Anatom. Rec. 146:113, MoNTAGNA, W., and HAMILTON, J. B. Histological studies of human testes. II. The distribution of glycogen and other HI0 4-Schiff reactive substances. Anatom. Rec. 112:231, MoWRY, R. W. Alcian blue techniques for histochemical study of acidic carbohydrates. ]. Ilistochem. 4:407, SwiFT, H. Cytochemical techniques for nucleic acids. Nucleic Acids. Acad. Press, New York, 1955.
THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE EFFECTS OF LIGATION OF CAUDA EPIDIDYMIDIS ON THE DOG TESTIS A. M. VARE, M.B.B.S.,
S S GURAYA and ARBANS J KAUR Department of Zoology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana , India
 Proc. Indian Acad, Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 90, Number 5, SeptcIl1ber 1981, pp. 49S-soi. o Printed in India. Effect of castration on some hydrolytic enzymes in the rat vas deferens: A histochemical study
Proc. Indian Acad, Sci. (Anim. Sci.), Vol. 90, Number 5, SeptcIl1ber 1981, pp. 49S-soi. o Printed in India. Effect of castration on some hydrolytic enzymes in the rat vas deferens: A histochemical study
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1
 ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
ON THE PRESENCE OF A CILIATED COLUMNAR EPITHELIAL CELL TYPE WITHIN THE BOVINE CERVICAL MUCOSA 1 R. I. Wordinger, 2 J. B. Ramsey, I. F. Dickey and I. R. Hill, Jr. Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Special Staining (I)
 Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
Special Staining (I) Carbohydrates 1- PERIODIC ACID SCHIFF'S (PAS ) Purpose: Glycogen is present in liver, kidney, skeletal and cardiac muscle. The PAS stain is used to demonstrate neutral polysaccharides
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The male reproductive system consists of primary sex organs (testes) and secondary or accessory sex organs. The secondary organs consist of a series of genital ducts (ductules
A Histochemical Study of Epithelial Mucin
 A Histochemical Study of Epithelial Mucin in the Chick Chorioallantois JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigun ABSTRACT Histochemical methods demonstrate
A Histochemical Study of Epithelial Mucin in the Chick Chorioallantois JAMES L. CONKLIN Department of Anatomy, The University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigun ABSTRACT Histochemical methods demonstrate
Transport of Sperm. Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation. Vas Efferentia. John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences
 Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences References: he Physiology of Reproduction, Knobil and Neill, 2006; Chapter on the Epididymis by Robaire ransport
Endocrinology of the Epididymis and Sperm Maturation John Parrish Department of Animal Sciences References: he Physiology of Reproduction, Knobil and Neill, 2006; Chapter on the Epididymis by Robaire ransport
DISTRIBUTION OF SEMINAL ANTIGENS AND ENZYMES IN THE RABBIT DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS 1
 DISTRIBUTION OF SEMINAL ANTIGENS AND ENZYMES IN THE RABBIT DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS 1 W. L. Johnson and A. G. Hunter University of Minnesota, St. Paul 55108 Summary Rabbit epididymal regions were examined immunologically
DISTRIBUTION OF SEMINAL ANTIGENS AND ENZYMES IN THE RABBIT DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS 1 W. L. Johnson and A. G. Hunter University of Minnesota, St. Paul 55108 Summary Rabbit epididymal regions were examined immunologically
Regional Histology and HistoChemistry of the Ductus Epididymis in the Rhesus Monkey (Macaca mulatta)
 BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 19, 1063-1069 (1978) Regional Histology and HistoChemistry of the Ductus Epididymis in the Rhesus Monkey (Macaca mulatta) DONALD J. ALSUM and ALAN G. HUNTER Department 0/Animal
BIOLOGY OF REPRODUCTION 19, 1063-1069 (1978) Regional Histology and HistoChemistry of the Ductus Epididymis in the Rhesus Monkey (Macaca mulatta) DONALD J. ALSUM and ALAN G. HUNTER Department 0/Animal
On the structure of the epididymal region and ductus deferens of
 J. Anat. (1971), 109, 3, pp. 423-435 423 With 17 figures Printed in Great Britain On the structure of the epididymal region and ductus deferens of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus) M. D. TINGARI Department
J. Anat. (1971), 109, 3, pp. 423-435 423 With 17 figures Printed in Great Britain On the structure of the epididymal region and ductus deferens of the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus) M. D. TINGARI Department
Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis
 93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
93 Morphogenesis of the residual body of the mouse testis By CASIMIR F. FIRLIT and JOSEPH R. DAVIS (From the Department of Pharmacology and Therapeutics, Stritch School of Medicine, and Graduate School,
Cytological Studies on Human Spermatogenic and Sustentacular (Sertoli) Cells
 Cytological Studies on Human Spermatogenic and Sustentacular (Sertoli) Cells By Setsuko Ogata Department of Anatomy, Tokyo Women's Medical College, Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan (Director : Prof. Dr. Kura Kubota)
Cytological Studies on Human Spermatogenic and Sustentacular (Sertoli) Cells By Setsuko Ogata Department of Anatomy, Tokyo Women's Medical College, Shinjuku, Tokyo, Japan (Director : Prof. Dr. Kura Kubota)
There is scanty information on the biochemistry
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.4, April 1973 Printed in U.S.A. ACTIVITY AND LOCALIZATION OF ISOCITRIC DEHYDROGENASE, ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE, ALANINE
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No.4, April 1973 Printed in U.S.A. ACTIVITY AND LOCALIZATION OF ISOCITRIC DEHYDROGENASE, ASPARTATE AMINOTRANSFERASE, ALANINE
LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON LIPID STAINED BY MALACHITE GREEN IN THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF THE RABBIT,
 LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON LIPID STAINED BY MALACHITE GREEN IN THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF THE RABBIT, HAMSTER AND MONGOOSE J. M. CUMMINS, M. H. BERNSTEIN and R. J. TEICHMAN Department
LIGHT AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPE STUDIES ON LIPID STAINED BY MALACHITE GREEN IN THE MALE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF THE RABBIT, HAMSTER AND MONGOOSE J. M. CUMMINS, M. H. BERNSTEIN and R. J. TEICHMAN Department
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
Male Reproductive System Constitution of male reproductive system Genital gland ----testis Genital ducts epididymis / ductus deferens / urinary duct Accessory sex glands Penis prostate gland Seminal vesicle
HISTOCHEMISTRY OF PHOSPHATASES IN THE EPIDIDYMIS OF RAM DURING POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT*
 HISTOCHEMISTRY OF PHOSPHATASES IN THE EPIDIDYMIS OF RAM DURING POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT* P.V.S. Kishore 1, Geetha Ramesh 2 and Sabiha Hayath Basha 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology, Madras Veterinary
HISTOCHEMISTRY OF PHOSPHATASES IN THE EPIDIDYMIS OF RAM DURING POSTNATAL DEVELOPMENT* P.V.S. Kishore 1, Geetha Ramesh 2 and Sabiha Hayath Basha 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy & Histology, Madras Veterinary
Basic histology 5/4/2015
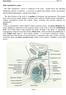 Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Male reproductive system The male reproductive system is composed of the testes, genital ducts (the adjoining epididymis, and the vas deferens, a accessory sex glands (the seminal vesicles, the prostrate
Light microscopic features of the rete testis, the vas efferens, the epididymis and the vas deferens in the adult rhesus monkey
 J. Biosci., Vol. 1, Number 2, June 1979, pp. 186 205. Printed in India. Light microscopic features of the rete testis, the vas efferens, the epididymis and the vas deferens in the adult rhesus monkey ASHA
J. Biosci., Vol. 1, Number 2, June 1979, pp. 186 205. Printed in India. Light microscopic features of the rete testis, the vas efferens, the epididymis and the vas deferens in the adult rhesus monkey ASHA
Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16. Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36. Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73
 Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Table of Contents Fixation... Questions 1 Answers 16 Processing... Questions 25 Answers 36 Instrumentation... Questions 43 Answers 58 Safety... Questions 67 Answers 73 Laboratory Mathematics & Solution
Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants
 J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
J. clin. Path. (1969), 22, 725-730 Congenital mesonephric defects in male infants with mucoviscidosis J. R. OLSON AND D. K. WEAVER From the Department ofpathology, The University of Michigan Medical Center,
Spontaneous electrical activity of the rat epididymis
 Spontaneous electrical activity of the rat epididymis in vitro A. Talo, Ulla-Marjut Jaakkola and Merja Markkula-Viitanen Zoophysiological Laboratory, Department ofbiology, University of Turku, SF-20500
Spontaneous electrical activity of the rat epididymis in vitro A. Talo, Ulla-Marjut Jaakkola and Merja Markkula-Viitanen Zoophysiological Laboratory, Department ofbiology, University of Turku, SF-20500
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
LABORATORY EXERCISES FOR MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM Slide #101 (1096). Testis, rat. sustentacular ( Sertoli ) cells Nuclei of Sustentacular cells Leydig cells Spermatogonia Spermatocytes Spermatids pale
Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey
 J. Biosci., Vol. 2, Number 3, September 1980, pp. 261-266. Printed in India. Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey ASHA PRAKASH, M. R. N. PRASAD and T.C. ANAND KUMAR
J. Biosci., Vol. 2, Number 3, September 1980, pp. 261-266. Printed in India. Ultrastructural studies on the epididymal spermatozoa in the rhesus monkey ASHA PRAKASH, M. R. N. PRASAD and T.C. ANAND KUMAR
Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/-
 Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Supplemental Material Results. Expression of acid base transporters in the kidney collecting duct in Slc2a7 -/- and Slc2a7 -/- mice. The expression of AE1 in the kidney was examined in Slc26a7 KO mice.
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1)
 Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Histology of Male Reproductive system (1) Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer Learning Objectives At the end of this lecture, the medical student will be able to: State the organization of the testis Define seminiferous
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1
 Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
Pathology of Male Reproductive System 1 Professor dr Ali Hassan Altimimi Professor of Pathology& Histology MSc, PHD, MD(UK) MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM The internal male genitalia consist of the testes with
STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
 FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No. 11, November 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
FERTILITY AND STERILITY Copyright 1973 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 24, No. 11, November 1973 Printed in U.S.A. STERILITY IN MALE ANIMALS INDUCED BY INJECTION OF CHEMICAL AGENTS INTO THE VAS DEFERENS*
Efferent Ducts and Epididymis
 increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
increase) the secretion of each of the androgen regulated proteins. Regulation of spermatogenesis is therefore an extremely complex cascade of cell-cell interactions with the Leydig cells supporting germ
Male Reproductive System
 Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
Male Reproductive System organs that function in: gamete and hormone production not all in abdominal cavity paired testicles = controlled by LH & FSH duct systems accessory glands Testis: Gross Histology
The Male Reproductive System
 The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
The Male Reproductive System YONG-MEI CHEN ( 陈咏梅 ) Dept. of Anatomy, Histology & Embryology Peking Union Medical College Tel:69156461 E-mail address: pumc_he@126.com Content Spermatogenesis Spermiogenesis
Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse
 J. Vet. Sci. (2003), 4(1), 21-28 J O U R N A L O F Veterinary Science Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse Tae-young Ha, Mee-jung Ahn, Yong-duk Lee, Jae-hyuk
J. Vet. Sci. (2003), 4(1), 21-28 J O U R N A L O F Veterinary Science Histochemical Detection of Glycoconjugates in the Male Reproductive System of the Horse Tae-young Ha, Mee-jung Ahn, Yong-duk Lee, Jae-hyuk
IN the skin of the mouse we find that the dermal papilla of growing hair
 (240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
(240 Cyclic Changes in Polysaccharides of the Papilla of the Hair Follicle By WILLIAM MONTAGNA, HERMAN B. CHASE, JANET D. MALONE, AND HELEN P. MELARAGNO (From Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island,
Preface 1. Fixation and Processing 1
 Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
Contents Preface xi 1. Fixation and Processing 1 Fixation 1 Processing 2 What Should Be Seen in a Well-Fixed, Well-Processed Specimen Stained with Hematoxylin and Eosin 3 Problems Encountered With Fixation
abruptly retrogress and remain quiescent throughout the winter. The insecti
 HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE SEMINAL VESICLE SECRETION OF THE INDIAN HEDGEHOG WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE CRYSTALLOID BODIES PUSHPAMALA P. BIDWAI and S. R. BAWA Department of Biophysics, Panjab University,
HISTOCHEMICAL STUDY OF THE SEMINAL VESICLE SECRETION OF THE INDIAN HEDGEHOG WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE CRYSTALLOID BODIES PUSHPAMALA P. BIDWAI and S. R. BAWA Department of Biophysics, Panjab University,
Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions
 ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions 1* 1 1 1 Manoj P.Ambali, Megha A. Doshi, Pratibha P. Patil, Shweta H. Chavan 1 Department of Anatomy,
ISSN 2231-4261 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Mucin Histochemistry Study of the Prostate in Normal and Malignant Lesions 1* 1 1 1 Manoj P.Ambali, Megha A. Doshi, Pratibha P. Patil, Shweta H. Chavan 1 Department of Anatomy,
SERO ANDONIAN AND LOUIS HERMO
 Journal of Andrology, Vol. 20. No. 3, May/June 1999 Copyright American Society of Andrology Cell- and Region-Specific Localization of Lysosomal and Secretory Proteins and Endocytic Receptors in Epithelial
Journal of Andrology, Vol. 20. No. 3, May/June 1999 Copyright American Society of Andrology Cell- and Region-Specific Localization of Lysosomal and Secretory Proteins and Endocytic Receptors in Epithelial
Cell Overview. Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD
 Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Cell Overview Hanan Jafar BDS.MSc.PhD THE CELL is made of: 1- Nucleus 2- Cell Membrane 3- Cytoplasm THE CELL Formed of: 1. Nuclear envelope 2. Chromatin 3. Nucleolus 4. Nucleoplasm (nuclear matrix) NUCLEUS
Yara Saddam. Amr Alkhatib. Ihsan
 1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
1 Yara Saddam Amr Alkhatib Ihsan NOTE: Yellow highlighting=correction/addition to the previous version of the sheet. Histology (micro anatomy) :- the study of tissues and how they are arranged into organs.
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function. Histology = study of tissues
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids function tissue shape aids function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings Connective
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease. By S. BRADBURY
 Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
Human Saliva as a Convenient Source of Ribonuclease 323 By S. BRADBURY (From the Cytological Laboratory, Department of Zoology, University Museum, Oxford) SUMMARY Saliva, heated to 80 C for 10 minutes
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT
 ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
ADVERSE EFFECTS OF VASECTOMY: SPERM GRANULOMA OF EPIDIDYMIDES V. P. DIXIT Reproduct ion Physiology Section, Department of Zoology, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur-302004 Summary: Rats and mice were vasectomized
18 Urinary system. 19 Male reproductive system. Female reproductive system. Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases
 Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Blok 11: Genital and Urinary Tract Diseases 18 Urinary System 19 Male Genital System 20 Female Genital System 18 Urinary system You should be able to: 1. Describe the structures and associated functions
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type?
 Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Histology Review Can you identify the Cell Structures? Can you identify the Stain? Can you identify the Cell type? 2.01 Border of Epithelia (fluorescence) M A: lamina basalis B: epithelium C: other tissues
Pitted pattern in the human epididymis
 Pitted pattern in the human epididymis M. Nistal, L. I\l=n~\iguez and R. Paniagua "Department of Morphology, School of Medicine, Autonomous University of Madrid, C Arzobispo Morcillo 2, E-28029 Madrid,
Pitted pattern in the human epididymis M. Nistal, L. I\l=n~\iguez and R. Paniagua "Department of Morphology, School of Medicine, Autonomous University of Madrid, C Arzobispo Morcillo 2, E-28029 Madrid,
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS
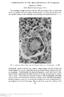 CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
CONTRIBUTION TO THE HISTOPATHOLOGY OF FILARIASIS PHILIP H. HARTZ Public Health Service, Curacao, N.W.I. The histologic changes caused by filariasis (Wucheria Bancrofti) are considered to be non-specific
Atlas of Stains. Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro
 Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Atlas of Stains Special Stains on Artisan Link Pro Intended use Routinely processed samples (paraffin-embedded) may be used. The preferred fixative is neutral buffered formalin. The clinical interpretation
Epithelial Tissue. Functions include: 1. Protection 4. Absorption 2. Secretion 5. Filtration 3. Sensory reception
 Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Tissues There are 4 primary tissue types in the human body: 1. Epithelial (covering/lining) 2. Connective (support) 3. Muscle (movement) 4. Nervous (control) Epithelium Epithelial Tissue Covers the surface
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Hersh Abdul Ham-Karim BVM&S, PG Dip, MSc and PhD Glandular Epithelium Groups of surface cells differentiate, proliferate, and penetrate underlying connective tissue. Their main
Variability in Weight and Histological Appearance of the Prostate of Beagle Dogs Used in Toxicology Studies
 Toxicologic Pathology, 36: 917-925, 2008 Copyright 2008 by Society of Toxicologic Pathology ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623308324958 Variability in Weight and Histological
Toxicologic Pathology, 36: 917-925, 2008 Copyright 2008 by Society of Toxicologic Pathology ISSN: 0192-6233 print / 1533-1601 online DOI: 10.1177/0192623308324958 Variability in Weight and Histological
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA)
 STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
STUDIES ON HISTOLOGICAL STRUCTURES OF THE ABDOMEN ON ADULT WORKER BEES (APIS MELLIFERA CARPATHICA) Petruţ T. 1, D. Condur 1, N. Velicu 1, V. Călin 1 1 Faculty of Veterinary Medicine Spiru Haret, 9-11 Energeticienilor
Histochemical Localization of Carbohydrates in the Mucosal Epithelium of the Alimentary Tract of the Skink Mabuya brevicollis
 J.K.A. U.: Sci., vol. I, pp. 113-124 (1409 A.H./1989 A.D Histochemical Localization of Carbohydrates in the Mucosal Epithelium of the Alimentary Tract of the Skink Mabuya brevicollis G.Y. DEHLAWIANDM.M.
J.K.A. U.: Sci., vol. I, pp. 113-124 (1409 A.H./1989 A.D Histochemical Localization of Carbohydrates in the Mucosal Epithelium of the Alimentary Tract of the Skink Mabuya brevicollis G.Y. DEHLAWIANDM.M.
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM
 1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
1 MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM SCPA 602 Anatomical Basis for Pathological Study Updated: 20.09.2018 Lect. Nisamanee Charoenchon, PhD nisamanee.cha@mahidol.ac.th Department of Pathobiology, Mahidol University
Lecture Overview. Chapter 4 Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues. Epithelial Tissues. Glandular Epithelium
 Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Visual Anatomy & Physiology First Edition Martini & Ober Chapter 4 Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Location General characteristics Functions Classification Glandular Epithelium 2 Where
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body
 Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
Unit I Problem 9 Histology: Basic Tissues of The Body - What is the difference between cytology and histology? Cytology: it is the study of the structure and functions of cells and their contents. Histology:
ALAEZI CM 1 *, ADISA JO 2, OKOROCHI EC 3 and OKECHI OO 4
 Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Global Journal of Scientific Researches Available online at gjsr.blue-ap.org 2014 GJSR Journal. Vol. 2(2), pp. 51-55, 28 February, 2014 E-ISSN: 2311-732X METHYL GREEN PYRONIN: A PROGRESSIVE NUCLEAR STAIN
Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard
 Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Okajimas Folia Anat. Jpn., 69(1): 25-34, May, 1992 Histological and Histochemical Investigations on Japanese Lizard Esophagus By Masatake IMAI and Taizo SHIBATA Department of Anatomy, Kanazawa Medical
Glands Histology lab 5 Notes by Lojayn Salah
 Glands Histology lab 5 Notes by Lojayn Salah There are two types of glands: - 1) Endocrine gland: collection of epithelial cells with no connection with the epithelial surface, it has no duct, its secretory
Glands Histology lab 5 Notes by Lojayn Salah There are two types of glands: - 1) Endocrine gland: collection of epithelial cells with no connection with the epithelial surface, it has no duct, its secretory
The Cytological and Chemical Orqanization of the
 The Cytological and Chemical Orqanization of the - Prostatic Epithelium of Didelphis virginicrncr Kerr JAN MARTAN AND JOHN M. ULEN Department of Zoology, The University of Michigun, Ann Arbor, Michigan
The Cytological and Chemical Orqanization of the - Prostatic Epithelium of Didelphis virginicrncr Kerr JAN MARTAN AND JOHN M. ULEN Department of Zoology, The University of Michigun, Ann Arbor, Michigan
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations
 Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
Histopathology: Cell necrosis and cytoplasmic accumulations These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you
(From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) Materials and Methods
 HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XI. THF. DISTRIBUTION OF /~-GLucURONIDASE* BY WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. (From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) PLATES
HISTOLOGY AND CYTOCHEMISTRY OF HUMAN SKIN XI. THF. DISTRIBUTION OF /~-GLucURONIDASE* BY WILLIAM MONTAGNA, PH.D. (From the Arnold Biological Laboratory, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island) PLATES
POSTNATAL DIFFERENTIATION AND REGIONAL HISTOLOGICAL VARIATIONS IN THE DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS OF RAMS*
 POSTNATAL DIFFERENTIATION AND REGIONAL HISTOLOGICAL VARIATIONS IN THE DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS OF RAMS* P.V.S.Kishore 1, Geetha Ramesh 2 and Sabiha Hayath Basha 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
POSTNATAL DIFFERENTIATION AND REGIONAL HISTOLOGICAL VARIATIONS IN THE DUCTUS EPIDIDYMIDIS OF RAMS* P.V.S.Kishore 1, Geetha Ramesh 2 and Sabiha Hayath Basha 3 Department of Veterinary Anatomy and Histology,
Dr. Abeer.c.Yousif. Histology -2 nd stage. What is histology?
 What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
What is histology? Histology is the science of microscopic anatomy of cells and tissues, in Greek language Histo= tissue and logos = study and it's tightly bounded to molecular biology, physiology, immunology
by authors and SVSBT.
 The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
The Indian Journal of Veterinary Sciences & Biotechnology (2018) Volume 13, Issue 4, 20-25 ISSN (Print) : 2394-0247 : ISSN (Print and online) : 2395-1176, abbreviated as IJVSBT 10.21887/ijvsbt.v13i4.11553
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3
 Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
Bio & 241 A&P Unit 1 / Lecture 3 Tissues All body tissues arise from three fundamental embryonic tissues. Endoderm: forms epithelial tissues lining internal organs such as the GI tract Mesoderm: connective
Ultrastractural features of the principal cell in the epididymis of the rhesus monkey
 Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 4, December 1982, pp. 469-479. Printed in India. Ultrastractural features of the principal cell in the epididymis of the rhesus monkey T. C, ANAND KUMAR, ASHA PRAKASH and M. R.
Biosci., Vol. 4, Number 4, December 1982, pp. 469-479. Printed in India. Ultrastractural features of the principal cell in the epididymis of the rhesus monkey T. C, ANAND KUMAR, ASHA PRAKASH and M. R.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION
 ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
ENHANCEMENT OF THE GRANULATION OF ADRFNERGIC STORAGE VESICLES IN DRUG-FREE SOLUTION TAKASHI IWAYAMA and J. B. FURNESS. From the Department of Zoology, University of Melbourne, Victoria, Australia. Dr.
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E
 Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
Slide 154: Pancreas, H&E the pancreas, located adjacent to the duodenum, is a mixed exocrine and endocrine gland; it is usually readily identifiable by the presence of the interspersed endocrine pancreatic
DURING the past ten years it has been suggested that the classical form
 163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
163 The Golgi Apparatus and Lipoidal Bodies in Exocrine and Endocrine Cells in the Pancreas of Man By DENNIS LACY (From the Department of Zoology and Comparative Anatomy, St. Bartholomew's Medical College)
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus
 Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
Occurrence of Ciliated Vesicle-Containing Reticular Cells in the Mouse Thymus By Takeshi Hoshino Department of Anatomy, Hokkaido University School of Medicine, Sapporo, Japan (Director : Prof. Takashi
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES
 EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
EDUCATIONAL COMMENTARY MORPHOLOGIC ABNORMALITIES IN LEUKOCYTES Educational commentary is provided through our affiliation with the American Society for Clinical Pathology (ASCP). To obtain FREE CME/CMLE
Epithelial Tissue. By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: different types of epithelial membranes.
 Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
Epithelial Tissue Objectives: By the end of this lecture, you should be able to: n Describe general characteristics of epithelial tissue. n Discuss microscopic structure and distribution of different types
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB
 PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
PRACTICAL HISTOLOGY LAB.1 ----------------------------------------------------------------------------- INTRODUCTION Cells are the smallest units of life, and are named according to their function. Cells
Intranuclear Inclusion Bodies in Epithelial Cells of Human Vas Deferens
 Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 Intranuclear Inclusion Bodies in Epithelial Cells of Human
Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: https://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 Intranuclear Inclusion Bodies in Epithelial Cells of Human
Tissues. tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function. cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function
 Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
Tissues tissue = many cells w/ same structure and function cell shape aids its function tissue shape aids its function Histology = study of tissues 4 types of tissues Epithelial coverings contact openings
THE MALE RABBIT. VII. STUDIES ON RESORPTION OF PH} THYMIDINE.LABELED SPERMATOZOA IN THE EPIDIDYMIS*
 Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE MALE RABBIT. VII. STUDIES ON RESORPTION OF PH} THYMIDINE.LABELED SPERMATOZOA IN THE
Copyright 1974 The American Fertility Society FERTILITY AND STERILITY Vol. 25, No.3, March, 1974 Printed in U.S.A. THE MALE RABBIT. VII. STUDIES ON RESORPTION OF PH} THYMIDINE.LABELED SPERMATOZOA IN THE
Freshwater Biological Association. FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132
 Freshwater Biological Association FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132 Title: A contribution to the knowledge of the skin albuminose cells of Torpedo ocellata Raf. Author(s) CELADA M. & DE PAOLI A.M. Reference:
Freshwater Biological Association FBA Translation (New Series) No. 132 Title: A contribution to the knowledge of the skin albuminose cells of Torpedo ocellata Raf. Author(s) CELADA M. & DE PAOLI A.M. Reference:
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh
 Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Basement membrane: What is the basement membrane? - It is a layer of ECM separating the epithelial cells from the underlying connective tissue Basement
CYTOMORPHOLOGY MODULE 28.1 INTRODUCTION OBJECTIVES 28.2 GENERAL GUIDELINES. Notes
 28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
28 CYTOMORPHOLOGY 28.1 INTRODUCTION Light microscopic examination of stained cells in smears is the method of choice of diagnostic cytology. It allows classification of most normal cells as to type and
REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF ANIMALS FED A DIET DEFICIENT IN VITAMIN A ALCOHOL BUT CON TAINING VITAMIN A ACID. I. THE MALE RAT
 HISTOLOGY OF THE LESIONS PRODUCED IN THE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF ANIMALS FED A DIET DEFICIENT IN VITAMIN A ALCOHOL BUT CON TAINING VITAMIN A ACID. I. THE MALE RAT J. McC. HOWELL, J. N. THOMPSON and G. A.
HISTOLOGY OF THE LESIONS PRODUCED IN THE REPRODUCTIVE TRACT OF ANIMALS FED A DIET DEFICIENT IN VITAMIN A ALCOHOL BUT CON TAINING VITAMIN A ACID. I. THE MALE RAT J. McC. HOWELL, J. N. THOMPSON and G. A.
PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
 CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
CELL INJURY UNIT I PREPARED BY P.DHARANI PRASAD II YEAR B.PHARM II SEM SUB:PATHOPHYSIOLOGY DETECTION OF CELLULAR CHANGES AFTER INJURY BY: LIGHT MICROSCOPY OR GROSS EXAMINATION DETECT CHANGES HOURS TO DAYS
J. Physiol. (I959) I46,
 465 J. Physiol. (I959) I46, 465-471 THE DISTRIBUTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND SOME OTHER SUBSTANCES IN THE ADRENAL CORTEX AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF ADRENOCORTICOTROPHIN BY J. K. BURNS* AND A. J. HALE From
465 J. Physiol. (I959) I46, 465-471 THE DISTRIBUTION OF RIBONUCLEIC ACID AND SOME OTHER SUBSTANCES IN THE ADRENAL CORTEX AFTER ADMINISTRATION OF ADRENOCORTICOTROPHIN BY J. K. BURNS* AND A. J. HALE From
Canadian Scientific Journal. Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell carcinoma of the lung
 Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Canadian Scientific Journal 2 (2014) Contents lists available at Canadian Scientific Journal Canadian Scientific Journal journal homepage: Histochemical polymorphism of keratin pearls in squamous cell
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia
 Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Histopathology: Cervical HPV and neoplasia These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about
Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice
 CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION 8, 339-346 (1984) C by Japan Society for Cell Biology Silver-Impregnation of the Golgi Complex in Epididymal Epithelial Cells of Mice Ikuo Yamaoka, Sumie Katsuta and Yoshimi
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies?
 Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
Explain the laboratory diagnosis of Rabies? The standard test for rabies testing is dfa. This test has been thoroughly evaluated for more than 40 years, and is recognized as the most rapid and reliable
androgen on the seminal vesicles it had neither a blocking effect on the penile
 MORPHOLOGICAL AND BEHAVIOURAL EFFECTS OF AN 'ANTIANDROGEN' IN MALE RATS F. A. BEACH and W. H. WESTBROOK Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, U.S.A. (Received
MORPHOLOGICAL AND BEHAVIOURAL EFFECTS OF AN 'ANTIANDROGEN' IN MALE RATS F. A. BEACH and W. H. WESTBROOK Department of Psychology, University of California, Berkeley, California 94720, U.S.A. (Received
TYPES OF EPITHELIA. Epithelia can be divided into two main groups. A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia.
 TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
TYPES OF EPITHELIA Epithelia can be divided into two main groups A-covering (or lining) epithelia B- Secretory (glandular) epithelia. Glands Glandular epithelial cells may synthesize, store, and secrete:
Morphology of the Epididymal Region of Turkeys Producing Abnormal Yellow Semen 1
 Morphology of the Epididymal Region of Turkeys Producing Abnormal Yellow Semen 1 REX A. HESS, RON J. THURSTON, and H. V. BIELLIER 2 Department of Poultry Science, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Morphology of the Epididymal Region of Turkeys Producing Abnormal Yellow Semen 1 REX A. HESS, RON J. THURSTON, and H. V. BIELLIER 2 Department of Poultry Science, Clemson University, Clemson, South Carolina
Glandular Epithelium. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Glandular Epithelium Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Glands Glandular epithelia are tissues formed by cells specialized to produce secretion. Secretion: if substances produced
Cell and Tissue Types. Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve
 Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
Cell and Tissue Types Epithelial, Connective, Muscle, Nerve Objectives Explain the major stages of the cell cycle and cellular division (mitosis). Describe specific events occurring in each of the phases
On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal
 Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
Dept. of Anat., Tokyo Med. and Dent. Univ. (Chief: Prof. T. KIRINO). On Three Cases of the Genuine Accessory Suprarenal Bodies in Man. In the course of studies on the ZUCKERKANDL's paraganglia, by careful
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System. VIBS 289 lab
 Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Medical School Histology Basics Male Reproductive System VIBS 289 lab Larry Johnson Texas A&M University OBJECTIVE To conduct a histologic examination of the testis (which produce spermatozoa), excretory
Epithelium tissue system
 Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Epithelium tissue system Histology : is the study of the microscopic anatomy (microanatomy) of cells and tissues of plants and animals. It is commonly performed by examining cells and tissues under a light
Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Activity in the Epididymis During Fetal and Postnatal Development in Rats
 Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Activity in the Epididymis During
Archives of Andrology Journal of Reproductive Systems ISSN: 0148-5016 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iaan19 Gamma-Glutamyl Transpeptidase Activity in the Epididymis During
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain
 Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia using 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-1527 Crystal Violet and Feulgen Stain Original research Comparison and Evaluation of Mitotic Figures
Histopathology: chronic inflammation
 Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
Histopathology: chronic inflammation These presentations are to help you identify, and to test yourself on identifying, basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information
(b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food materials 2. Acidification of food (absorption of dietary Fe in small intestine) 3. Partial chemical digest
 (1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
(1) General features a) Stomach is widened portion of gut-tube: between tubular and spherical; Note arranged of smooth muscle tissue in muscularis externa. 1 (b) Stomach s function 1. Dilution of food
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY. DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes.
 DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
DEFINED Involves the study of function that results from disease processes. What is pathology? Pathology is the branch of medical sciences that treats the essential nature of disease, especially the changes
Lecture Overview. Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology. Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9. Introduction to Tissues
 Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Marieb s Human Anatomy and Physiology Marieb Hoehn Chapter 4 Tissues: The Living Fabric Epithelial Tissues Lecture 9 Lecture Overview Introduction to Tissues Epithelial Tissues Location General characteristics
Variations in the Appearance of Human Elastic Cartilage
 The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
The Ohio State University Knowledge Bank kb.osu.edu Ohio Journal of Science (Ohio Academy of Science) Ohio Journal of Science: Volume 69, Issue 6 (November, 1969) 1969-11 Variations in the Appearance of
